Compositions and methods for degradation of misfolded proteins
A technology of misfolding and composition, applied in the field of compositions and methods for degrading misfolded proteins, capable of solving problems such as poor system understanding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0240] Formulations of the pharmaceutical compositions herein may be prepared by any method known or hereafter developed in the art of pharmacy. In general, these methods of preparation include the step of bringing into association the active ingredient with the carrier or one or more other accessory ingredients, and then, if necessary or desired, shaping or packaging the product into the desired unit-dose or multi-dose unit.
[0241] As used herein, a "unit dose" is an individual quantity of a pharmaceutical composition containing a predetermined quantity of an active ingredient. The amount of active ingredient is usually equal to the dose of active ingredient to be administered to the subject, or a convenient fraction of the dose, such as for example one-half or one-third of the dose. Unit dosage forms can be for single daily administration or multiple daily administrations (eg, about 1 to 4 or more times per day). When multiple daily doses are used, the unit dosage form ma...
Embodiment 1
[0278] Example 1: A cellular system that degrades misfolded proteins and protects against neurodegeneration
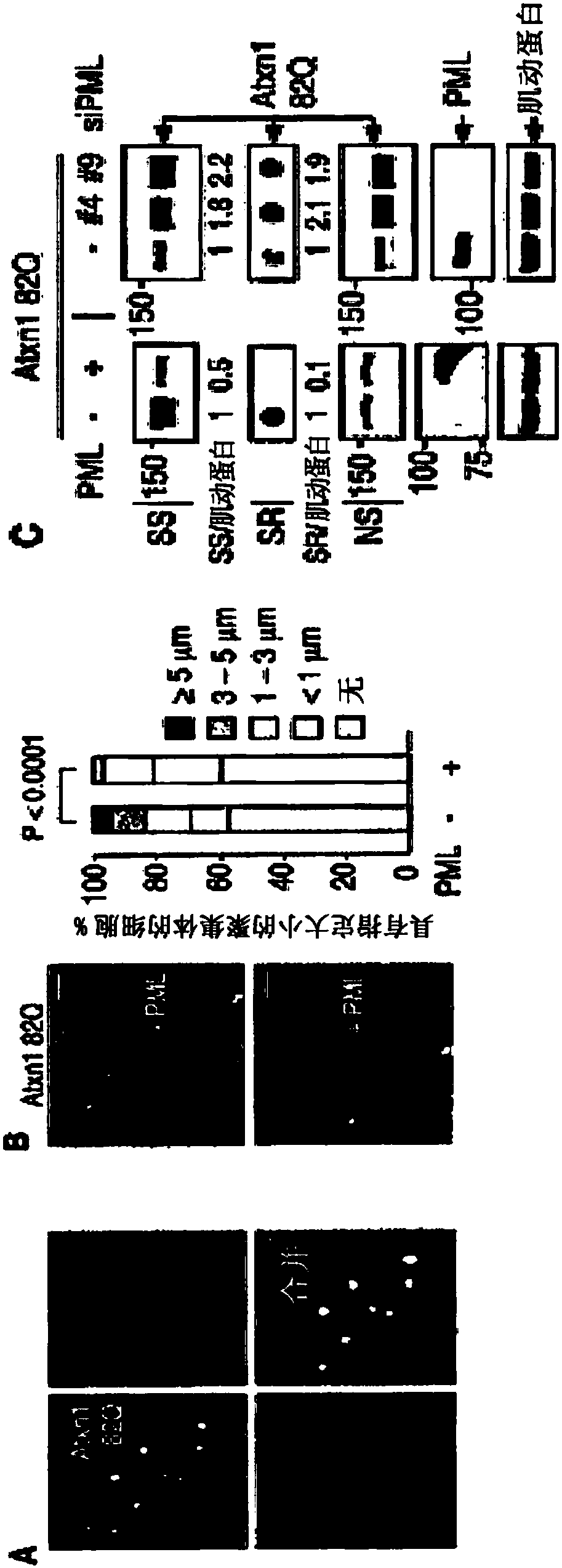
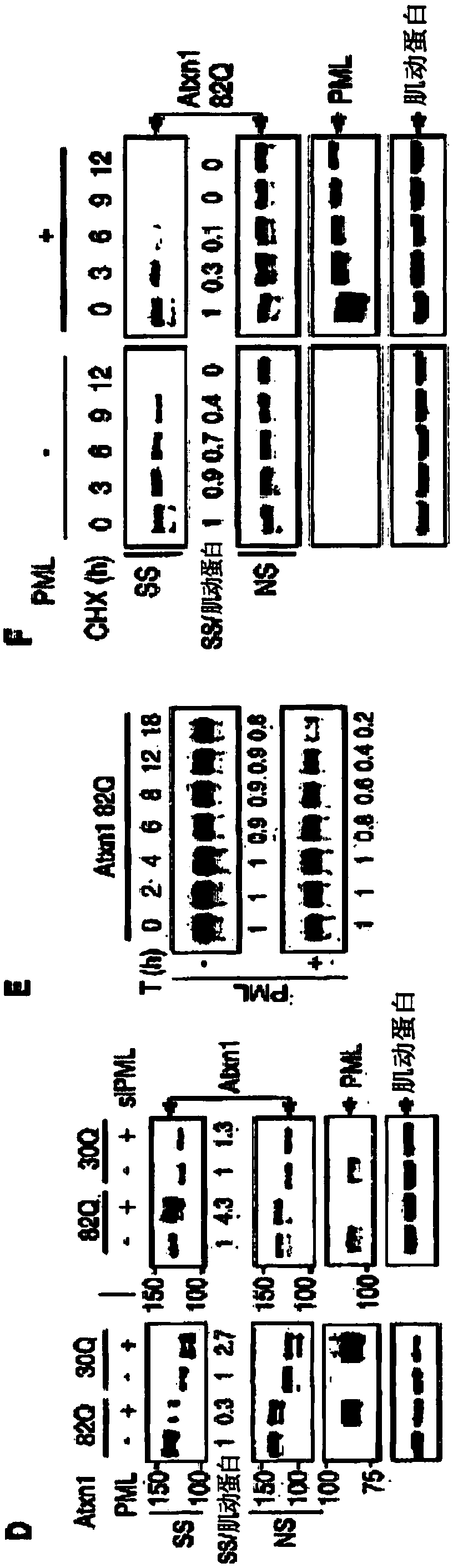
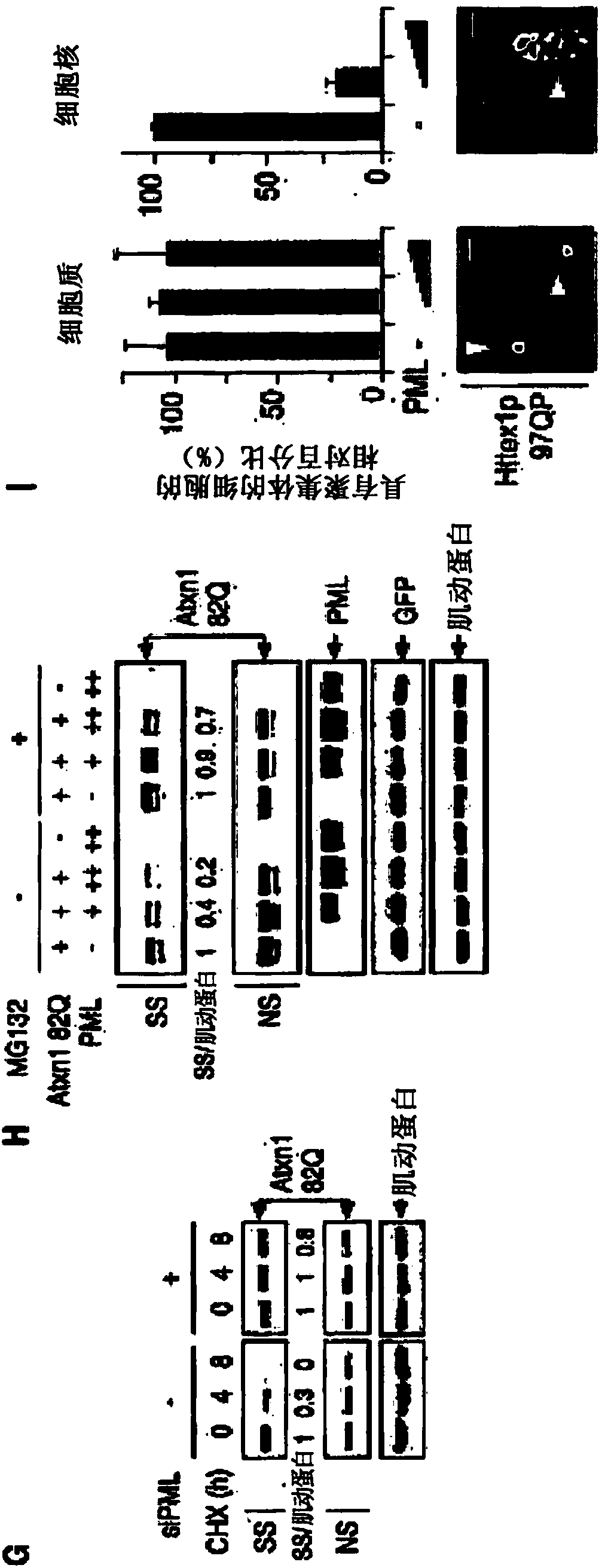
