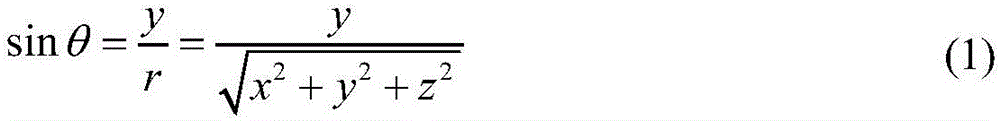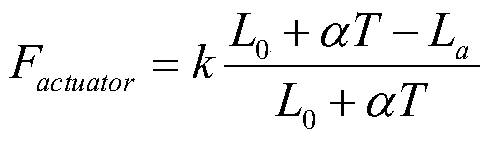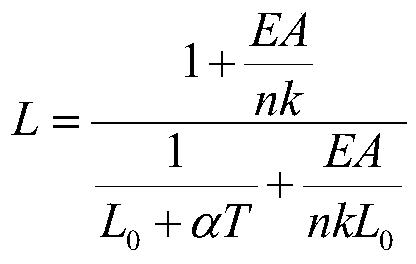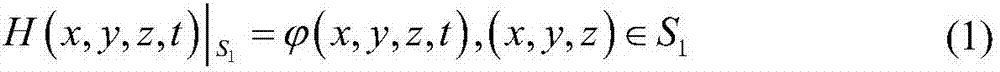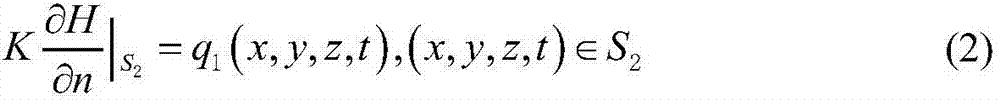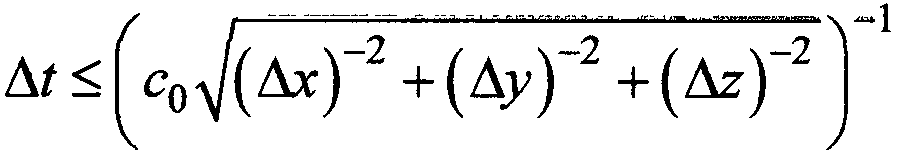Patents
Literature
58 results about "Exact differential equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, an exact differential equation or total differential equation is a certain kind of ordinary differential equation which is widely used in physics and engineering.
Shale gas well productivity evaluation and prediction method
ActiveCN104389594AAccurate Capacity ForecastImprove economic efficiencyInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsMatrix differential equationDesorption
The invention discloses a shale gas well productivity evaluation and prediction method. The method comprises the following steps: an expression of a differential equation of a single-phase seepage mathematical model is obtained; the differential equation is solved and represented by a pressure form to obtain a seepage velocity and output formula; a deliverability equation is determined through fitting production data; the derived output formula is arranged to obtain a shale gas horizontal well staged fracturing output formula; boundary pressure (pe) required to be known can be known from the shale gas output formula; and as shale gas has the influences of absorption and desorption, a deviation factor is required to be corrected to obtain formation pressure of a shale gas reservoir. The prediction method deduces the deliverability equation for a shale vertical well and a horizontal well according to the desorption and dispersion characteristics of the shale gas, so that a shale gas output evaluation method is built, the precise output prediction is obtained, and the economic efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU CHUANGYUAN OIL & GAS TECH DEV
3D TTI double-phase medium seismic wave field value simulation method based on finite difference method
ActiveCN105044771AImplement iterative solutionEnables real-time propagation simulationSeismic signal processingDouble phaseFinite difference method
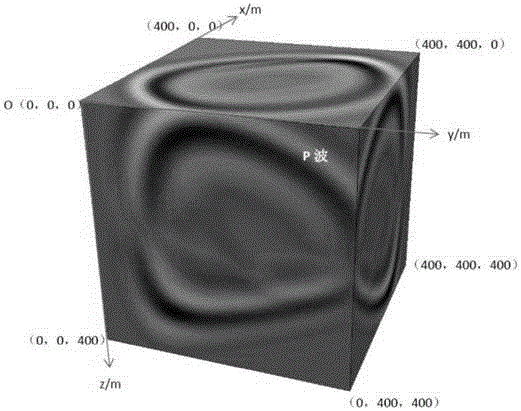
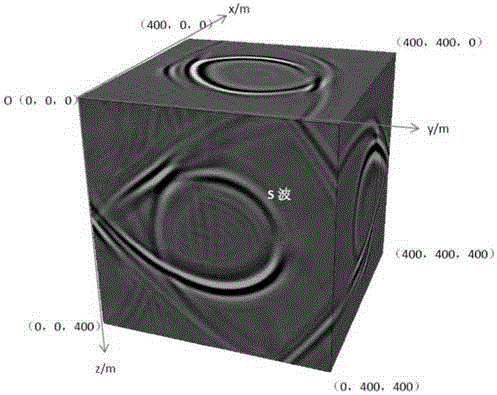
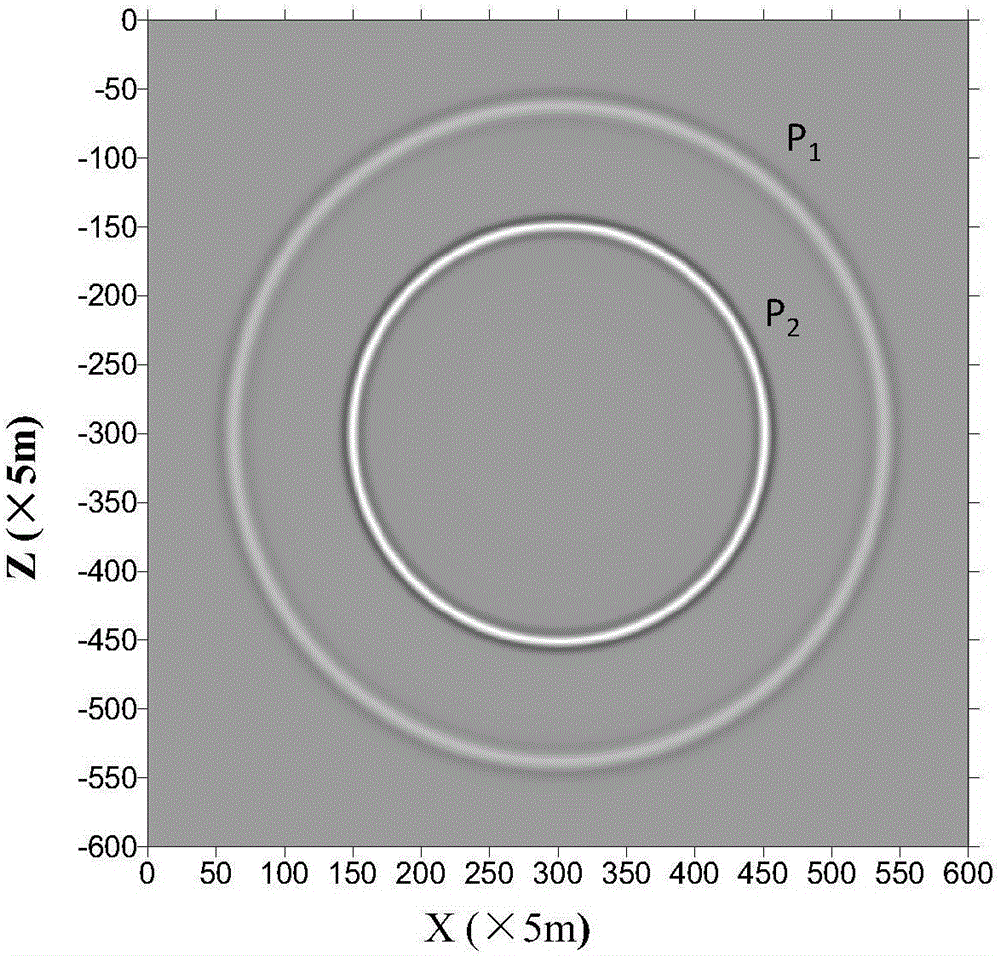
The invention discloses a 3D TTI double-phase medium seismic wave field value simulation method based on a finite difference method. The 3D TTI double-phase medium seismic wave field value simulation method comprises steps of obtaining a solid and fluid stress tensor and a solid and flow strain tensor and transforming the tensors to a constitutive equation, obtaining a geometry equation according to the corresponding relation of stress and the displacement, obtaining a motion differential equation according to the constitutive equation, the geometry equation and the fluid motion relative to the solid and the corresponding relation between the stress and the displacement, taking the divergence on two ends of the motion differential equation to obtain a first longitudinal wave equation and a second longitudinal wave equation of the seismic wave, as for the first longitudinal wave equation and the second longitudinal equation, enabling a partial derivative to y to be zero and performing difference discrete on the space partial derivative and the time partial derivative by employing an 2N order precision expansion formula and a 2-order precision center difference form to obtain a first difference equation and a second difference equation, and performing boundary absorbing condition processing on the first difference equation and the second difference equation to obtain the corresponding seismic wave field value. The invention realizes the real-time transmission simulation of the physics seismic wave field.
Owner:北京多分量地震技术研究院
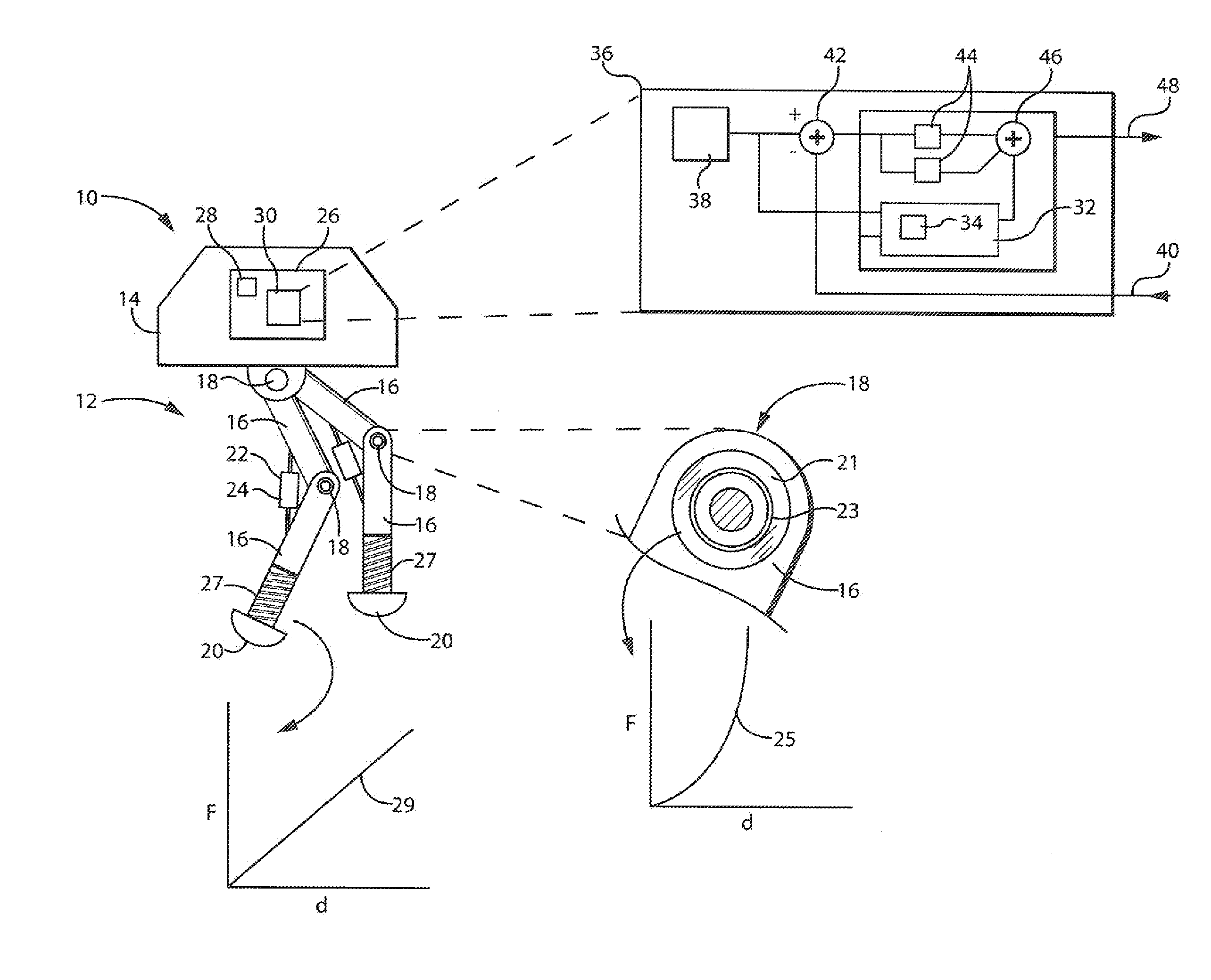
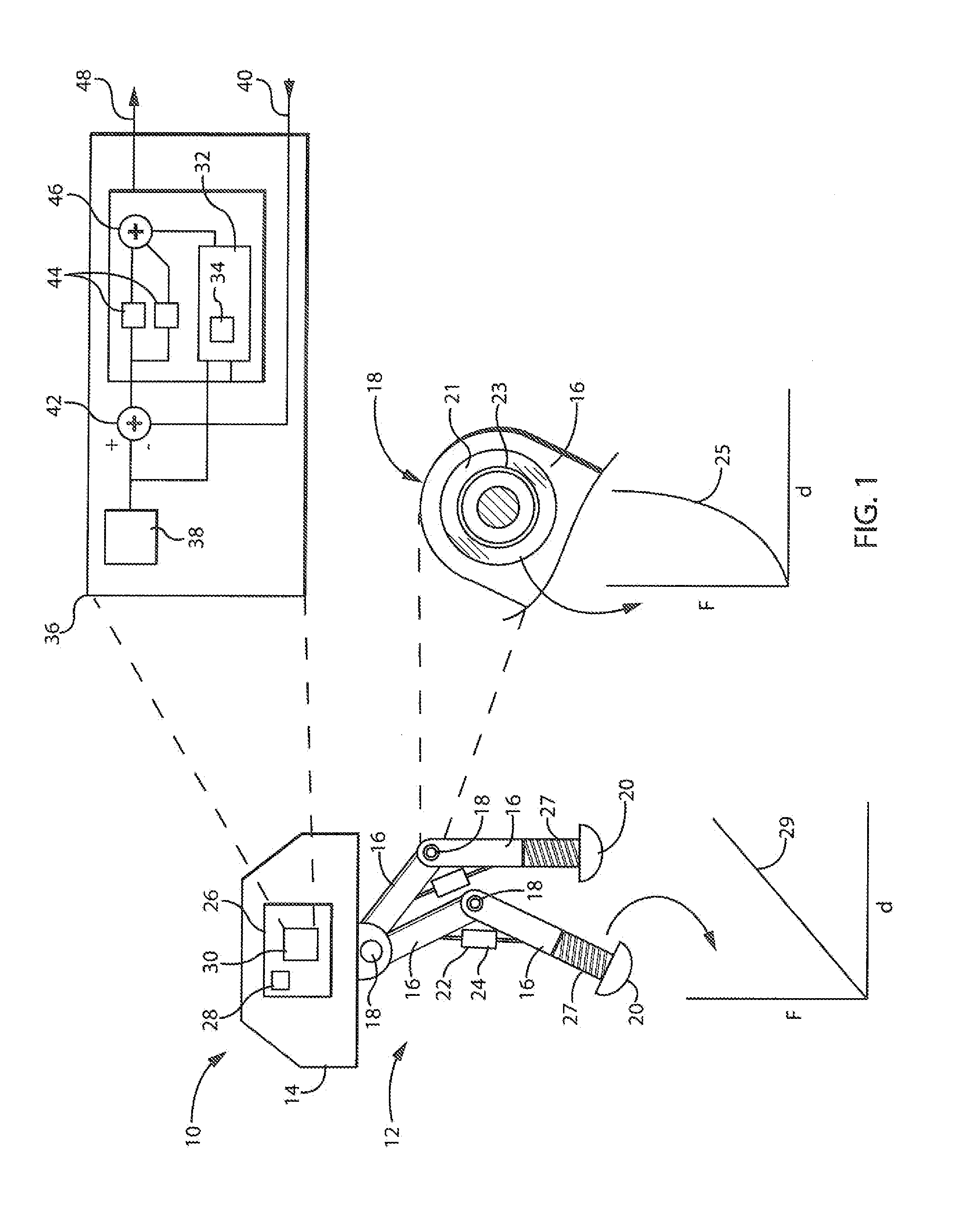
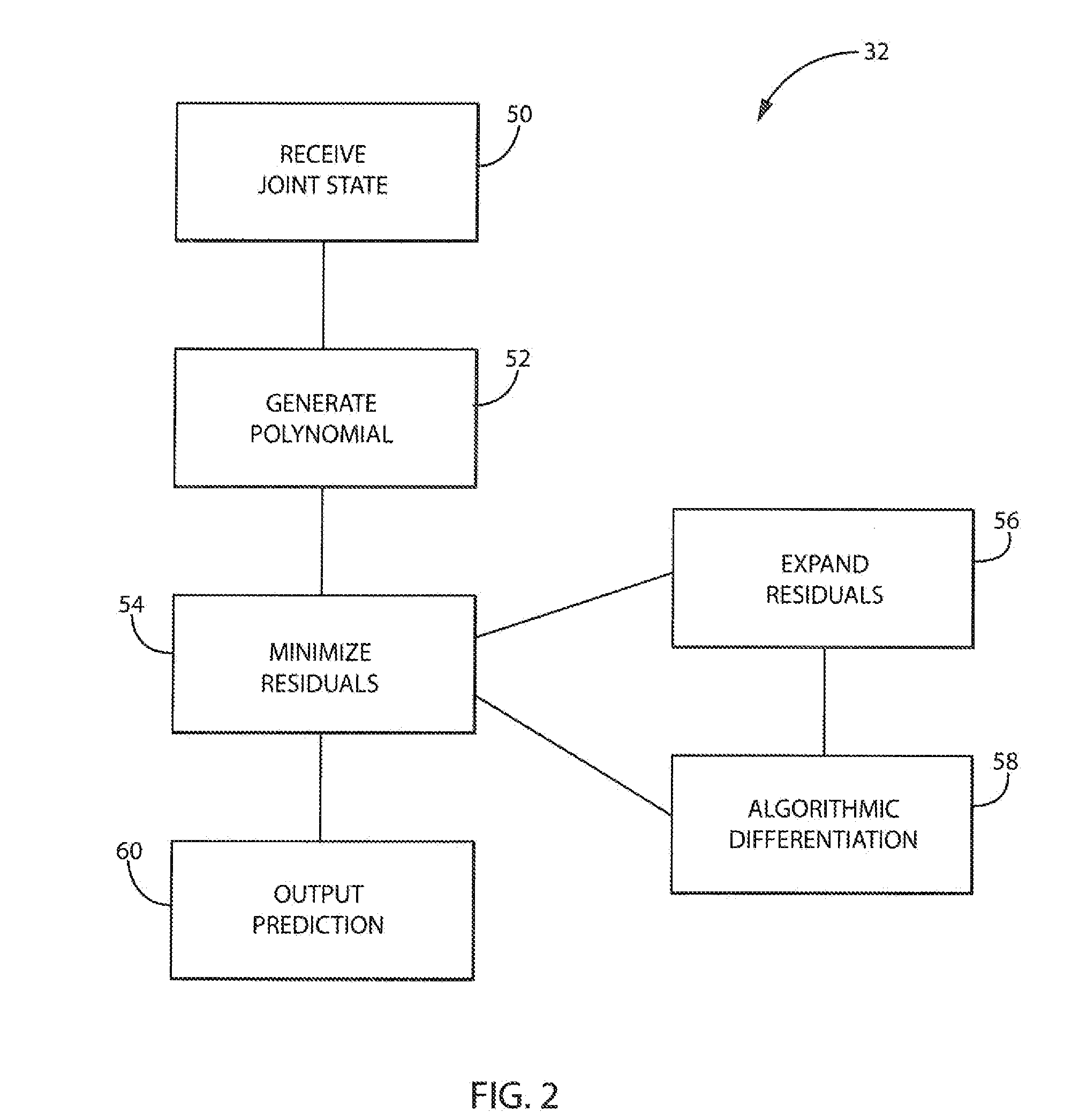
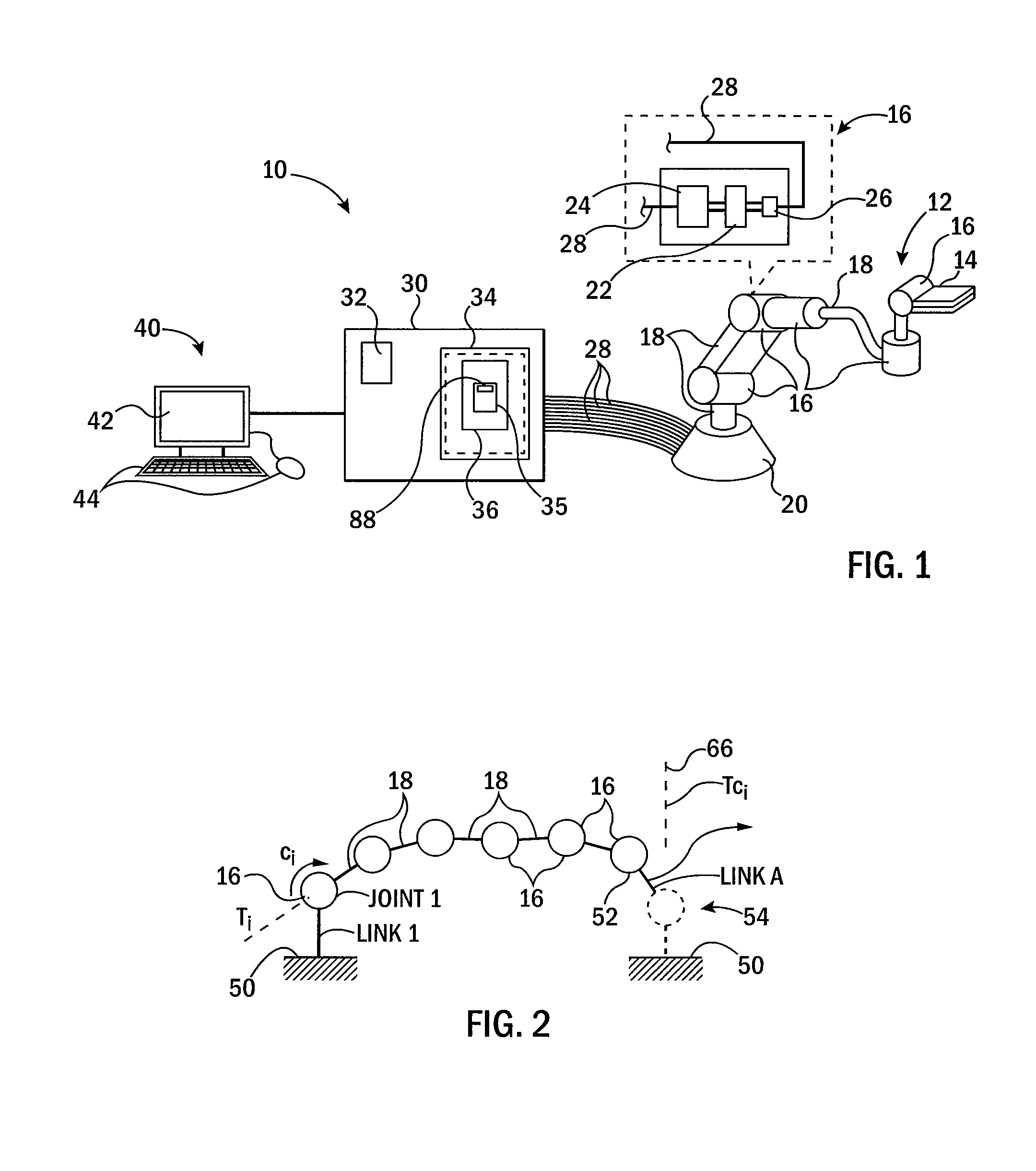
Dynamic Predictor for Articulated Mechanisms
ActiveUS20150005941A1Stable and accurate solutionImproved polynomial approximationProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEquation of the centerEngineering
A dynamic predictor usable for rapid and accurate calculation of joint commands of an articulated dynamical mechanism describes the relationship between the joints in the form of a differential equation. The predictor solves this differential equation for predicted joint states by fitting a polynomial equation having free parameters describing the predicted joint states to the differential equations by minimizing the differential equation residuals. This minimization employs a series expansion allowing algorithmic differentiation.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
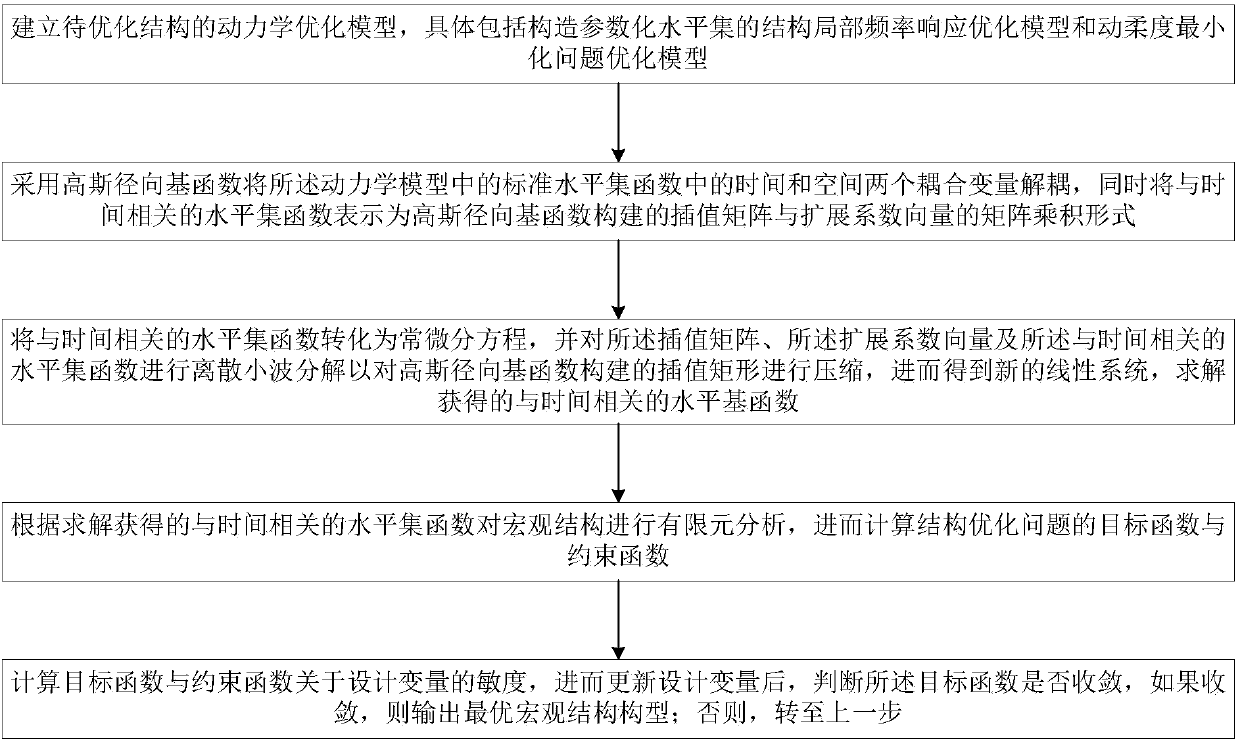
Efficient structure frequency response topological optimization method
