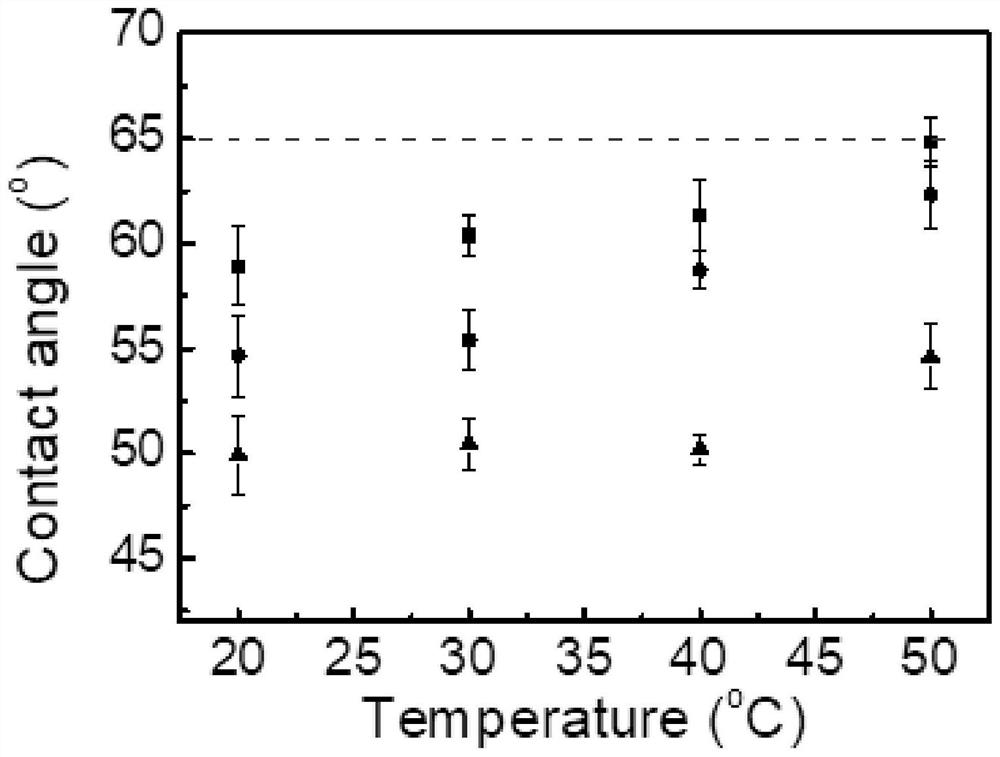
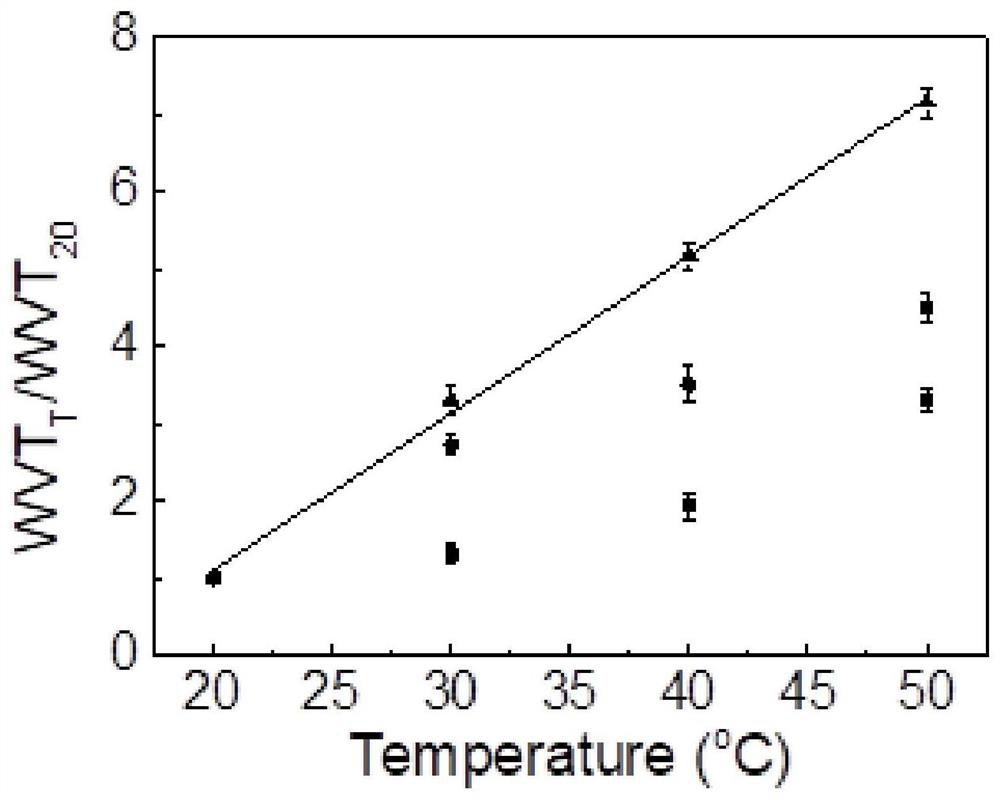
A method for achieving linear regulation of comfort and anti-bacterial adhesion by cross-linking thermosensitive microgels on the surface of fabrics
A microgel and comfortable technology, applied in textiles and papermaking, plant fibers, fiber processing, etc., can solve problems such as the effect of fabric hand feel, and achieve the effect of convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
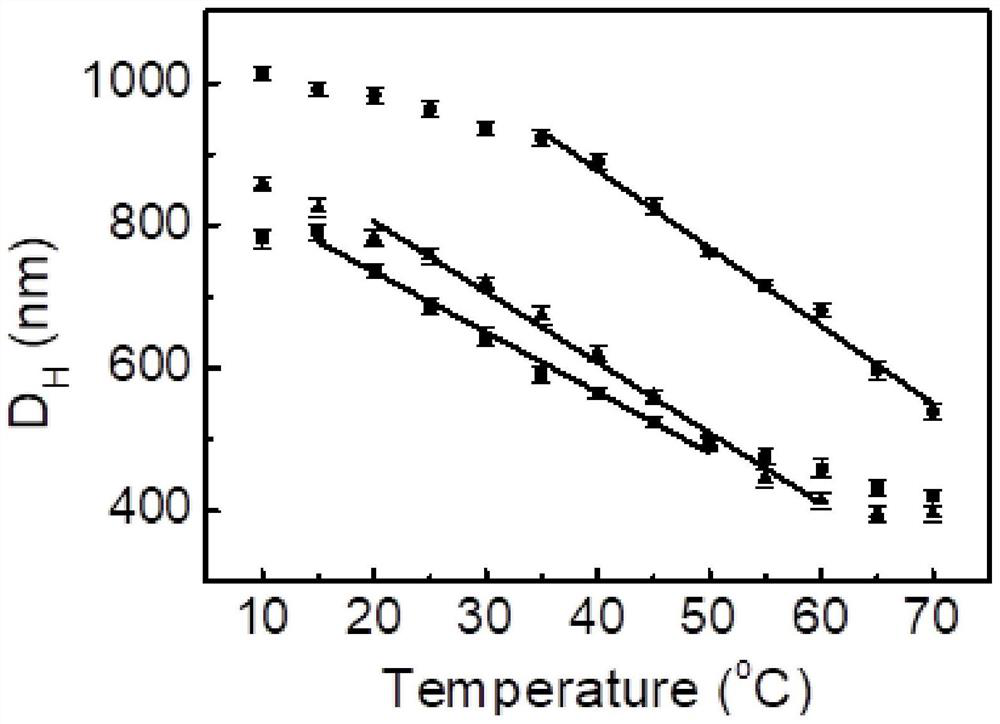
[0050] The percentages mentioned in this embodiment are all mole percentages. Thermosensitive microgels with linear response were synthesized using two monomers with different LCST values. Put a certain concentration of microgel into a clean cuvette, and use a nanoparticle size and molecular weight analyzer to measure the change of microgel emulsion with temperature. Include the following steps:
[0051] 1) the MEO 2 MA and OEGMA 300 The microgel synthesized with a molar ratio of 2:1 was formulated into a suitable concentration;
[0052] 2) Put the emulsion into a clean cuvette;
[0053] 3) Test the average particle diameter of the microgel emulsion every 5°C with a nanoparticle size and molecular weight analyzer.
[0054] Measure 3 times on the same sample at the same temperature and take the average value. The emulsion temperature range is 10-70°C. It can be seen that within 10-70°C, P(MEO 2 MA-co-OEGMA 300 -co-EGMA) microgel particle size decreases gradually with i...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The percentages mentioned in this embodiment are all mole percentages. Thermosensitive microgels with linear response were synthesized using two monomers with different LCST values. Put a certain concentration of microgel into a clean cuvette, and use a nanoparticle size and molecular weight analyzer to measure the change of microgel emulsion with temperature. Include the following steps:
