Optimization algorithm for solving seepage free surface based on radial base point interpolation method
An interpolation method and seepage technology, applied in the field of geotechnical engineering, can solve problems such as immature theory, and achieve the effect of simplifying the work process, high precision, and ensuring the integration accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
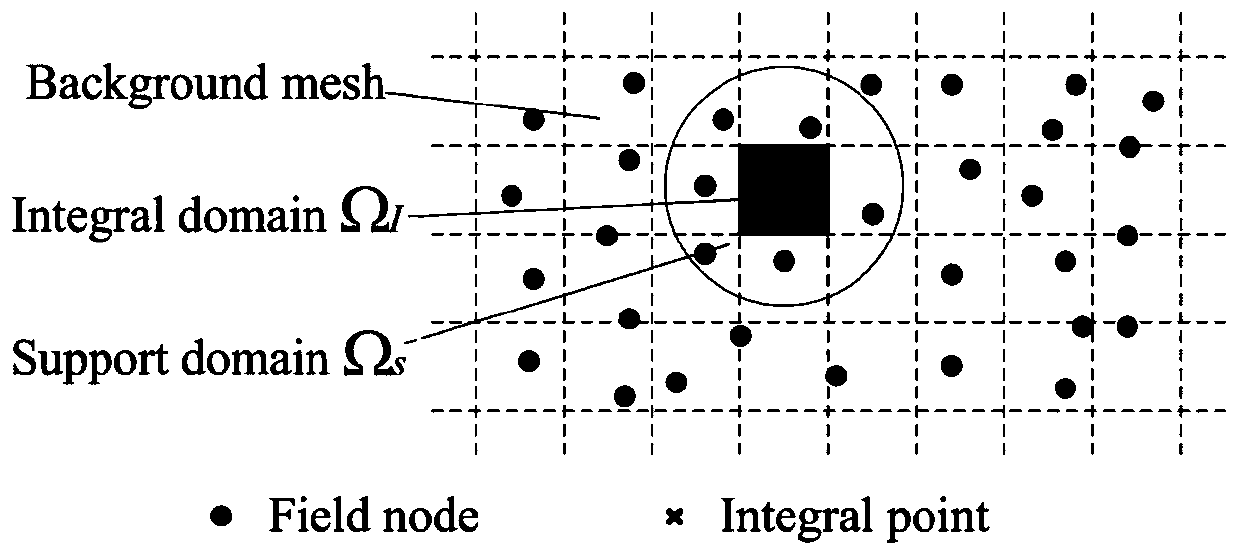
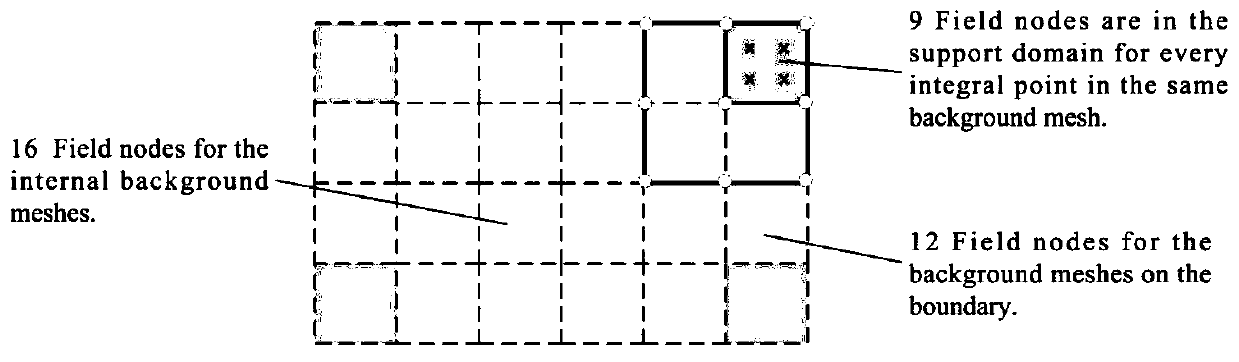
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
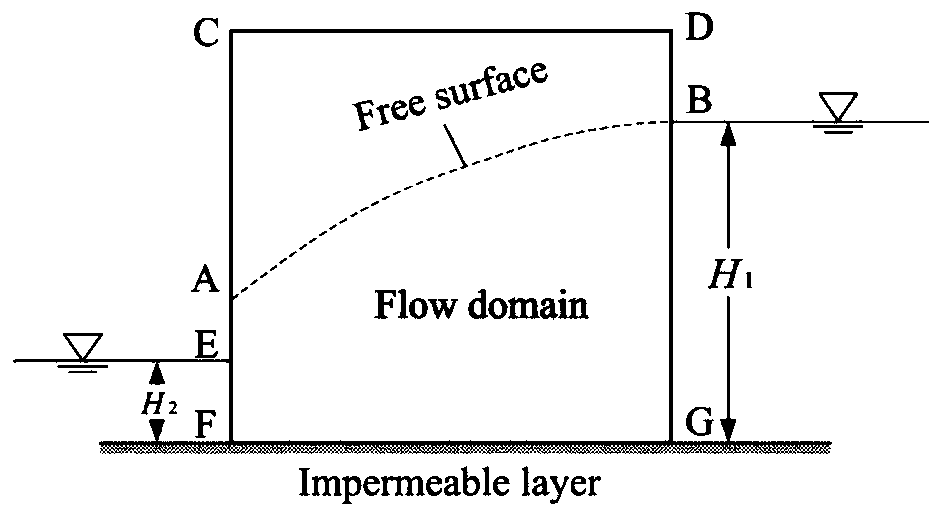
[0111] like Figure 5 As shown, the homogeneous and isotropic rectangular dam body is a calculation example with a theoretical solution. The height of the dam body is 1m, the width is 0.5m, the upstream water head is 1m, the downstream water head is 0.5m, and the permeability coefficient is 0.1. The grid is divided into a 10×20 quadrilateral grid. The theoretical solution is given by Hornung U et al., and the numerical solution is obtained by the method of the present invention. The data comparison between theoretical solution and numerical solution is shown in Table 1.
[0112] Table 1: Calculation results for a homogeneous rectangular dam
[0113]
[0114] According to the data in Table 1, it can be seen that the error of the seepage free surface calculated by the method of the present invention is very small, the position of the free surface is basically consistent with the theoretical solution, and the maximum error is only 0.37%, which is better than most numerical m...
Embodiment 2
