Complex texture prediction method based on video coding
A technology of video coding and prediction method, applied in the multimedia field, can solve the problems such as the inability to further reduce the theoretical limit entropy operation complexity, the insufficient use of pixel texture correlation, the easy misjudgment of predicted pixel components, etc., to reduce the theoretical limit entropy, The effect of improving the image coding compression ratio and reducing the possibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
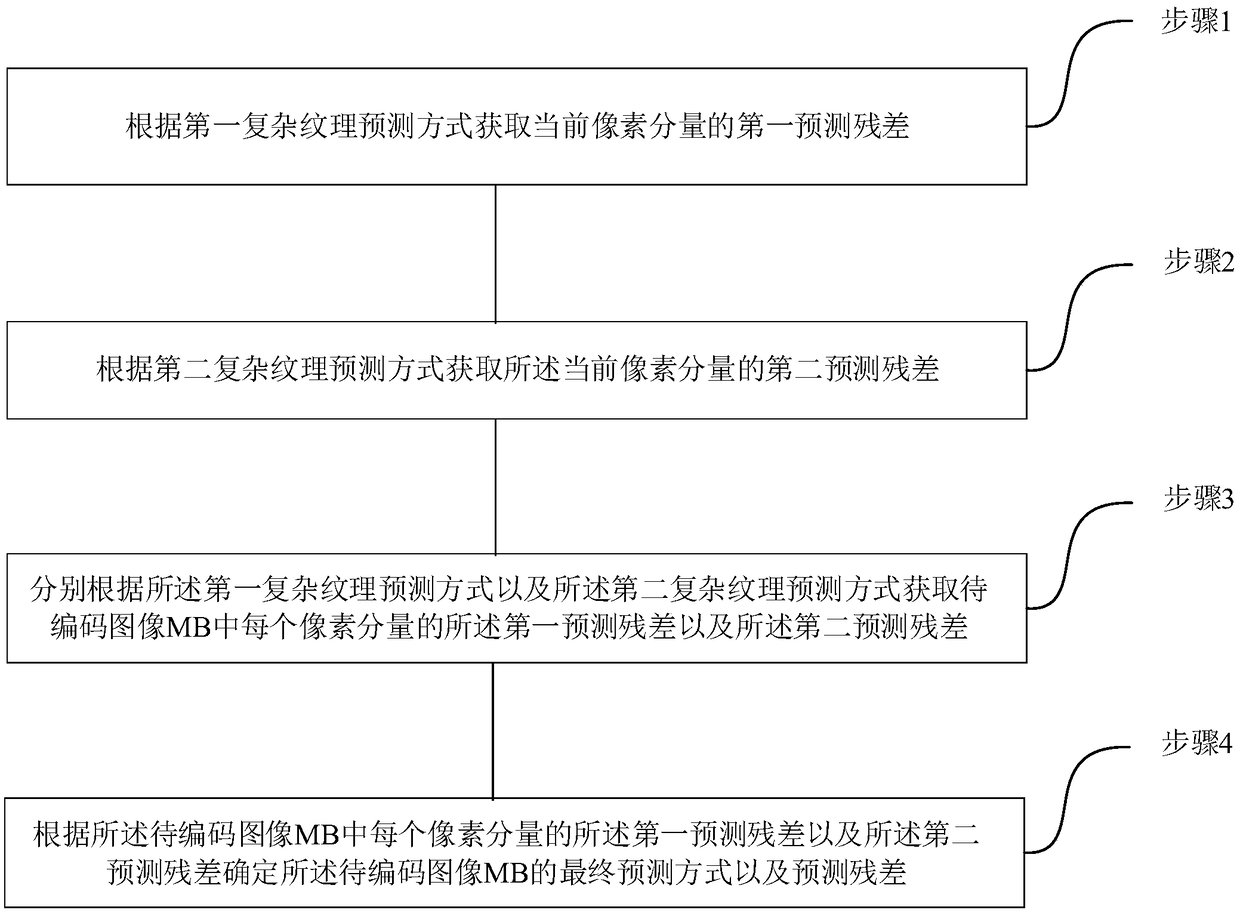
[0050] See figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic flowchart of a video coding-based complex texture prediction method provided by an embodiment of the present invention. The method comprises the steps of:
[0051] Step 1. Obtain the first prediction residual of the pixel component to be encoded according to the first complex texture prediction method;
[0052] Step 2. Obtain the second prediction residual of the pixel component to be encoded according to the second complex texture prediction method;
[0053] Step 3. Obtain the first prediction residual and the second prediction residual of each pixel component in the image MB to be encoded according to the first complex texture prediction mode and the second complex texture prediction mode respectively;
[0054] Step 4. Determine the final prediction mode and the final prediction residual of the image MB to be encoded according to the first prediction residual and the second prediction residual of each pixel component in the...