[0057] 1) the MEO 2 MA and OEGMA 300 The microgel synthesized with a molar ratio of 1:1 was formulated into a suitable concentration;
[0058] 2) Put the emulsion into a clean cuvette;
[0059] 3) Test the average particle diameter of the microgel emulsion every 5°C with a nanoparticle size and molecular weight analyzer.
[0060] Measure 3 times on the same sample at the same temperature and take the average value. The emulsion temperature range is 10-70°C. It can be seen that within 10-70°C, P(MEO 2 MA-co-OEGMA 300 -co-EGMA) microgel particle size decreases gradually with i...
Embodiment 3
[0062] The percentages mentioned in this embodiment are all mole percentages. Thermosensitive microgels with linear response were synthesized using two monomers with different LCST values. Put a certain concentration of microgel into a clean cuvette, and use a nanoparticle size and molecular weight analyzer to measure the change of microgel emulsion with temperature. Include the following steps:
[0063] 1) the MEO 2 MA and OEGMA 300 The microgel synthesized with a molar ratio of 1:2 was formulated into a suitable concentration;
[0064] 2) Put the emulsion into a clean cuvette;
[0065] 3) Test the average particle diameter of the microgel emulsion every 5°C with a nanoparticle size and molecular weight analyzer.
[0066] Measure 3 times on the same sample at the same temperature and take the average value. The emulsion temperature range is 10-70°C. It can be seen that within 10-70°C, P(MEO 2 MA-co-OEGMA 300-co-EGMA) microgel particle size decreased gradually with in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com