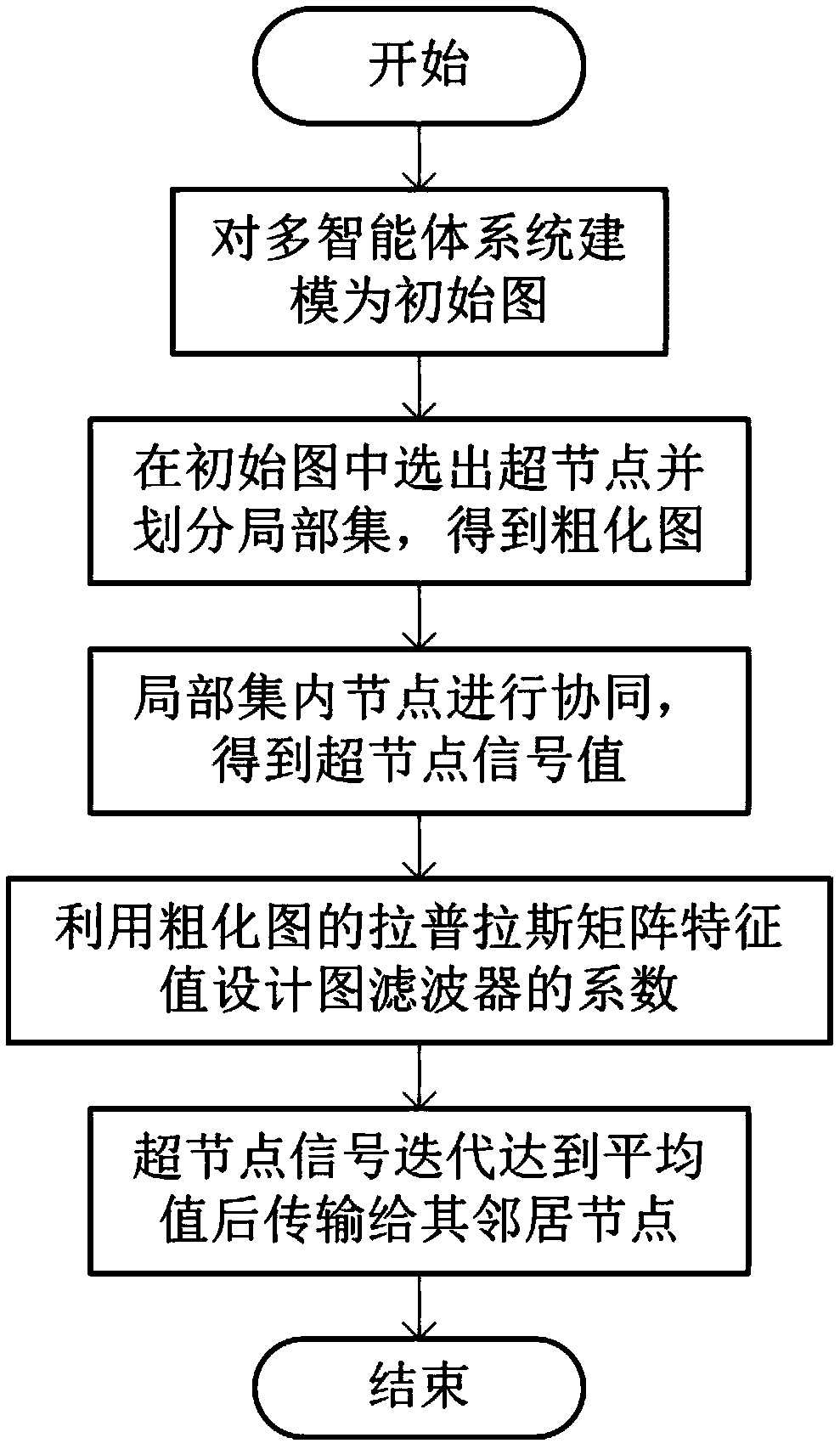
Multi-agent system consistency method based on signal coarsening on graph
A multi-agent system and multi-intelligence technology, applied in the field of multi-agent systems, can solve problems such as slow convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
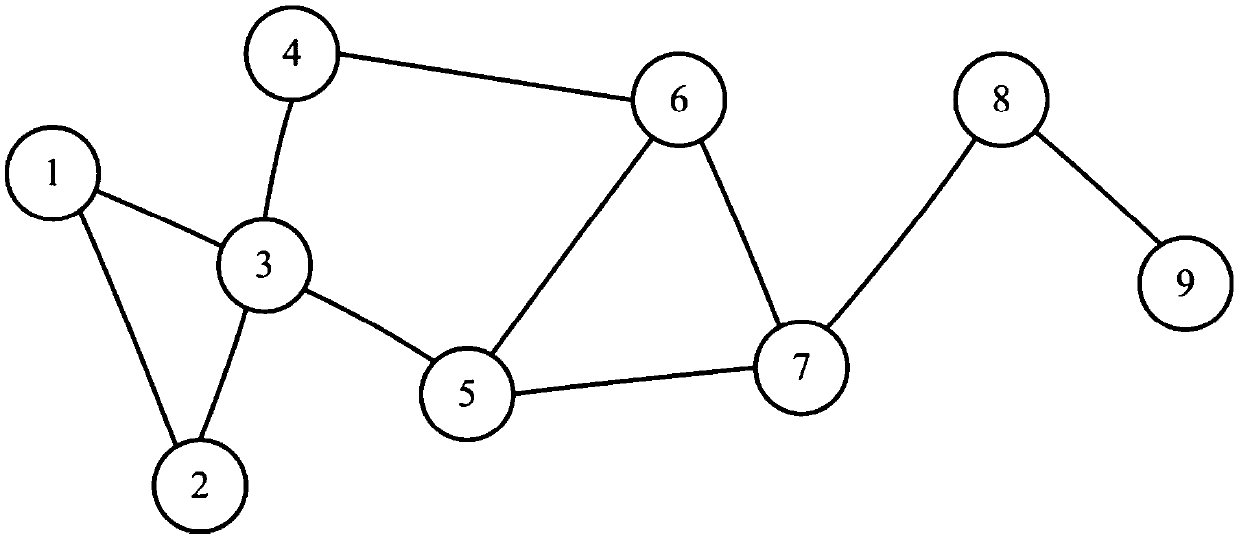
[0057] Create a node numbered 1-9, the signal initial value x(0)=[-98-36-57-24-6] T A graph model such as figure 2 shown. In the figure, node 3 has the largest degree, and it is selected as the first super node, numbered as A, and its neighbor nodes 1, 2, 4, 5 and the edges between them are divided into a local set; then node 4 and Node 6, the edge between node 5 and node 6, node 5 and node 7, select node 7 as the second super node in the remaining part of the graph (when there are nodes with the same degree, select according to the numbering order) , numbered B, forms the second local set with nodes 6, 8 and the edges between them; finally, node 9 alone forms the third local set, and the number of the third supernode is C. The number of initial graph nodes is 9, and the number of roughened graph nodes is 3. Coordinate the nodes in each local set, and the signal value of the super node Connect the edges between the super nodes, and the roughened graph after completion i...
example 2
[0059] A comparison between the method proposed by Izumi S et al. and the present invention is given. The iterative formula of the method proposed by Izumi S et al. is, x(t+1)=(I-ε t L)x(t), where lambda max is the largest eigenvalue of the initial graph Laplacian matrix. The inventive method iterative formula is x(t+1)=(I-ε t L)x(t), where