Embodiment 2
[0082] This embodiment describes in detail the first complex texture prediction method proposed by the present invention on the basis of the above embodiments, and the prediction method includes the following steps:
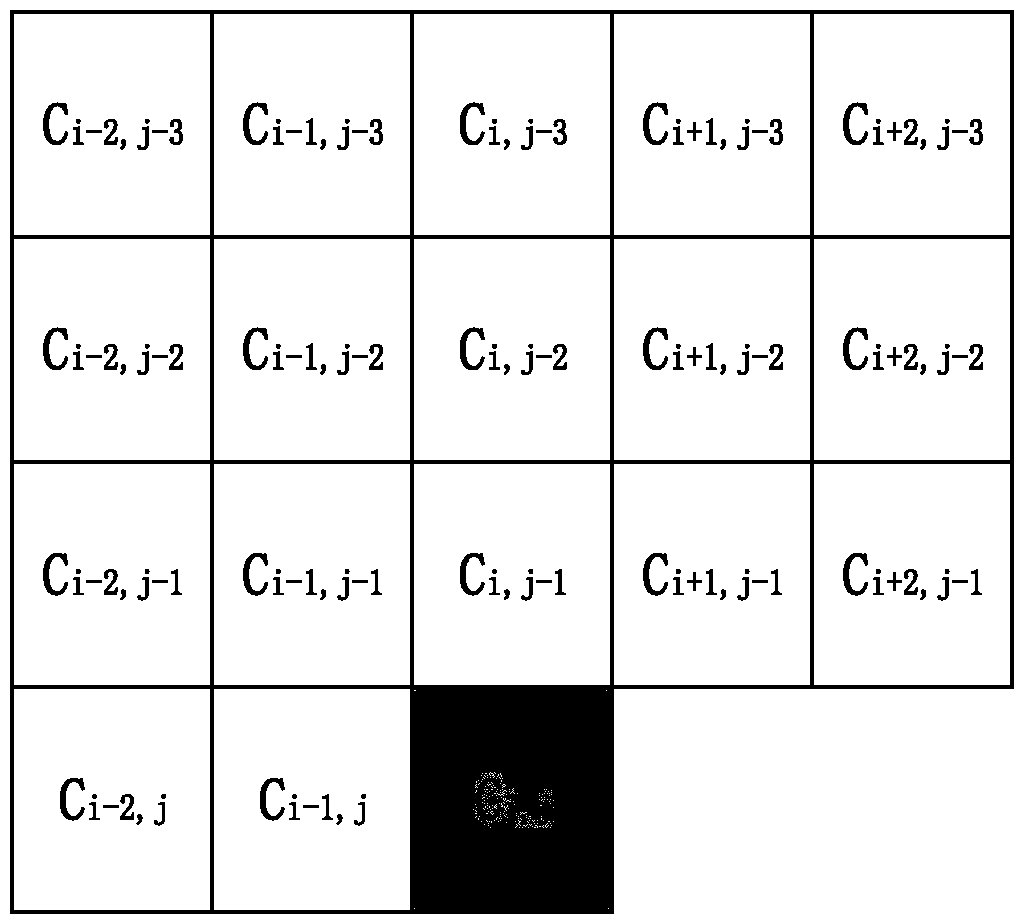
[0083] Step 1, define reconstruction pixel components;
[0084] Define the pixel component to be encoded as Cij, select K reconstructed pixel components encoded around the pixel component to be encoded, and number the encoded K reconstructed pixel components, and the numbering order can be specified, where K≥1.
