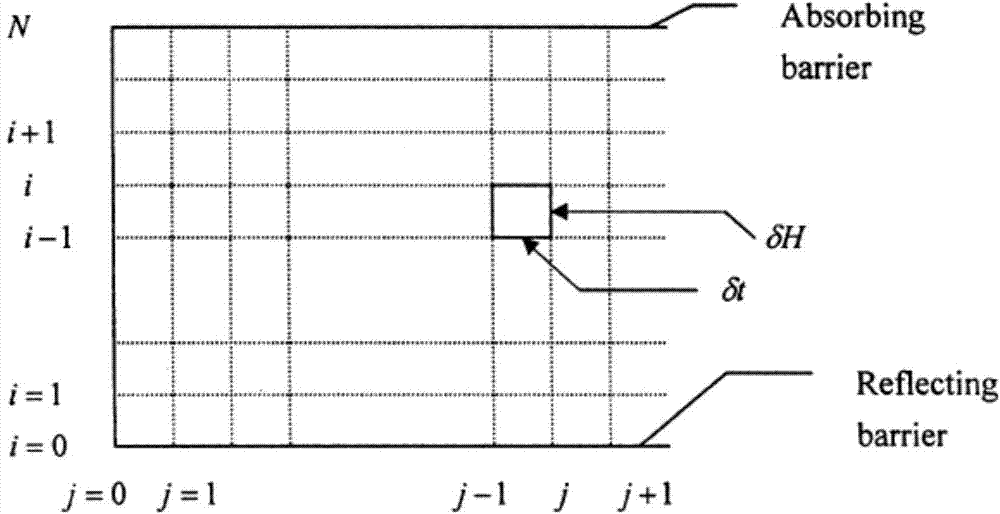
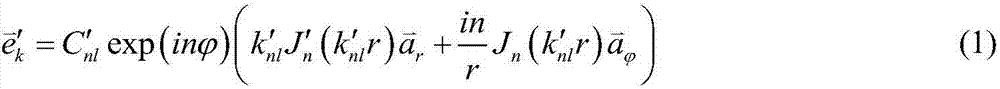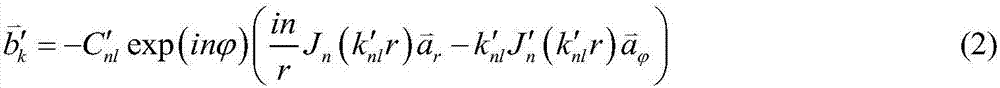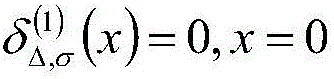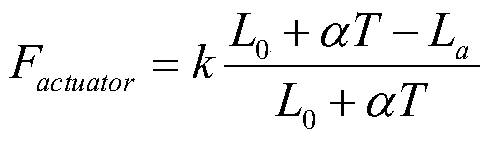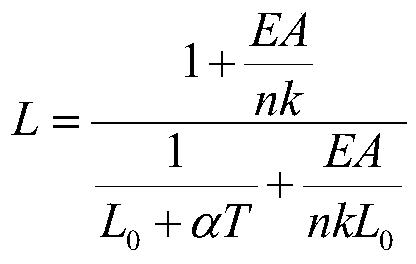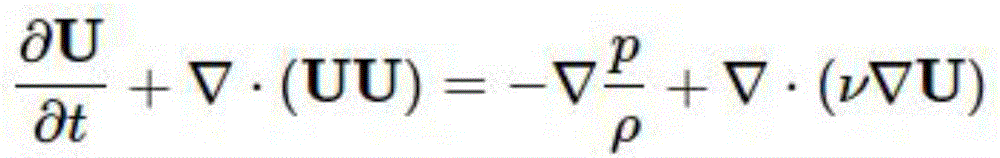Patents
Literature
32 results about "Stochastic partial differential equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stochastic partial differential equations (SPDEs) generalize partial differential equations via random force terms and coefficients, in the same way ordinary stochastic differential equations generalize ordinary differential equations.
Efficient segmentation of piecewise smooth images
InactiveUS20080107351A1Improve performanceImage enhancementImage analysisConvolutionStochastic partial differential equation
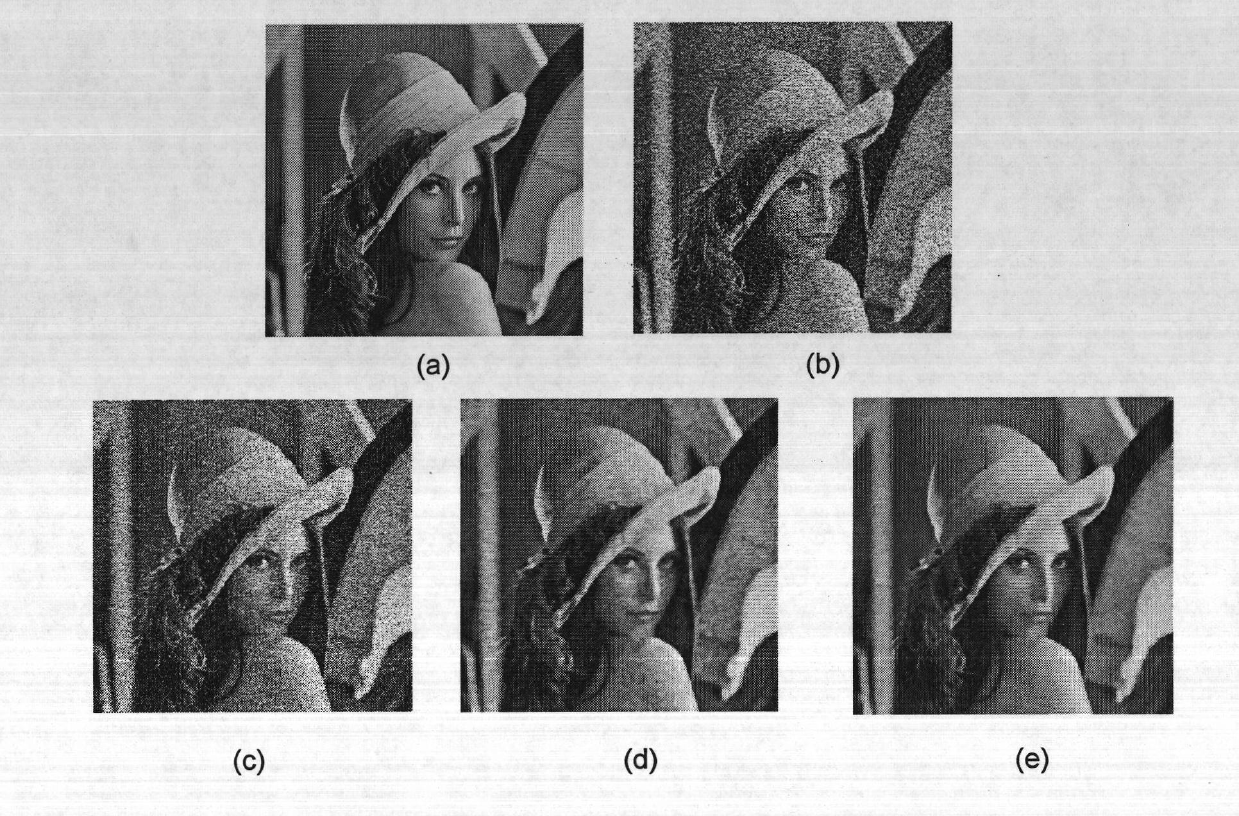
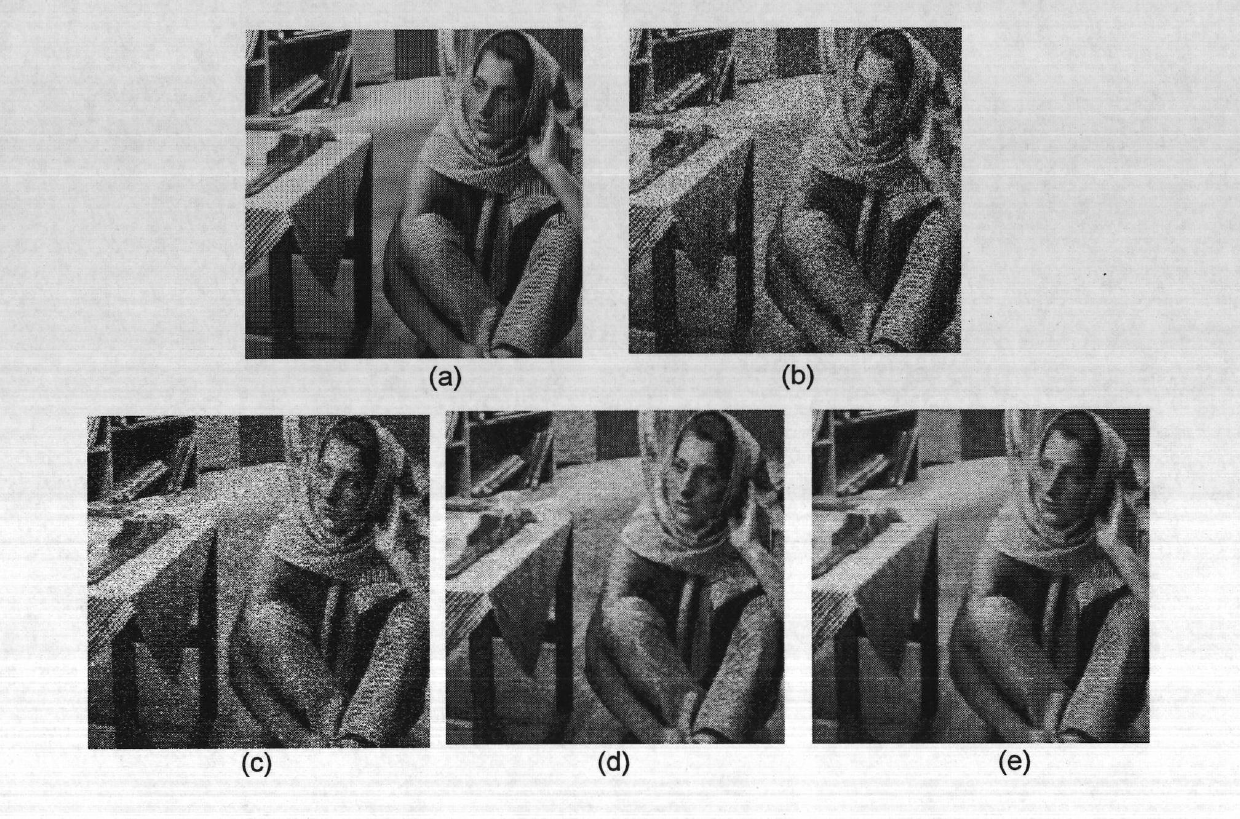
A fast and robust segmentation model for piecewise smooth images is provided. Local statistics in an energy formulation are provided as a functional. The shape gradient of this new functional gives a contour evolution controlled by local averaging of image intensities inside and outside the contour. Fast computation is realized by expressing terms as the result of convolutions implemented via recursive filters. Results are similar to the general Mumford-Shah model but realized faster without having to solve a Poisson partial differential equation at each iteration. Examples are provided. A system to implement segmentation methods is also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
MPM hybrid algorithm applied to numerical simulation of ECR ion source
ActiveCN107577639AAccurate descriptionReduce computational complexityComplex mathematical operationsComputation complexityMaxwell's equations
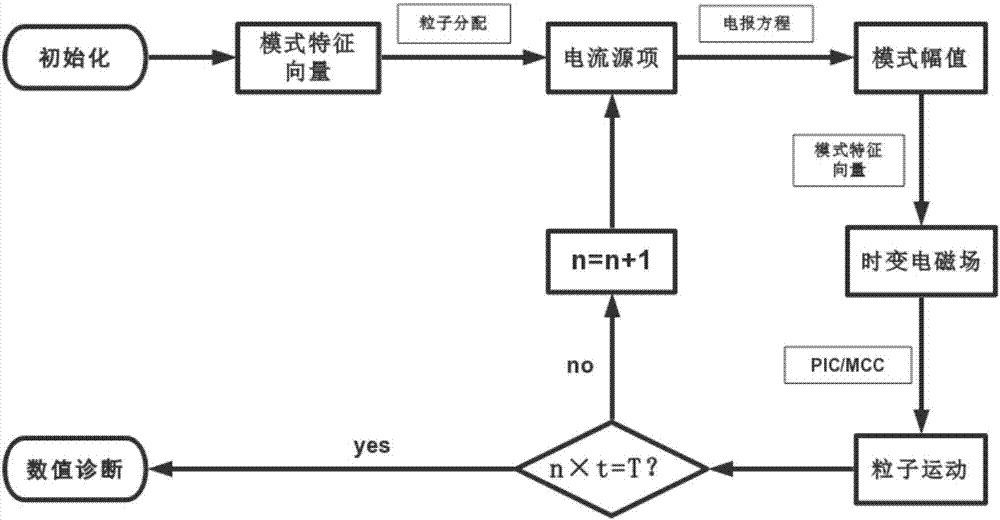
The invention belongs to the field of numerical simulation technology of ECR ion sources, and particularly relates to an MPM hybrid algorithm applied to numerical simulation of an ECR ion source. Thealgorithm is suitable for use in an ECR ion source structure. The MPM hybrid algorithm of simulation of the ECR ion source is established through combining an MAGY theory and PIC / MCC simulation algorithms, a time-varying electromagnetic field is described by the MAGY theory, self-consistent interaction of charged particles and the electromagnetic field is described by the PIC algorithm, and inter-particle collision processes are described by the MCC algorithm. A complex and complete solving process which originally needs to be carried out on Maxwell's equations is enabled to be simplified to solving on a set of coupled one-dimensional partial differential equations about mode amplitudes, relatively larger time step length can also be taken due to that compared with high-frequency cycles, changes of the mode amplitudes are slower, and computational complexity and a computational amount are greatly reduced. In addition, an electromagnetic model is adopted, and thus compared with adoptingan electrostatic model, the algorithm can more accurately describe an actual physical process.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
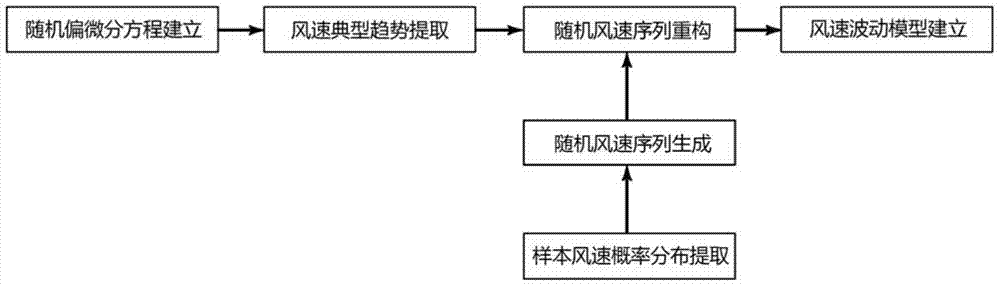
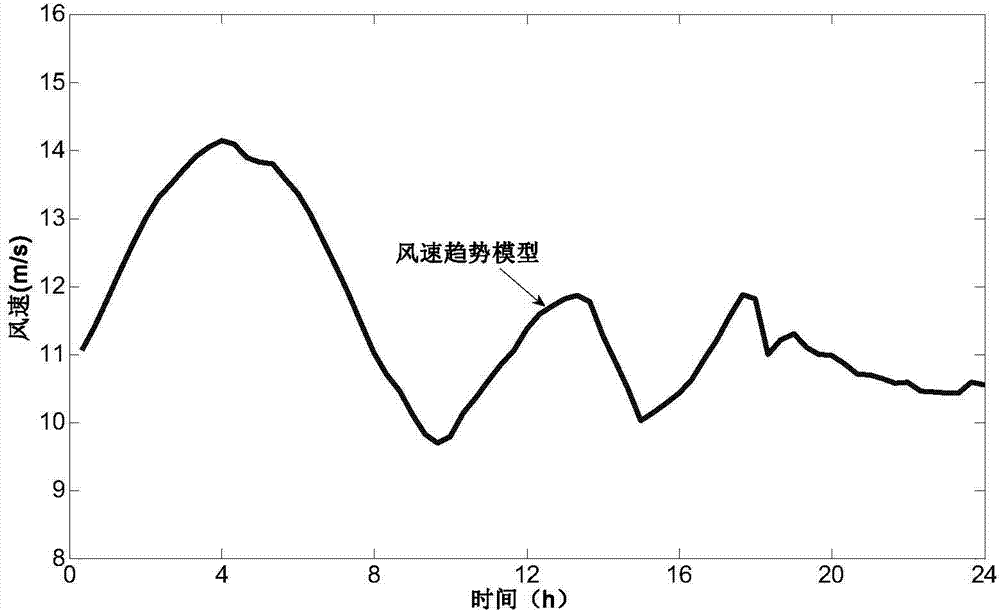
Stochastic partial differential equation based wind speed fluctuation characteristic modeling method
InactiveCN104850710ASpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringElliptic partial differential equation
The invention provides a stochastic partial differential equation based wind speed fluctuation characteristic modeling method, comprising steps of: according to sample wind speed data, constructing a stochastic partial differential equation about wind speed variation, and obtaining a typical wind speed variation sequence by solving the stochastic partial differential equation; then, by fitting a probability distribution function of the sample wind speed, randomly generating a wind speed sequence, and using the solved typical wind speed variation sequence to reconstruct the random wind speed sequence according to the principle of least square method, thereby obtaining a final wind speed model; finally, verifying correctness of the modeling method through comparison with a measured wind speed sequence. The method provided by the invention can effectively depict the real wind speed fluctuation characteristics, and overcome the problem that the existing wind speed model can only consider the probability distribution of wind speed from one aspect; the wind speed model established by using the method provided by the invention can not only reflect the conditions of the probability distribution of wind speed, but also show the fluctuation characteristic of the wind speed within a required study period.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +3
