Equation for analyzing propagation law of malicious program and malicious program propagation prediction method
A malicious program and equation system technology, applied in the field of big data security, can solve the problem of no malicious program prediction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
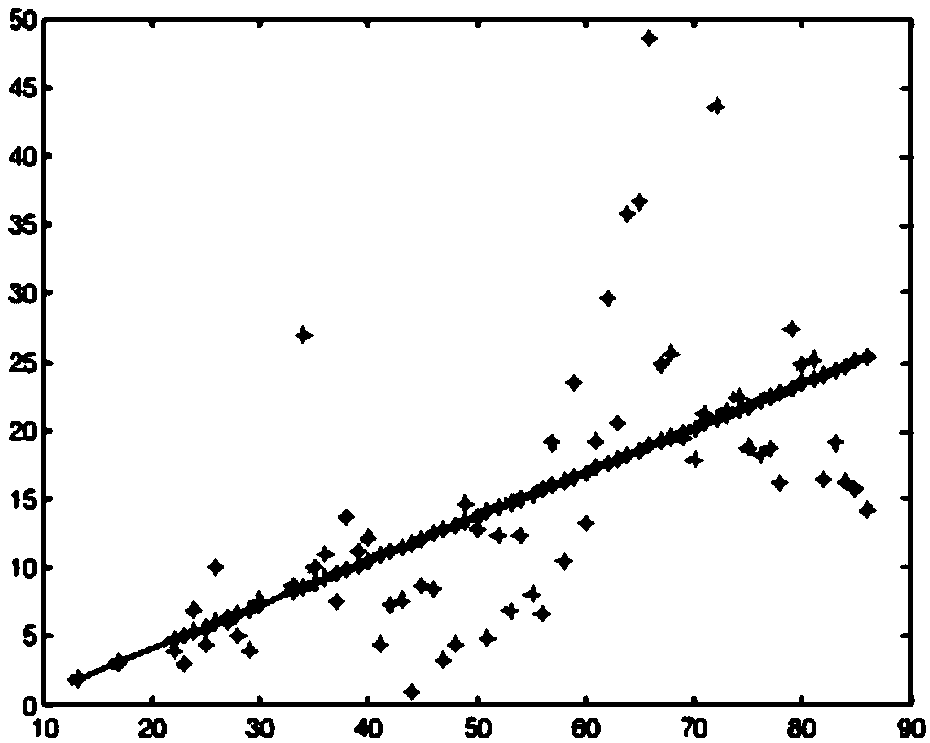
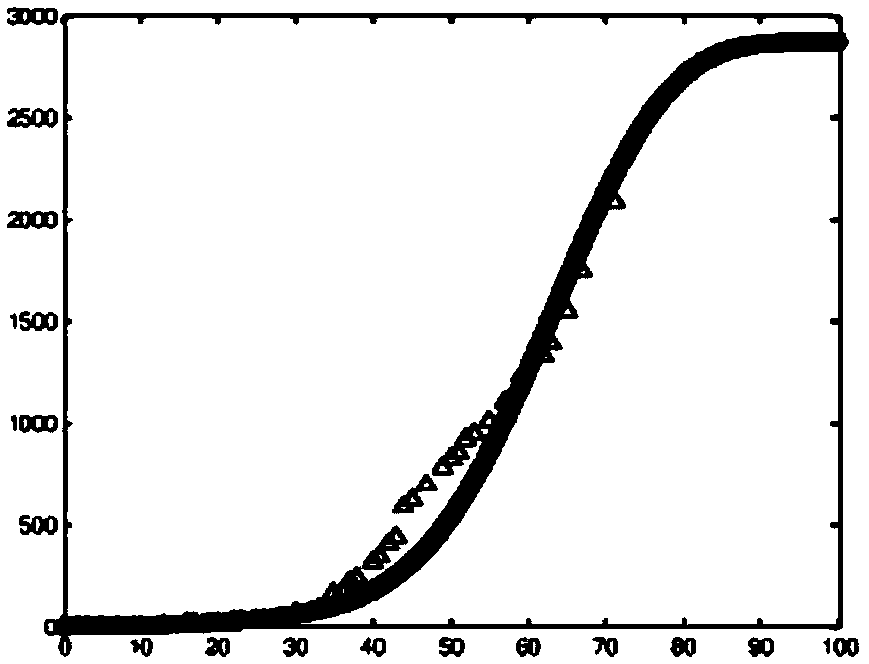
[0039] Example 1 The initial establishment of the method, such as Figure 4 .
[0040] use as figure 2 The four-compartment model shown, where,
[0041] Healthy Devices—Denote Healthy Devices with S
[0042] Freely infected devices (infected)—let I represent the number of infected devices that have not been confirmed to be infectious
[0043] Confirmed equipment (isolated) - use P to indicate that it has been isolated and withdrawn from the infected system, and will not infect other equipment
[0044] Repaired or damaged equipment (including "repaired equipment" and "damaged equipment") - use R to represent its number, and no longer participate in the spread of malicious programs. Note: Generally, it is rare for equipment damage caused by malicious program damage, so the impact of equipment damage is not considered in this method.
[0045] The construction process of the differential equation:
[0046] 1. Let the infection rate be λ 1 , indicating the ratio of infect...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2 Confirmation of coefficients, such as Figure 4 .
[0057] The first is big data statistics: analyze and predict according to business needs, so obtain device data (in days) infected by malicious programs within a period of time (generally the time period closest to the current time).
[0058] Then obtain relevant parameters sequentially according to the actual situation.
[0059] 1) Initial value function I(t)=φ(t), t∈[-T,0]. This is the starting function of the differential equation with delay, which can be obtained by statistics and fitting based on the data in the actual environment. The processing method of this method is to set the value of the initial function based on the average value of the infected device counted by big data, which is called the initial value.
[0060] 2) T value, that is, the incubation period. In an actual network environment, the period from when a device carrying a malicious program receives a malicious program file to whe...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3 method to solve, such as Figure 4 .
[0067] Repeatedly adjust the parameters λ, j, T, φ(t), so that these parameters can conform to the statistical characteristics of the actual data, so that the theoretical value and the actual value can reach the most consistent degree.
[0068] Substitute the above parameter values into the differential equation system. Since we cannot find the analytical solution of the equations, we use the Runge-Kutta method in numerical analysis to solve the equations.
[0069] The solution process of the Runge-Kutta method:
[0070] Let the initial problem be stated as follows
[0071] y'=f(t,y),y(t 0 )=y 0
[0072] where y'=f(t,y) corresponds to The resulting RK4 equation is as follows:
[0073]
[0074] in
[0075] k 1 =f(t n ,y n )
[0076]
[0077]
[0078] k 4 =f(t n +h,y n +hk 3 )
[0079] Thus, the next value (y n+1 ) by the current value (y n ) plus the product of the time interval (h) and an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com