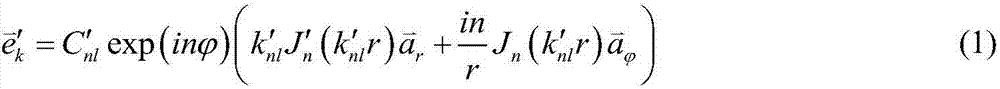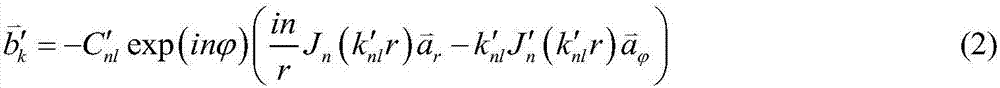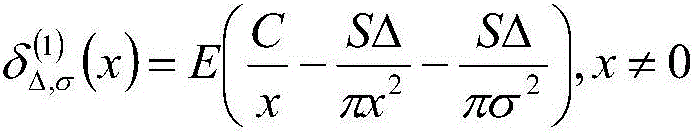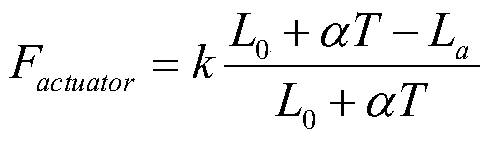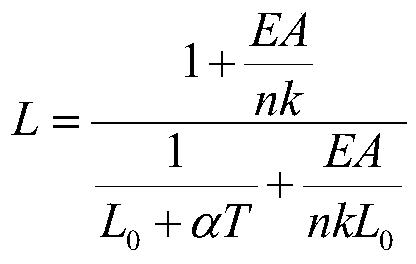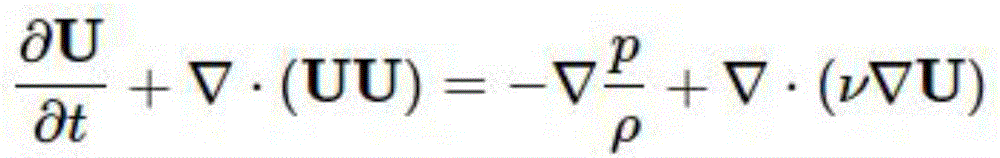Patents
Literature
30 results about "Elliptic partial differential equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Second order linear partial differential equations (PDEs) are classified as either elliptic, hyperbolic, or parabolic. Any second order linear PDE in two variables can be written in the form Auₓₓ+2Buₓy+Cuyy+Duₓ+Euy+Fu+G=0, where A, B, C, D, E, F, and G are functions of x and y and where uₓ=∂u/∂x and similarly for uₓₓ,uy,uyy,uₓy. A PDE written in this form is elliptic if B²-AC<0, with this naming convention inspired by the equation for a planar ellipse.
Progressive addition power lens
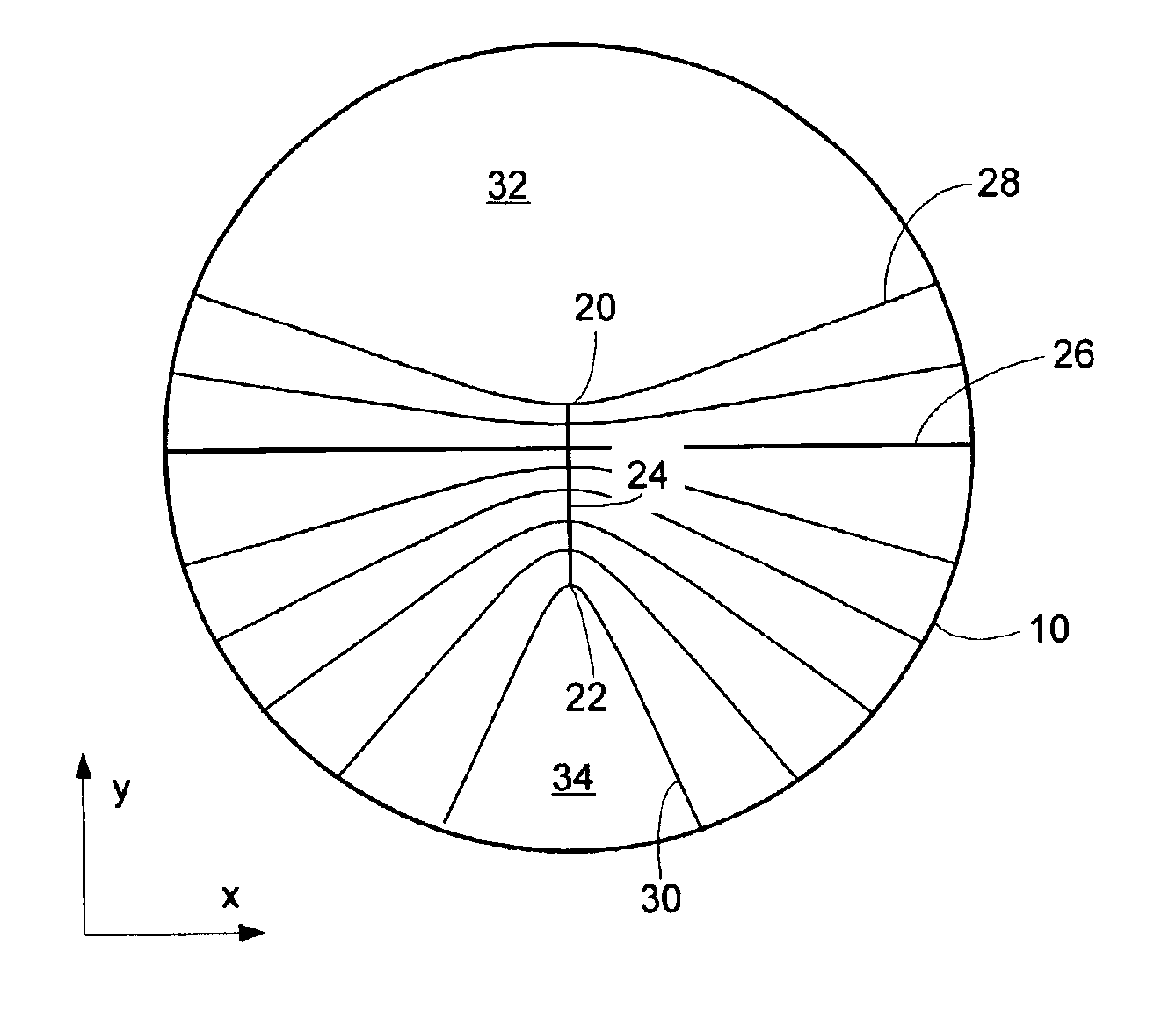
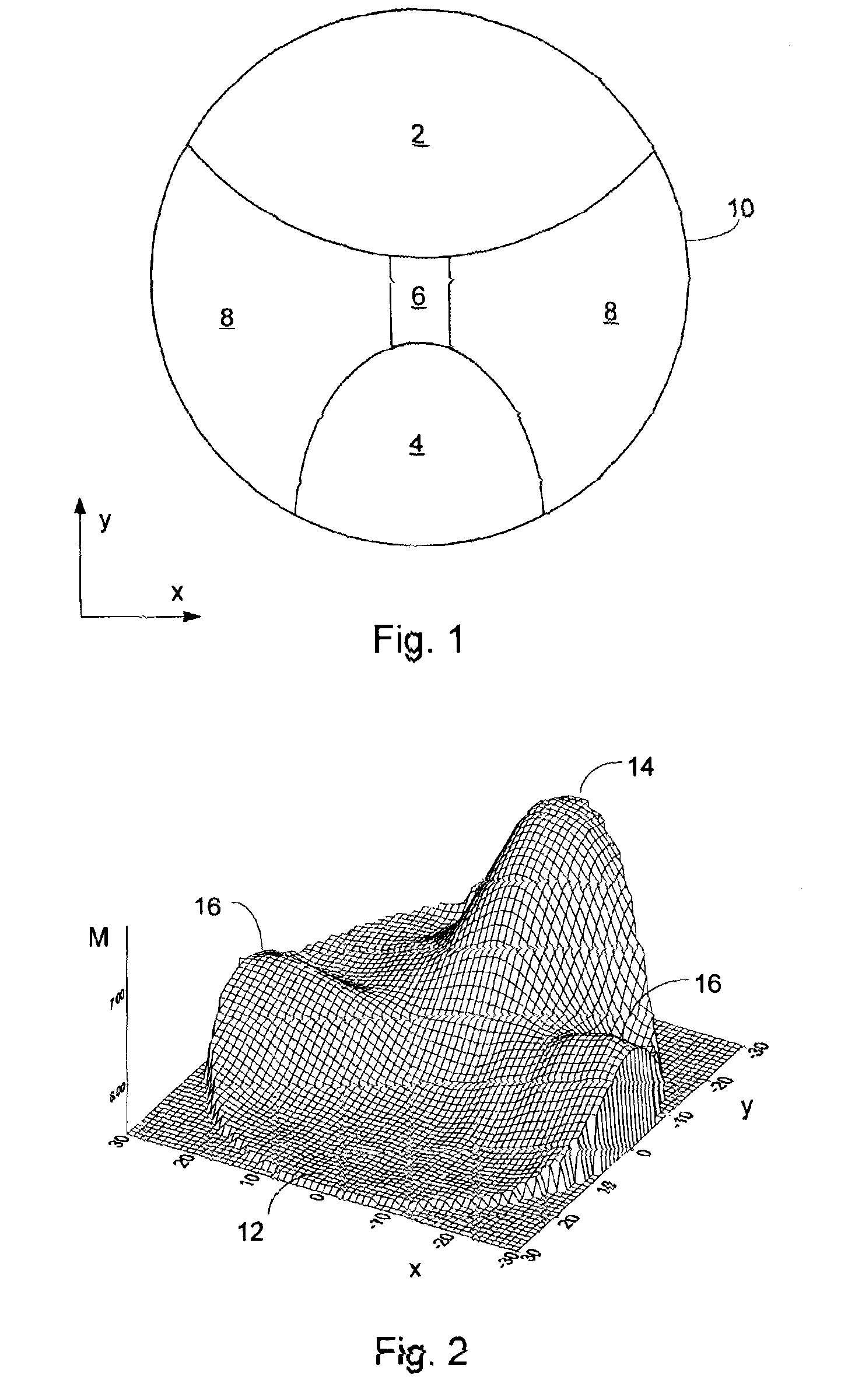
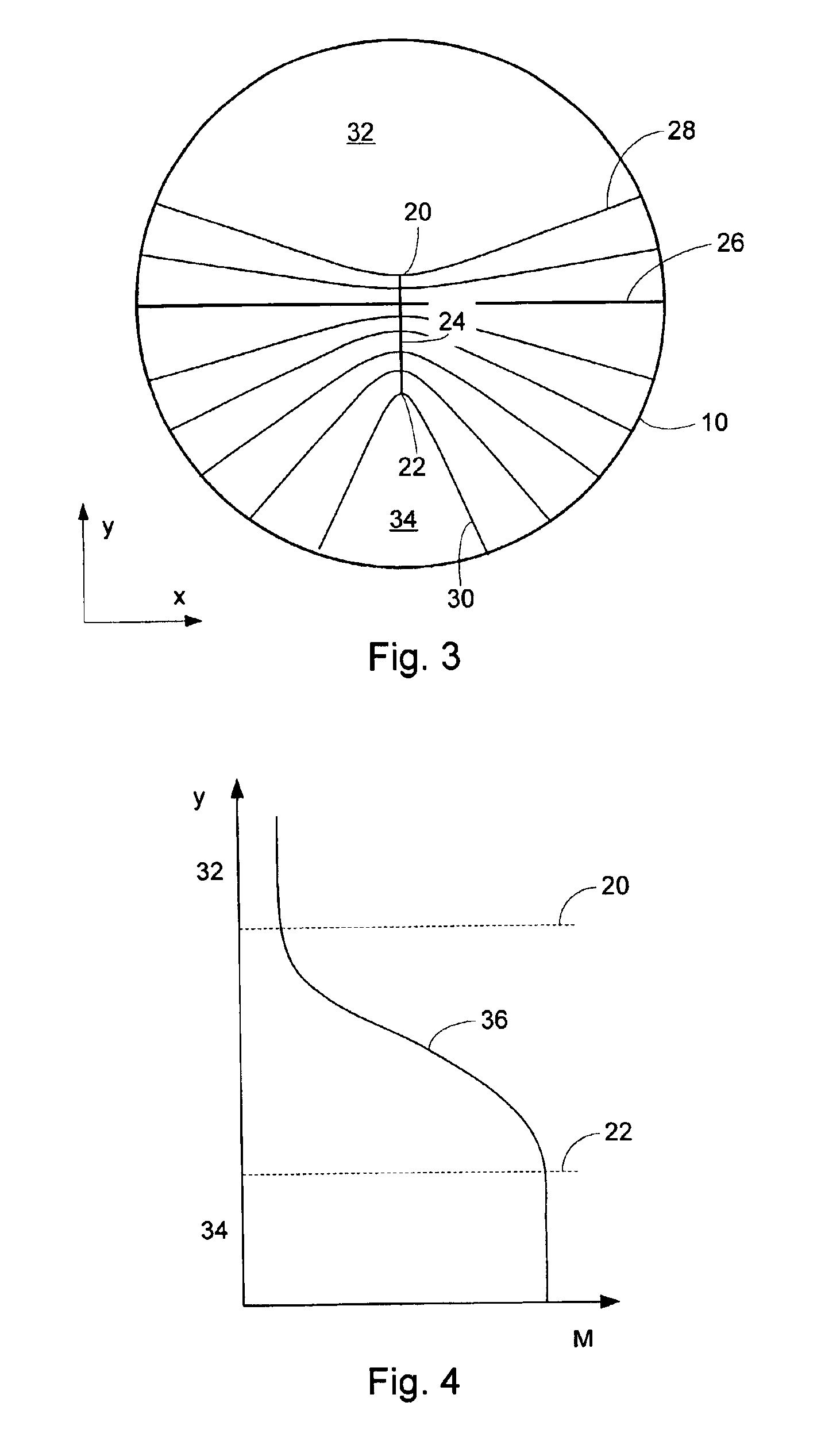
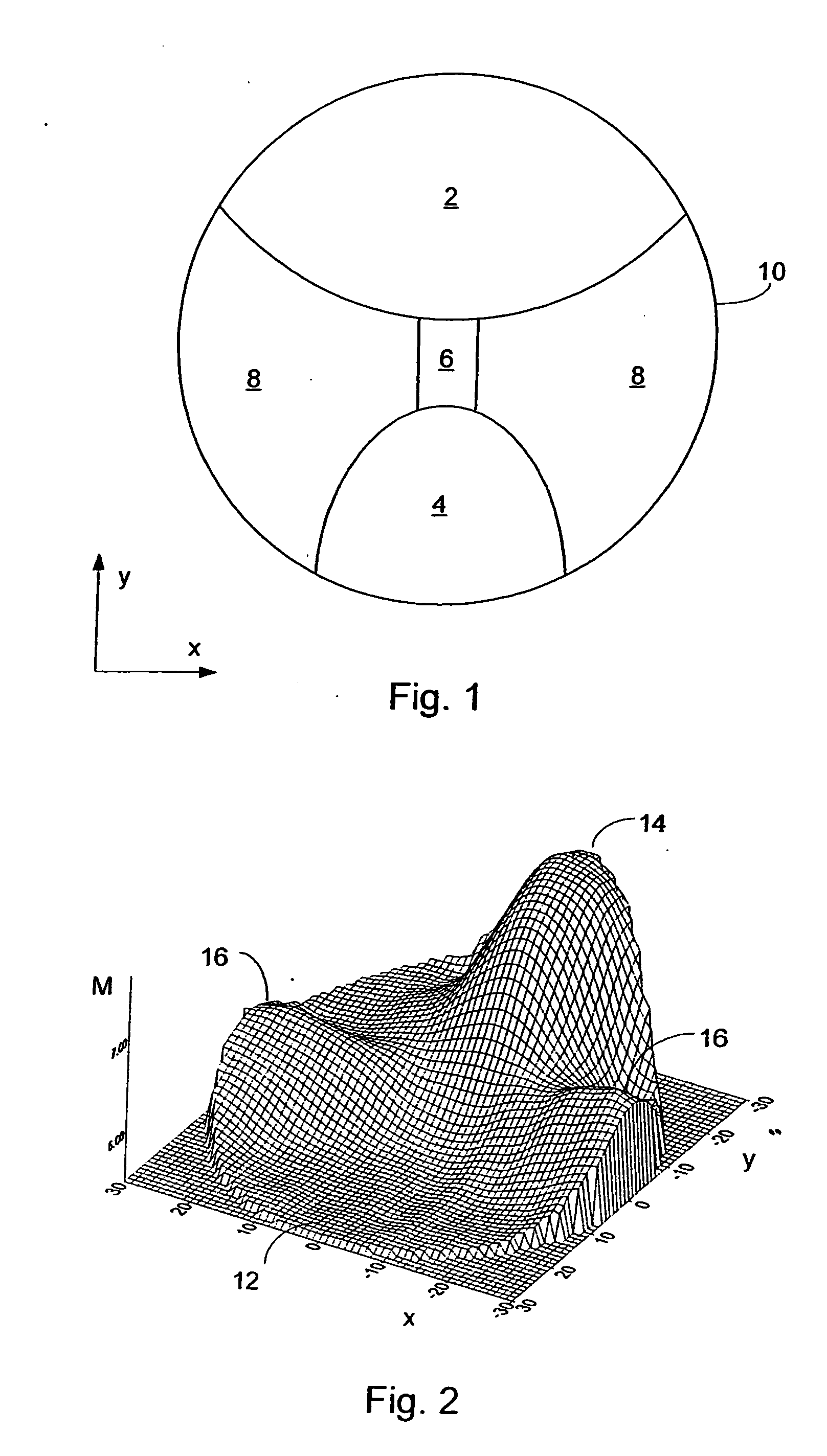
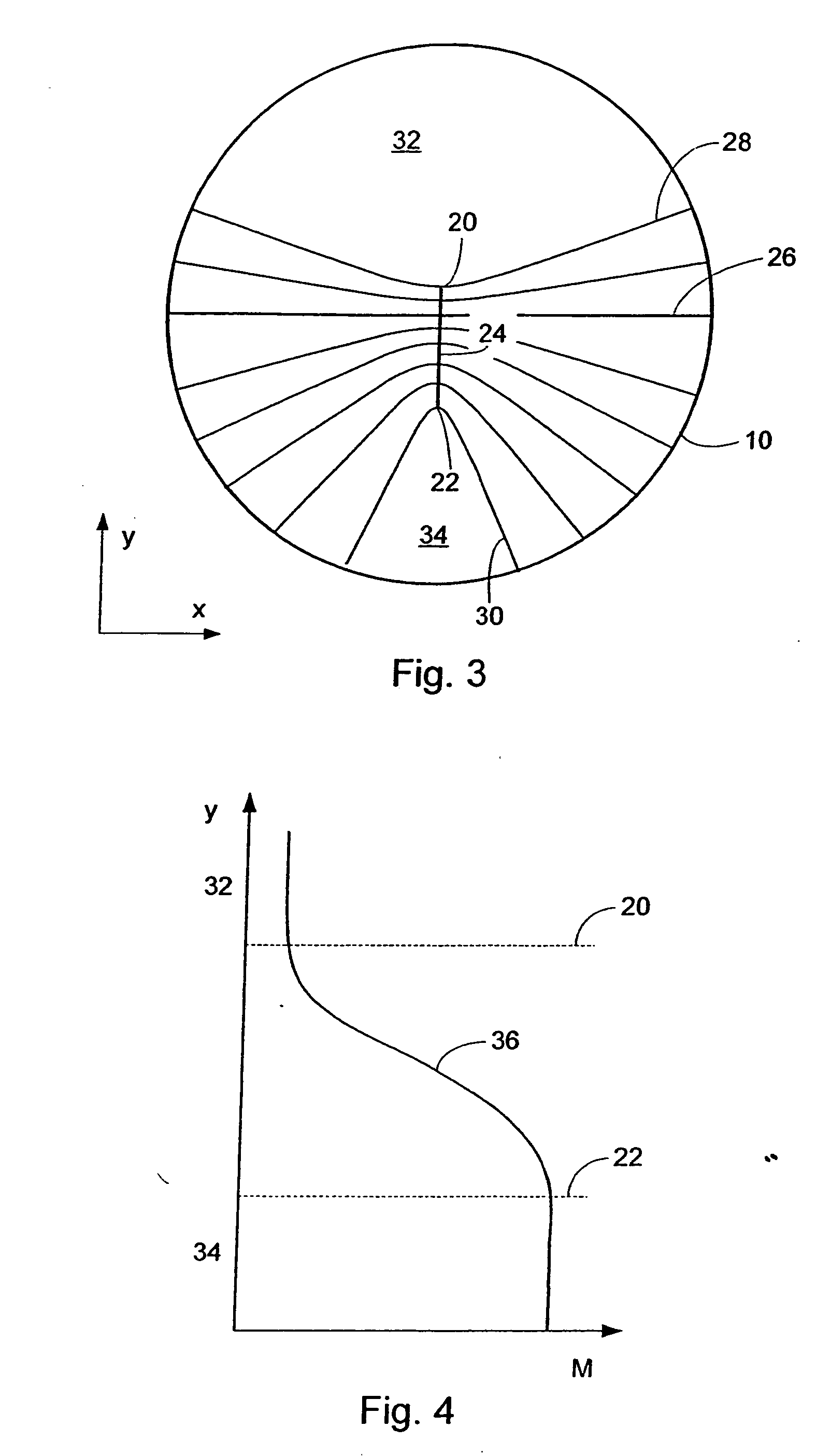
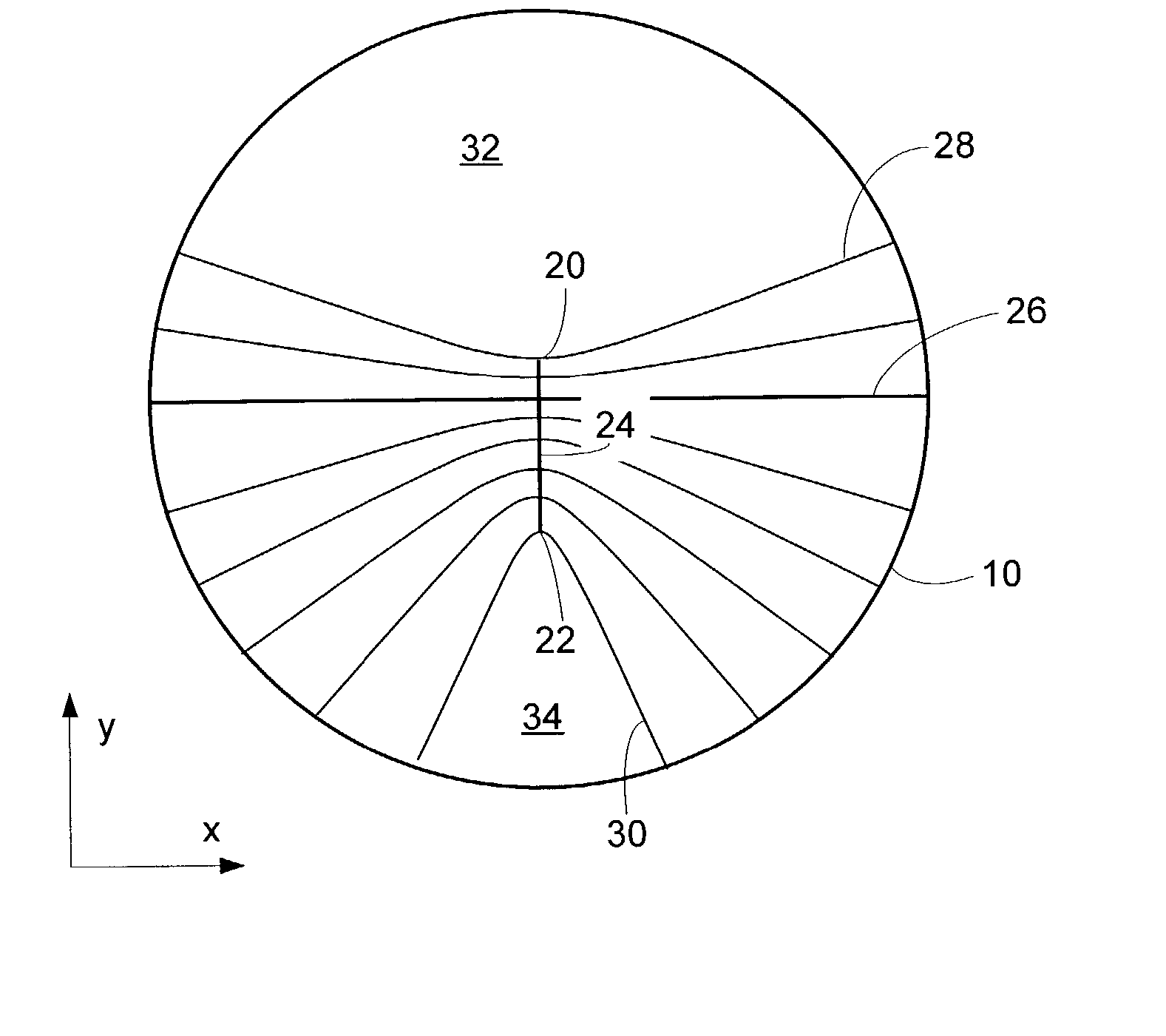
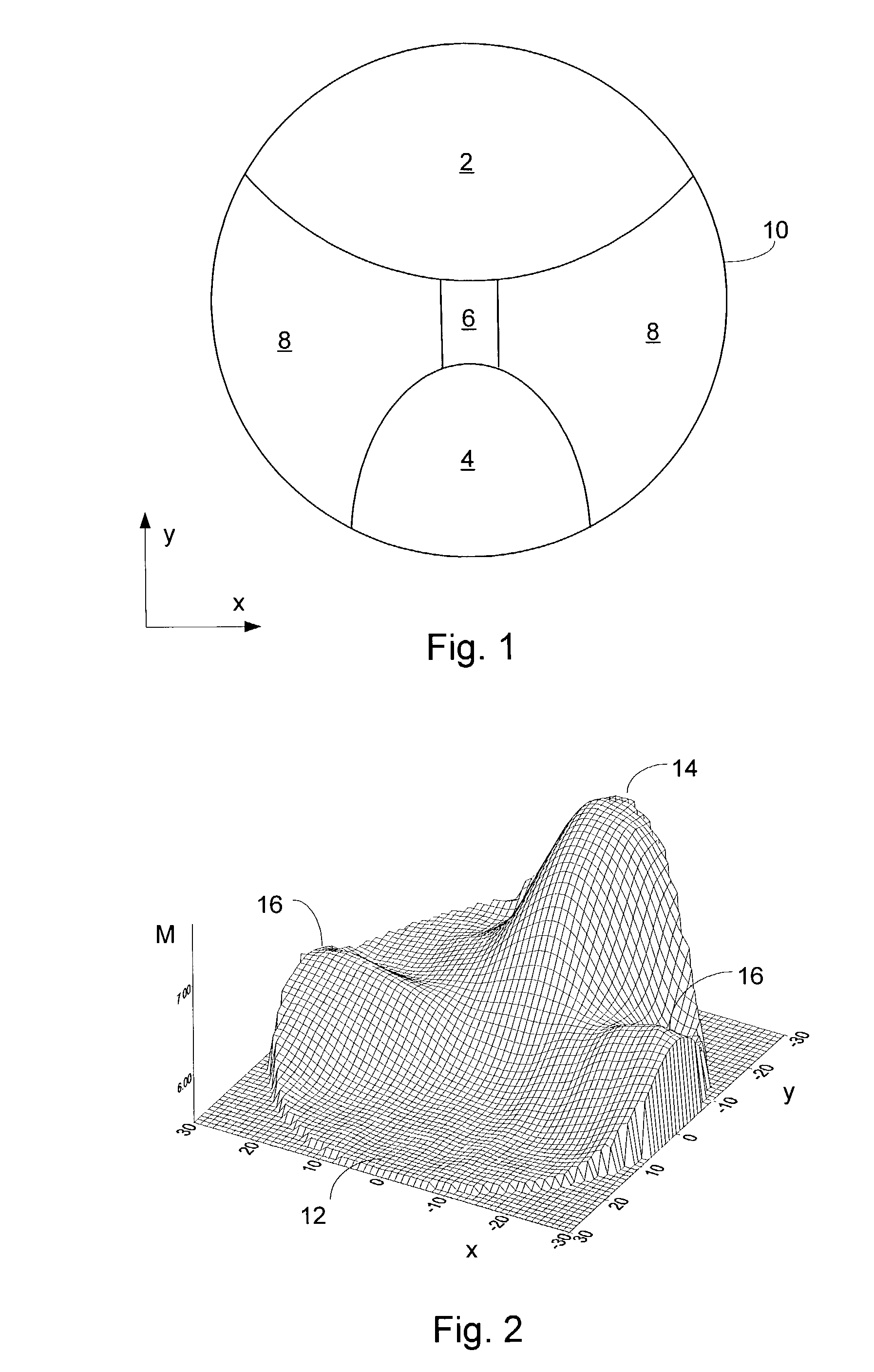
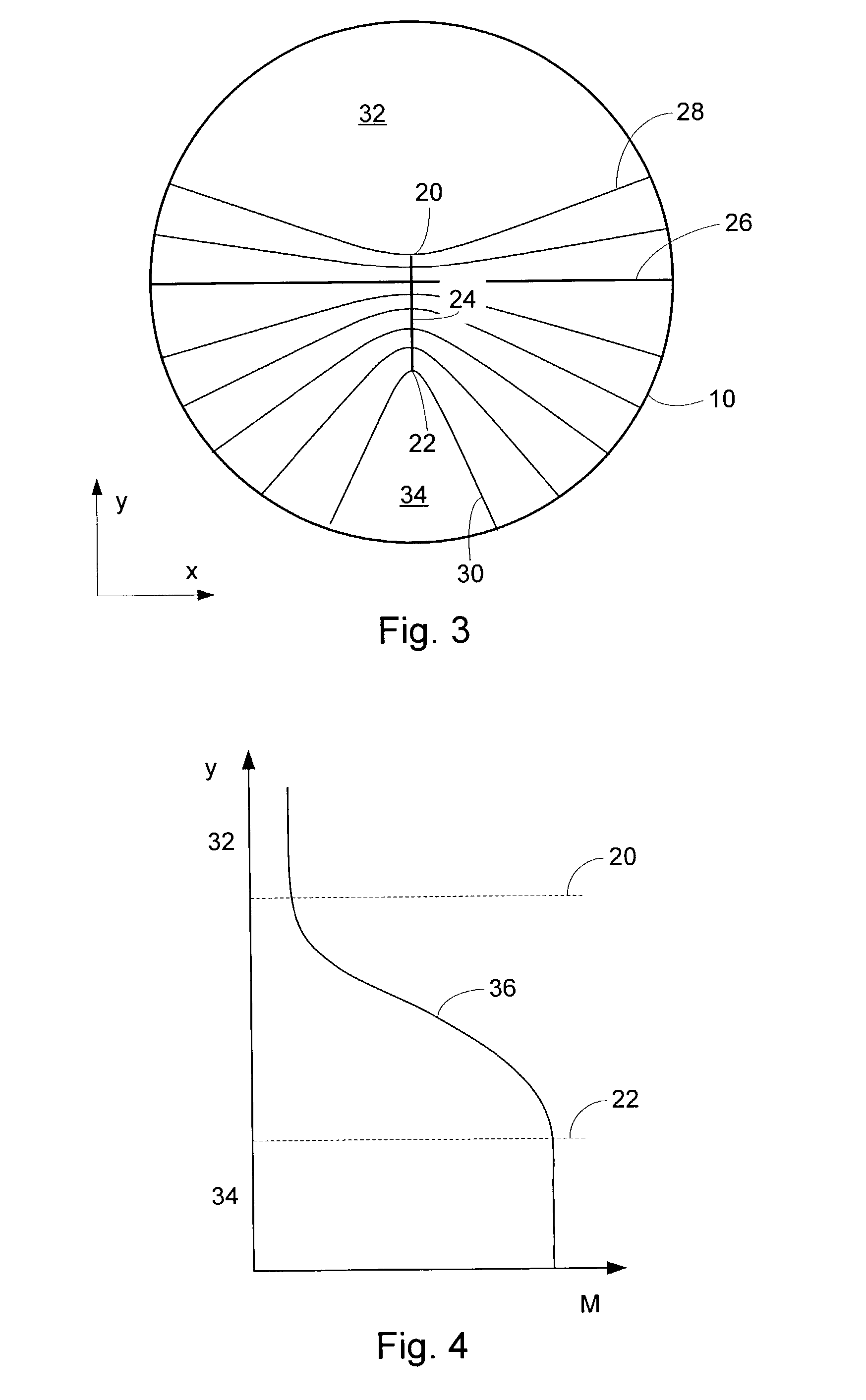
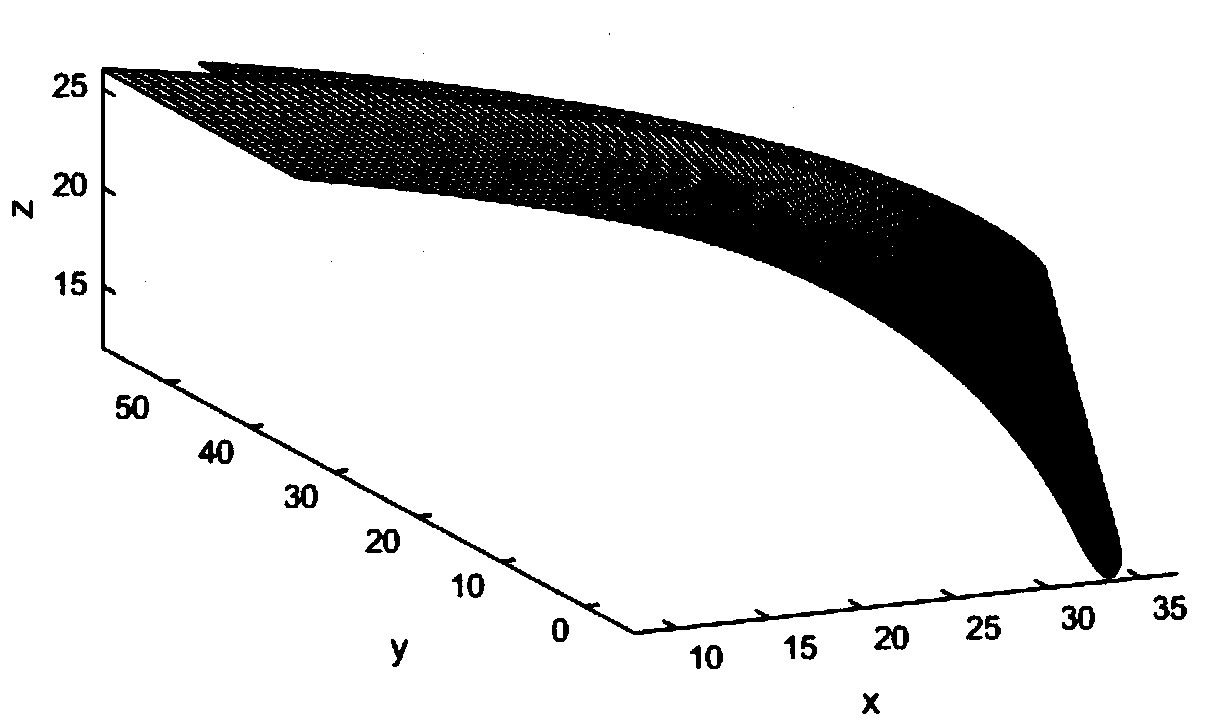
A system and method for designing a progressive lens. Mean power is specified at points distributed over the entire surface of the lens and lens height is specified around the edge of the lens. Lens height is determined at the points consistent with the specified mean power and the lens edge height in part by solving a partial differential equation of the elliptic type subject to the lens edge height as a boundary condition. A successive over-relaxation technique may be employed to converge on the solution to the partial differential equation, and an over-relaxation factor may be determined to most efficiently relax the equation.
Owner:CROSSBOWS OPTICAL
Progressive addition power lens
InactiveUS20050012895A1Effective areaReduces peak of astigmatismOptical partsSuccessive over-relaxationRelaxation equation
A system and method for designing a progressive lens are provided. Mean power is specified at points distributed over the entire surface of the lens and lens height is specified around the edge of the lens. Lens height is determined at the points consistent with the specified mean power and the lens edge height in part by solving a partial differential equation of the elliptic type subject to the lens edge height as a boundary condition. A successive over-relaxation technique may be employed to converge on the solution to the partial differential equation, and an over-relaxation factor may be determined to most efficiently relax the equation.
Owner:CROSSBOWS OPTICAL
Progressive addition power lens
A system and method for designing a progressive lens. Mean power is specified at points distributed over the entire surface of the lens and lens height is specified around the edge of the lens. Lens height is determined at the points consistent with the specified mean power and the lens edge height in part by solving a partial differential equation of the elliptic type subject to the lens edge height as a boundary condition. A successive over-relaxation technique may be employed to converge on the solution to the partial differential equation, and an over-relaxation factor may be determined to most efficiently relax the equation.
Owner:CROSSBOWS OPTICAL
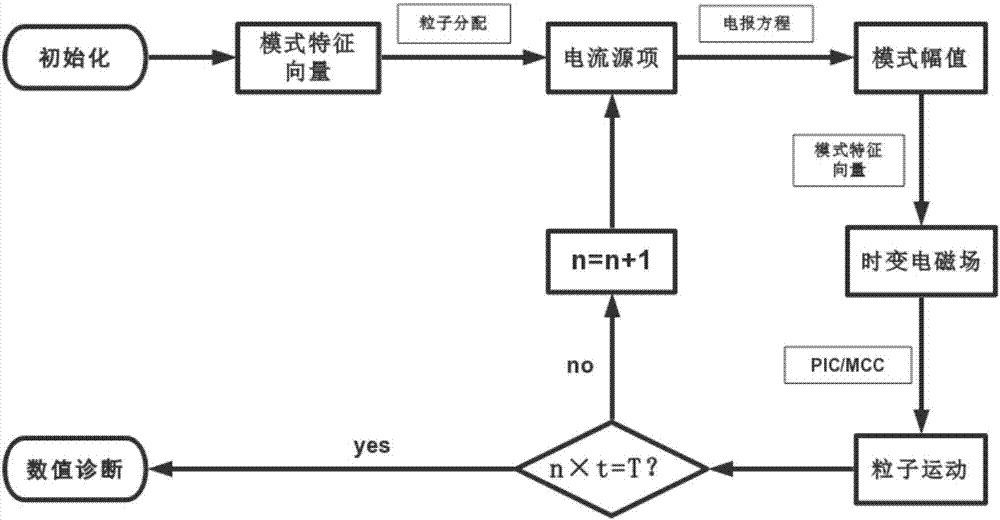
MPM hybrid algorithm applied to numerical simulation of ECR ion source
ActiveCN107577639AAccurate descriptionReduce computational complexityComplex mathematical operationsComputation complexityMaxwell's equations
The invention belongs to the field of numerical simulation technology of ECR ion sources, and particularly relates to an MPM hybrid algorithm applied to numerical simulation of an ECR ion source. Thealgorithm is suitable for use in an ECR ion source structure. The MPM hybrid algorithm of simulation of the ECR ion source is established through combining an MAGY theory and PIC / MCC simulation algorithms, a time-varying electromagnetic field is described by the MAGY theory, self-consistent interaction of charged particles and the electromagnetic field is described by the PIC algorithm, and inter-particle collision processes are described by the MCC algorithm. A complex and complete solving process which originally needs to be carried out on Maxwell's equations is enabled to be simplified to solving on a set of coupled one-dimensional partial differential equations about mode amplitudes, relatively larger time step length can also be taken due to that compared with high-frequency cycles, changes of the mode amplitudes are slower, and computational complexity and a computational amount are greatly reduced. In addition, an electromagnetic model is adopted, and thus compared with adoptingan electrostatic model, the algorithm can more accurately describe an actual physical process.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Signal processing methods
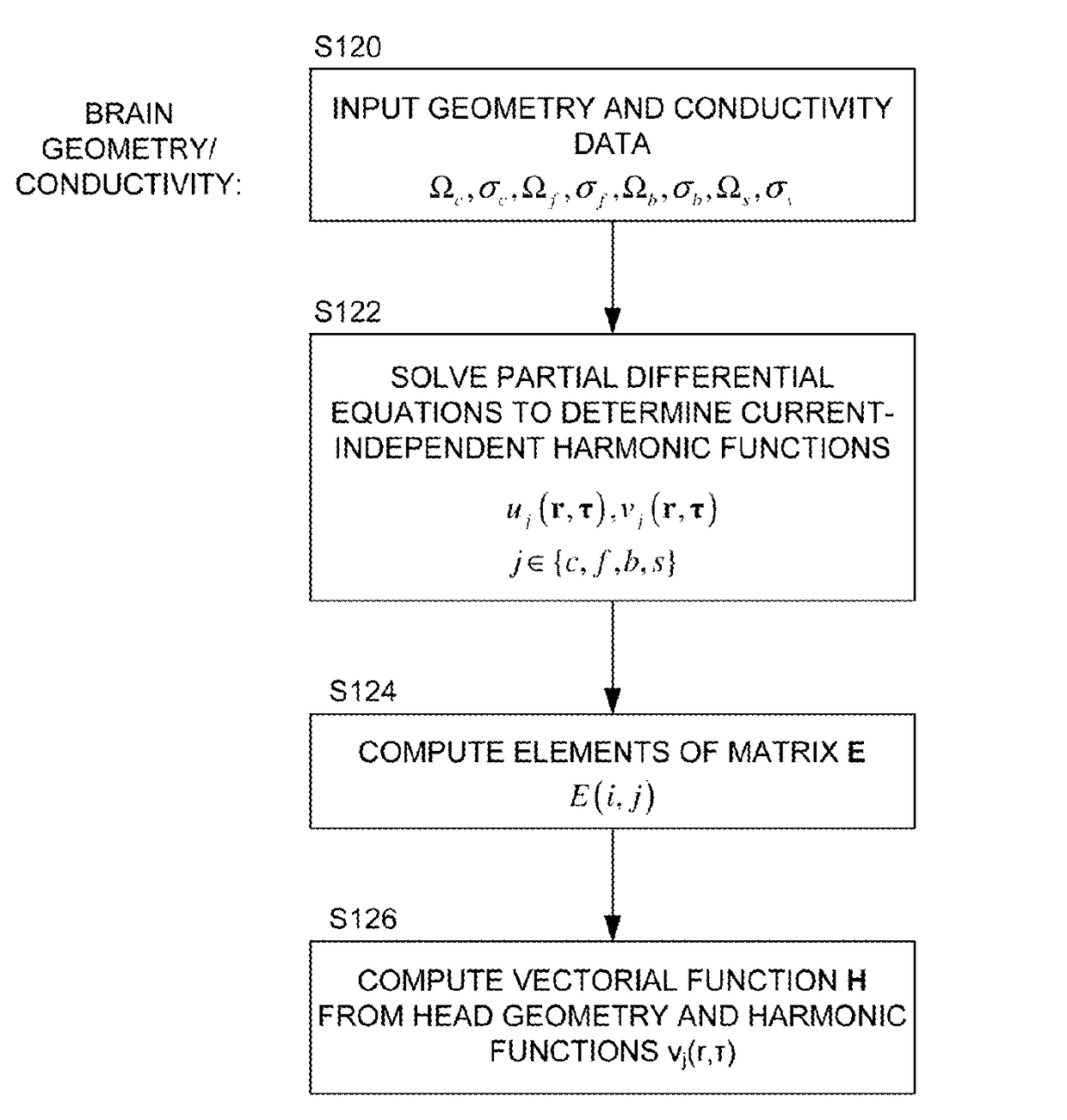
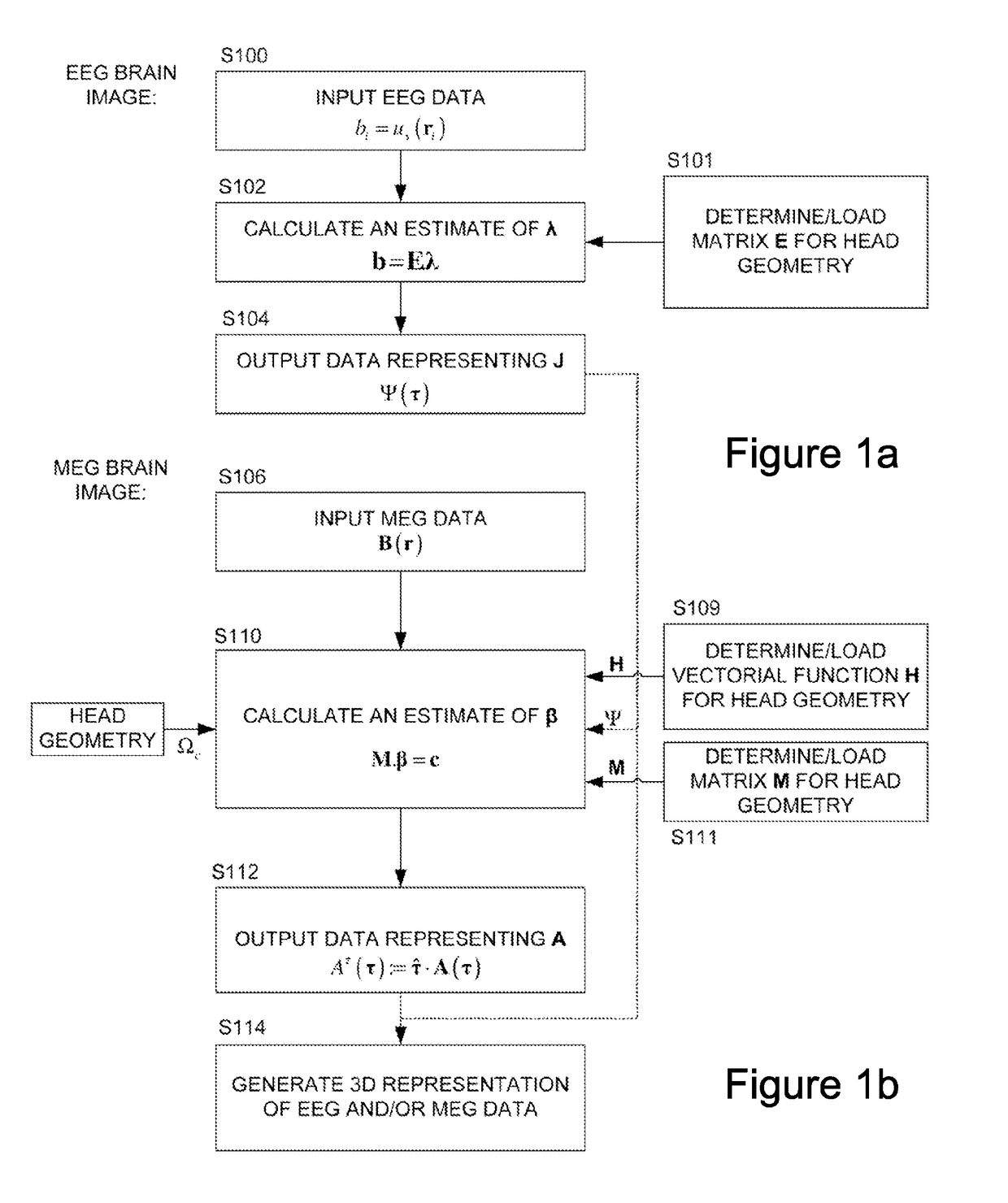
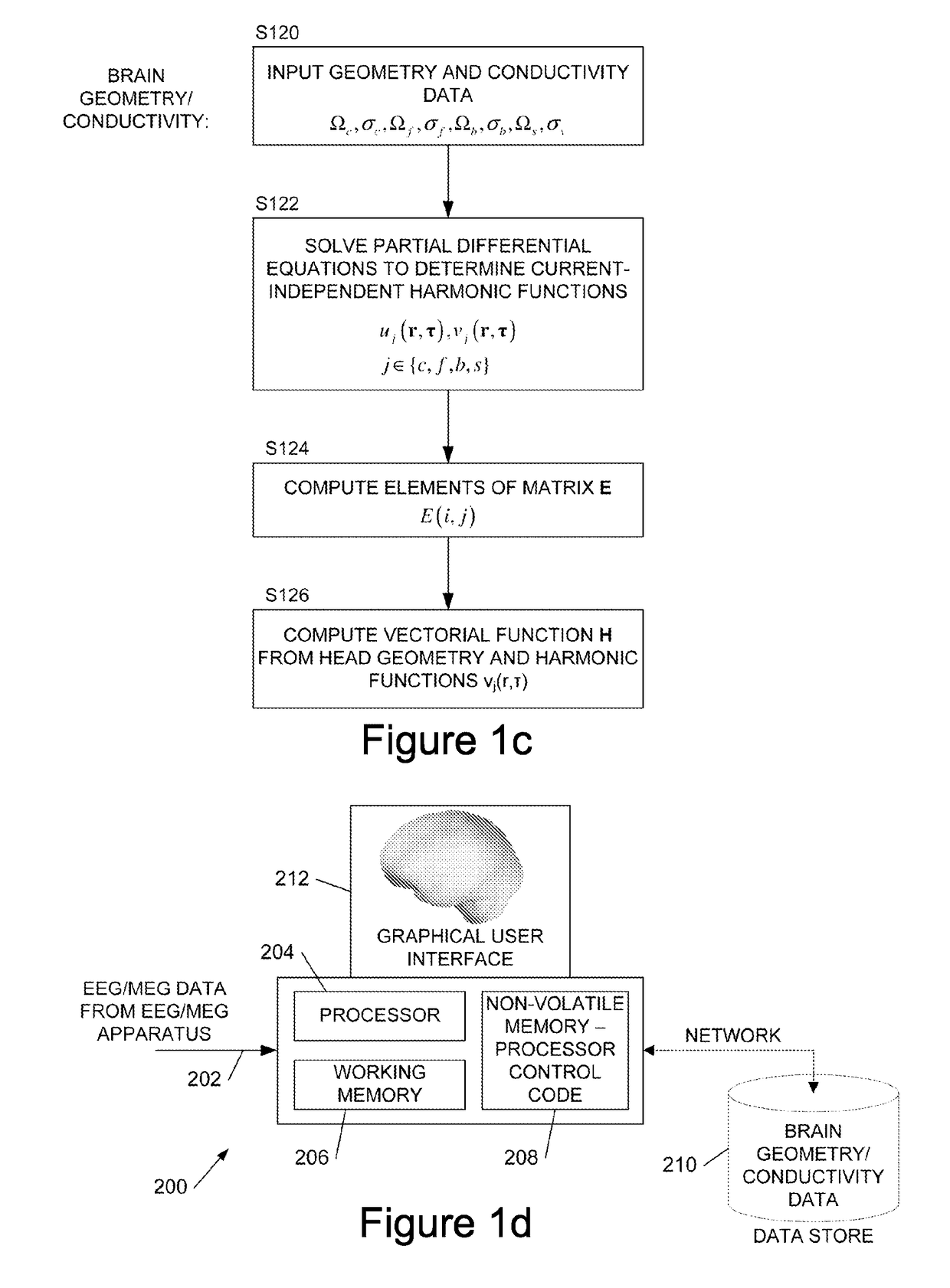
ActiveUS20170095174A1Calculation can be costlyElectroencephalographyImage enhancementExact differential equationImaging data