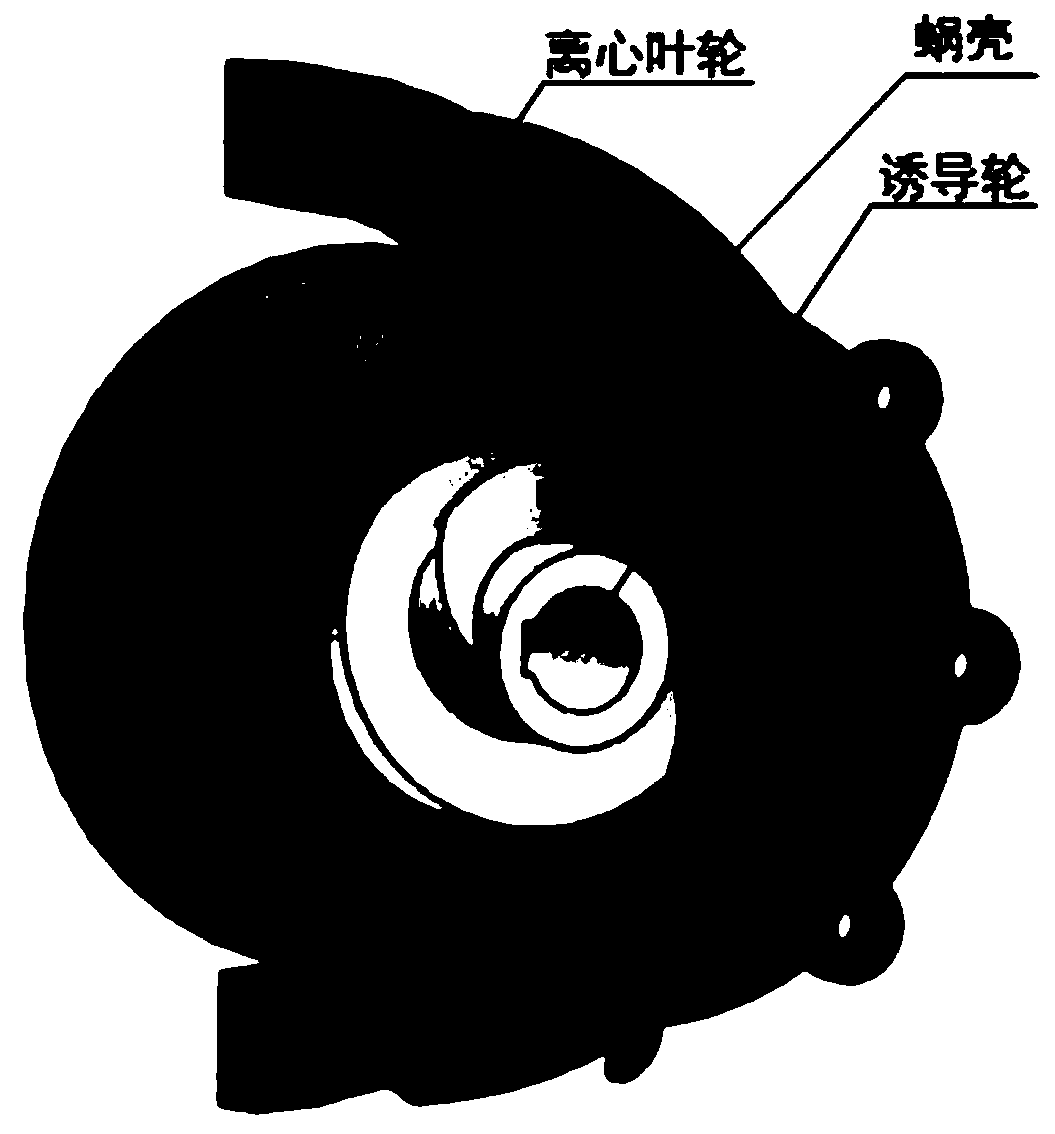
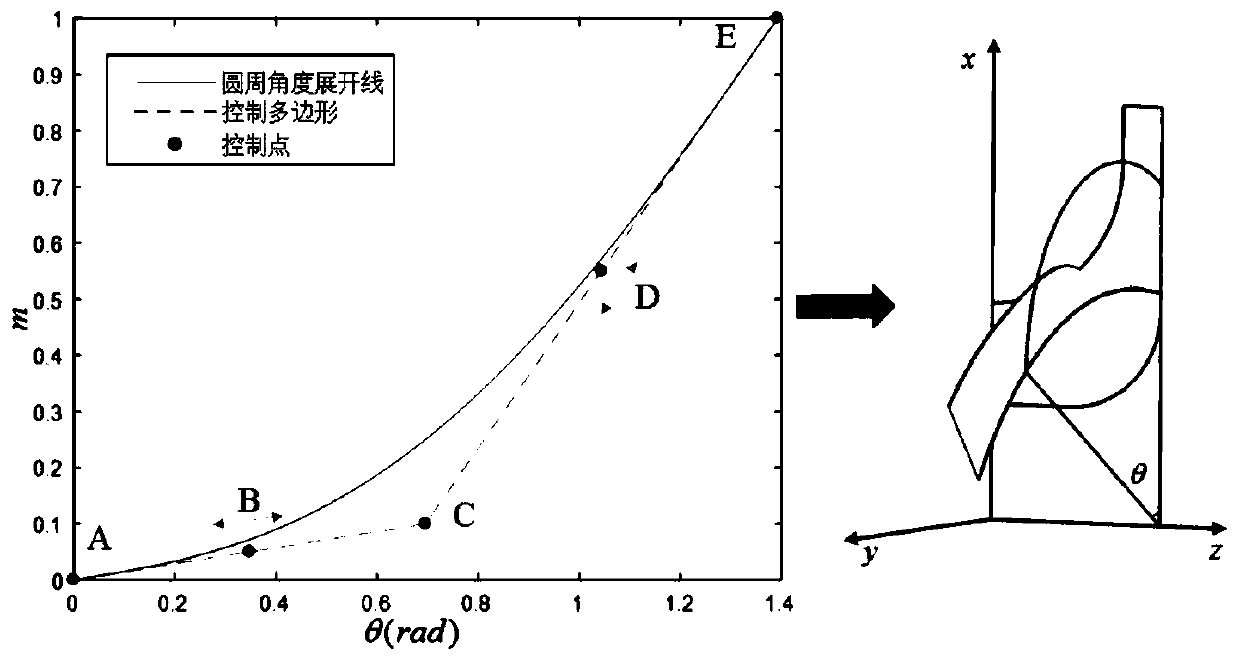
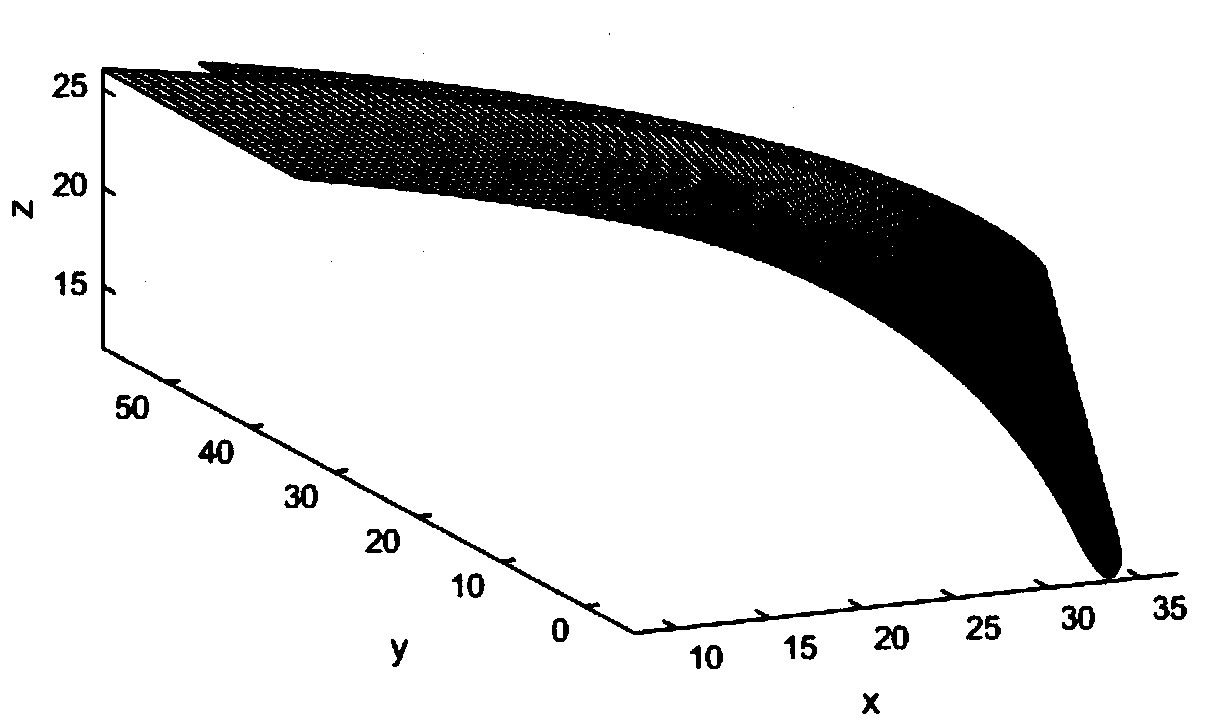
Aviation centrifugal pump blade profile optimization design method
ActiveCN110008653APerfect agreement predictive valueCompletely consistent test valueGeometric CADSustainable transportationAviationBatch processing
The invention discloses an aviation centrifugal pump blade profile optimization design method. Under a Matlab platform, a five-point four-time bezier curve and a linear function are adopted to controlthe blade profile circumference angle distribution and the product superposition change rule, and internal flow field numerical simulation is carried out on 15 sets of design results through a software UG and Fluent combined batch processing method. On the basis of obtaining a calculation space boundary condition through curved surface interpolation, numerical solution is carried out on the dual-harmonic partial differential equation by adopting a central difference format, and a hypercurved surface performance agent model is sestaboished. Global optimization is carried out on the design variable based on an artificial fish swarm algorithm by taking the highest efficiency as an objective function. The result shows that the hypersurface agent model based on the double harmonic equation canensure that the test value and the predicted value are completely consistent, the wake effect in the optimized centrifugal impeller flow is obviously weakened, and the hydraulic efficiency is improved by 5.4% compared with that of a prototype pump.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Aircraft Guidance Based on Partial Differential Equation for Miss Distance
InactiveUS20160266582A1Navigational calculation instrumentsTarget-seeking controlGuidance systemMatrix differential equation
A guidance, navigation and control (GNC) system guides an aircraft based on a special partial differential equation (PDE). The system does not depend on a predetermined desired flight path. To overcome effects of unpredictable wind speed and direction, systems and methods effectively repeatedly determine the worst landing the wind can cause and issue flight control commands that minimize among these worst outcomes. A function C that satisfies the PDE calculates smallest miss distance a guidance system can bring about by appropriately steering an aircraft, given the aircraft's current heading, current location relative to a target and current remaining amount of time to fly. The system repeatedly determines at least a component of a current gradient of the function C. A value of the gradient component is used to select an appropriate flight control command, such as turn left or turn right.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
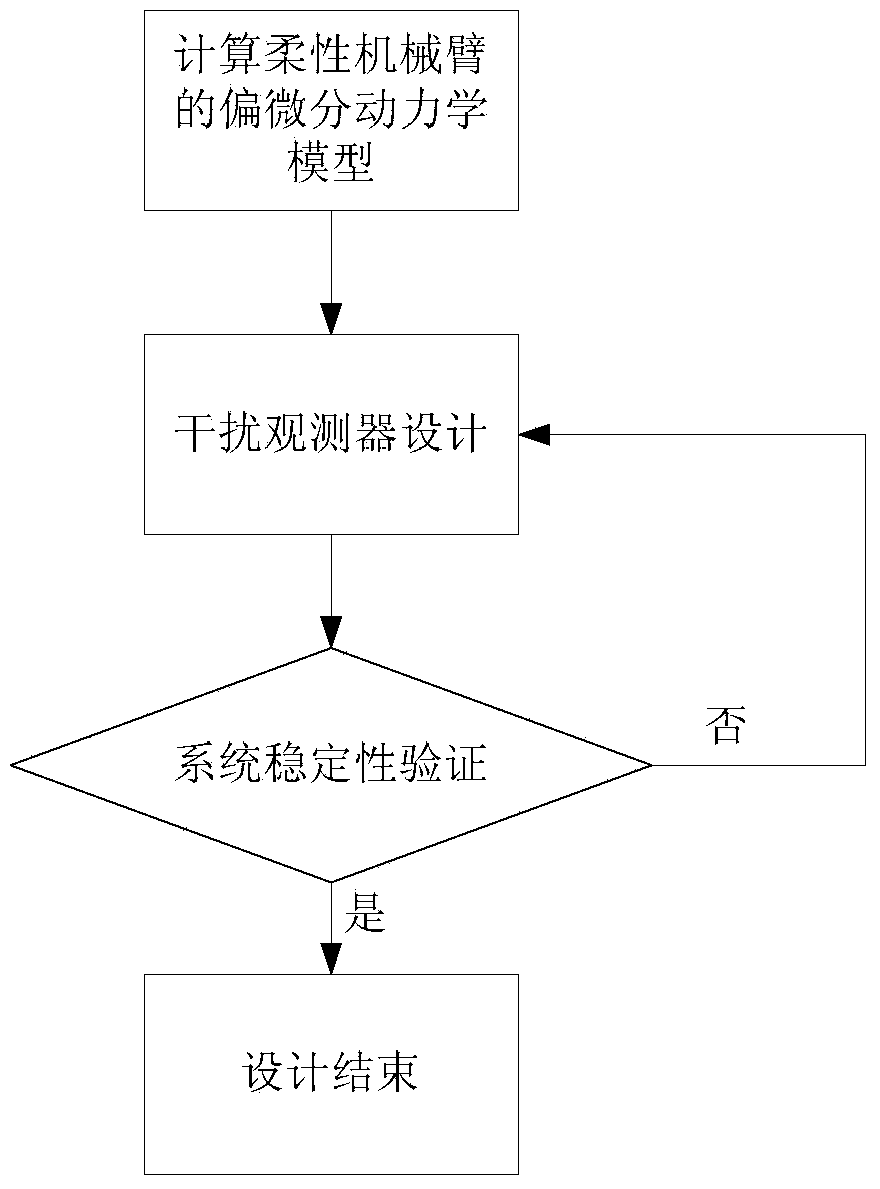
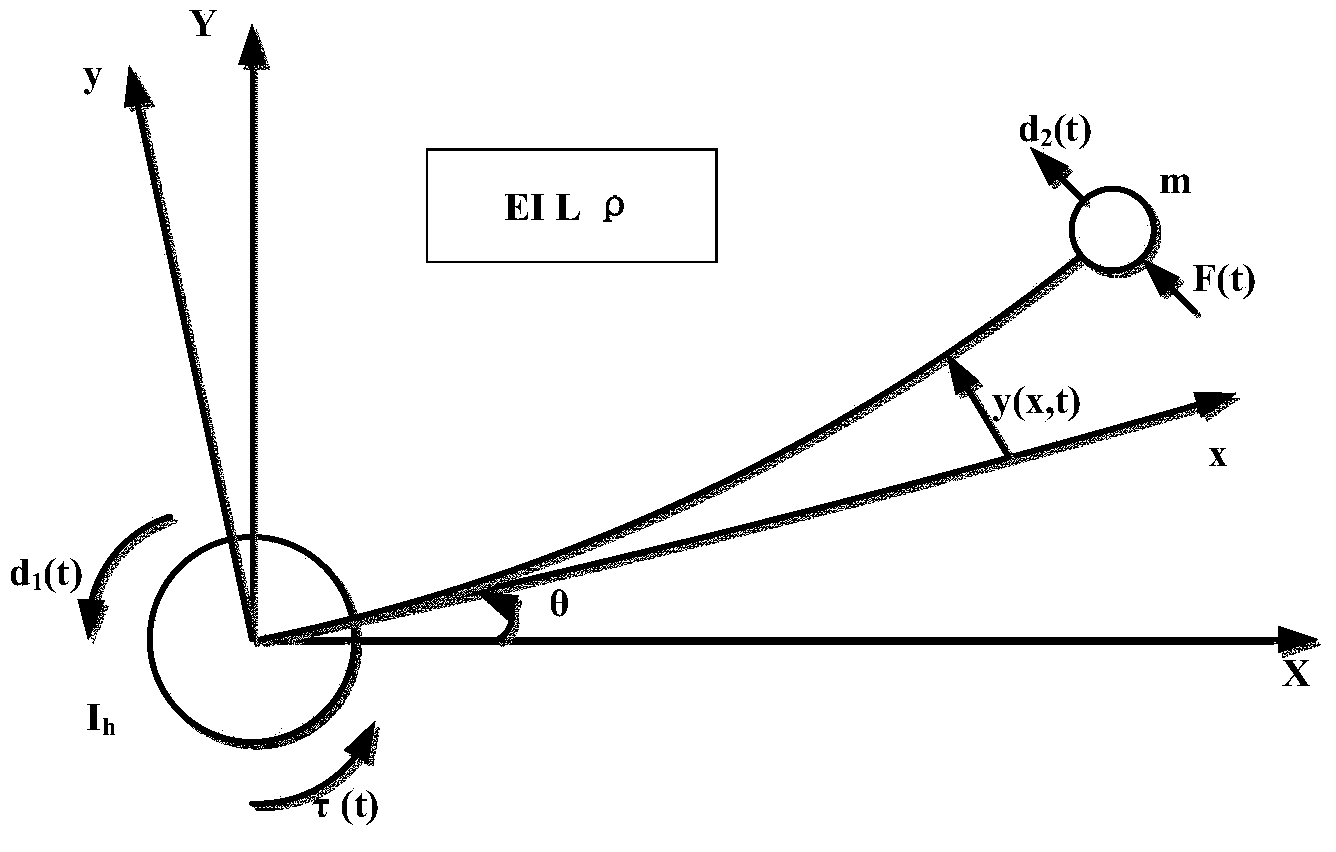
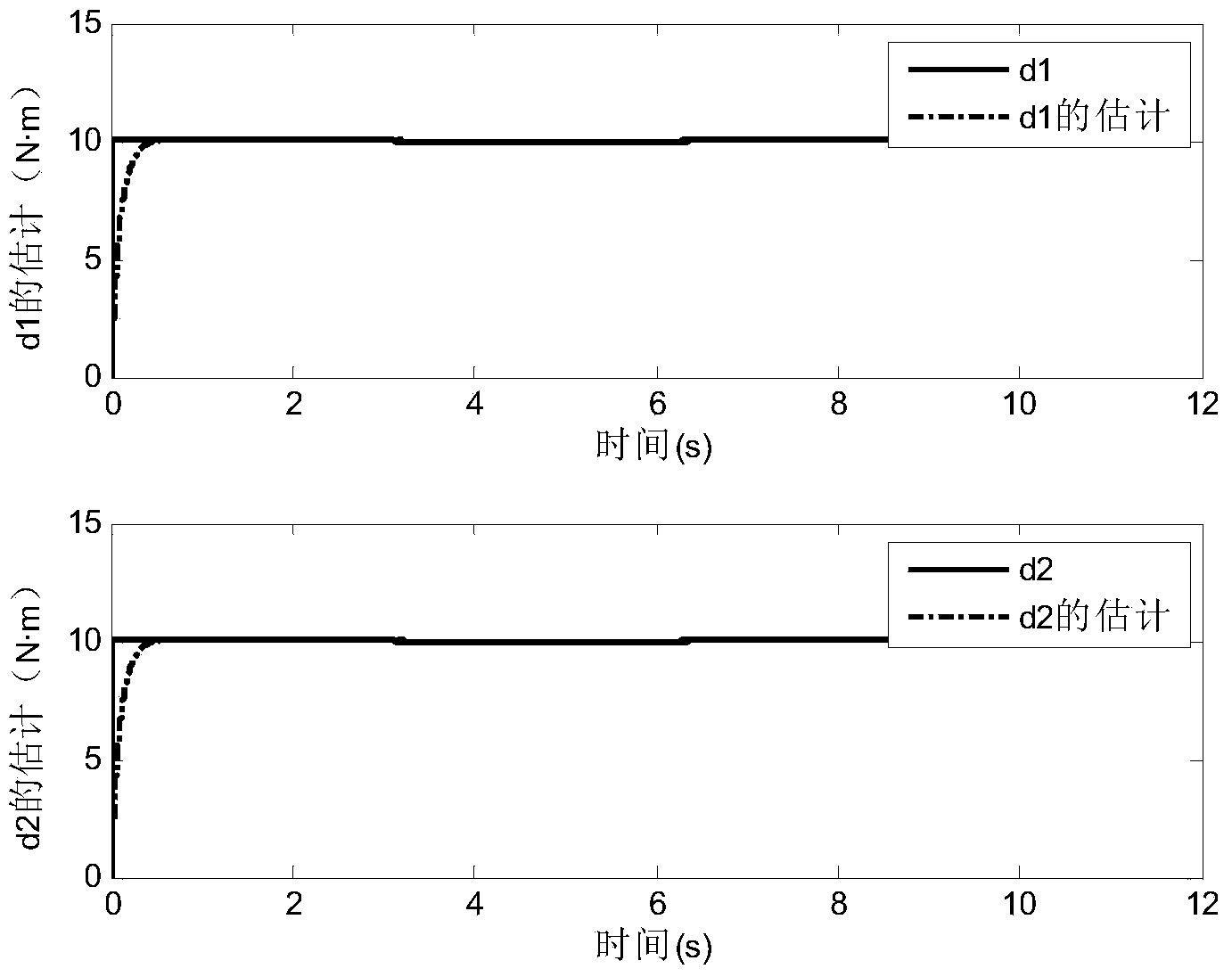
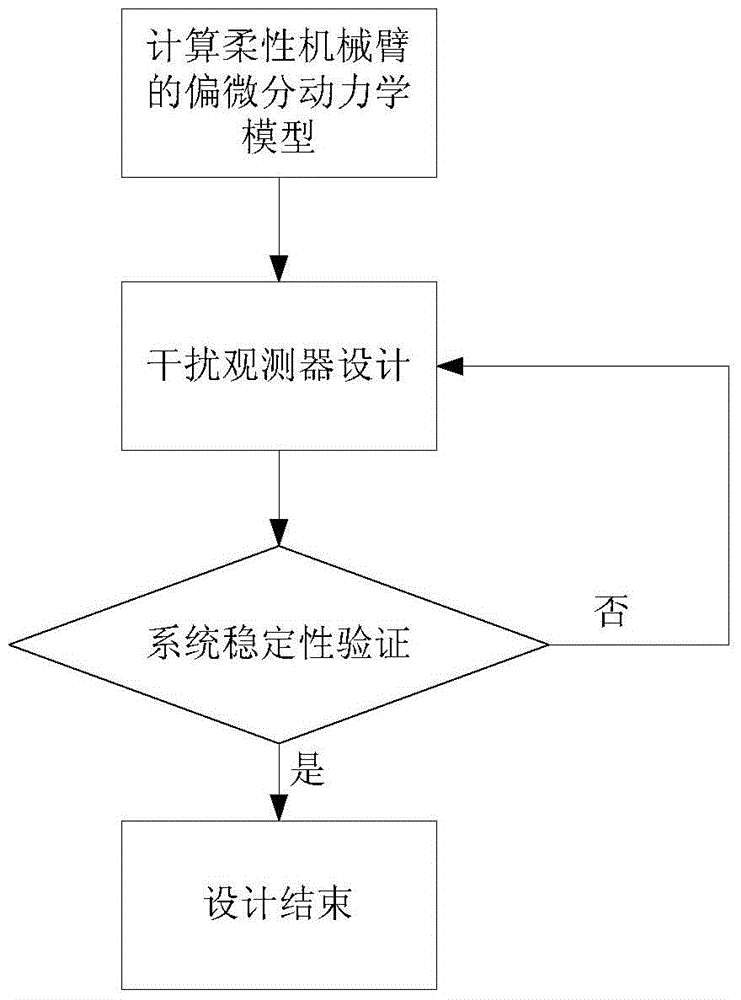
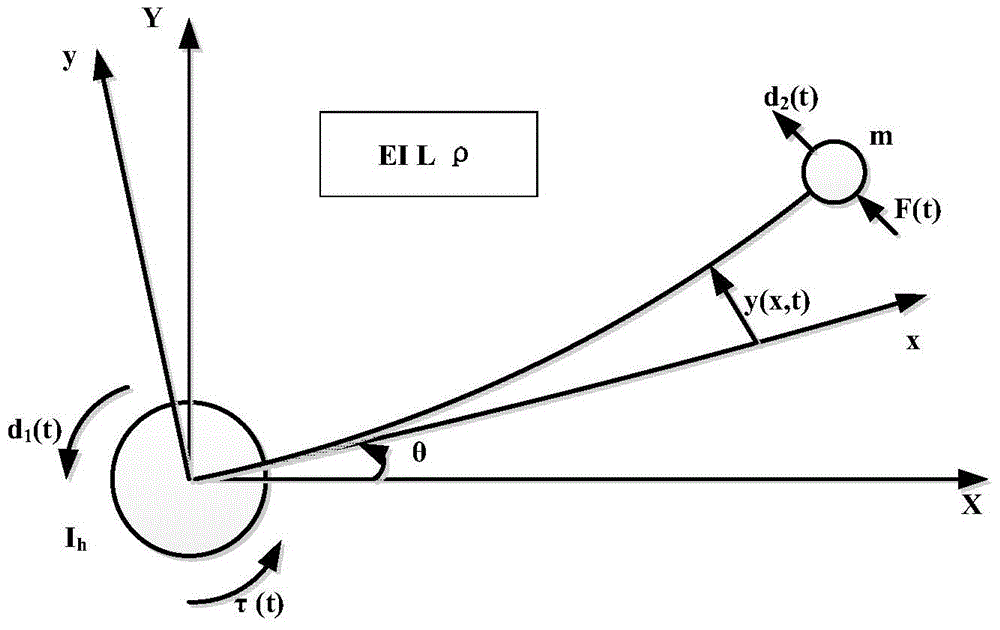
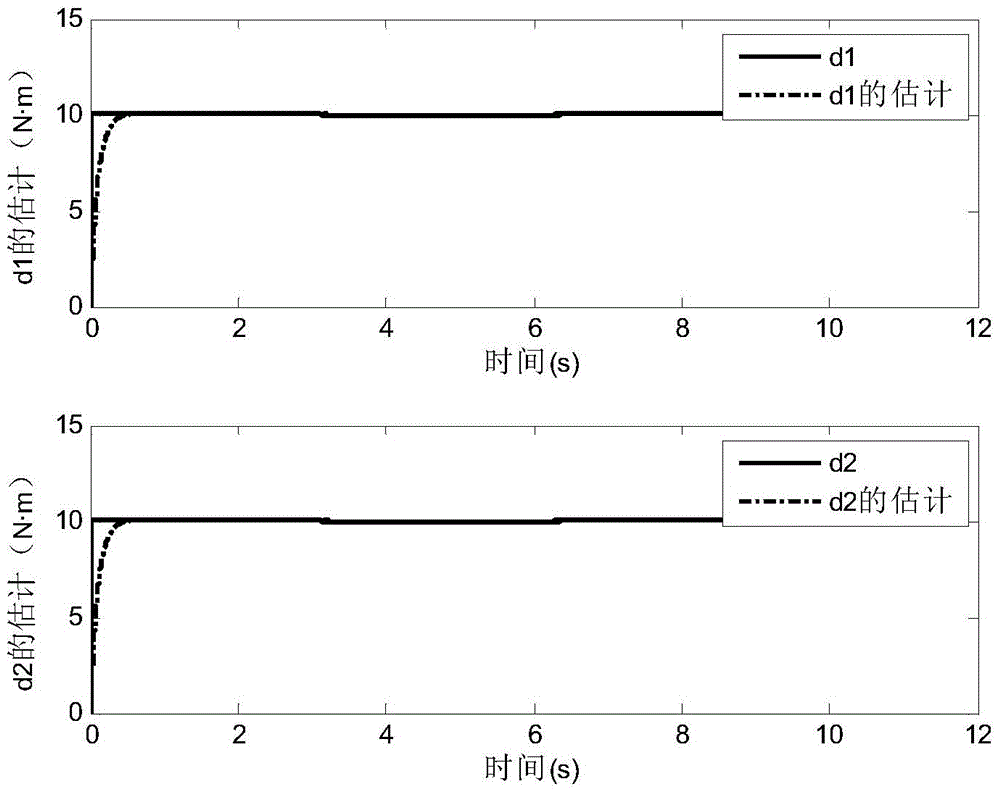
Method for designing flexible mechanical arm disturbance observer based on partial differential equation
ActiveCN104020664ARealize interference observationAdaptive controlMatrix differential equationEngineering
The invention provides a method for designing a flexible mechanical arm disturbance observer based on a partial differential equation. The method includes the four steps that firstly, dynamic modeling of a flexible mechanical arm is conducted; secondly, the disturbance observer is designed; thirdly, stability of the disturbance observer is verified; fourthly, design is finished. According to the method, firstly the Hamilton principle is used, so that a PDE model of a whole system is obtained; then, based on the model, the reasonable disturbance observer is designed so that external unknown disturbance can be estimated; finally, a proper Lyapunov function is designed, so that the designed observer is analyzed and the stability of the observer is verified.