[0116] like Image 6 As shown, although there is no theoretical solution for the homogeneous trapezoidal dam, many scholars have studied it to verify the stability and accuracy of their own programs when facing inclined surfaces. The dam body in this example is a trapezoid with a lower bottom width of 7m, an upper bottom width of 2m, and a height of 5m. The downstream is a trapezoidal surface, and the upstream is a vertical surface. The upstream water head is 5m, and the downstream water head is 7m. Use a 20×20 quadrilateral grid.
[0117] according to Image 6 In the model shown, the calculation result of the present invention is very close to the result of Lacy, but the difference is that many scholars will use regular quadrilateral and triangular grids to discretize the dam body area to ensure calculation accuracy when calculating this example. However, this example uses an irregular background grid, and the number of grids is also less than that of the predecessors. How...
Embodiment 3
[0119] like Figure 7 As shown, a dam with a clay core is a relatively common situation in actual engineering, so this example can be selected to verify the stability of the present invention when dealing with material interfaces and the feasibility of engineering promotion. In this example, the trapezoidal dam has a lower bottom width of 150m, an upper bottom width of 30m, and a height of 37.5m, and a clay core wall with a lower bottom width of 30m and an upper bottom width of 6m is filled. The upstream water head is 37.5m, and the downstream water head is 6.25m. The ratio of the permeability coefficient of the clay core to the rest of the area is 1 / 10. The grid division still adopts irregular grids with a number of 50×6.
[0120] In many traditional methods, when dealing with material interfaces, in order to improve the accuracy of the solution, the material interface is usually treated as an internal escape surface. In the present invention, the result close to the actual ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bottom width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com