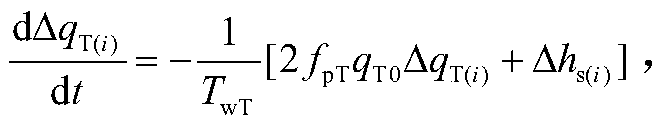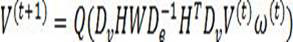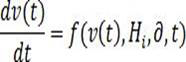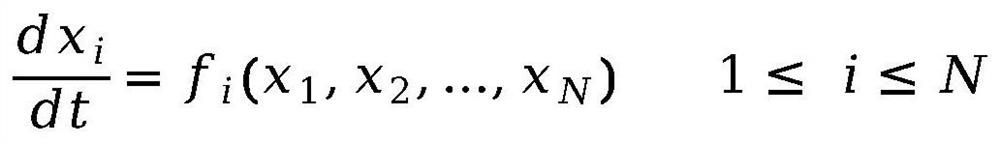Patents
Literature
58 results about "Differential equation models" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Systems and methods to determine elastic properties of materials
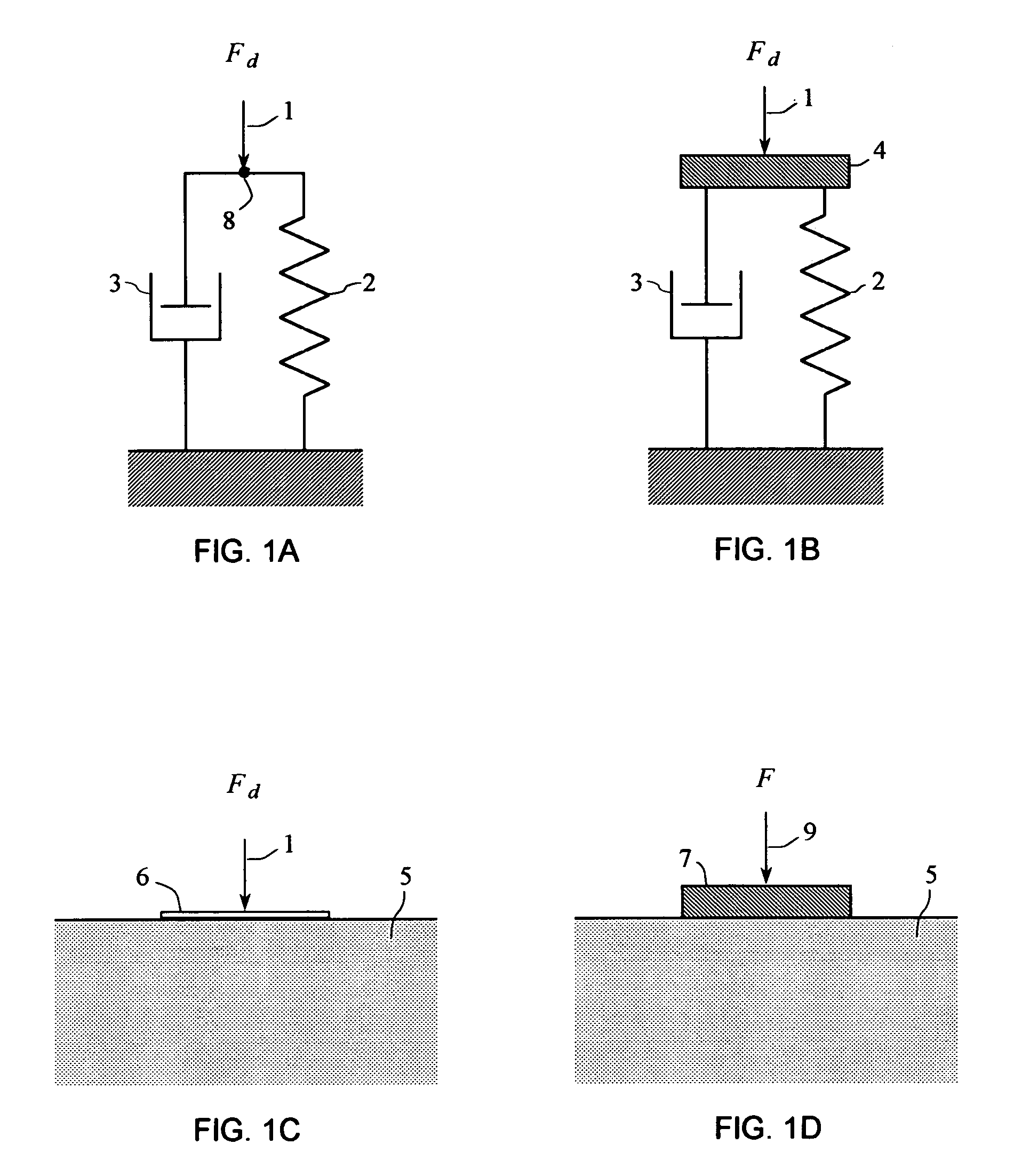
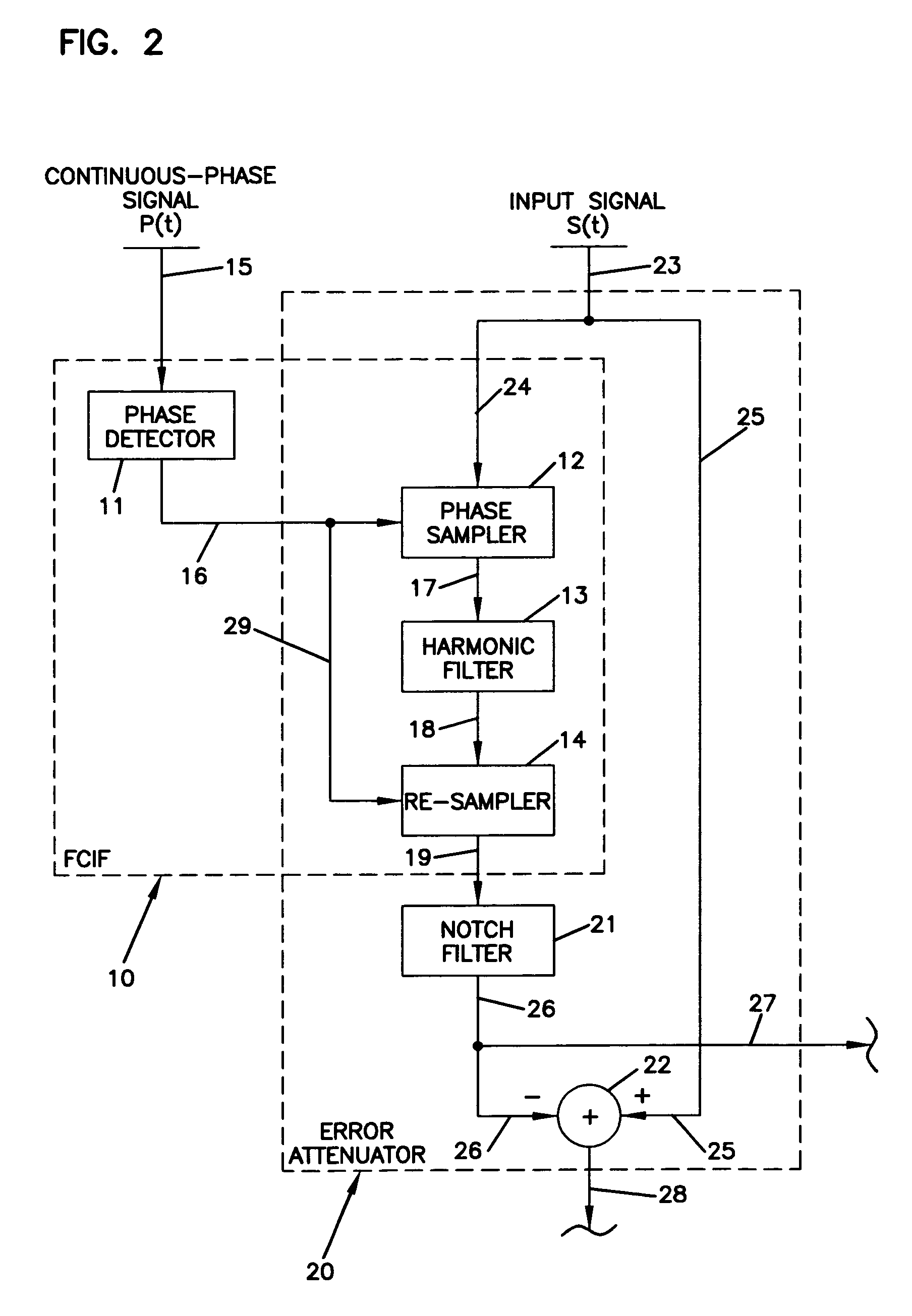
InactiveUS20050267695A1Elastic properties can be determinedInherent in massVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTime domainHarmonic
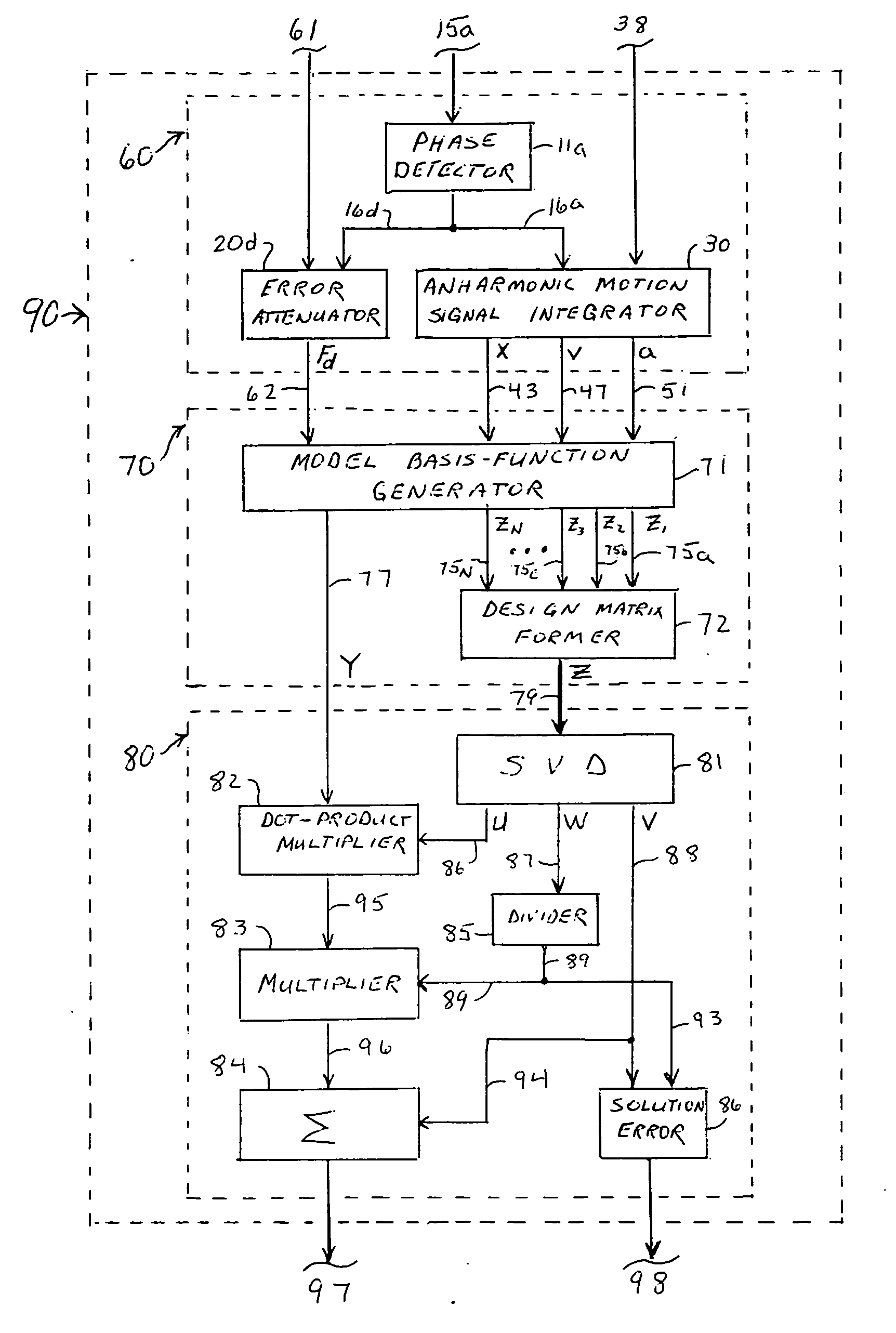
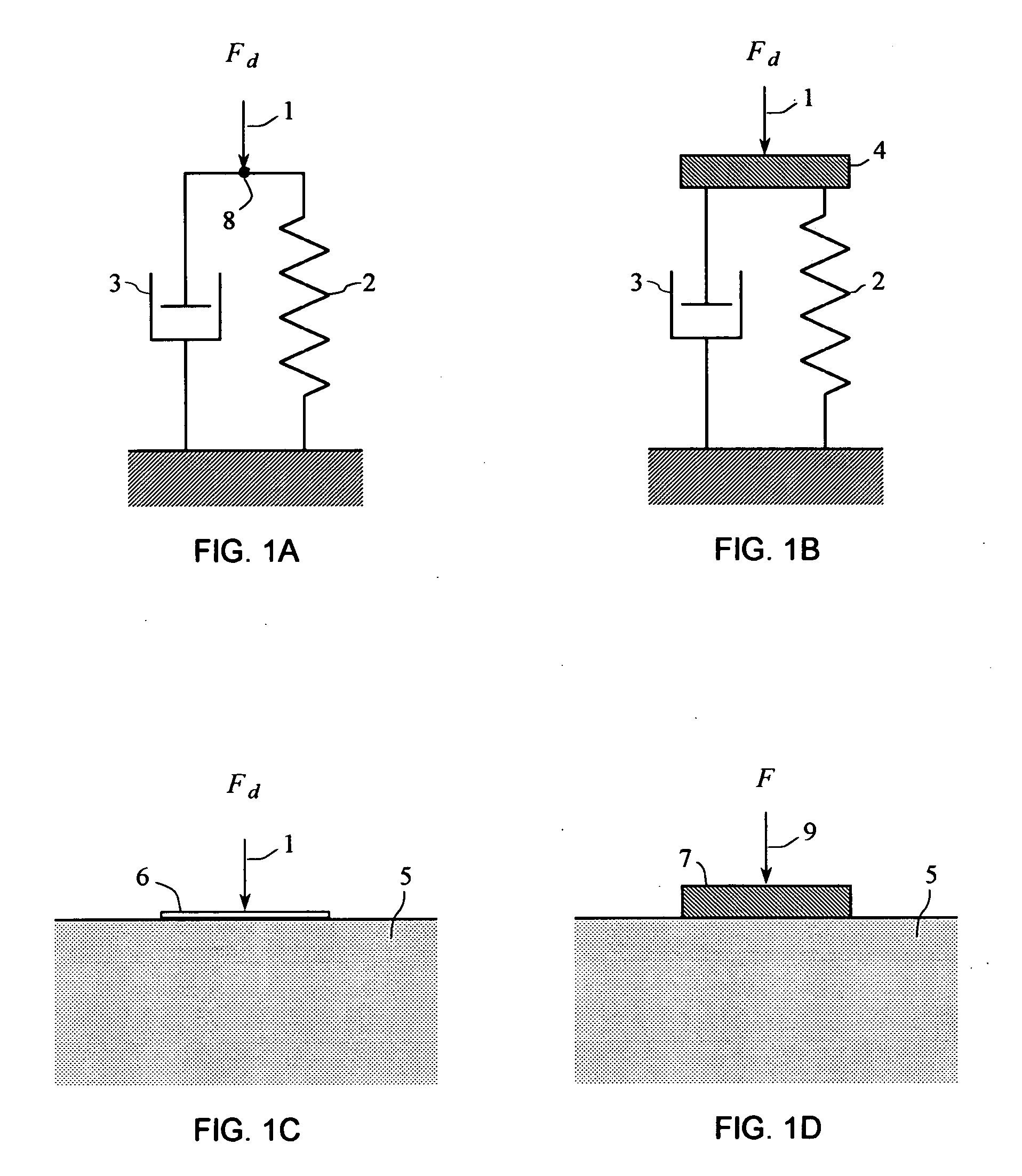
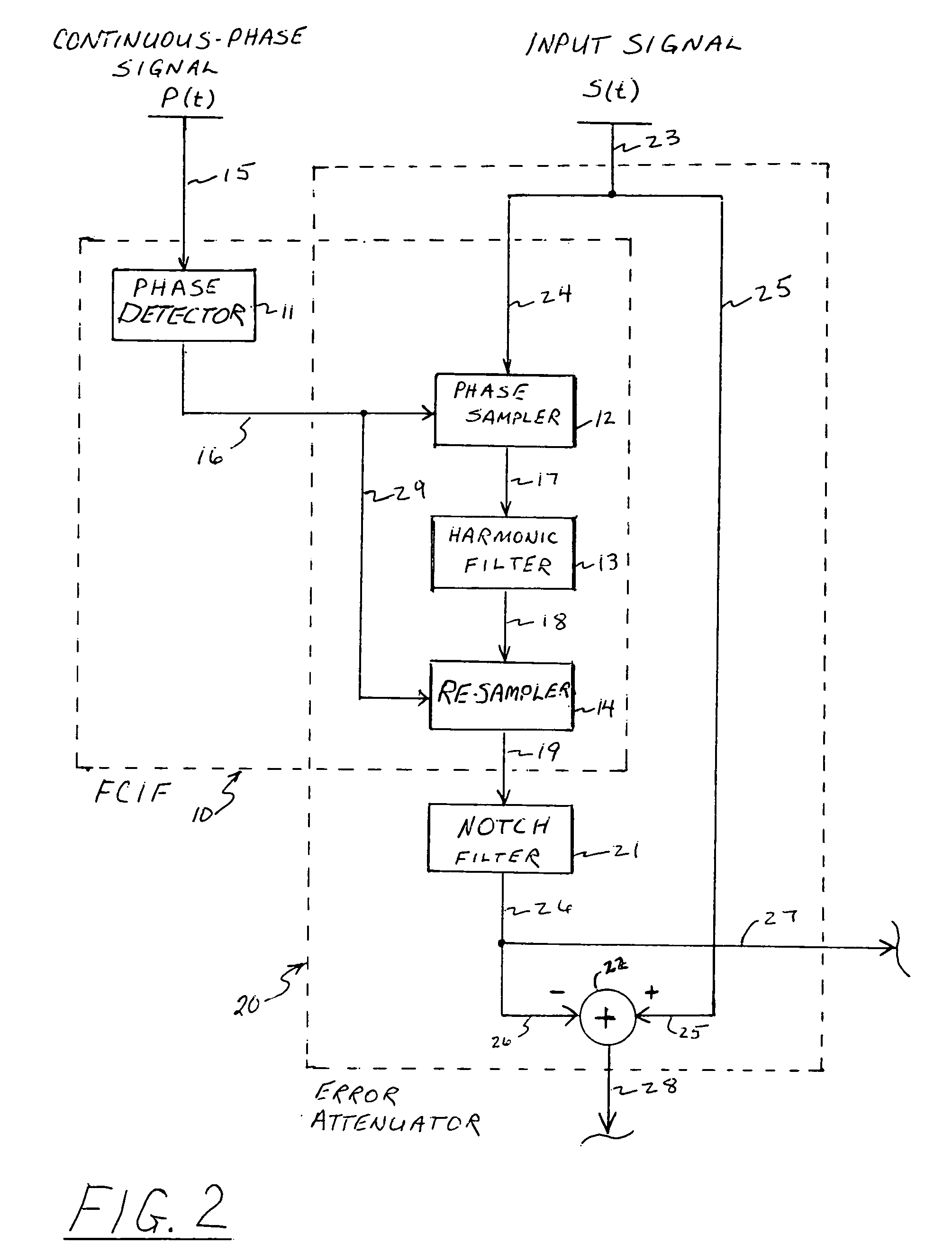
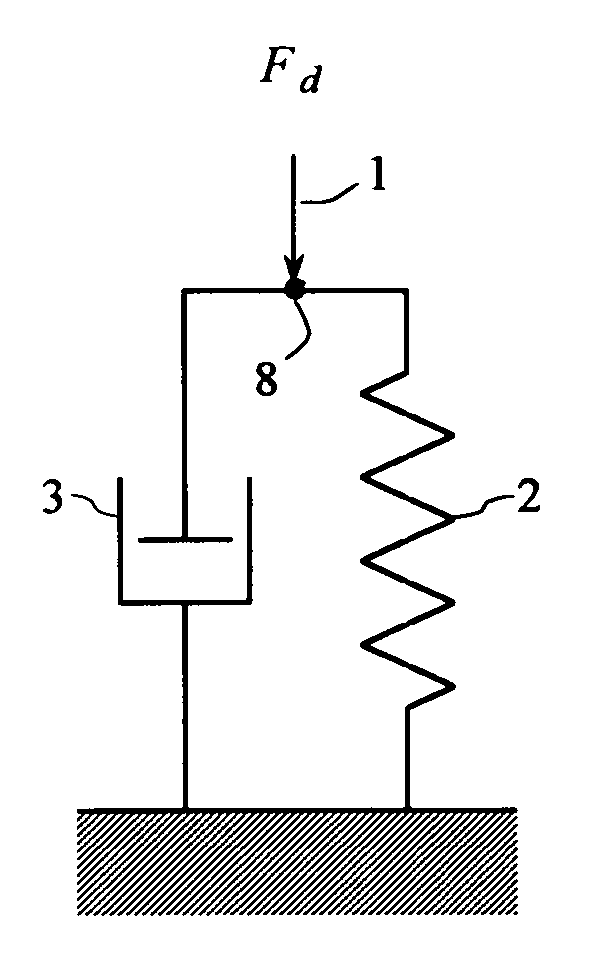
The present invention provides systems and methods to use a measured driving-point response of a nonlinear material to determine one or more elastic properties of the material. The present invention takes advantage of the full information represented by the transient component, the steady-state component, the anharmonic components, and the nonlinear response components of a measured driving-point response of a real nonlinear material, without limitation in the use of large-amplitude forces. The elastic properties are determined by forming and solving a time-domain system of linear equations representing a differential equation model of the driving-point motions of the material. Based on a single, short duration, large-amplitude driving point measurement, both linear and nonlinear properties can be determined; both large-amplitude and near-zero amplitude properties can be determined; and elastic-wave speed and elastic moduli and their variation with depth can be determined. The present invention also provides a system and a method to filter an input signal to either attenuate or preserve each of one or more selected harmonic components that are harmonics of a phase reference signal.