InactiveCN107315872AFrequency Response Topology Optimization Method for Efficient StructuresGuaranteed smoothnessDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsElement analysis
The invention belongs to the technical field related to structure topological optimization design, and discloses an efficient structure frequency response topological optimization method. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) decoupling two coupling variables including time and space in a standard level set function in a dynamic model of which the structure is to be optimized, and meanwhile, expressing the level set function related to time as a matrix product form; (2) converting a partial differential equation of the time-related level set function into an ordinary differential equation so as to obtain a new linear system, and solving to obtain the time-related level set function; (3) carrying out finite element analysis on a macrostructure so as to calculate a target function and a constraint function of a structure optimization problem; and (4) calculating the sensitivity, which relates to a design variable of the target function and the constraint function obtained in the (3), and judging whether the target function is convergent or not after the design variable is updated. By use of the method, a discrete wavelet transform technology is adopted to carry out recompression on an interpolation matrix, efficiency is improved, and cost is lowered.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
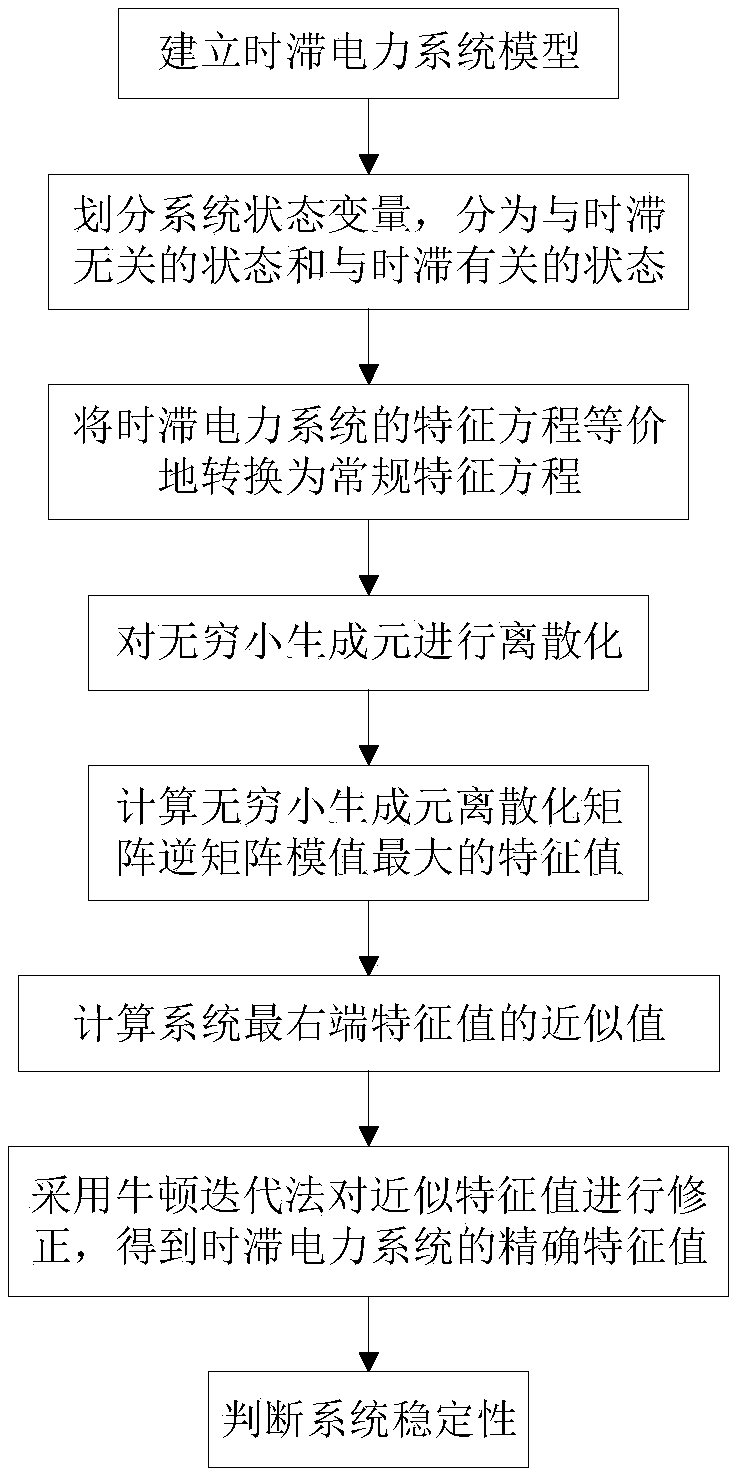
Lyapunov stability analysis method of time delay electric system
InactiveCN103227467AReduce dimensionalityThe number of variables to be requested is reducedAc network circuit arrangementsLyapunov stabilityTime delays
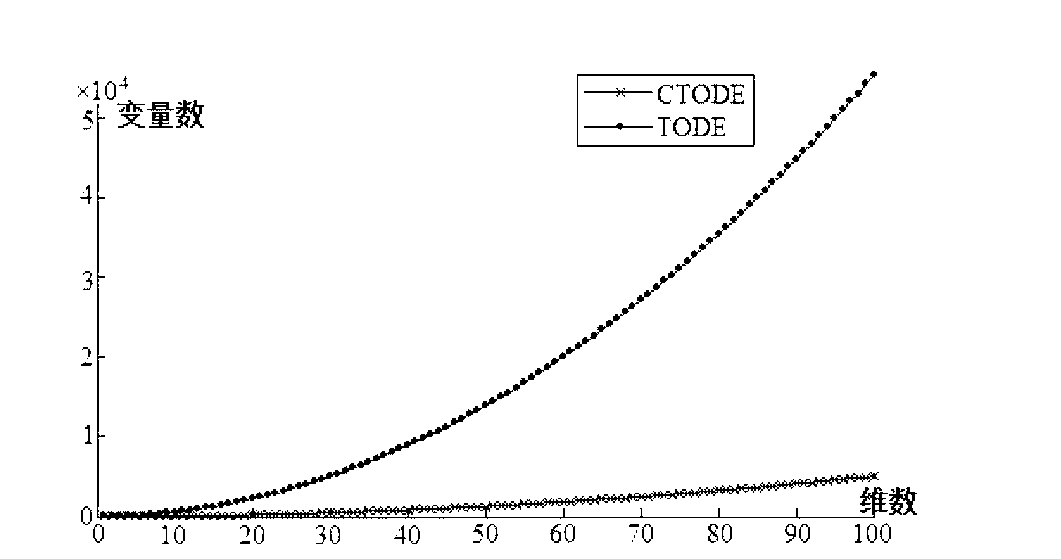
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric systems. In order to solve the problem of low stability analysis computing efficiency of the original time delay electric system, effectively reduce the dimensionality of a time delay differential equation and achieve higher computing efficiency, the invention adopts a technical scheme that a Lyapunov stability analysis method of a time delay electric system comprises the following steps of establishing a constraint time delay differential equation (CTODE) model of the electric system, rearranging and reorganizing system states in a manner that the states (z1 to z) not considering time delay influence are at the front and the states (z2 to z) considering the time delay influence are at the back, obtaining a CTODE model corresponding to the original time delay system, and basing on a new stability criterion of the CTODE model. The method is mainly applied to the electric system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Space debris recovery control method based on tethered technology
ActiveCN106516177AOut-of-plane oscillation suppressionStable recyclingCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsPartial differential equationEngineering
The invention discloses a space debris recovery control method based on a tethered technology. The space debris recovery control method is characterized by comprising the following steps that 1, the tether elasticity is considered, a space tethered debris system is researched by adopting an elastic rod module, and a system dynamics differential equation is built according to a class II Lagrange equation; 2, the system dynamics equation in the step 1 is rewrote into a non-dimensional system dynamics equation; 3, the in-surface outer pivot angle vibration abatement problem of nonlinear time-varying system dynamics equation in the recovery process is researched, and the tether length change analysis control law and the in-surface pitch angle value range in the expectation equilibrium position in the debris recovery process are inferred; and 4, the stability of the system and the value range, keeping stable asymptotically, of a pitch angle in an expectation surface are further analyzed through the Floquet theory. Through the space debris recovery control method, the effect that debris is stably recovered nearby an on-orbit spacecraft can be ensured, and meanwhile the safety in the recovery process especially the safety in the end time can be ensured.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Signal processing methods
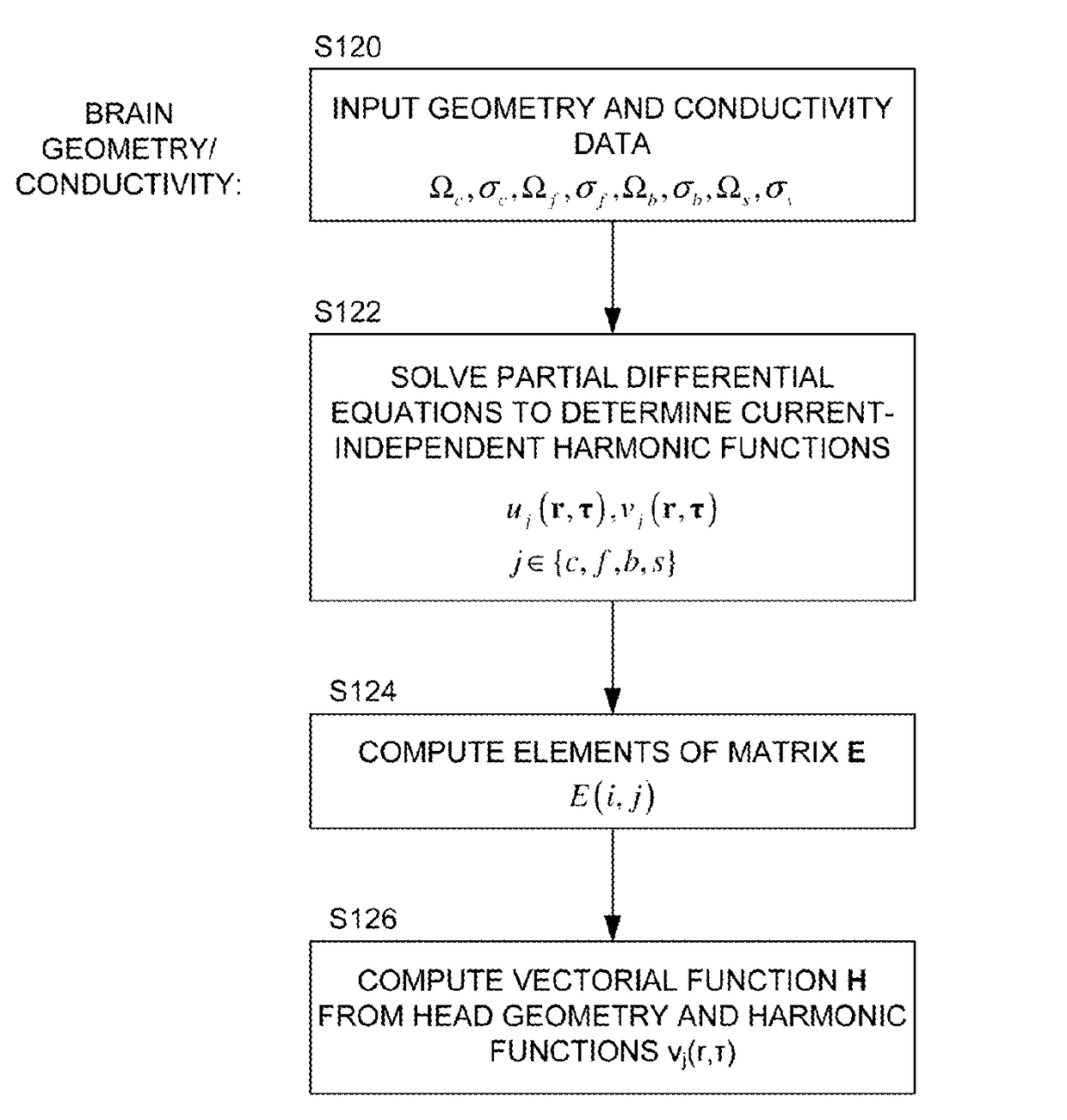
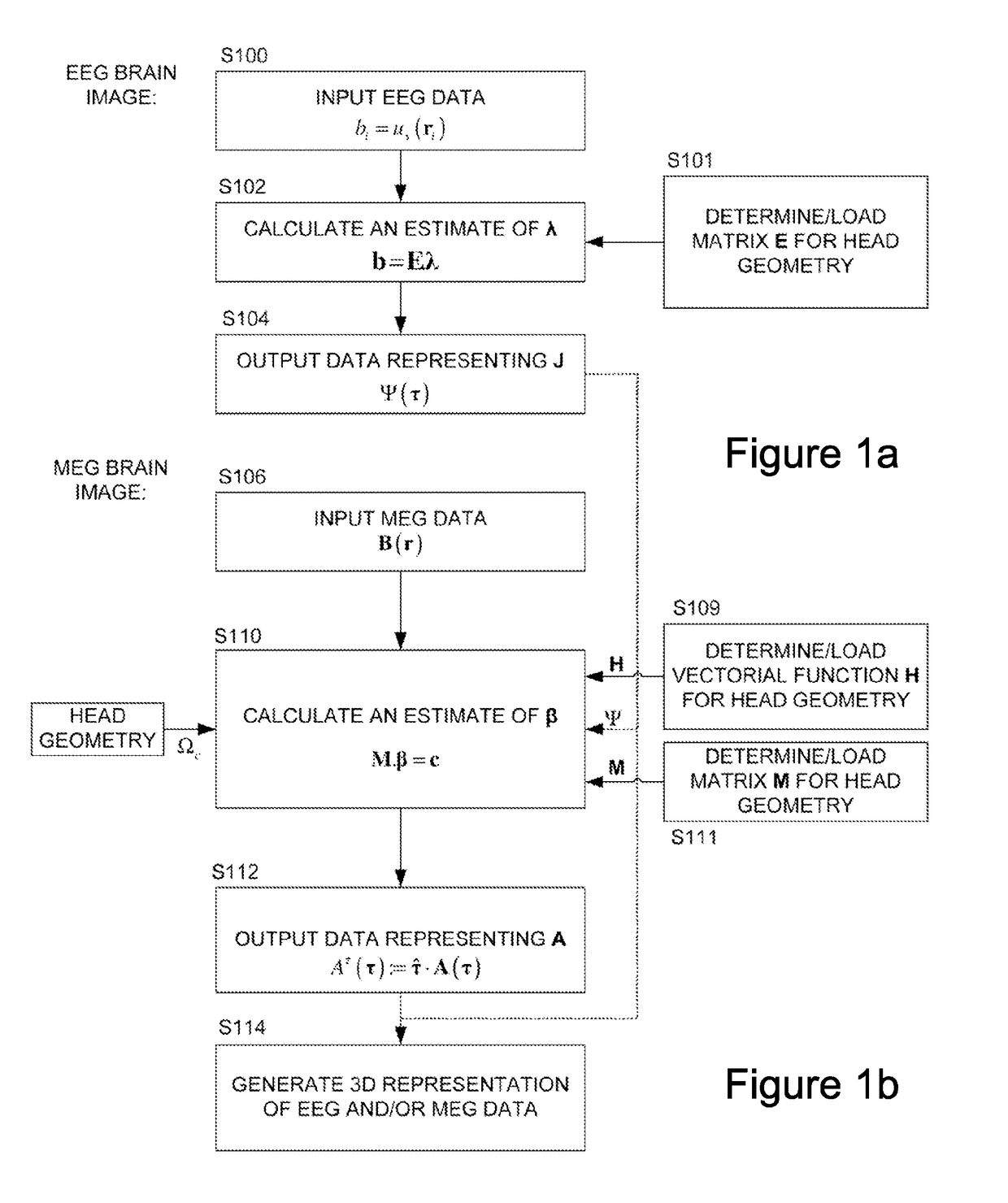
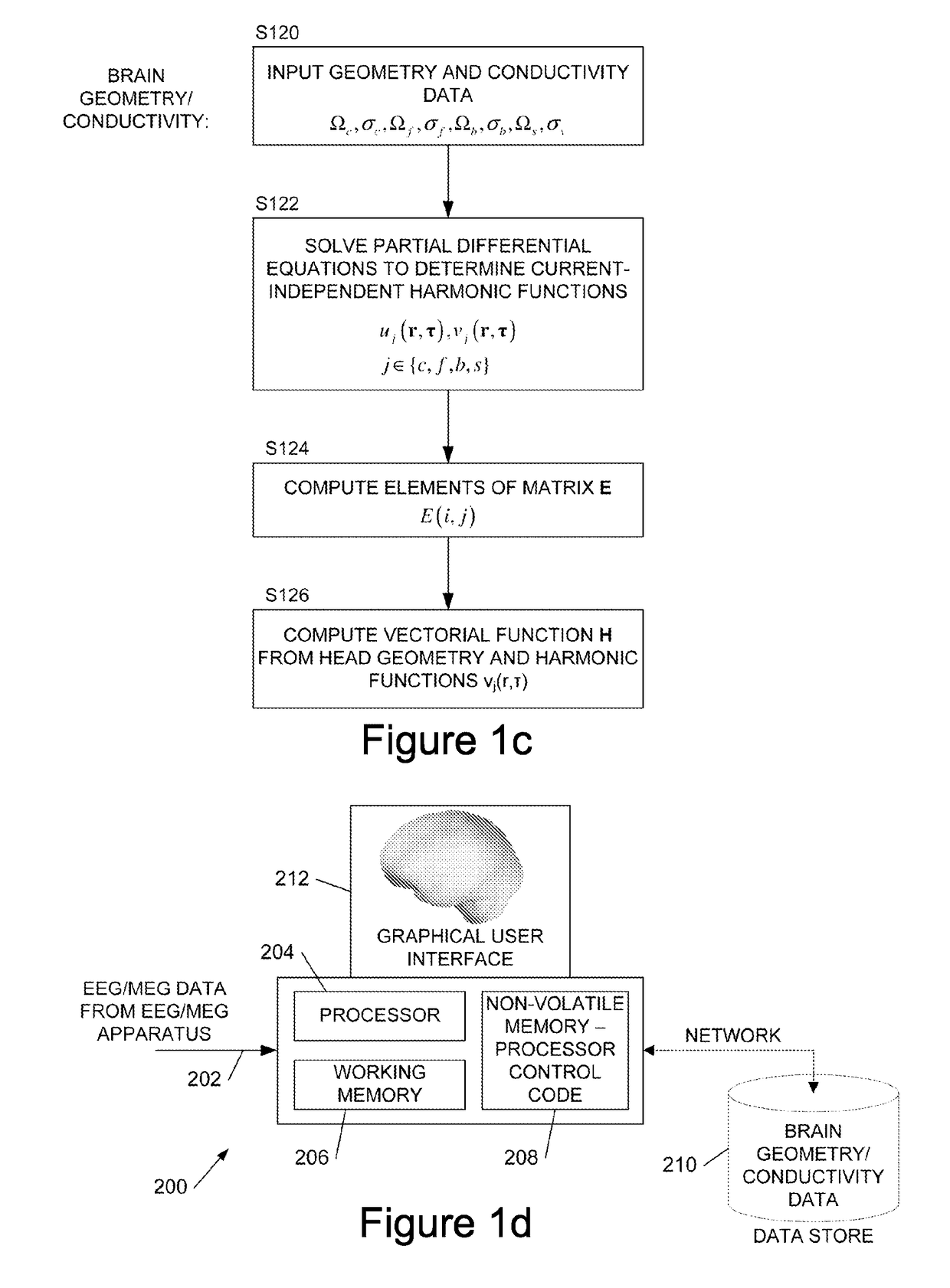
ActiveUS20170095174A1Calculation can be costlyElectroencephalographyImage enhancementExact differential equationImaging data