We describe a method of processing an EEG and / or MEG signal to generate image data representing a 3D current distribution, J, within the brain, the method comprising: capturing a plurality of electric and / or magnetic measurements from the exterior of the head; solving an integral equation for a part of said current distribution to generate said image data representing said 3D current distribution, wherein said integral equation comprises an integral of a first function representing said part of said current distribution and of a second function (∇τvs (r, τ)) representing the geometry and conductivity of the head independent of said current distribution; wherein said solving comprises: modelling the head as at least two regions separated by at least one internal boundary, and solving a set of partial differential equations, one for each said internal region, each partial differential equation comprising a geometry-conductivity function (w(r, τ)) representing the geometry and conductivity of the respective region, wherein said solving is subject to a boundary condition that either i) the gradients of the functions across the or each said internal boundary are smooth when conductivity is taken into account, or ii) a normal component of the electric field of said part of said current distribution is continuous across the or each said internal boundary, and wherein said geometry-conductivity function for an outermost said region of said head defines said second function (∇Tvs (r, τ))
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
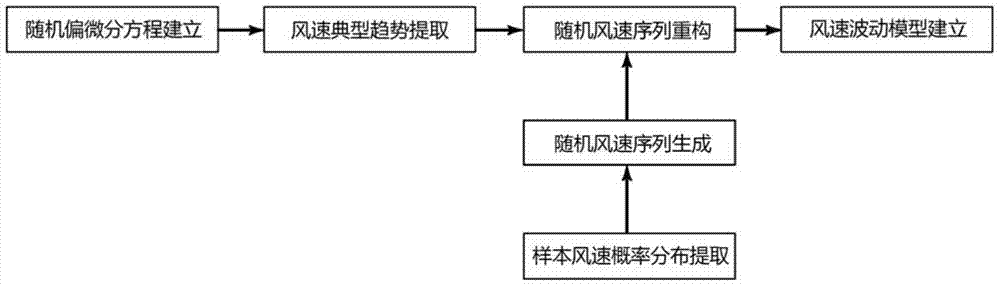
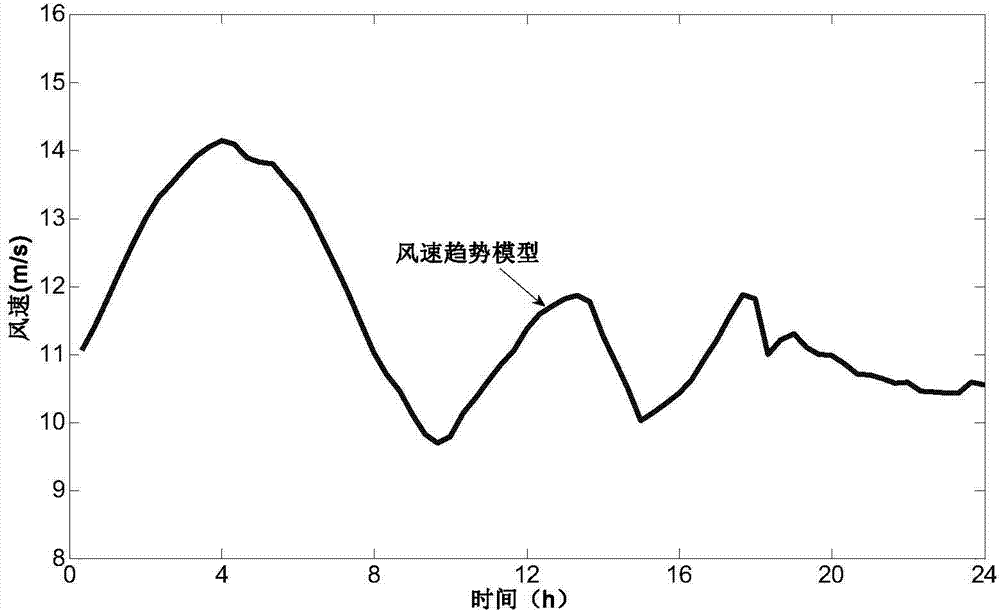
Stochastic partial differential equation based wind speed fluctuation characteristic modeling method
InactiveCN104850710ASpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringElliptic partial differential equation
The invention provides a stochastic partial differential equation based wind speed fluctuation characteristic modeling method, comprising steps of: according to sample wind speed data, constructing a stochastic partial differential equation about wind speed variation, and obtaining a typical wind speed variation sequence by solving the stochastic partial differential equation; then, by fitting a probability distribution function of the sample wind speed, randomly generating a wind speed sequence, and using the solved typical wind speed variation sequence to reconstruct the random wind speed sequence according to the principle of least square method, thereby obtaining a final wind speed model; finally, verifying correctness of the modeling method through comparison with a measured wind speed sequence. The method provided by the invention can effectively depict the real wind speed fluctuation characteristics, and overcome the problem that the existing wind speed model can only consider the probability distribution of wind speed from one aspect; the wind speed model established by using the method provided by the invention can not only reflect the conditions of the probability distribution of wind speed, but also show the fluctuation characteristic of the wind speed within a required study period.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +3
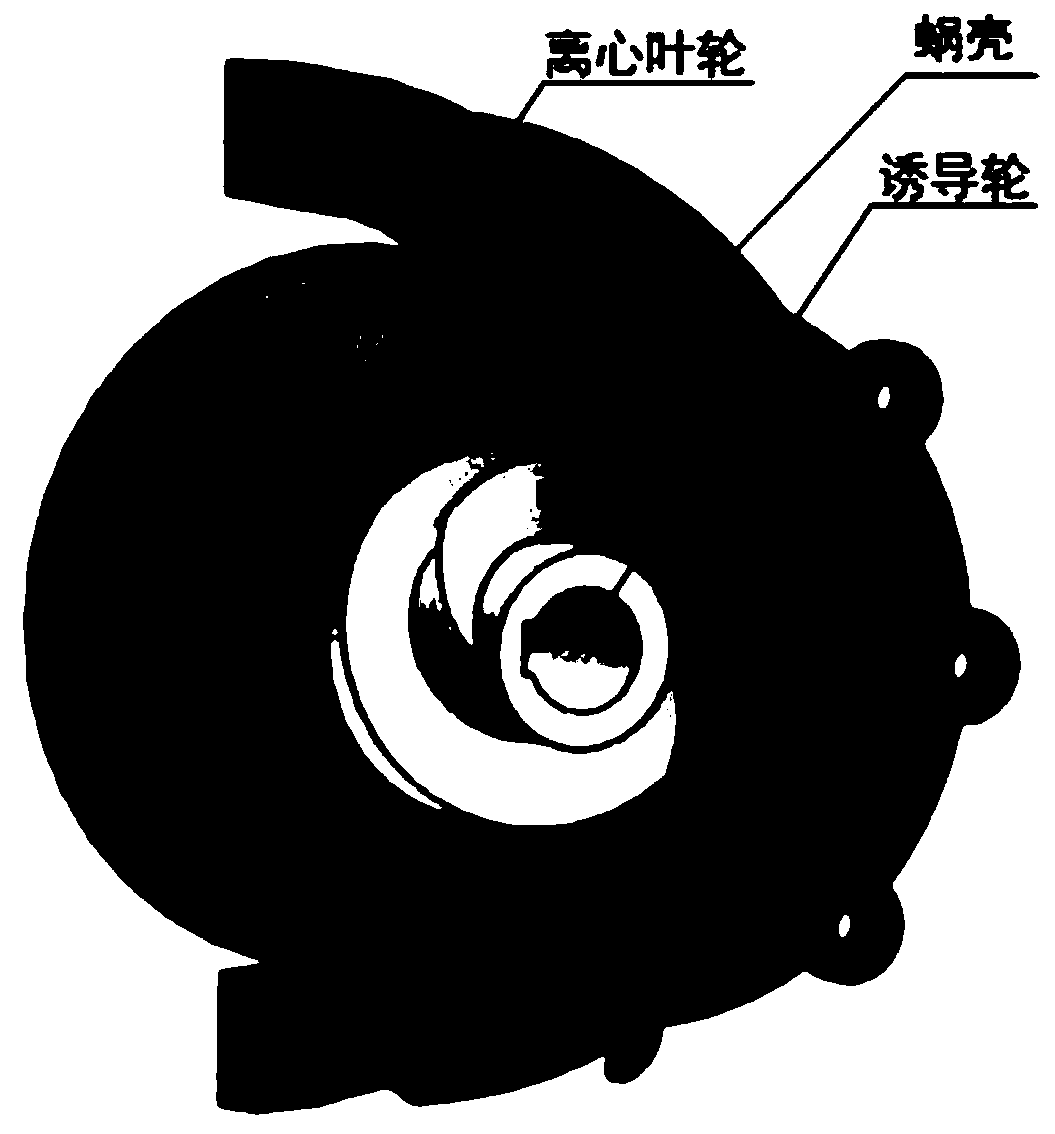
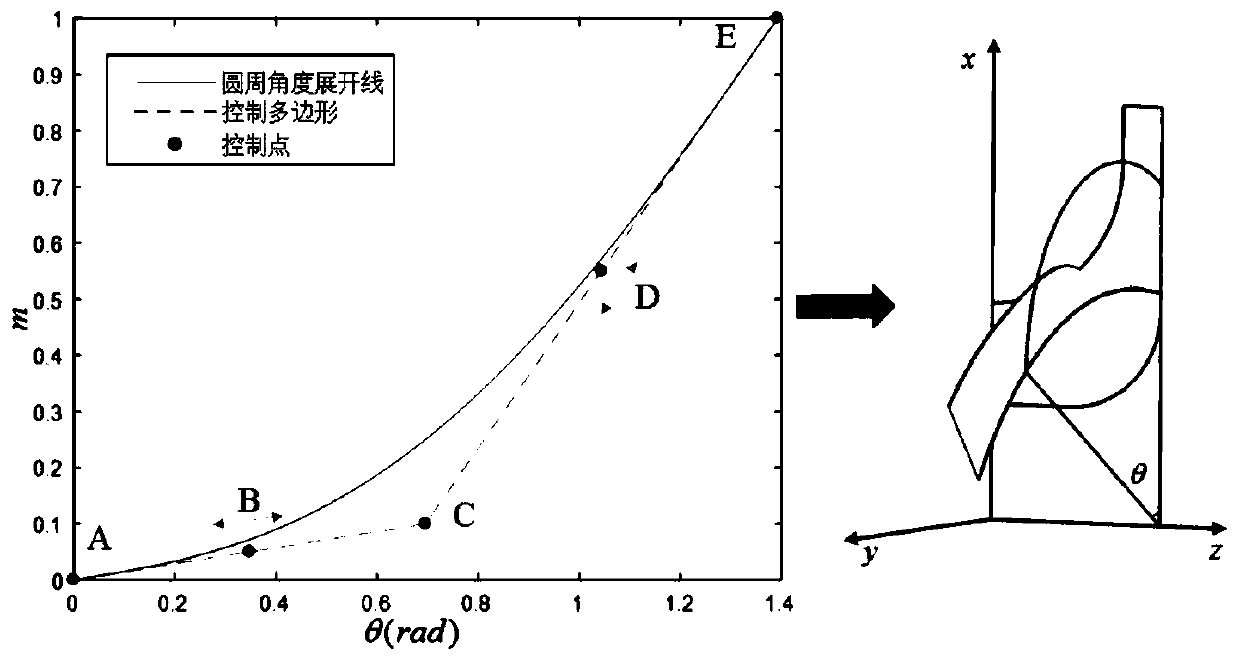
Aviation centrifugal pump blade profile optimization design method
ActiveCN110008653APerfect agreement predictive valueCompletely consistent test valueGeometric CADSustainable transportationAviationBatch processing
The invention discloses an aviation centrifugal pump blade profile optimization design method. Under a Matlab platform, a five-point four-time bezier curve and a linear function are adopted to controlthe blade profile circumference angle distribution and the product superposition change rule, and internal flow field numerical simulation is carried out on 15 sets of design results through a software UG and Fluent combined batch processing method. On the basis of obtaining a calculation space boundary condition through curved surface interpolation, numerical solution is carried out on the dual-harmonic partial differential equation by adopting a central difference format, and a hypercurved surface performance agent model is sestaboished. Global optimization is carried out on the design variable based on an artificial fish swarm algorithm by taking the highest efficiency as an objective function. The result shows that the hypersurface agent model based on the double harmonic equation canensure that the test value and the predicted value are completely consistent, the wake effect in the optimized centrifugal impeller flow is obviously weakened, and the hydraulic efficiency is improved by 5.4% compared with that of a prototype pump.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Aircraft Guidance Based on Partial Differential Equation for Miss Distance
InactiveUS20160266582A1Navigational calculation instrumentsTarget-seeking controlGuidance systemMatrix differential equation
A guidance, navigation and control (GNC) system guides an aircraft based on a special partial differential equation (PDE). The system does not depend on a predetermined desired flight path. To overcome effects of unpredictable wind speed and direction, systems and methods effectively repeatedly determine the worst landing the wind can cause and issue flight control commands that minimize among these worst outcomes. A function C that satisfies the PDE calculates smallest miss distance a guidance system can bring about by appropriately steering an aircraft, given the aircraft's current heading, current location relative to a target and current remaining amount of time to fly. The system repeatedly determines at least a component of a current gradient of the function C. A value of the gradient component is used to select an appropriate flight control command, such as turn left or turn right.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
