A short-time excitation temperature rise equivalent test method adapted to nonlinear heat dissipation conditions
An equivalent testing, non-linear technology, applied in the field of efficiency testing, can solve problems such as decreased accuracy, and achieve the effects of reducing the risk of high temperature damage, reducing energy consumption, and being easy to operate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0027] Specific implementation mode 1: This implementation mode records a short-time excitation temperature rise equivalent test method adapted to nonlinear heat dissipation conditions, and the steps of the method are as follows:
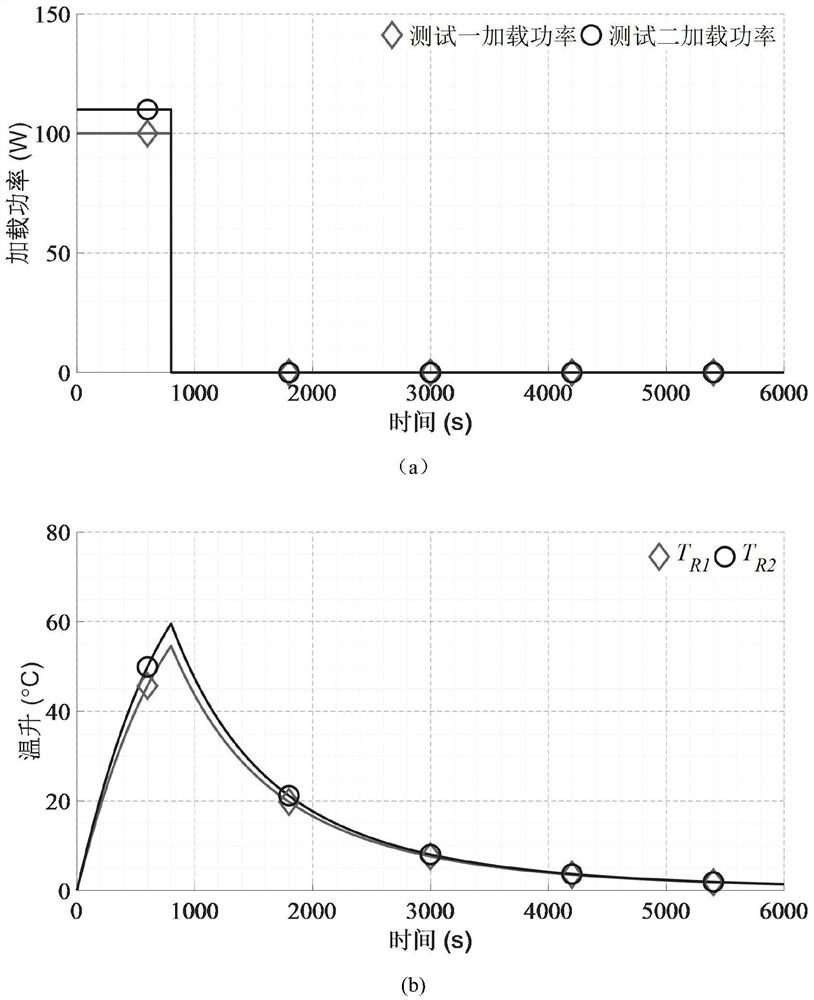
[0028] Step 1: This method requires two short-time tests of the motor with different loading levels. For the convenience of expression, the one with a smaller loading level is recorded as test 1, and the one with a larger loading level is recorded as test 2. The loading level of test 2 is It is k times of test 1, 1
[0029] First, the motor works for a short time under the loading condition of test 1, so that the motor starts from the initial time t under the load condition of test 1 0 start working till t 1 time, followed by t 1 Remove the load at all times, so that the motor is cooled under the same cooling conditions as when it was loaded (referring to natural cooling, air cooling, etc., the state remains unchanged), and record the tempera...