Owner:GERMAN PETER THOMAS
Systems and methods to determine elastic properties of materials
InactiveUS7107159B2Elastic propertyInherent ambiguityVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTime domainHarmonic
The present invention provides systems and methods to used a measured driving-point response of a nonlinear material to determined one or more elastic properties of the material. The present invention takes advantage of the full information represented by the transient component, the steady-state component, the anharmonic components, and the nonlinear response components of a measured driving-point response of a real nonlinear material, without limitation in the use of large-amplitude forces. The elastic properties are determined by forming and solving a time-domain system of linear equations representing a differential equation model of the driving-point motions of the material. Based on a single, short duration, large-amplitude driving point measurement, both linear and nonlinear properties can be determined; both large-amplitude and near-zero amplitude properties can be determined; and elastic-wave speed and elastic moduli and their variation with depth can be determined.
Owner:GERMAN PETER THOMAS
Lyapunov stability analysis method of time delay electric system
InactiveCN103227467AReduce dimensionalityThe number of variables to be requested is reducedAc network circuit arrangementsLyapunov stabilityTime delays
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric systems. In order to solve the problem of low stability analysis computing efficiency of the original time delay electric system, effectively reduce the dimensionality of a time delay differential equation and achieve higher computing efficiency, the invention adopts a technical scheme that a Lyapunov stability analysis method of a time delay electric system comprises the following steps of establishing a constraint time delay differential equation (CTODE) model of the electric system, rearranging and reorganizing system states in a manner that the states (z1 to z) not considering time delay influence are at the front and the states (z2 to z) considering the time delay influence are at the back, obtaining a CTODE model corresponding to the original time delay system, and basing on a new stability criterion of the CTODE model. The method is mainly applied to the electric system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for designing stability parameters of self-adapting filter of self-balancing system of magnetic suspension rotor
ActiveCN104950919AGuaranteed stabilityImprove self-balancing accuracyAdaptive networkControl using feedbackStability parameterAdaptive filter
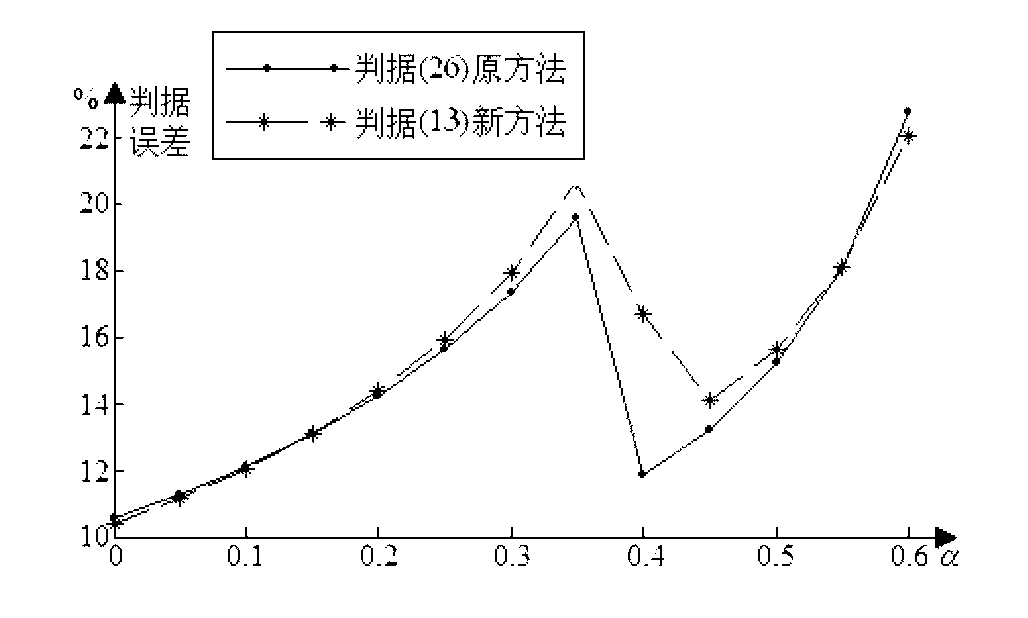
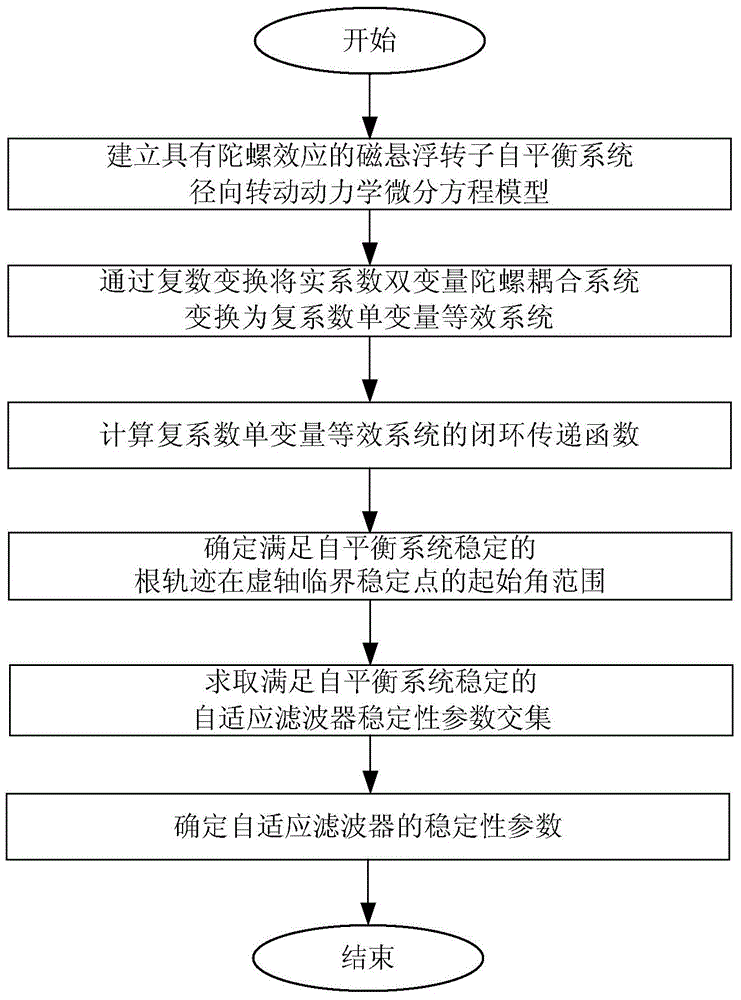
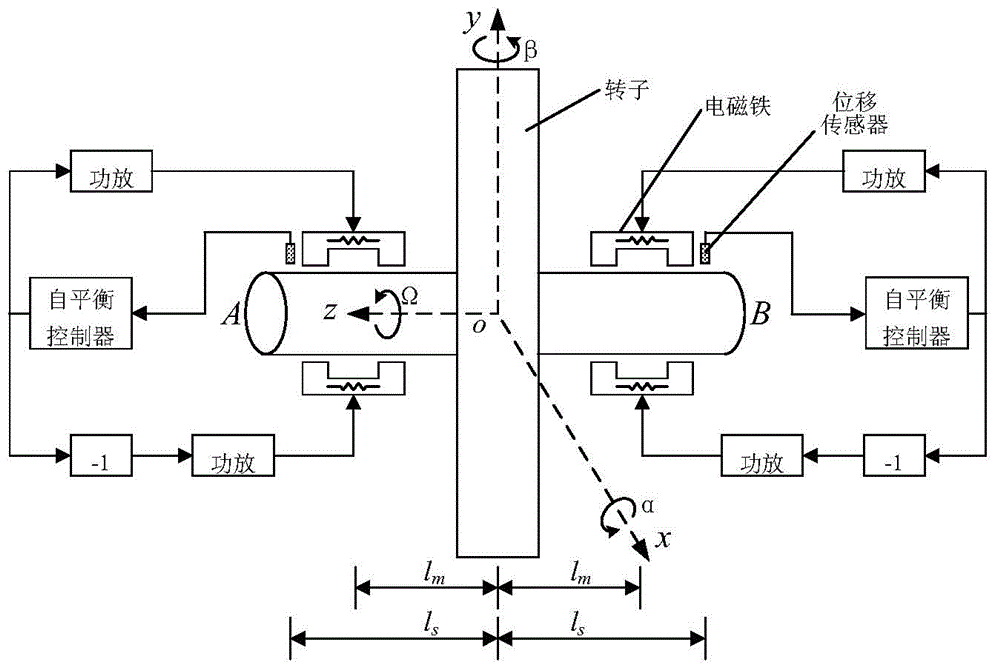
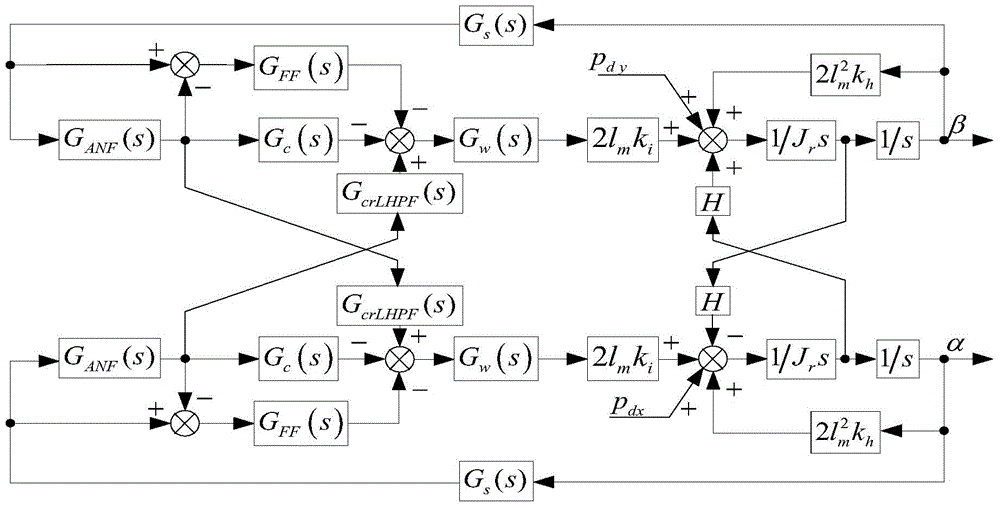
The invention discloses a method for designing stability parameters of a self-adapting filter of a self-balancing system of a magnetic suspension rotor. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a radial rotation dynamics differential equation model of the self-balancing system of the magnetic suspension rotor with a gyroscopic effect; converting a real coefficient bivariate gyroscopic coupling system into a complex coefficient univariate equivalent system through complex transformation; calculating a closed-loop transfer function of the complex coefficient univariate equivalent system; determining a start angle range of a root locus, which meets the stability requirement of the self-balancing system, at a critical stable point of an imaginary axis; resolving a stability parameter intersection of the self-adapting filter; finally, determining the stability parameters of the self-adapting filter. While the rotor speed is estimated and tracked in real time so as to improve the self-balancing precision, the stability of the self-balancing system of the magnetic suspension rotor with the gyroscopic effect within a full speed range is ensured. The method disclosed by the invention is simpler and more convenient than other methods, and is especially suitable for practical magnetic suspension rotor systems.
Owner:北京高孚动力科技有限公司
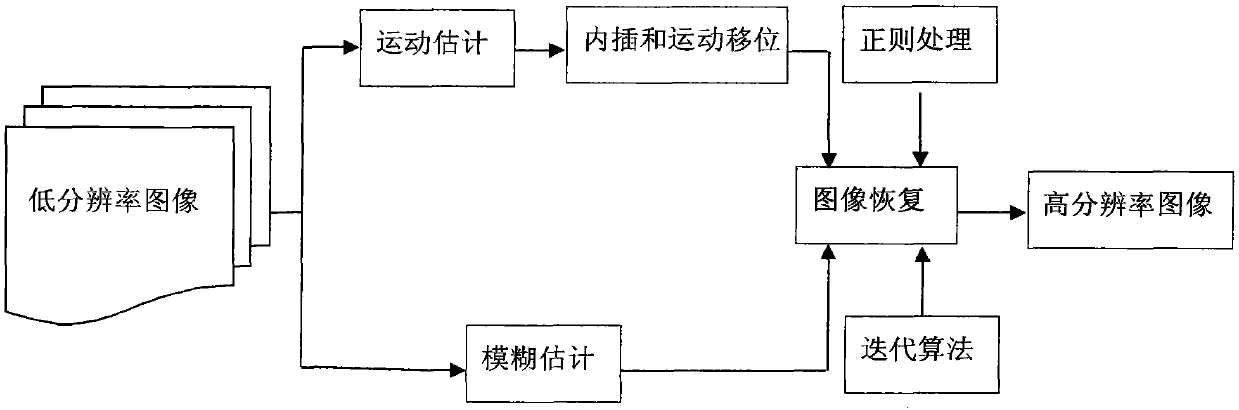
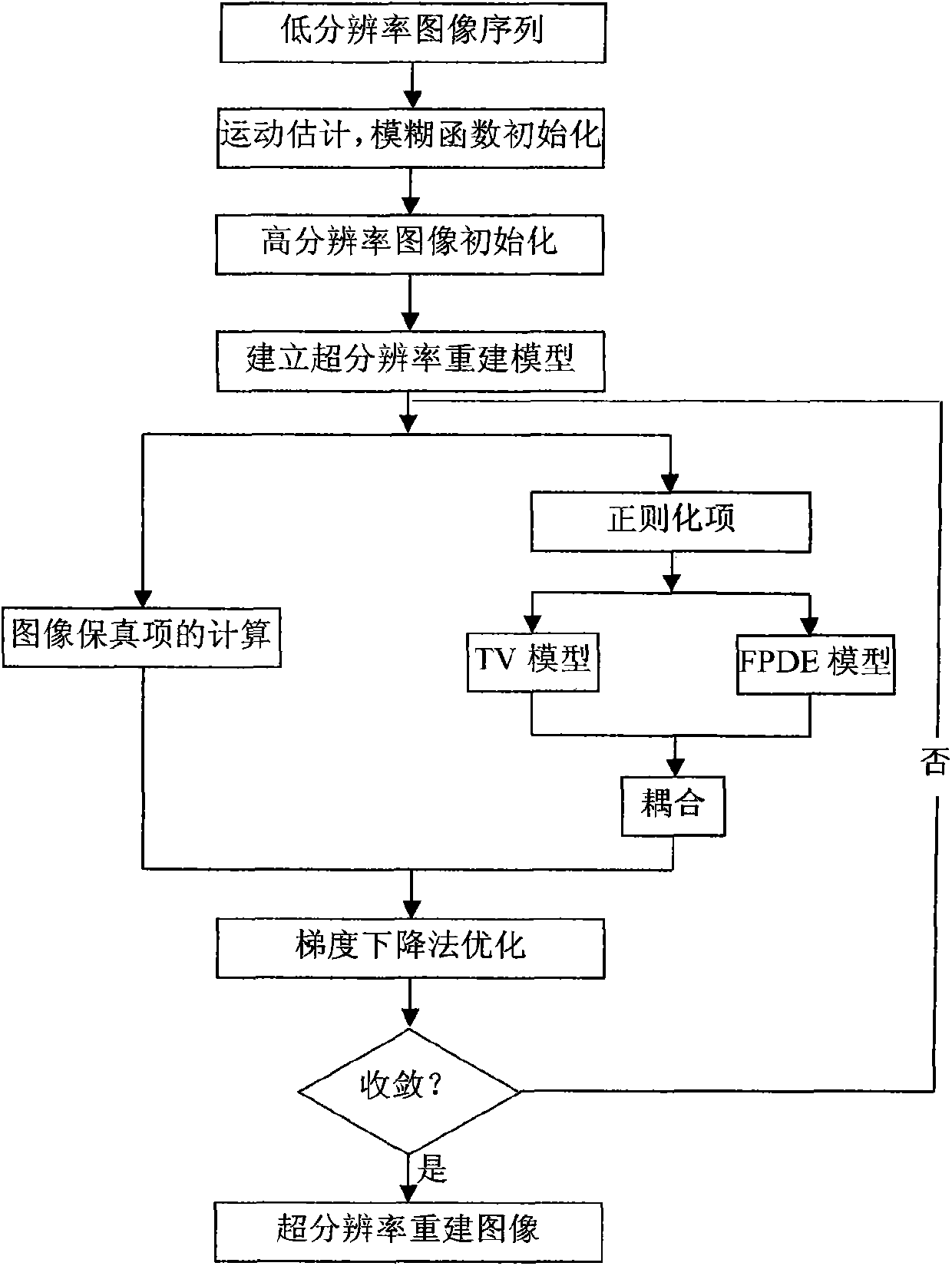
Super-resolution image reconstruction method based on coupled partial differential equation model
InactiveCN103473752AQuality improvementKeep the edgeImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionPartial differential equation
The invention discloses a super-resolution image reconstruction method based on a coupled partial differential equation model. According to the reconstruction method, two partial differential models are coupled through defining a weighting function by utilizing the respective advantages of TV (Total Variation) and FPDE (Fourth Partial Differential Equation) in image restoration, a large weight is adopted for a TV model at an image edge area so as to maintain the edge and texture details of images, the large weight is adopted for an FPDE model at an image flatness area so as to inhibit a staircase effect generated by the TV model, new models serve as normalization items to reconstruct a super-resolution images, and the visual effect of image reconstruction can be enhanced.