We describe a method of processing an EEG and / or MEG signal to generate image data representing a 3D current distribution, J, within the brain, the method comprising: capturing a plurality of electric and / or magnetic measurements from the exterior of the head; solving an integral equation for a part of said current distribution to generate said image data representing said 3D current distribution, wherein said integral equation comprises an integral of a first function representing said part of said current distribution and of a second function (∇τvs (r, τ)) representing the geometry and conductivity of the head independent of said current distribution; wherein said solving comprises: modelling the head as at least two regions separated by at least one internal boundary, and solving a set of partial differential equations, one for each said internal region, each partial differential equation comprising a geometry-conductivity function (w(r, τ)) representing the geometry and conductivity of the respective region, wherein said solving is subject to a boundary condition that either i) the gradients of the functions across the or each said internal boundary are smooth when conductivity is taken into account, or ii) a normal component of the electric field of said part of said current distribution is continuous across the or each said internal boundary, and wherein said geometry-conductivity function for an outermost said region of said head defines said second function (∇Tvs (r, τ))
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
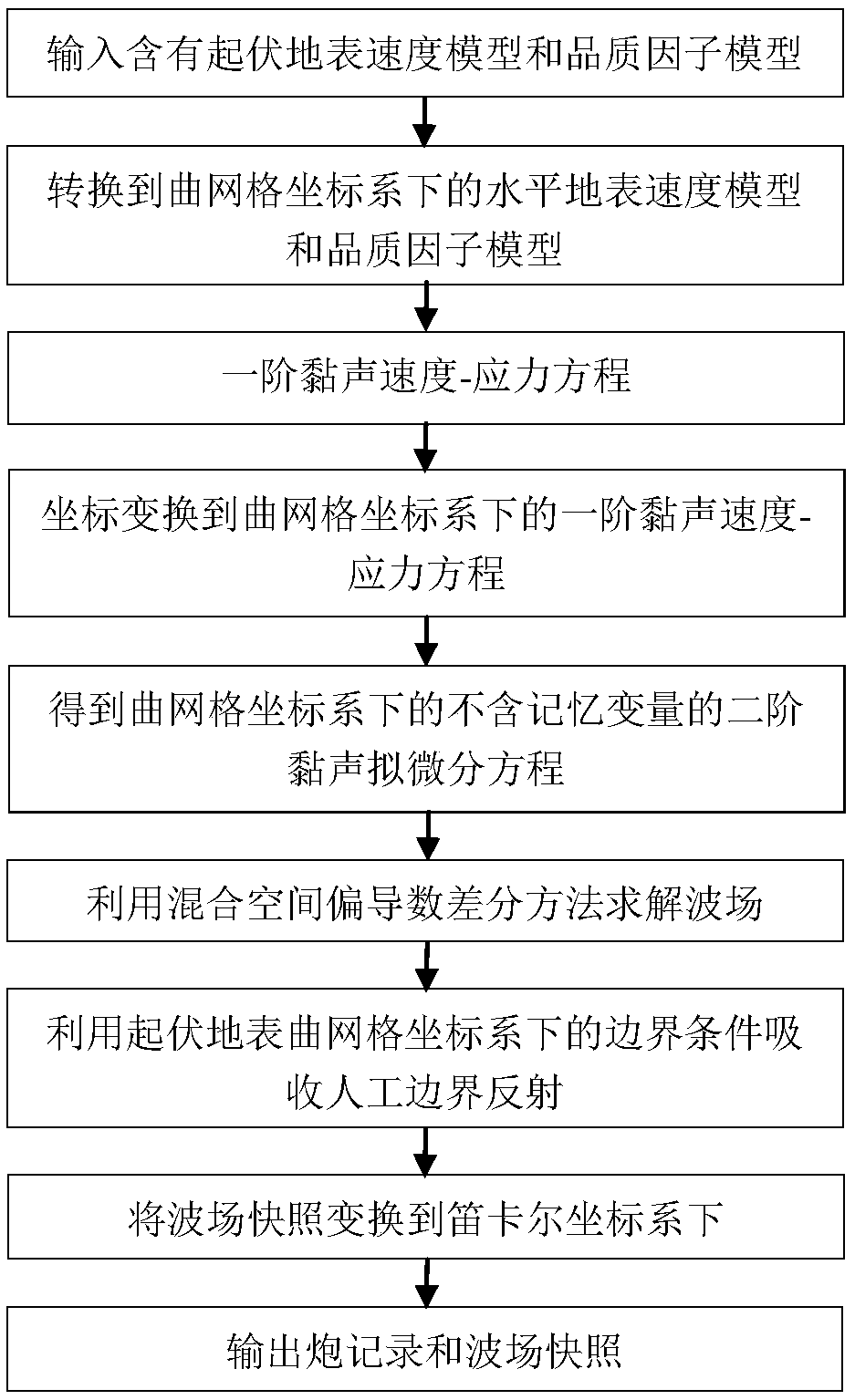
Viscous-acoustic undulating surface forward modeling system and method based on viscous-acoustic quasi-differential equation
ActiveCN108646293AOvercoming the Effects of SimulationAccurate wave field characteristicsSeismic signal processingMatrix differential equationAcoustic medium
The present invention provides a viscous-acoustic undulating surface forward modeling system and method based on a viscous-acoustic quasi-differential equation, belonging to the field of oil exploration. The method comprises the following steps of: performing irregular mesh generation of speed and quality factors, mapping the speed and quality factors in a mesh coordinate system, mapping a traditional first-order viscous-acoustic-stress equation to a curved mesh coordinate system, and applying the first-order viscous-acoustic-stress equation in the curved mesh coordinate system to deduce a second-order viscous-acoustic quasi-differential equation without memory variables in the same coordinate system. The new viscous-acoustic equation can better control the amplitude loss and phase dispersion caused by the viscous-acoustic medium to more accurately simulate the propagating precision of the viscous-acoustic medium of the undulating surface in a seismic wave, and when the equation is solved, a mixed space partial derivative difference method is provided to perform solution, and a new boundary condition suitable for an undulating surface curved mesh coordinate system is provided to absorb artificial boundary reflection.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
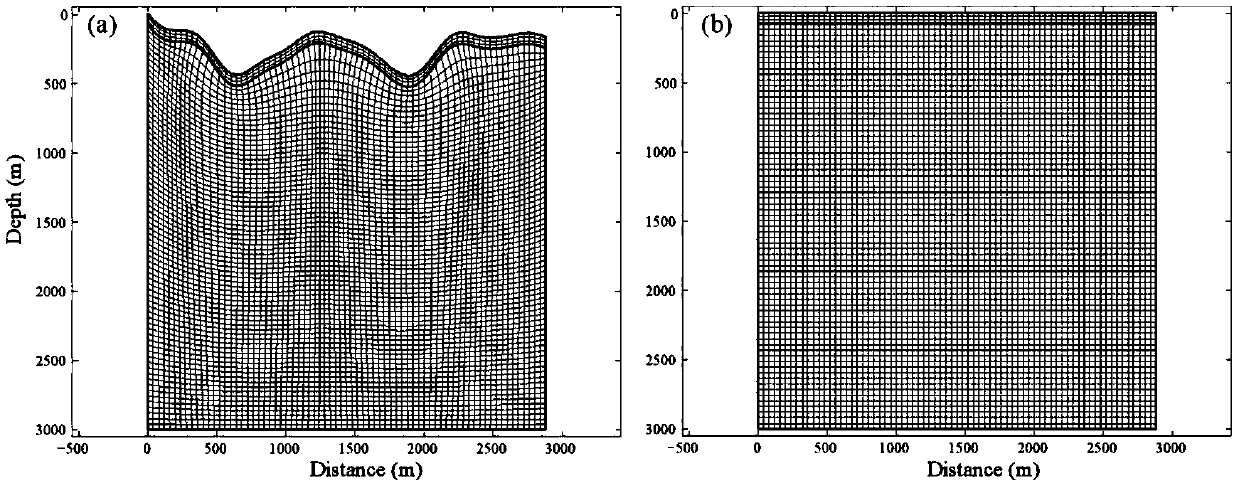
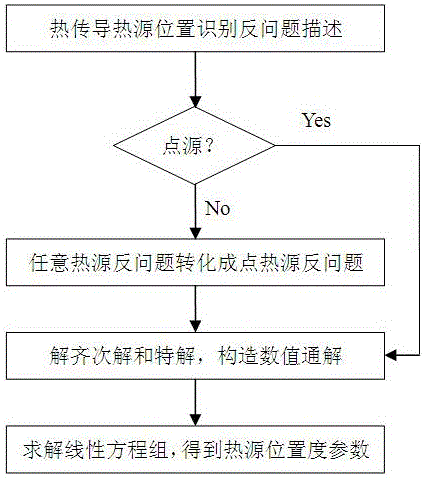
Numerical value general solution method for heat conduction heat source position recognition inverse problem
ActiveCN105677993AFast inversionAdaptableDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceExact differential equation
The invention relates to a numerical value general solution method for a heat conduction heat source position recognition inverse problem. The numerical value general solution comprises the following steps that a heat conduction source position recognition inverse problem is described, the next step is directly executed if a heat conduction source is a point source, and if the heat conduction source is a non-point source, a conversion algorithm is adopted to convert the non-point source inverse problem into a point source inverse problem, and then the next step is executed; a homogeneous solution and a particular solution are calculated to construct a numerical value general solution; a system of linear equations is solved, and heat source position parameters are obtained. According to the method, the numerical value general solution meeting a heat conduction differential equation and using the heat source parameters as variables is constructed based on the finite element numerical solution, the heat conduction position recognition inverse problem is converted into a multivariate function extremum problem, and the heat source parameters are rapidly obtained through inversion. The method not only can inverse the point heat source position, but also can inverse the positions of heat sources in any shape, thereby being wide in application range, high in adaptability and good in engineering application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TIANCHONG VEHICLE LAMP GROUP
Radar altimeter assistance method aiming to inertial navigation
InactiveCN105841699AHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar altimeterNavigation system
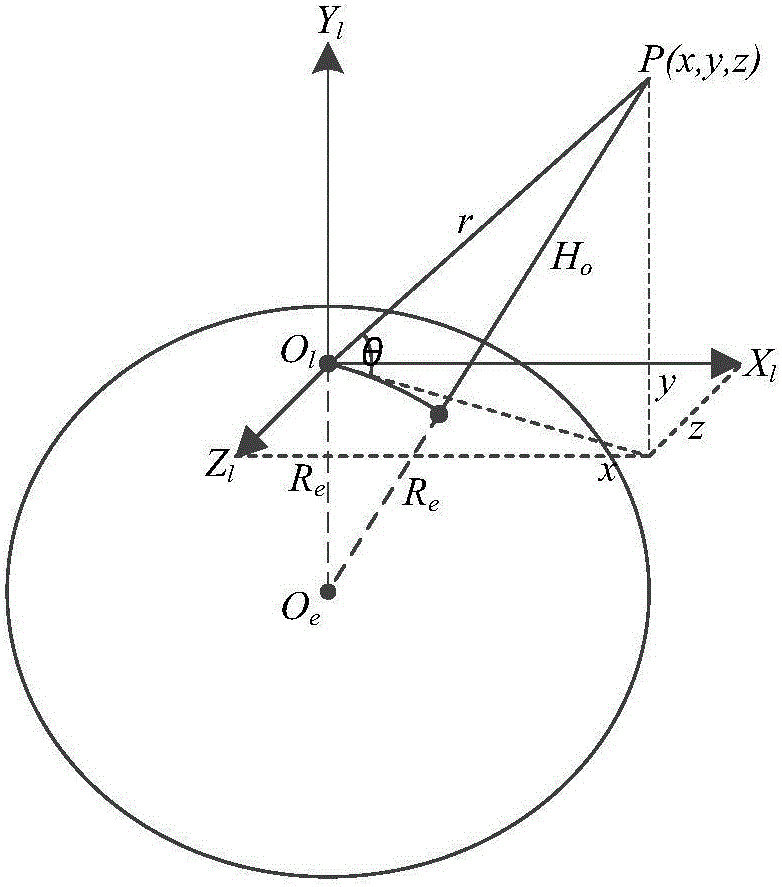
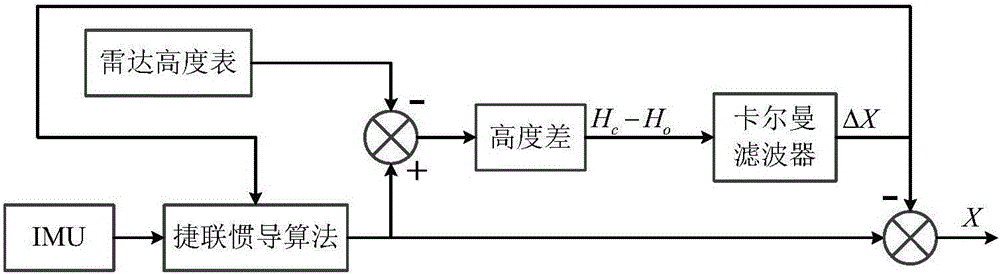
