Compressive sensing of light transport matrix
A compressed sensing and optical transmission technology, applied in 3D image processing, image data processing, image data processing, etc., can solve the problems of difficult processing and storage tasks, restricting the efficient use of optical transmission matrices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
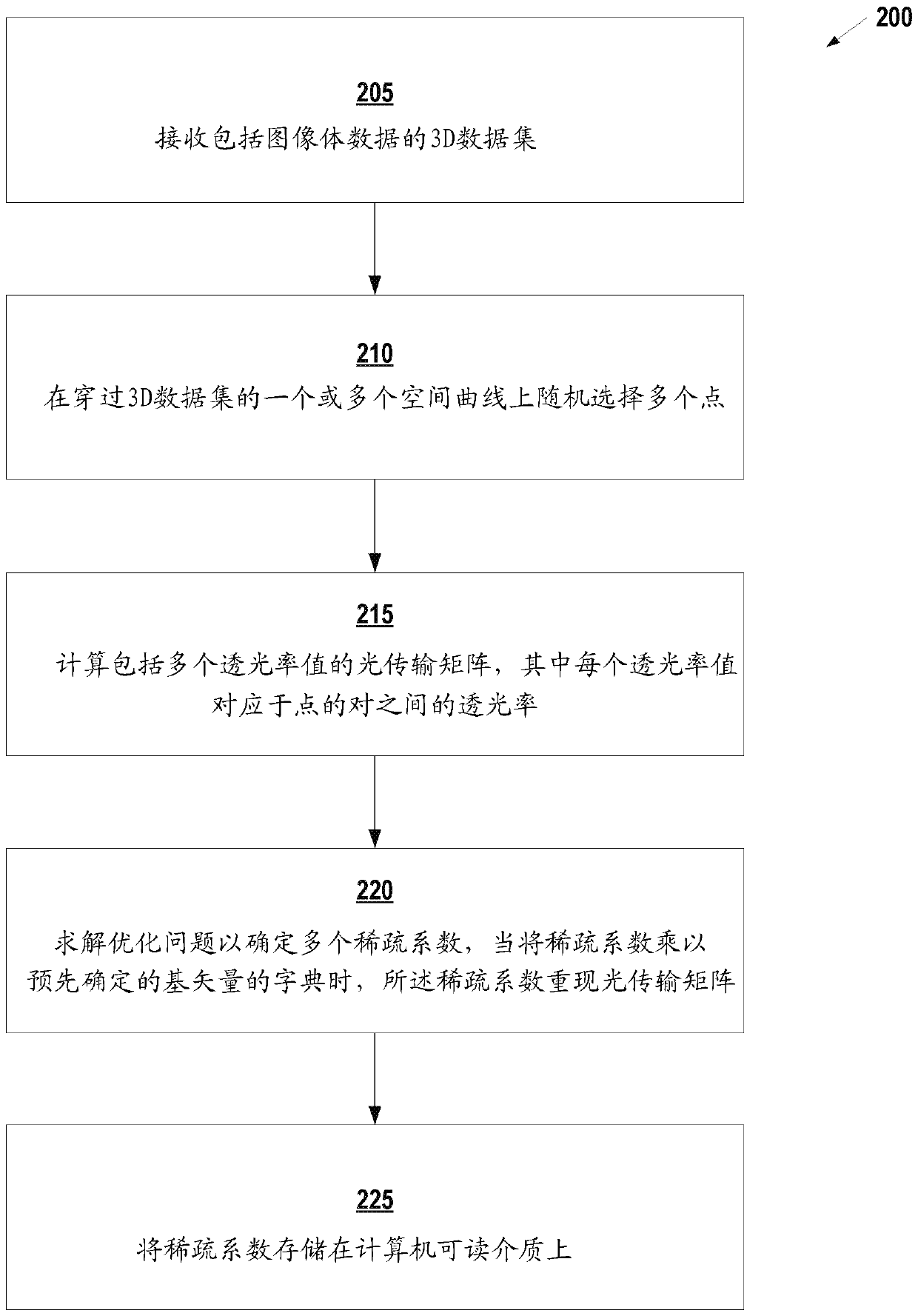
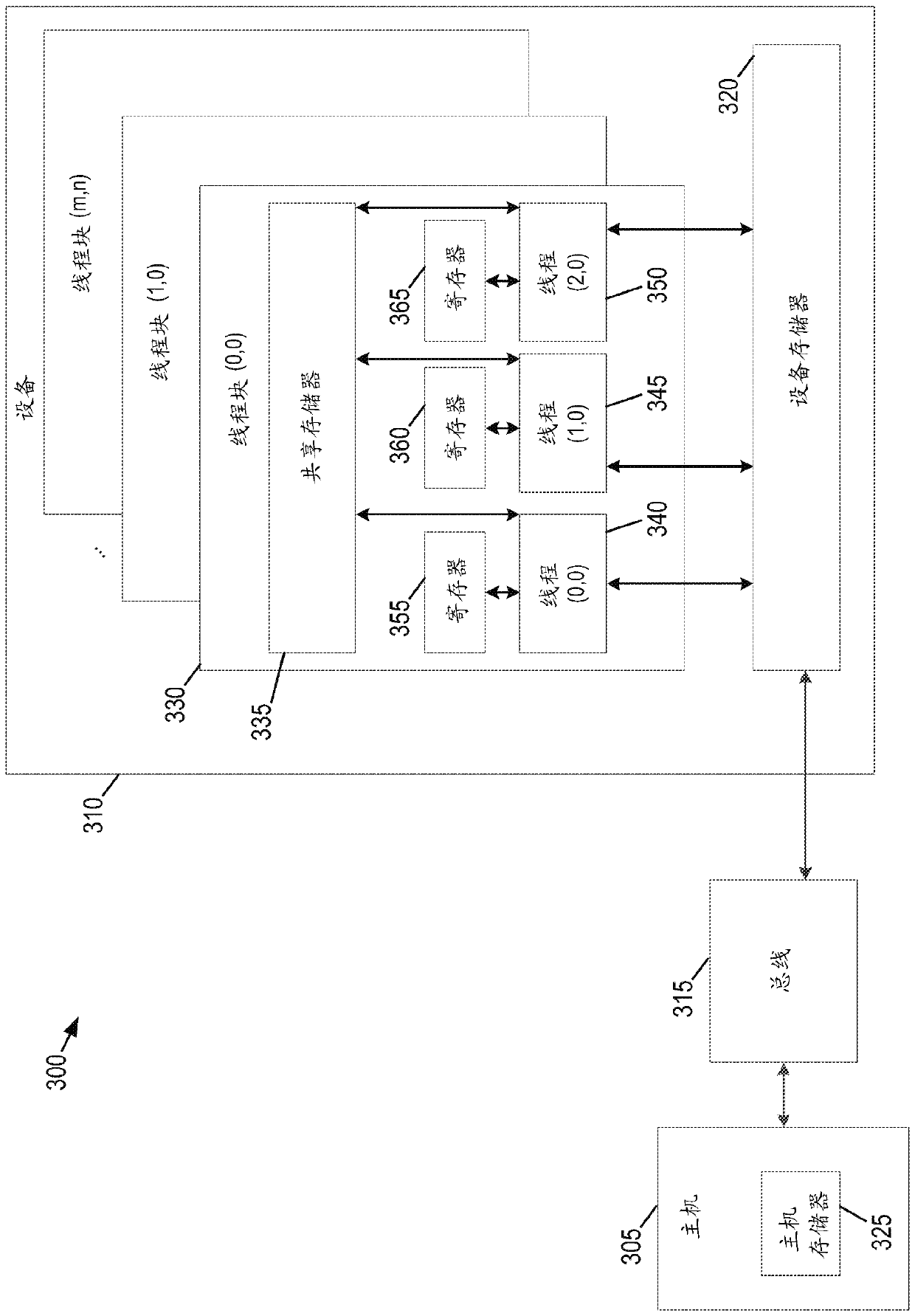
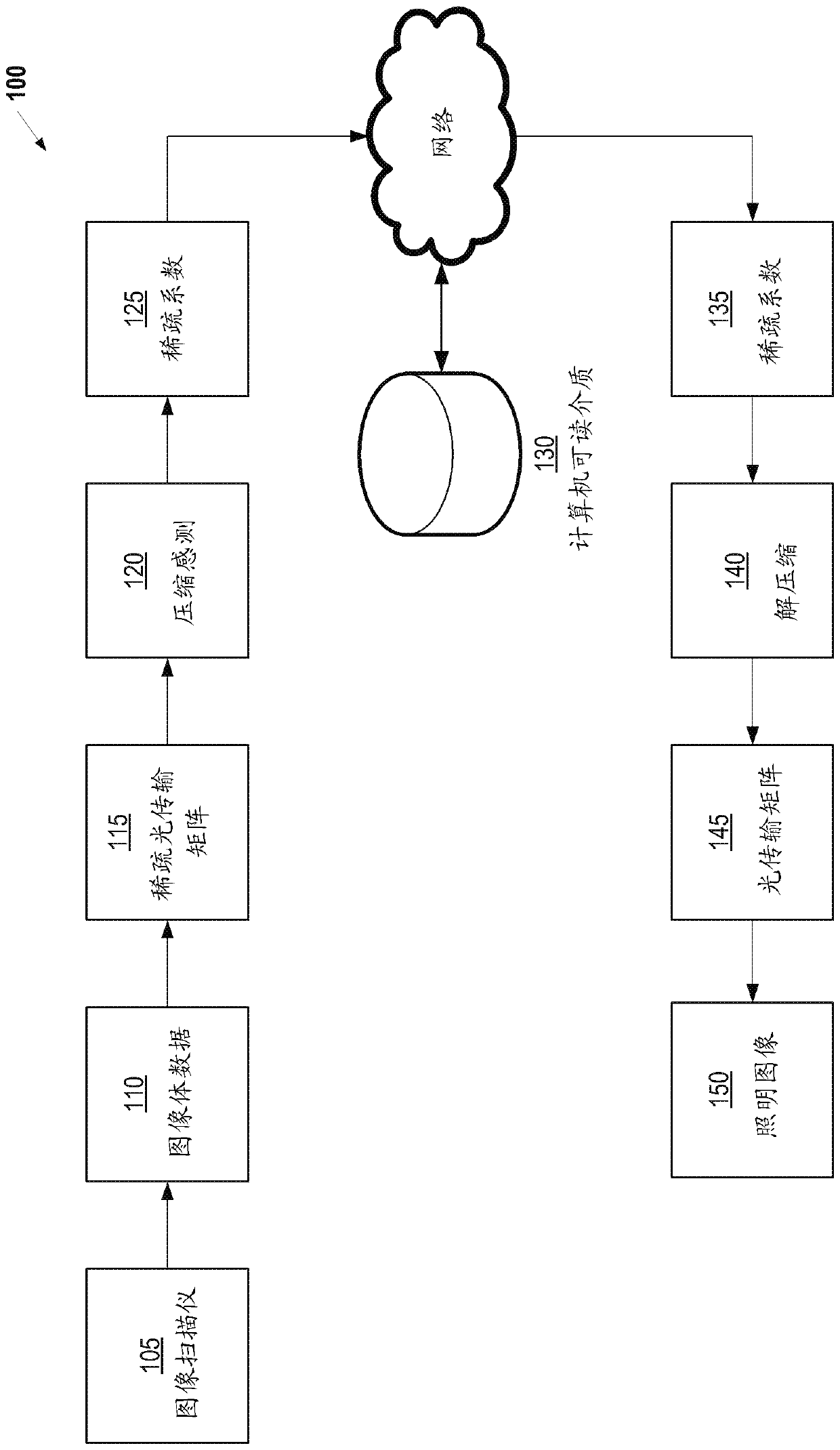
[0018] The following disclosure describes the present invention based on several embodiments related to methods, systems and devices related to compressed sensing (CS) of optical transmission matrices. The optical transmission matrix is a very large matrix. Its size is defined by all possible combinations of points and their relationship. But with the help of CS, and in some embodiments with the aid of other basic observations in the rendering (ie, rapid decline in visibility between points, sparsity of visibility signal frequencies), the size of the matrix can be significantly reduced. Therefore, CS can be used to reconstruct the optical transmission matrix from a small amount of samples. After reconstructing the matrix, any given two points and their visibility to each other can be known in advance. Therefore, there will be no need to explore the space. Without exploration, only large contribution samples can be detected, and noise-free images can be generated.
[0019] f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com