Owner:GUODIAN SCI & TECH RES INST
Directional partial differential equation filtering method for striped projection images
InactiveCN106447716AImprove calculation accuracyReduce computing timeImage analysisUsing optical meansPattern recognitionFilter effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical detection and image processing, proposes a new method for values to solve the partial differential equation, so that the partial differential equation filtering effect is improved. The directional partial differential equation filtering method for striped projection images includes the steps of 1. inputting a stripe projection image u with noise; 2. discretizing a stripe projection image u; 3. calculating the included angles Theta i, j between the strip direction and the x-axis direction; 4. performing adoption to obtain the time step Delta t; 5. performing adoption to obtain the iteration frequency Nc; 6. for the each iteration, obtaining the first-order partial derivative and the second-order partial derivative of each pixel of the image u; 7. obtaining the value solution (as shown in the description) of each pixel of the image u; 8. repeating step 6 and 7 until the set largest iteration frequency Nc is reached to stop the iteration, the value solution (as shown in the description) at this time is a filtering image. The directional partial differential equation filtering method is applied to image processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image coherent speckle suppression method
ActiveCN106971382AImprove radiometric resolutionKeep edge informationImage enhancementImage analysisSparse constraintNormal density
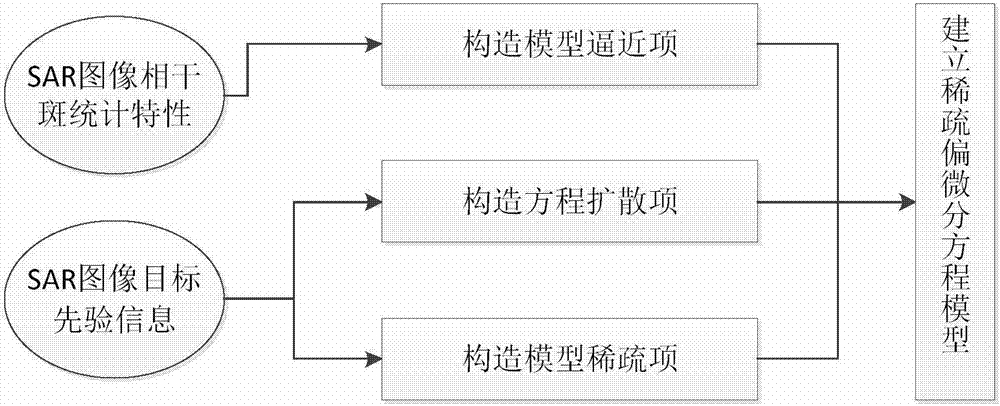
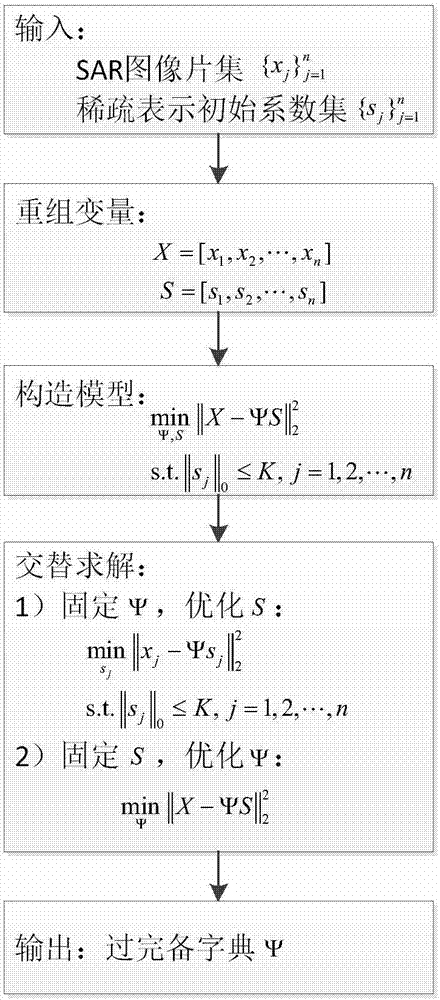
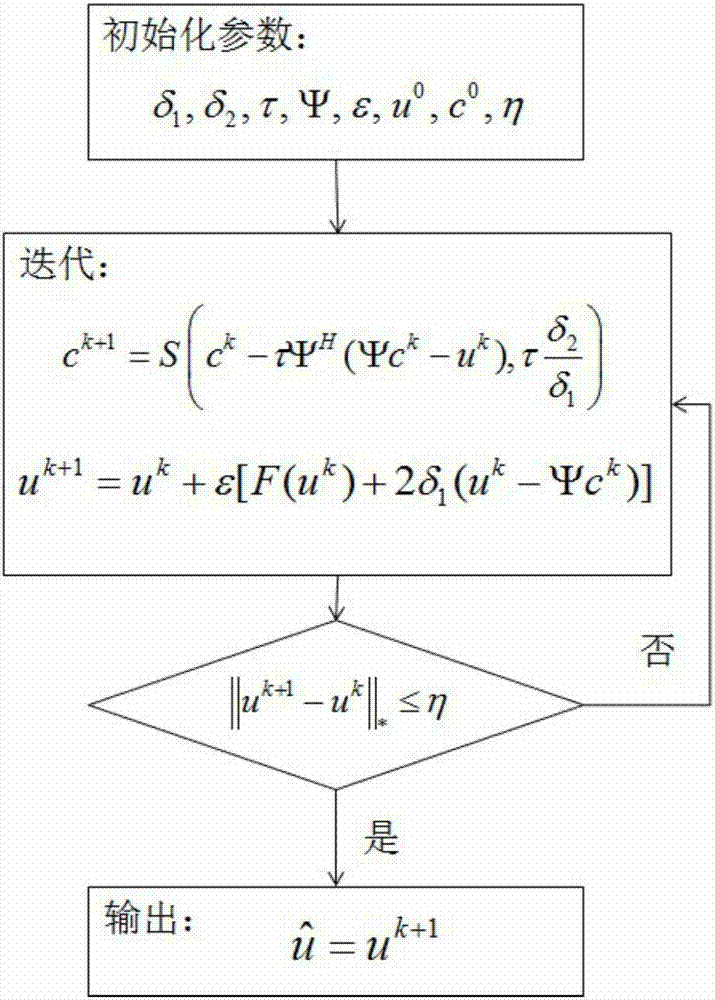
The present invention provides an SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image coherent speckle suppression method. According to the method, the probability density function of multiplicative noises and prior information are utilized to construct the approximation term, diffusion term and sparse constraint of a model; a sparse partial differential equation model is established; and alternate optimization is adopted to obtain a solution, so that a coherent speckle-suppressed SAR image can be obtained. With the sparse partial differential equation-based SAR image coherent speckle suppression method of the invention adopted, the defects of a traditional filtering method and a partial differential equation method can be eliminated; and the coherent speckles of the image can be suppressed, the radiation resolution of the SAR image can be improved, and at the same time, the edge information and scattering characteristics of a radar target can be well retained, the quality improvement of the SAR image can be realized effectively, the numerical solution of the model can be obtained robustly, and therefore, the method is easy to implement.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
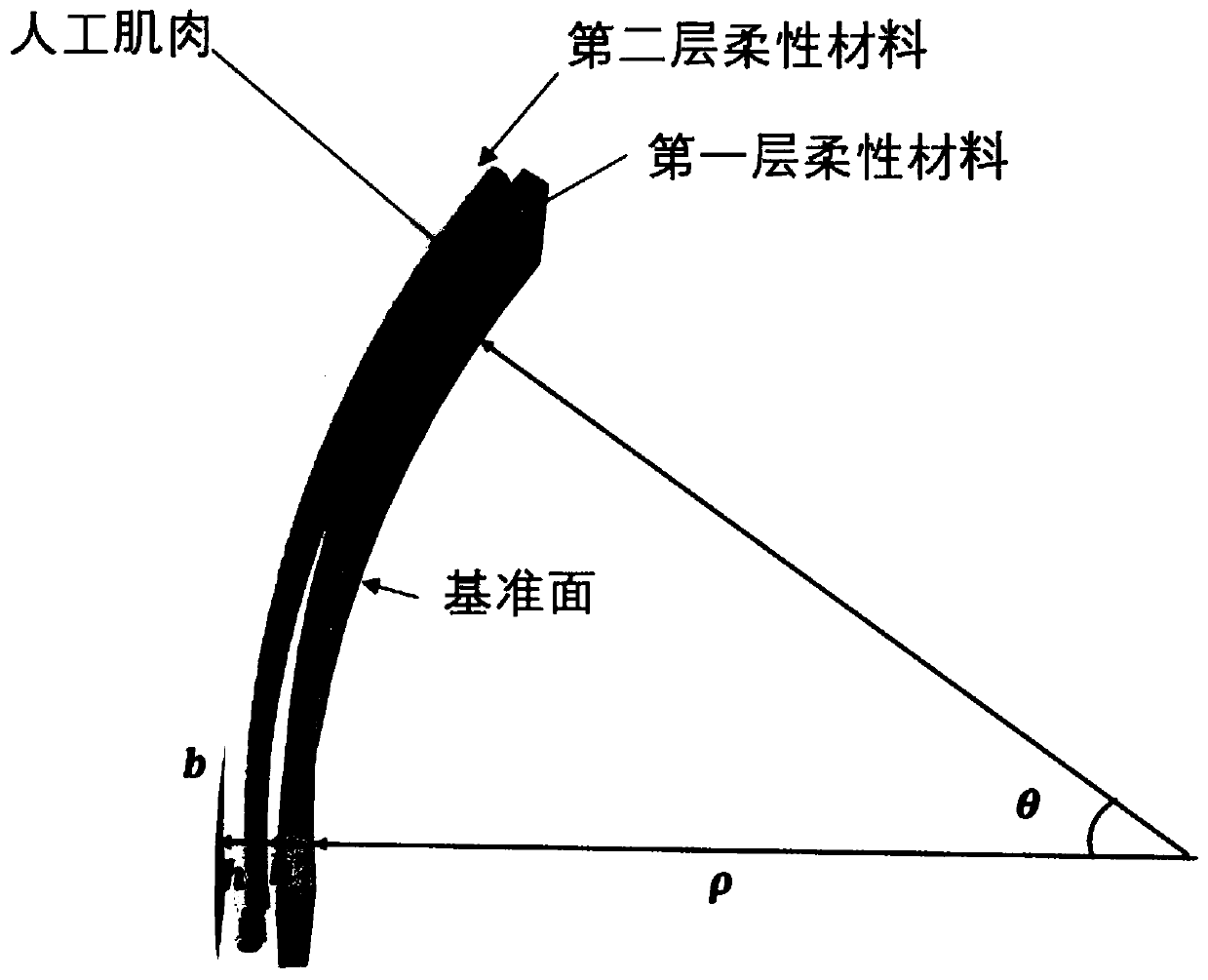
Elastic soft robot kinematical modeling method based on constant curvature assumption
ActiveCN110181506AAchieving Shape PredictionAvoid damageProgramme-controlled manipulatorWorking temperatureEngineering
The invention provides an elastic soft robot kinematical modeling method based on a constant curvature assumption, and belongs to the field of robot kinematical modeling. According to the method, by means of the Kirchhoff bar theory and the constant curvature assumption, firstly, equations of force, displacement and control quantities corresponding to artificial muscles implanted into a flexible material of an elastic soft robot are established; then the actual length of the elastic soft robot at the working temperature is calculated, and mechanical parameters of the flexible material are usedfor calculation; and finally, the section inertia moment about a neutral surface is calculated, the curvature radius and the angle of the elastic soft robot at the working temperature are calculated,the true shape of the elastic soft robot at the working temperature is obtained, and kinematical modeling is completed. According to the method, the modeling process is simple and convenient, the influences of elastic deformation of the elastic soft robot are considered, numerical calculation of partial differential equations is not involved, and the relationship between the shape of the elasticsoft robot and the parameters of the artificial muscle in the elastic soft robot can be rapidly established.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Efficient segmentation of piecewise smooth images