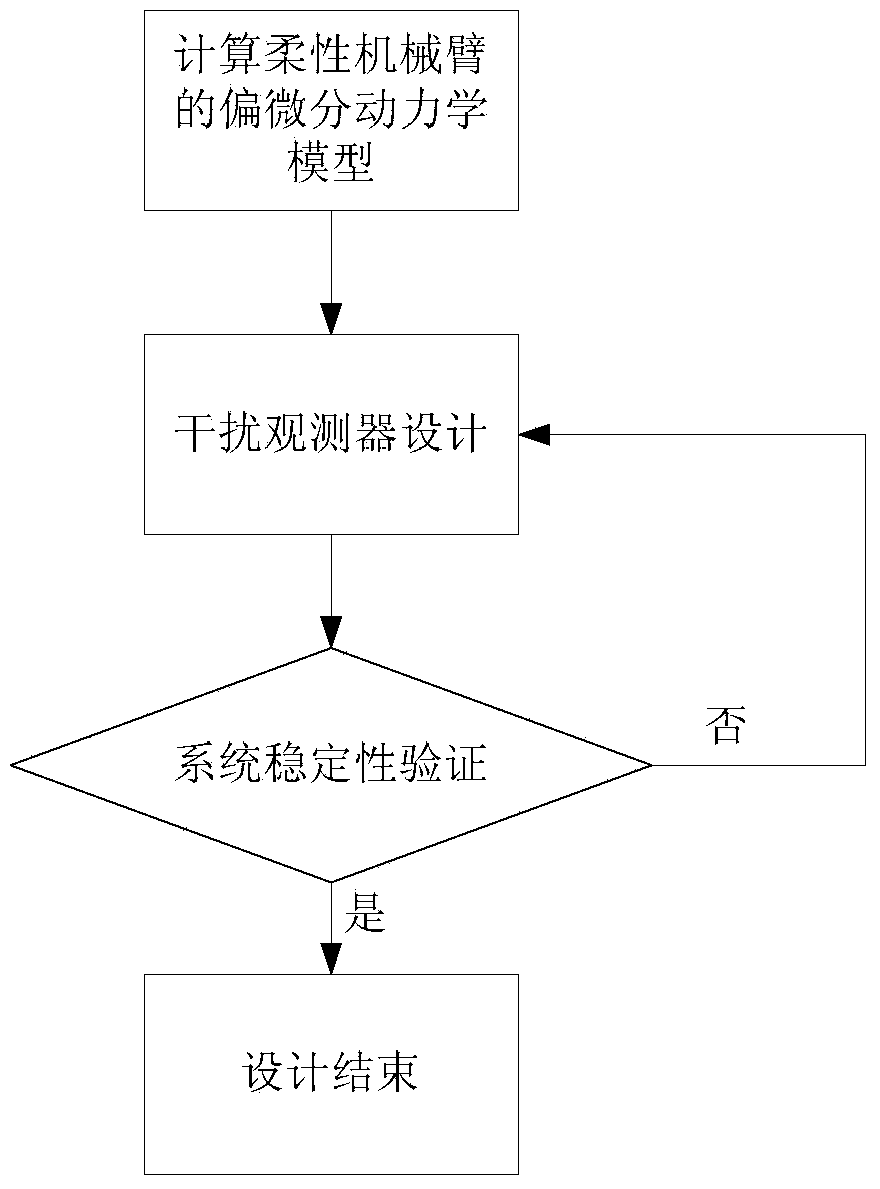
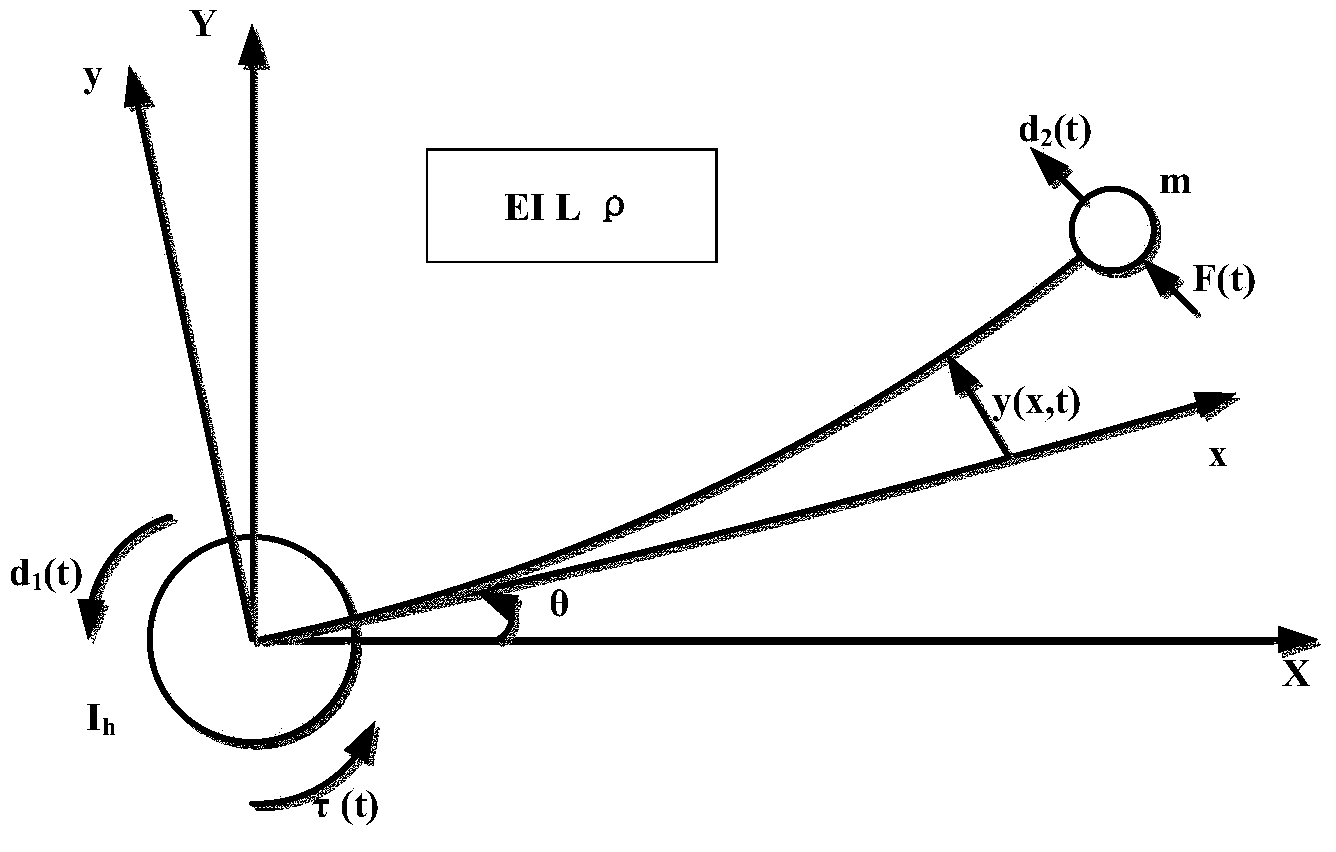
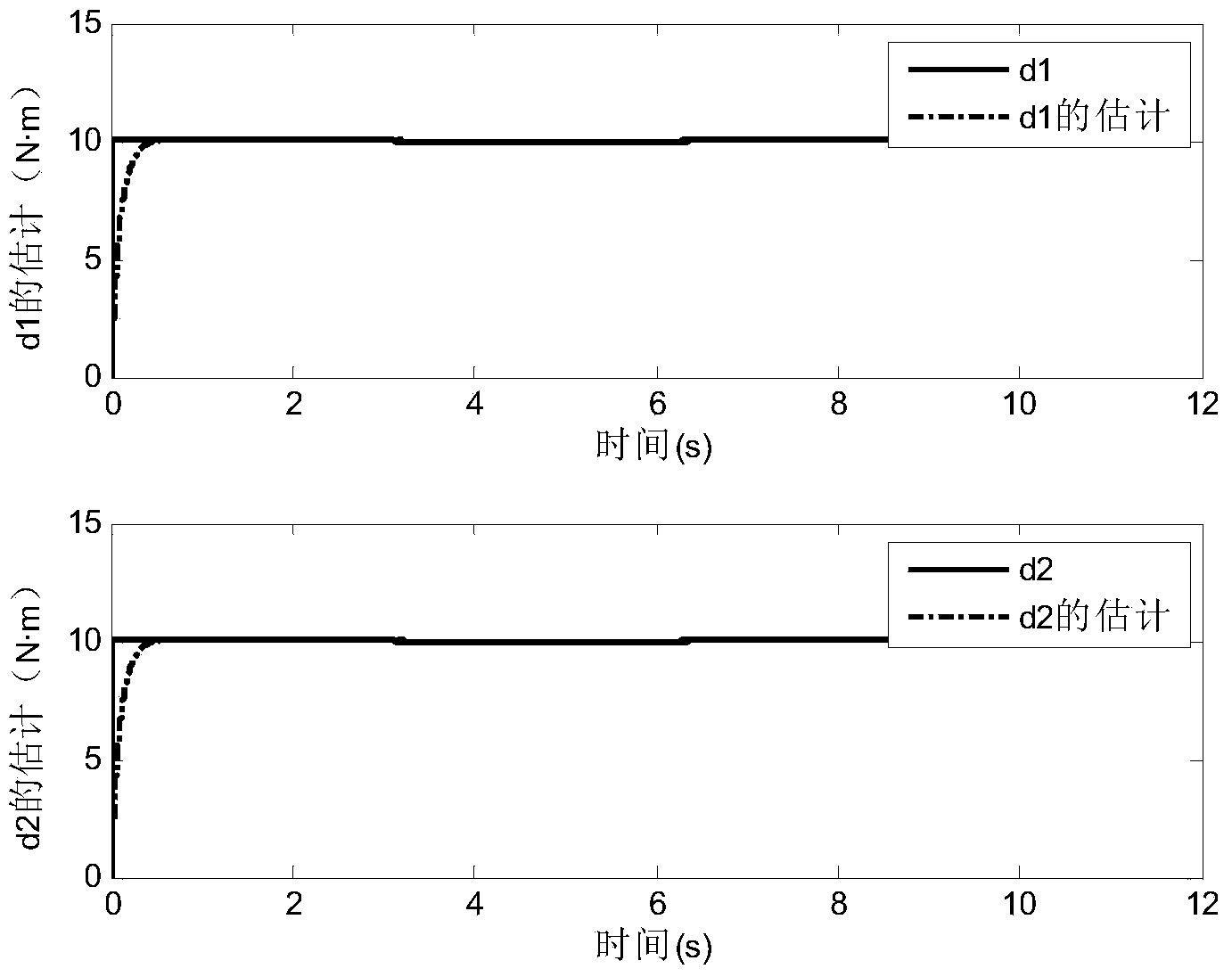
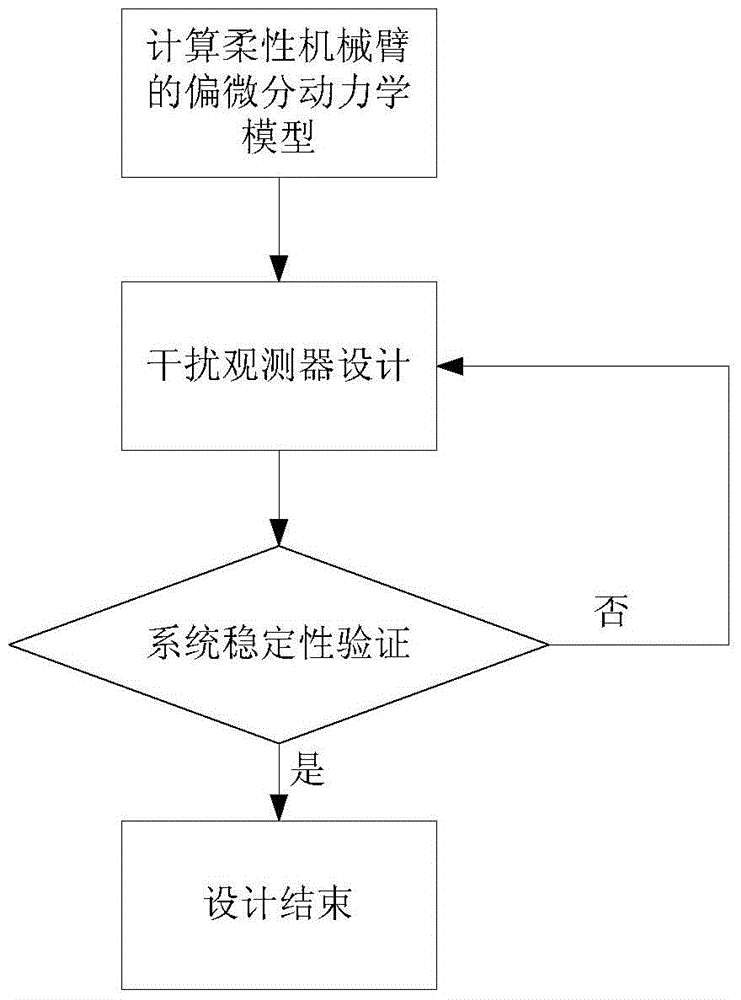
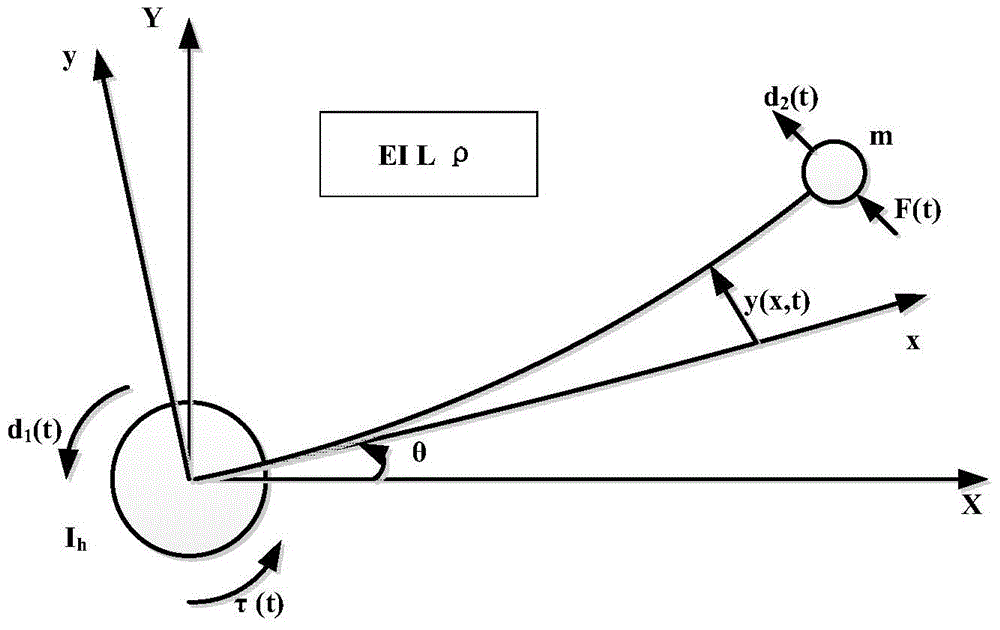
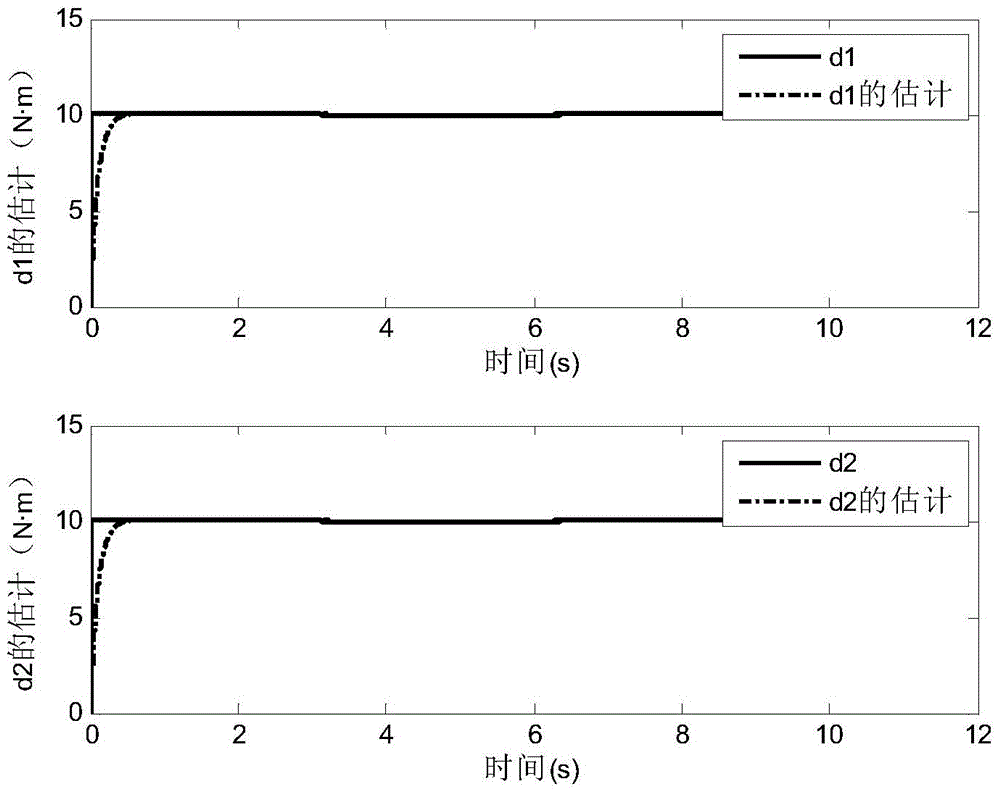
Method for designing flexible mechanical arm disturbance observer based on partial differential equation
ActiveCN104020664ARealize interference observationAdaptive controlMatrix differential equationEngineering
The invention provides a method for designing a flexible mechanical arm disturbance observer based on a partial differential equation. The method includes the four steps that firstly, dynamic modeling of a flexible mechanical arm is conducted; secondly, the disturbance observer is designed; thirdly, stability of the disturbance observer is verified; fourthly, design is finished. According to the method, firstly the Hamilton principle is used, so that a PDE model of a whole system is obtained; then, based on the model, the reasonable disturbance observer is designed so that external unknown disturbance can be estimated; finally, a proper Lyapunov function is designed, so that the designed observer is analyzed and the stability of the observer is verified.
Owner:GUODIAN SCI & TECH RES INST
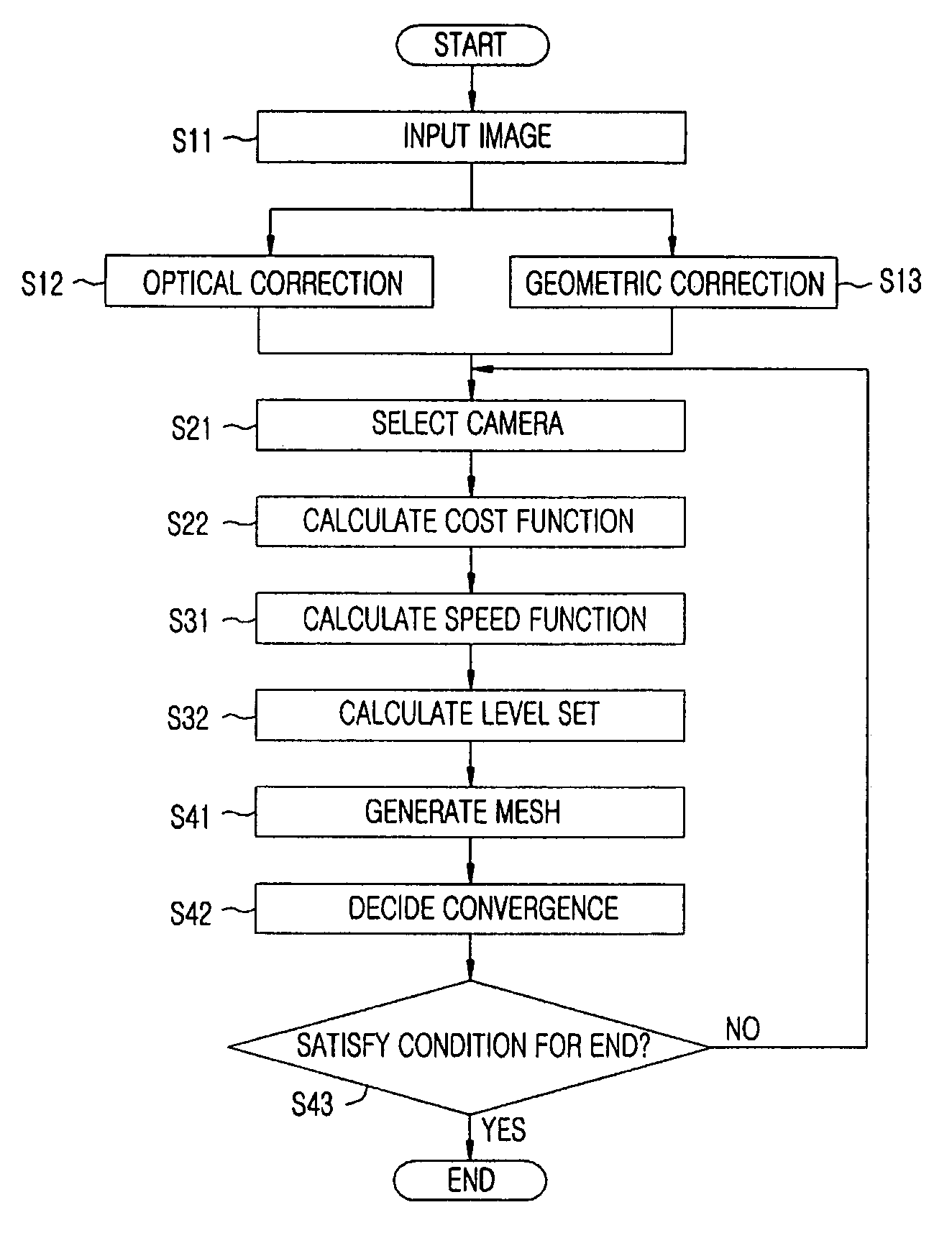
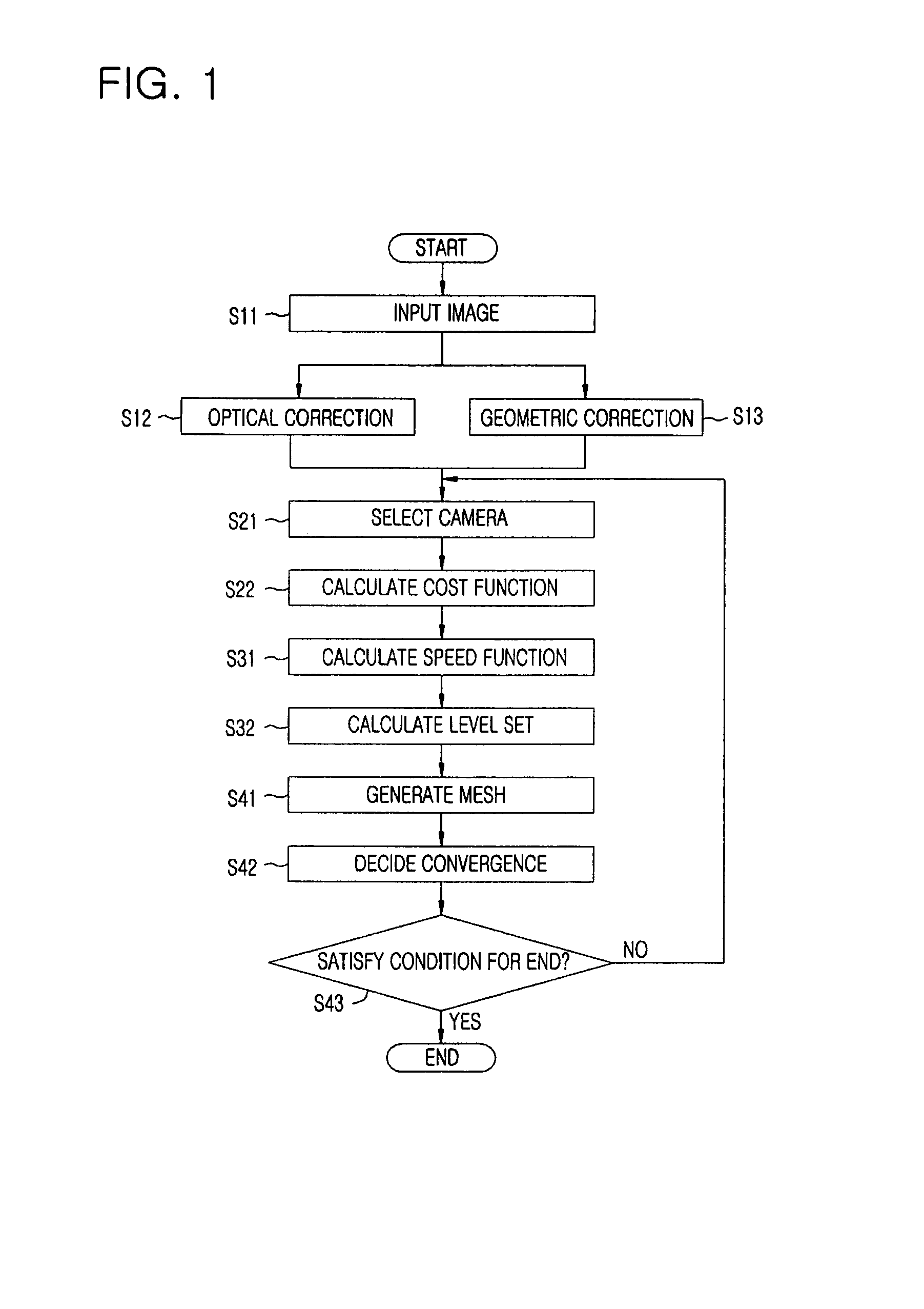
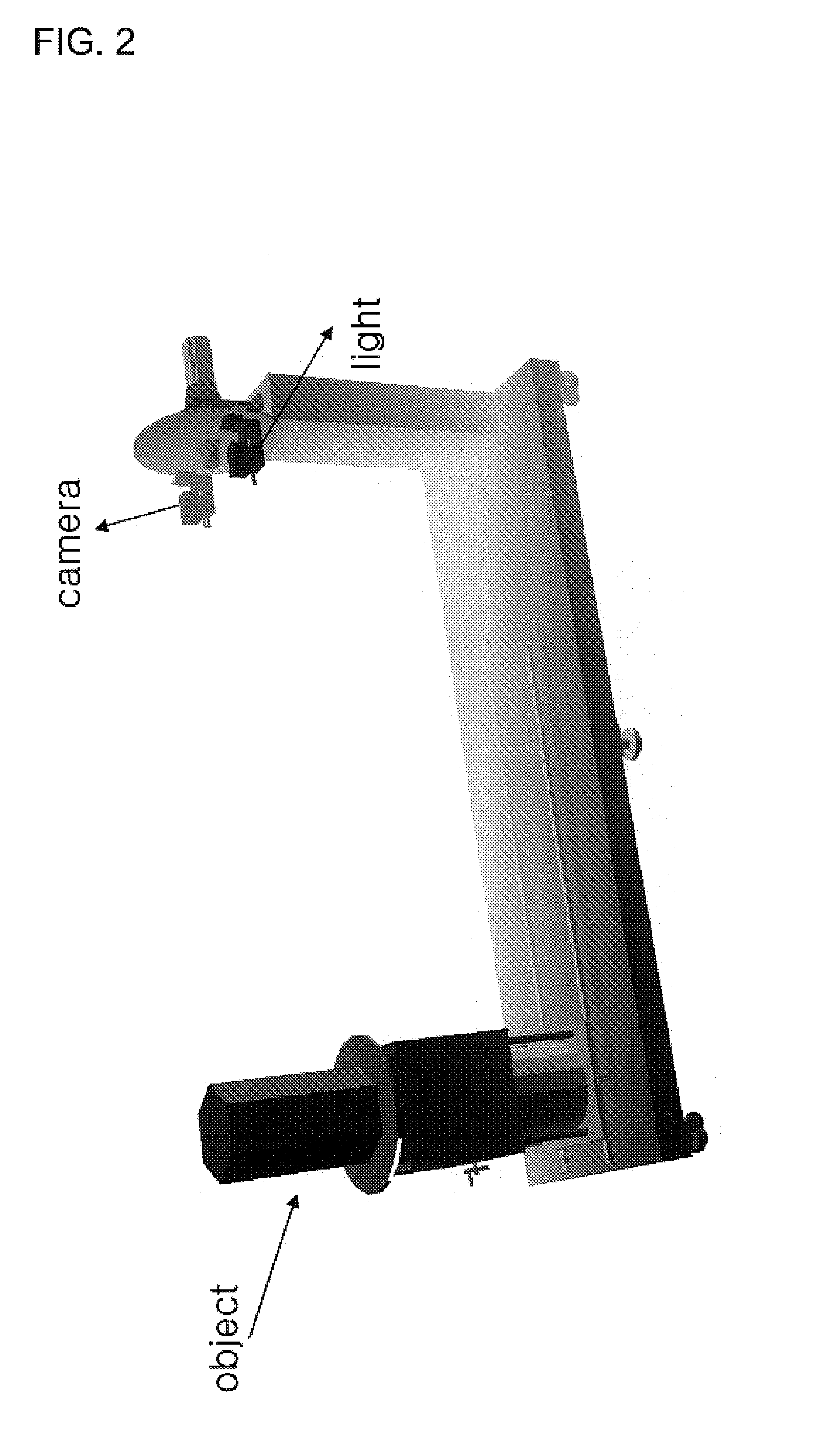
Method for modeling three dimensional shape of objects using level set solutions on partial differential equation derived from helmholtz reciprocity condition
InactiveUS7684614B2Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThree dimensional shapeFirst-order partial differential equation
A method for modeling a three dimensional shape of object using a level set solution on a partial differential equation derived from a Helmholtz reciprocity condition is provided. The method includes the steps of: a) inputting an image pair satisfying a Helmholtz reciprocity condition; b) performing an optical correction and simultaneously performing a geometric correction; c) performing a camera selection to select cameras capable of seeing a point (X, Y, Z), and defining and calculating a cost function by the Helmholtz reciprocity condition; d) calculating a speed function of a PDE that minimizes the cost function obtained in the step c); and e) generating a three dimension mesh model from a set of points configuring the object surface provided from the step d), and deciding a final three dimension mesh model by comparing cost function values.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Directional partial differential equation filtering method for striped projection images
InactiveCN106447716AImprove calculation accuracyReduce computing timeImage analysisUsing optical meansPattern recognitionFilter effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical detection and image processing, proposes a new method for values to solve the partial differential equation, so that the partial differential equation filtering effect is improved. The directional partial differential equation filtering method for striped projection images includes the steps of 1. inputting a stripe projection image u with noise; 2. discretizing a stripe projection image u; 3. calculating the included angles Theta i, j between the strip direction and the x-axis direction; 4. performing adoption to obtain the time step Delta t; 5. performing adoption to obtain the iteration frequency Nc; 6. for the each iteration, obtaining the first-order partial derivative and the second-order partial derivative of each pixel of the image u; 7. obtaining the value solution (as shown in the description) of each pixel of the image u; 8. repeating step 6 and 7 until the set largest iteration frequency Nc is reached to stop the iteration, the value solution (as shown in the description) at this time is a filtering image. The directional partial differential equation filtering method is applied to image processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
High accuracy surface modeling method based on big data
InactiveCN106683185AReduce storage requirementsReduce computing time3D modellingDecompositionDiscretization
