MIF and application of MIF in prediction of metabolic adverse reactions induced by second-generation antipsychotic drugs
A technology for antipsychotic drugs and metabolic abnormalities, which is applied in biological testing, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection, and can solve problems such as metabolic adverse reactions, abnormal glucose metabolism, and restricted drug use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Clinical Sample Evaluation
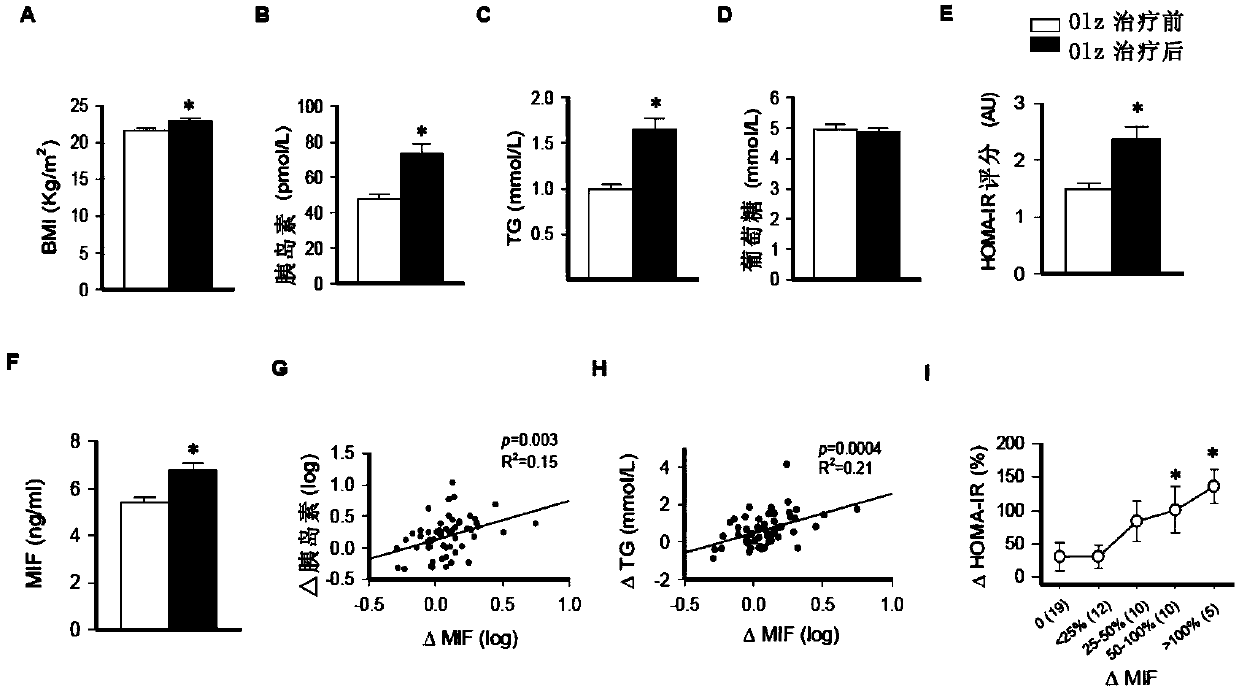
[0077] The basic information of 56 first-episode drug-naïve patients treated with olanzapine monotherapy is shown in Table 1.
[0078] Although fasting plasma glucose levels did not change, in these subjects ( figure 1 A-1C), body mass index (BMI), insulinemia and triglyceridemia were all significantly increased ( figure 1 D). The insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) score (index of metabolic dysfunction) also increased from a baseline level of 1.5 to 2.5 ( figure 1 E). Notably, in these patients, plasma MIF concentrations increased after olanzapine treatment ( figure 1 F), and these measures are associated with increased hyperinsulinemia ( figure 1 G), hypertriglyceridemia ( figure 1 H) and insulin resistance score ( figure 1 I) related.