The invention provides a radar altimeter assistance method aiming to inertial navigation. In the method, a measurement quantity is constructed in the manner of calculating earth core altitude of an air vehicle according to position vectors outputted by the inertial navigation, calculating earth core altitude minus earth ellipsoidal radius to obtain the calculated altitude height of the air vehicle, obtaining observed altitude height by means of a measurement value from the radar altimeter with other algorithms, and calculating altitude height minus the observed altitude height to obtain a difference as the measurement quantity, and finally deriving a total differential equation of the measurement quantity. The invention provides a particular embodiment, wherein a strapdown inertial navigation / radar altimeter combined navigation system is formed on the basis of the measurement quantity. Estimation on position error status quantity is achieved, diffusion of position error is inhibited and positioning precision is increased through an indirect method Kalman filtering with feedback compensation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Aluminium alloy hot rolled strip transverse thickness distribution modeling method based on spectral method
ActiveCN103514344AGuaranteed accuracyReduce precisionSpecial data processing applicationsBalanced truncationControl system design
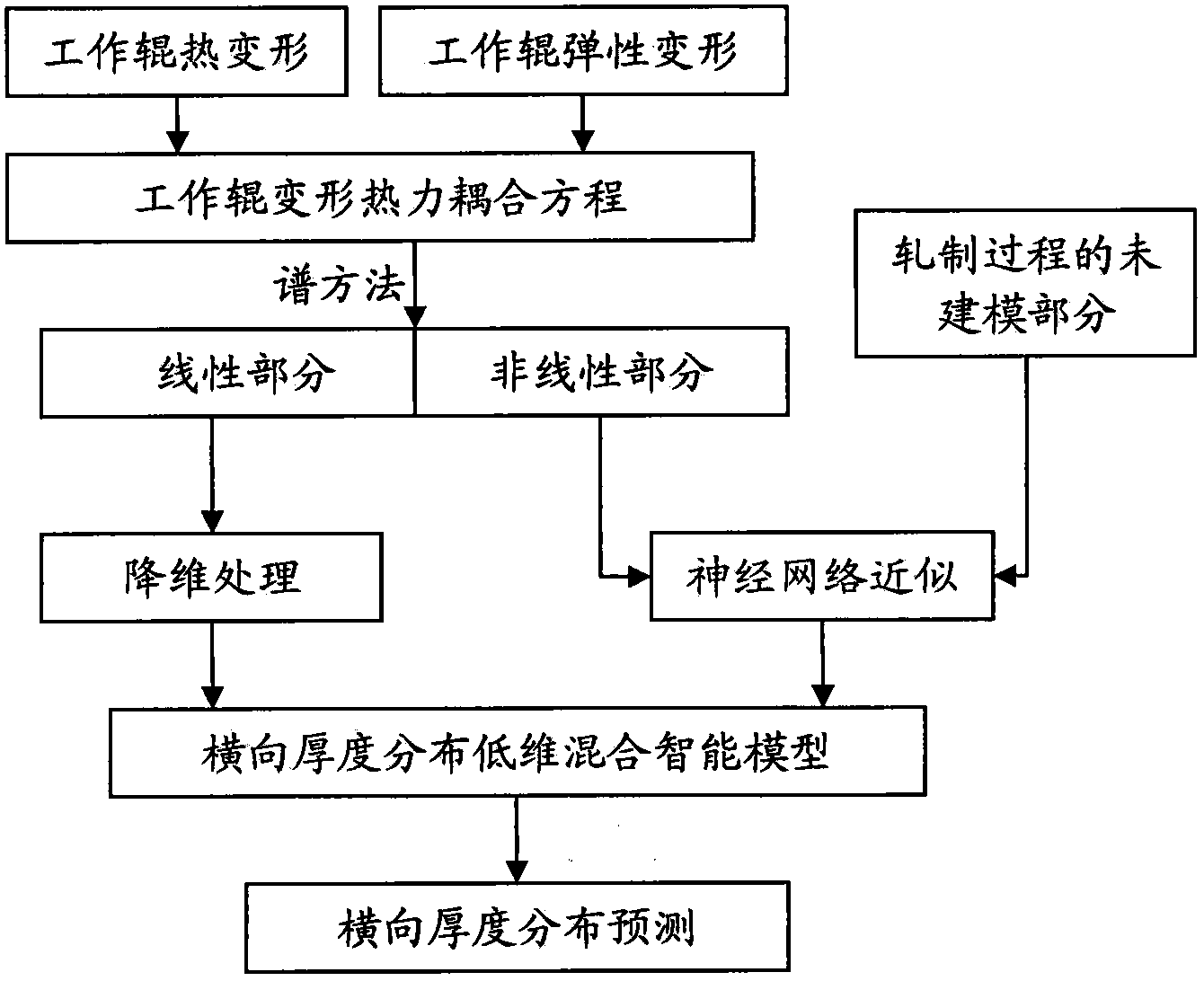
The invention provides an aluminium alloy hot rolled strip transverse thickness distribution modeling method based on a spectral method. The influence of the thermal coupling effect of rolling force, roll bending force and a temperature field in the rolling process on roller deformation and strip transverse thickness distribution is studied, and a partial differential equation of work roller deformation with a thermal coupling effect is obtained; a characteristic function of a space linear operator corresponding to the equation is chosen as a space primary function, and the spectral method is used for conducting low dimensional approximation modeling to obtain a finite dimension nonlinear ordinary differential equation set; the linear part of the ordinary differential equation set is subjected to dimensionality reduction processing by a balanced truncation method or an optimization method, the nonlinear part and the non-modeled part in the approximate rolling process of a neural network are used for obtaining an intelligent hybrid module with the dimension being very low, and therefore the purpose of quickly forecasting strip transverse thickness distribution is achieved. The aluminium alloy hot rolled strip transverse thickness distribution modeling method based on the spectral method has the advantages that from the aspect of the mechanism of the rolling process, little computing amount is used, the model with the dimension being very low is obtained, accordingly, the real-time performance of forecasting of the strip transverse thickness distribution in the rolling process is improved, and a foundation of system optimization and control system design can be laid.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Computation method capable of tracking Davinan equivalence parameter base on total differential equation
ActiveCN101350524AConvenient and accurate fixationEasy to operateAc network voltage adjustmentComplex mathematical operationsMatrix differential equationElectric power system
The present invention provides a method which is used for calculating Thevenin equivalent parameters of power system. The active power and reactive power of a tidal current equation are respectively used for differentiating the Thevenin equivalent parameters so as to form a total differential equation system; the total differential equation system is solved with the Thevenin equivalent parameters as variables, so as to acquire the Thevenin equivalent parameters. The method overcomes the serious error in the existing calculating which assumes the invariable Thevenin equivalent parameters between two time steps, has the characteristics of strong adaptability, simple use and small amount of calculation, and can be used for analysis, calculation and on-site installation of the power system which requires a Thevenin equivalent system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Method, system and apparatus for fault detection
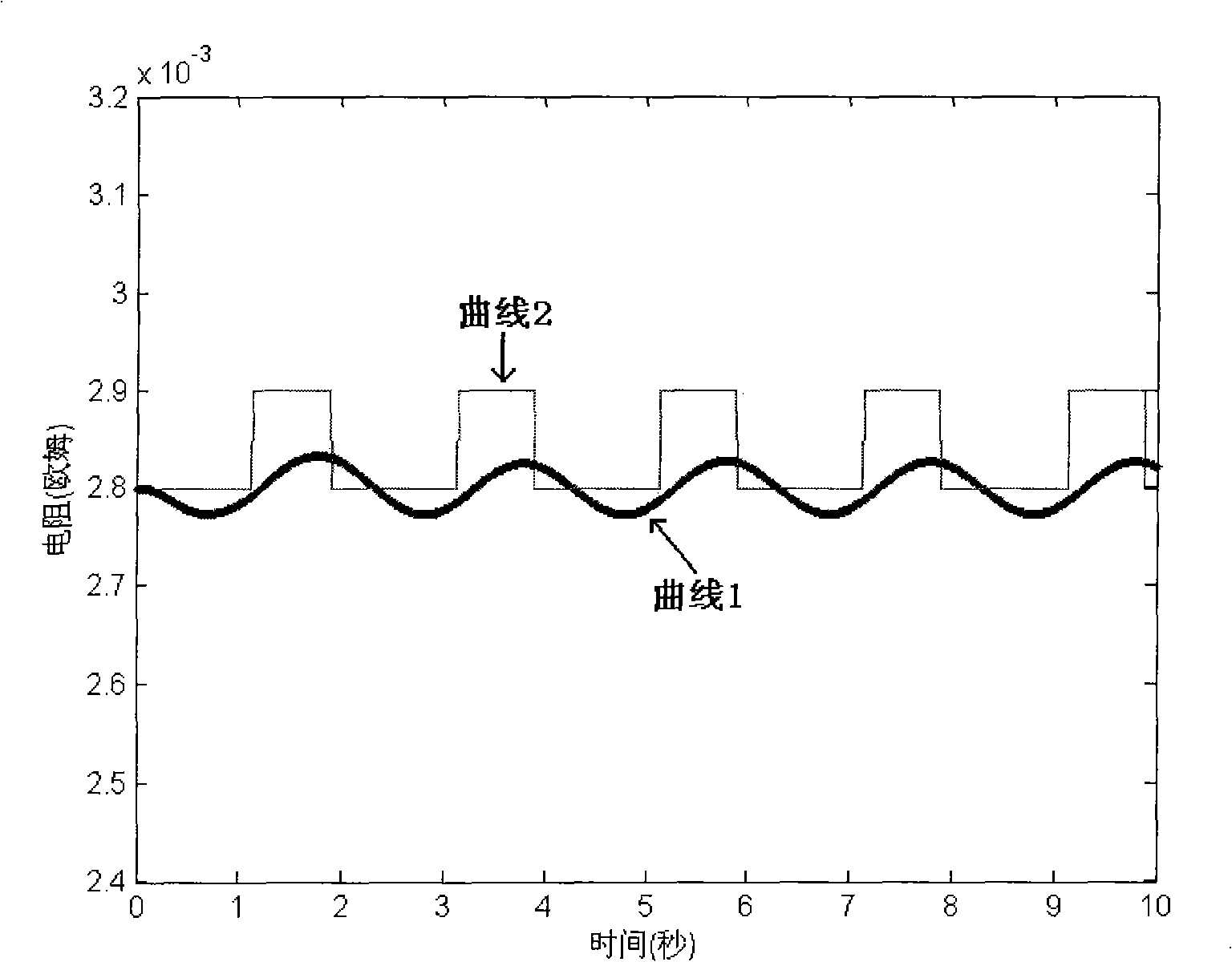
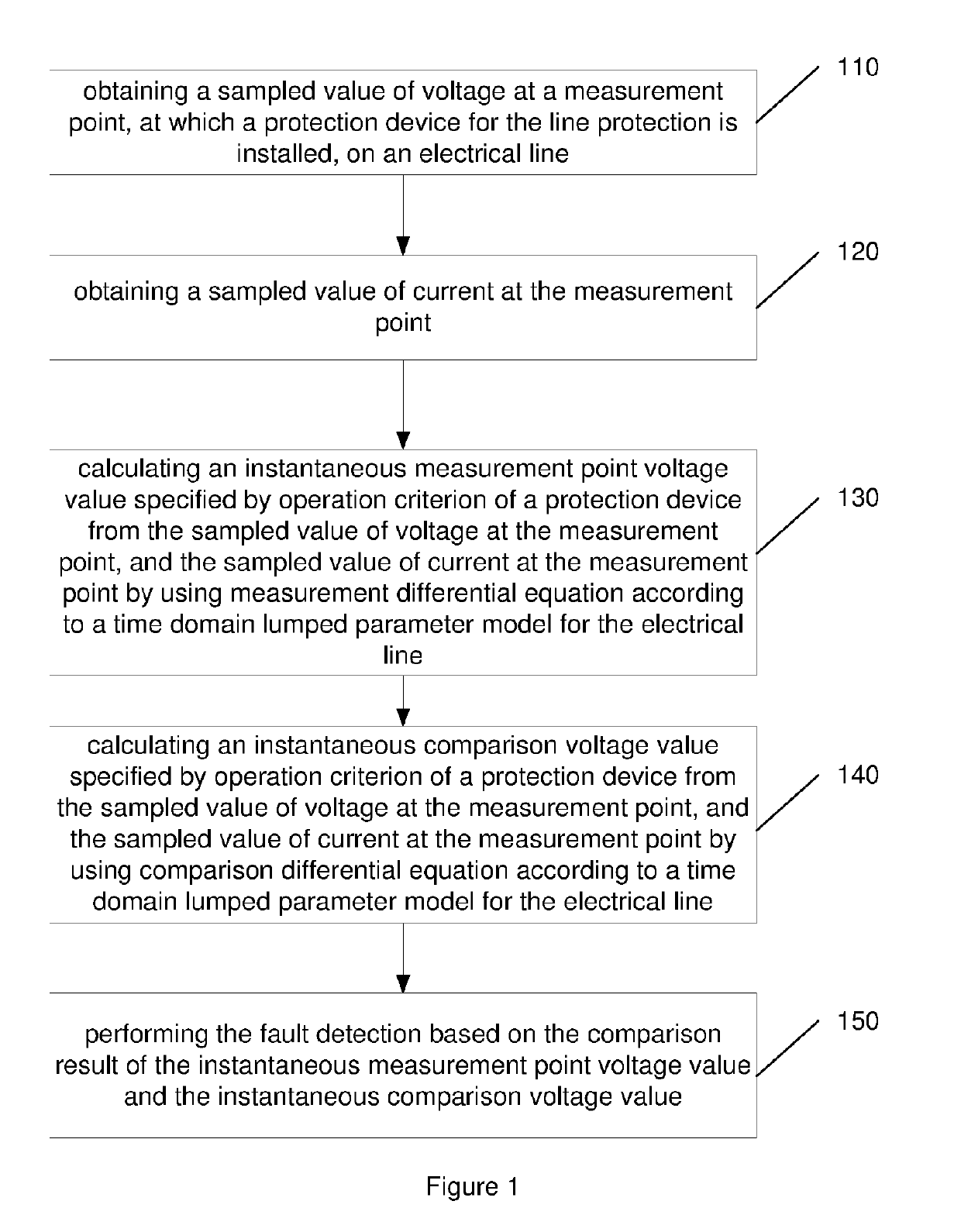
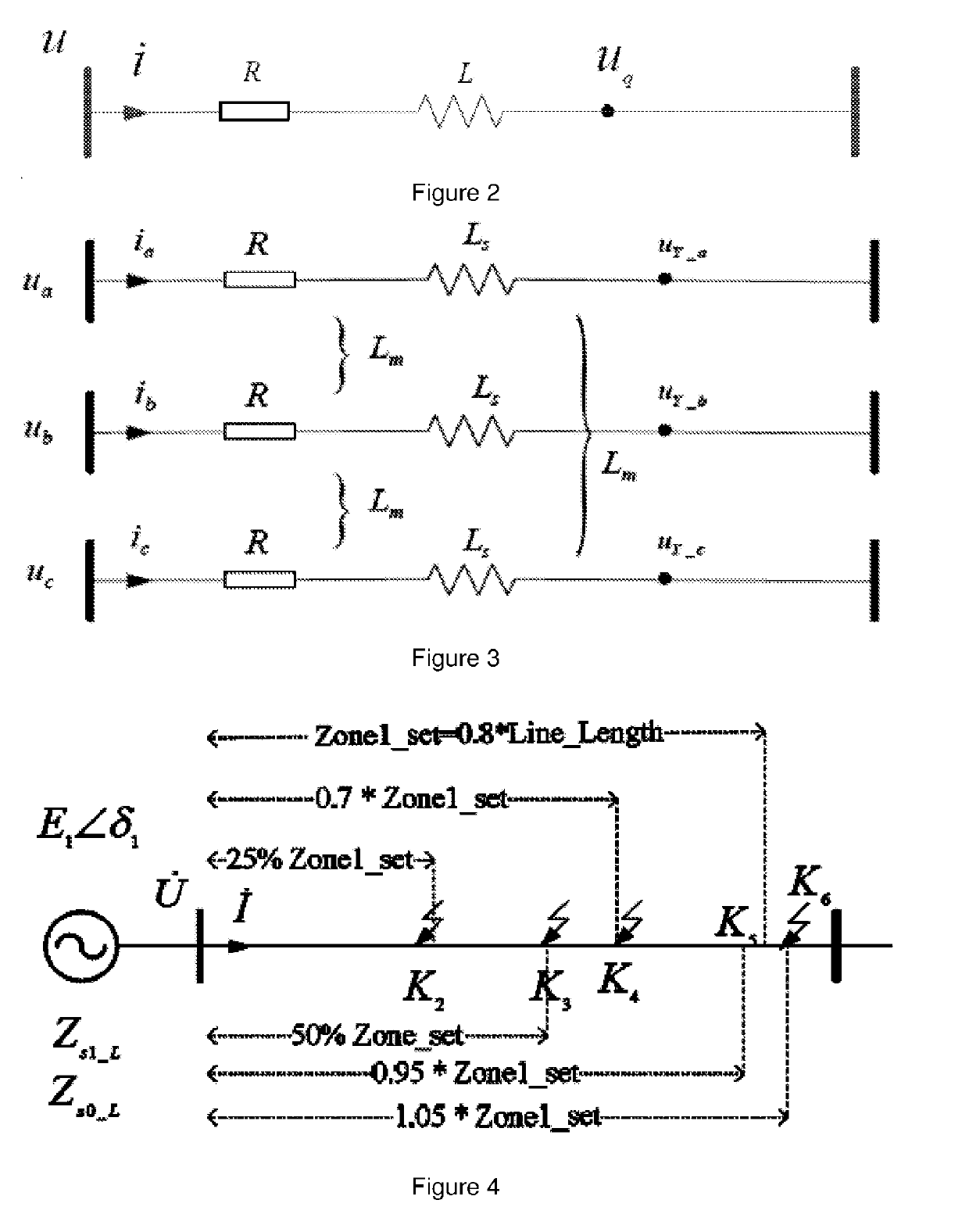
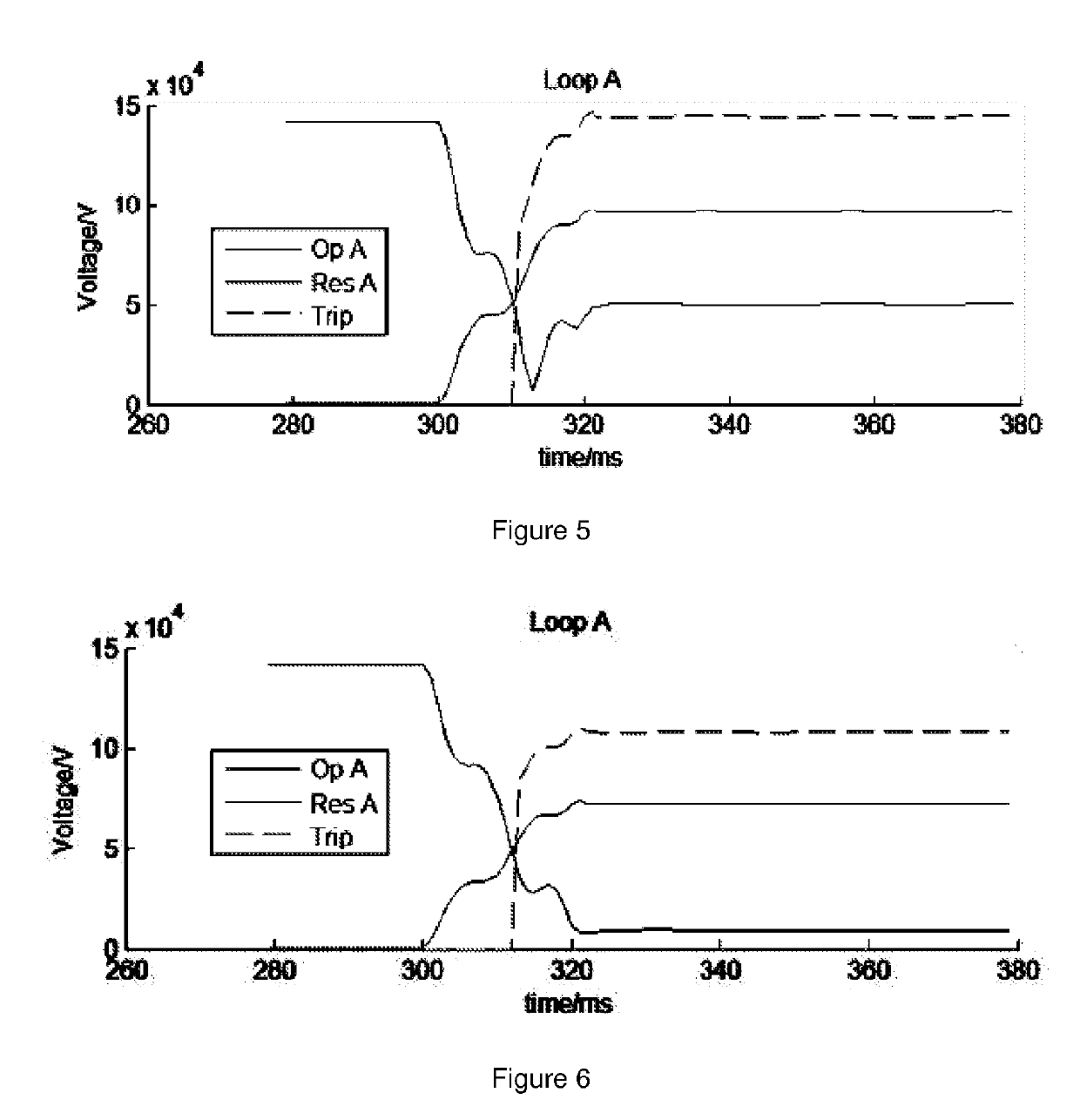
PendingUS20190293705A1Improve abilitiesFault location by conductor typesElectric power transmissionMeasurement point