InactiveUS7889941B2Image enhancementImage analysisLocal statisticsHyperbolic partial differential equation
A fast and robust segmentation model for piecewise smooth images is provided. Local statistics in an energy formulation are provided as a functional. The shape gradient of this new functional gives a contour evolution controlled by local averaging of image intensities inside and outside the contour. Fast computation is realized by expressing terms as the result of convolutions implemented via recursive filters. Results are similar to the general Mumford-Shah model but realized faster without having to solve a Poisson partial differential equation at each iteration. Examples are provided. A system to implement segmentation methods is also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
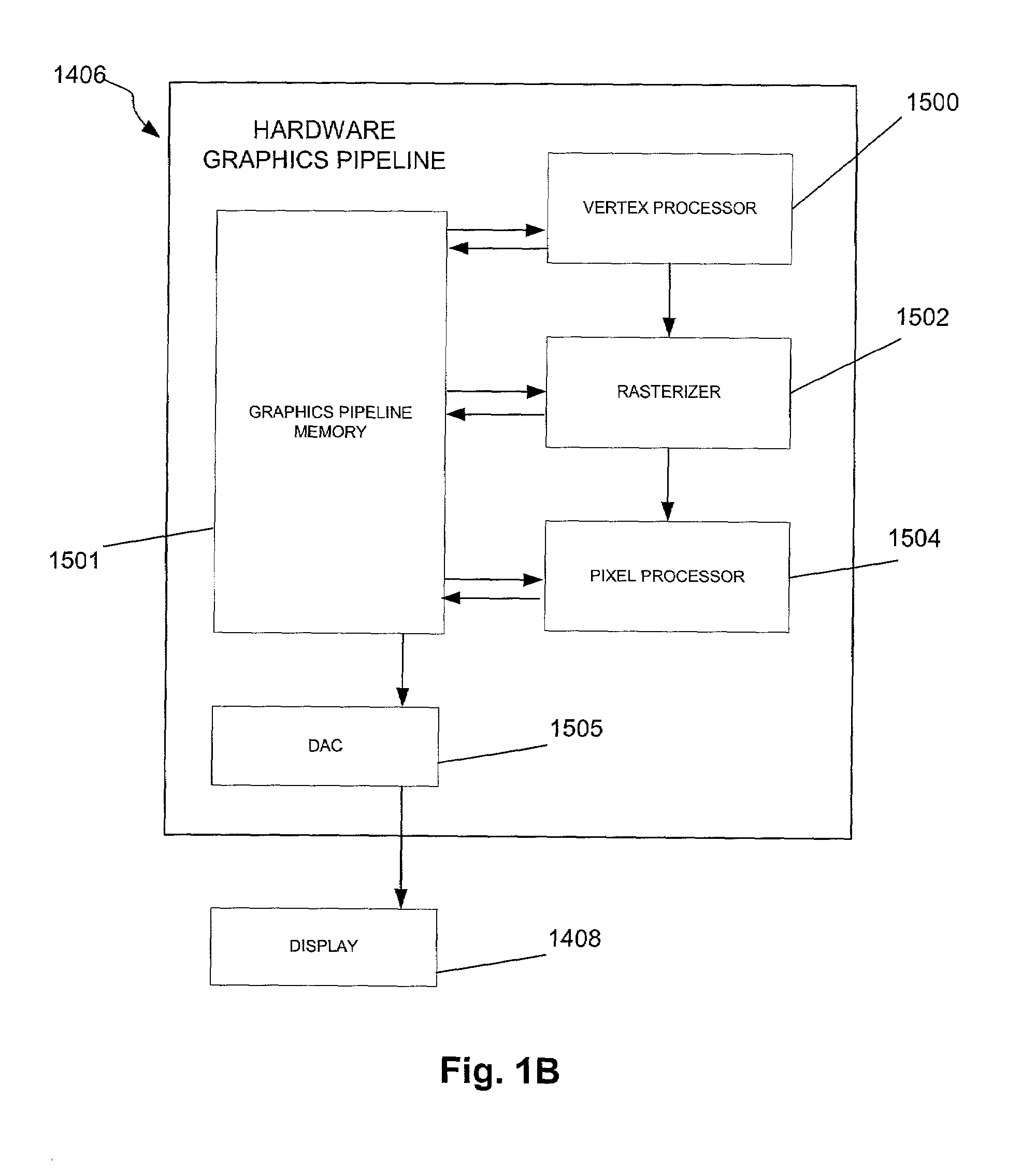
System and method for calculating partial differential equations in a hardware graphics pipeline
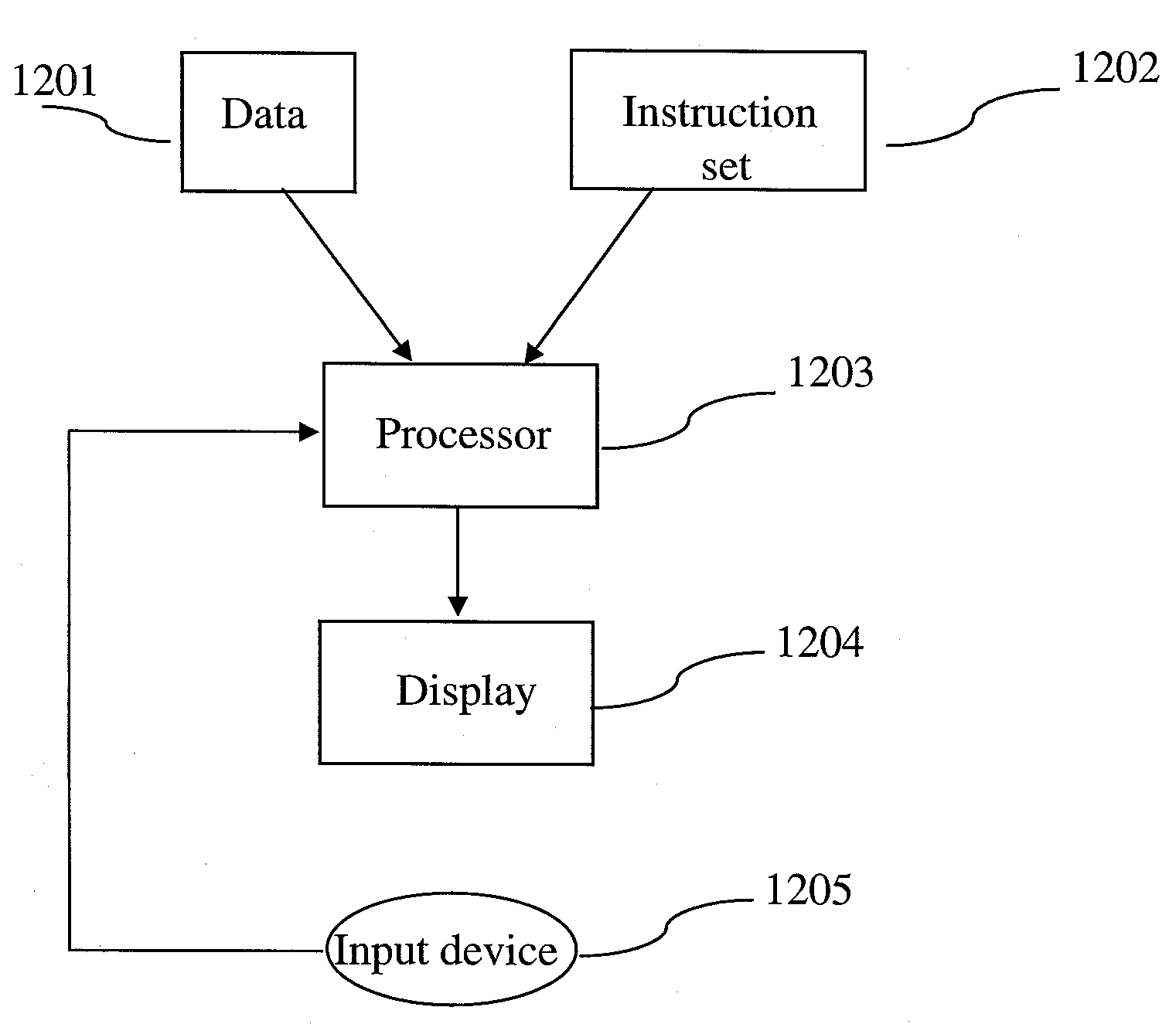
InactiveUS7454320B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsComputation using non-denominational number representationMatrix differential equationComputational science
A system and method are provided for computing partial differential equations in a hardware graphics pipeline. Initially, input is received in a hardware graphics pipeline. Next, the input is processed to generate a solution to a partial differential equation utilizing the hardware graphics pipeline.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Gait contour extraction method
InactiveCN105631452AGood localization effectImprove clarityCharacter and pattern recognitionSymbol of a differential operatorGait
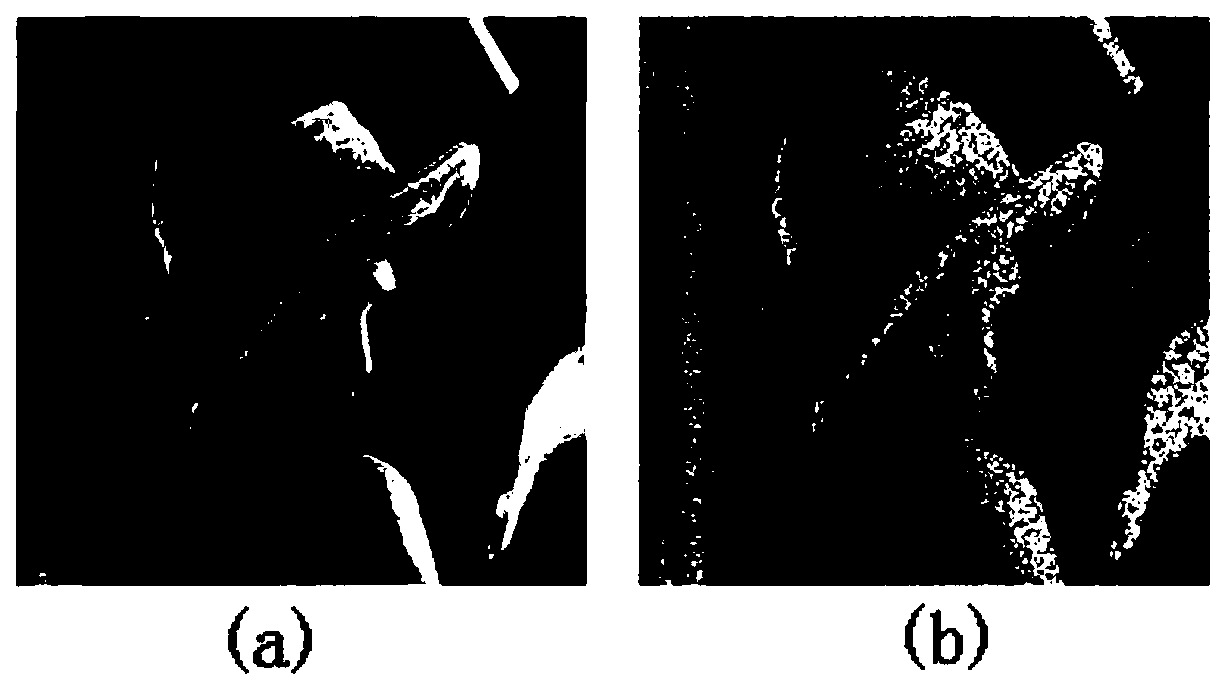
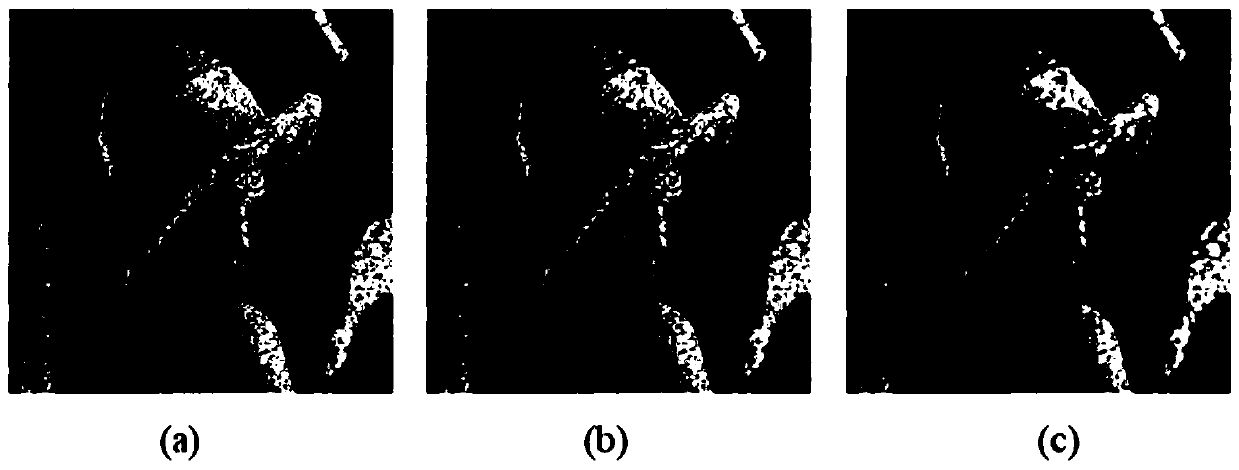
Provided is a gait contour extraction method. A level set function is expressed in a spatial-temporal discrete grid. First, an SDF (Sign Distance Function) is constructed, and initialization for zeroing is carried out; then, the numerical solution of a partial differential equation is solved; and finally, re-initialization is carried out through a curvilinear sign distance function, whether the numerical value is stable or not is judged, iteration is stopped if the numerical value is stable, or the process is repeated. The gait contour extraction method has a good localization effect for image boundaries. The image edge and regional information are combined, and the definition and distinctiveness of the gait contour are improved.
Owner:安徽勤勉知识产权代理有限公司
Wind speed fluctuation characteristic modeling method based on stochastic partial differential equations
InactiveCN105930547AImprovement of modeling method for wind speed fluctuation characteristicsSpecial data processing applicationsReceiver operating characteristicControl objective
The invention belongs to the technical field of a modeling method, and discloses a wind speed fluctuation characteristic modeling method based on stochastic partial differential equations (SPDE). A wind farm modeling method is proposed to establish a wind farm stochastic model, the wind farm operating characteristics are simulated, in order to achieve predictable and controllable goal services of large scale wind power generation, through simulation comparison between a wind farm equivalent model and a detailed model, the rationality of the modeling method is verified, and a wind farm model considering random fluctuations in the wind speed and direction in the study of wind farm dynamic characteristics and the influence thereof on a power grid. The invention can adjust the predictable angles of fluctuation wind speed and direction randomly, and improves the wind speed fluctuation modeling method.