Owner:杨勇
Method for measuring power frequency parameters of superhigh/extrahigh-voltage alternating-current (direct-current) power transmission circuit
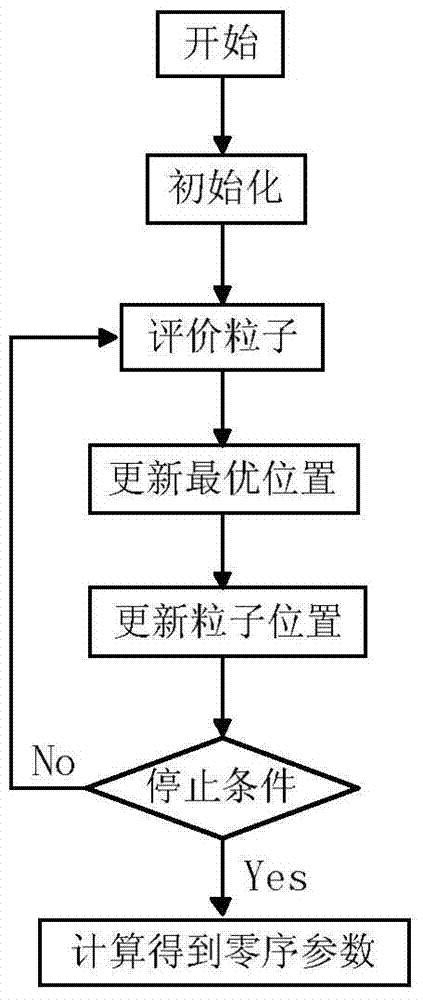
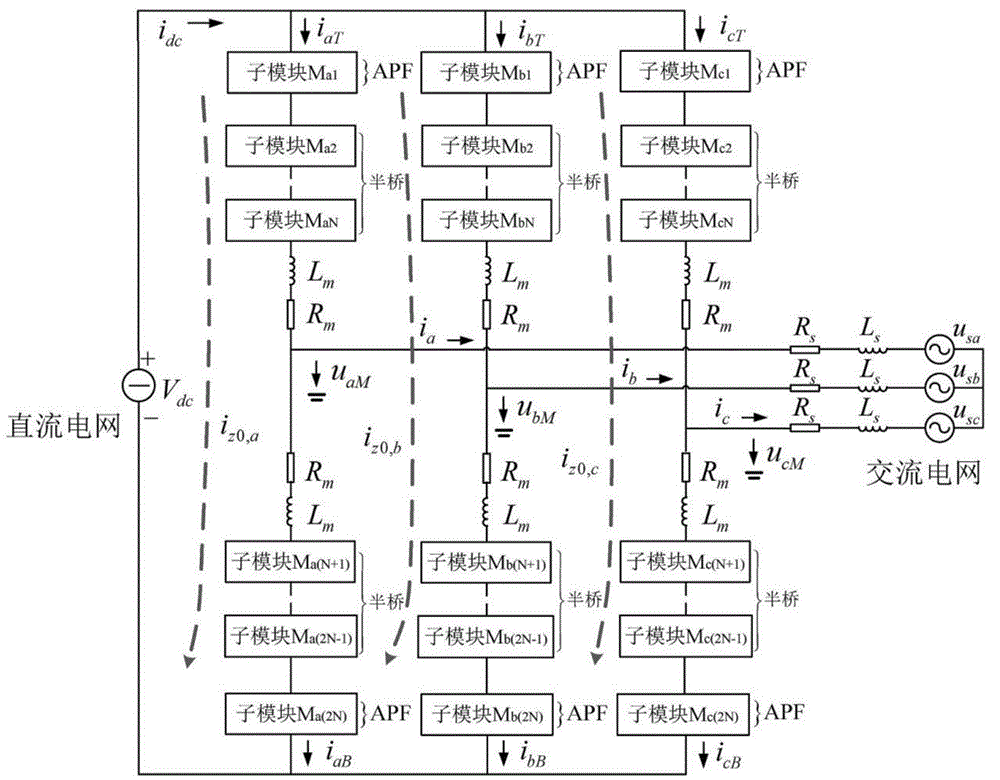
The invention discloses a method for measuring power frequency parameters of superhigh / extrahigh-voltage alternating-current (direct-current) power transmission circuit. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of synchronously measuring zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current on the head end and the tail end of the power transmission circuit, obtaining a power-frequency zero-sequence voltage phasor and a power-frequency zero-sequence current phasor by utilizing a Fourier filtering method, solving the power-frequency zero-sequence parameters of the power transmission circuit on the basis of a differential equation model and particle swarm optimization of the power transmission circuit, considering the influence of electromagnetic coupling between a distributive capacitor and the circuit on the power transmission circuit on the measurement of the power-frequency zero-sequence parameters, so that the precision of the power-frequency zero-sequence parameter measurement result of the power transmission circuit can be improved. The method is not only suitable for measuring the power-frequency zero-sequence parameter of a single-circuit and a multi-circuit superhigh / ultrahigh voltage alternating-current power transmission circuit, particularly suitable for measuring the power-frequency zero-sequence parameters of a double-circuit and four-circuit superhigh / ultrahigh voltage alternating-current power transmission circuit of a same tower and also suitable for remotely measuring the power-frequency parameters of the superhigh / ultrahigh voltage direct-current power transmission circuit.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Hybrid multilevel converter and variable switching frequency trajectory optimization control method thereof
InactiveCN104135180AAchieving Circulation SuppressionVerify feasibilityDc-ac conversion without reversalCapacitanceFull bridge
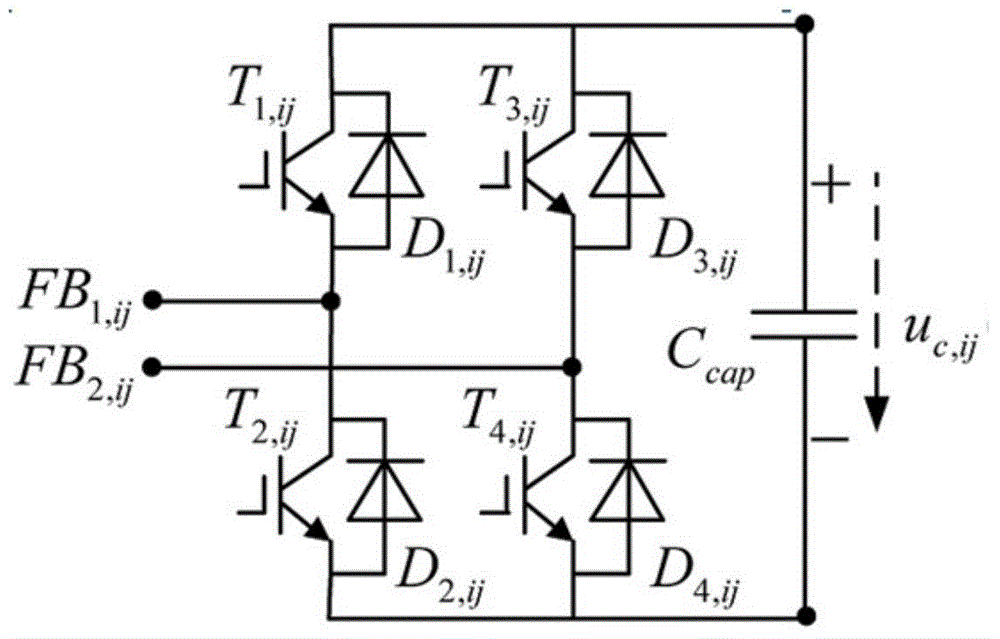
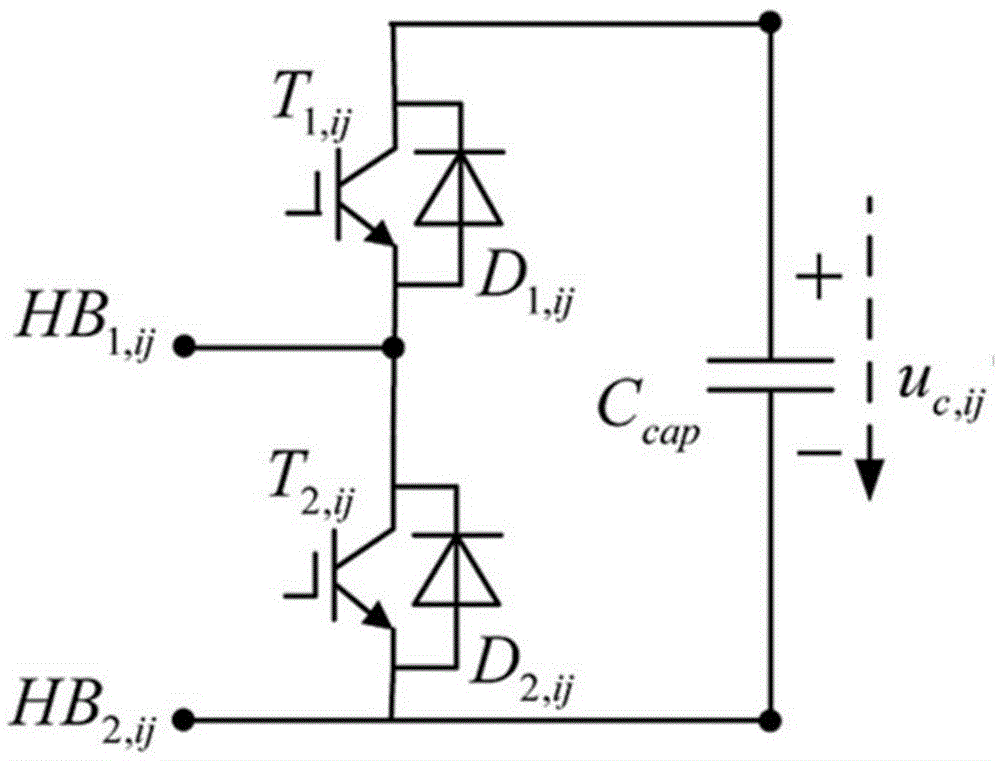
The invention discloses a hybrid multilevel converter and a variable switching frequency trajectory optimization control method thereof. The hybrid multilevel converter is connected between a direct current power grid and a three-phase alternating current power grid. The variable switching frequency trajectory optimization control method of the hybrid multilevel converter comprises the following steps that S1, differential equation models of the hybrid multilevel converter are established; S2, discretization state equations from the (K+1)th step to the (K+delta)th step are deduced; S3, a feasible sampling point set of output current predicted values is determined; S4, the optimal value f<theta> of an objective function f<theta>(k) is obtained, a switching function vector S<theta,opt>[k] corresponding to a feasible predicted position is used as a kth-step switching signal of the hybrid multilevel converter, data loading of a digital signal processor is completed, and a PWM switching signal is sent out at the moment corresponding to the optimal predicated position of a current trajectory. According to the hybrid multilevel converter and the variable switching frequency trajectory optimization control method of the hybrid multilevel converter, submodule direct current bus capacitance and voltage stable control of all full-bridge inverters and all half-bridge inverters of an upper bridge arm and a lower bridge arm can be achieved, rapid trajectory tracking of a current on the alternating current side can be achieved, and variable switching frequency optimization control can be achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for deciding radial rotation stability of magnetic suspension rotor system
InactiveCN1851719ASuitable for real system applicationSpecial data processing applicationsNutationMotion dynamics
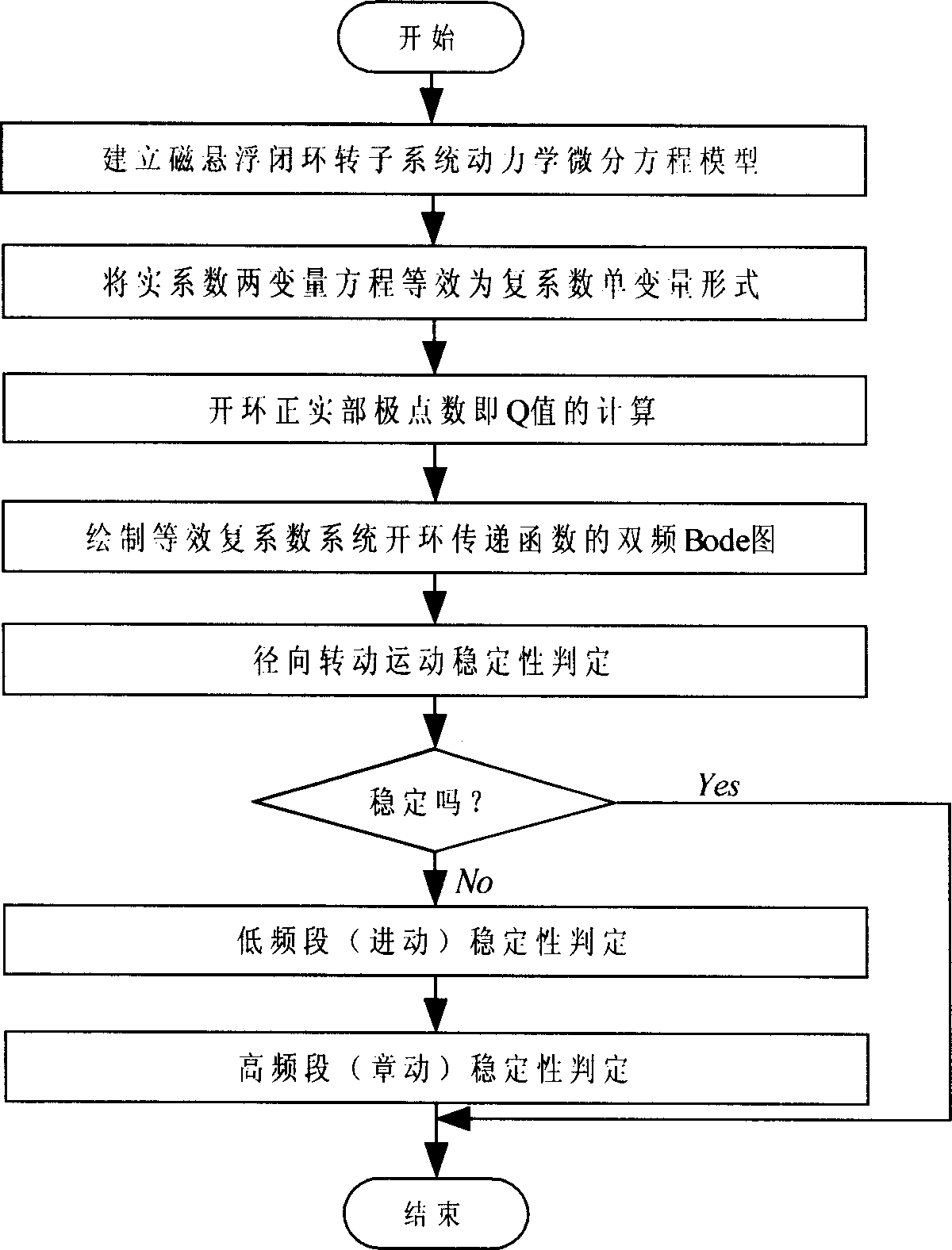
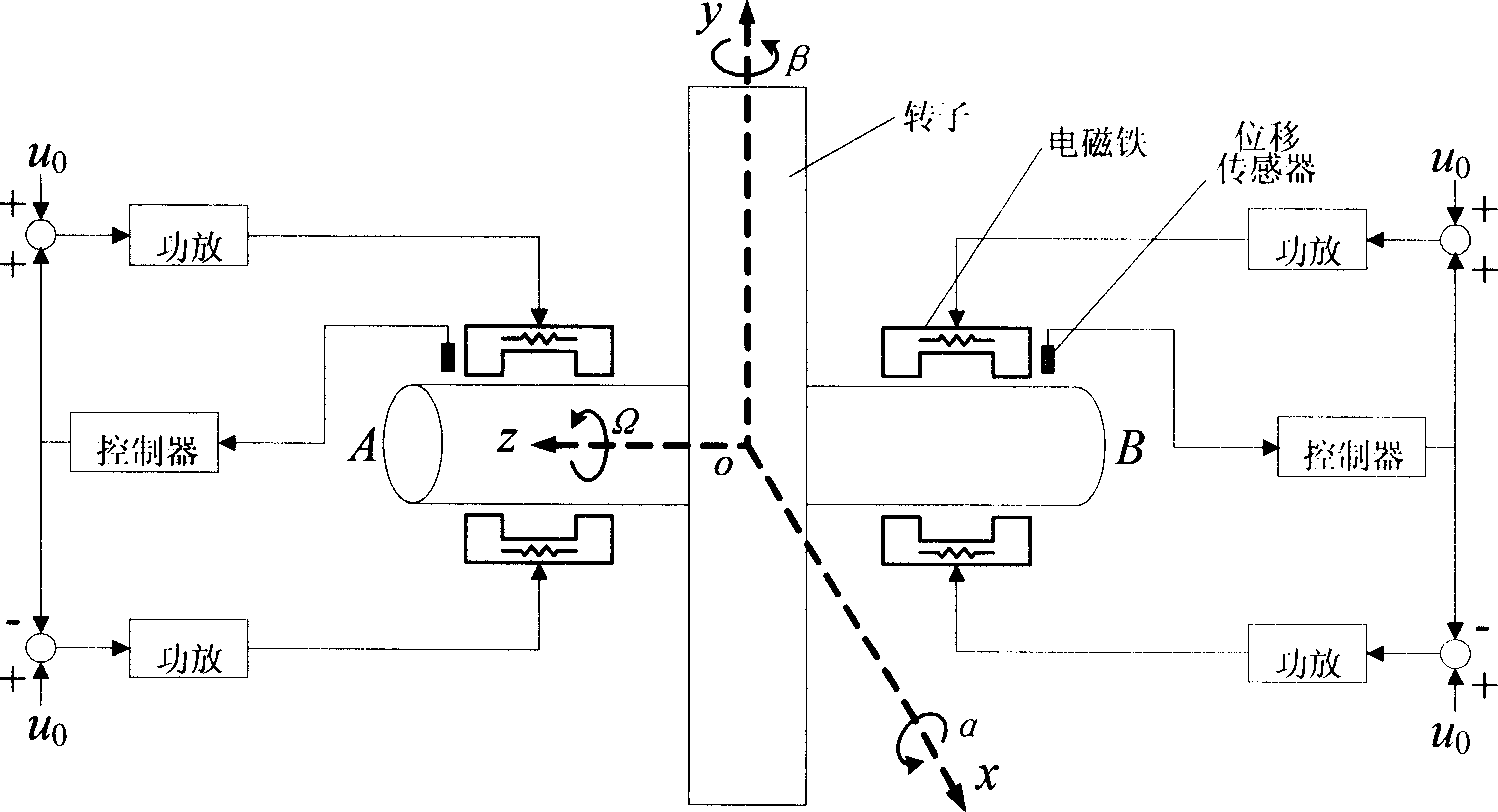
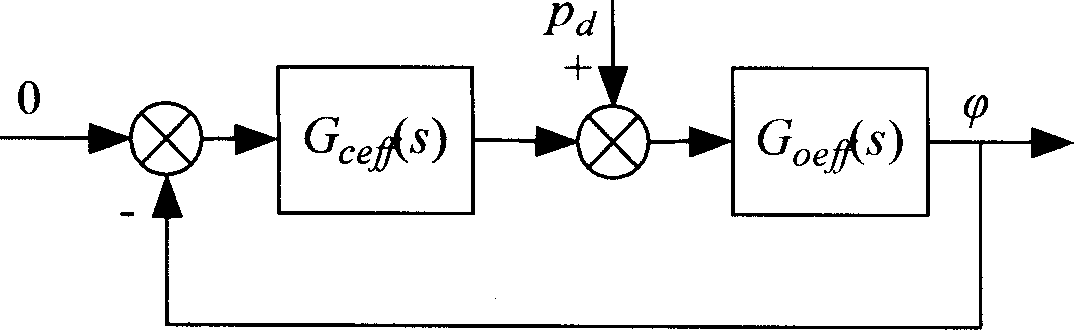
A method for judging magnetic suspension rotor system stability, includes through establishing magnetic suspension rotor system radial rotational motion dynamics differential equation model, adopting plurality conversion converting real coefficient two variable equation to complex system monovariant form, to obtain monovariant equivalent system, then drawing open loop transfer function dual frequency Bode chart of equifinality complex system, utilizing generalized classic frequency field stability criteria judging rotor precession and nutation stability, providing require condition for designing raising system stability correction link. The present invention converts multivariable system to equifinality monovariant system, thereby capable of using classical monovariant control theory to proceed stability analysis, relative usual multivariable method such as state space analysis method etc, not only very visual but also having good robustness, thus more fitting real system application.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Information spreading model based on cellular automaton
InactiveCN107194819ARich stateRealize intuitive simulationData processing applicationsBiomolecular computersAnalysis studyInformation propagation
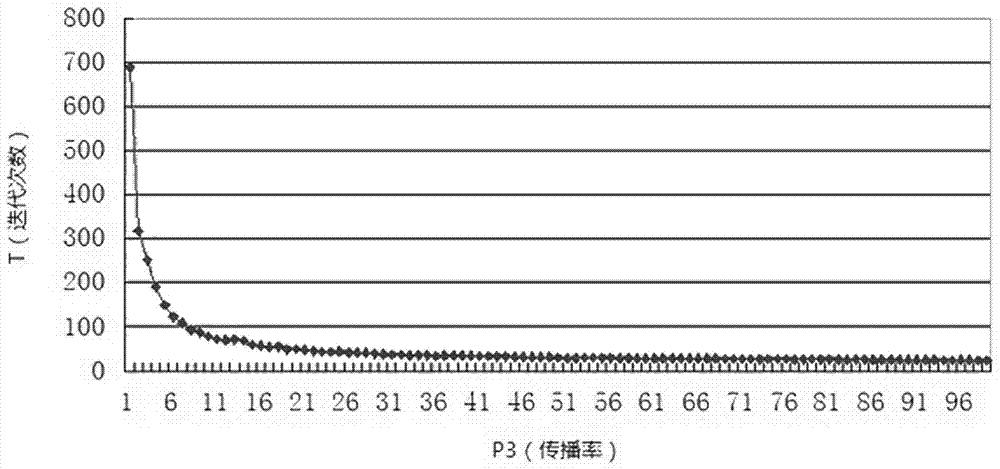
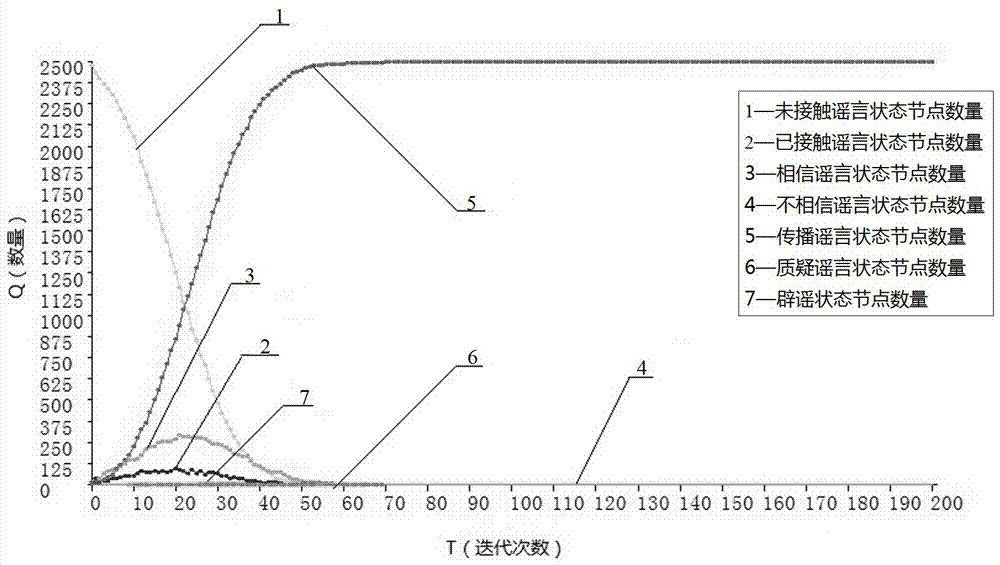
The invention provides an information spreading model based on a cellular automaton, comprising the evolution rule, parameter and algorithm of the model and main technological indexes for measuring states. On such a basis, user states are divided into sever types, a rumor spreading process is analyzed and researched, and a rumor spreading mechanism is revealed according to differences of different parameter comparison results. A rumor spreading control strategy is further provided, and a great suppression effect on a final information spreading extent is achieved. Simulation of the model built based on the cellular automaton starts with microcosm to reflect macroscopic behaviors of groups, a simulation result is more intuitional, meanwhile, the model is flexible in structure, and can randomly change the control strategy during an evolutionary process, which is incomparable with a traditional differential equation model. Real data and a simulation experiment result have a relative high fitting degree, so that the built model has the actual application value, and can provide a support for making the rumor control strategy.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
