Thread importance based processor core partitioning
A processor core, an important technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, digital data processing components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as consuming a lot of power, battery exhaustion, frustration, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
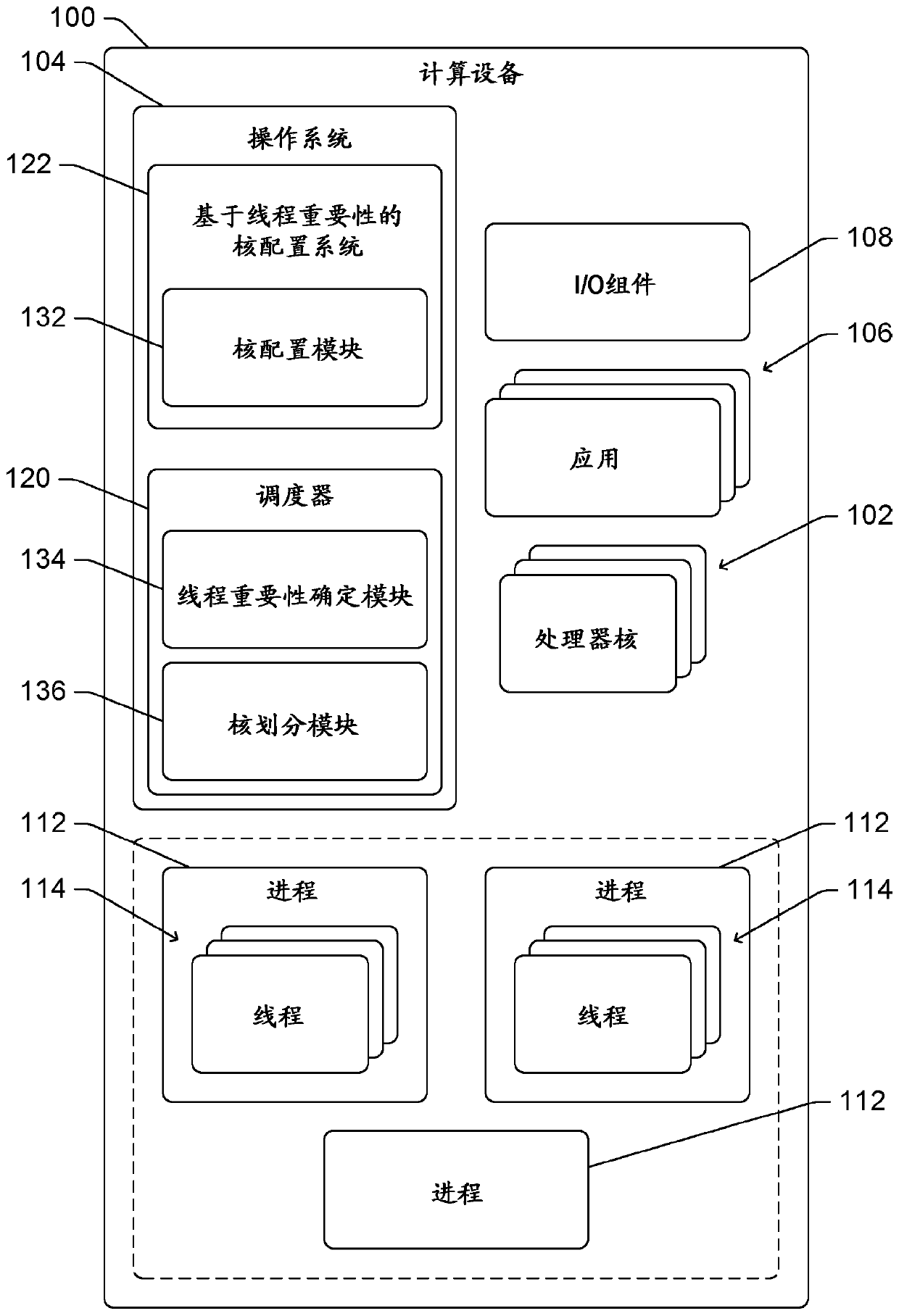
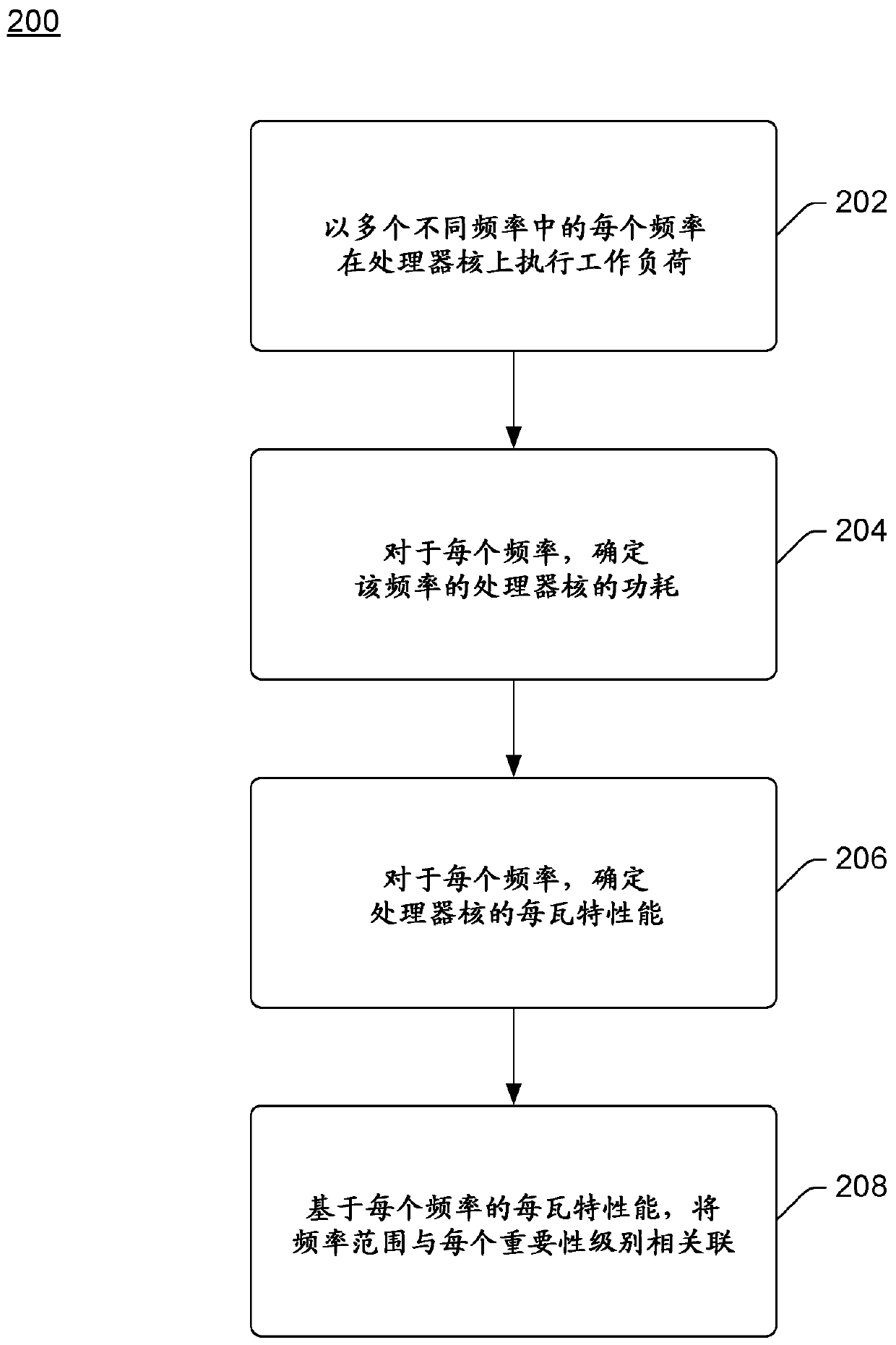
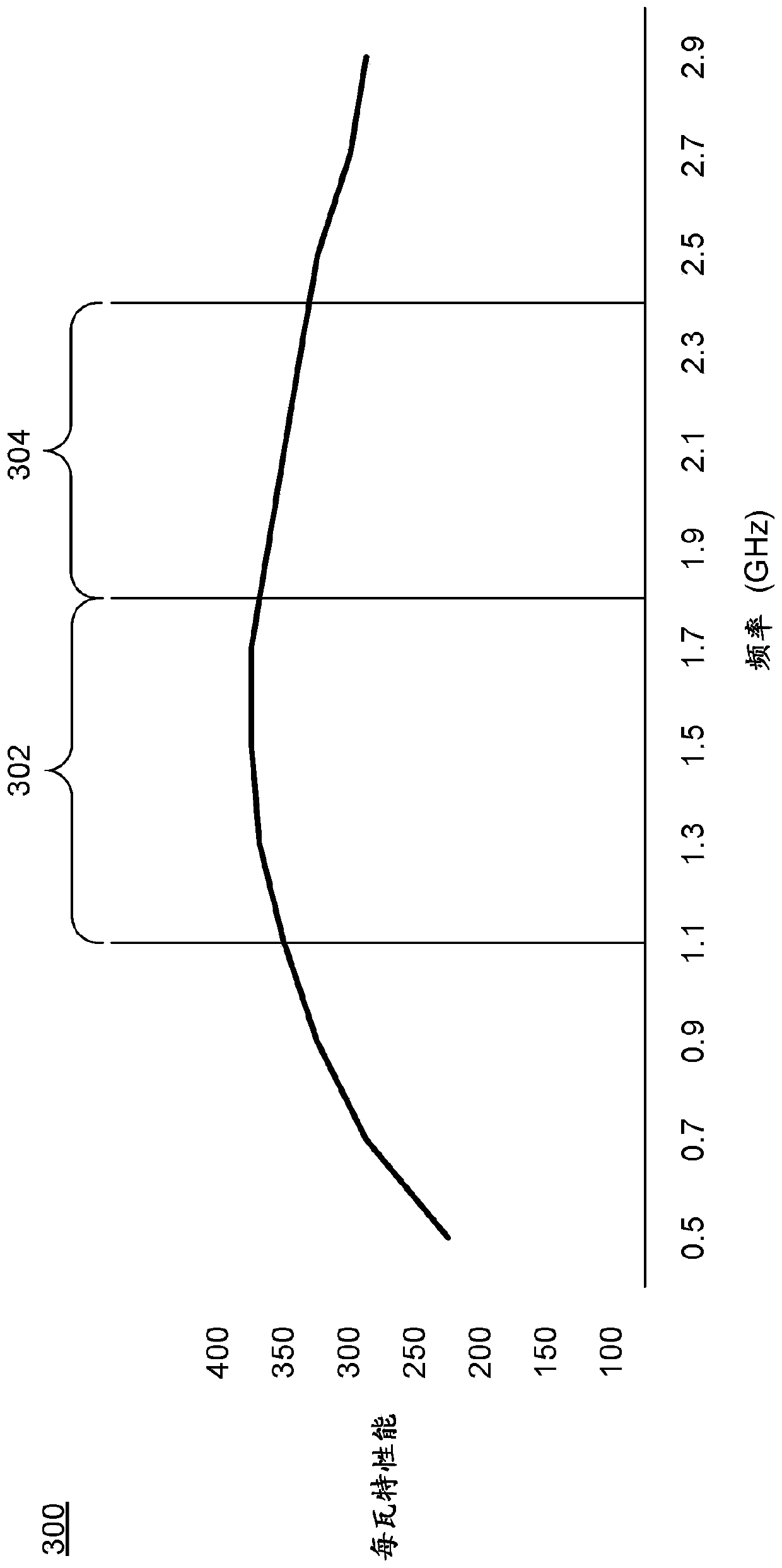
[0012] This article discusses processor core partitioning based on thread importance. A computing device includes one or more processors, and each processor includes one or more processor cores (also referred to herein simply as cores). Various programs run on a computing device as one or more processes, each process including one or more threads. Each processor core supports a variety of different frequency ranges, also known as p-states, and can operate to run threads in any of these different frequency ranges. The efficiency of a processor core varies across frequency ranges and is usually not linear. For example, the amount of work done by a processor increases approximately linearly with the frequency of the processor core, but the amount of power consumed to perform the workload may increase at a faster rate (eg, exponentially).
[0013] Threads in a computing device are assigned one of several importance levels. There may be two levels of importance (eg, important an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com