The invention relates to a high accuracy surface modeling method based on big data. The method comprises the following steps: creating geographic coordinate information and to-be-tested variable sampling values of all sampling points; turning a to-be-tested regional space into a grid point form through discretization, and establishing a sampling equation; conducting high order difference discretization on a partial differential equation set of a surface, obtaining a corresponding algebraic system, combining the algebraic system and the sampling equation to form an equality constrain least squares problem, converting the problem into a solve cross cutting object function minimum value problem, and then converting the minimum value problem into a solve symmetry indeterminate equation set; randomly selecting iteration initial values; blocking a coefficient matrix, and storing the block matrixes after decomposition; solving an HASM equation set through a block line projection iterative method, and determining whether a solving result is convergent; determining whether a solution meets demands of a Gauss and C.odazzi equation set; and outputting a high accuracy simulation surface model. Large-scale problems can be solved, the needed storage space is small, and defects of HASM for solving large-scale problems are prevented.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Directional partial differential equation filtering method used for electronic speckle interference fringe pattern
The invention discloses a directional partial differential equation filtering method used for an electronic speckle interference fringe pattern. The directional partial differential equation filtering method includes the steps of (1) inputting the electronic speckle interference fringe pattern u, (2) discretizing the electronic speckle interference fringe pattern u; (3) calculating the included angle theta<i,j> of the fringe direction and the x-axis direction; (4) obtaining a time step delta<t> in a self-adaptive mode; (5) obtaining iterations N<c>; (6) determining first-order partial derivatives u<x> and u<y> and second-order partial derivatives u<xx>, u<xy> and u<yy> of every pixel of the pattern u for every iteration; (7) determining the numerical solution of every pixel of the pattern u on the basis of the discretization format of a directional partial differential equation; (8) obtaining a filtered pattern when the numerical value of the largest set iteration N<c> is reached. The directional partial differential equation filtering method used for the electronic speckle interference fringe pattern can be widely used for filtering of high-noise electronic speckle interference fringe patterns.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
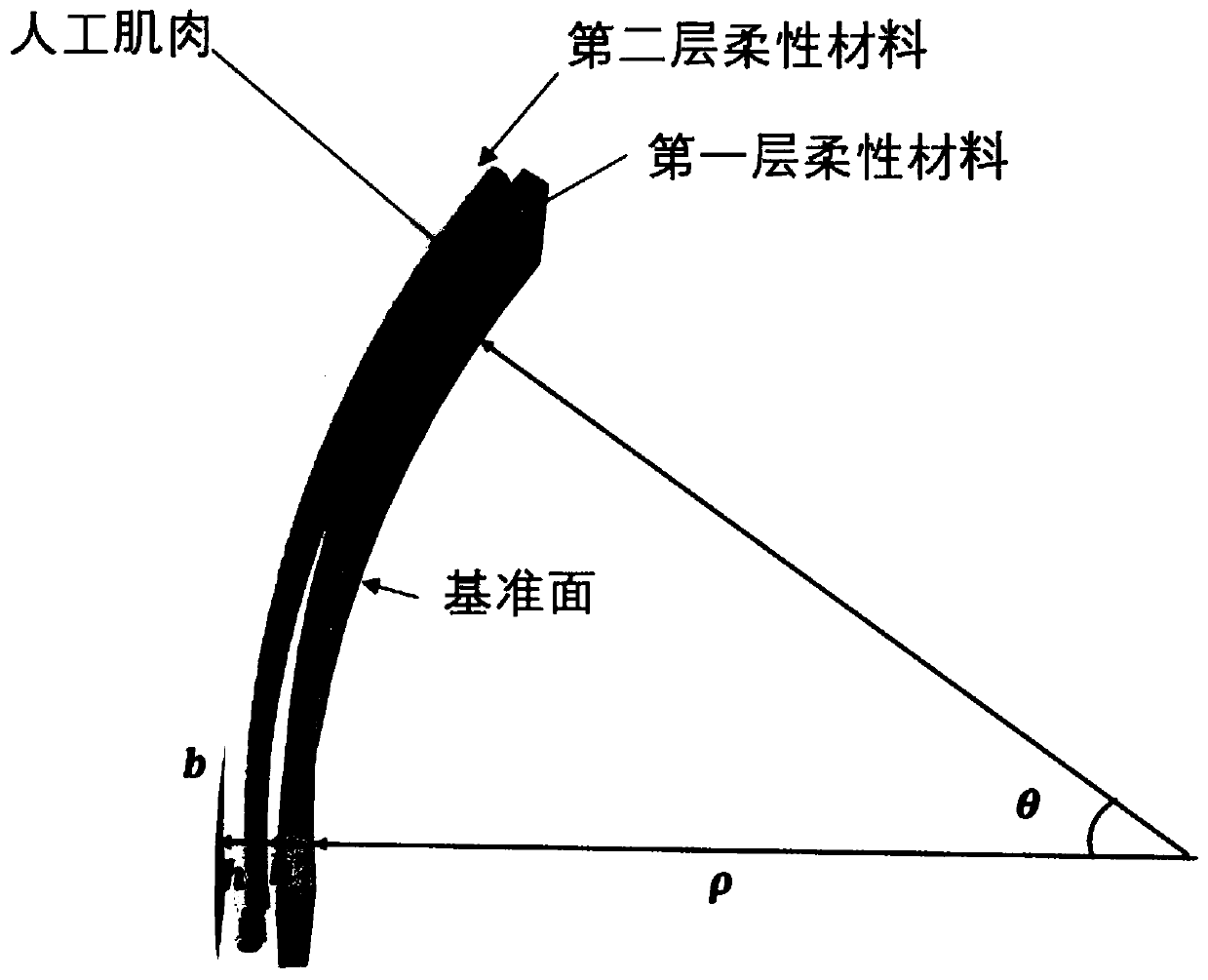
Elastic soft robot kinematical modeling method based on constant curvature assumption
ActiveCN110181506AAchieving Shape PredictionAvoid damageProgramme-controlled manipulatorWorking temperatureEngineering
The invention provides an elastic soft robot kinematical modeling method based on a constant curvature assumption, and belongs to the field of robot kinematical modeling. According to the method, by means of the Kirchhoff bar theory and the constant curvature assumption, firstly, equations of force, displacement and control quantities corresponding to artificial muscles implanted into a flexible material of an elastic soft robot are established; then the actual length of the elastic soft robot at the working temperature is calculated, and mechanical parameters of the flexible material are usedfor calculation; and finally, the section inertia moment about a neutral surface is calculated, the curvature radius and the angle of the elastic soft robot at the working temperature are calculated,the true shape of the elastic soft robot at the working temperature is obtained, and kinematical modeling is completed. According to the method, the modeling process is simple and convenient, the influences of elastic deformation of the elastic soft robot are considered, numerical calculation of partial differential equations is not involved, and the relationship between the shape of the elasticsoft robot and the parameters of the artificial muscle in the elastic soft robot can be rapidly established.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Efficient segmentation of piecewise smooth images
InactiveUS7889941B2Image enhancementImage analysisLocal statisticsHyperbolic partial differential equation
A fast and robust segmentation model for piecewise smooth images is provided. Local statistics in an energy formulation are provided as a functional. The shape gradient of this new functional gives a contour evolution controlled by local averaging of image intensities inside and outside the contour. Fast computation is realized by expressing terms as the result of convolutions implemented via recursive filters. Results are similar to the general Mumford-Shah model but realized faster without having to solve a Poisson partial differential equation at each iteration. Examples are provided. A system to implement segmentation methods is also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Gait contour extraction method
InactiveCN105631452AGood localization effectImprove clarityCharacter and pattern recognitionSymbol of a differential operatorGait
Provided is a gait contour extraction method. A level set function is expressed in a spatial-temporal discrete grid. First, an SDF (Sign Distance Function) is constructed, and initialization for zeroing is carried out; then, the numerical solution of a partial differential equation is solved; and finally, re-initialization is carried out through a curvilinear sign distance function, whether the numerical value is stable or not is judged, iteration is stopped if the numerical value is stable, or the process is repeated. The gait contour extraction method has a good localization effect for image boundaries. The image edge and regional information are combined, and the definition and distinctiveness of the gait contour are improved.