Owner:YANTAI NANSHAN UNIV
Image denoising method based on non-downsampling wavelet transform and improved four-order partial differential equation
InactiveCN108416738AAvoid secondary pollutionEasy to identifyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage denoising
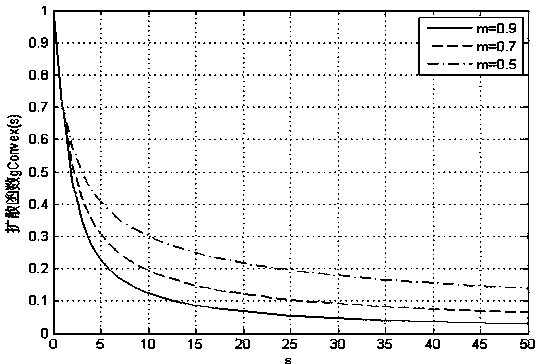
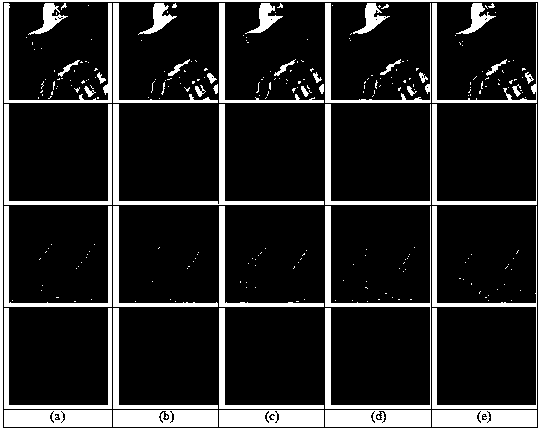
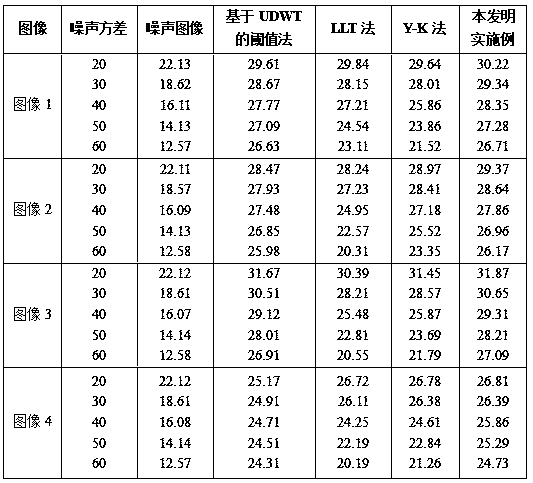
The invention discloses an image denoising method based on non-downsampling wavelet transform and an improved four-order partial differential equation, and belongs to the field of image processing. The image denoising method comprises the steps of constructing a novel convexity-preserving diffusion function and establishing an improved four-order partial differential denoising model on the basis of the convexity-preserving diffusion function, wherein the corresponding energy function has a globally unique minimum value solution; combining the gaussian filtering with a laplacian operator to overcome the defect that a Y-K model is too sensitive to noise; applying the improved four-order partial differential denoising model to a non-downsampling wavelet transform high-frequency sub-band to suppress the generation of false edges and massive effects. Experiment comparison shows that the image denoising method can be used for removing image noise while retaining the image texture and other detail information.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
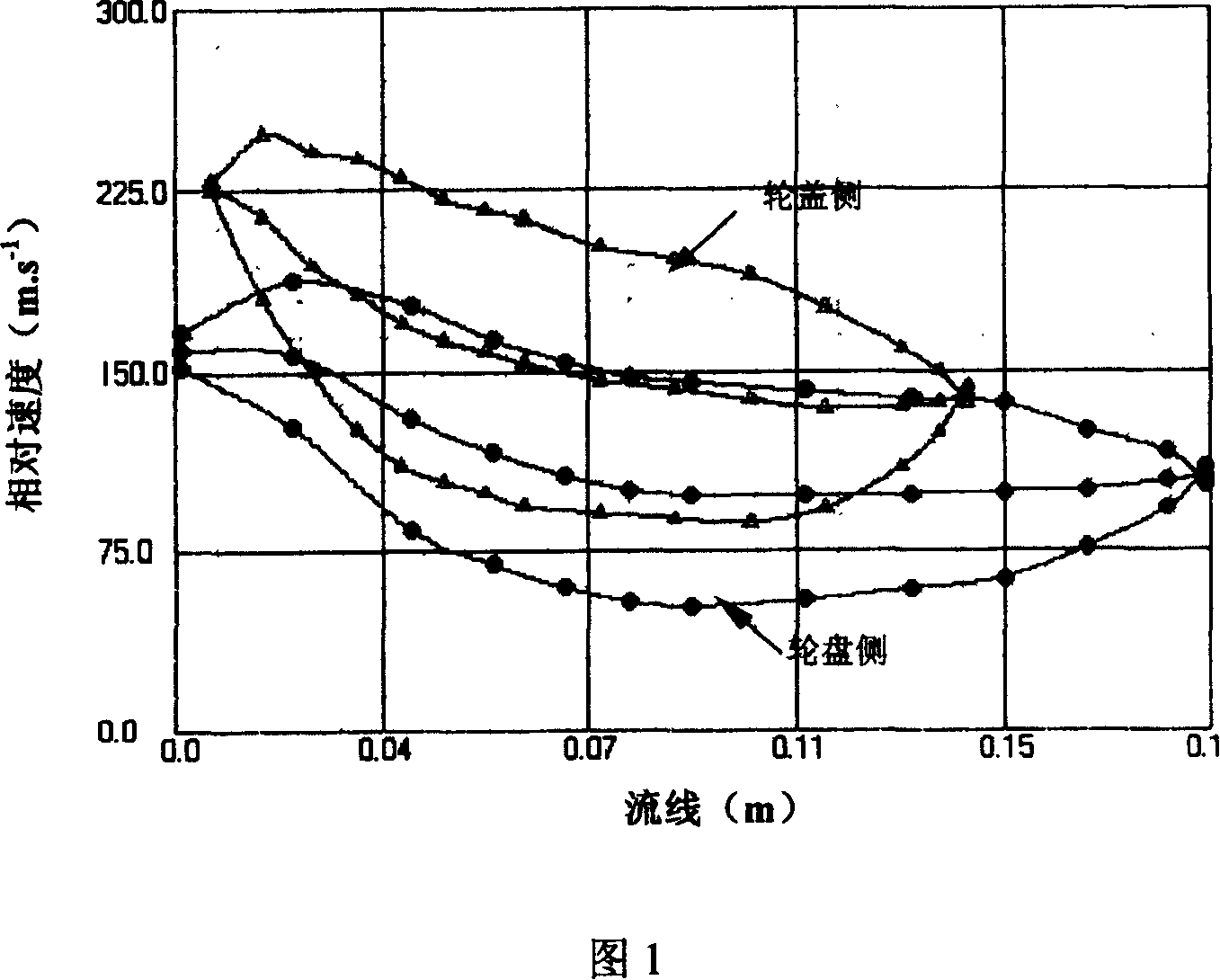
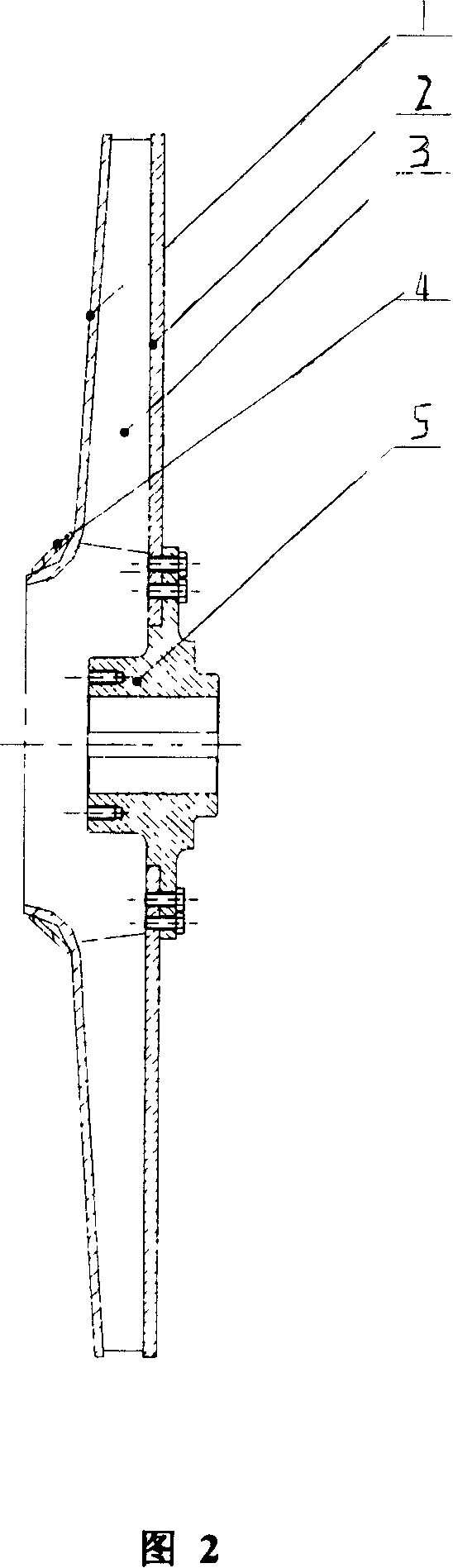
Blade type optimized designing method of turbine compression fluid machine
InactiveCN100370148CReduce energy consumptionGuaranteed uptimePump componentsPumpsImpellerMatrix differential equation
A method for designing the profile of blade used for turbine-type fluid compressing machinery includes such steps as simplifying the flow procedure controlled by N-S partial differential equation to become the flow procedure controlled by ordinary differential equation, creating state equation, normalizing the equation to become relative optimal control mode, using the installation exit angle of blade as control variable, and iterative calculating to the 3D geometric model of blade and said ordinary differential equation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
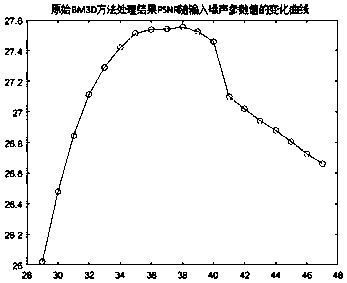
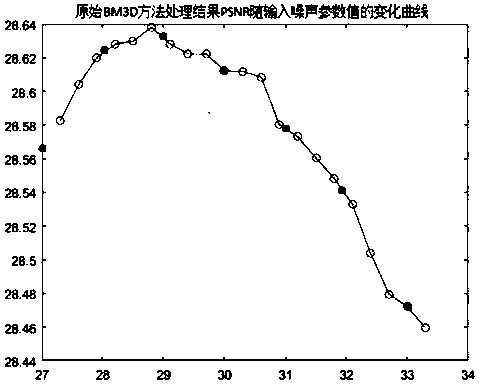
Non-parameterized image restoration method based on partial differential equation and BM3D (Block-matching and 3D filtering)
ActiveCN107798663AIncreased value and operational efficiencyImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMatrix differential equation
The invention provides a non-parameterized image restoration method based on a partial differential equation and a BM3D (Block-matching and 3D filtering) and belongs to the technical field of image processing. In a conventional BM3D improved method, a parameter estimation is obtained by use of an existing noise parameter estimation method, and is then introduced into an original BM3D method, however, the result is unstable. In the image restoration method, a denoising process and a noise variance estimation process of the conventional BM3D improved are improved by use of the partial differential equation, the method is characterized by closely fusing with pretreatment of the partial differential equation, and the improved BM3D method is enabled to have high precision and stability. The non-parameterized image restoration method based on the partial differential equation and the BM3D can be applied to various fields of image processing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
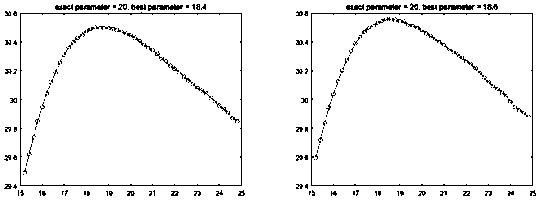
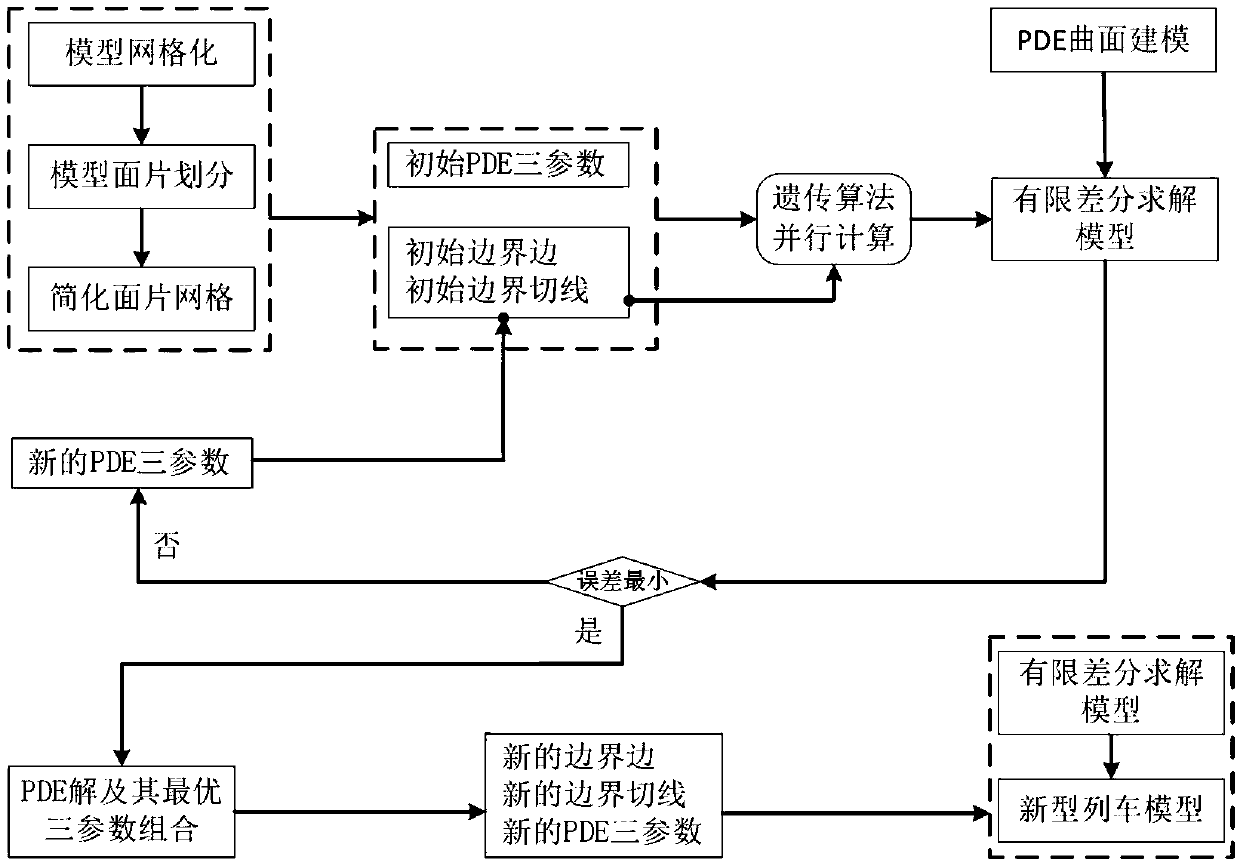
Train head model parameterization control method based on four-order partial differential equation
The invention discloses a train head model parameterization control method based on a four-order partial differential equation; the method comprises the following steps: 1, using the four-order partial differential equation to parameterize train head model surface patches; 2, calculating to obtain boundary conditions needed to solve the partial differential equation; 3, obtaining space positions of grid points corresponding to the partial differential equation numerical solution; 4, determining whether the error between the grid points corresponding to the partial differential equation numerical solution and a target point is smaller than a set threshold or not; 5, obtaining the grid point position corresponding to the partial differential equation numerical solution when the target pointis approached at the closest level and the corresponding partial differential equation so as to control patch local deformation parameters; 6, adjusting train head model shape control parameters so asto obtain a new train head model. The method utilizes a few parameters to not only control large scale deformation of the train head model, and can adjust the shape in a local small scope, thus providing more degree of freedom for train head model design and aerodynamic optimization.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Optimization algorithm for solving seepage free surface based on radial base point interpolation method
ActiveCN110443432AMake sure it's fully alignedGuaranteed integral accuracyClimate change adaptationForecastingNODALMatrix differential equation
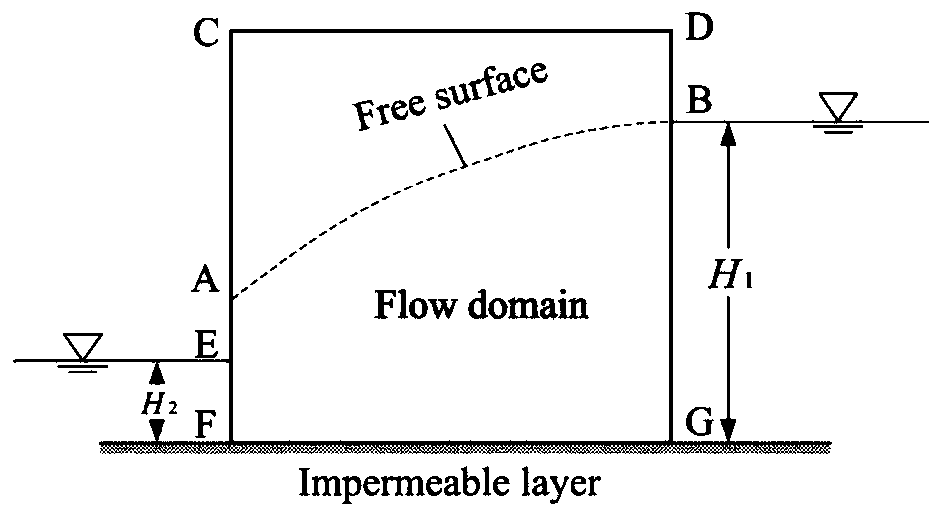
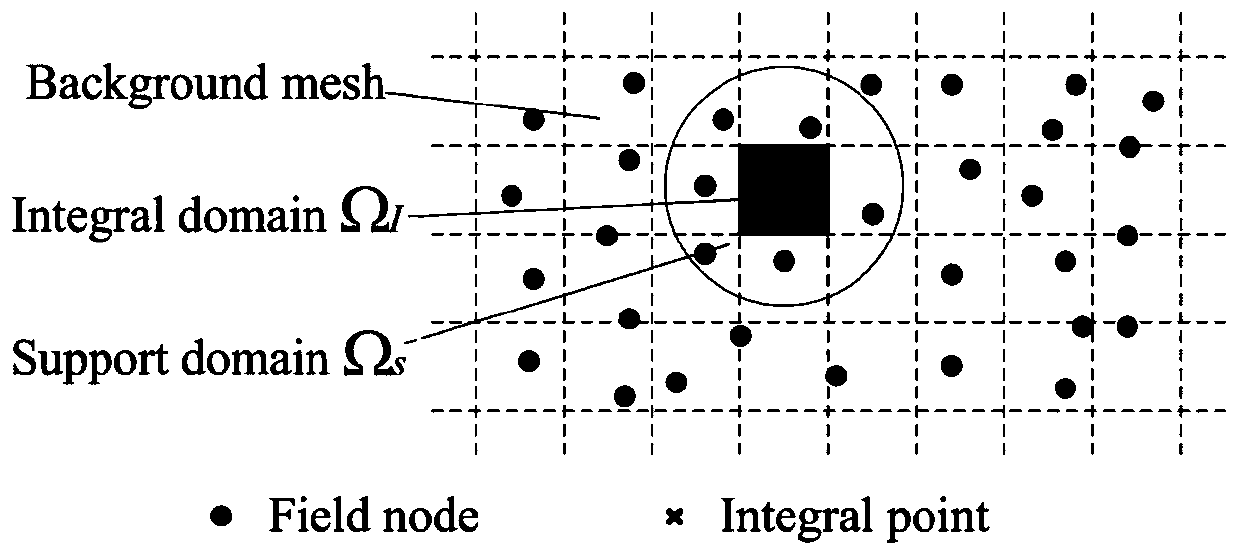
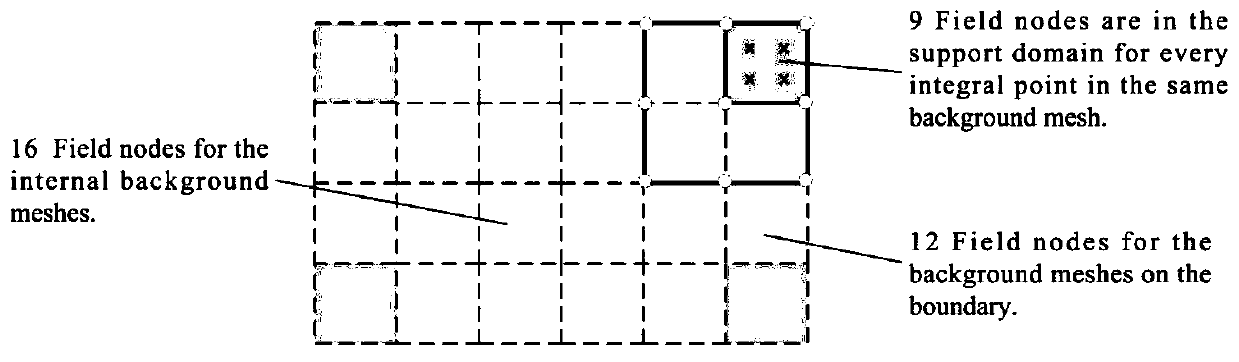
The invention relates to a meshless method seepage free surface solving method based on a radial base point interpolation method. The meshless method seepage free surface solving method comprises thefollowing steps: 1) determining a control equation; 2) determining boundary conditions; 3) determining an RPIM control equation; solving a partial differential equation by adopting RPIM, dispersing aproblem domain into a series of field nodes, introducing an integral rigidity matrix into a background grid in order to facilitate integration and assembly, integral points existing in the backgroundgrid, each integral point having a support domain, and interpolating the field nodes in the support domains to obtain information on the integral points. According to the method, the seepage free surface can be solved conveniently and quickly, the precision is high, the working process can be simplified, and engineering practice can be better guided.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gait contour extraction method
InactiveCN104463162AGood localization effectImprove clarityCharacter and pattern recognitionMatrix differential equationGait
The invention discloses a gait contour extraction method, and relates to the technical field of gait contour extraction. The extraction method includes the steps that a horizontal set function is shown in a space-time discrete grid; an SDF function is firstly constructed; initialization for zero returning is accordingly carried out; a numerical solution of a partial differential equation is solved; reinitialization is carried out through a curvilinear symbol distance function; whether a numerical value is stable or not is judged; if iteration is stopped, the steps are repeatedly executed. The gait contour extraction method has the good localization effect on image boundaries, the image edges and regional information are combined, and the definition and the distinctiveness of the gait contour are improved.
