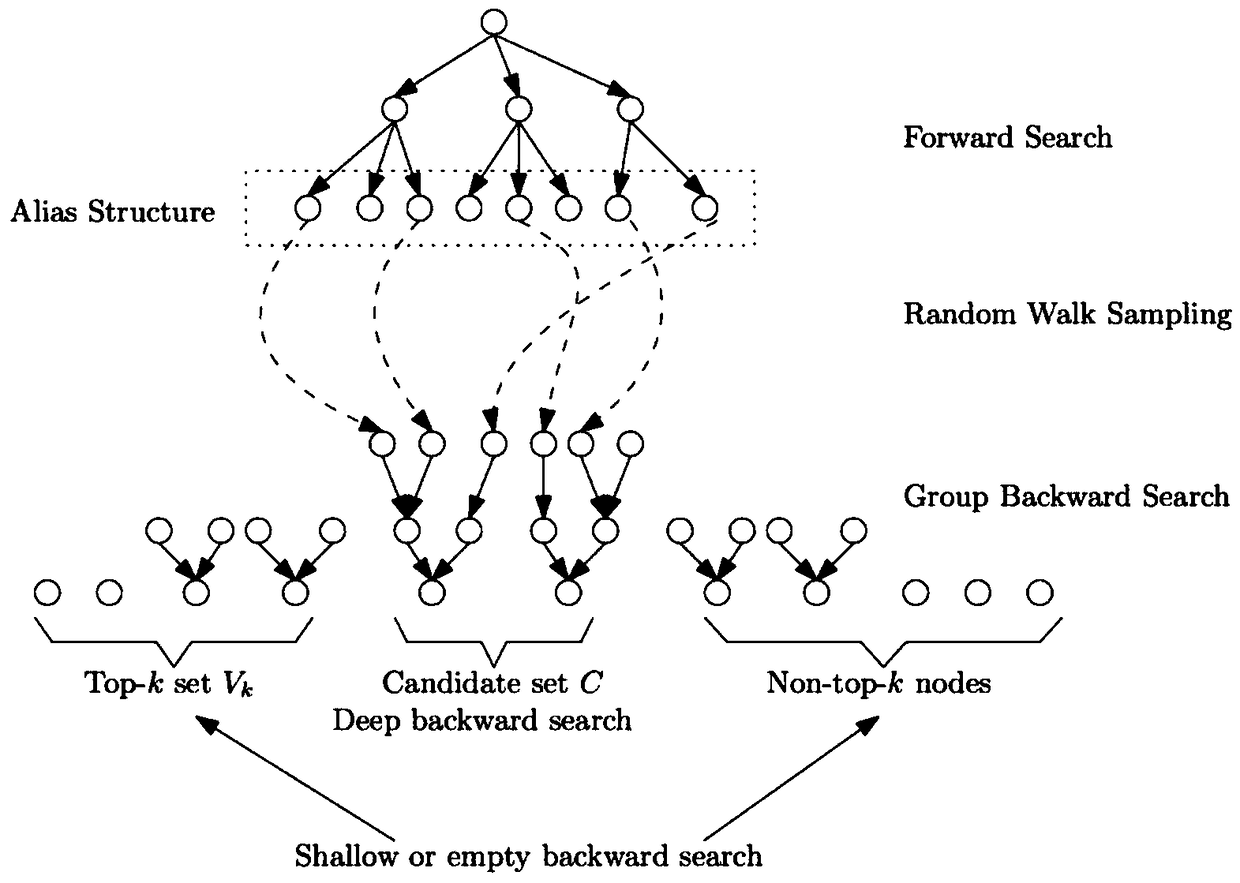
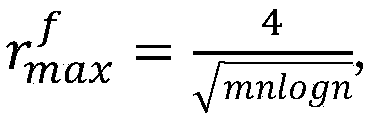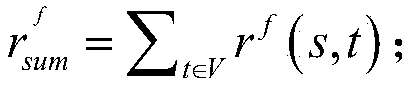TopPPR method for calculating large graph node proximity
A technology of proximity and nodes, which is applied in computing, computer components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inapplicability and inaccurate results returned by Top-kPPR, achieve good accuracy and running time, reduce time overhead, The effect of high computational efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0050] The identifiers involved in the present invention and their meanings are shown in Table 1 below.
[0051] Table 1 Identifiers and their meanings
[0052]
[0053] The present invention first briefly introduces the basic definition of PPR and the definition of its accuracy.
[0054] PPR definition:
[0055] Let G=(V,E) represent a directed graph, V is the point set in the graph, the number of points is n, E is the edge set in the graph, the number of edges is m. Given a source point s ∈ V, an attenuation factor α, define a topological random walk starting from the source point s, each step of which either stops at the current point with the probability of α, or (1 -α) random walk to any neighbor node of the current point. Then for all points v∈V in the graph, the exact PPR value π(s,v) from s to v is equal to the probability of a random w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com