Owner:安徽勤勉知识产权代理有限公司
Free-form discovery of differential equations
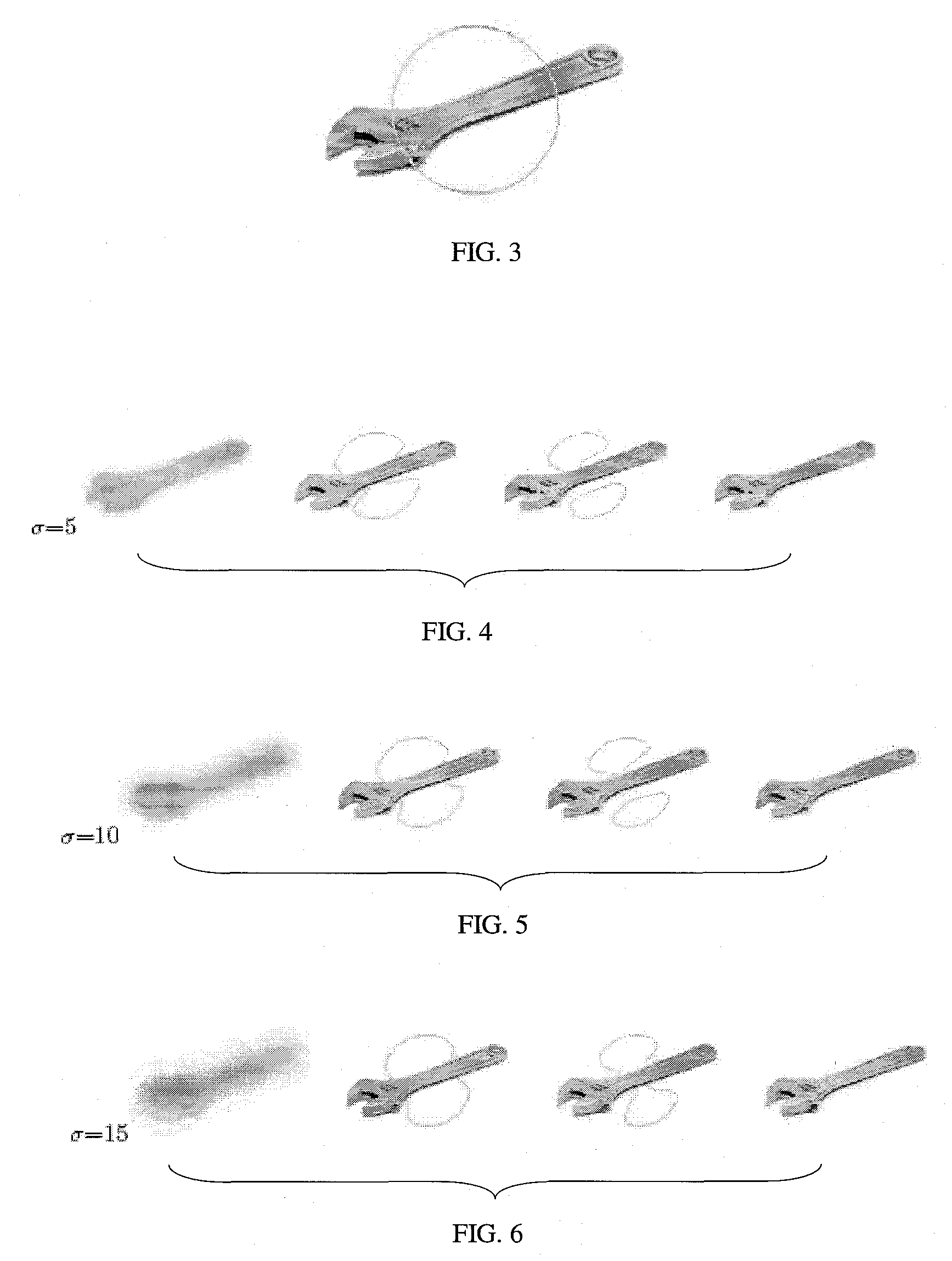
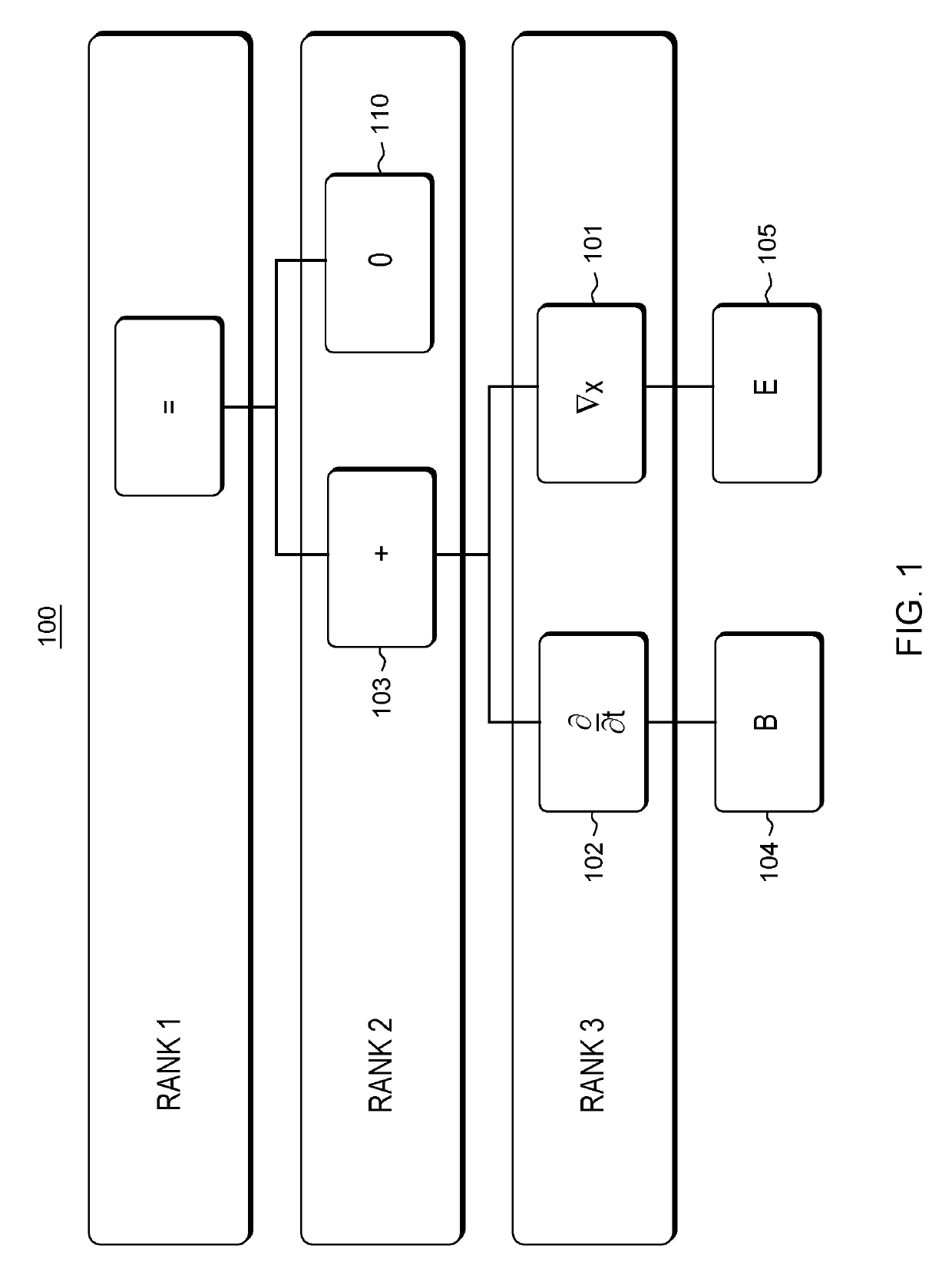
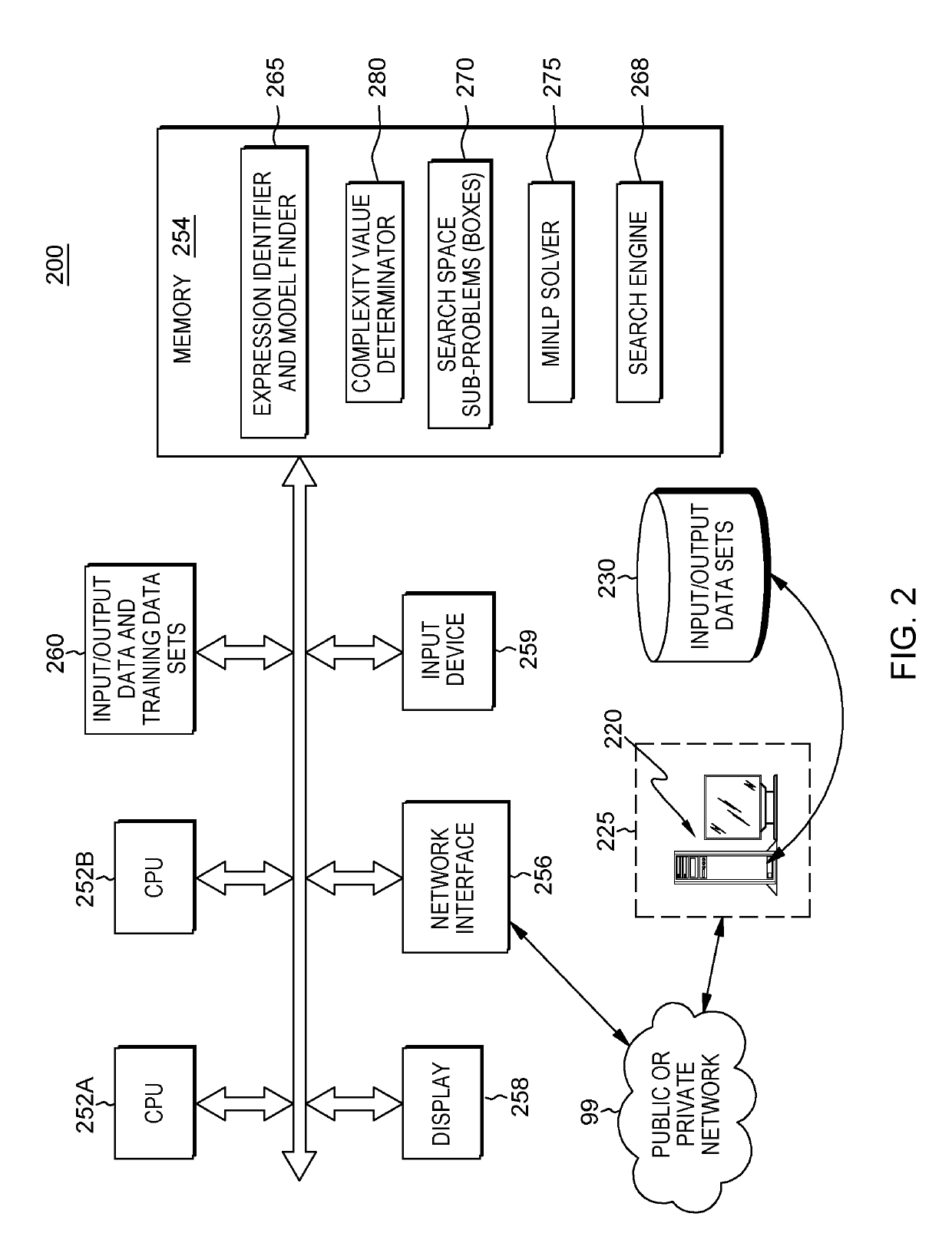
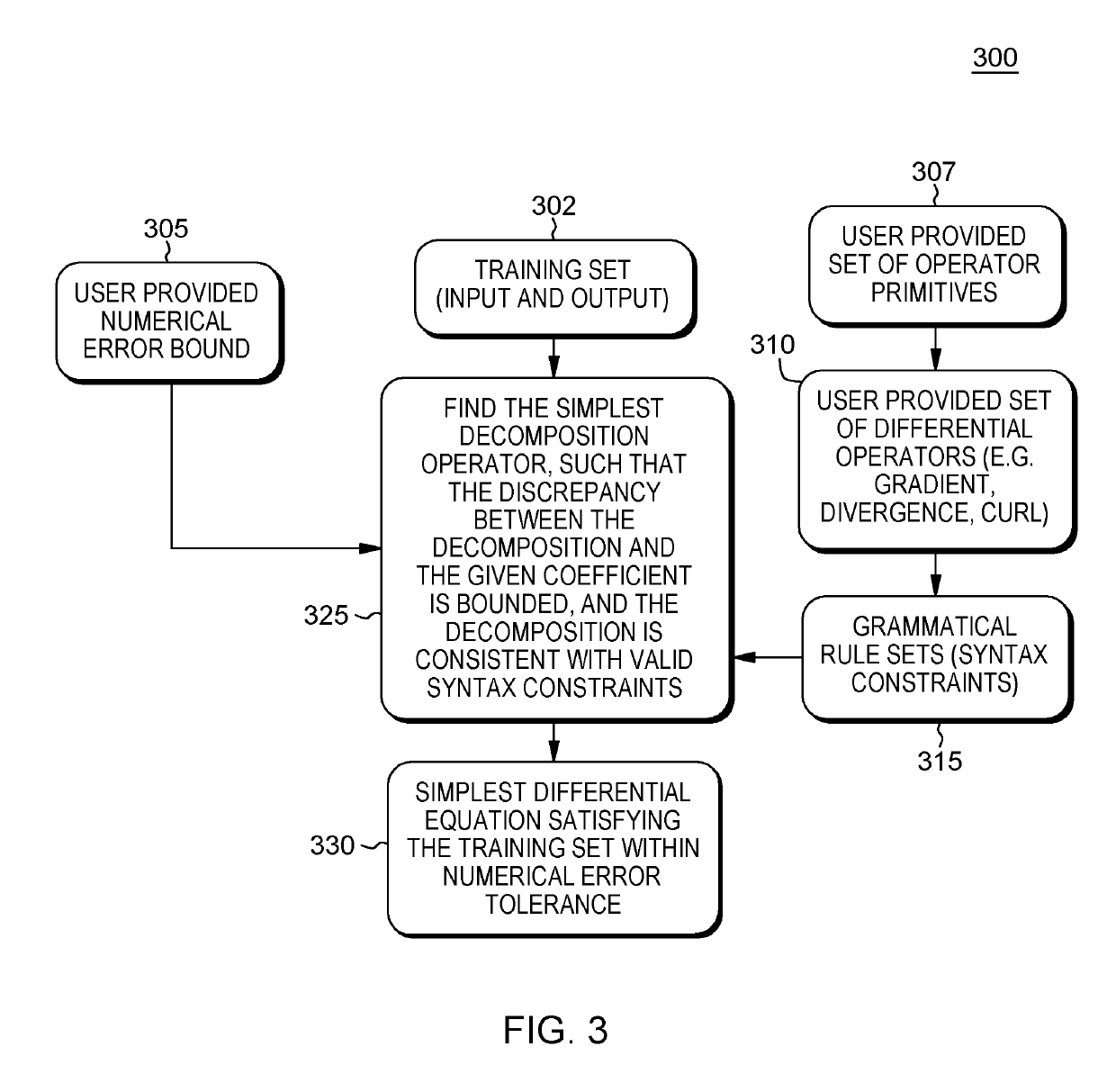
Free-form discovery of differential equations for modeling a physical system or process under investigation that includes defining a formal language sentence grammar that describes admissible relationships between quantities, and incorporating the use of such grammar for free-(functional) form, automatic discovery of differential equations. The method requires minimum knowledge of the desired differential equation and is universally applicable to ordinary and partial differential equations. From received training set data representing inputs to the physical system and measured outputs, a numerical error bound data, primitive operators, differential equation operators, variables, coefficients and grammatical rules that define the syntax of valid expressions, the system finds a model characterized by sources of error to find a simplest (minimum complexity) mathematical expression comprising differential operators such that a discrepancy between the observed data and the value of the mathematical expression is bounded, and the mathematical expression is consistent with valid syntax constraints.