[0085] Preferably, as figure 2 as shown, figure 2 A reference schematic diagram for reconstructing pixel components in the first complex texture prediction mode provided by the embodiment of the present invention; set the sequence number of the pixel component to be encoded as Cij, the sequence number of the reconstructed pixel component on the left side of the pixel component Cij to be encoded, and the number i starts from the right Sorting in desce...
Embodiment 3
[0105] On the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments, the present invention illustrates the first complex texture prediction method. The method includes the following steps:
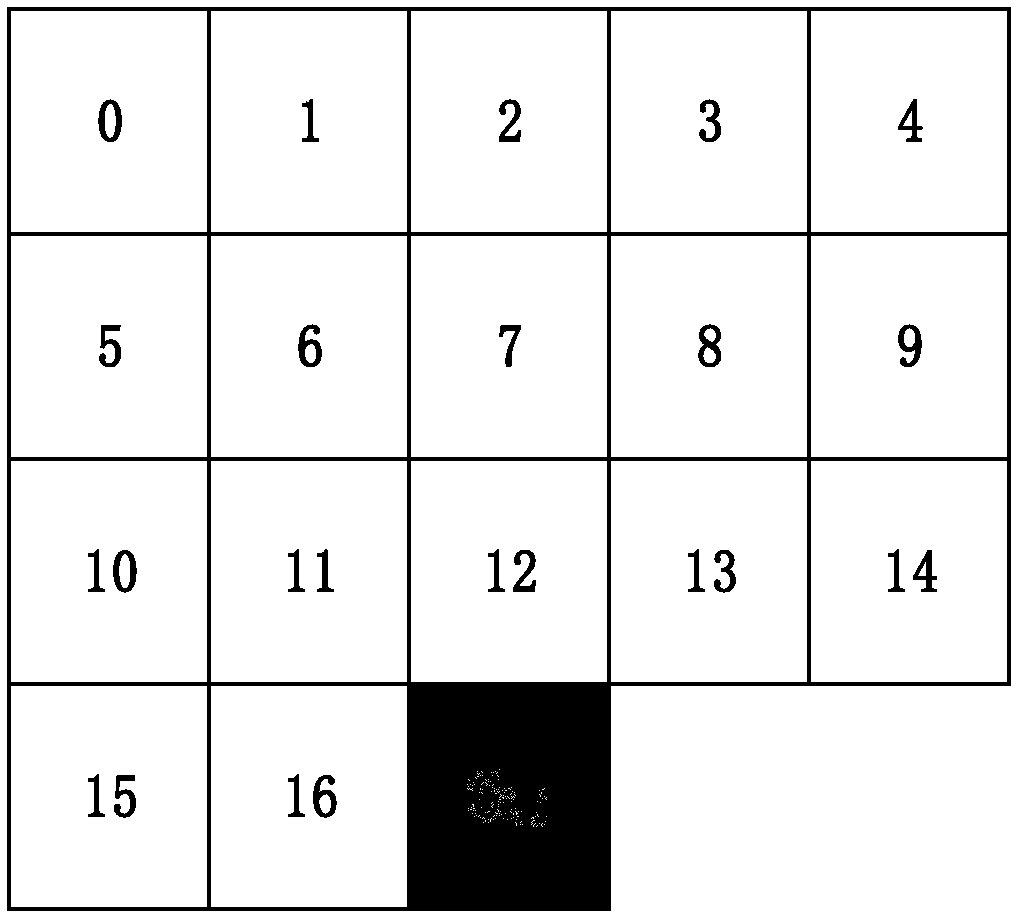
[0106] Step 1, define reconstruction pixel components;
[0107] Define the pixel component to be encoded as Cij, select K reconstructed pixel components encoded around the pixel component Cij to be encoded, and number the encoded K reconstructed pixel components, and the numbering order can be specified, where K≥1.
[0108] Preferably, the coded K reconstructed pixel components are numbered, and the numbers are sorted from top to bottom and from left to right, and the serial numbers are arranged from 0 to K-1.
[0109] In this embodiment, 17 reconstructed pixel components around the pixel component Cij to be encoded are taken as an example for illustration, as image 3 as shown, image 3 Another reference schematic diagram of reconstructed pixel components in the first complex texture prediction meth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com