Owner:ANHUI COSWIT INFORMATION TECH
Simulated fighting method
InactiveCN105631384AGood localization effectImprove clarityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMatrix differential equationElliptic partial differential equation
Provided is a simulated fighting method. A level set function is expressed in a spatial-temporal discrete grid. First, an SDF (Sign Distance Function) is constructed, and initialization for zeroing is carried out; then, the numerical solution of a partial differential equation is solved; and finally, re-initialization is carried out through a curvilinear sign distance function, whether the numerical value is stable or not is judged, iteration is stopped if the numerical value is stable, or the process is repeated. The simulated fighting method has a good localization effect for image boundaries. The image edge and regional information are combined, and the definition and distinctiveness of the gait contour are improved.
Owner:安徽勤勉知识产权代理有限公司
Method for calculating nonlinear partial differential equation by dual-grid iteration
InactiveCN106339352AImprove computing efficiencyHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsElliptic partial differential equationNonlinear partial differential equation
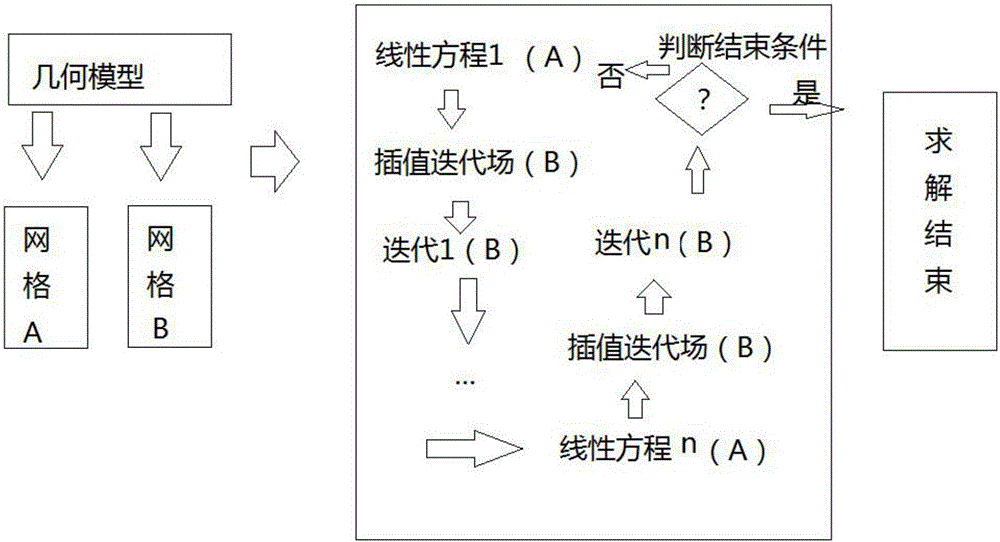
The invention discloses a method for calculating a nonlinear partial differential equation by dual-grid iteration. The method comprises the following steps: (a) establishing a three-dimensional geometric model of the nonlinear partial differential equation; (b) performing grid dissection on the three-dimensional geometric model, and dividing into two sets of grids, namely grids A and girds B, wherein the grids A are non-fitted grids, and the grids B are polyhedral fitting grids; (c) interpolating initial and boundary data into non-fitting parts of the grids A by using interpolations with four orders or above; (d) decomposing the nonlinear partial differential equation into a plurality of linear equations by using an iterative technique, wherein the linear equation is solved by using the grids A and using a four-order algorithm, and interpolating into the grids B to obtain fields in the fitting grids B; (e) performing iterative computation in the grids B; (f) repeating the steps (d) and (e) until the solving is ended. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high calculation efficiency, low cost and high precision by adopting dual-grid solving.
Owner:苏州中源广科信息科技有限公司
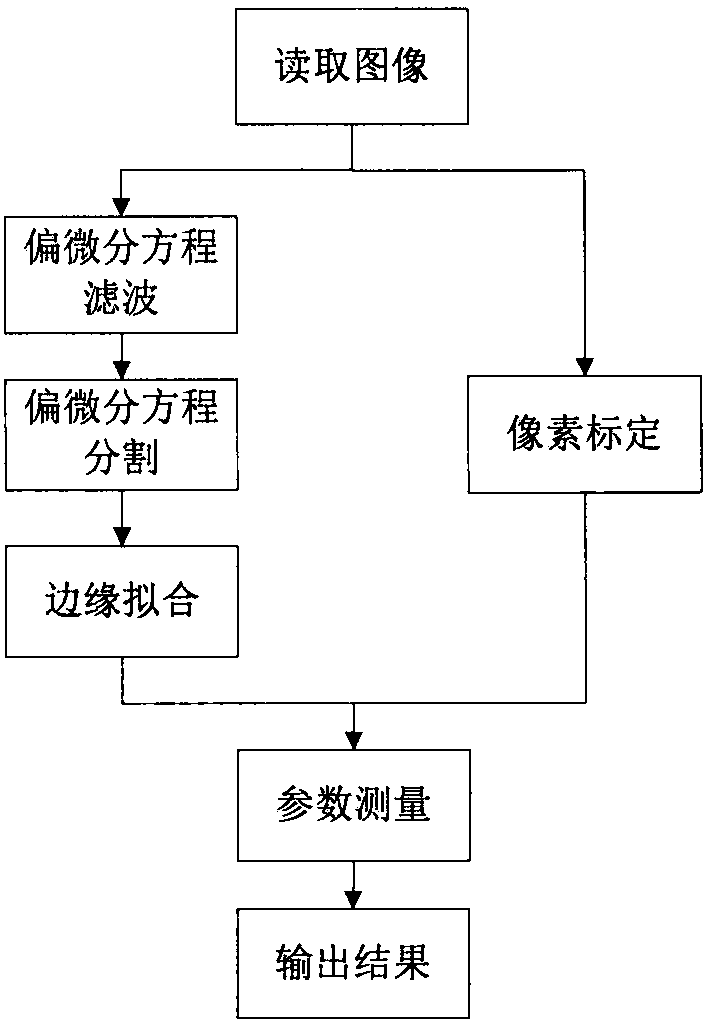
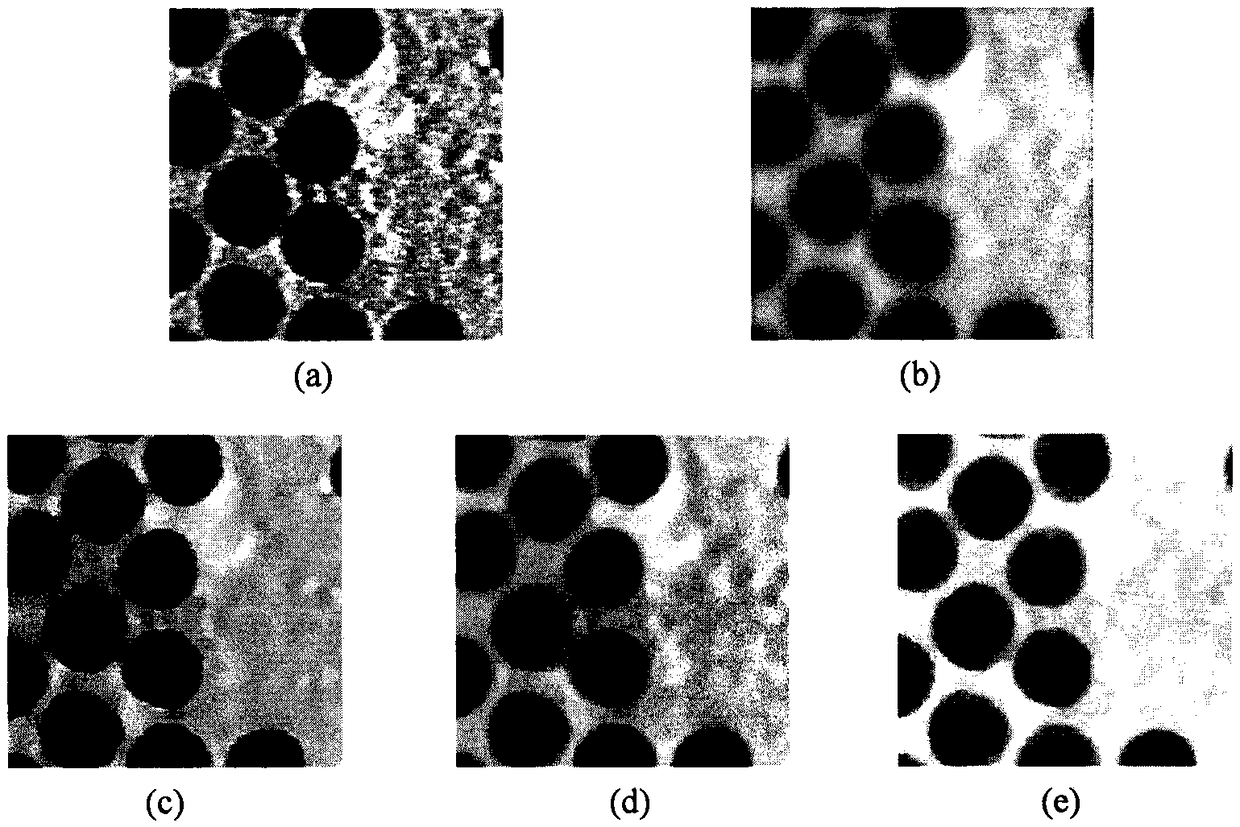
A Nanoparticle Size Measurement Method Based on Partial Differential Equation
ActiveCN105931277BImprove efficiencyHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisHyperbolic partial differential equationElectric power
The invention discloses a nanoparticle size measurement method based on partial differential equations, which includes: 1) inputting a nanoparticle image I, performing pixel-level multiplication of the filtering results of the average curvature flow model and the PM model to obtain a filtered image u; 2) Use the local region fitting model (RSF) to segment the image u; 3) Pixel calibration to obtain the actual size corresponding to each pixel in the image; 4) Use the convexity C of the target conv Select non-adhesive particles; 5) Obtain the diameter of spherical nanoparticles by performing least square circle fitting on the particle boundaries, and at the same time obtain the inscribed circle diameter r c , circumscribed circle diameter r i , and the sphericity of nanoparticles. The present invention can be widely used in high-tech fields that require nanoparticle size measurement technology, such as catalytic science, medical drugs, new materials, power industry, and composite materials.
Owner:思腾合力(天津)科技有限公司
Gait contour simulation method
InactiveCN105631386AGood localization effectImprove clarityCharacter and pattern recognitionMatrix differential equationAlgorithm
Provided is a gait contour simulation method. A level set function is expressed in a spatial-temporal discrete grid. First, an SDF (Sign Distance Function) is constructed, and initialization for zeroing is carried out; then, the numerical solution of a partial differential equation is solved; and finally, re-initialization is carried out through a curvilinear sign distance function, whether the numerical value is stable or not is judged, iteration is stopped if the numerical value is stable, or the process is repeated. A new variational level set model combining the image edge and regional information is adopted. The gait contour simulation method has a good localization effect for image boundaries. The image edge and regional information are combined, and the definition and distinctiveness of the gait contour are improved.