A method, system and apparatus for fault detection in line protection for a power transmission system. The method includes: obtaining a sampled value of voltage at a measurement point, at which a protection device for the line protection is installed, on an electrical line; obtaining a sampled value of current at the measurement point; calculating an instantaneous measurement point voltage value specified by operation criterion of a protection device from the sampled value of voltage at the measurement point and the sampled value of current at the measurement point by using measurement differential equation according to a time domain lumped parameter model for the electrical line; calculating an instantaneous comparison voltage value specified by operation criterion of a protection device from the sampled value of voltage at the measurement point and the sampled value of current at the measurement point by using comparison differential equation according to a time domain lumped parameter model for the electrical line; and performing the fault detection based on the comparison result of the instantaneous measurement point voltage value and the instantaneous comparison voltage value. The method transfers the distance relay to the format of voltage comparison, calculate the voltage using differential equation instead of vector, and compare the amplitude of calculated voltages. It designs a time-domain distance protection which has strong ability to resist DC components and harmonics including high frequency harmonic and low frequency harmonic.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY LTD
Simplified analysis method for inherent frequency and stability of rotational symmetric structure
ActiveCN106528959ASimplify the analytical analysis processEasy to studyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationDynamic equationPartial differential equation
The invention discloses a simplified analysis method for an inherent frequency and the stability of a rotational symmetric structure. The method comprises the steps of establishing a complete dynamic differential equation of a system, a dynamic differential equation adopting a no-extension hypothesis, and a dynamic differential equation adopting an extension hypothesis: establishing the complete dynamic differential equation of the system; establishing the dynamic differential equation adopting the no-extension hypothesis; establishing the dynamic differential equation adopting the extension hypothesis; introducing coordinate conversion for converting the three dynamic differential equations to a support follow-up coordinate system so as to obtain corresponding three constant coefficient partial differential dynamic equations; performing discrete processing on the three constant coefficient partial differential dynamic equations in the support follow-up coordinate system to obtain three constant differential matrix equations; obtaining an eigenvalue of the complete dynamic differential equation and eigenvalues of two simplified dynamic differential equations; and analyzing a parametrically excited vibration mode characteristic and a dynamic stability change law of the rotational symmetric structure according to the three eigenvalues. According to the method, a specific analysis expression of system eigenvalues can be obtained more clearly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Kinematic Predictor for Articulated Mechanisms
ActiveUS20120303318A1Simple definitionImprove accuracyDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsMatrix differential equationKinematics
A predictor usable for rapid and accurate calculation of joint commands of an articulated mechanism describes relationship between the joints in the form of a differential equation. The predictor solves this differential equation by direct substitution of a power series for each of its variables and the combining of selected sets of coefficients of these power series into linear systems of equations which may be solved to determine power series coefficients to arbitrary order.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
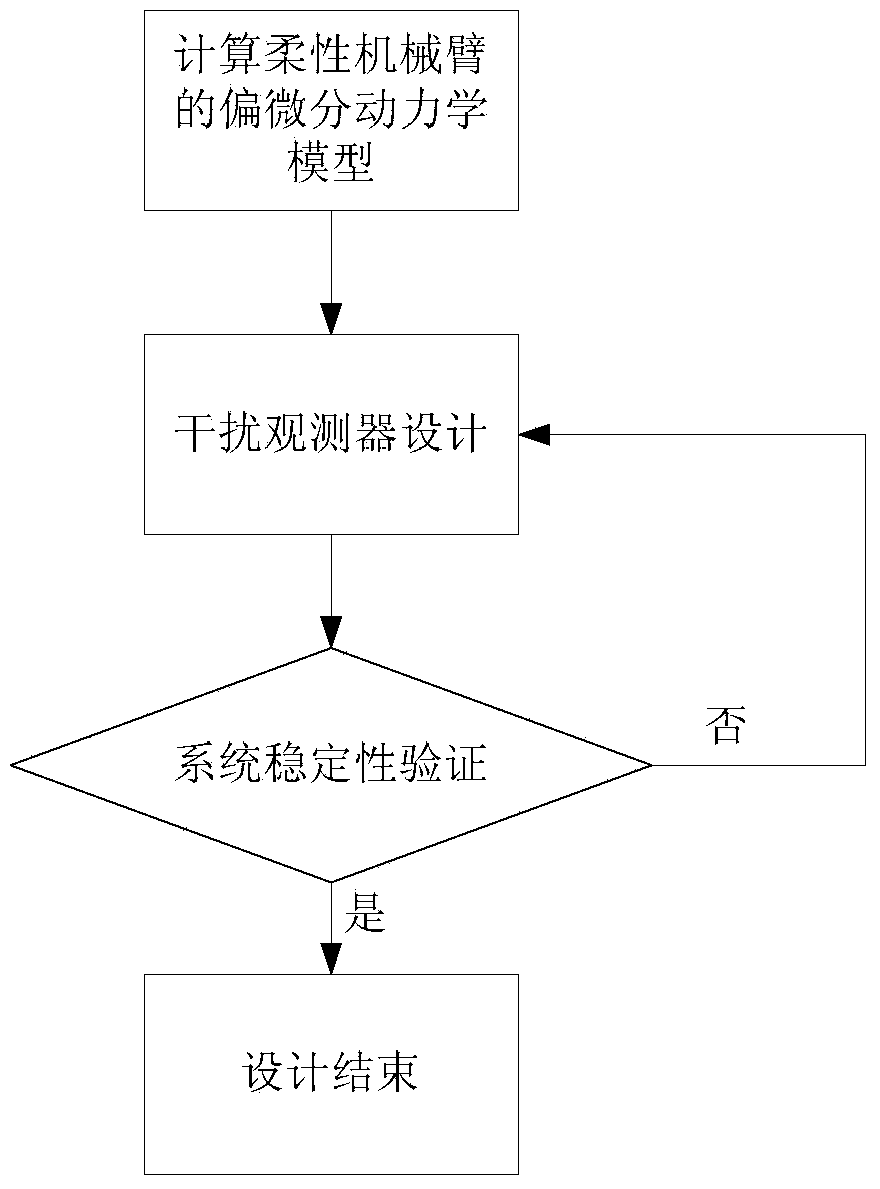
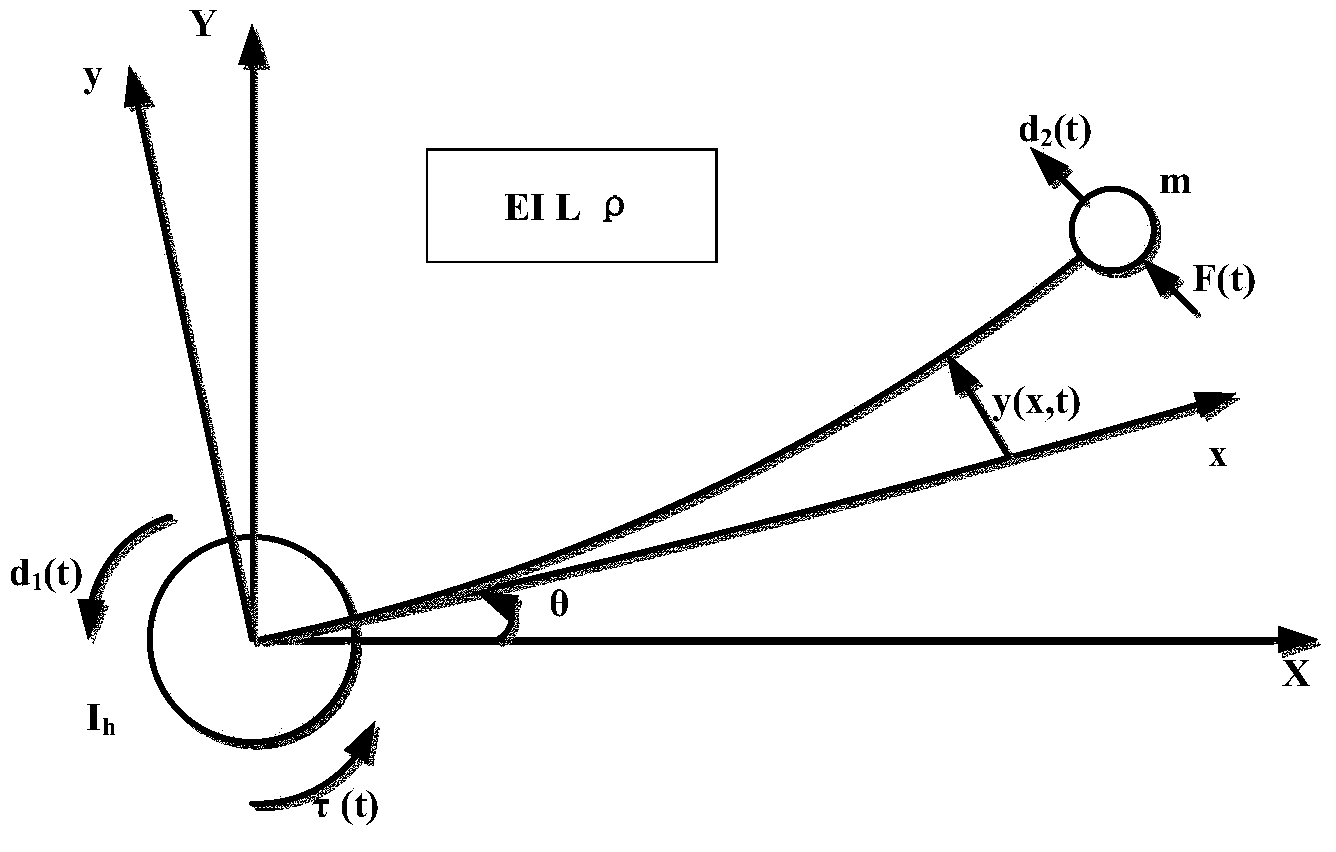
Method for designing flexible mechanical arm disturbance observer based on partial differential equation
ActiveCN104020664ARealize interference observationAdaptive controlMatrix differential equationEngineering
The invention provides a method for designing a flexible mechanical arm disturbance observer based on a partial differential equation. The method includes the four steps that firstly, dynamic modeling of a flexible mechanical arm is conducted; secondly, the disturbance observer is designed; thirdly, stability of the disturbance observer is verified; fourthly, design is finished. According to the method, firstly the Hamilton principle is used, so that a PDE model of a whole system is obtained; then, based on the model, the reasonable disturbance observer is designed so that external unknown disturbance can be estimated; finally, a proper Lyapunov function is designed, so that the designed observer is analyzed and the stability of the observer is verified.