Owner:IBM CORP
Blade type optimized designing method of turbine compression fluid machine
InactiveCN100370148CReduce energy consumptionGuaranteed uptimePump componentsPumpsImpellerMatrix differential equation
A method for designing the profile of blade used for turbine-type fluid compressing machinery includes such steps as simplifying the flow procedure controlled by N-S partial differential equation to become the flow procedure controlled by ordinary differential equation, creating state equation, normalizing the equation to become relative optimal control mode, using the installation exit angle of blade as control variable, and iterative calculating to the 3D geometric model of blade and said ordinary differential equation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
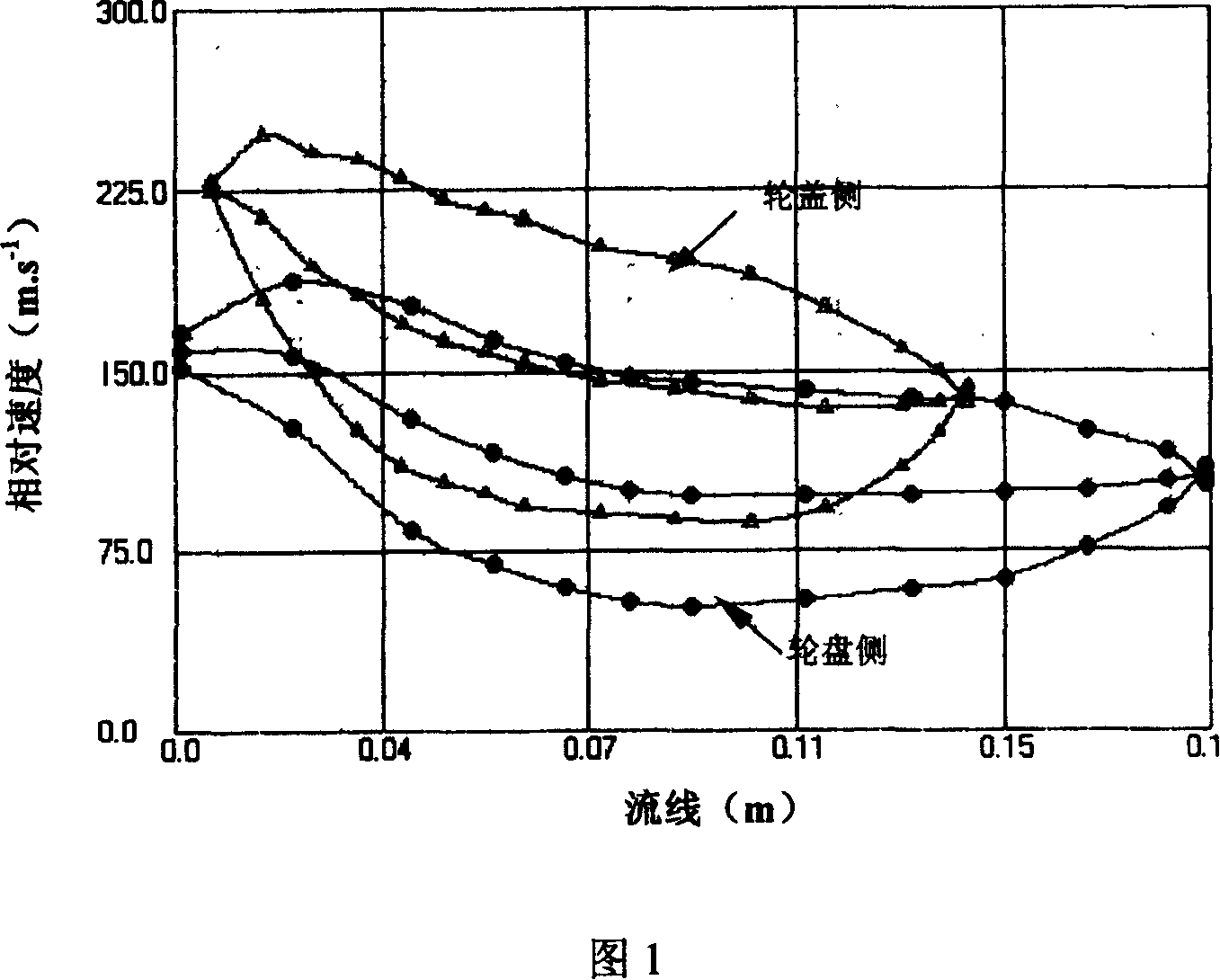
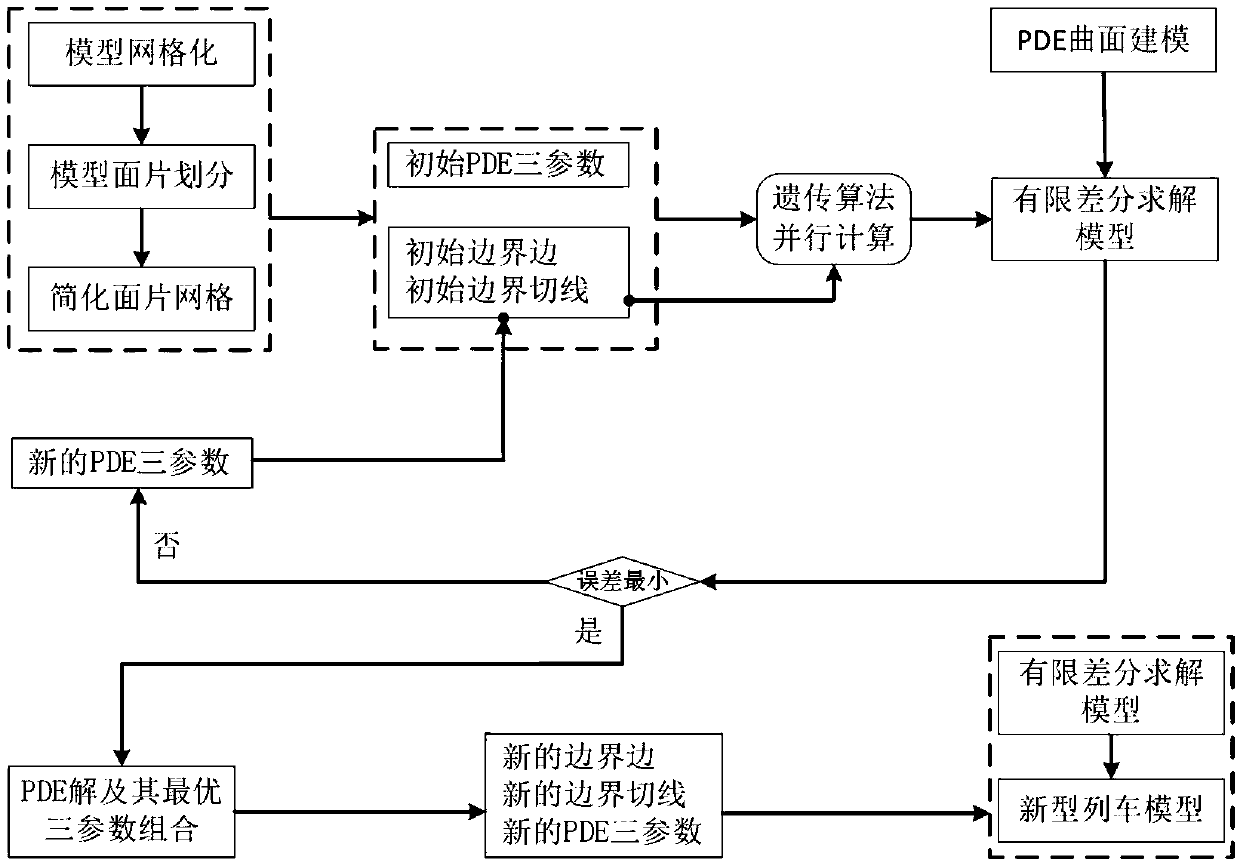
Train head model parameterization control method based on four-order partial differential equation
The invention discloses a train head model parameterization control method based on a four-order partial differential equation; the method comprises the following steps: 1, using the four-order partial differential equation to parameterize train head model surface patches; 2, calculating to obtain boundary conditions needed to solve the partial differential equation; 3, obtaining space positions of grid points corresponding to the partial differential equation numerical solution; 4, determining whether the error between the grid points corresponding to the partial differential equation numerical solution and a target point is smaller than a set threshold or not; 5, obtaining the grid point position corresponding to the partial differential equation numerical solution when the target pointis approached at the closest level and the corresponding partial differential equation so as to control patch local deformation parameters; 6, adjusting train head model shape control parameters so asto obtain a new train head model. The method utilizes a few parameters to not only control large scale deformation of the train head model, and can adjust the shape in a local small scope, thus providing more degree of freedom for train head model design and aerodynamic optimization.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
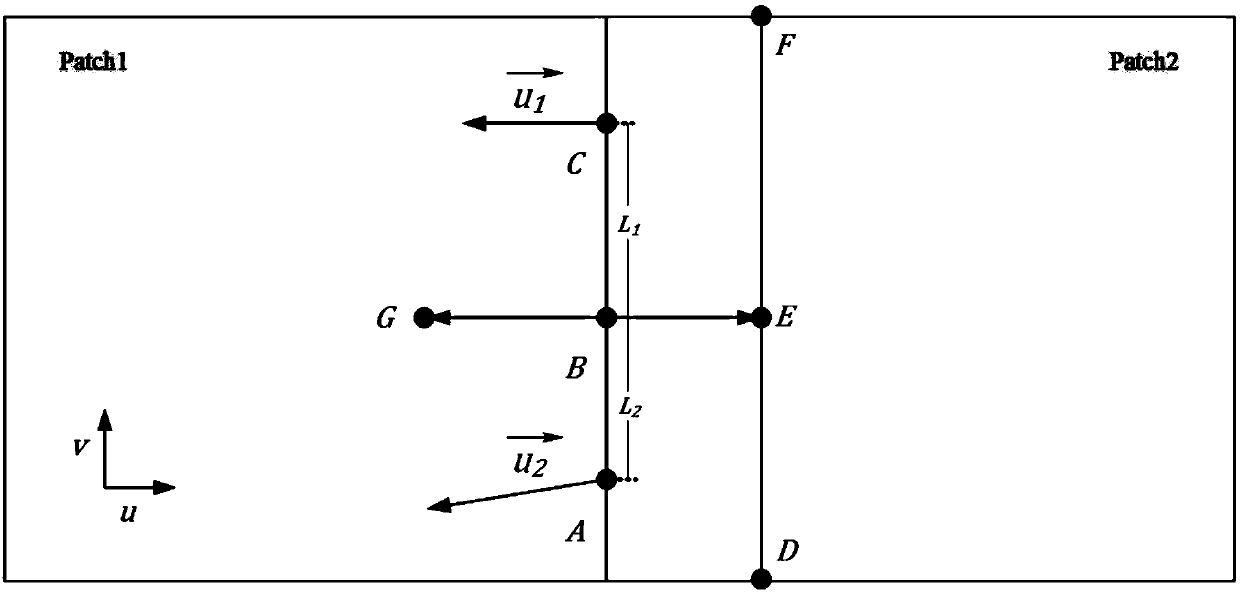
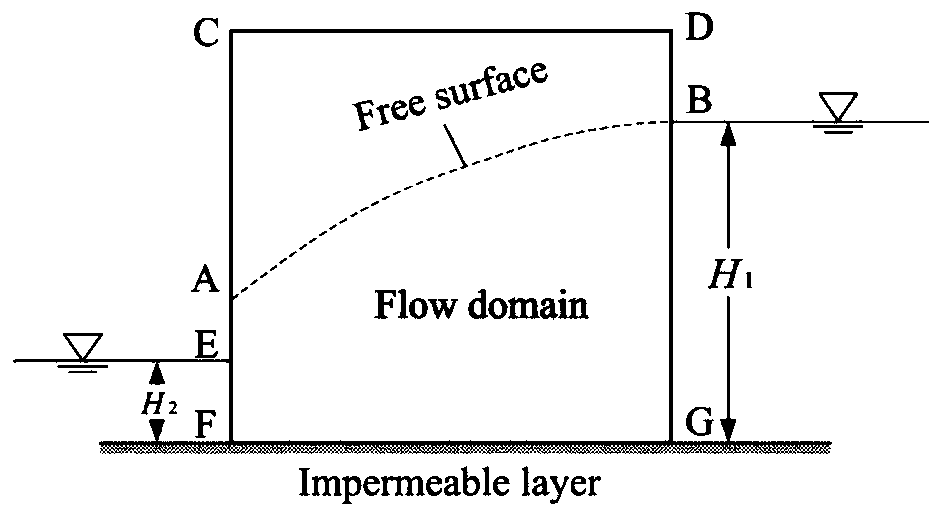
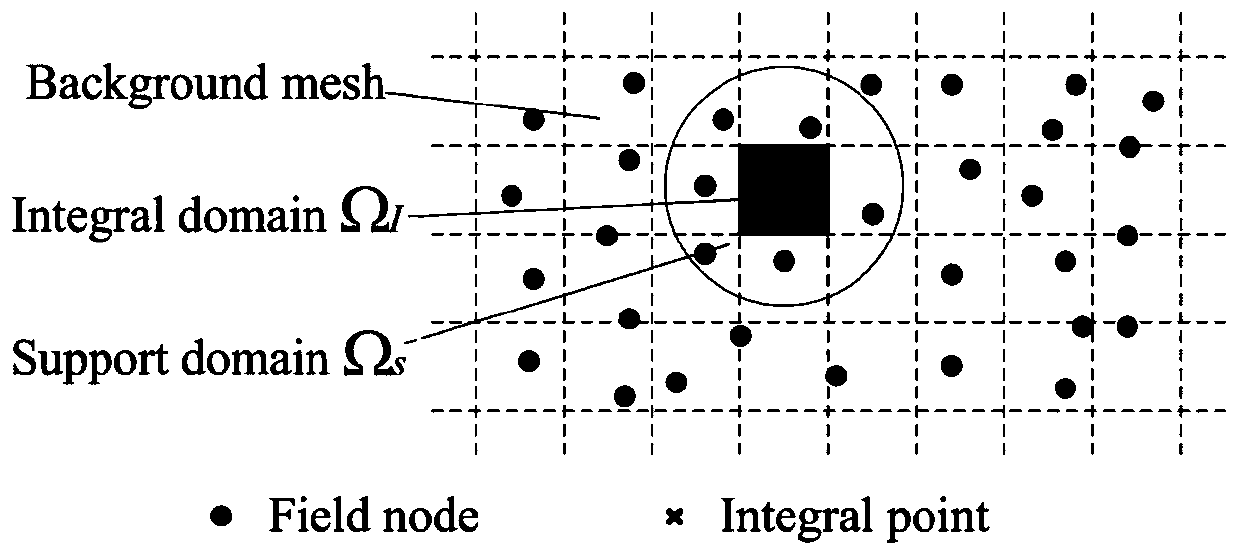
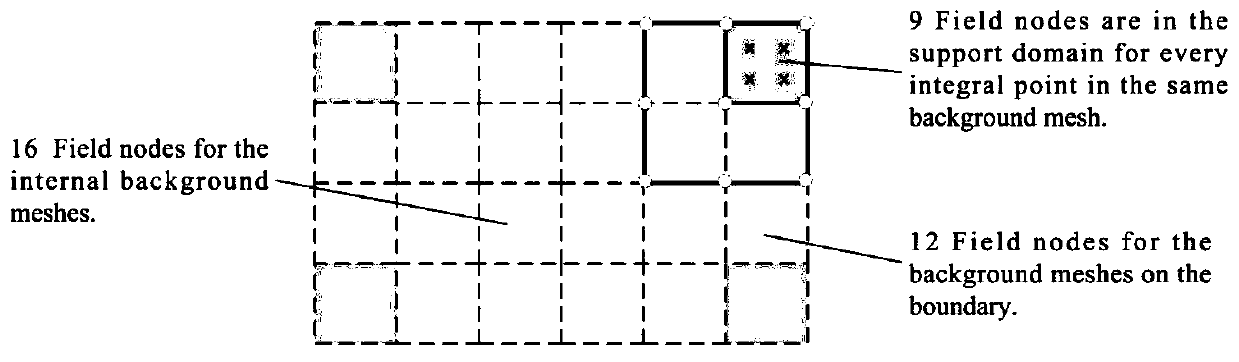
Optimization algorithm for solving seepage free surface based on radial base point interpolation method
ActiveCN110443432AMake sure it's fully alignedGuaranteed integral accuracyClimate change adaptationForecastingNODALMatrix differential equation
The invention relates to a meshless method seepage free surface solving method based on a radial base point interpolation method. The meshless method seepage free surface solving method comprises thefollowing steps: 1) determining a control equation; 2) determining boundary conditions; 3) determining an RPIM control equation; solving a partial differential equation by adopting RPIM, dispersing aproblem domain into a series of field nodes, introducing an integral rigidity matrix into a background grid in order to facilitate integration and assembly, integral points existing in the backgroundgrid, each integral point having a support domain, and interpolating the field nodes in the support domains to obtain information on the integral points. According to the method, the seepage free surface can be solved conveniently and quickly, the precision is high, the working process can be simplified, and engineering practice can be better guided.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
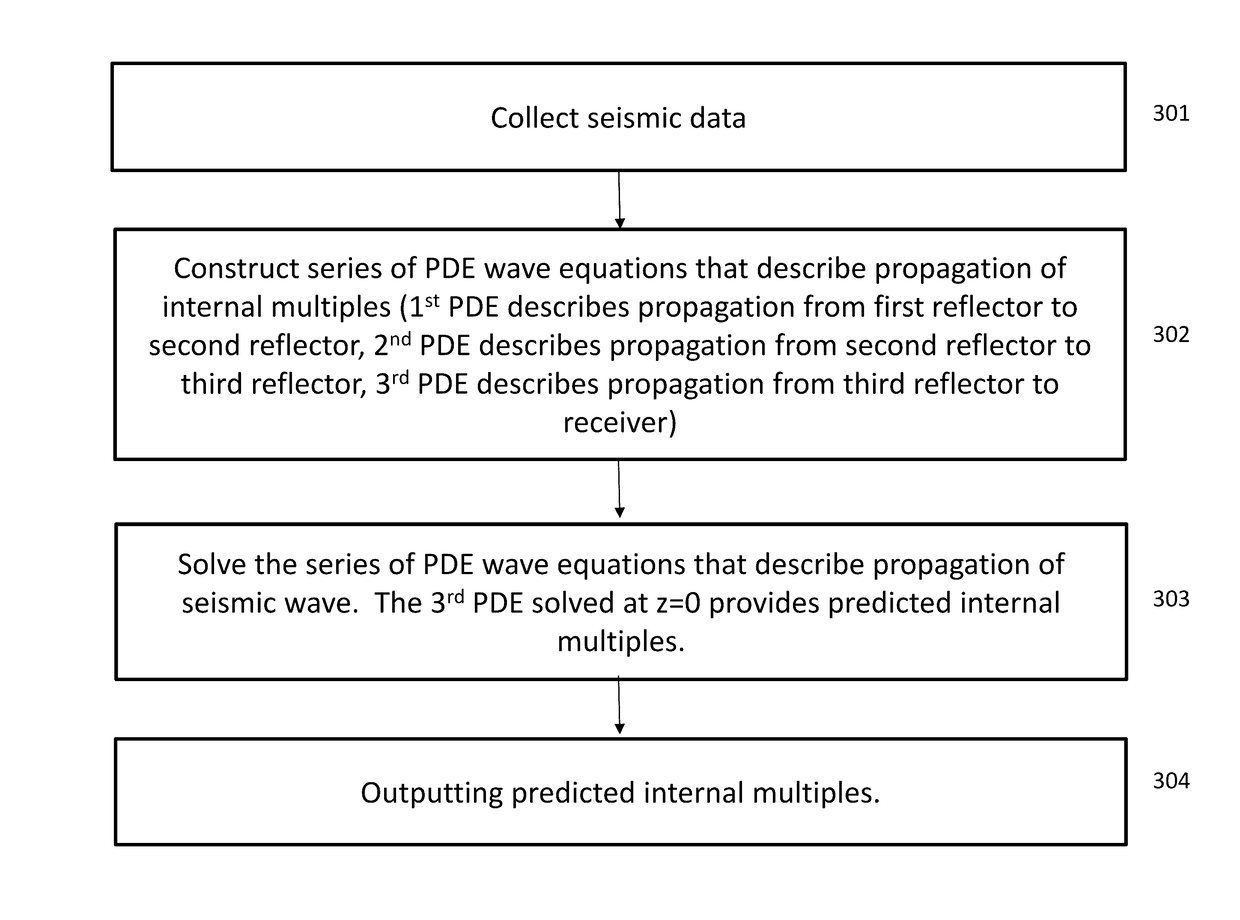
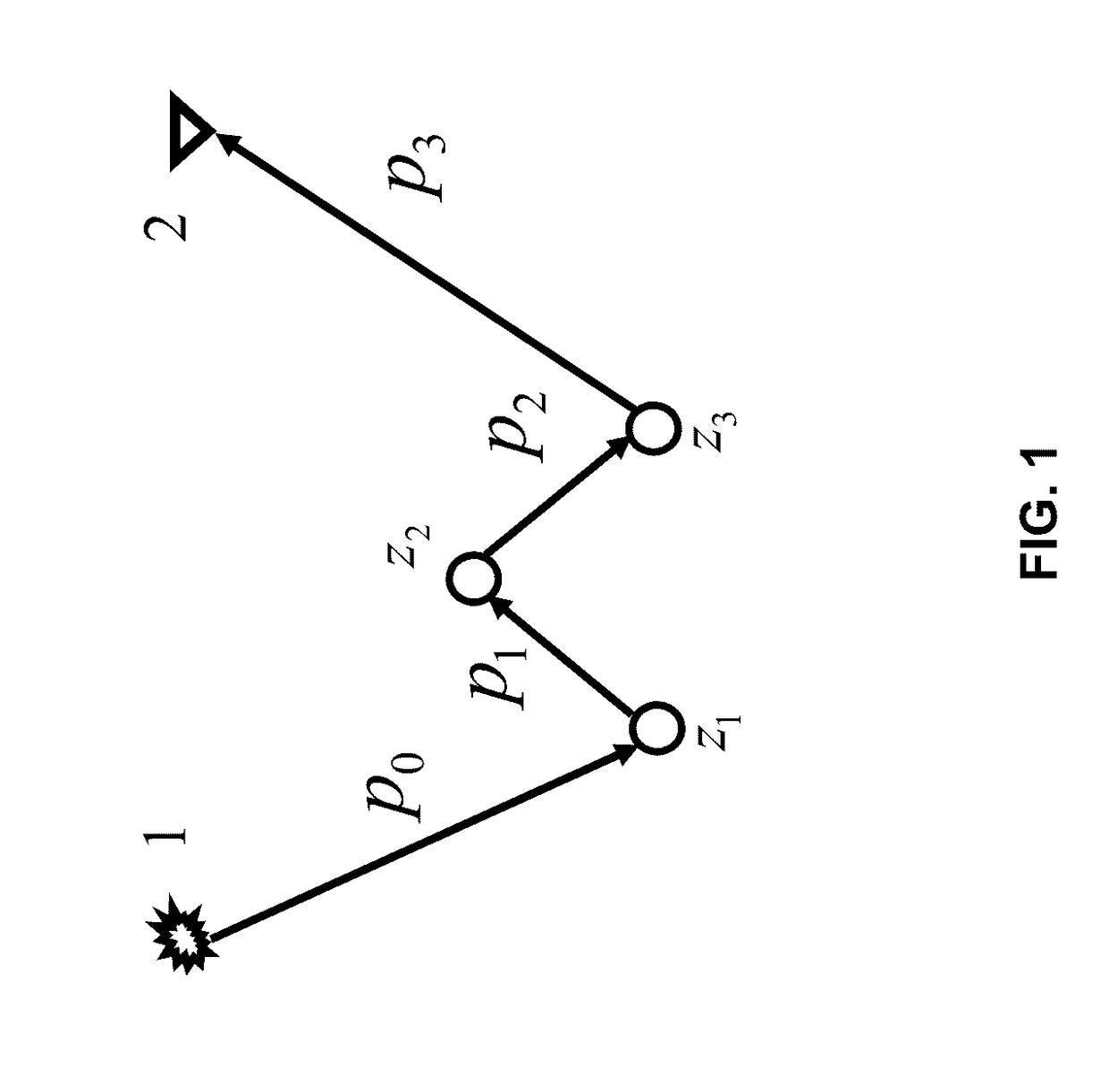
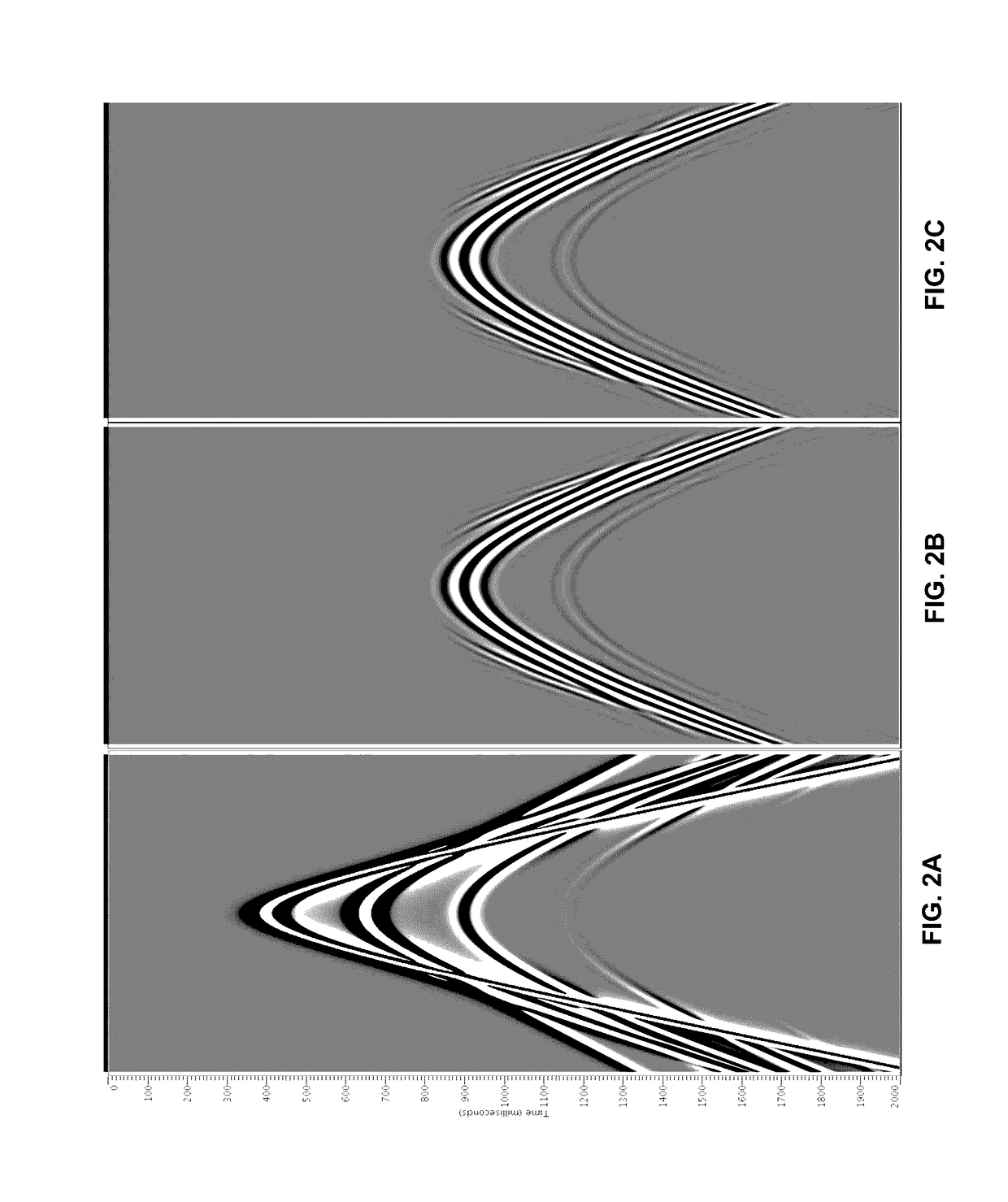
Efficient internal multiple prediction methods
Methods for processing seismic data are described. The method includes: obtaining seismic data; solving a series of partial differential wave equations, wherein a first partial differential wave equation describes propagation of a seismic wave going from a first reflector to a second reflector, wherein a second partial differential wave equation describes propagation of a seismic wave going from a second reflector to a third reflector, and wherein a third partial differential wave equation describes propagation of a seismic wave going from a third reflector to a seismic receiver, wherein outputting predicted internal multiples for further imaging or attenuation.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Simulated fighting method
InactiveCN105631384AGood localization effectImprove clarityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMatrix differential equationElliptic partial differential equation
Provided is a simulated fighting method. A level set function is expressed in a spatial-temporal discrete grid. First, an SDF (Sign Distance Function) is constructed, and initialization for zeroing is carried out; then, the numerical solution of a partial differential equation is solved; and finally, re-initialization is carried out through a curvilinear sign distance function, whether the numerical value is stable or not is judged, iteration is stopped if the numerical value is stable, or the process is repeated. The simulated fighting method has a good localization effect for image boundaries. The image edge and regional information are combined, and the definition and distinctiveness of the gait contour are improved.