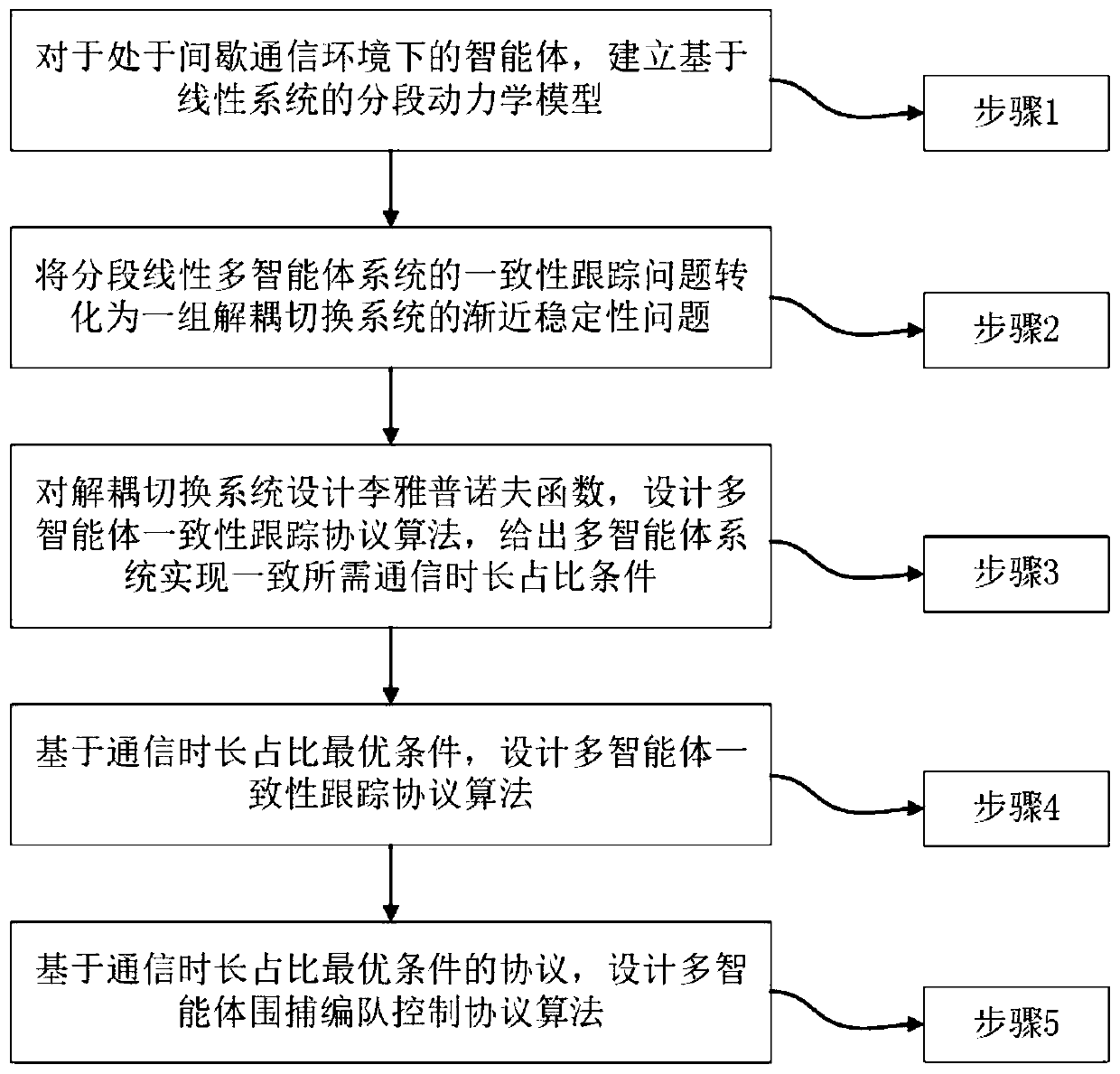
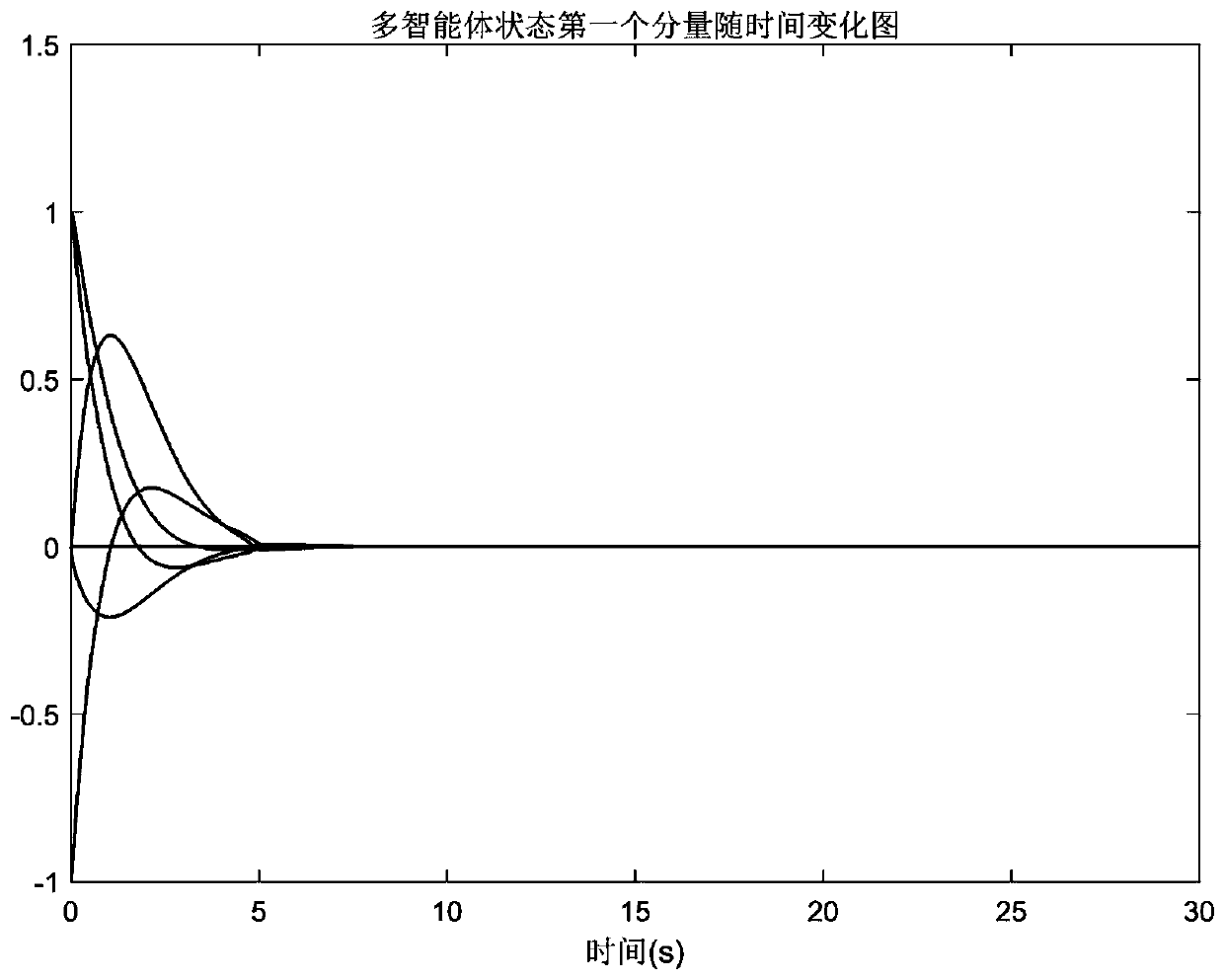
Multi-agent consistency tracking protocol design method suitable for multiple agents in communication under DoS attack
ActiveCN110716582AConsistency Tracking ImplementationOptimizing communication duration conditionsPosition/course control in three dimensionsProtocol designMulti-agent system
The invention discloses an uncertain multi-agent consistency tracking protocol design method for multiple agents in communication under DoS attack. The method comprises the following steps: for the multiple agents in communication under DoS attack, constructing a differential equation model of the agents; based on a switching system stability theory, transforming a multi-agent system consistency tracking problem into an asymptotic stability problem of a group of decoupling switching system; through a linear matrix inequality (LMI), constructing a decoupling switching system Lyapunov function,designing a multi-agent coordination consistency tracking protocol algorithm and communication duration proportion condition; and based on the linear matrix inequality (LMI) and the least communication duration proportion, designing the multi-agent consistency tracking protocol algorithm; and based on the linear matrix inequality (LMI) and the least communication duration proportion, designing a multi-agent rounding control algorithm.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Equation for analyzing propagation law of malicious program and malicious program propagation prediction method
ActiveCN109190375AUnderstanding Diffusion TrendsPlatform integrity maintainanceDiffusionInfection rate
The invention relates to an equation for analyzing the propagation law of malicious programs. As shown in Formula 1, the invention also relates to a malicious software diffusion prediction method based on a differential equation model. The method comprises the following steps: the number and information of malicious programs and the type of malicious programs are counted according to a selected area to obtain statistical data; data analysis is conducted to calculate the statistical data and to obtain the initial value, latency, infection rate and controlled rate; the initial value, incubationperiod, infection rate and controlled rate are substituted into the equations; a Kutta method is used to solve the problem, and the number of infected equipment is predicted. The invention adopts thebig data technology and the ordinary differential equation model to analyze and predict the equipment infected by the malicious program, so as to understand the spreading trend of the malicious program and formulate the related strategy.
Owner:密信(北京)数字科技有限公司
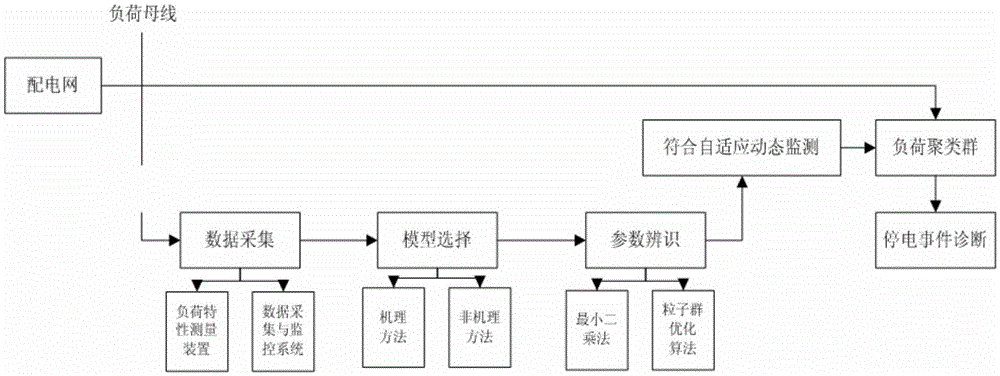
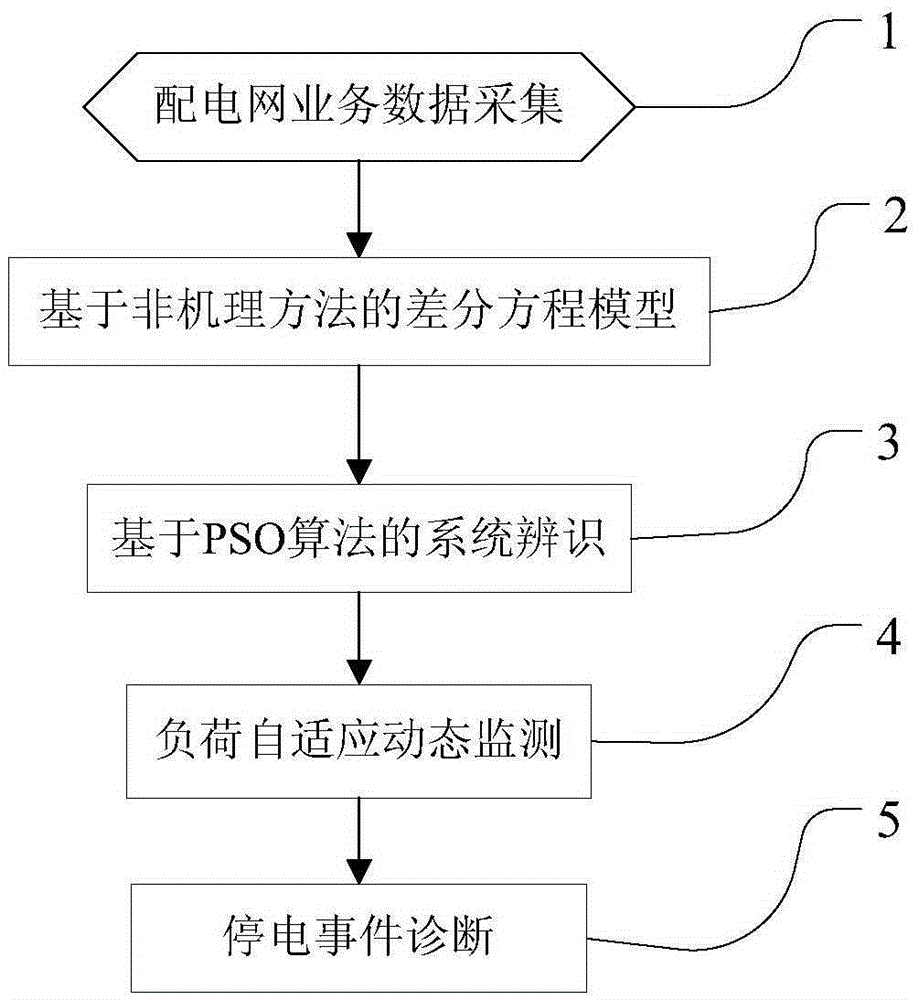
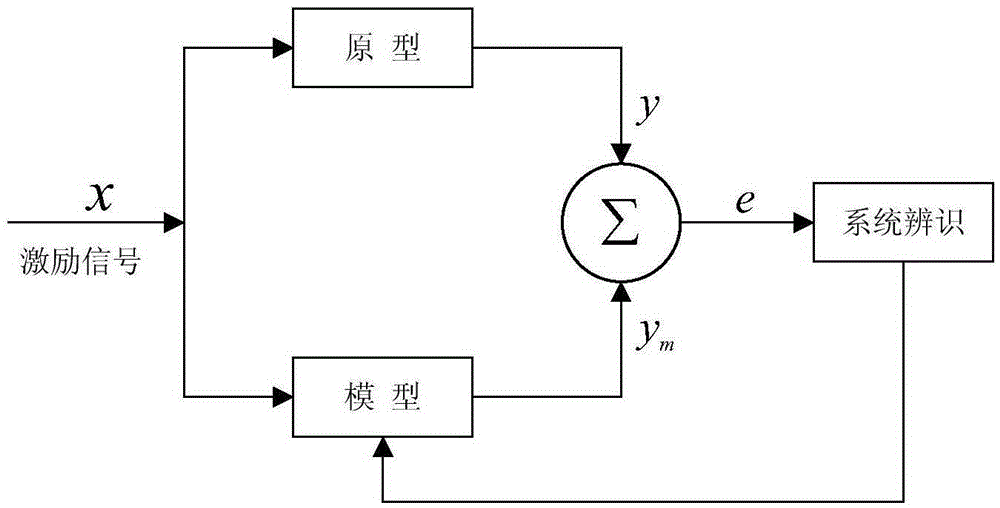
Adaptive dynamic load monitoring method for power distribution network power failure events
ActiveCN105406461AImprove accuracyImprove effectivenessAc network circuit arrangementsEntropy weight methodData modeling
The invention discloses an adaptive dynamic load monitoring method for power distribution network power failure events. According to the method, weights of four indexes, such as planned power failure time, power failure alarm time, power failure beginning time and power failure continuity time are calculated on the basis of an entropy weight method and by utilizing power distribution network business data, and the weights are integrated into one index; a differential equation model is established on the basis of a non-mechanism method to carry out data modeling, and parameters of the model are identified on the basis of the particle swarm optimization algorithm; an adaptive dynamic load monitoring model is calculated and verified, and power failure event diagnosis analysis and calculation result discuss are carried out according to a load cluster group. The method is advantaged in that, through model calculation and verification, the effect is substantially better than that of a dynamic monitoring model. The method is applied to actual business data analysis or other related fields, input data mining can be effectively carried out, load characteristic classification and decision are realized, and power failure event monitoring accuracy and validity are improved.
Owner:BEIHAI POWER SUPPLY BUREAU OF GUANGXI GRID +1
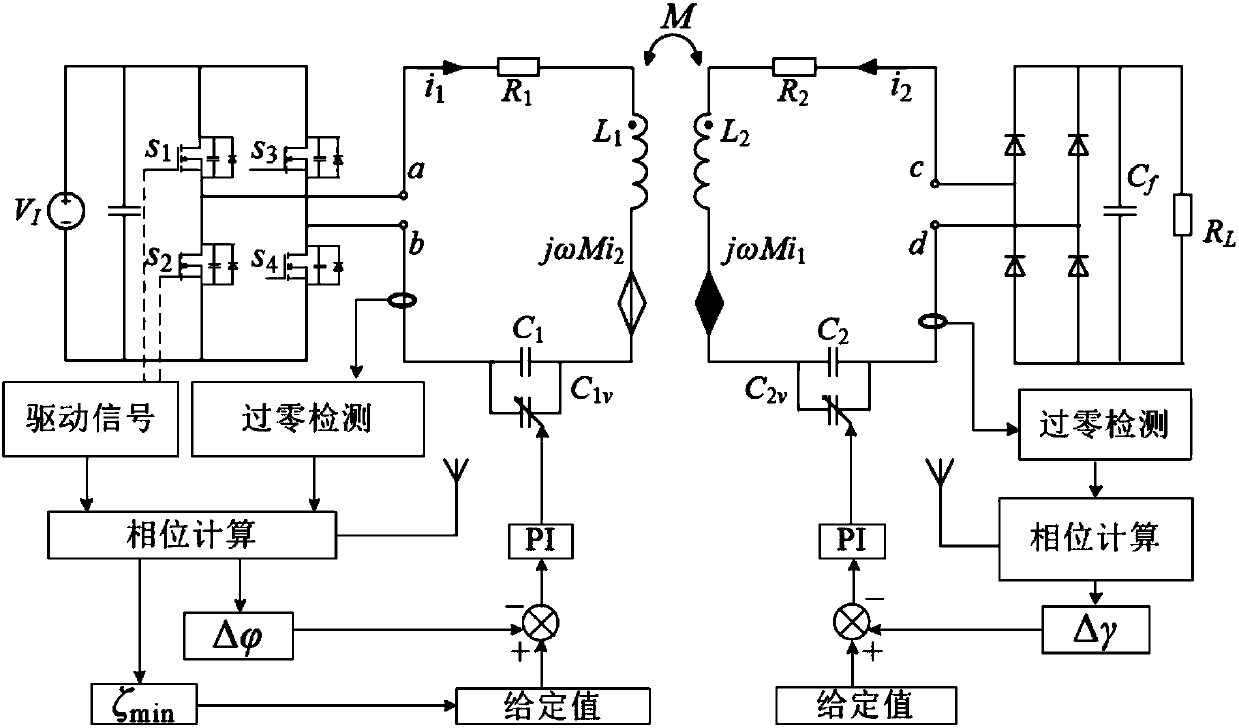
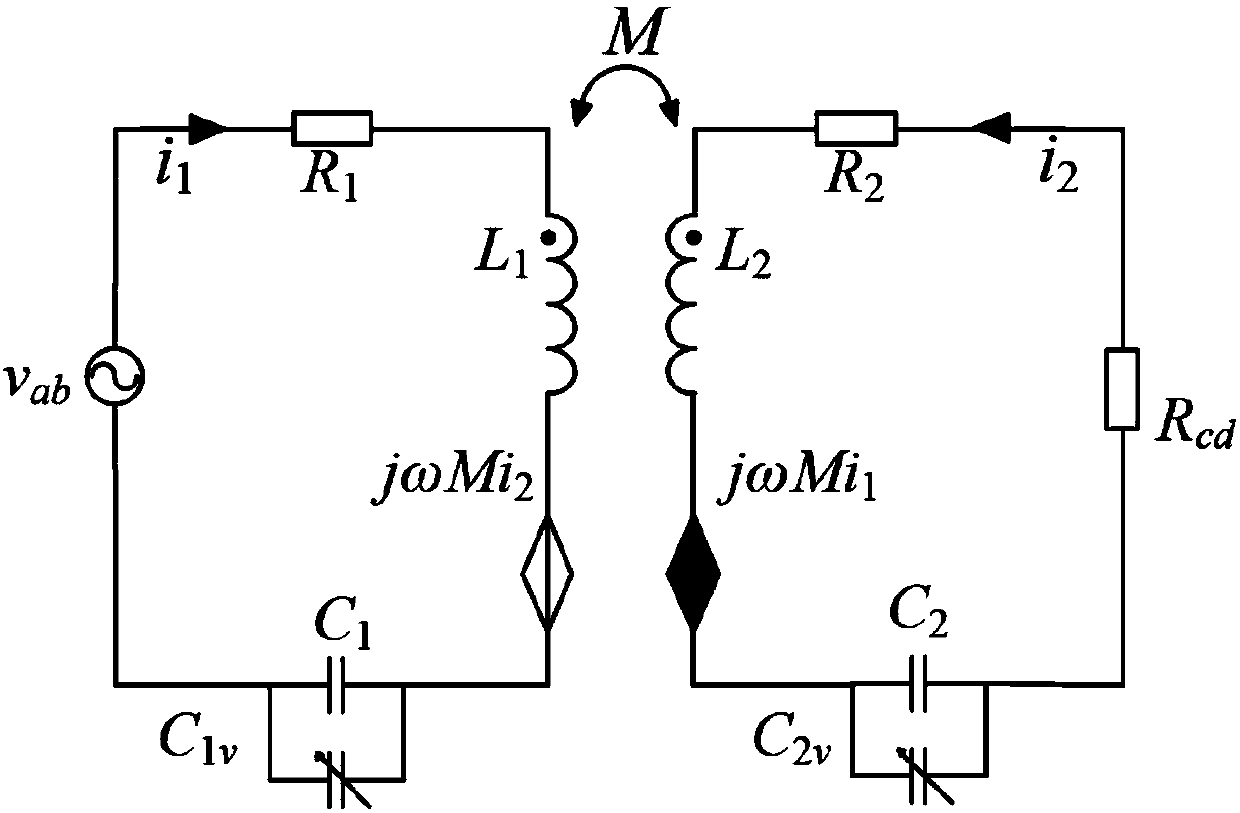
Radio energy transmission system tuning feedback control method considering dynamic performance
ActiveCN107834713AGuaranteed stabilityImprove transmission efficiencyCircuit arrangementsCoupled mode theoryClosed loop feedback
The invention relates to a radio energy transmission tuning control technology, in particular to a radio energy transmission system tuning feedback control method considering dynamic performance. Themethod includes the steps of obtaining the phase nonlinear differential equation model of the transmitting end and the receiving end of a system through analysis by utilizing a coupling mode theory and a circuit theory; utilizing a small signal linearization method to linearize a phase nonlinear differential equation model nearby a system resonance point, and analyzing the closed-loop dynamic performance of the system; taking the linear model as a controlled object and the phase value of the output voltage of an inverter circuit of the system as a reference phase, and forming a system tuning closed-loop feedback control loop by using the phase value of the transmitting end and the phase difference value of the transmitting end and the receiving end as the given values of the system transmitting end and the receiving end control loops when the system works in a resonance state. The control method can quickly and accurately control a magnetic coupling wireless energy transmission systemto work under the working states of high transmission efficiency and power, and has good robustness for detuning disturbance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image coherent speckle suppression method
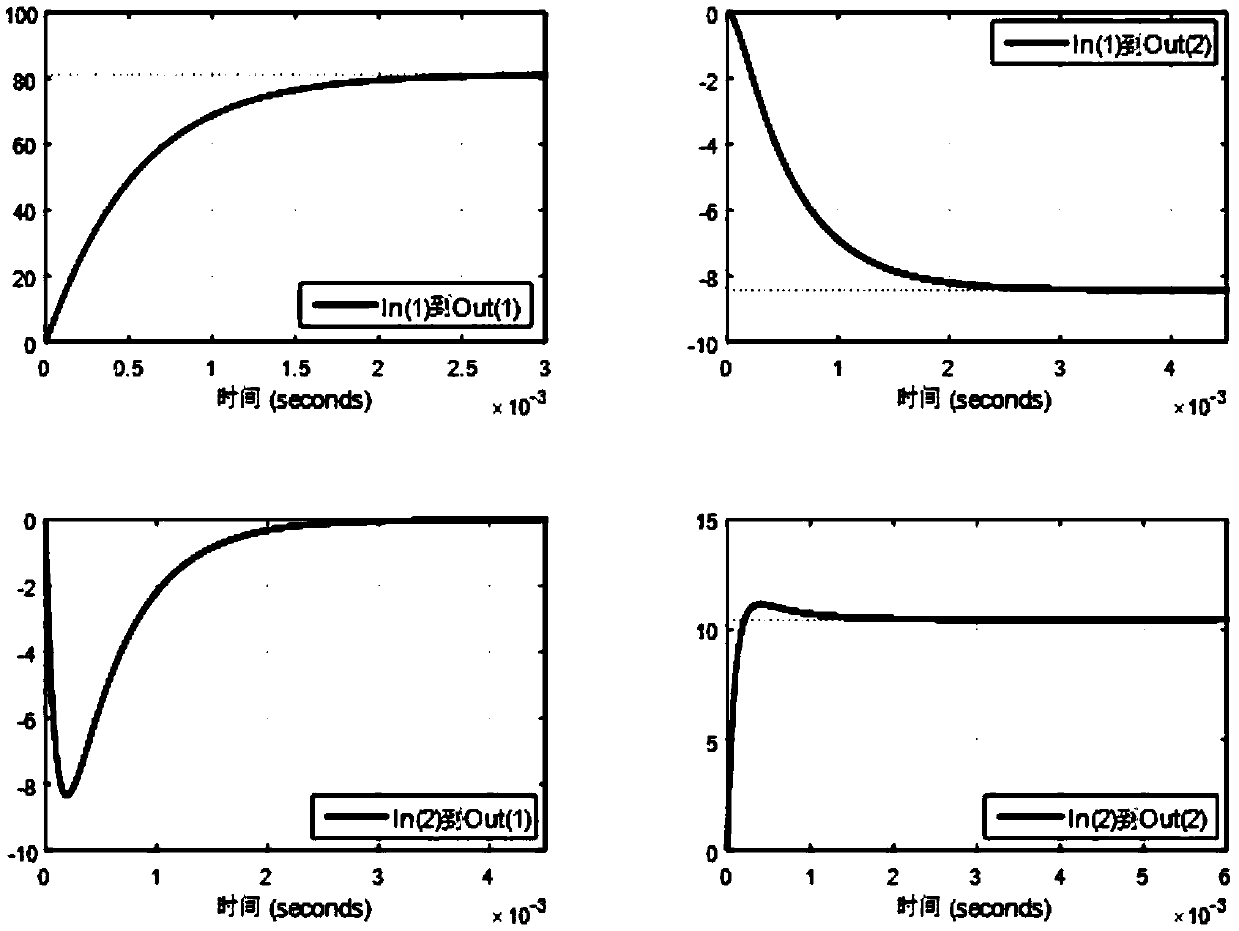
ActiveCN106971382AImprove radiometric resolutionKeep edge informationImage enhancementImage analysisSparse constraintNormal density
