A data cross-storage method based on blockchain cross-chain
A cross-storage and blockchain technology, applied in the field of computer blockchain, can solve the problem of difficulty in ensuring the security and integrity of the blockchain, and achieve the effect of saving memory and ensuring security and integrity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
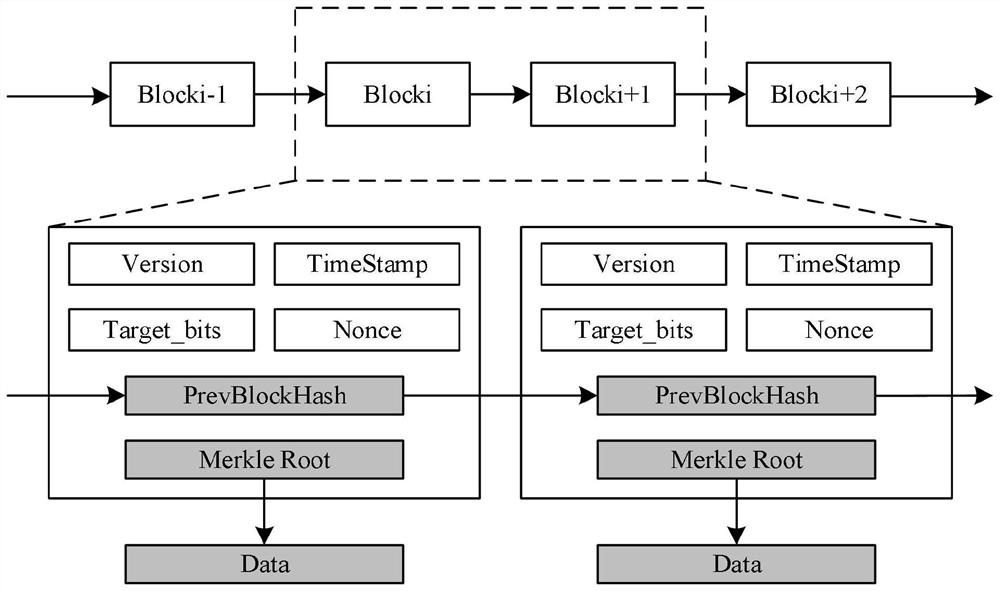
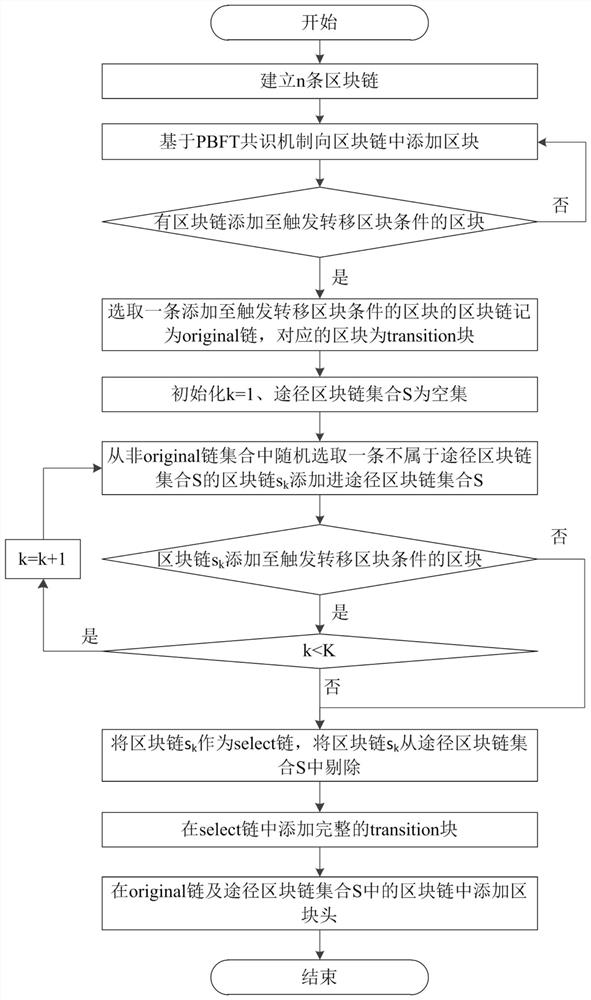
[0043] Such as figure 2 As shown, the data cross-storage method based on blockchain cross-chain of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0044] Step 1: Establish n blockchains, add blocks to the blockchain based on the PBFT consensus mechanism, if there is a blockchain added to the block that triggers the block transfer condition, perform steps 2 to 5; if there is no block The chain is added to the block that triggers the block transfer condition, and continues to add blocks to the blockchain based on the PBFT consensus mechanism.