Embodiment 2
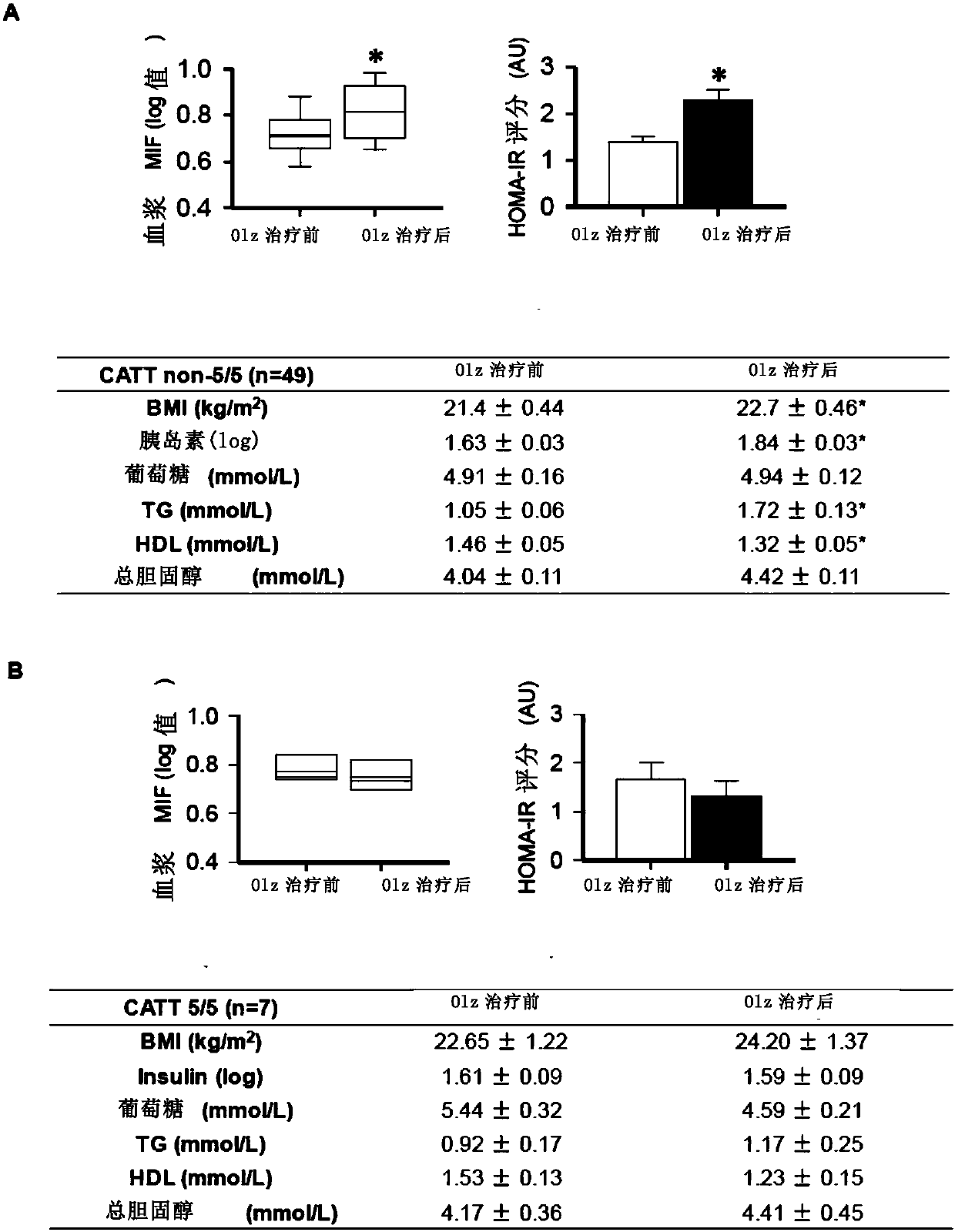
[0080] Effect of MIF gene variation on olanzapine-induced metabolic side effects
[0081] Patients were classified as low or high expressing based on a-794CATT5 / 5 genotype (CATT 5 / 5, i.e. lowest MIF expression level), or non-794CATT5 / 5 genotype (CATT not 5 / 5, i.e. higher MIF expression) MIF genotype. Compared with the untreated group, the high MIF genotype group (CATT non-5 / 5) showed increased plasma MIF, HOMA-IR score and BMI, as well as increased plasma levels of insulin, triglycerides and decreased HDL ( figure 2 A). In contrast, in patients with CATT 5 / 5, olanzapine treatment did not alter plasma MIF levels, HOMA IR score, BMI, or other measures of metabolism (i.e., insulin, glucose, triglycerides, HDL, and total cholesterol) ( figure 2 B). Thus, these data suggest that MIF gene variants affect the development of olanzapine-induced metabolic side effects.
Embodiment 3
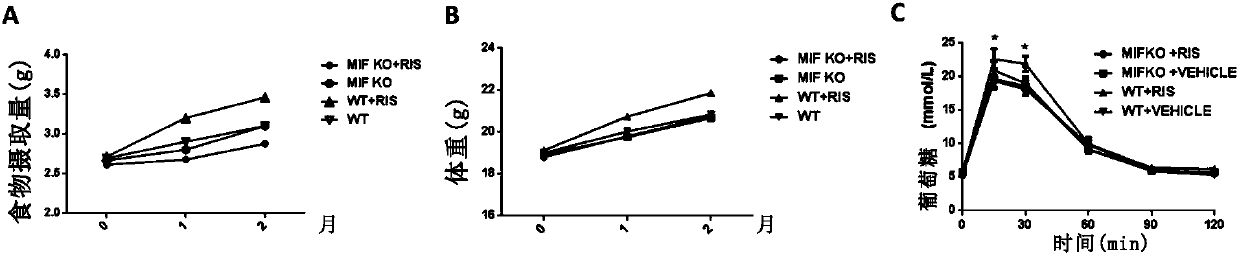
[0083] Effect of MIF gene variation on risperidone-induced metabolic side effects
[0084] After risperidone was administered to C57 / B6J wild-type and Mif- / - mice for four weeks, the glucose and lipid metabolism phenotypes of the mice were detected.
[0085] The result is as image 3 As shown, after risperidone treatment, the body weight and food intake of wild-type mice increased, but Mif- / - mice before and after risperidone treatment had no significant changes ( image 3 A, 3B). In addition, after risperidone treatment, the glucose tolerance of mice increased (statistically significant), while Mif- / - mice before and after risperidone treatment had no significant changes ( image 3 C). The above results indicated that risperidone-induced symptoms of glucose and lipid metabolism disorders were confirmed to be related to MIF in C57 / B6J mice.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com