The present invention provides an SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image coherent speckle suppression method. According to the method, the probability density function of multiplicative noises and prior information are utilized to construct the approximation term, diffusion term and sparse constraint of a model; a sparse partial differential equation model is established; and alternate optimization is adopted to obtain a solution, so that a coherent speckle-suppressed SAR image can be obtained. With the sparse partial differential equation-based SAR image coherent speckle suppression method of the invention adopted, the defects of a traditional filtering method and a partial differential equation method can be eliminated; and the coherent speckles of the image can be suppressed, the radiation resolution of the SAR image can be improved, and at the same time, the edge information and scattering characteristics of a radar target can be well retained, the quality improvement of the SAR image can be realized effectively, the numerical solution of the model can be obtained robustly, and therefore, the method is easy to implement.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
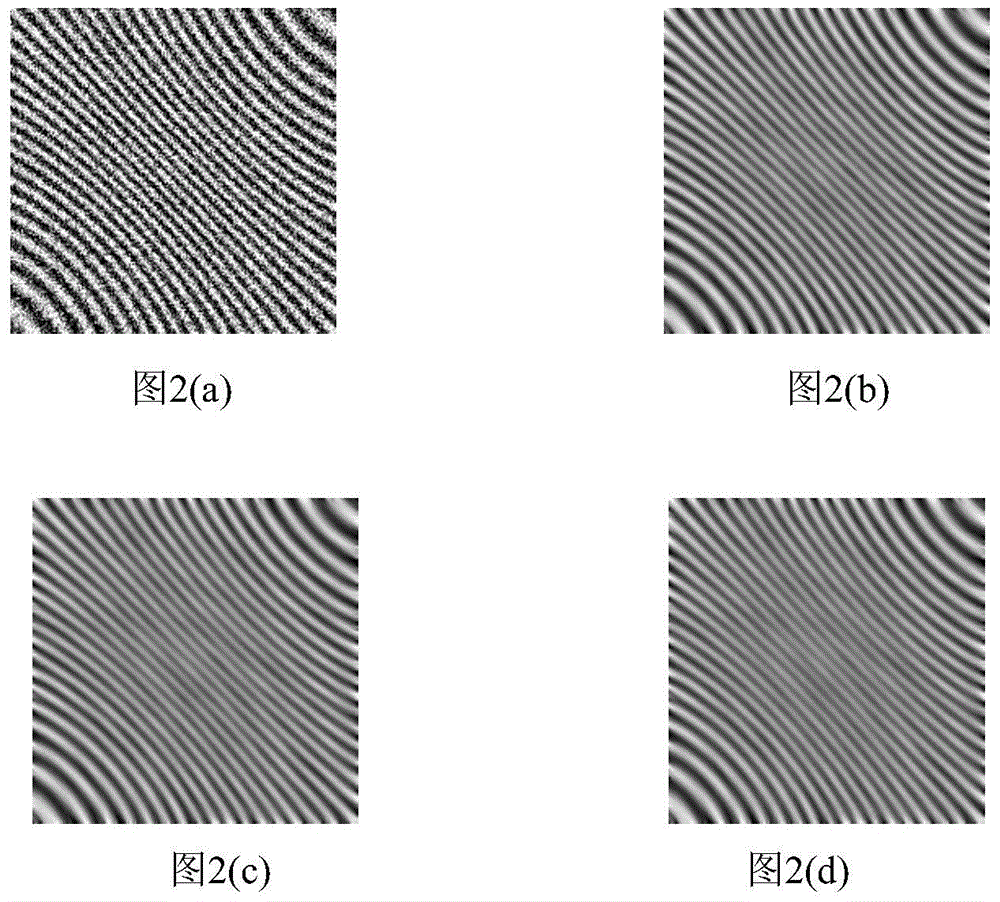
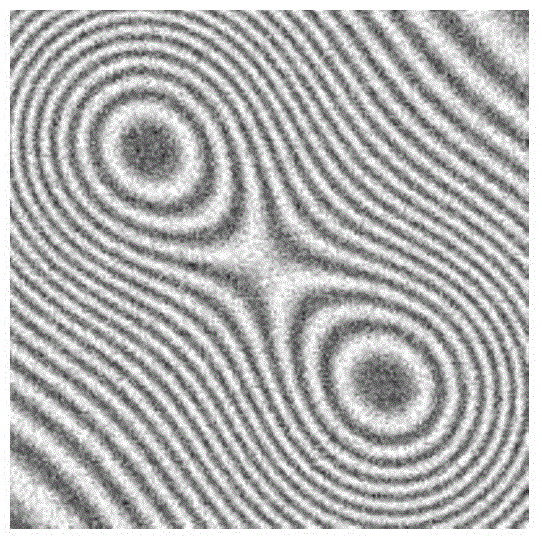
Directional partial differential equation filtering method used for electronic speckle interference fringe pattern
The invention discloses a directional partial differential equation filtering method used for an electronic speckle interference fringe pattern. The directional partial differential equation filtering method includes the steps of (1) inputting the electronic speckle interference fringe pattern u, (2) discretizing the electronic speckle interference fringe pattern u; (3) calculating the included angle theta<i,j> of the fringe direction and the x-axis direction; (4) obtaining a time step delta<t> in a self-adaptive mode; (5) obtaining iterations N<c>; (6) determining first-order partial derivatives u<x> and u<y> and second-order partial derivatives u<xx>, u<xy> and u<yy> of every pixel of the pattern u for every iteration; (7) determining the numerical solution of every pixel of the pattern u on the basis of the discretization format of a directional partial differential equation; (8) obtaining a filtered pattern when the numerical value of the largest set iteration N<c> is reached. The directional partial differential equation filtering method used for the electronic speckle interference fringe pattern can be widely used for filtering of high-noise electronic speckle interference fringe patterns.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Fingerprint texture image denoising enhancing method and system
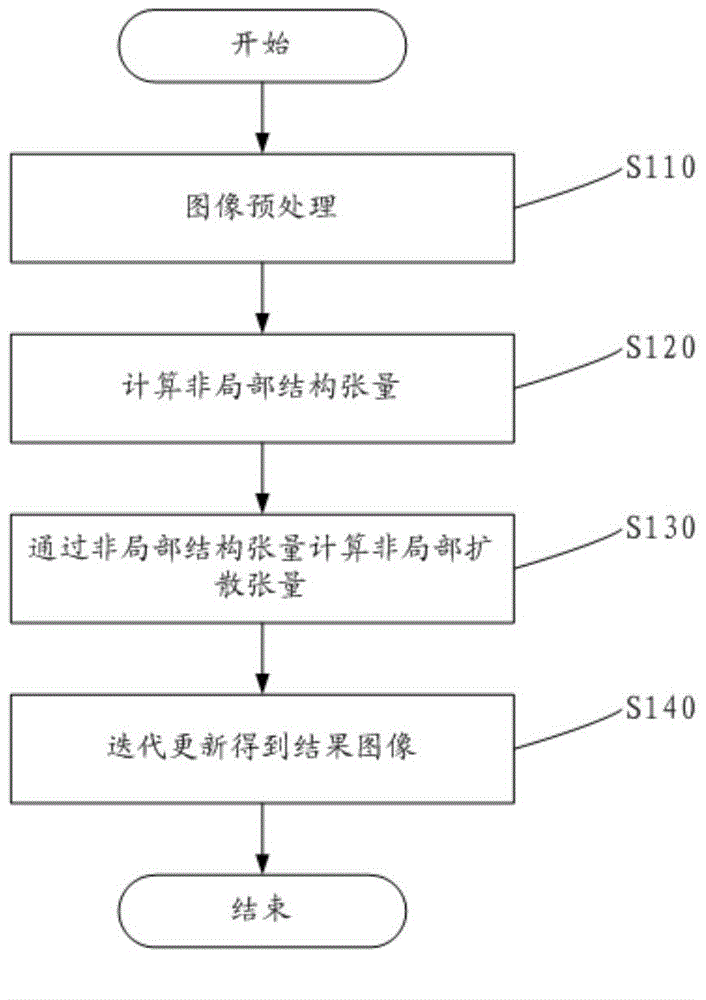
InactiveCN104537371AImprove Noise RobustnessFully excavatedImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImage denoisingPartial differential equation
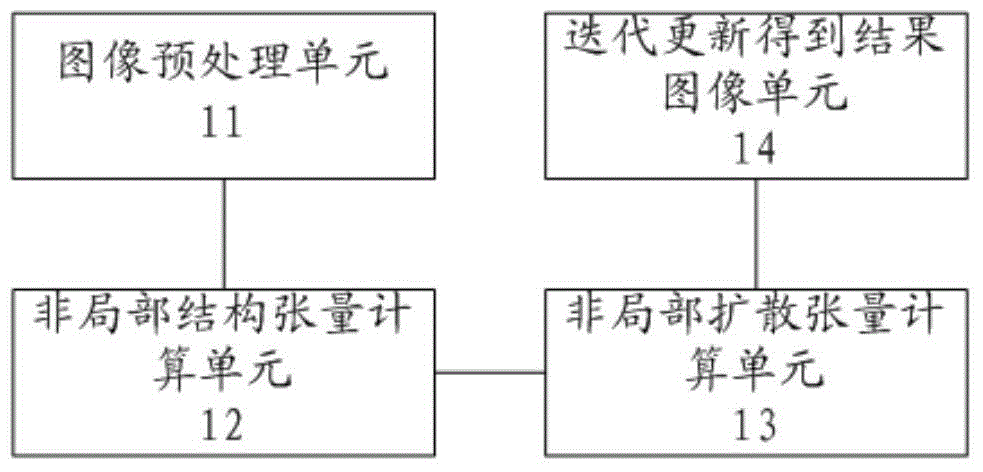
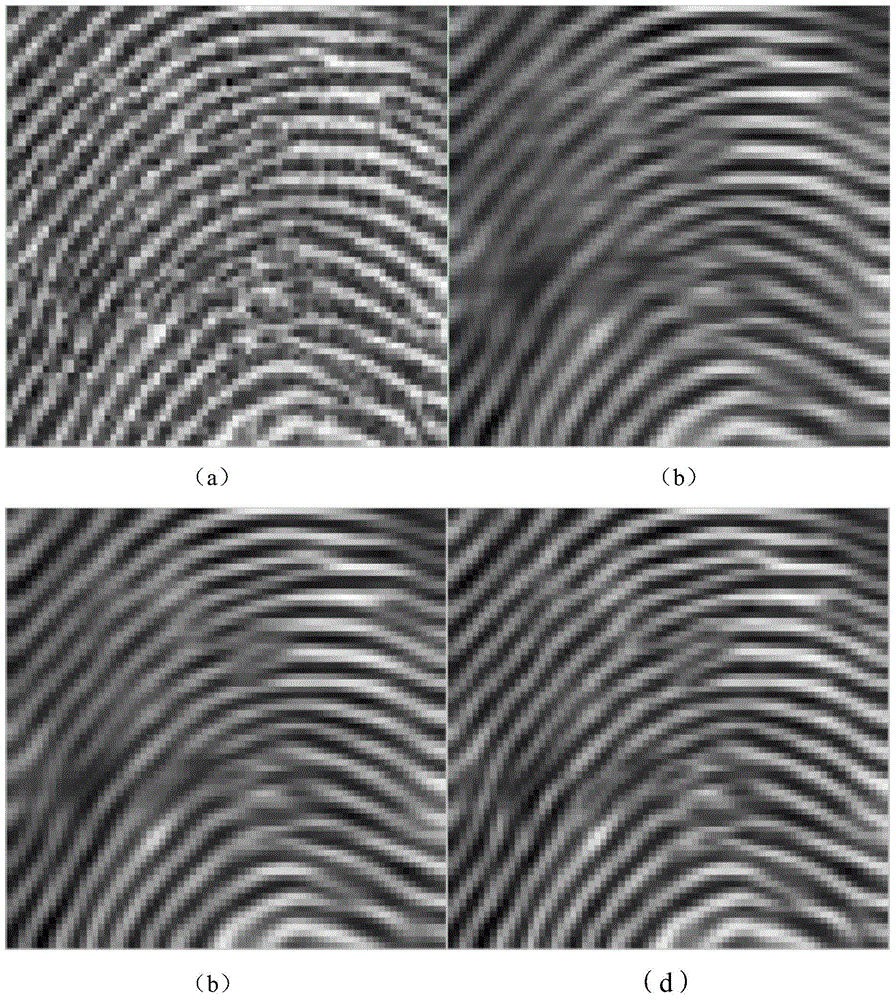
The invention relates to a fingerprint texture image denoising enhancing method. According to the method, a non-local diffusion tensor diffusion-fluctuation partial differential equation model is provided. The method comprises the following steps that an image is preprocessed; the non-local structure tensor is calculated; the non-local diffusion tensor is calculated through the non-local structure tensor; iteration updating is carried out, and a result image is obtained. The texture characteristic can be enhanced while the noise is eliminated, a certain repairing function of the fracture texture is achieved, and the fingerprint recognition can be carried out more accurately in the later process.
Owner:ENC DATA SERVICE CO LTD
Method for establishing one-tube multi-machine differential equation model through multi-machine form of tunnel and surge shaft
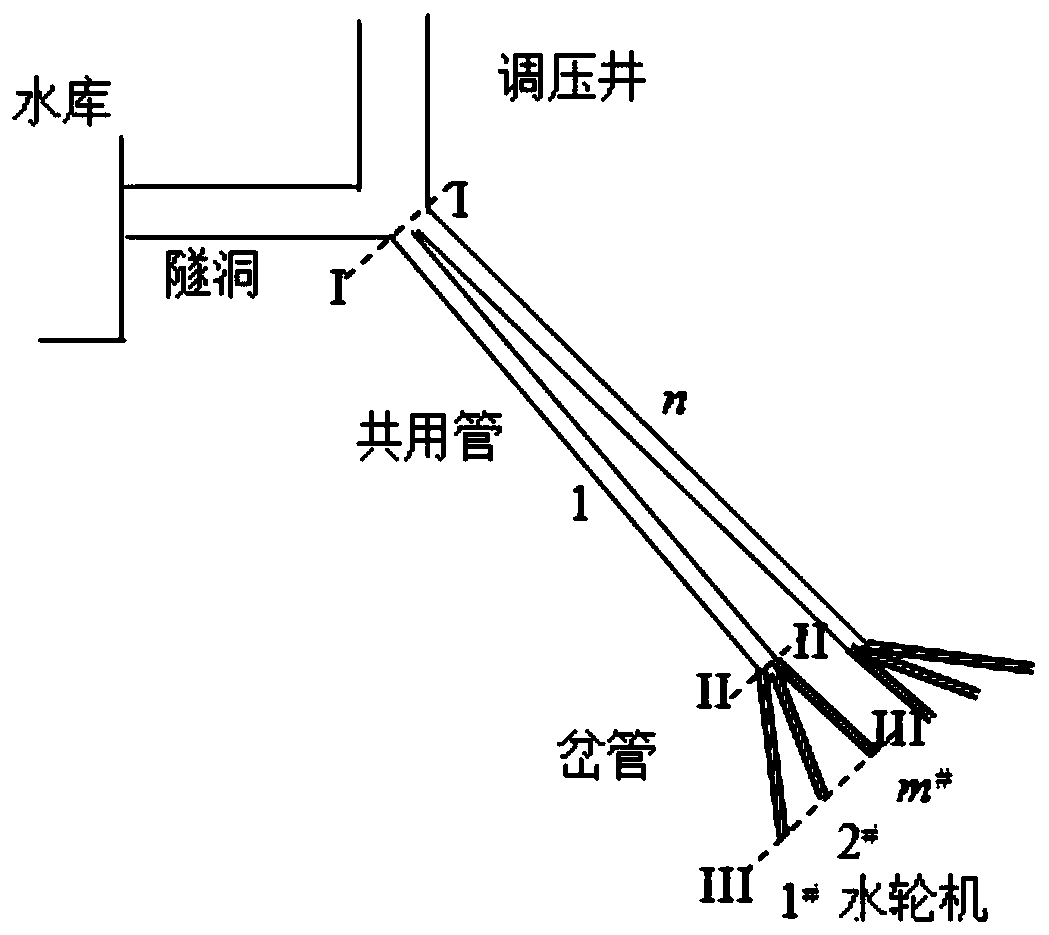
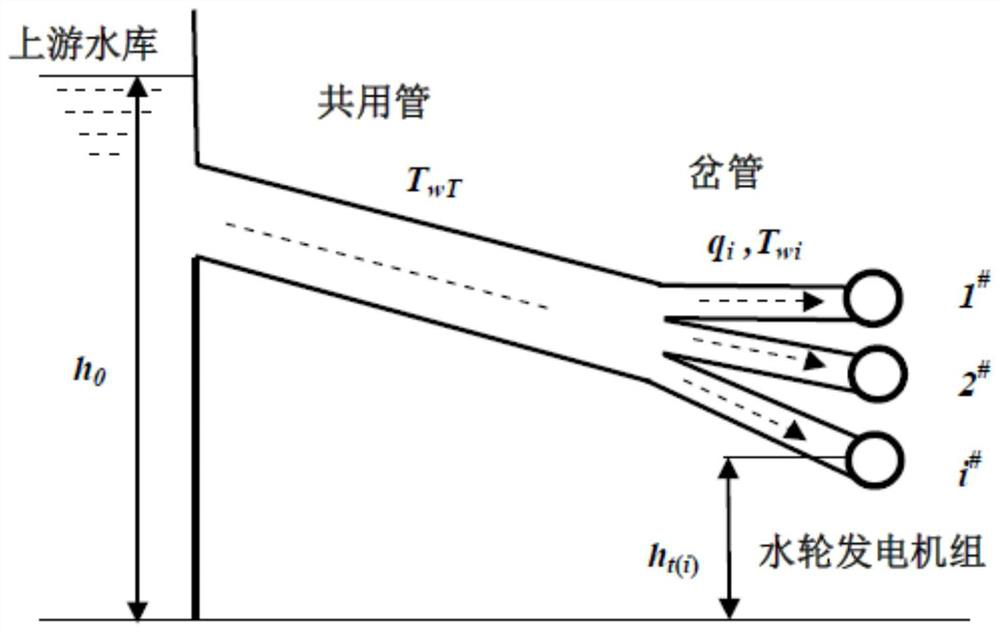
ActiveCN110222362ASolve multi-machine modeling problemsSatisfy the principle of superpositionHydro energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationNonlinear control designMulti machine
The invention relates to a method for establishing a one-tube multi-machine differential equation model through a multi-machine form of a tunnel and a surge shaft, and belongs to the technical field of stability analysis and control of water turbines and hydraulic power units. N paths of steel pipes are arranged behind the surge shaft, m branch pipes are arranged at the tail end of each path of steel pipe, and the total number of the units is n * m; the hydraulic system dynamically comprises a tunnel, a surge shaft, a shared pipeline and a bifurcated pipe. The rated flow Qr and the rated waterhead Hr of the water turbine are taken as base values, the unit of Qr is 3 meters per second, and the unit of Hr is meter, the specific steps are as follows: 1. Dynamically decomposing the hydraulicpower of a tunnel and a surge shaft into a multi-machine form; and 2, constructing a differential algebraic multi-machine model of the one-pipe multi-machine belt surge shaft. The method provides a convenient calculation method and means for researching the stability of the complex hydraulic system and the hydropower station under the condition of electromechanical multi-field coupling and the multi-machine cooperative nonlinear control design of the hydropower station.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Inverter modeling method including amplitude limiter and related device
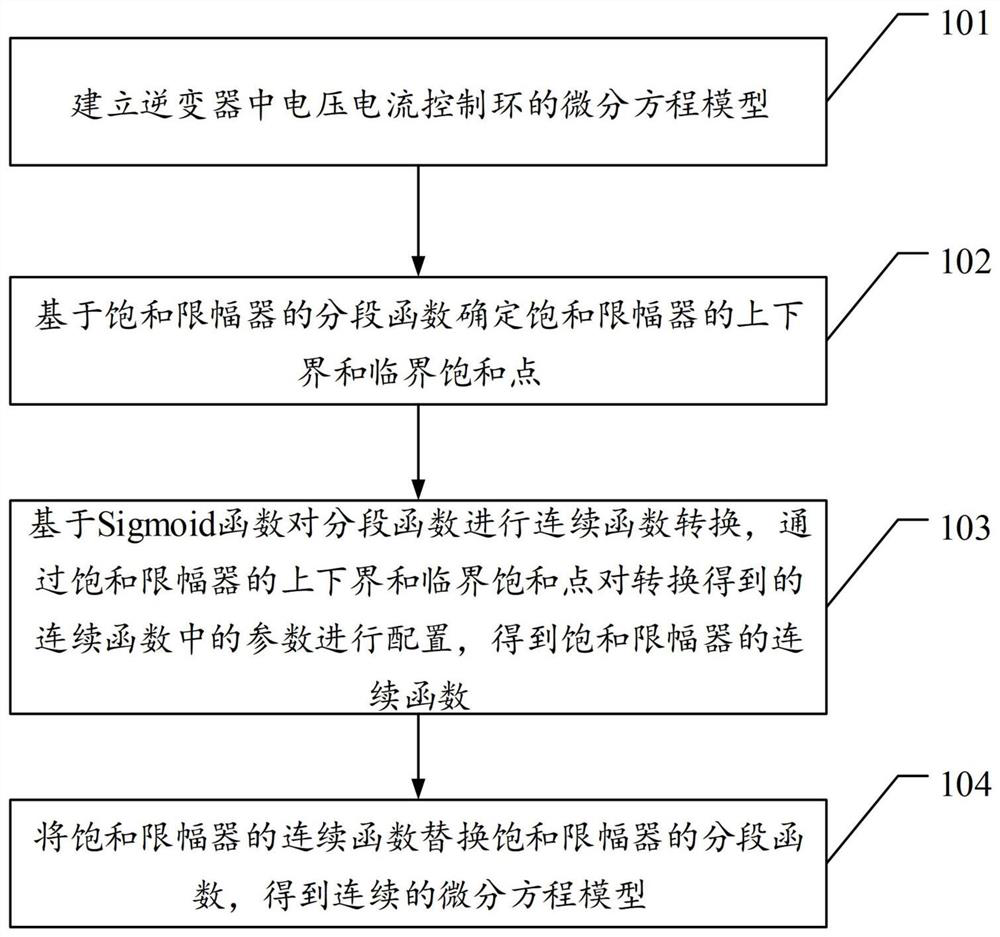
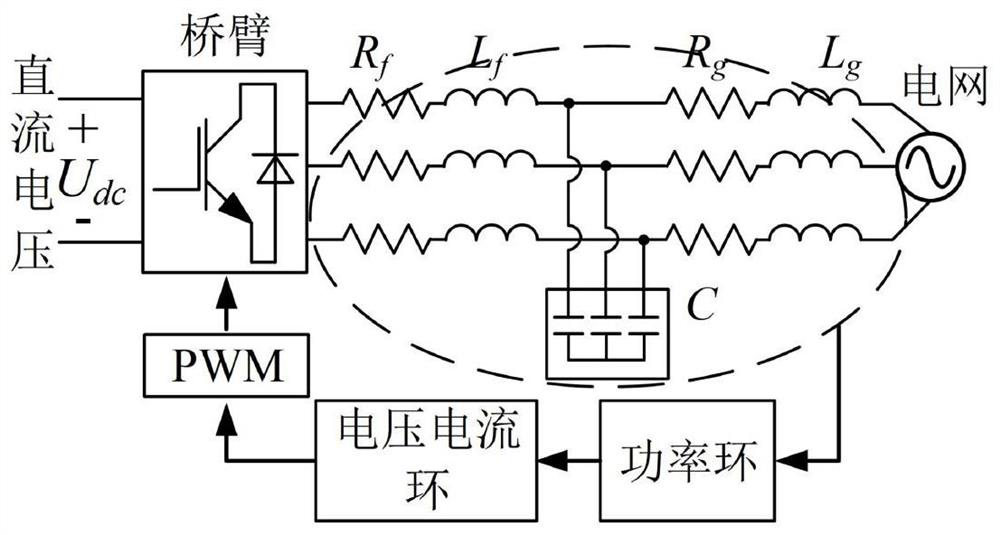
ActiveCN111628504AAvoid the problem that non-derivable "singularities" cannot existResolve continuitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsComplex mathematical operationsClassical mechanicsInverter
The invention discloses an inverter modeling method including an amplitude limiter and a related device. The method comprises the steps of building a differential equation model of a voltage and current control loop in an inverter, wherein the differential equation model comprises a piecewise function of a saturation amplitude limiter; determining the upper and lower boundaries and a critical saturation point of the saturation limiter based on the piecewise function of the saturation limiter; performing continuous function conversion on the piecewise function based on a Sigmoid function, and configuring parameters in the continuous function obtained by conversion through the upper and lower bounds of the saturation limiter and a critical saturation point to obtain a continuous function ofthe saturation limiter; and replacing the piecewise function of the saturation limiter with the continuous function of the saturation limiter to obtain a continuous differential equation model, thereby solving the technical problem that the inverter modeling through the differential equation requires that the inverter model has continuity and cannot be applied to the inverter comprising the limiter in the prior art.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Data-driven complex system mechanism automatic learning method, system and equipment