[0045] Among them, the transfer block condition is a fixed step condition or an indefinite step condition; when the transfer block condition is a fixed step condition, if the block chain is added to the 2mth block (m=1,2,3,... ...), then the 2mth block triggers the transfer block condition; when the transfer block condition is an indefinite step condition, if the block chain is added to the 2nd m Block block (m=1,2,3,...), then t...
Embodiment 2
[0070] The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment above is that:
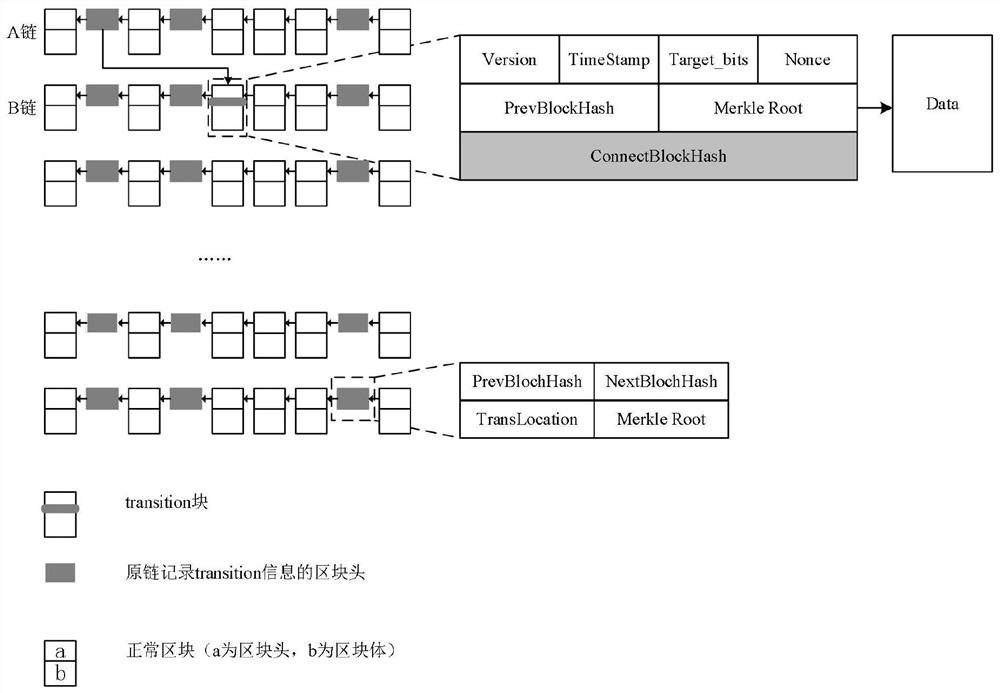
[0071] Such as Figure 4 As shown, blockchain A is added to the 4th block, the 4th block triggers the transfer block condition, and the 4th block is recorded as a transition block. Block chain C is randomly selected, and block chain C is added to the second block. When the transition block of block chain A is connected to block chain C, this block is also a transition block for block chain C. At this time, for blockchain C, it is also necessary to select a suitable blockchain to migrate the block, and select blockchain D through random selection. Query blockchain D. Blockchain D is connected to the fifth block. Blockchain D is not added to the block that triggers the transfer block condition. The transition block of blockchain A can be connected to the block through blockchain C. On the block chain D, so that the block chain D is used as the select chain, and the obtained path block...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The difference between the third embodiment and the second embodiment above is that:
[0078] Such as Figure 5 As shown, blockchain A is added to the 8th block, and the 8th block triggers the transition block condition, and the 8th block is recorded as a transition block. Block chain E is randomly selected, and block chain E is added to the second m Block block, continue to select the block chain. After randomly selecting all blockchains (the order is E->F->D->B->I->G->C->J->H), it is found that all blockchains are just connected to the first 2 m block, the transition block of blockchain A can be connected to the finally selected blockchain H through the 8 blockchains of the route, so that the blockchain H is used as the select chain, and the set of route blockchains S={ E,F,D,B,I,G,C,J}.
[0079] At this point, add a complete transition block in blockchain H, and add block headers in blockchain A and blockchains E, F, D, B, I, G, C, and J.
[0080] Among them, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com