Embodiment 1
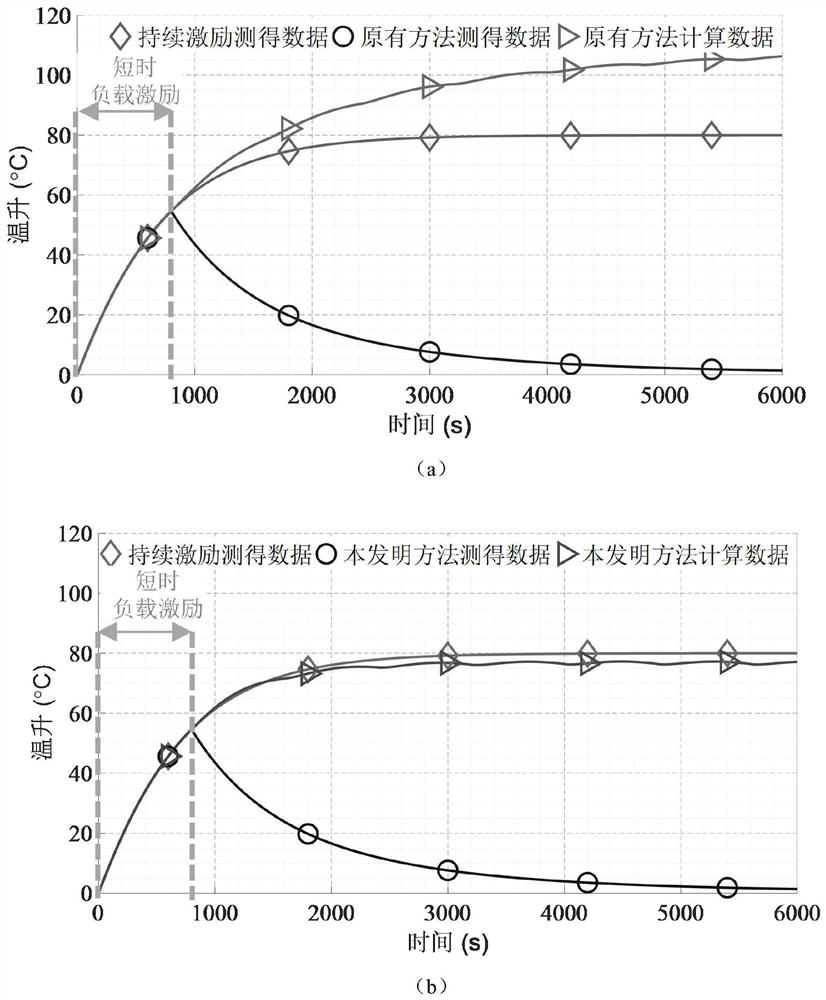
[0037] Embodiment 1 records a short-term excitation temperature rise equivalent test method adapted to nonlinear heat dissipation conditions, which is a first-order heat transfer relationship, and the heating surface of the heating element directly contacts the air, so it is most seriously affected by natural convection. Among them, the natural convection heat transfer coefficient α has a nonlinear relationship with the temperature rise ΔT, and the expression is about:
[0038] The specific test steps are as follows:
[0039]Step 1: This embodiment requires two short-term tests of the motor with different loading levels. For the convenience of expression, the one with a smaller loading level is recorded as Test 1, the loading power is 100W, and the one with a larger loading level is recorded as Test 1 2. The loading power is 200W, and the loading degree of test 2 is twice that of test 1, k=2;
[0040] First, the motor works for a short time under the loading condition of Te...
Embodiment 2
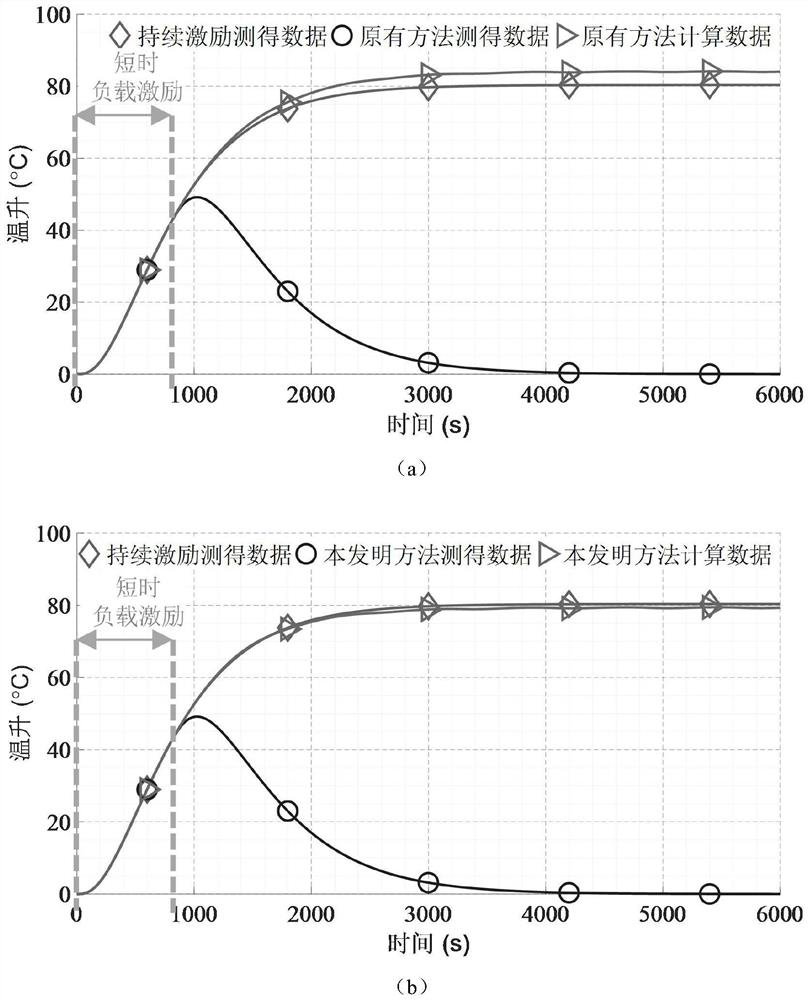
[0047] Embodiment 2 records a short-time excitation temperature rise equivalent test method adapted to nonlinear heat dissipation conditions, which is a third-order heat transfer relationship, the heat of the heating element is transferred to other objects, and the heat dissipation surface of the outermost object directly contacts the air , the temperature rise test point is the heat dissipation surface of the outermost object. The heat dissipation surface is affected by natural convection, and its natural convection heat transfer coefficient α has a nonlinear relationship with the temperature rise ΔT, and its expression is approximately: The specific test steps are as follows:
[0048] Step 1: This method requires two short-term tests of the motor with different loading levels. For the convenience of expression, the one with a smaller loading level is recorded as Test 1, the loading power is 100W, and the one with a larger loading level is recorded as Test 2. , the loading ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com