Owner:安徽勤勉知识产权代理有限公司
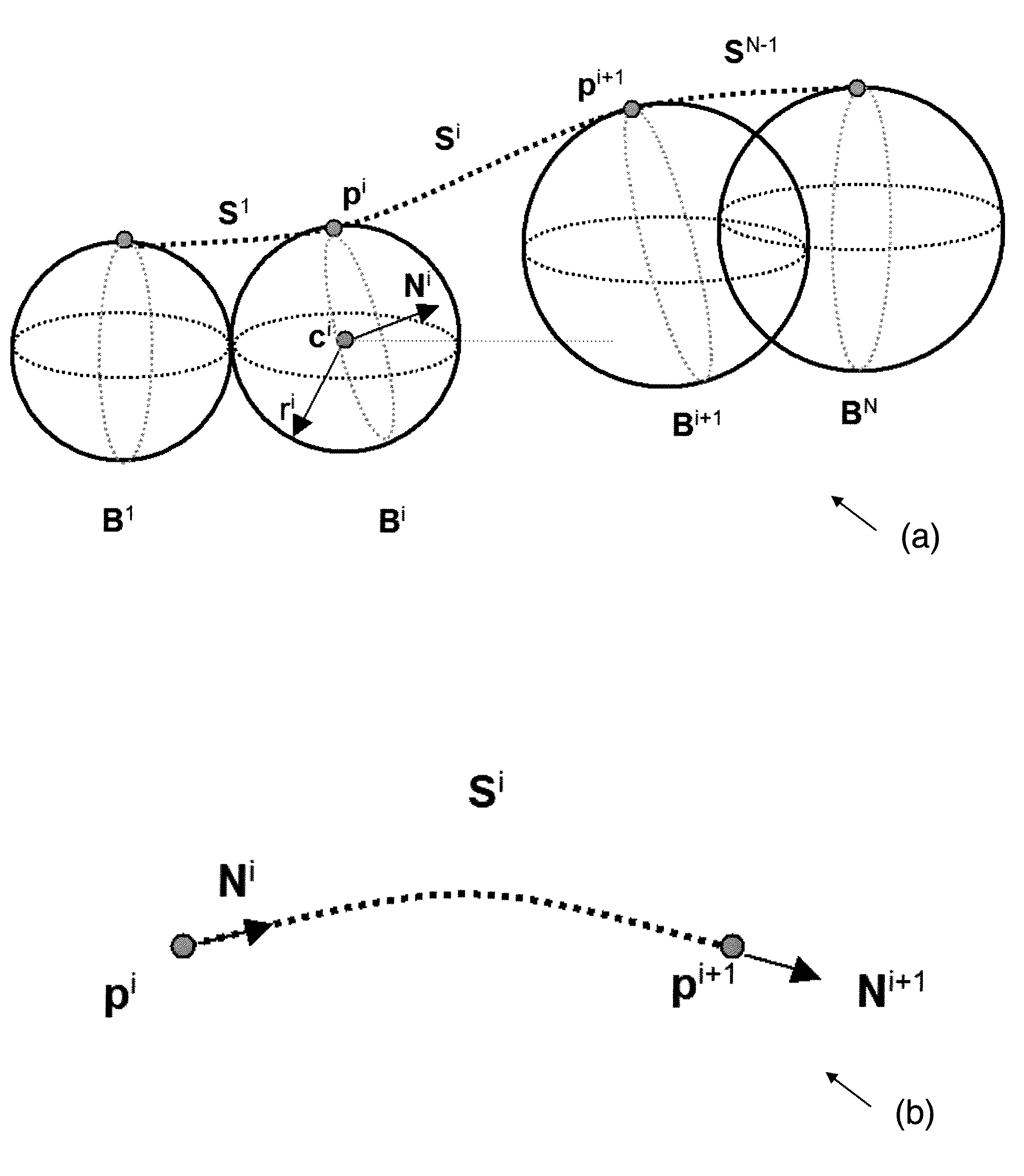
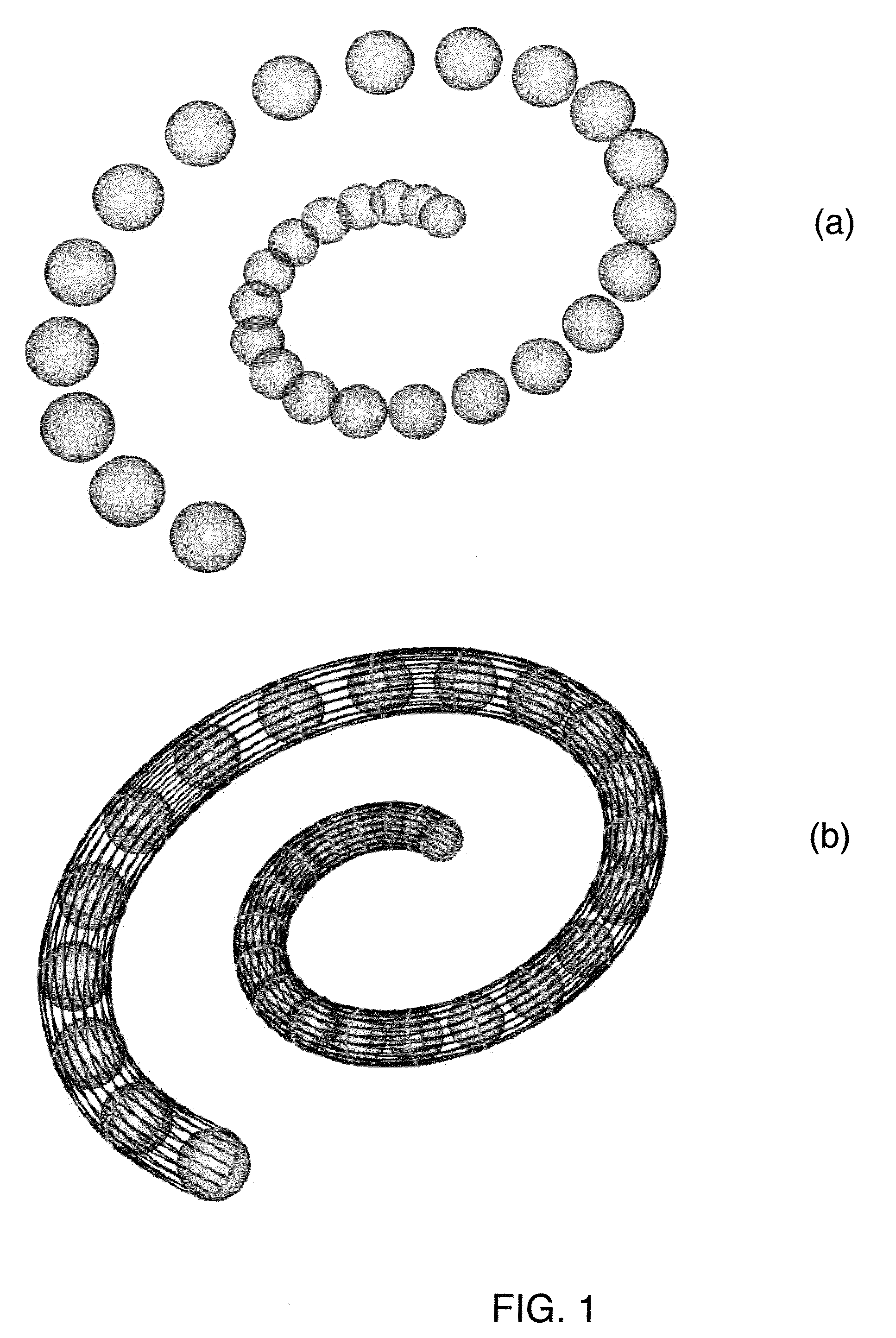
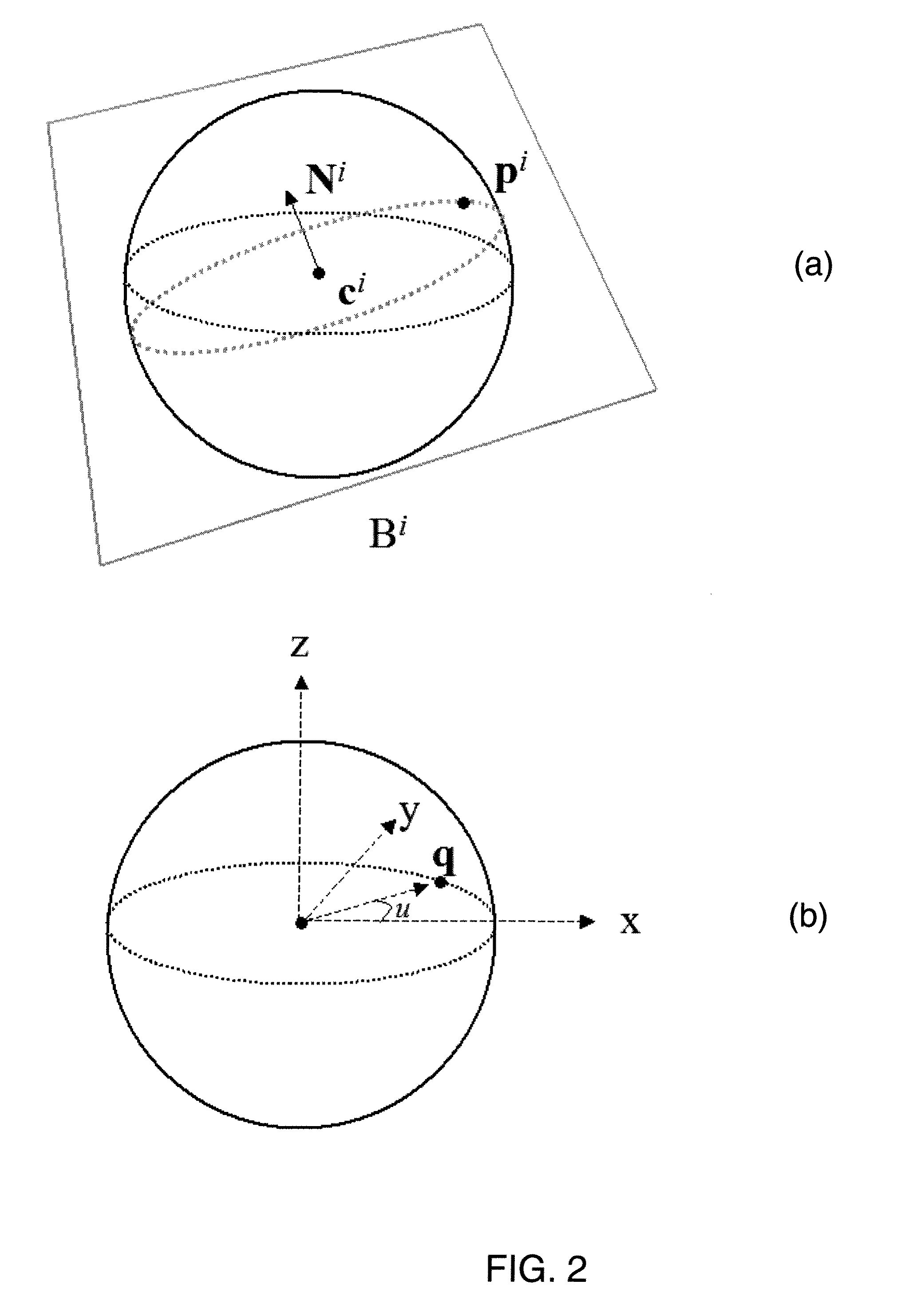
3D ball skinning using partial differential equations for generation of smooth tubular surfaces
InactiveUS8218910B2Character and pattern recognition3D modellingMatrix differential equationSkin surface
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
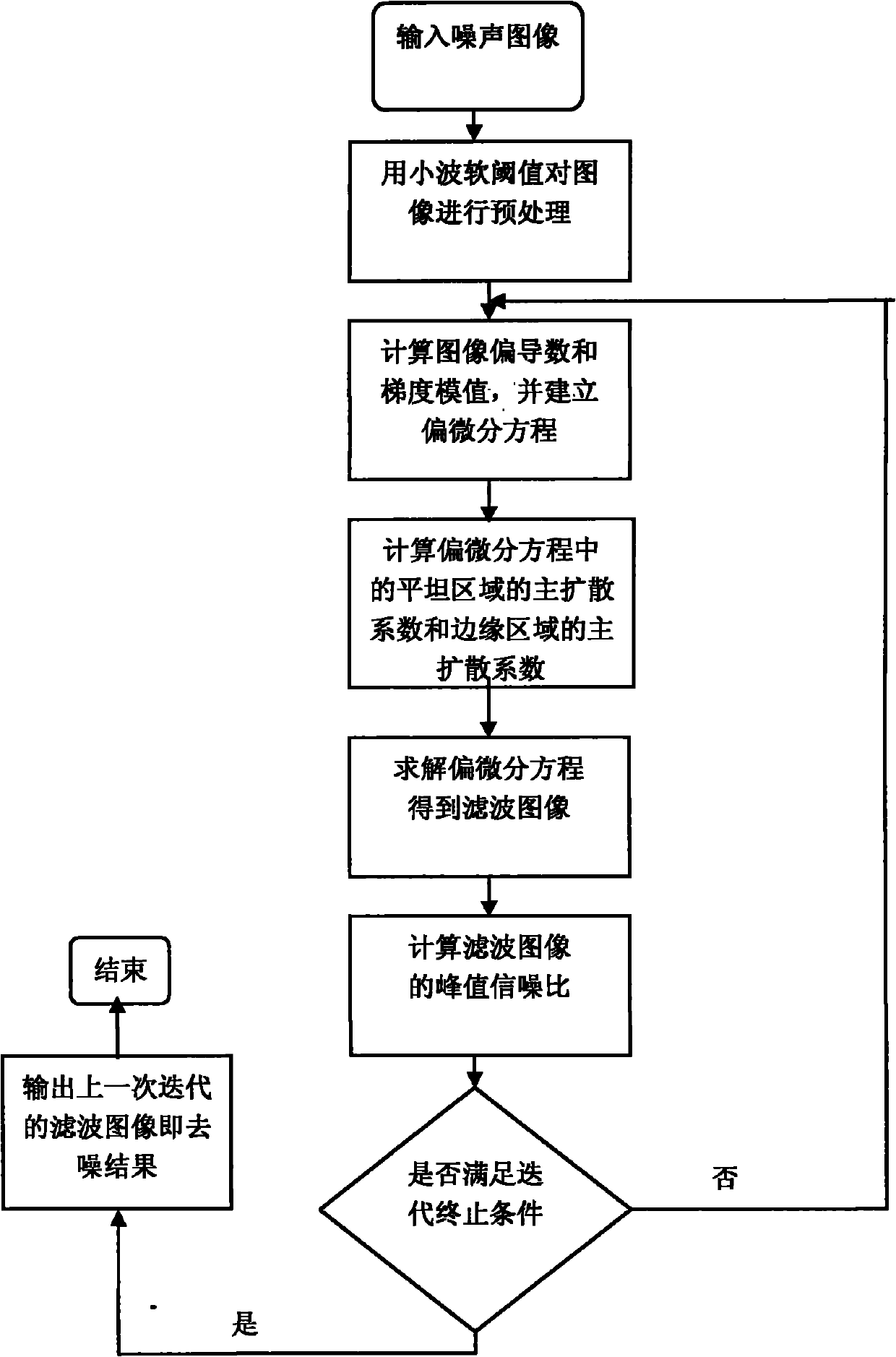
Denoising method of strong noise pollution image on basis of partial differential equation
InactiveCN101916433BImprove denoising effectAccurate calculationImage enhancementPattern recognitionPeak value
The invention discloses a denoising method of a strong noise pollution image on the basis of partial differential equation, mainly solving the problem of poor traditional denoising effect of the strong noise pollution image. The realization process comprises: (1) pretreating an input noise image u0, and recording the result as u; (2) calculating the partial derivative sum of the image u; (3) calculating the gradient module value of the image u; (4) according to the gradient and the gradient module value, building the partial differential equation; (5) calculating diffusion coefficients and psi in the partial differential equation; (6) utilizing the coefficients and psi, solving the partial differential equation to obtain a filter image; (7) calculating the peak signal to noise ratio PSNR of the filter image; and (8) repeating steps 2 to 7, when the PSNR value of the filter image output iteratively one time is smaller than that output iteratively in the previous time, stopping iteration, and outputting the previously iterated filter image. The invention has simple calculation and high operation speed, can better keep image texture details while smoothening strong noise and can be used for denoising a natural image with strong noise pollution.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
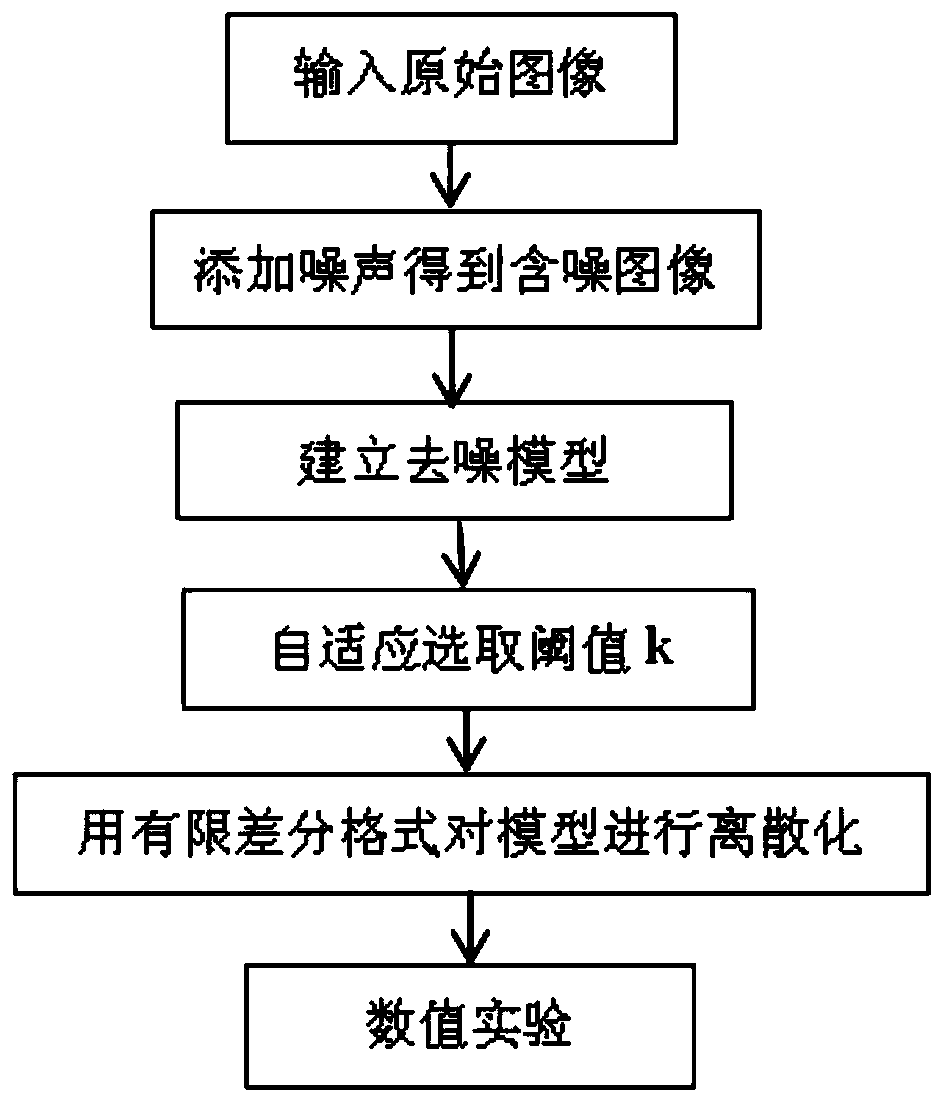
Self-adaptive threshold image denoising method based on four-order partial differential equation
ActiveCN110009591AEasy to keepRemove multiplicative noiseImage enhancementImage denoisingSample image
The invention discloses a self-adaptive threshold image denoising method based on a four-order partial differential equation, and the method comprises the steps: S1, inputting an original sample imageu, and adding noise to the original sample image u to obtain a noise-containing image u0; S2, constructing a denoising model based on a four-order partial differential equation: wherein delta is a Laplacian operator, k (k > 0) is a threshold value and used for judging the characteristics of the image; S3, selecting the threshold value k (k > 0) by adopting a self-adaptive threshold value method;S4, discretizing the denoising model by adopting a finite difference method, and solving the denoising model by adopting an iteration method to obtain a denoised image. According to the method, multiplicative noise can be effectively removed, meanwhile, image edge detail information is reserved, and compared with a classical denoising model, the denoising effect is better.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
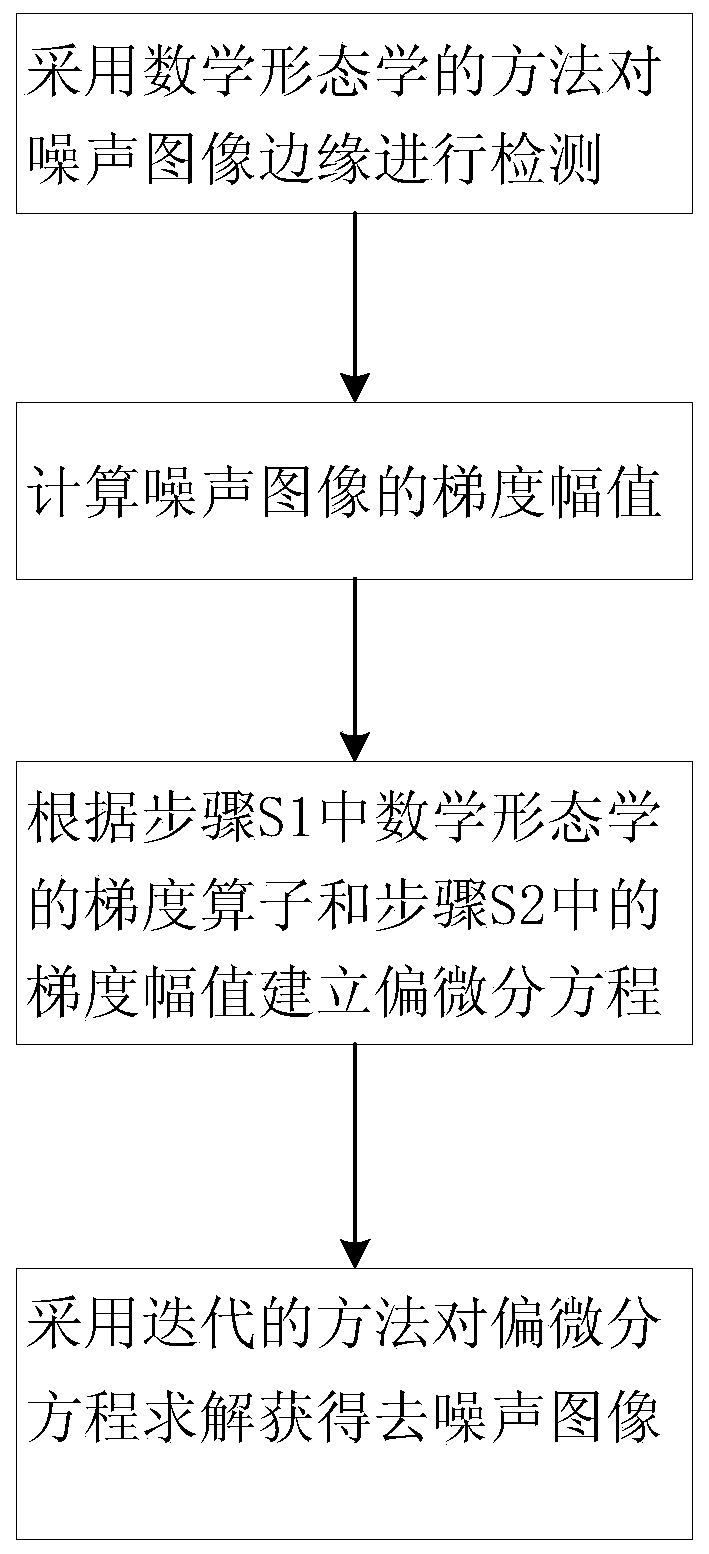
Image Denoising Method Based on Mathematical Morphology for Fourth Order Partial Differential Equation
ActiveCN106127716BGood image edgesImprove visual effectsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMathematical morphology
The invention discloses a fourth-order partial differential equation image denoising method based on mathematical morphology, which includes the following steps: S1 uses the method of mathematical morphology to detect the edge of the noise image; S2 calculates the gradient amplitude of the noise image; S3 according to The gradient operator of mathematical morphology in step S1 and the gradient amplitude in step S2 establish a partial differential equation. S4 uses an iterative method to solve the partial differential equation to obtain a denoised image. The present invention performs image denoising based on the fourth-order partial differential equation of mathematical morphology, which better maintains the edges of the processed image and has better visual effects.