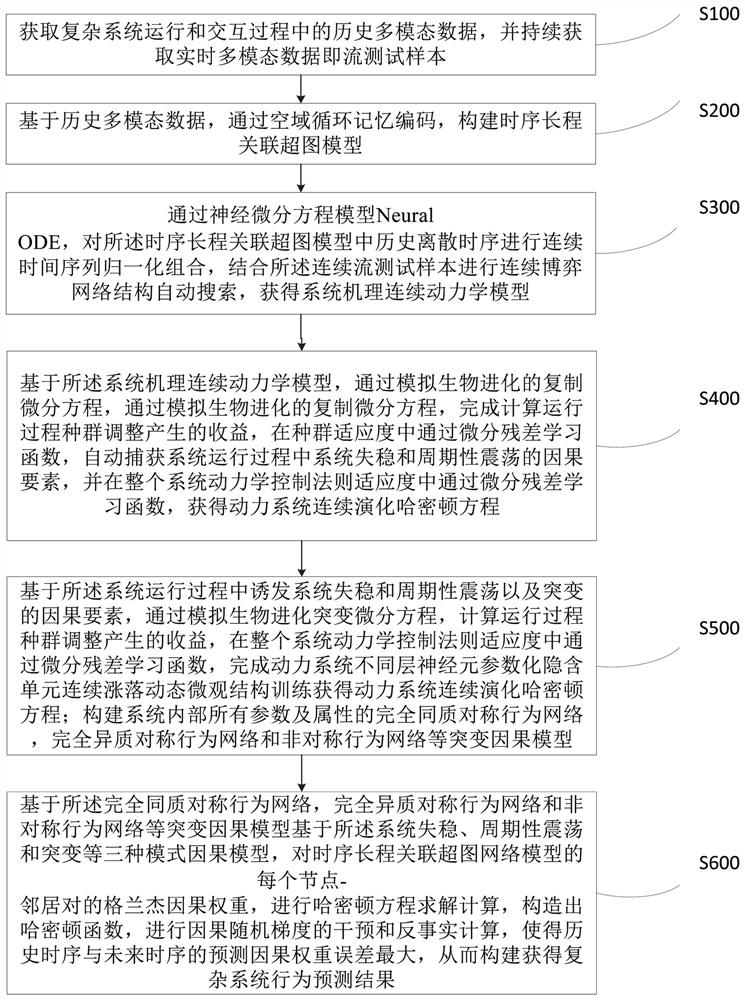
ActiveCN113177626ACapable of self-evolutionImprove description accuracyArtificial lifeMachine learningEngineeringComplex system
The invention belongs to the field of big data and machine learning, particularly relates to a data-driven complex system mechanism automatic learning method, a system and equipment, and aims to solve the problems that an existing system modeling technology is difficult to predict a behavior trend from field observation data, a reconstructed mechanism model is not matched with physical observation data, the robustness is poor and the like. The method comprises the steps of obtaining historical multi-modal data and real-time multi-modal data, constructing a time sequence long-range correlation hypergraph model through airspace circulation memory coding, performing normalized combination on the hypergraph model through a neural differential equation model, and performing automatic iterative search on a continuous game network structure to obtain a system mechanism continuous dynamic model, and performing biological evolution simulation to obtain a causal model, and recalculating an association weight to obtain an active early warning system. According to the method, non-linearity, emergence, balance step, adaptability and special property description of a feedback loop of a complex system are realized, and the prediction accuracy of the model is improved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
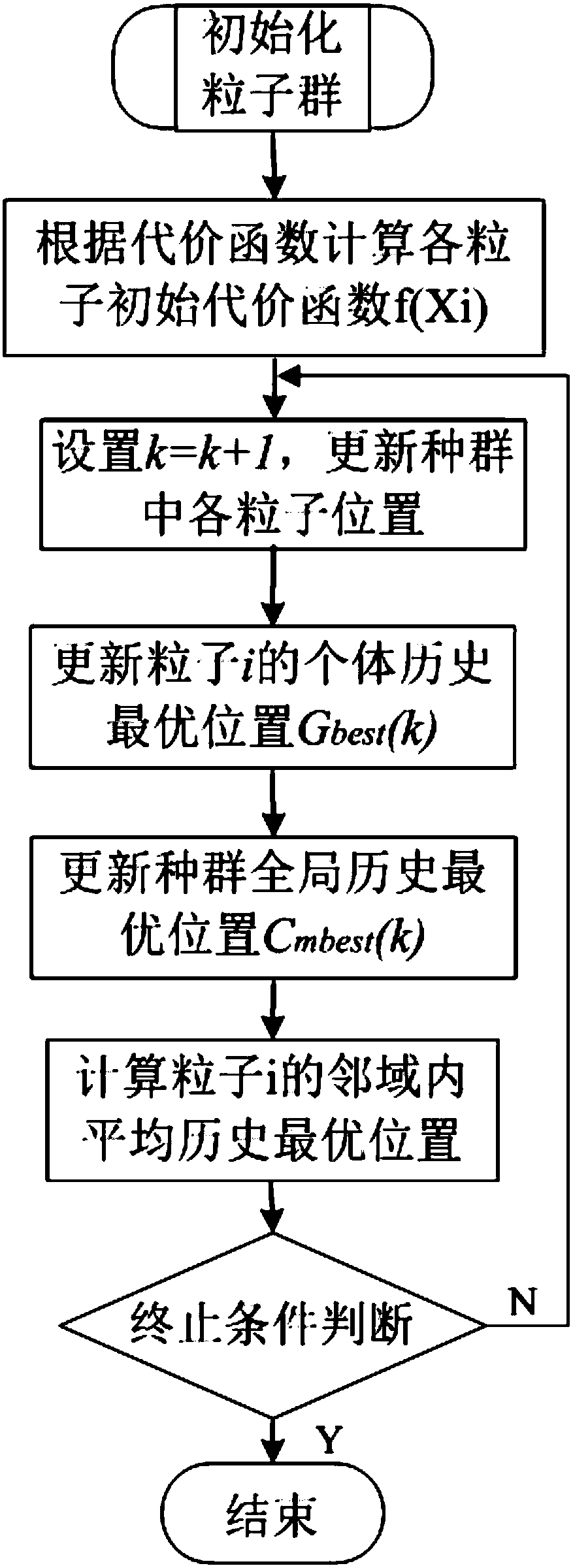
Random drift particle swarm optimization method having von Neumann structure
InactiveCN106875001AImprove global search performanceLimit global search capabilitiesForecastingArtificial lifeAlgebraic constraintModel parameters
The invention discloses a random drift particle swarm optimization method having a von Neumann structure. For biological network modeling, such as synthetic gene loop modeling, a differential equation model of a biological system needs to be established, and model parameters are inferred according to observed values; and in the parameter calculating process, an appropriate objective function and restraint conditions need to be defined first, and meanwhile, support of an optimization algorithm is needed. Parameter estimation of a differential equation is equivalent to a problem of nonlinear programming having differential-algebraic constraints, and an appropriate parameter set is found to fit measurement data; for the boundedness that optimization calculation in the parameter estimation process is easy to run into partial optimization, the von Neumann structure is introduced to the random drift particle swarm optimization algorithm to enhance global search capability; and the improved algorithm is improved for the boundedness of a full-mesh global topological structure, and adopts a local topological structure to serve as an inter-particle information sharing mode, so that global search capability of the algorithm is enhanced, and high-reliability model parameters can be given.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Gear fault classification detection method and system based on meshing rigidity identification
ActiveCN114354187AEliminate the effects of feature decay or even changeFailure sensitiveMachine part testingKineticsAlgorithm
The invention discloses a gear fault classification detection method and system based on meshing rigidity. A dynamic differential equation model is constructed for a gear box, and a box body vibration signal vector matrix generated by the gear box to be detected in a stable operation state under the given rotating speed and load is collected; carrying out corresponding bearing force modeling according to the type of a meshing gear, and reconstructing a box vibration signal vector matrix to obtain a bearing force intermediate variable and a displacement vector of a full node; and finally, gear meshing rigidity is obtained through the full-node displacement vector, and gear fault classification is realized by extracting the amplitude at the characteristic frequency. According to the method, dynamics and a transmission path modeling method are combined, an analytic mathematical description of vibration transmission in the whole process from gear meshing to box vibration is established, the influence of a structure transmission path in the identified meshing rigidity is eliminated, and therefore the method can be used for fault classification detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hybrid control method for an electrical converter
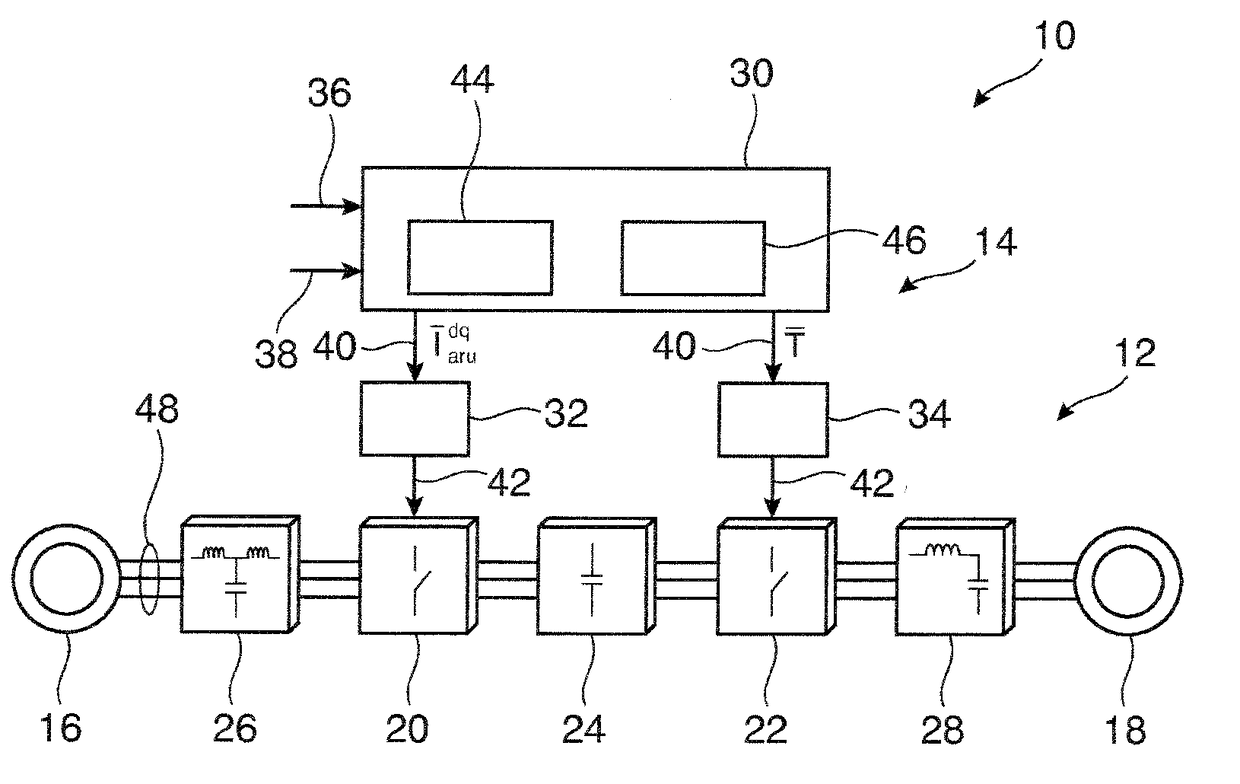
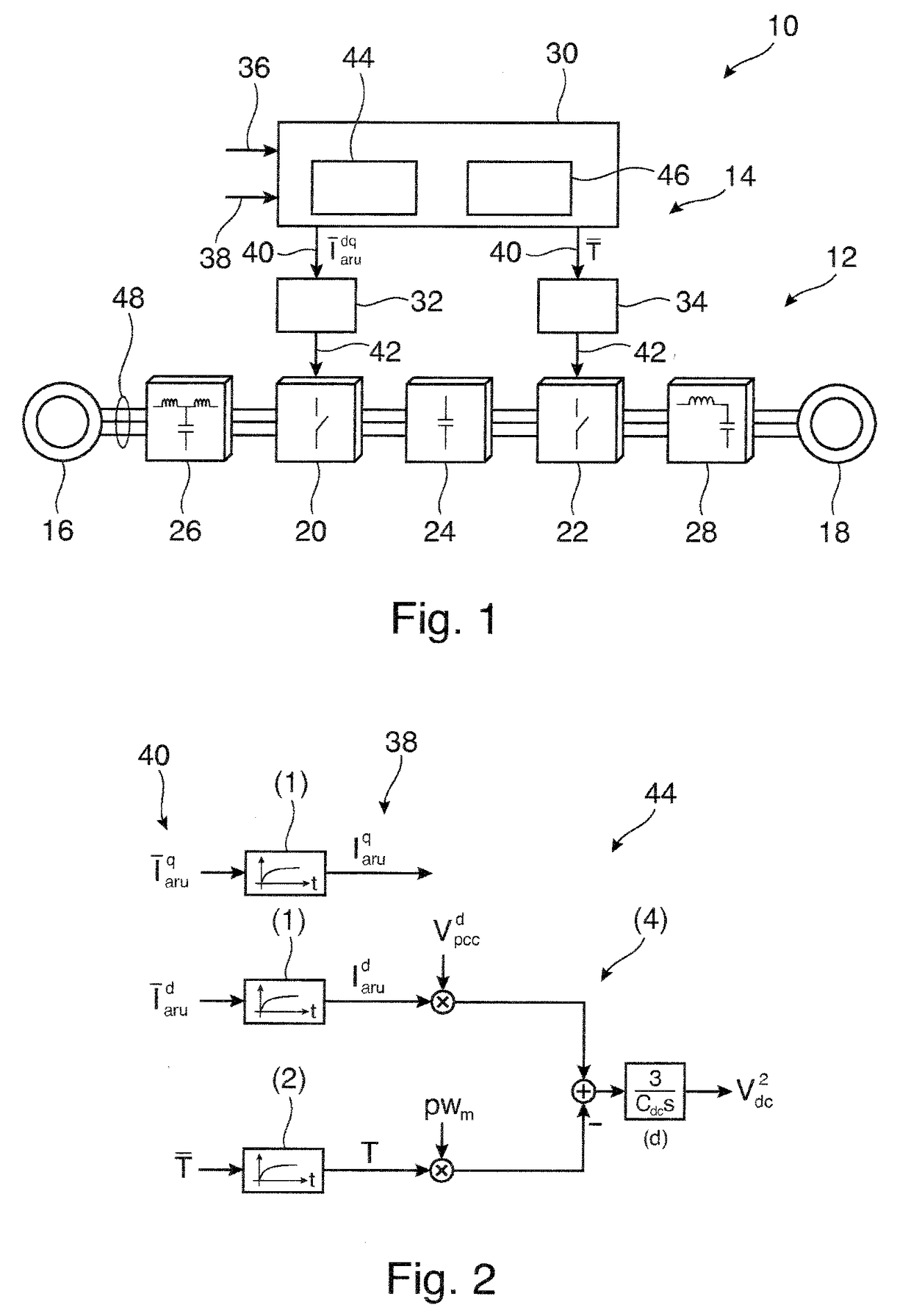
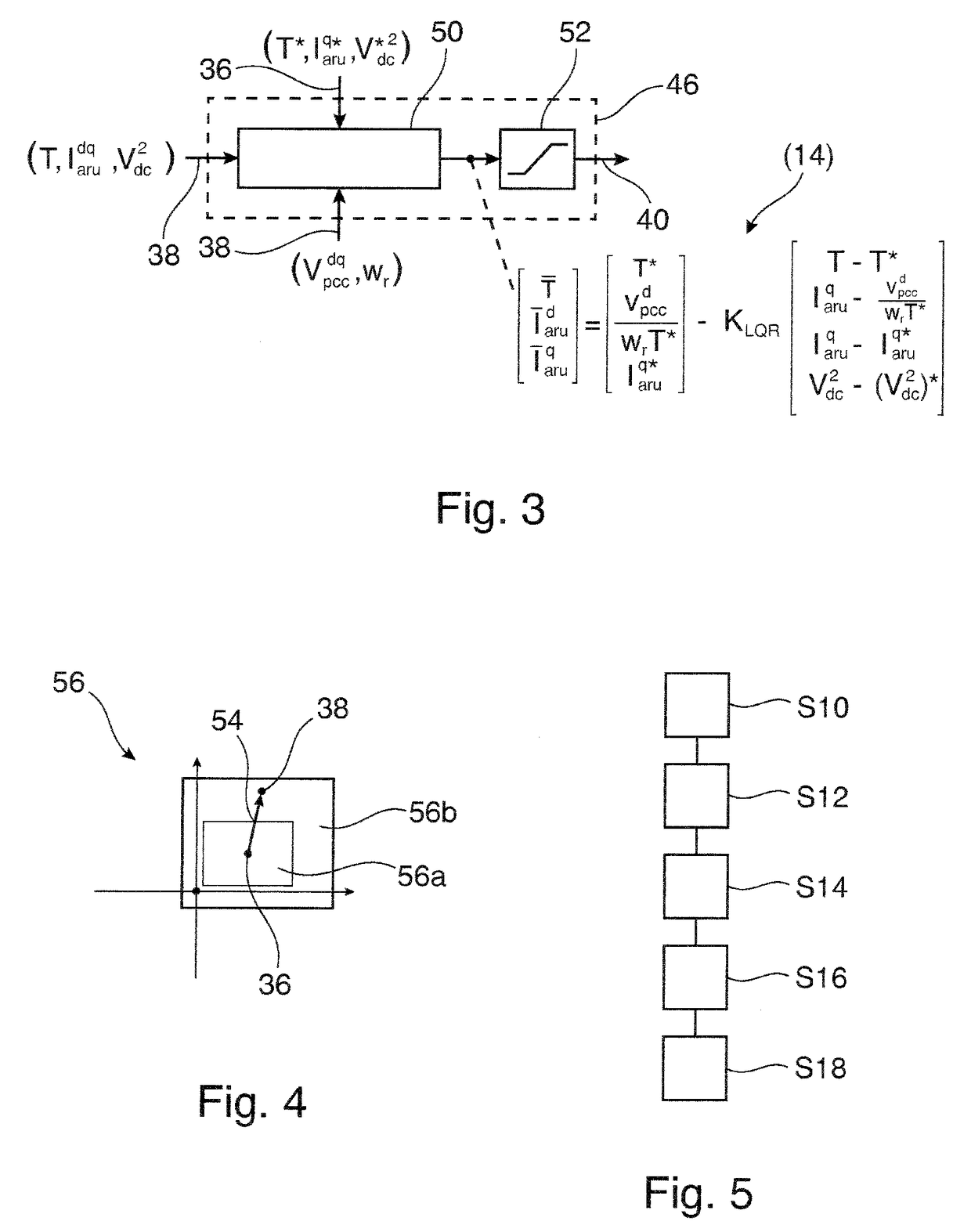
ActiveUS20180062531A1Fast and reliable and flexible reactingConstant levelEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcLoop controlOperating point
An electrical converter comprises at least one of an active rectifier and an inverter interconnecting an electrical source with an electrical load. A method for controlling an electrical converter comprises: receiving at least one estimated control variable, which is estimated from measurement values measured in the electrical converter; receiving at least one outer loop control variable provided by an outer control loop, the at least one outer loop control variable providing a desired steady-state operation point of the electrical converter; determining a control region based on a control error, which is a difference between the at least one estimated control variable and the at least one outer loop control variable, wherein the control region is defined by one or more intervals of one or more control variables; selecting control parameters based on the control region, wherein, when the control error is in an inner control region, first control parameters are selected, and, when the control error is outside the inner control region but inside an outer control region, second control parameters are selected; switching, based on the control error, between two and more control methods, which differ in control parameters, by predicting at least one reference control value based on a solution of a physical model of the electrical converter, which comprises the selected control parameters, the physical model being based on differential equations modelling the at least one estimated control variable and the solution being based on a constraint minimizing a difference between the at least one estimated control variable and the at least one outer loop control variable; and determining switching states of the electrical converter based on the reference control value.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Partial differential equation image amplification method based on angular point protection