Owner:安徽勤勉知识产权代理有限公司
Method for calculating nonlinear partial differential equation by dual-grid iteration
InactiveCN106339352AImprove computing efficiencyHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsElliptic partial differential equationNonlinear partial differential equation
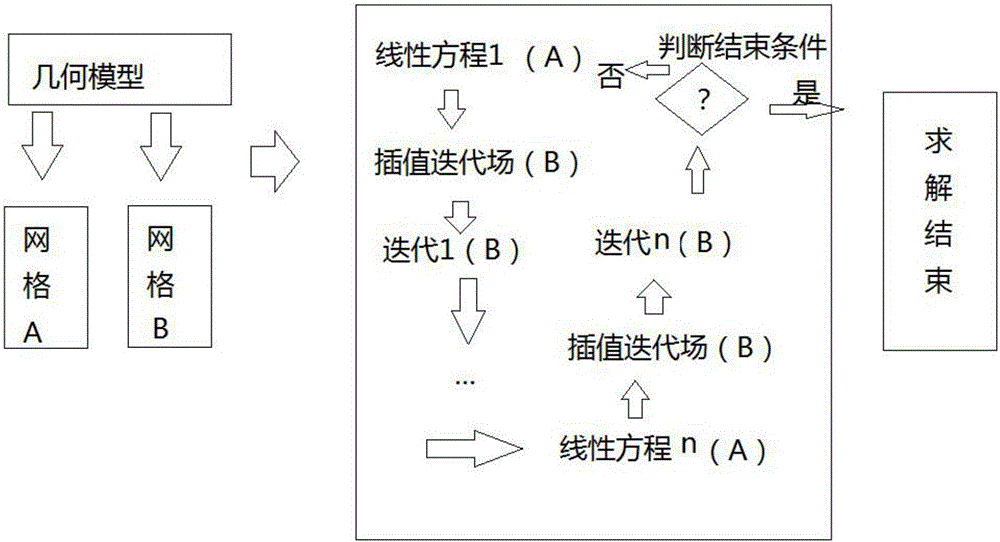
The invention discloses a method for calculating a nonlinear partial differential equation by dual-grid iteration. The method comprises the following steps: (a) establishing a three-dimensional geometric model of the nonlinear partial differential equation; (b) performing grid dissection on the three-dimensional geometric model, and dividing into two sets of grids, namely grids A and girds B, wherein the grids A are non-fitted grids, and the grids B are polyhedral fitting grids; (c) interpolating initial and boundary data into non-fitting parts of the grids A by using interpolations with four orders or above; (d) decomposing the nonlinear partial differential equation into a plurality of linear equations by using an iterative technique, wherein the linear equation is solved by using the grids A and using a four-order algorithm, and interpolating into the grids B to obtain fields in the fitting grids B; (e) performing iterative computation in the grids B; (f) repeating the steps (d) and (e) until the solving is ended. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high calculation efficiency, low cost and high precision by adopting dual-grid solving.
Owner:苏州中源广科信息科技有限公司
Computation method capable of tracking Davinan equivalence parameter base on total differential equation
ActiveCN101350524BConvenient and accurate fixationEasy to operateAc network voltage adjustmentComplex mathematical operationsElectric power systemSimulation
The present invention provides a method which is used for calculating Thevenin equivalent parameters of power system. The active power and reactive power of a tidal current equation are respectively used for differentiating the Thevenin equivalent parameters so as to form a total differential equation system; the total differential equation system is solved with the Thevenin equivalent parametersas variables, so as to acquire the Thevenin equivalent parameters. The method overcomes the serious error in the existing calculating which assumes the invariable Thevenin equivalent parameters between two time steps, has the characteristics of strong adaptability, simple use and small amount of calculation, and can be used for analysis, calculation and on-site installation of the power system which requires a Thevenin equivalent system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
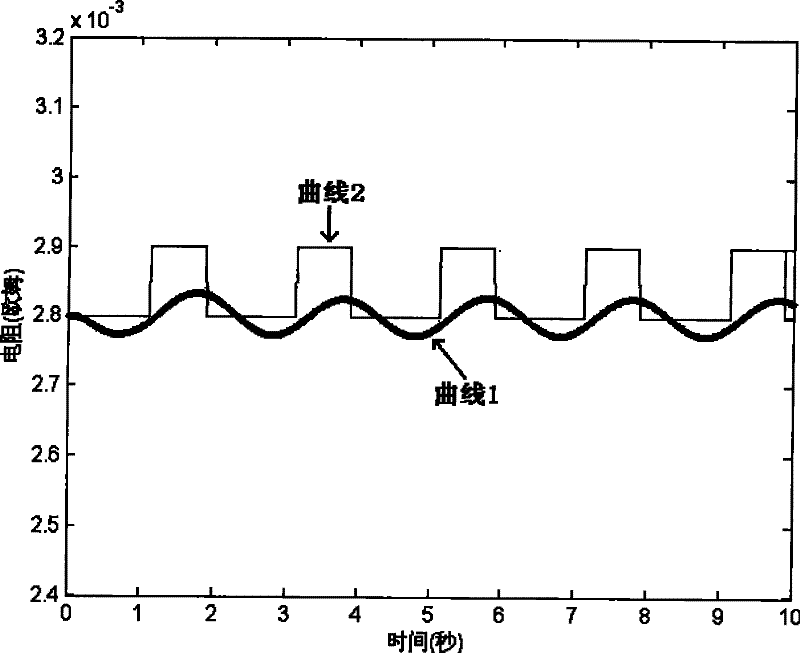
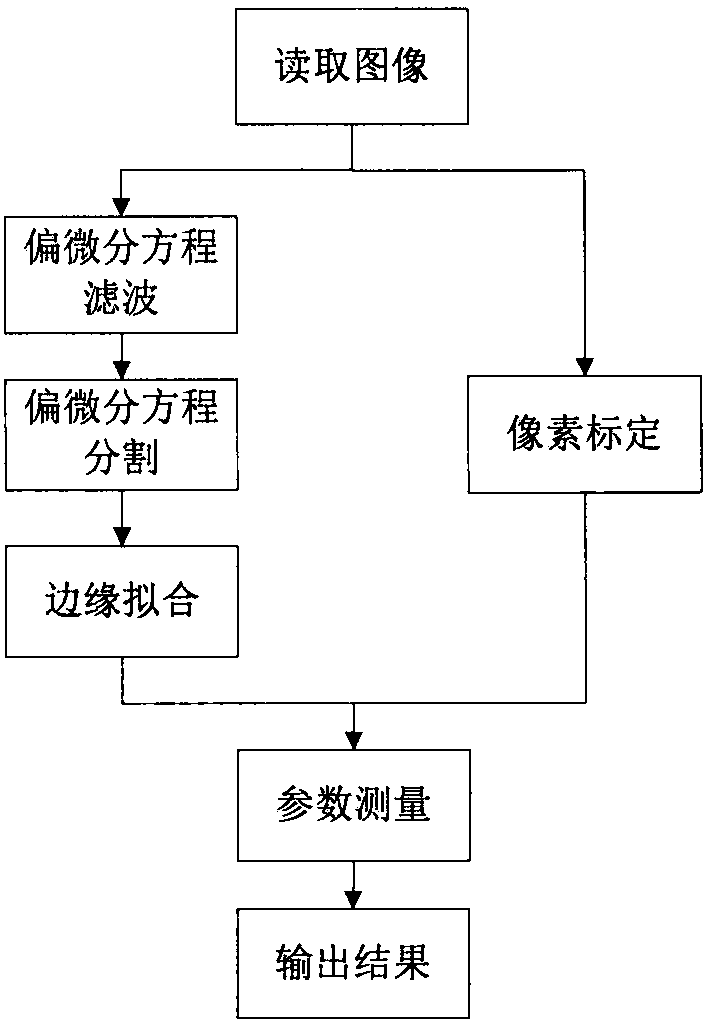
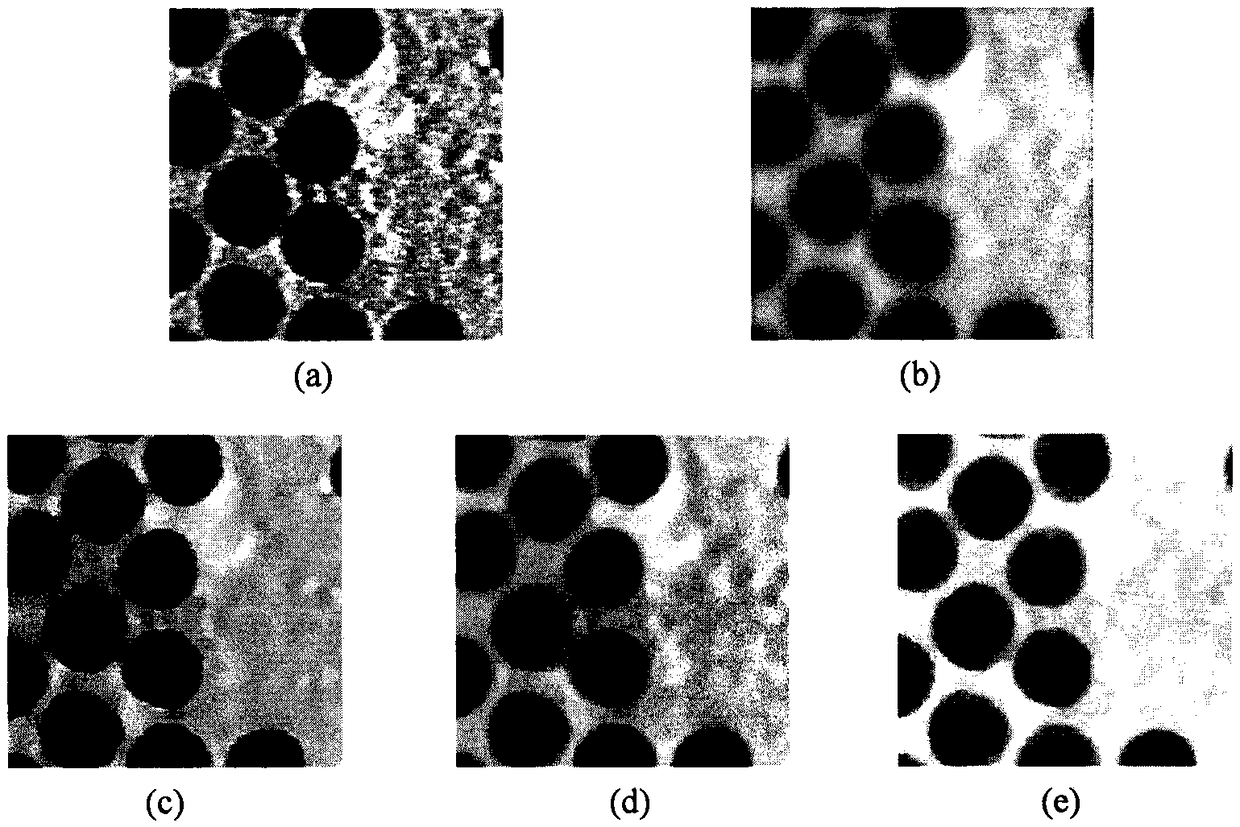
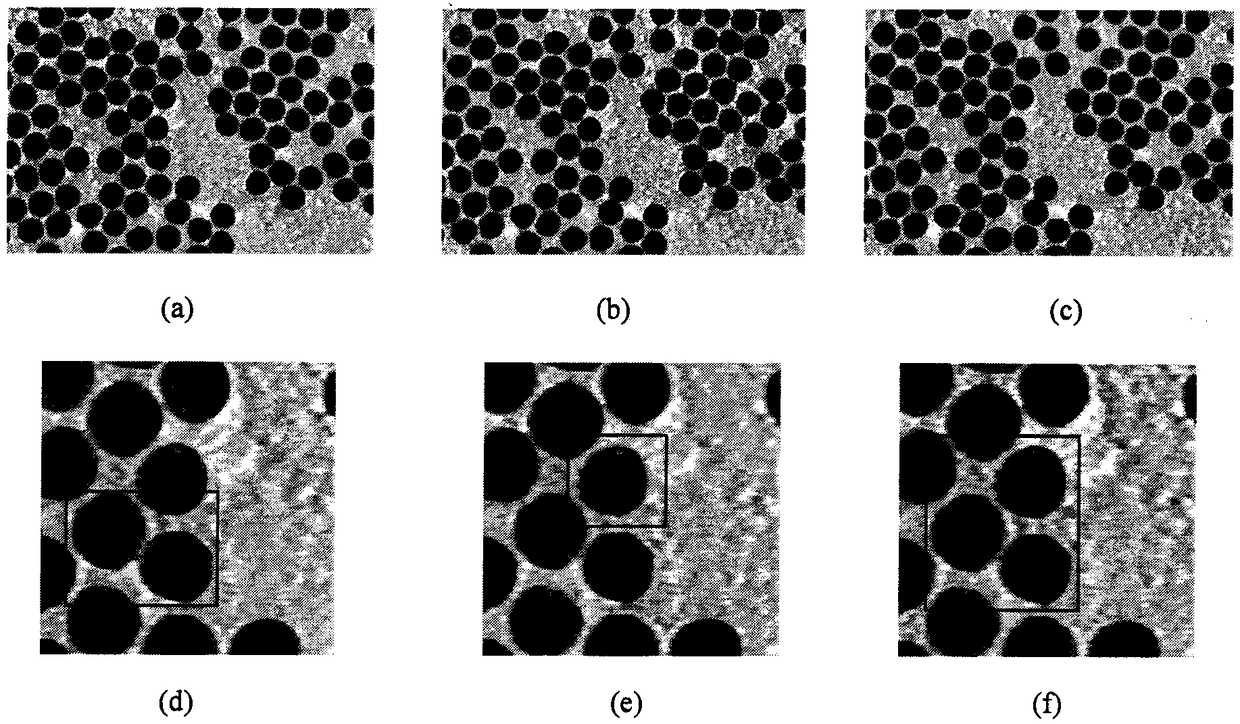
A Nanoparticle Size Measurement Method Based on Partial Differential Equation
ActiveCN105931277BImprove efficiencyHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisHyperbolic partial differential equationElectric power
The invention discloses a nanoparticle size measurement method based on partial differential equations, which includes: 1) inputting a nanoparticle image I, performing pixel-level multiplication of the filtering results of the average curvature flow model and the PM model to obtain a filtered image u; 2) Use the local region fitting model (RSF) to segment the image u; 3) Pixel calibration to obtain the actual size corresponding to each pixel in the image; 4) Use the convexity C of the target conv Select non-adhesive particles; 5) Obtain the diameter of spherical nanoparticles by performing least square circle fitting on the particle boundaries, and at the same time obtain the inscribed circle diameter r c , circumscribed circle diameter r i , and the sphericity of nanoparticles. The present invention can be widely used in high-tech fields that require nanoparticle size measurement technology, such as catalytic science, medical drugs, new materials, power industry, and composite materials.
Owner:思腾合力(天津)科技有限公司
Method for obtaining optimal transmission mapping in high-dimensional area and related product
PendingCN114842101AReduce operational complexityImprove computing efficiencyReconstruction from projectionComplex mathematical operationsFast Fourier transformComputational physics
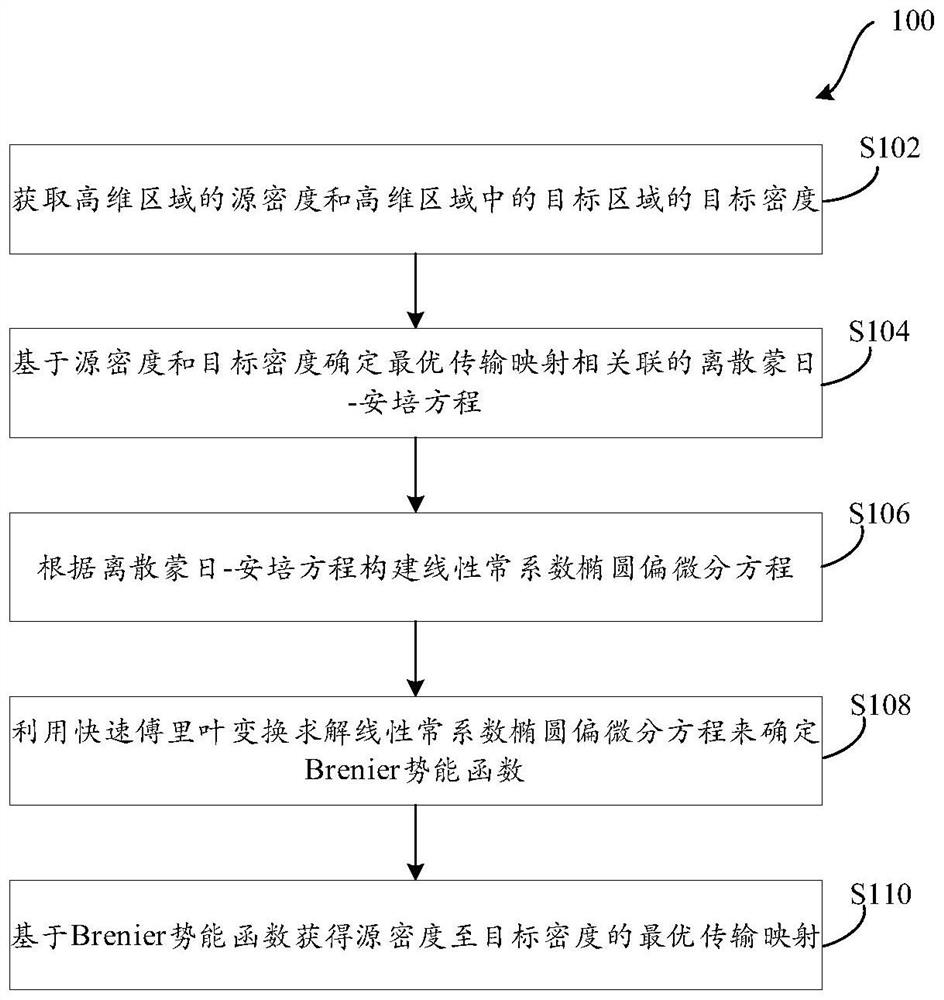
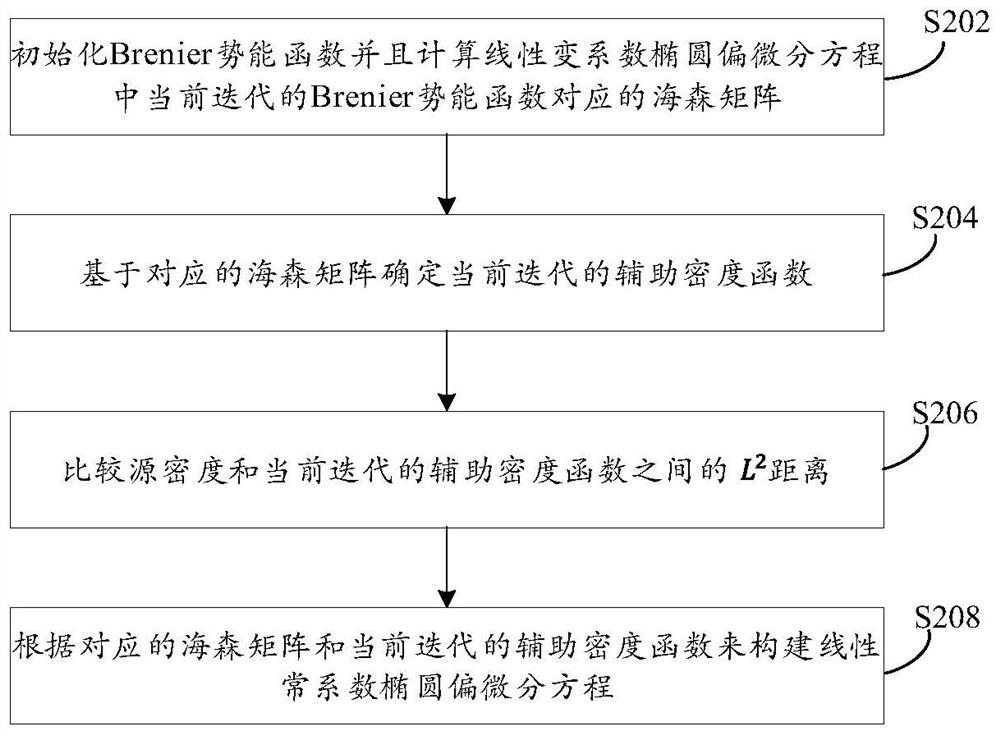
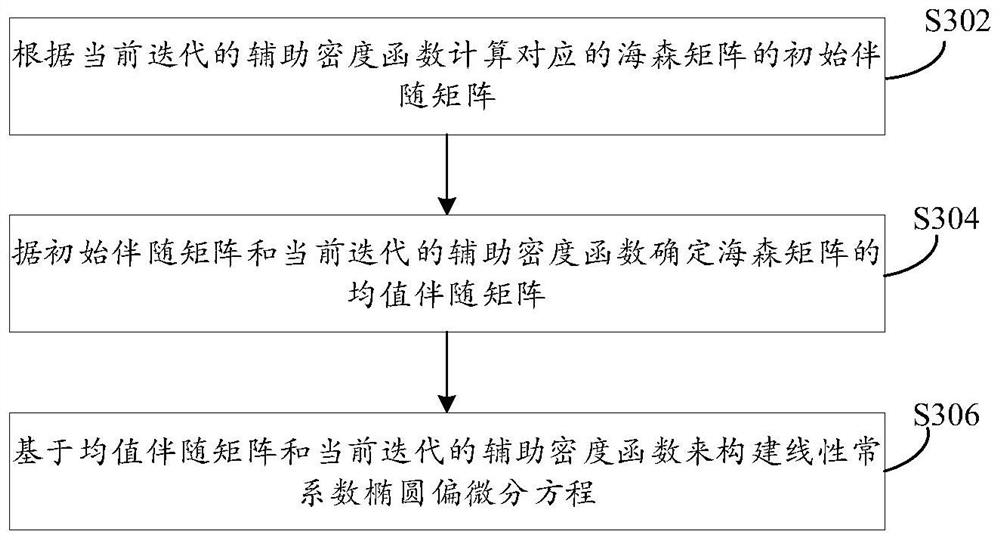
The invention relates to a method for acquiring optimal transmission mapping in a high-dimensional region and a related product. The method is executed by a computing device, and comprises the following steps: acquiring a source density of a high-dimensional region and a target density of a target region in the high-dimensional region; determining a discrete Mongolian-Ampere equation associated with optimal transmission mapping based on the source density and the target density, wherein the discrete Mongolian-Ampere equation comprises a Brenier potential energy function; constructing a linear constant coefficient ellipse partial differential equation according to the discrete Monte day-Ampere equation; solving the linear constant coefficient elliptic partial differential equation by using fast Fourier transform to determine the Brenier potential energy function; and obtaining the optimal transmission mapping from the source density to the target density based on the Brenier potential energy function. By using the scheme of the invention, the optimal transmission mapping in the high-dimensional region can be quickly and accurately obtained.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Denoising method of strong noise pollution image on basis of partial differential equation