Owner:GUODIAN SCI & TECH RES INST
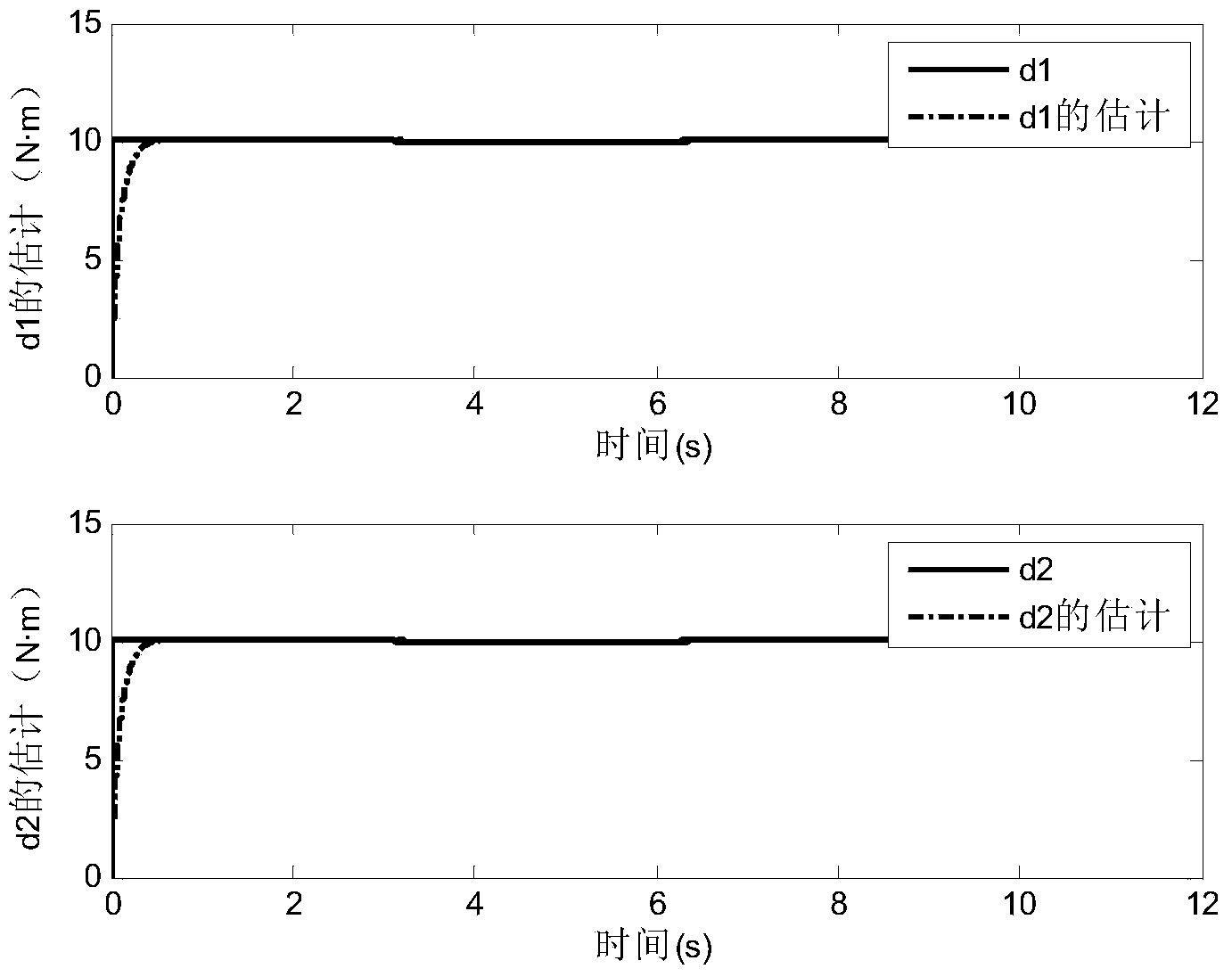
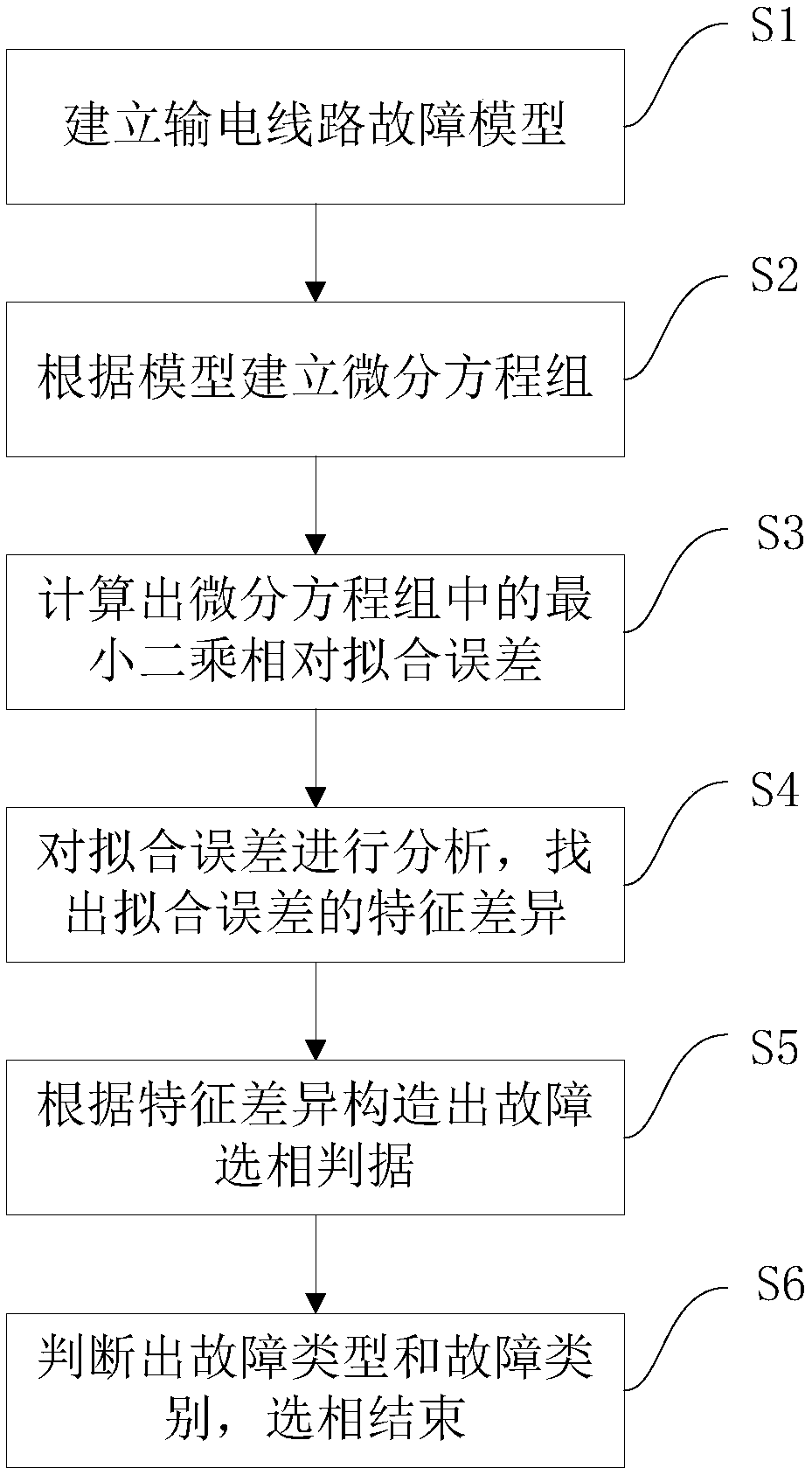
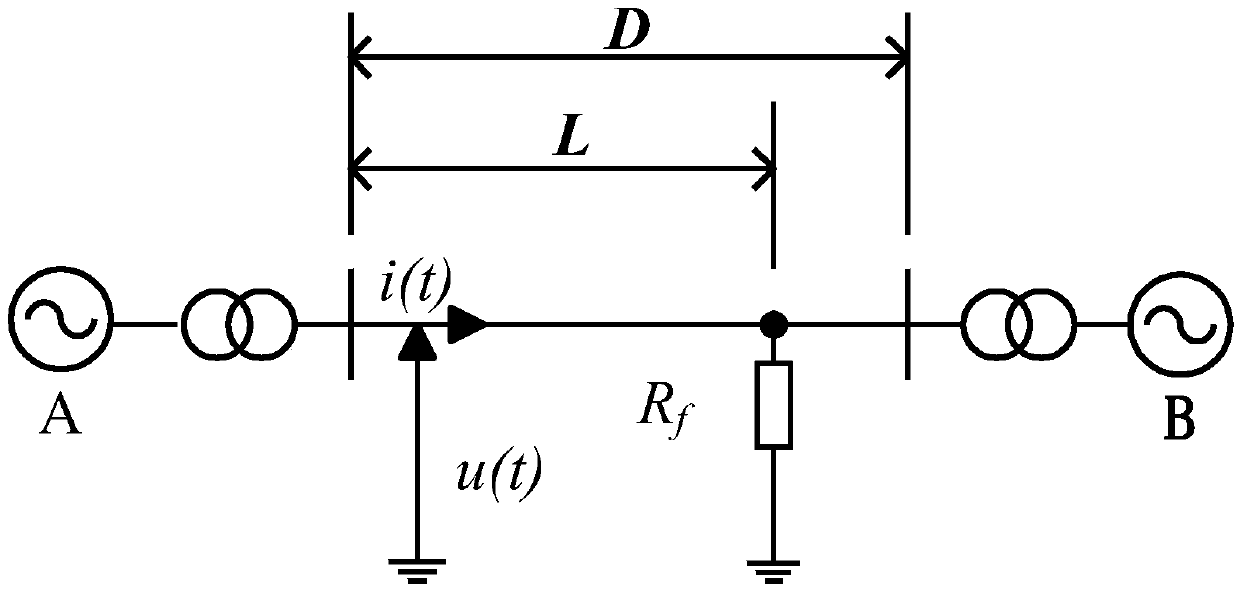
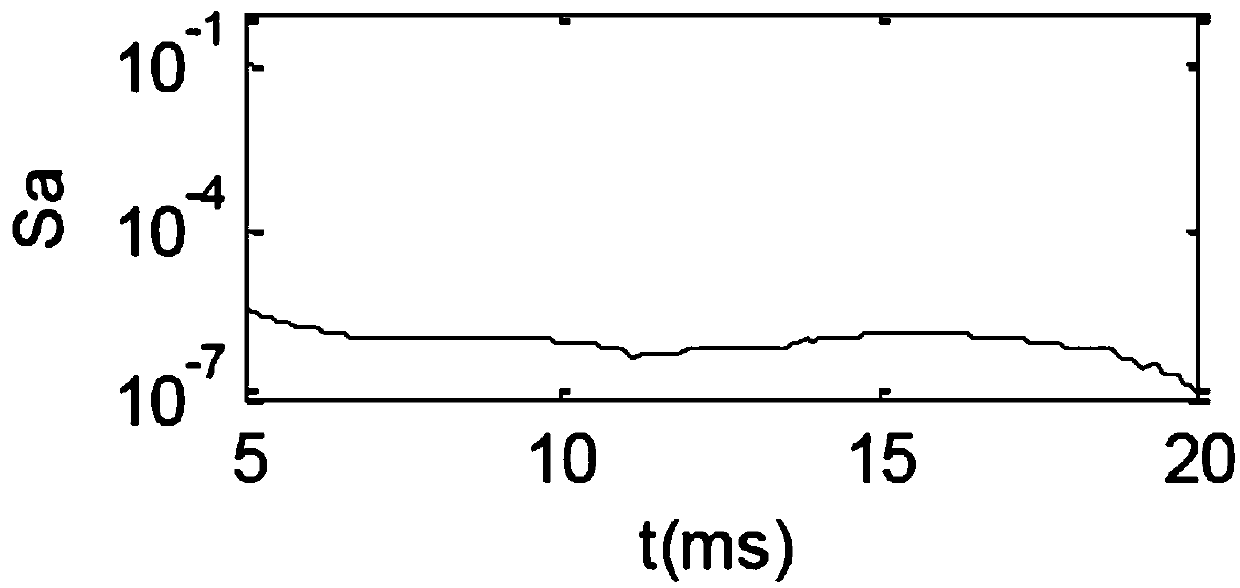
Quick phase selection method based on fitting error of line differential equation algorithm
InactiveCN108646129AQuick photo selectionImprove reliabilityElectrical testingPolyphase network asymmetry measurementsPartial differential equationFault model
The invention discloses a quick phase selection method based on a fitting error of a line differential equation algorithm. The quick phase selection method based on a fitting error of a line differential equation algorithm includes the steps: establishing a fault model for different faults in a power transmission line; establishing power transmission line differential equations; solving the differential equations by means of the least square method, and calculating the least square relative fitting error in the differential equations; analyzing the least square relative fitting error, and finding out the characteristic difference of the least square relative fitting error under different fault types; according to the characteristic difference, constructing fault phase selection criterion for different faults; and determining the fault type and the fault phase, and then ending the phase selection. The quick phase selection method based on a fitting error of a line differential equationalgorithm has the advantages of being able to solve six types of line differential equations corresponding to single phase and interphase faults when the line malfunctions, analyzing the characteristics and the correlation of the least square fitting errors of the line differential equations so as to realize quick fault phase selection, wherein the typical phase selection speed is 5-6ms, being free from influence of the fault position and the transition resistor, being suitable for a weak power supply system, and being high in reliability.
Owner:STATE GRID CHONGQING ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Solving a Solute Lubrication Equation for 3D Droplet Evaporation on a Complicated OLED Bank Structure
InactiveUS20110196657A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationMatrix differential equationDiffusion
The present invention is directed to simulating a droplet of a fluid, and may be embodied in a system, method or a computer-readable medium encoded with instructions for a processor to carry out such simulation. The present invention may evaluate differential equations, which may represent an approximation of behavior over time of the droplet on a non-flat substrate. The behavior that the differential equations represent may include diffusion in the droplet and evaporation of the droplet.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
High accuracy surface modeling method based on big data
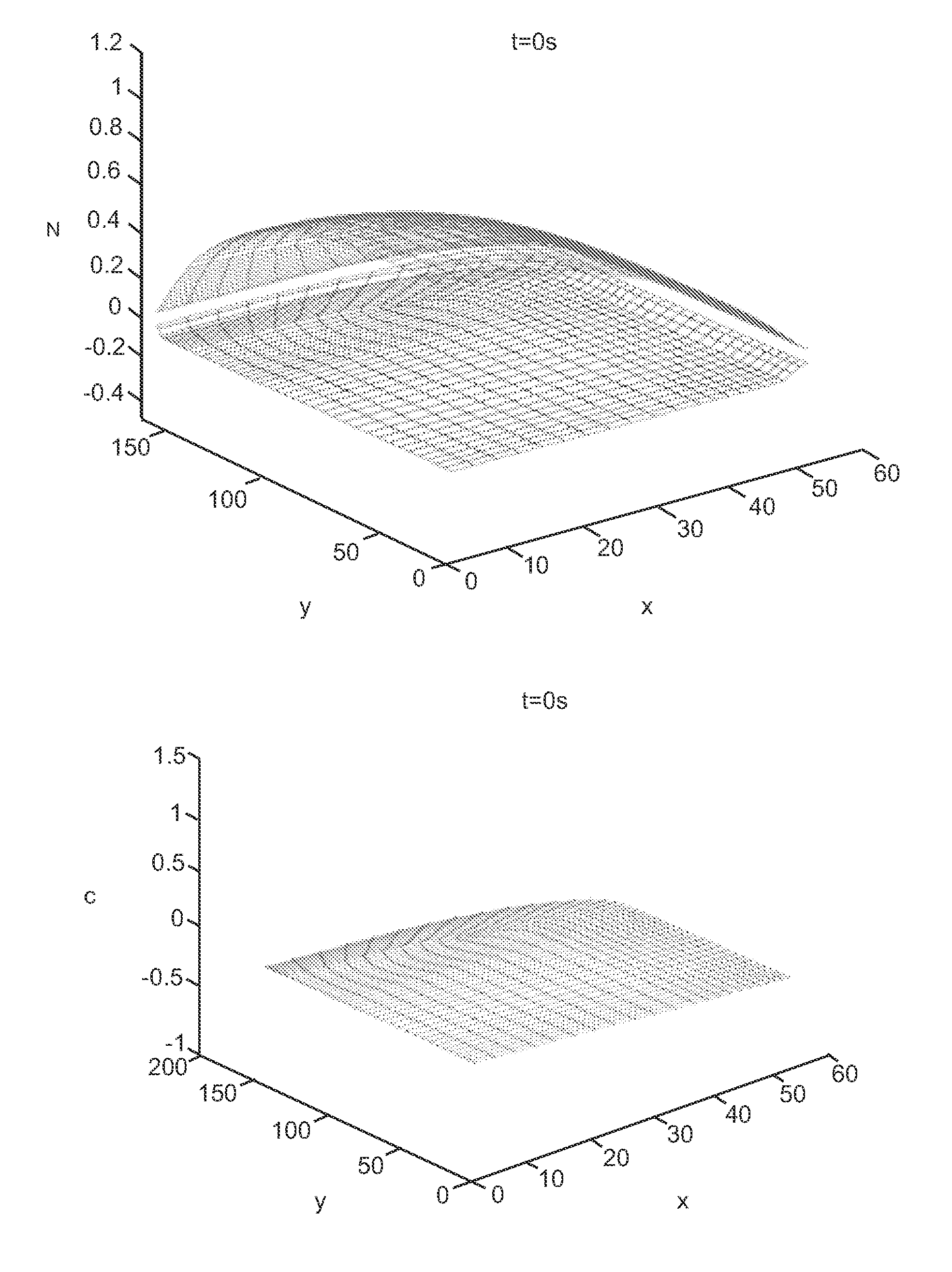
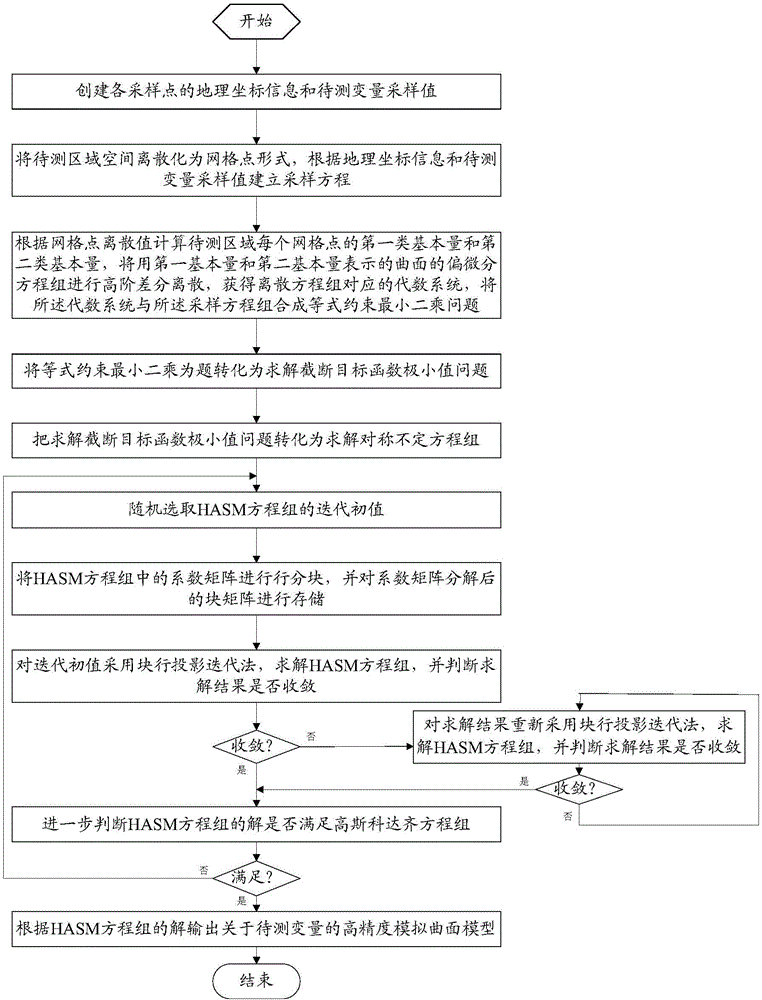
InactiveCN106683185AReduce storage requirementsReduce computing time3D modellingDecompositionDiscretization
The invention relates to a high accuracy surface modeling method based on big data. The method comprises the following steps: creating geographic coordinate information and to-be-tested variable sampling values of all sampling points; turning a to-be-tested regional space into a grid point form through discretization, and establishing a sampling equation; conducting high order difference discretization on a partial differential equation set of a surface, obtaining a corresponding algebraic system, combining the algebraic system and the sampling equation to form an equality constrain least squares problem, converting the problem into a solve cross cutting object function minimum value problem, and then converting the minimum value problem into a solve symmetry indeterminate equation set; randomly selecting iteration initial values; blocking a coefficient matrix, and storing the block matrixes after decomposition; solving an HASM equation set through a block line projection iterative method, and determining whether a solving result is convergent; determining whether a solution meets demands of a Gauss and C.odazzi equation set; and outputting a high accuracy simulation surface model. Large-scale problems can be solved, the needed storage space is small, and defects of HASM for solving large-scale problems are prevented.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Delayed power system stability analysis method based on low-order EIGD (Explicitly Infinitesimal Generator Discretization)
ActiveCN108647906AFully consider the impact of time lagImprove computing efficiencyResourcesComplex mathematical operationsElectric power systemDiscretization
The invention discloses a delayed power system stability analysis method based on low-order EIGD (Explicitly Infinitesimal Generator Discretization). The method comprises the steps of establishing a delayed power system model for a power system, and linearizing the delayed power system model, that is, expressing the delayed power system model through a delayed differential equation; re-ranking state variables of the delayed power system in the delayed differential equation, and dividing the state variables into delay-independent state variables and delay-dependent state variables; transformingthe delayed differential equation into an ordinary differential equation by use of an infinitesimal generator, thereby equivalently transforming a characteristic equation of the delayed power systeminto an ordinary characteristic equation, and further transforming calculation for characteristic values of the delayed power system into calculation for characteristic values of the infinitesimal generator. According to the delayed power system stability analysis method based on the low-order EIGD, through re-ranking of the state variable of the system, discretization of the delay-independent state variables is removed, the number of dimensions of a discretization matrix is reduced, and therefore, the calculated amount for calculation of key characteristic values of a DCPPS (Delayed Cyber-Physical Power System) is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for realizing perfectly matched layer through auxiliary differential equation in plasma
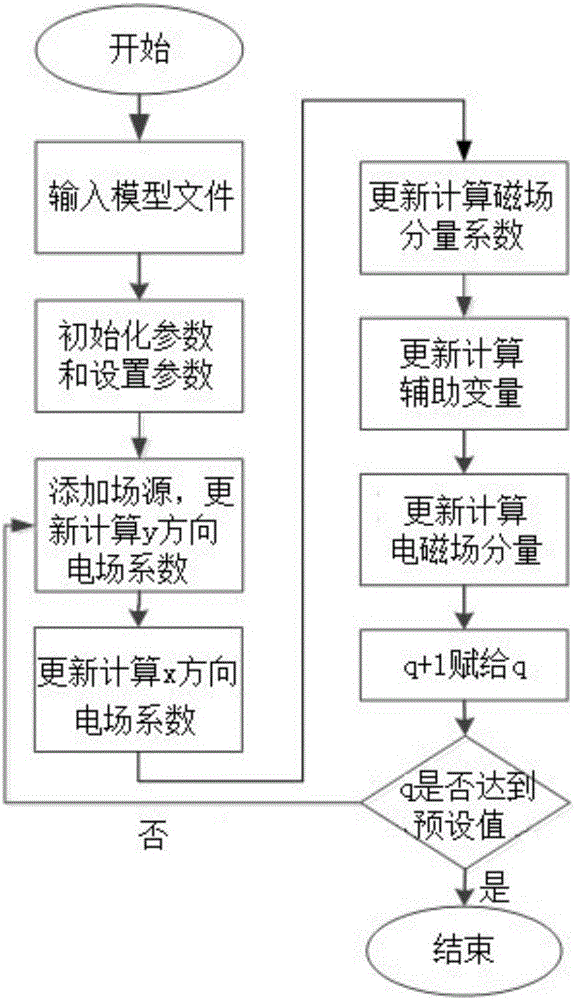
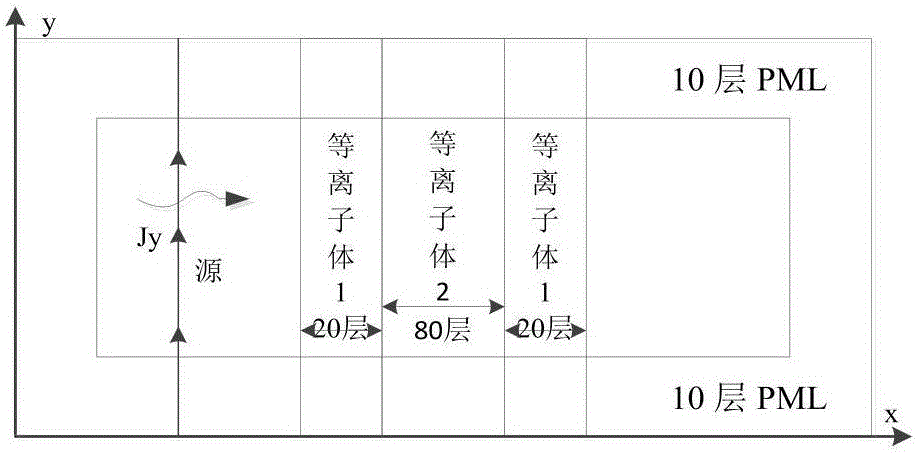
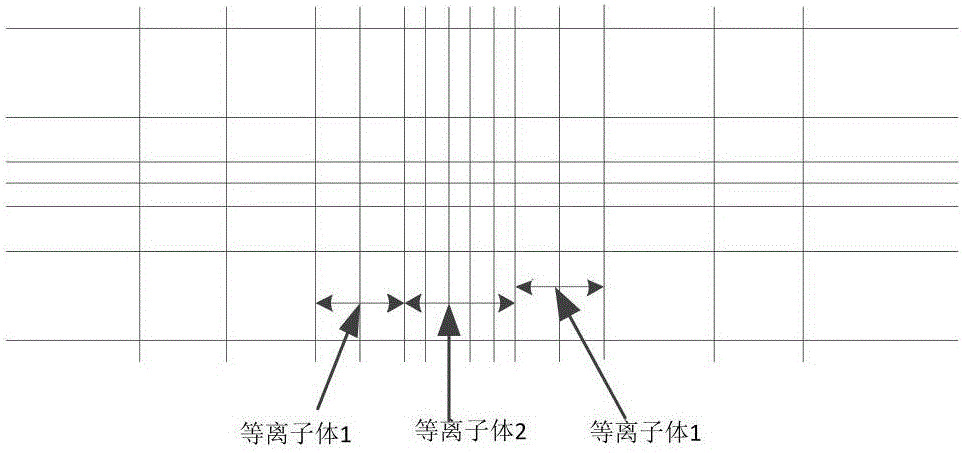
ActiveCN105808504ATime step sizeSimple calculationComplex mathematical operationsElectromagnetic fieldAbsorption effect
