A sugarcane distribution recognition method based on optical remote sensing data
A technology of optical remote sensing and recognition methods, applied in image data processing, character and pattern recognition, image analysis, etc., can solve the problems of land fragmentation, cloud cover, low, interference recognition accuracy, etc., to achieve the benefit of agricultural management and planning Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
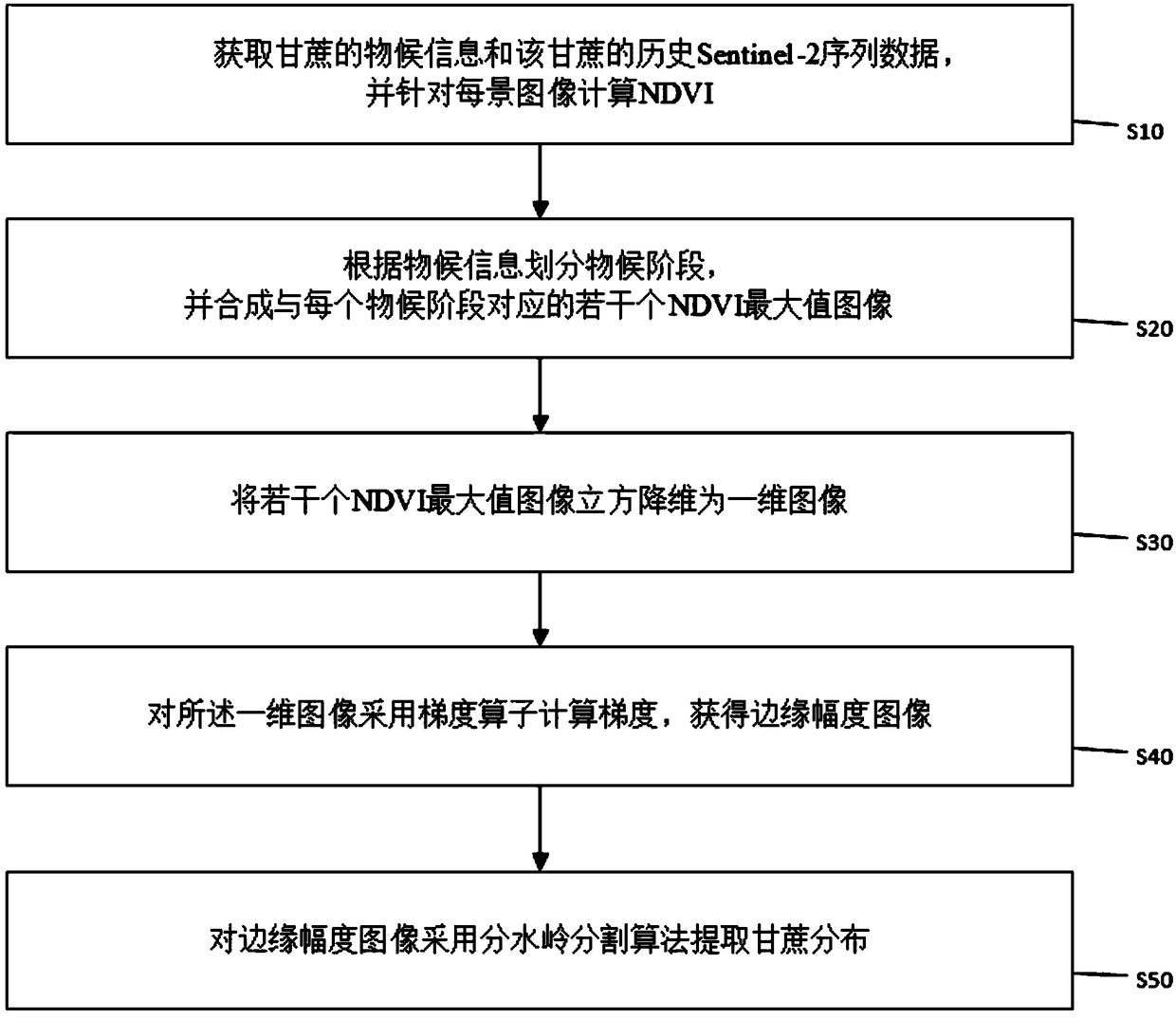
[0076] The following takes the sugarcane distribution identification in Zhanjiang City, Guangdong Province, China as an example to describe in detail:
[0077] 1. Since Zhanjiang City is located in the south of China, the temperature and rainfall are sufficient all year round. Then refer to expert knowledge and according to the phenological information of Zhanjiang local sugarcane, select an appropriate time interval and divide it into 5 phenological stages. Please refer to Table 1.
[0078] Table 1 Sugarcane phenological stages in Zhanjiang City
[0079] seedling stage
From January 1st to March 31st
tillering stage
From April 1st to June 25th
Jointing stage
From June 26th to August 10th
elongation period
From August 11th to November 30th
maturity
From December 1st to December 31st
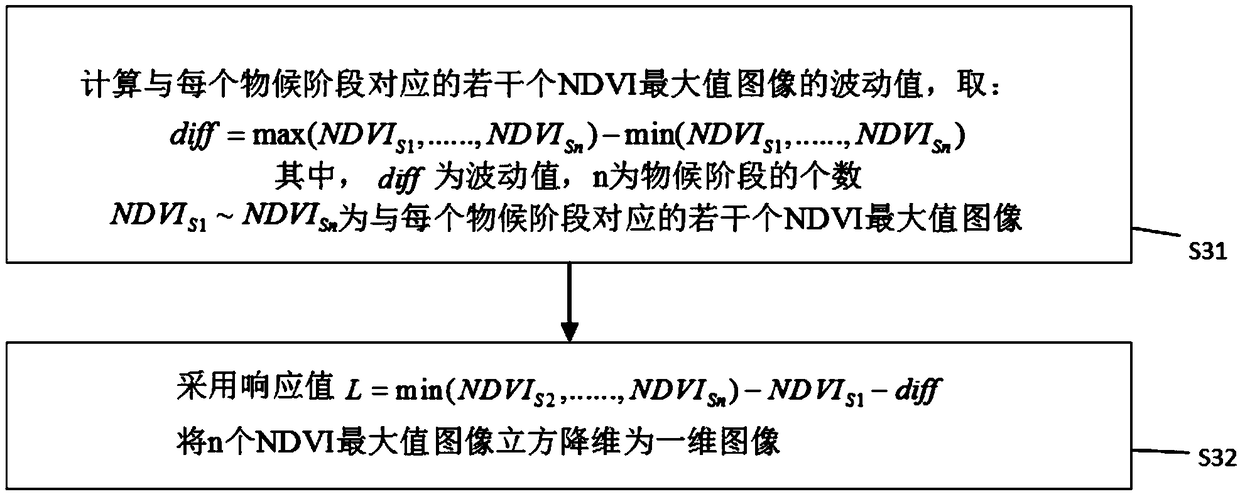
[0080] 2. Please refer to 5. Use the following formula to synthesize the 5 NDVI maximum images corresponding to the 5 phenological sta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com