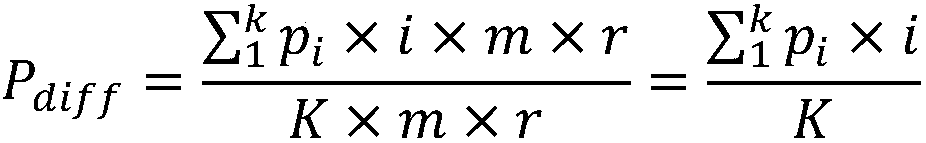Privacy protection k-means clustering method
A privacy protection and clustering method technology, applied in the fields of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer parts, etc., can solve the problems of inapplicability of databases and less data mining work, and achieve a wide range of applications and good clustering accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
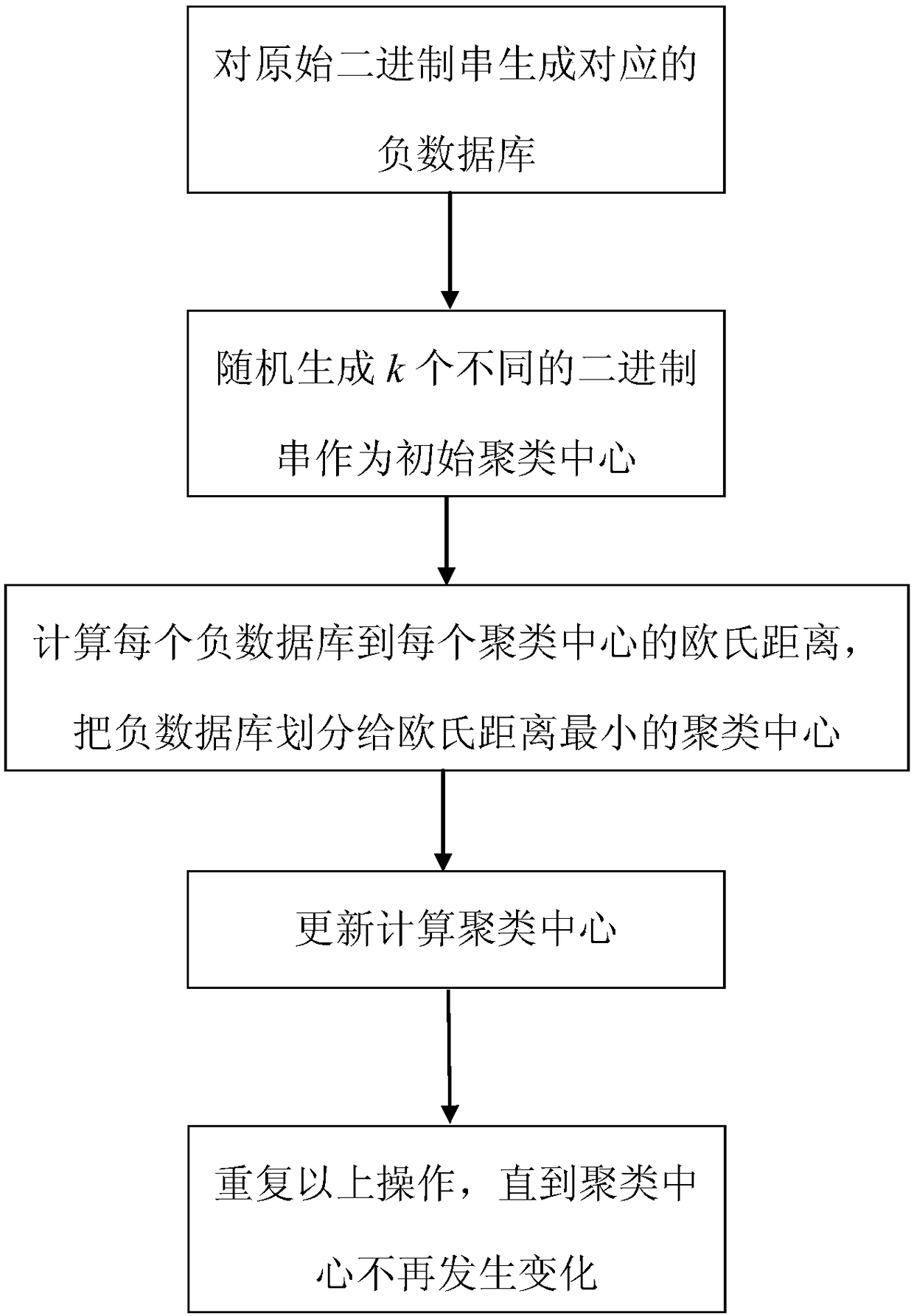
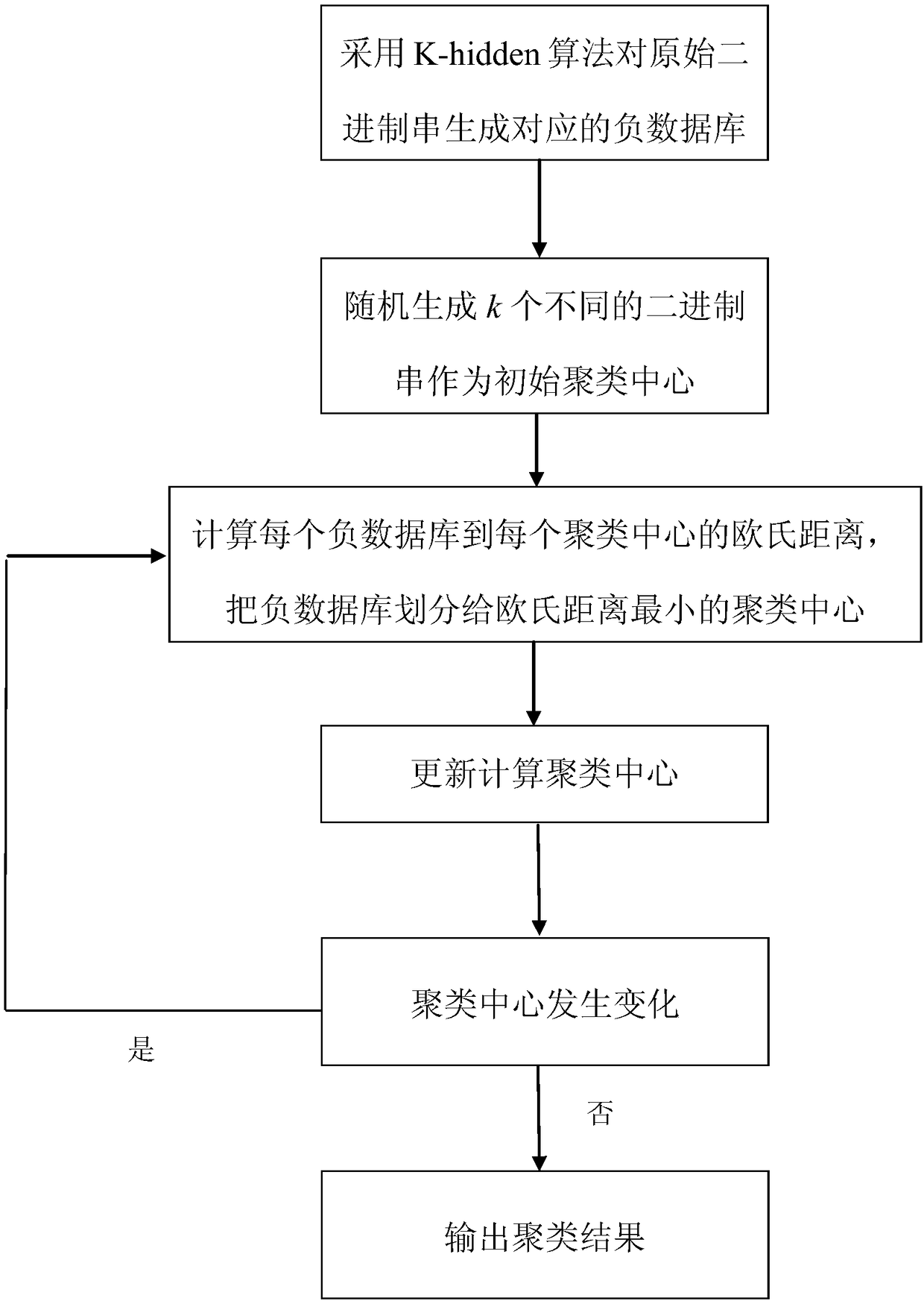
[0029] The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. A privacy protection k-means clustering method based on a negative database in this embodiment includes:
[0030] Step 1. Convert each piece of data of X in the database that needs to be clustered into a binary string. Here, take the iris data set commonly used for clustering as an example. There are 150 instances in the iris data set, and each instance contains 4 The attributes are all floating-point numbers. Here, the floating-point number is multiplied by 10 and converted into a decimal number, and then the decimal number is converted into a binary number. Since the length of each binary string must be the same, the remaining bits are filled with 0. For example, if the value of a certain attribute is 3.5, the converted binary number is 10011. If the maximum number of digits of this attribute is six digits, add zeros in front to make up six digits, that is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com