InactiveCN104899828AImprove visual effectsImprove signal-to-noise ratioGeometric image transformationPattern recognitionAngular point
The invention discloses a partial differential equation image amplification method based on angular point protection. The partial differential equation image amplification method comprises the following steps: 1) inputting an image I, and calculating the definition R1 of the image I; 2) carrying out discretization on an image u; 3) calculating an angular point Cu of the image; 4) inputting the values of parameters k, [delta]t, [gamma] and a; 5) adaptively obtaining a fidelity term coefficient [lambda]; 6) for each iteration, obtaining the first-order partial derivatives ux and uy and the second-order partial derivatives uxx, uxy, uyy, u[eta][eta] and u[zeta][zeta] of each pixel of the image u; 7) on the basis of a discrete form of a directional partial differential equation model, obtaining a numerical solution ui,j<n+1> of each pixel of the image u; 8) calculating the definition Ru(n+1) of an evolution image u<n+1> obtained in the step 7); and 9) when a maximum iteration frequency judgment formula is met, taking the numerical solution ui,j<n+1> as an amplified image. The partial differential equation image amplification method can be widely applied to the field of digital image amplification.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
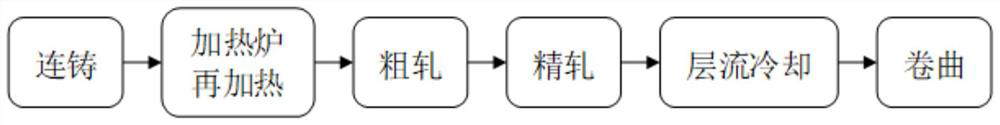
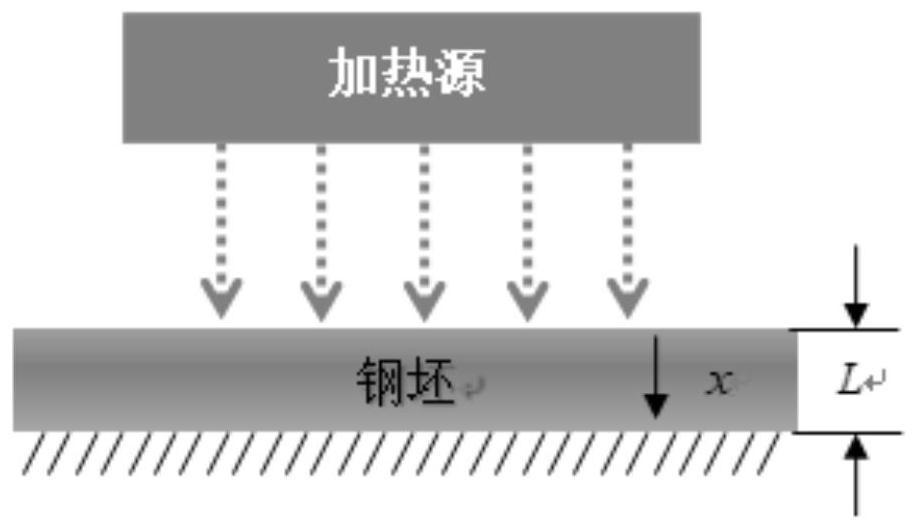
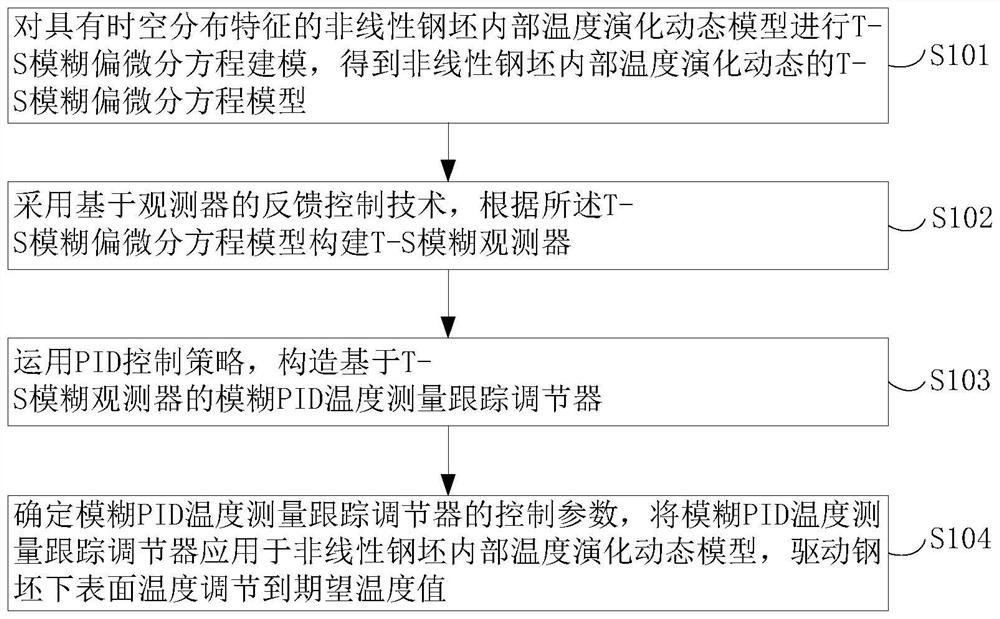
Fuzzy PID temperature adjusting method for steel billet reheating in strip steel hot continuous rolling production
The invention provides a strip steel hot continuous rolling production billet reheating fuzzy PID temperature adjusting method and belongs to the field of strip steel hot continuous rolling production. The method comprises the following steps of performing T-S fuzzy partial differential equation modeling on a nonlinear billet internal temperature evolution dynamic model with spatial and temporal distribution characteristics to obtain a T-S fuzzy partial differential equation model of nonlinear billet internal temperature evolution dynamic; constructing a T-S fuzzy observer according to the T-S fuzzy partial differential equation model by adopting an observer-based feedback control technology; constructing a fuzzy PID temperature measurement tracking regulator based on a T-S fuzzy observer by applying a PID control strategy; and determining control parameters of the fuzzy PID temperature measurement tracking regulator, applying the fuzzy PID temperature measurement tracking regulator to the nonlinear billet internal temperature evolution dynamic model, and driving the billet lower surface temperature to be regulated to an expected temperature value. According to the method, non-intrusive steel billet temperature surface measurement and adjustment can be realized, so the lower surface temperature of the steel billet reaches an expected temperature value.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for calculating differential equation of one-tube multi-machine hydroelectric generating set adjusting system
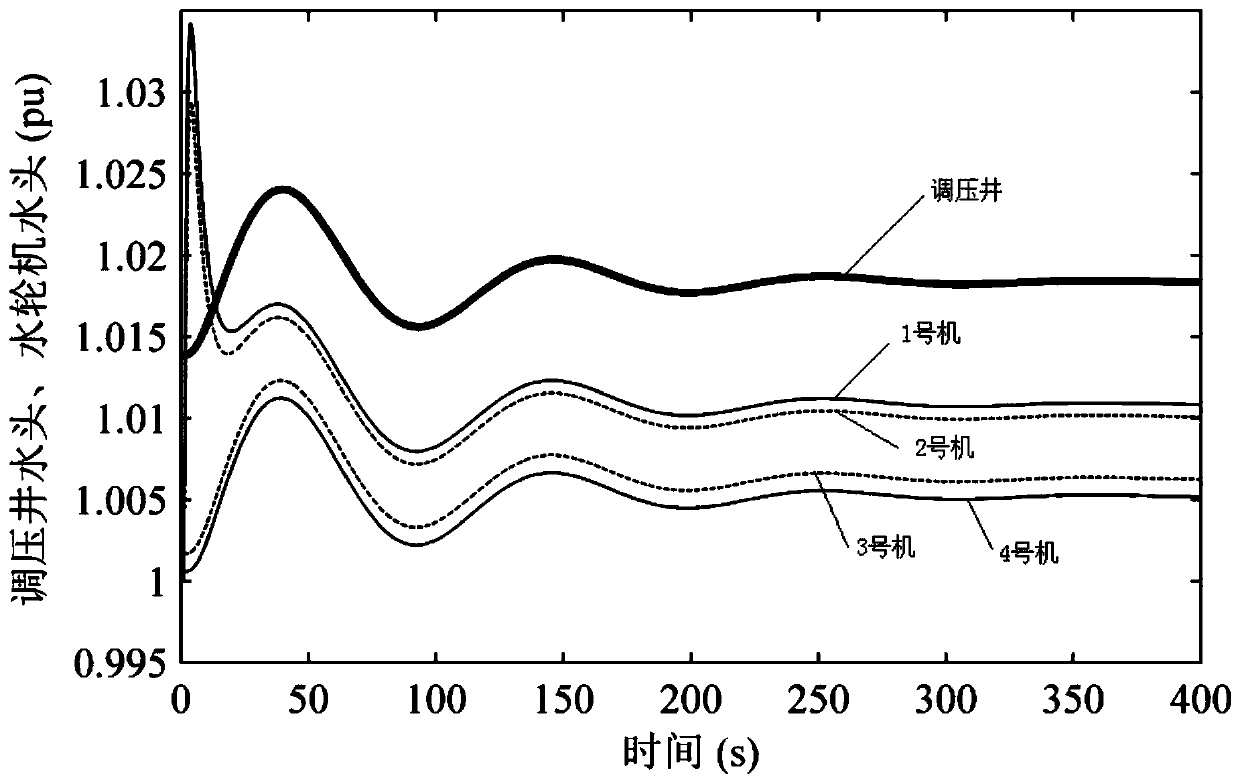
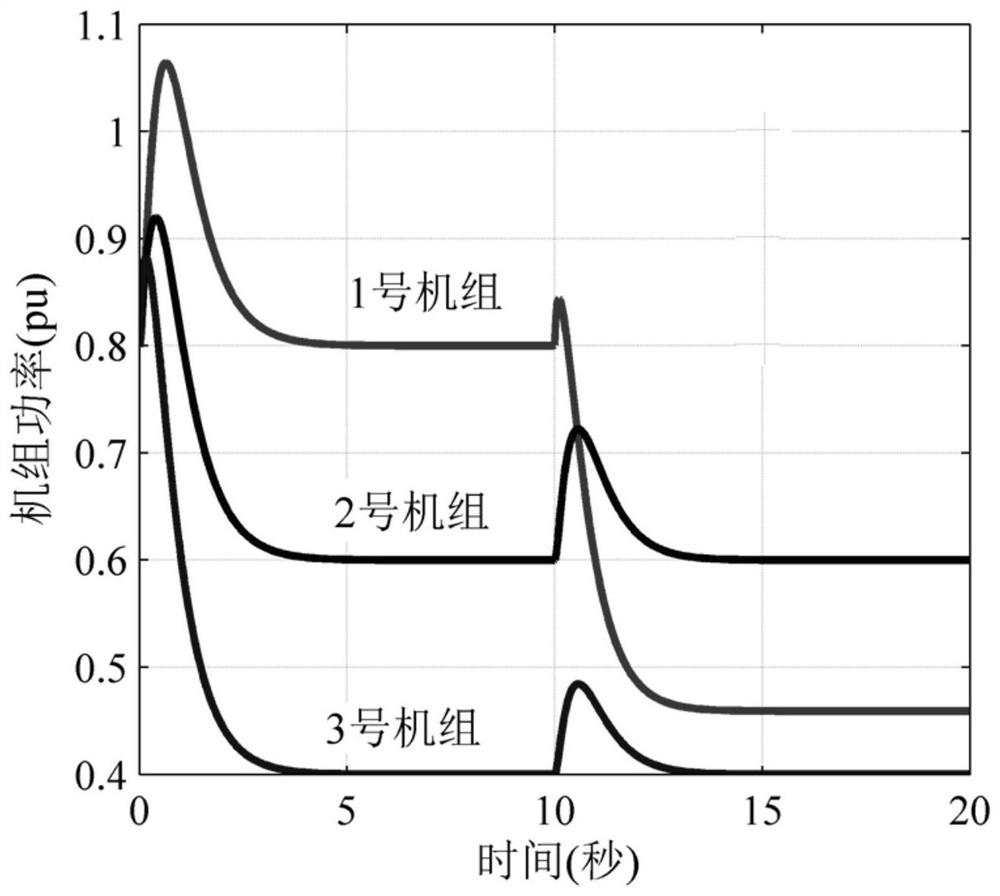
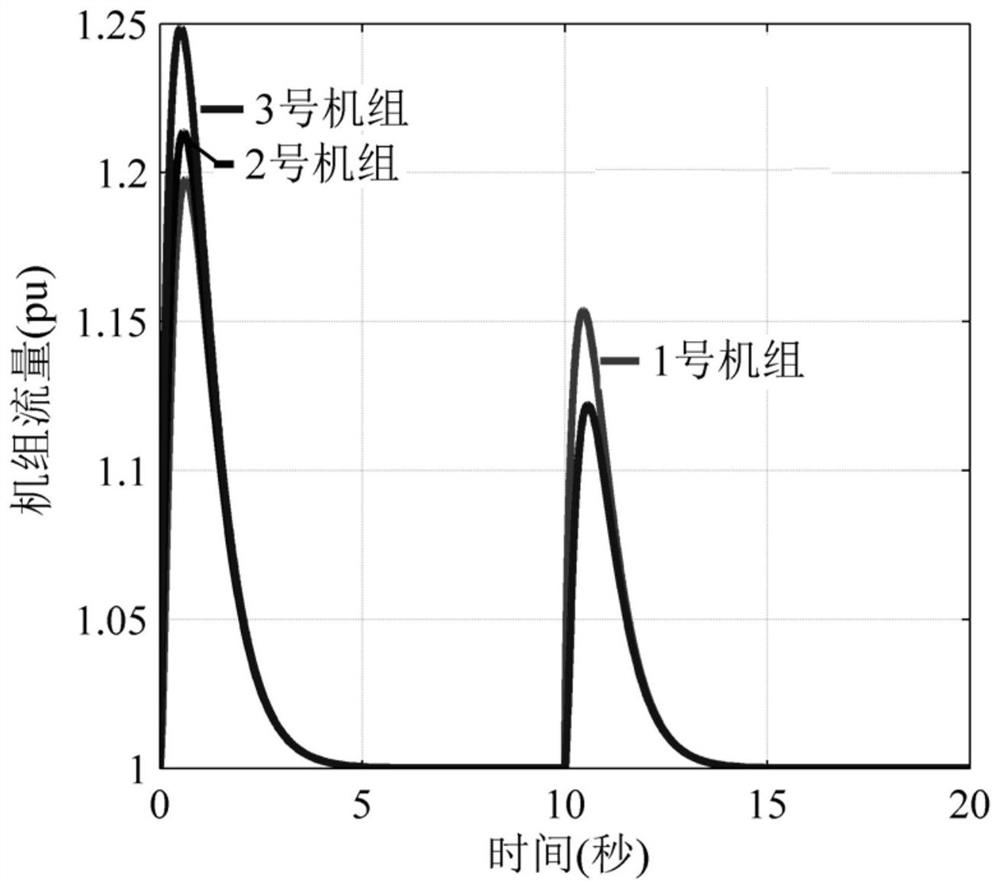
ActiveCN112651180AEasy to analyzeFirmly connectedDesign optimisation/simulationMulti machine systemWater turbine
The invention relates to a differential equation calculation method for a one-pipe multi-machine hydroelectric generating set adjusting system and belongs to the technical field of stability analysis and control of water turbines and hydroelectric generating sets. The method comprises steps of hydraulic coupling of a one-pipe multi-machine system under rigid water attack being represented by using dynamic parameters of a hydraulic system and state variables of multiple units, dynamically converting hydraulic power sharing a pipeline into a differential equation model of flow of each unit, constructing a water turbine torque differential equation model and a hydraulic speed regulation system model on the basis of the hydraulic power, and establishing a hydraulic torque differential equation model and a hydraulic speed regulation system model; wherein the generator system models jointly form a one-tube multi-machine hydroelectric generating set adjusting system differential equation model; and under the condition that multiple units act at the same time, transient changes of water heads, flow and output of all the water turbines being calculated. The method provides a convenient calculation method and means for researching the regulation performance of each water-turbine generator set and the cooperative control design among a plurality of water-turbine generator sets under the water-turbine-electricity multi-factor coupling condition.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thermoelectric hydrogen multi-energy-flow comprehensive energy system and optimal scheduling method thereof
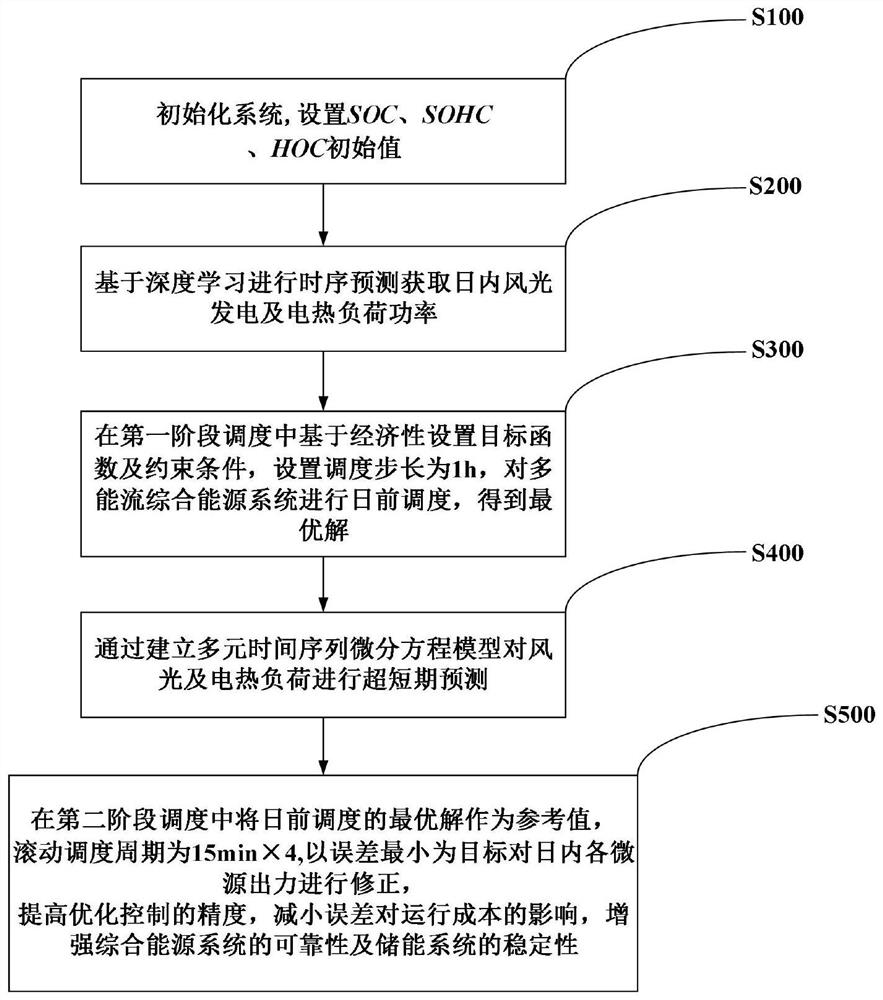
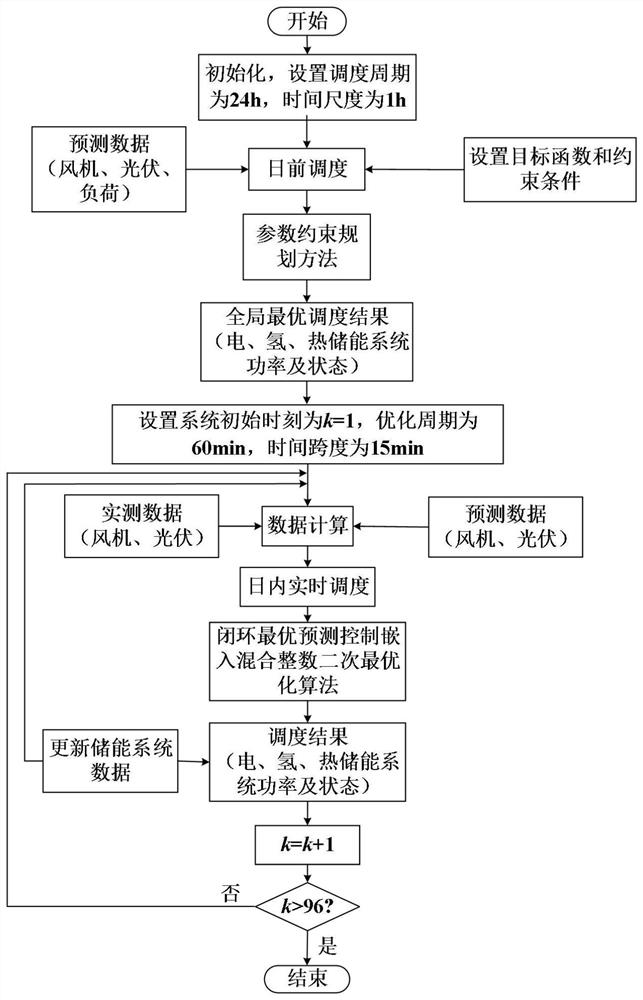
ActiveCN113850474ARun fastReduce wasteForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationIntegrated energy systemSolar power
The invention discloses a heat-electricity-hydrogen multi-energy-flow comprehensive energy system and an optimal scheduling method thereof, the multi-energy-flow comprehensive energy system adopts a heat-electricity-hydrogen multi-energy-flow comprehensive energy system, and the optimal scheduling method comprises the following steps: initializing the system; performing time sequence prediction based on deep learning to obtain intra-day wind-solar power generation and electric heating load power; in the first-stage scheduling, an objective function and a constraint condition are set based on economy, a scheduling step length is set, day-ahead scheduling is carried out on the multi-energy-flow integrated energy system, and an optimal solution is obtained; performing ultra-short-term prediction on the wind-light and electric heating load by establishing a multivariate time sequence differential equation model; in the second-stage scheduling, the optimal solution of the day-ahead scheduling is used as a reference value, the output of each micro source in the day is corrected with the minimum error as a target based on a rolling scheduling period, the precision of optimization control is improved, the influence of the error on the operation cost is reduced, and the reliability of a comprehensive energy system and the stability of an energy storage system are enhanced.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Time-domain analysis method for dynamic temperature difference power generation system segmented on basis of temperature difference thermocouple material