The invention discloses a method for realizing a perfectly matched layer through an auxiliary differential equation in plasma. The method comprises the following specific steps: 1, inputting a model file; 2, performing initialization and setting a parameter of the model file in the step 1; 3, calculating an electric field component coefficient E<y><q> by using the parameter in the step 2; 4, calculating an electric field component coefficient E<x><q> by using the parameter in the step 2; 5, calculating a magnetic field component coefficient H<z><q> by using the electric field component coefficients obtained in the step 3 and the step 4; 6, calculating intermediate variable coefficients psi<x><q> and psi<y><q> by using the electric field component coefficients in the step 3 and the step 4; 7, updating and calculating an auxiliary variable of an electromagnetic field component coefficient in a whole computational domain; 8, updating and calculating an electromagnetic field component of an observation point; and 9, assigning q+1 to q, judging whether q is up to a preset value or not, returning the step 3 if q is not up to the preset value, and ending if q is up to the preset value. The method has the advantages of low calculation speed, low memory consumption, and very good absorption effects on low-frequency and evanescent waves.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Elastic soft robot kinematical modeling method based on constant curvature assumption
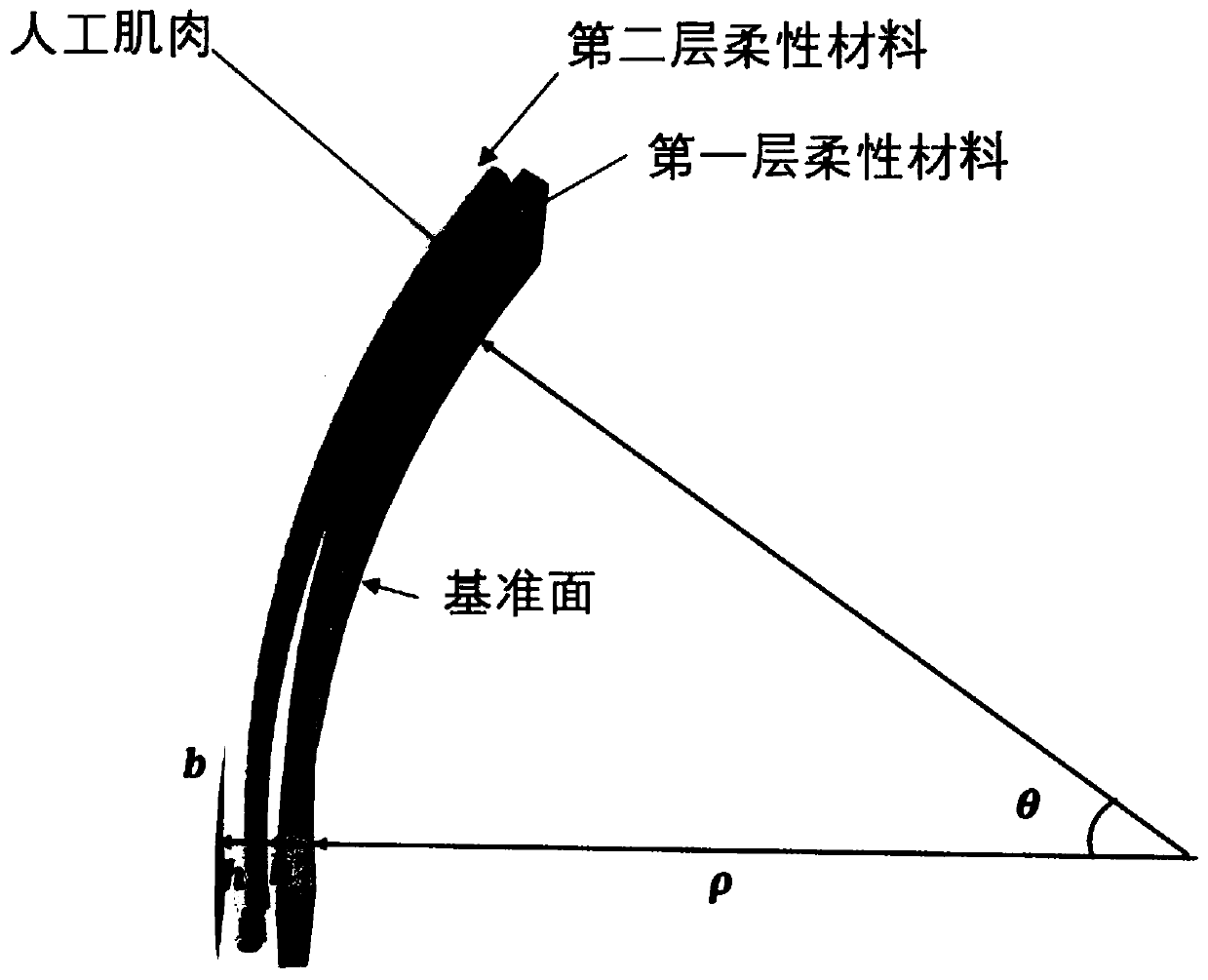
ActiveCN110181506AAchieving Shape PredictionAvoid damageProgramme-controlled manipulatorWorking temperatureEngineering
The invention provides an elastic soft robot kinematical modeling method based on a constant curvature assumption, and belongs to the field of robot kinematical modeling. According to the method, by means of the Kirchhoff bar theory and the constant curvature assumption, firstly, equations of force, displacement and control quantities corresponding to artificial muscles implanted into a flexible material of an elastic soft robot are established; then the actual length of the elastic soft robot at the working temperature is calculated, and mechanical parameters of the flexible material are usedfor calculation; and finally, the section inertia moment about a neutral surface is calculated, the curvature radius and the angle of the elastic soft robot at the working temperature are calculated,the true shape of the elastic soft robot at the working temperature is obtained, and kinematical modeling is completed. According to the method, the modeling process is simple and convenient, the influences of elastic deformation of the elastic soft robot are considered, numerical calculation of partial differential equations is not involved, and the relationship between the shape of the elasticsoft robot and the parameters of the artificial muscle in the elastic soft robot can be rapidly established.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
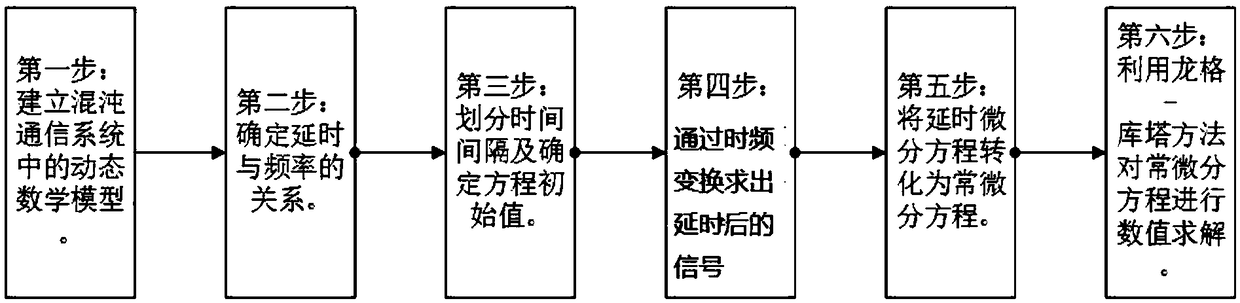
Analysis method of similar frequency-dependent delay electro-optic phase chaotic dynamics
InactiveCN108768609AUser identity/authority verificationDesign optimisation/simulationRunge–Kutta methodMatrix differential equation
The invention discloses an analysis method of similar frequency-dependent delay electro-optic phase chaotic dynamics. The method is executed according to the following steps: step 1, building a dynamic mathematical model in a chaotic communication system; step 2, determining a relation between delay and frequency; step 3, dividing time interval and determining an equation initial value; step 4, solving a delay signal of each moment in one period of time after delay through Fourier time-frequency transformation; step 5, converting a delay differential equation into an ordinary differential equation; step 6, performing numerical solution for the ordinary differential equation of the step 5 through a Runge-Kutta method. The method provided by the invention can accurately solve a differential-integral equation having frequency-dependent delay, and can accurately analyze chaotic dynamics and chaotic communication having frequency-dependent delay feedback.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
One-dimension left-handed material Crank-Nicolson perfectly matched layer realizing algorithm based on auxiliary differential equation
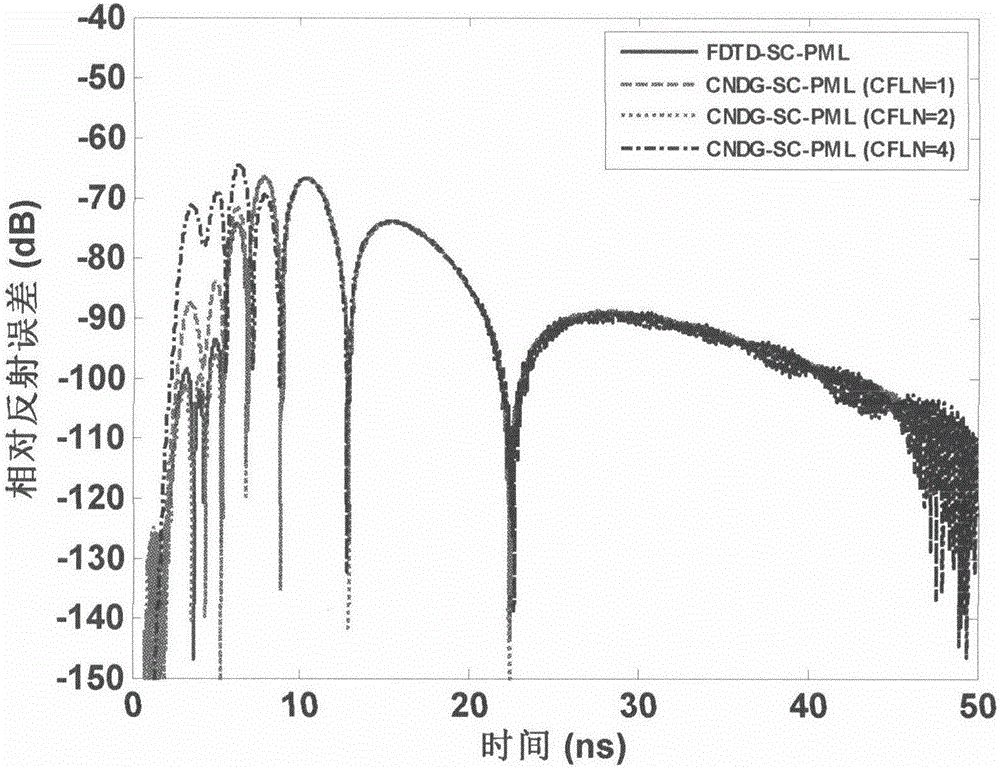
InactiveCN105550451AElimination of Second Order Differential EquationsReduce complexityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDiscretizationExact differential equation
The invention relates to a one-dimension left-handed material Crank-Nicolson perfectly matched layer realizing algorithm based on an auxiliary differential equation, and belongs to the technical field of numerical simulation. The method aims at reducing the left-handed material FDTD (Finite-Different Time-Domain) computational domain, and simulating a computer finite memory space into an infinite space. The one-dimension left-handed material Crank-Nicolson perfectly matched layer realizing algorithm has the technical characteristics that in a process of converting a plurality of stretched coordinate variables from the frequency domain to the time domain, the second-order differential in the stretched variables is eliminated by an improved auxiliary differential equation method, so that the number of the introduced auxiliary variables is obviously lowered, and a memory is optimized; then, a time domain Maxwell equation is subjected to discretization by a Crank-Nicolson time domain finite differential method; an explicit iteration equation of an electric field is deduced out; and finally, a value of an electromagnetic field component is obtained. The one-dimension left-handed material Crank-Nicolson perfectly matched layer realizing algorithm has the advantages that the unconditional stability is realized; the electromagnetic calculation is accelerated; and the memory is saved.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
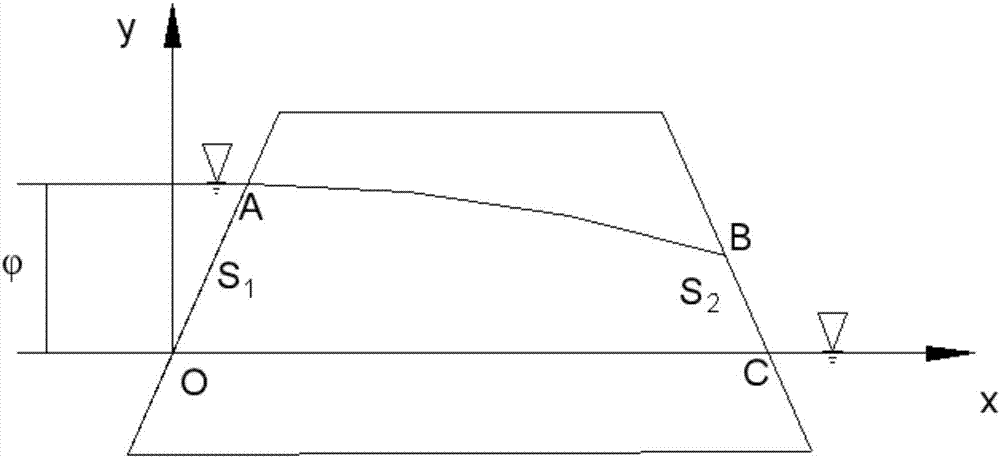
Seepage solving method based on conditions of seepage boundaries and differential equation of motion
The invention provides a seepage solving method based on conditions of seepage boundaries and a differential equation of motion. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: step 1, accurately measuring macroscopic geometric features of a study object, and establishing a corresponding geometric feature description equation; step 2, studying seepage coefficient distribution features of the study object, and establishing seepage coefficient distribution equations of the study object in a study area; step 3, studying boundary condition flow and water head features of the study object, and establishing a corresponding boundary condition flow and water head expression equation; and step 4, selecting the water head expression equation to enable the same to meet the corresponding differential equation of motion and the flow and water head boundary condition equations, and carrying out solving for each corresponding constant coefficient. The provision of the method has a promoting action on seepage movement study and application of various built structures and natural bodies such as dams, slopes, subgrades, tunnels, roadways and culverts.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
A safety design method for water tank used in airtightness test of aeroengine casing
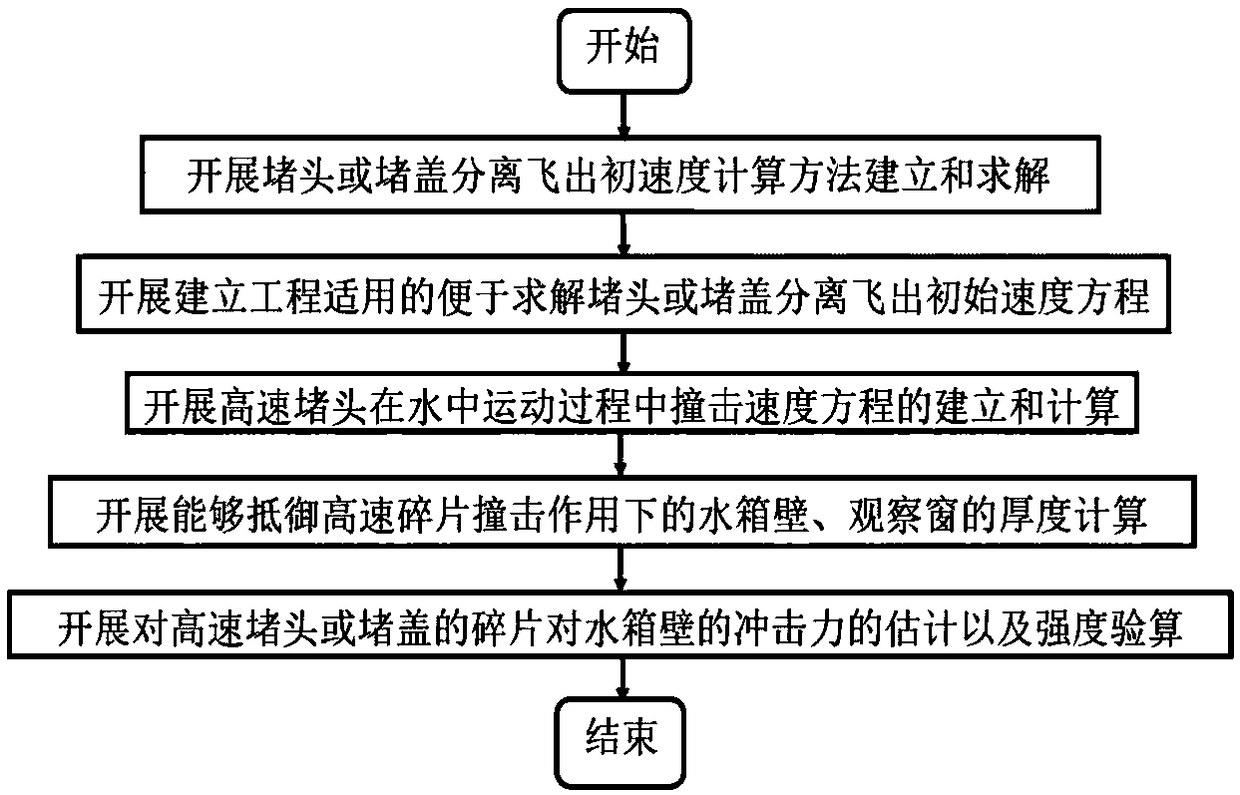
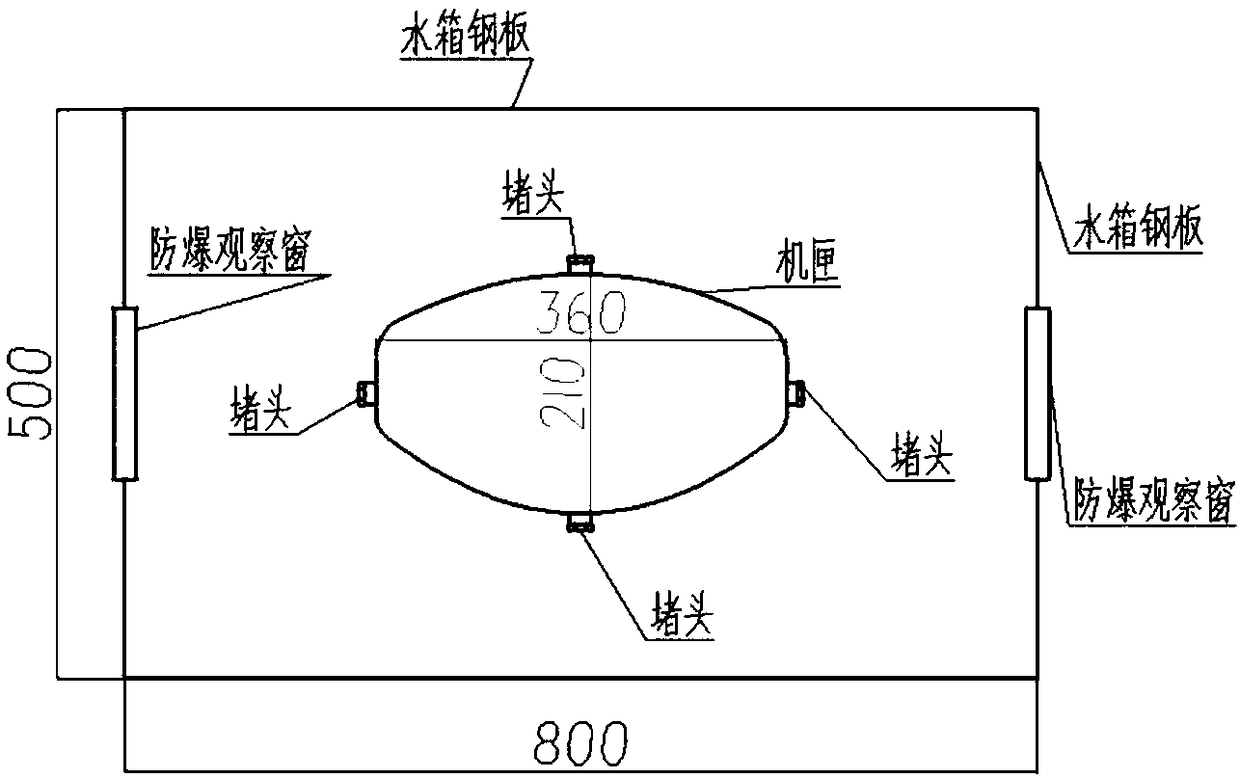
ActiveCN109255140AClear thinkingAccurate and efficient solutionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAviationAngular velocity
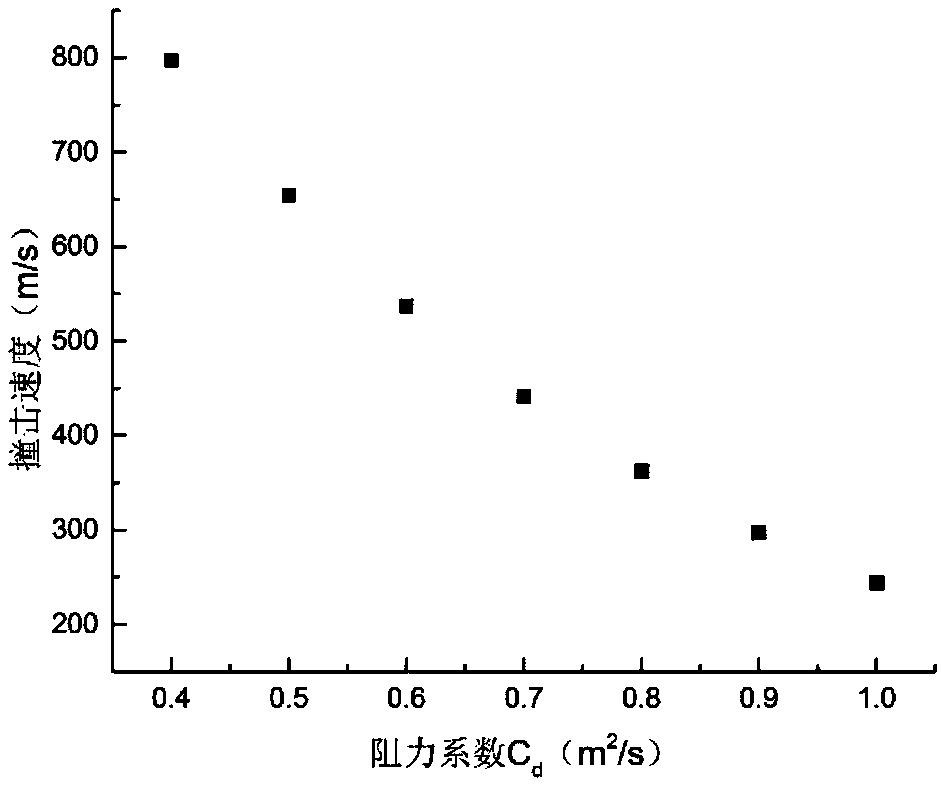