λ' max is the largest eigenvalue of the coarsened graph Laplacian matrix. The iteration termination condition is that the difference between the signal value of each node and the signal value after the previous iteration is less than 10 -4 . Comparing the number of iterations, the results are as follows Figure 5 shown. The iteration time is compared, and the results are shown in Table 1. Compared with the existing invention 1, the number of iterations of the algorithm of the present invention is reduced by 72.12% on average, and the iteration time of the algorithm of the present invention is reduced by 77.43% compared with the ...
example 3
[0064] A comparison between the method proposed by Yi J W et al. and the invention of the present invention is given. The iterative formula of the method proposed by Yi J W et al. is x(t+1)=(I-ε t L)x(t), where p is the number of different eigenvalues of the Laplace matrix of the initial graph (0=λ 1 2 …p ). The inventive method: iterative formula is x (t+1)=(I-ε t L)x(t), where Where m is the number of different eigenvalues of the Laplacian matrix of the coarsening graph (0=λ 1 2 …m ). Comparing the number of iterations, the results are as follows Image 6 shown. The iteration time is compared, and the results are shown in Table 2. Compared with the method proposed by Yi J W et al., the number of iterations of the algorithm of the present invention is reduced by 78.62% on average, and the iteration time of the algorithm of the present invention is reduced by 74.25% compared with the existing invention 1 algorithm when the number of nodes is greater than 1000.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com