Owner:七腾机器人有限公司
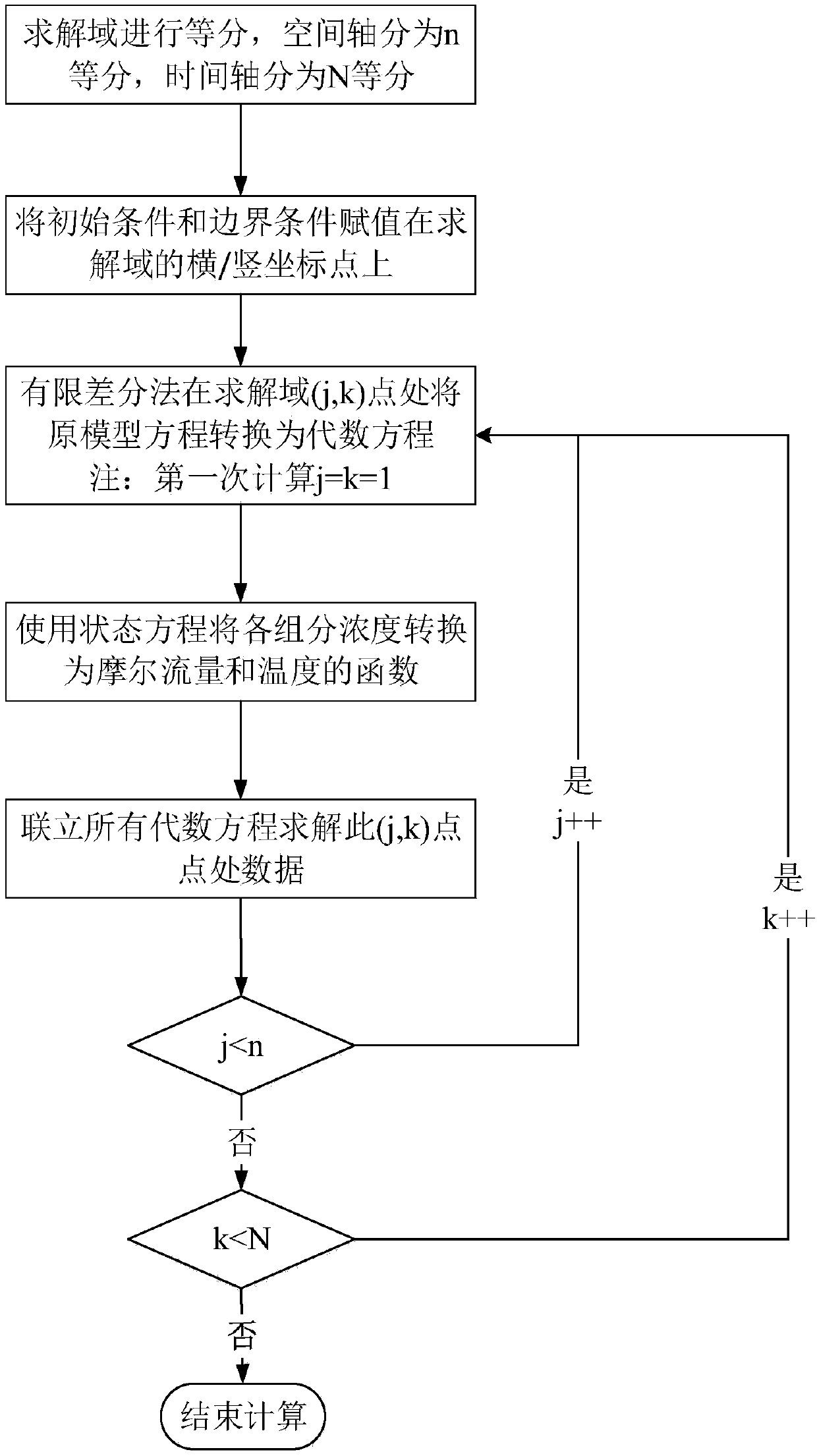
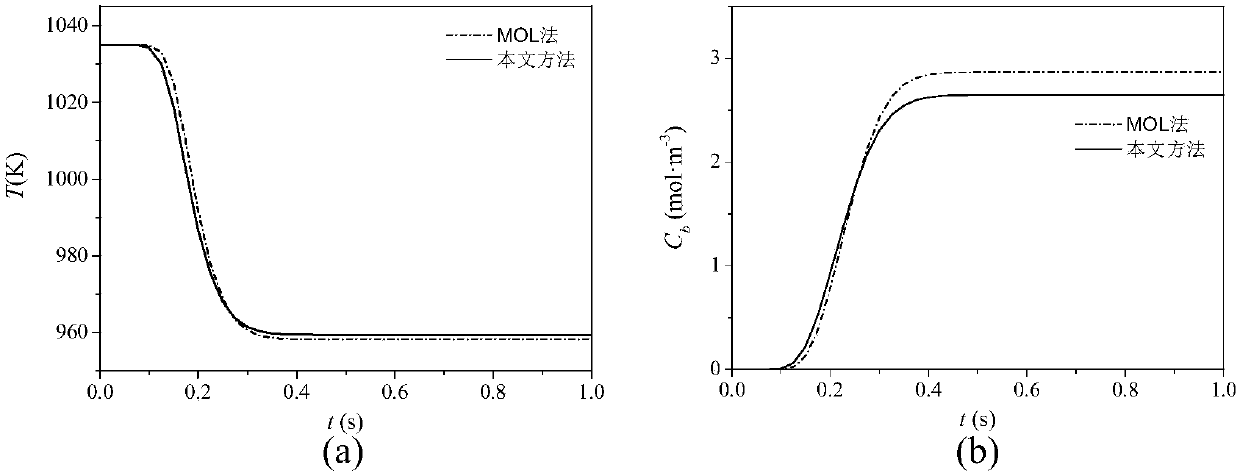
Dynamic model solution method for one-dimensional plug flow reactor
InactiveCN108446480AReduce calculation errorsThe end result is preciseDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingAlgebraic equationGas phase
The present invention relates to a dynamic model solution method for a one-dimensional plug flow reactor with the feedstock of gas. The method comprises: starting from a mechanism model of a plug flowreactor (ideal tubular reactor), discretizing partial differential equations for describing the dynamics model into algebraic equations by using a finite difference method; converting the concentration in the model equation into a function of the temperature and gas molar flow by using a gas state equation; and by using simultaneous equations, solving to obtain distribution of the temperature andcomposition of the plug flow reactor with the space and time. The method disclosed by the present invention can be used for the calculation method for the ideal tubular reactor with the feedstock component of the gas phase, and the assumption that the gas volume flow must be set to a constant parameter in the previous solution process is overcome, so that the dynamic model solution result of thereactor is more accurate.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Continuous reinforcement learning system and method based on stochastic differential equation
ActiveCN110502721AAvoid the disadvantages of controlling itselfAdaptableCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsMatrix differential equationState parameter
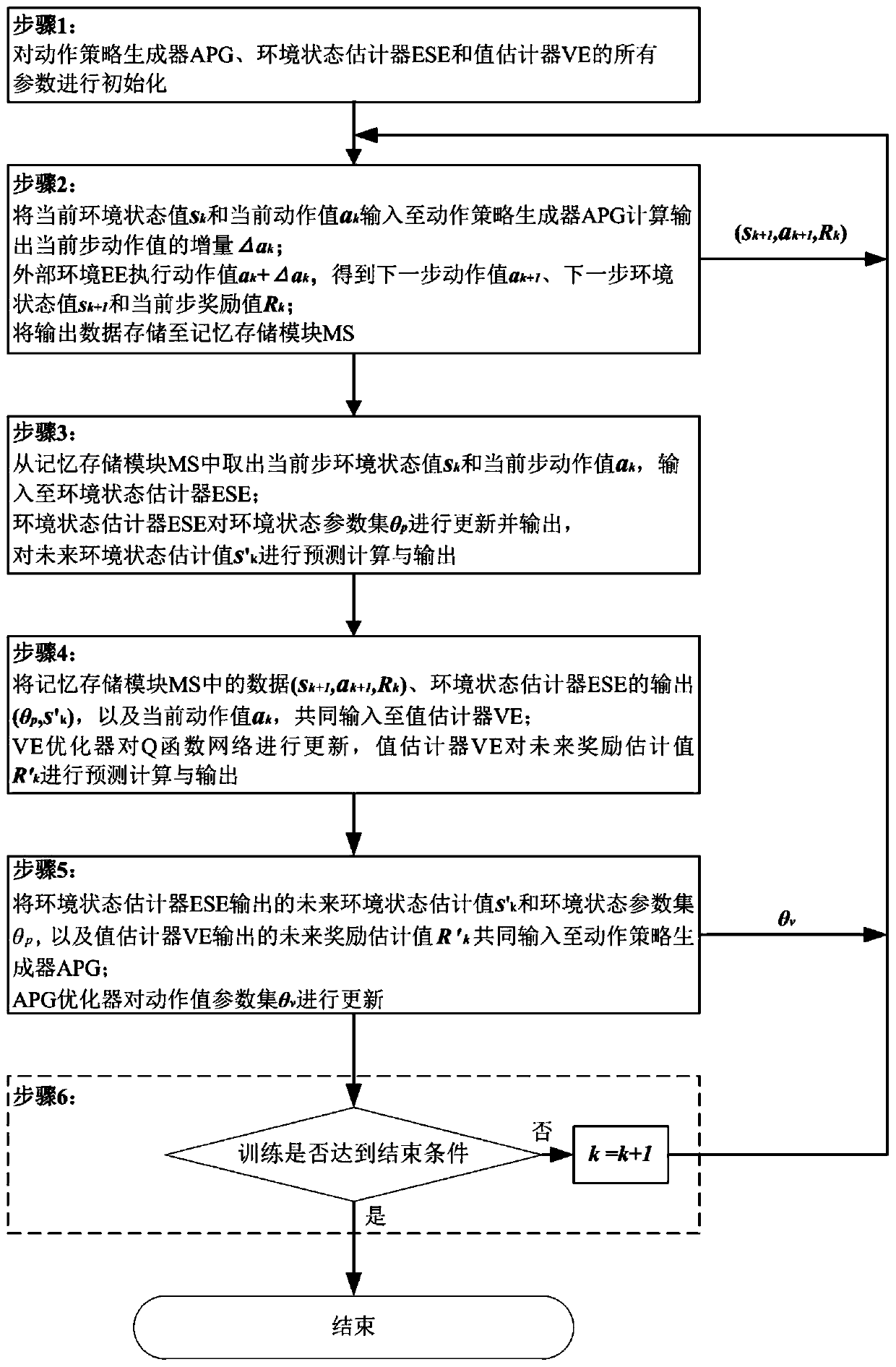
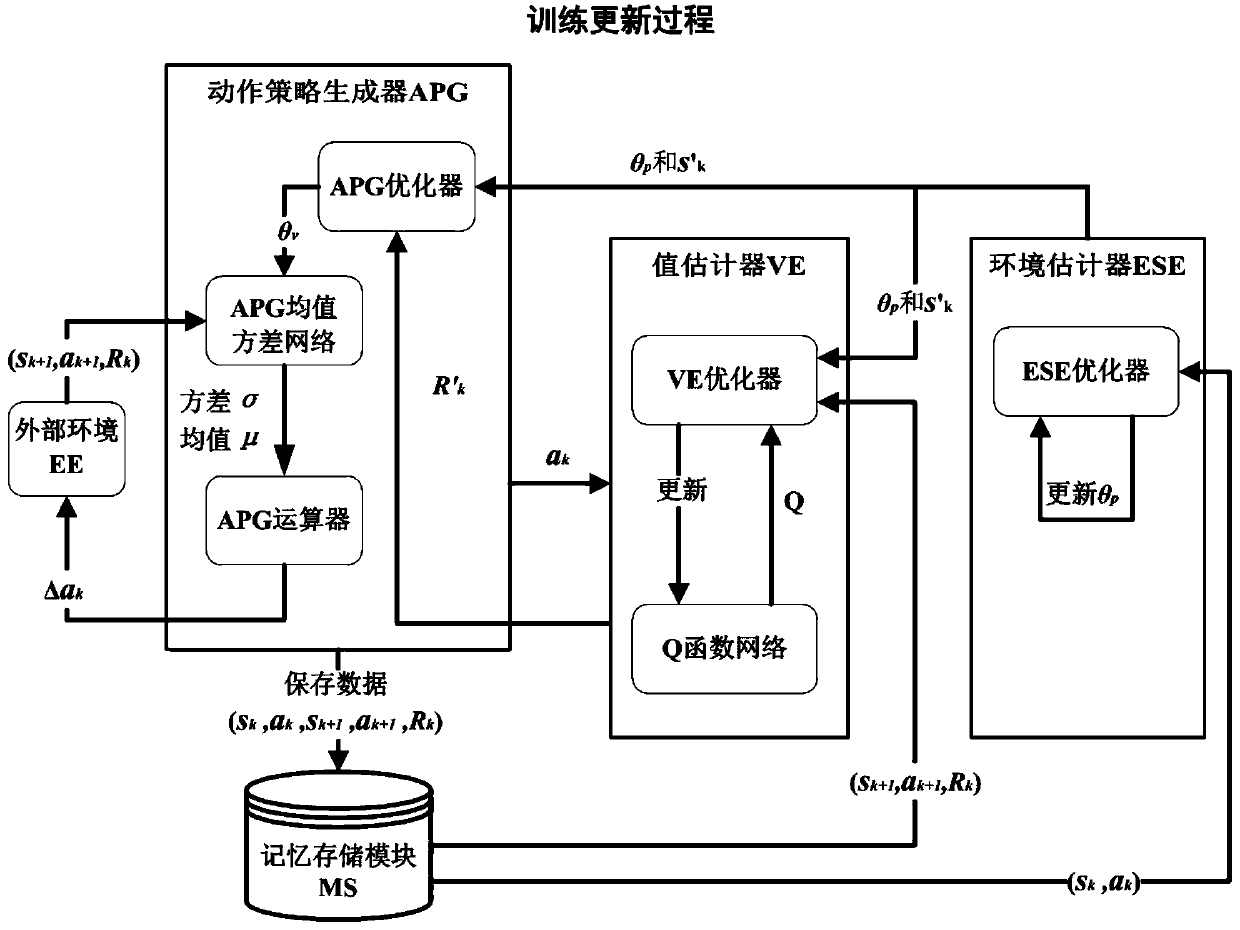
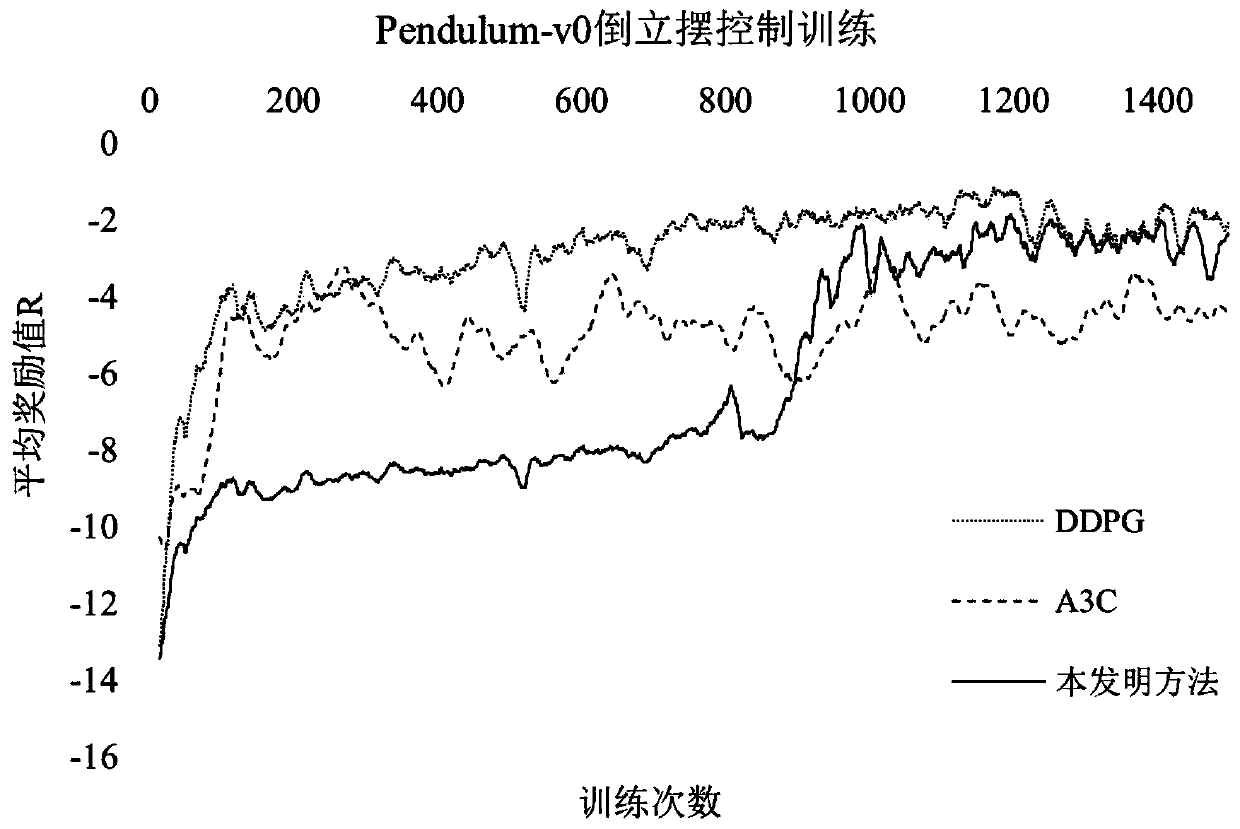
The invention discloses a continuous reinforcement learning system and method based on a stochastic differential equation. The system comprises an action strategy generator APG, an environment state estimator ESE, a value estimator VE, a memory storage module MS and an external environment EE. The method comprises the following specific steps: an action strategy generator APG, an environment stateestimator ESE and a value estimator VE are initialized; an action strategy generator APG calculates an output action value increment delta ak; the external environment EE outputs a next action valueak + 1, a next environment state value sk + 1 and a current reward value Rk and stores the values in a memory storage module MS; the environment state estimator ESE updates the environment state parameter set theta p and predicts a future environment state estimated value s'k; the VE optimizer updates the Q function network and predicts a future reward estimation value R'k; and the APG optimizer updates the action value parameter set theta v. The method is based on a stochastic differential equation as a basic model, continuity of action control can be achieved, variance of the training process can be controlled, and actions can be selected by predicting changes of the environment so as to achieve better environment interaction.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
A Design Method of Disturbance Observer for Flexible Manipulator Based on Partial Differential Equation
ActiveCN104020664BRealize interference observationAdaptive controlMatrix differential equationElliptic partial differential equation
Owner:GUODIAN SCI & TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com