A safety design method for water tank used in airtightness test of aeroengine casing is disclosed. Based on the relevant technical parameters of the water tank and the machine case with specific requirements, By using the equations of motion and gas state, combining with dimensionless time and pressure and initial conditions, the second order differential equations of dimensionless pressure and flight angle of plug fracture are established, the differential equations can be used to calculate different internal pressures, the initial and angular velocities of the plug fragment as it exits at the debris size, and then the mechanics equation is established by using the fluid mechanics principle, a method for calculating the impact velocity of plug considering the resistance coefficient of medium is established, the theorem of kinetic energy and the law of conservation of energy are used to model and estimate the wall thickness of water tank, the impact force of plug fragment and the impact strength of fragment. In order to meet the needs of engineering calculation, a conservative formula for calculating the initial velocity of plug separation is established. Finally, the safety designscheme of water tank for aero-engine casing airtightness test which meets the technical requirements can be obtained.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Two-dimensional vacuum Crank-Nicolson complete matching layer implementation algorithm based on auxiliary differential equation
InactiveCN105760596AReduce computational complexityImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMatrix differential equationTime domain
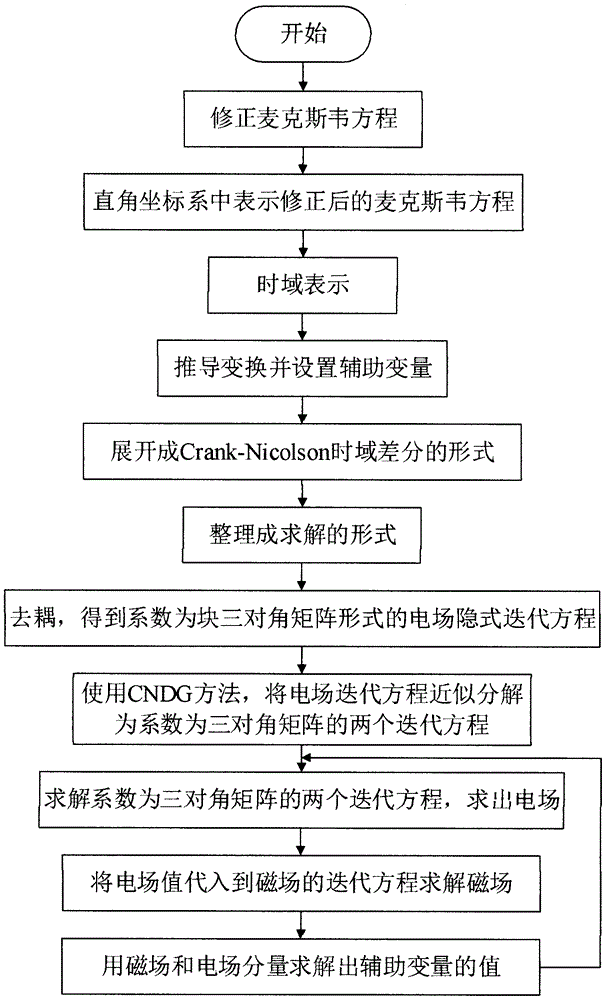
The invention relates to a two-dimensional vacuum Crank-Nicolson complete matching layer implementation algorithm based on an auxiliary differential equation and belongs to the technical field of numerical simulation.The method aims at reducing a vacuum FDTD computational domain and simulating limited memory space of a computer into infinite space.The implementation algorithm is technically characterized in that in the process that a two-dimensional modified Maxwell equation with plural stretching coordinate variables is converted into the time domain finite difference from the frequency domain, a Douglas-Gunn (DG) algorithm is utilized, an iteration equation with coefficients being block tridiagonal matrixes is approximately decomposed into two iteration equations with coefficients being tridiagonal matrixes, wherein the two iteration equations can be efficiently solved, and computational efficiency is obviously improved.The implementation algorithm has the advantages of achieving unconditional stability, increasing the electromagnetic field computational speed and saving memory.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Fast computer algorithms for solving differential equations
InactiveUS20050010381A1Improve “ real time ” performanceImprove performanceComputation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsBoundary valuesAnalog computer
The invention consists of means which computes the numerical solution of an interconnected system of first order differential equations in a single computational pass. The method in effect treats the digital computer as a close approximation to an analog computer whose solutions are instantaneous. This is in contradistinction to the prior art regarding digital computer solutions of first order differential equations that utilize repetitive computational passes over the same time interval to obtain numerical solutions, and which further generates estimates of future values extrapolated from past values of state variables. The invention inserts an auxiliary function existing between, and at, the times marking the computational intervals. The invention rests on three postulates regarding the auxiliary function: a first postulate expands on the Euler formulation of the solution of a differential equation by including the unknown sought after state variable in an expanded Euler formulation. a second postulate introduces an integratable auxiliary equation existing in the computational interval that is bounded by successive sample times. Parameters of the auxiliary functions are determined by using boundary values of the system state equations, a third postulate separates the system auxiliary equation into at least a first and a second part. A first part is the set of independent solutions of each first order differential equation within a system of first order differential equations; a second part incorporates the interconnections between the first order solutions of the state variables, and. a fourth postulate adds to the above by choosing the state equation for each independent first order differential equation, in a system of differential equations, as the integratable auxiliary equation; furthermore choosing the solution of the chosen auxiliary equations as the definite integral of each auxiliary equation; and furthermore obtaining the overall system state via simultaneous solution of the resulting system of algebraic
Owner:MAUDAL INGE
Method, program, and system for solving ordinary differential equation
InactiveUS20110225225A1Reduce the amount of calculationComplex mathematical operationsComputing operations for equation solvingRunge–Kutta methodAlgorithm
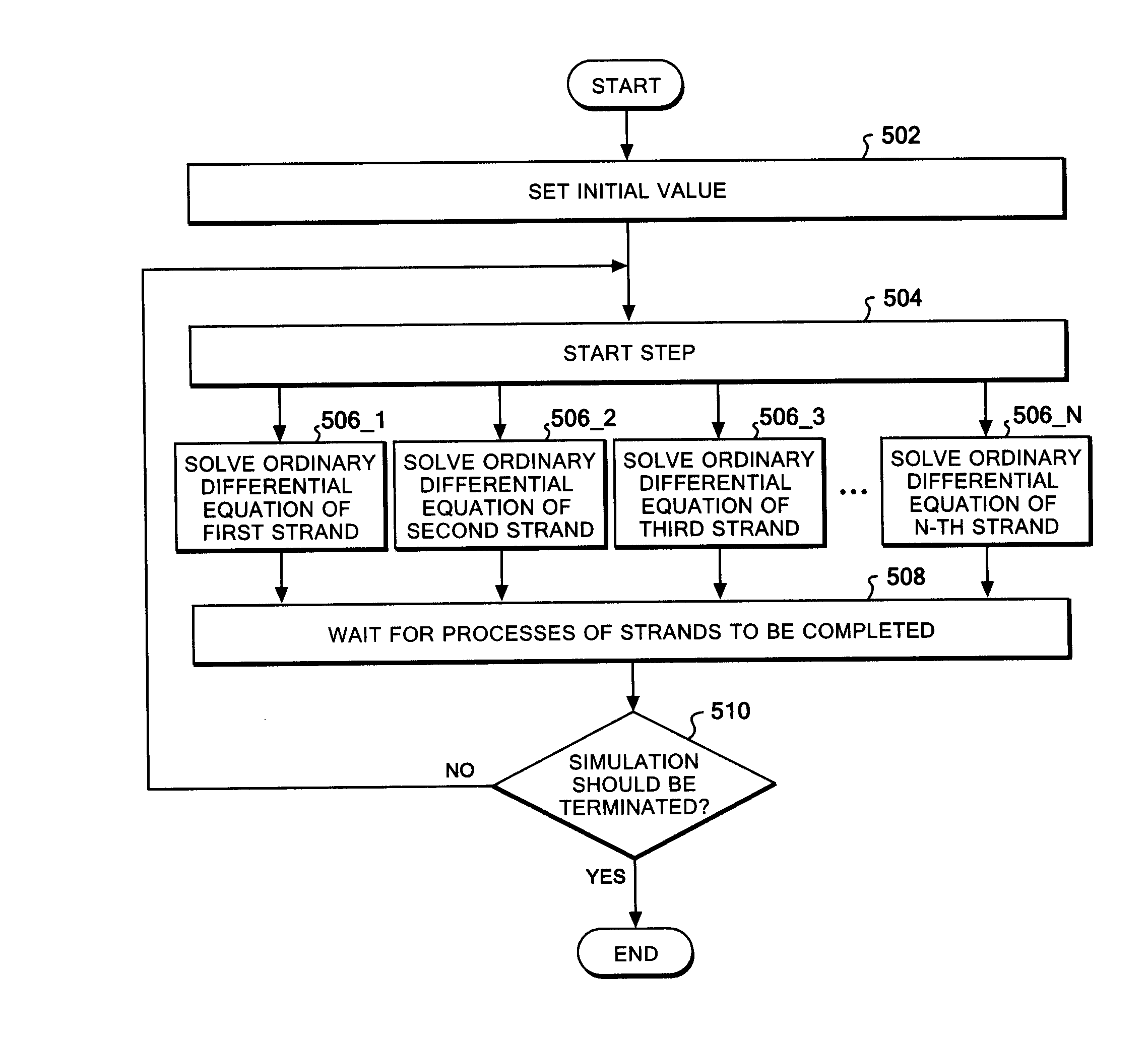
Each ordinary differential equation of simultaneous ordinary differential equations is solved with an embedded Runge-Kutta method. A difference Δ between an N-th order approximation and an (N+1)th order approximation is computed, and it is determined whether the difference is smaller than a predetermined threshold Δ0. If Δ≦Δ0, then a step size is determined using a predetermined computation formula containing Δ0 / Δ, and then the process proceeds to next computation. A strand having an error of Δ>Δ0 is directed to execute recomputation using a step size calculated based on Δ0 / Δ. Then the strand having the error executes recomputation by using a computed interpolated value. When the strand's error becomes smaller than the threshold Δ0 the strand reaches the same time step as the strands computing the other ordinary differential equations having no error. The process thereby proceeds to next computation of the whole simultaneous ordinary differential equations.
Owner:IBM CORP
Gait contour extraction method
InactiveCN105631452AGood localization effectImprove clarityCharacter and pattern recognitionSymbol of a differential operatorGait
Provided is a gait contour extraction method. A level set function is expressed in a spatial-temporal discrete grid. First, an SDF (Sign Distance Function) is constructed, and initialization for zeroing is carried out; then, the numerical solution of a partial differential equation is solved; and finally, re-initialization is carried out through a curvilinear sign distance function, whether the numerical value is stable or not is judged, iteration is stopped if the numerical value is stable, or the process is repeated. The gait contour extraction method has a good localization effect for image boundaries. The image edge and regional information are combined, and the definition and distinctiveness of the gait contour are improved.
Owner:安徽勤勉知识产权代理有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com