InactiveCN107122576ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical field strengthAlgebraic equation
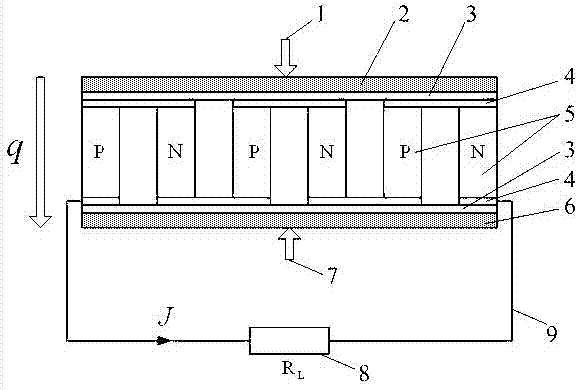
The invention provides a time-domain analysis method for a dynamic temperature difference power generation system segmented on the basis of a temperature difference thermocouple material. The method comprises steps as follows: firstly, a thermoelectric partial differential equation model and boundary conditions of basic physical properties of the dynamic temperature difference power generation system segmented on the basis of the temperature difference thermocouple material are established; secondly, a thermal circuit and an electric circuit of the system are more specifically analyzed and subjected to time and space discretization processing, an algebraic equation of physical quantities of internal nodes and boundary nodes of an area is established in terms of energy conservation, iteration solution is executed by starting from a time initial value, and finally, numerical solutions of temperature and electric field intensity of all positions in the dynamic temperature difference power generation system segmented on the basis of the temperature difference thermocouple material can be obtained. By means of analysis for the numerical solutions of temperature and electric field intensity in the dynamic temperature difference power generation system, the temperature difference power generation system can be further analyzed and designed specifically, and a result is more accurate.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
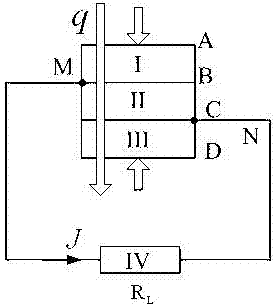
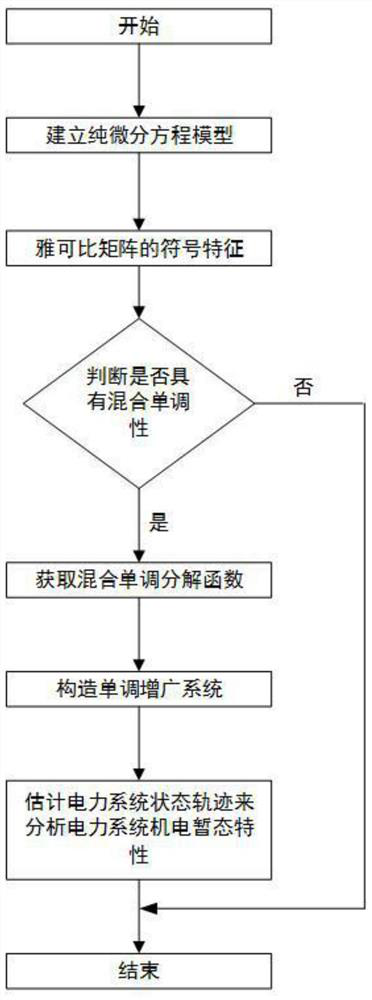
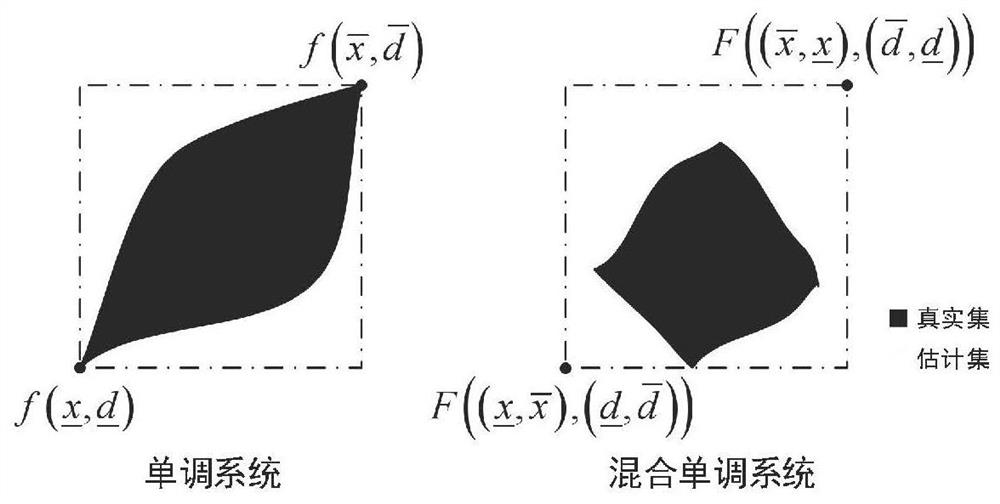
Electromechanical transient characteristic analysis method for power system based on hybrid monotonic characteristics
ActiveCN111709155ASolve the problem of increasing difficulty in transient characteristic analysisData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationElectric power systemAnalytical expressions
The invention discloses an electromechanical transient characteristic analysis method for a power system based on hybrid monotonic characteristics. The electromechanical transient characteristic analysis method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing an electromechanical transient pure differential equation model of the power system; s2, according to the pure differential equation model inS1, obtaining an element analytical expression in a corresponding Jacobian matrix, analyzing symbol characteristics of the Jacobian matrix of the power system in multiple stages, and if values of non-diagonal elements of the Jacobian matrix J (x) of f (x) are kept constant and non-positive or constant and non-negative, determining that a mixed monotonic decomposition function exists; and S3, constructing a monotonous augmentation system by adopting the mixed monotonous decomposition function, estimating an uncertain power system state trajectory according to the solution of the augmentation system, and analyzing the electromechanical transient characteristics of the power system through the state trajectory. According to the method, a quantitative analysis result can be provided for the uncertainty problem, the problem that in the prior art, the power grid transient characteristic analysis difficulty is increased is solved, and a new method is provided for power system transient characteristic analysis.
Owner:STATE GRID NINGXIA ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Multi-factor model optimization method for gene regulatory network
PendingCN113486952AHigh simulationParameters are easy to adjustCharacter and pattern recognitionArtificial lifeNon linear dynamicEngineering
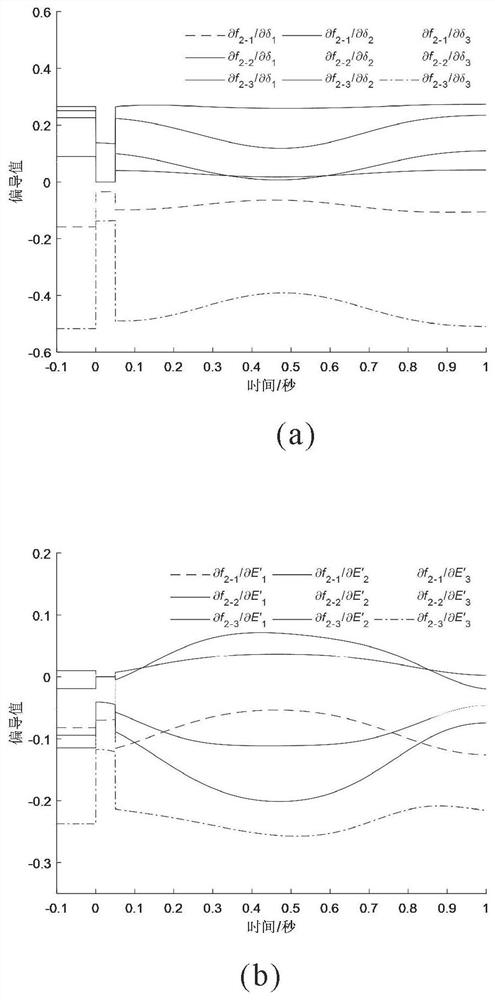
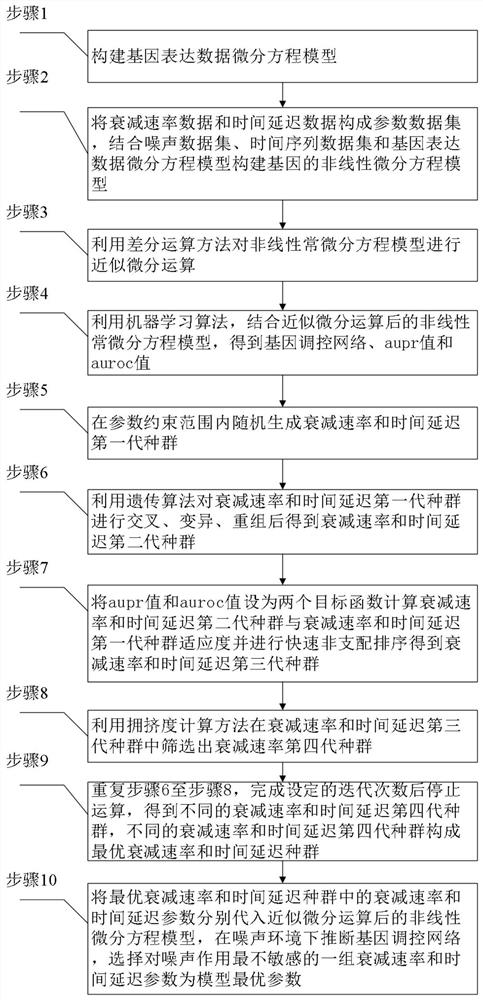
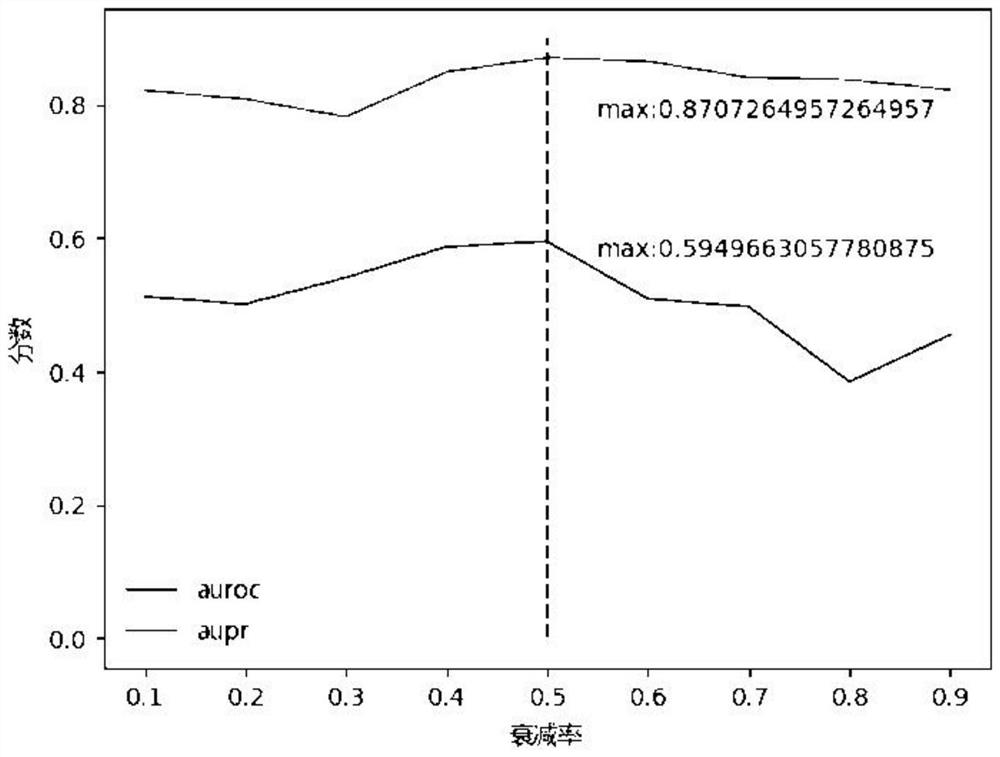
The invention discloses a multi-factor model optimization method for a gene regulatory network, which comprises the following steps: inferring the gene regulatory network by utilizing a nonlinear differential equation model and a differential operation method of a gene and combining a machine learning algorithm, and optimizing a key parameter attenuation rate based on a multi-objective optimization idea and a genetic algorithm. According to the invention, the effects of noise, attenuation rate and time delay are introduced on the basis of a traditional differential equation model, a nonlinear regulation and control function is trained based on a machine learning algorithm, and the nonlinear dynamic process of gene expression can be better simulated; the algorithm is used for optimizing the attenuation rate and time delay of important parameters influencing gene expression, and then a more accurate and efficient mathematical model is constructed to deduce the gene regulation network from gene expression data.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Kinetic Modeling Method for Direct Coal Liquefaction Reaction
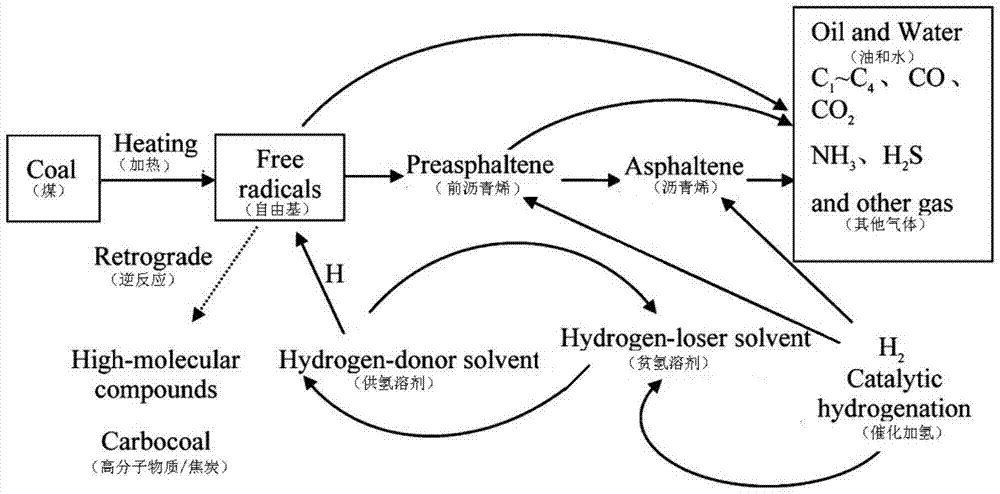
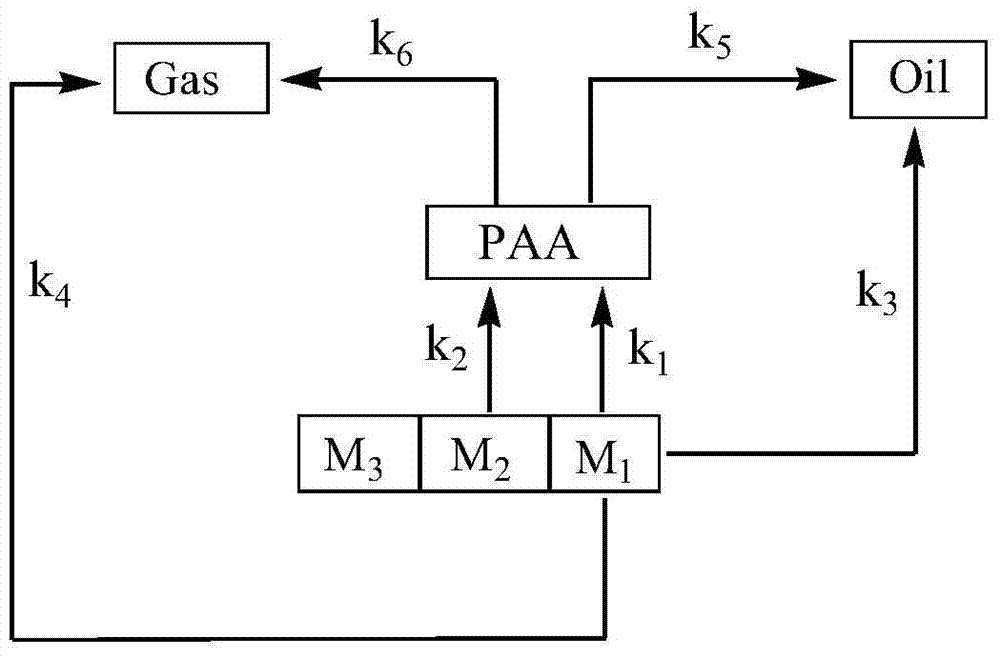
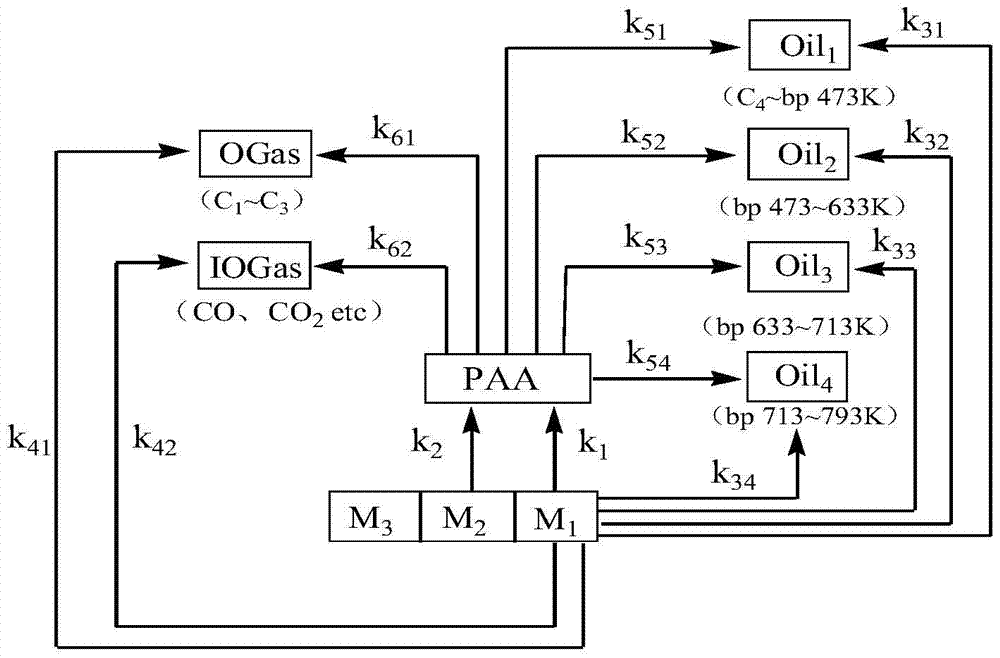
ActiveCN104462754BAccurate predictionHigh precisionLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionSpecial data processing applicationsDifferential equation modelsProcess simulation
The invention provides a coal direct liquefaction reaction kinetic model modeling method. The method includes: step S1: dividing raw coal, intermediate products of direct coal liquefaction reaction and liquefied oil into 11 aggregates; step S2: constructing a reaction network according to the reaction mechanism of direct coal liquefaction; step S3: establishing a reaction network according to the reaction network Coal direct liquefaction reaction model differential equation; Step S4: Solve the coal direct liquefaction reaction model differential equation, determine the parameters in the coal direct liquefaction reaction model differential equation and estimate each parameter; Step S5: Establish the coal direct liquefaction reaction product internal Gas component prediction correlation model and liquefied oil narrow fraction prediction correlation model. The invention can be used for the simulation calculation of the direct coal liquefaction reaction, and has high precision, so that the flow simulation of the coal direct liquefaction reaction stage is closer to the actual reaction, so that the composition of the reaction liquefied oil and gas can be accurately predicted.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com