InactiveCN101916433BImprove denoising effectAccurate calculationImage enhancementPattern recognitionPeak value
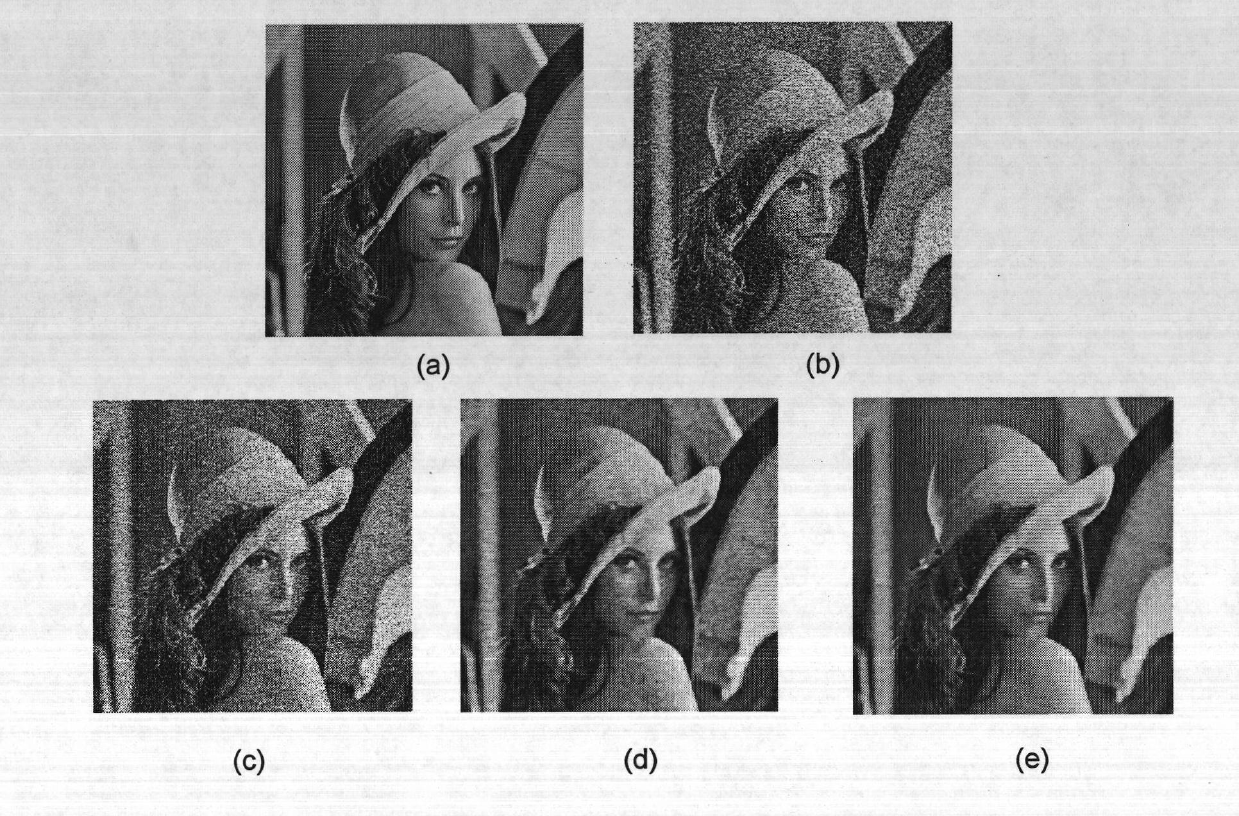
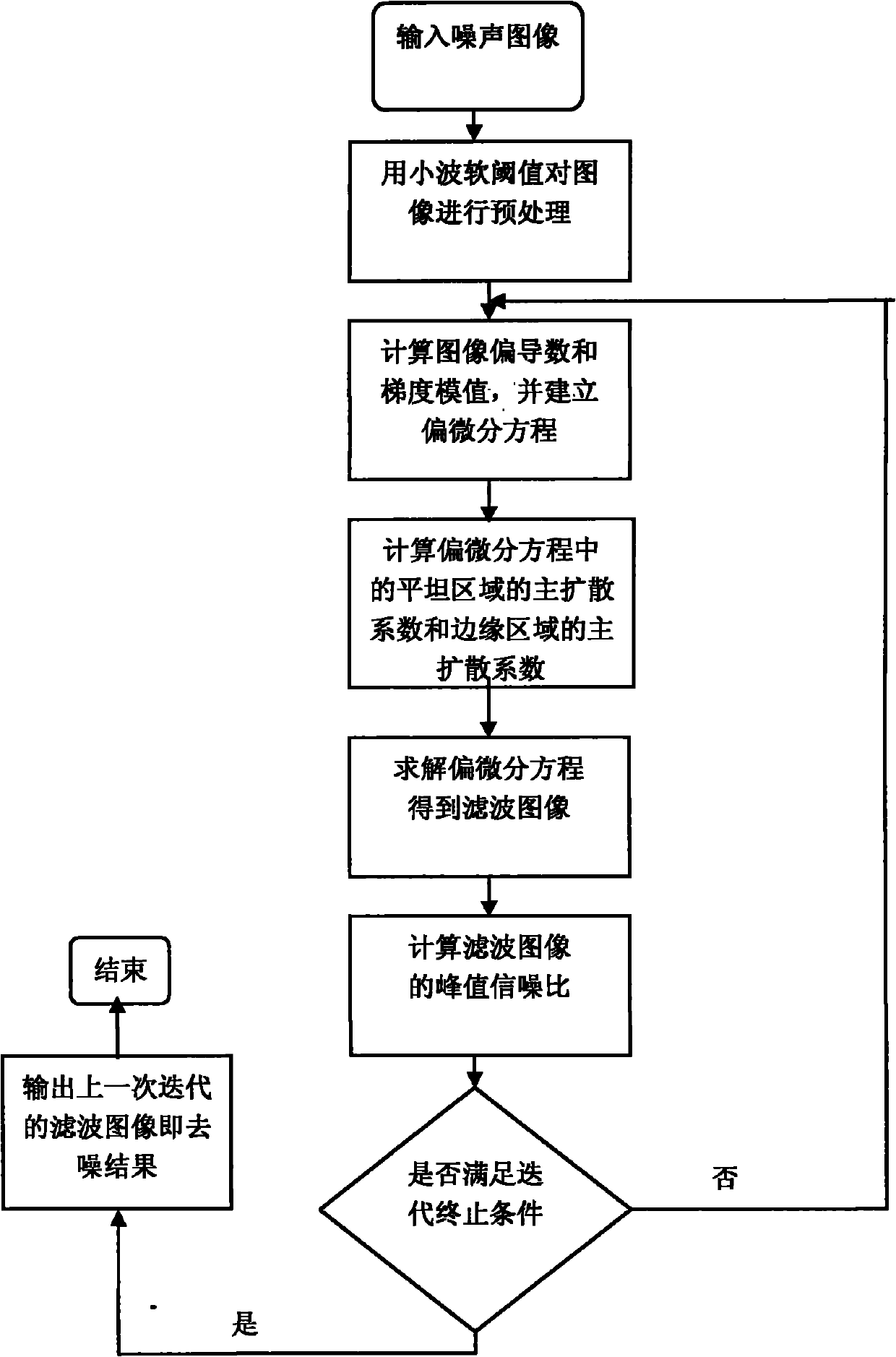
The invention discloses a denoising method of a strong noise pollution image on the basis of partial differential equation, mainly solving the problem of poor traditional denoising effect of the strong noise pollution image. The realization process comprises: (1) pretreating an input noise image u0, and recording the result as u; (2) calculating the partial derivative sum of the image u; (3) calculating the gradient module value of the image u; (4) according to the gradient and the gradient module value, building the partial differential equation; (5) calculating diffusion coefficients and psi in the partial differential equation; (6) utilizing the coefficients and psi, solving the partial differential equation to obtain a filter image; (7) calculating the peak signal to noise ratio PSNR of the filter image; and (8) repeating steps 2 to 7, when the PSNR value of the filter image output iteratively one time is smaller than that output iteratively in the previous time, stopping iteration, and outputting the previously iterated filter image. The invention has simple calculation and high operation speed, can better keep image texture details while smoothening strong noise and can be used for denoising a natural image with strong noise pollution.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
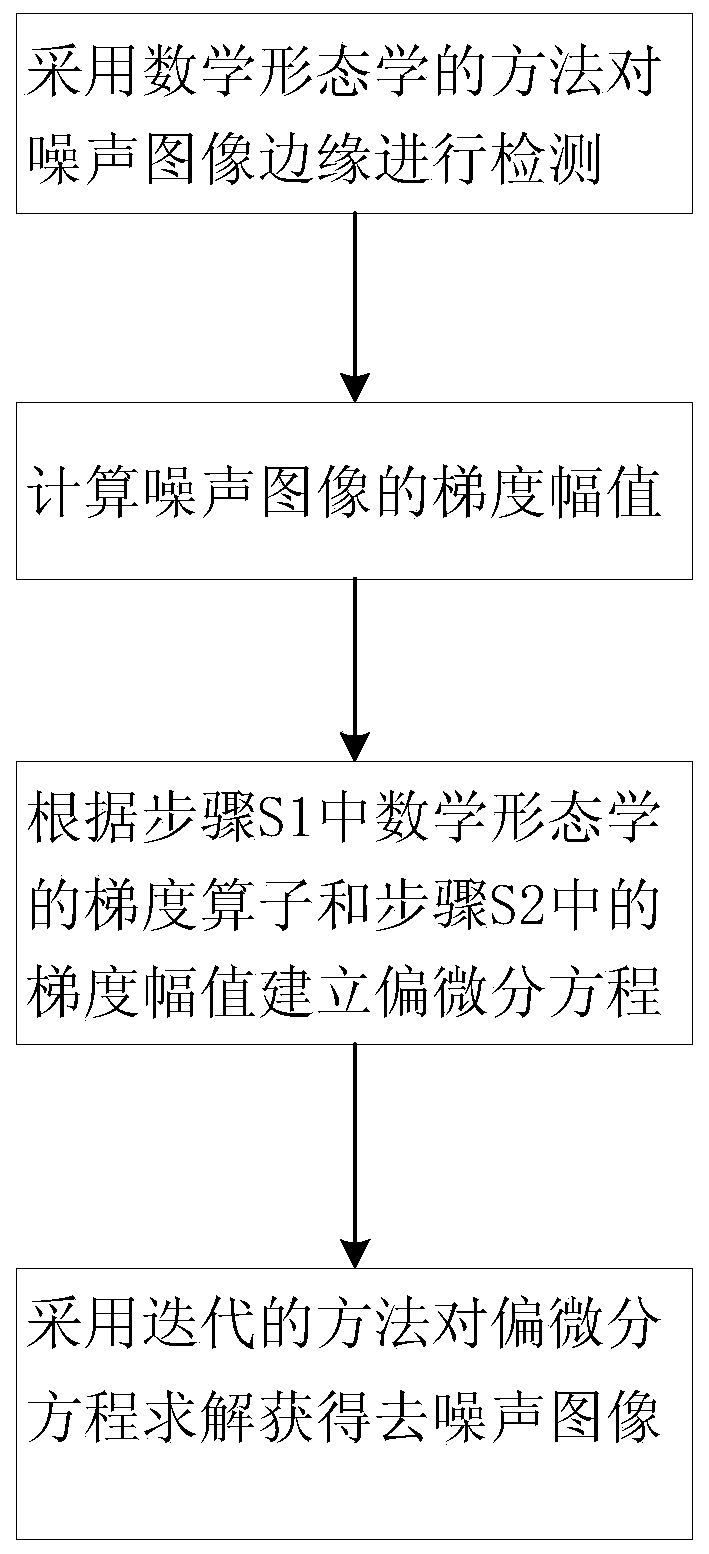
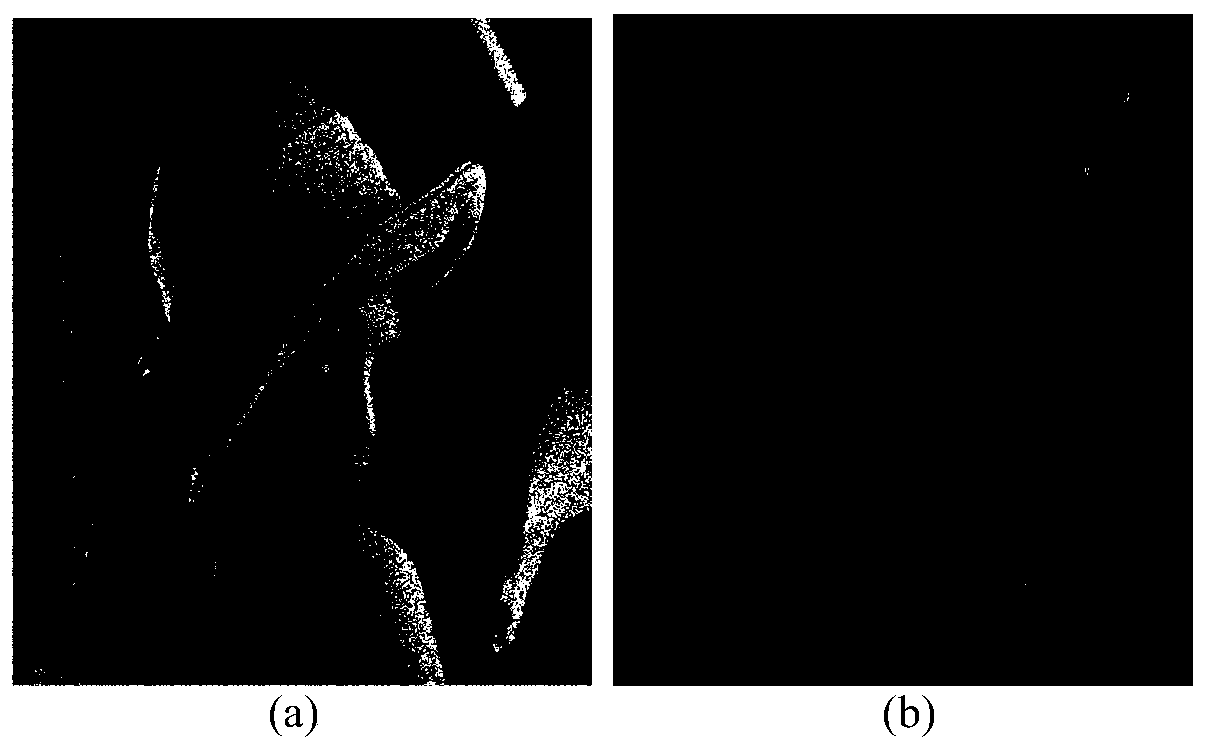
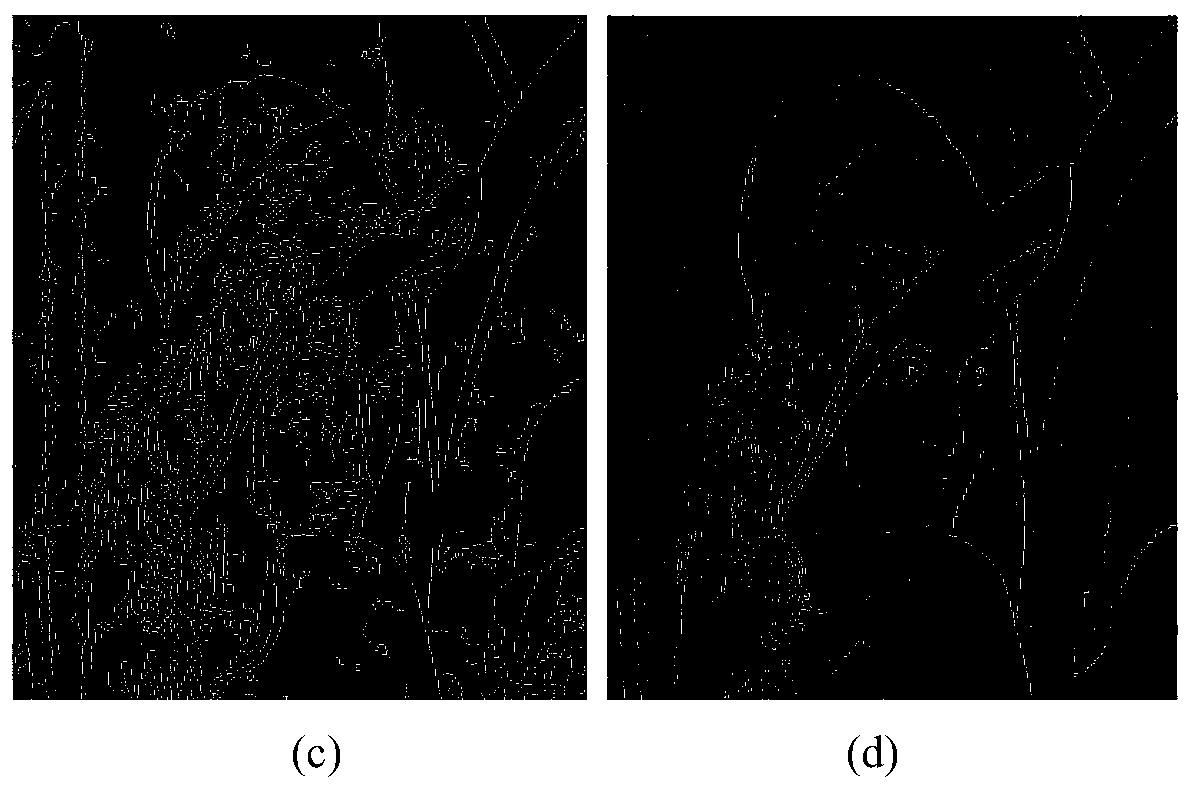
Image Denoising Method Based on Mathematical Morphology for Fourth Order Partial Differential Equation
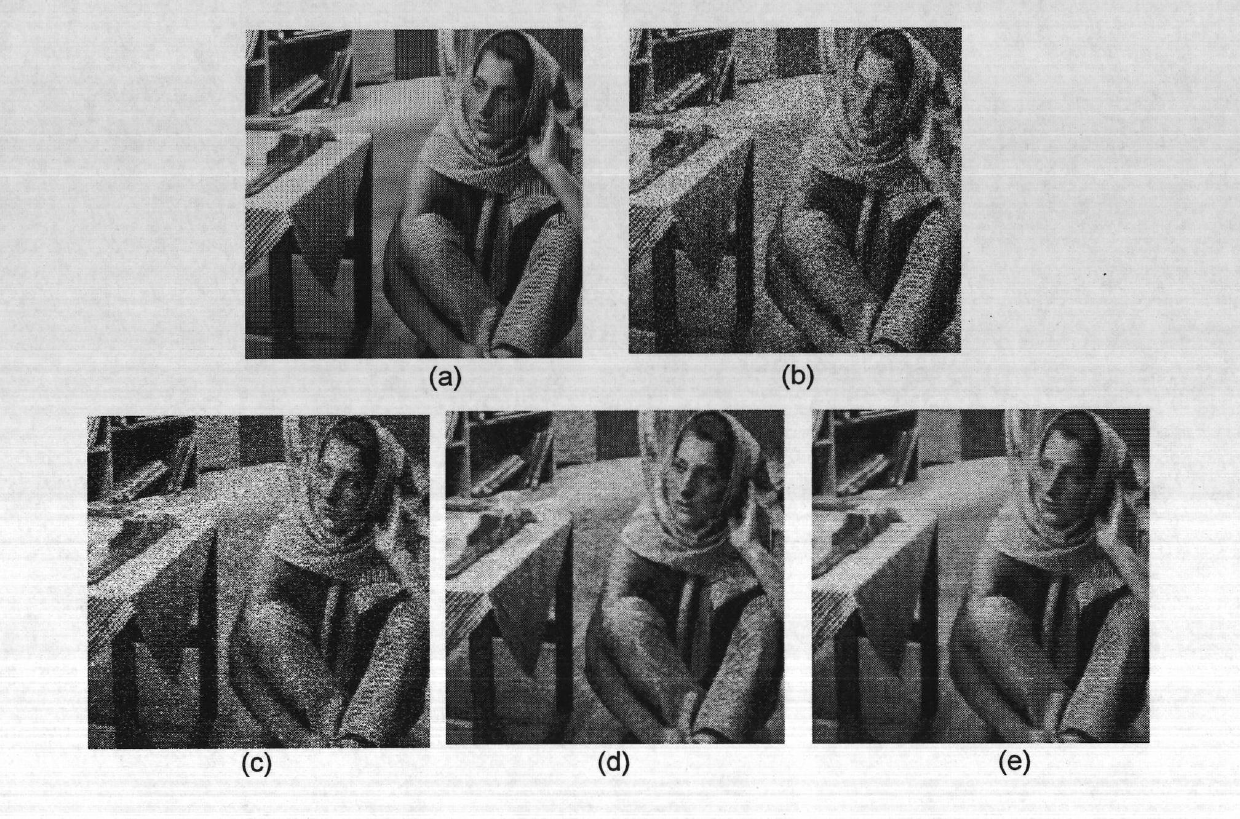
ActiveCN106127716BGood image edgesImprove visual effectsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMathematical morphology
The invention discloses a fourth-order partial differential equation image denoising method based on mathematical morphology, which includes the following steps: S1 uses the method of mathematical morphology to detect the edge of the noise image; S2 calculates the gradient amplitude of the noise image; S3 according to The gradient operator of mathematical morphology in step S1 and the gradient amplitude in step S2 establish a partial differential equation. S4 uses an iterative method to solve the partial differential equation to obtain a denoised image. The present invention performs image denoising based on the fourth-order partial differential equation of mathematical morphology, which better maintains the edges of the processed image and has better visual effects.
Owner:七腾机器人有限公司
A Design Method of Disturbance Observer for Flexible Manipulator Based on Partial Differential Equation
ActiveCN104020664BRealize interference observationAdaptive controlMatrix differential equationElliptic partial differential equation
Owner:GUODIAN SCI & TECH RES INST
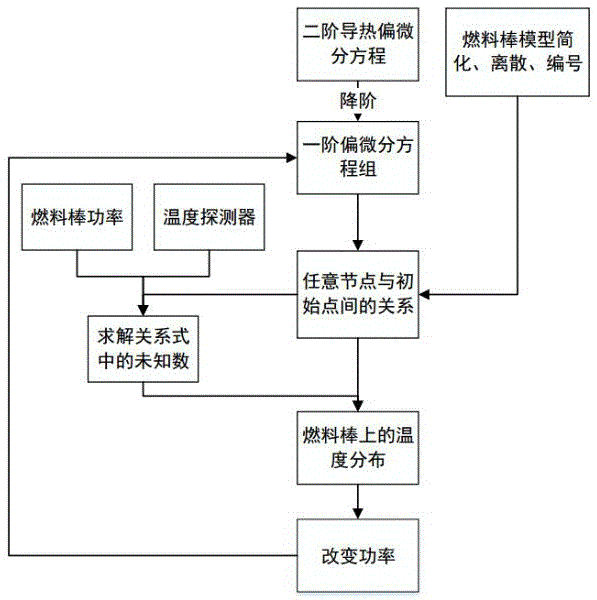
Simulation method for efficiently solving unsteady heat conduction problem of reactor core fuel rod
InactiveCN106611076AGuaranteed safe operationComputationally efficientComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer resourcesMathematical model
The invention discloses a simulation method for efficiently solving an unsteady heat conduction problem of a reactor core fuel rod. The method comprises the following steps of (1) carrying out reasonable simplification on an actual fuel rod model, building a geometrical model and carrying out discrete numbering on the model; (2) changing an original second-order partial differential equation into two first-order partial differential equation sets by using an order reduction method; (3) building a relation of physical quantities, about the physical quantities of an initial point, of any point on a mathematic model; (4) solving unknown quantities in the relation by using known boundary conditions; and (5) solving temperature parameters of required positions at different moments. A highest-order matrix is always kept in two-dimension in a calculation process no matter that the geometrical model is transformed, so that the occupied computer resource is small, and the simulation method can be used for quickly and accurately predicting the temperature parameters of the model, and is particularly very effective for solving the heat conduction problem with fast changes in boundary conditions.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com