[0279] Misfolded proteins impair cellular function and lead to disease. How these proteins are detected and degraded is not well understood. Experiments presented herein show that PML (also known as TRIM19) and the SUMO-dependent ubiquitin ligase RNF4 work together to promote the degradation of misfolded proteins in the mammalian nucleus. PML selectively interacts with misfolded proteins through distinct substrate recognition sites and binds these proteins to small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMOs) through its SUMO ligase activity. The SUMOylated misfolded protein is then recognized and ubiquitinated by RNF4, and the misfolded protein is subsequently targeted for proteasomal degradation. Furthermore, it is shown herein that PML deficiency accelerates polyglutamine (polyQ) disease in a mouse model of spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1). These findings reveal a mamm...
Embodiment 2
[0401] Example 2: TRIM proteins can recognize misfolded proteins and promote their degradation
[0402] The triple domain-containing (TRIM) family consists of a large number of proteins in the cells of multicellular animals, ranging from about 20 in C. elegans to over 70 in mice and humans. These proteins share a characteristic TRIM or RBCC motif at their N-termini, which consists of a RING domain, one or two B-boxes (similar to the RING domain, coordinated by zinc ions) and a coiled-coil region. This is followed by a more variable C-terminal region in TRIM proteins and contains different motifs (Hakeyama, 2011, Nat Rev Cancer, 11:792-804; Ozato et al., 2008, Nat Rev Immunol, 8:849 -860). TRIM proteins regulate a range of cellular processes, including those that protect against cancer and viral infection. Biochemically, some TRIM proteins display ubiquitin E3 ligase activity, which is attributed to the RING domain within the TRIM / RBCC region. In addition, at least some TR...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com