Metadata management method and device
A management method and metadata technology, applied in digital data processing, data processing input/output process, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as large read amplification, waste of cache resources, and increased processor burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
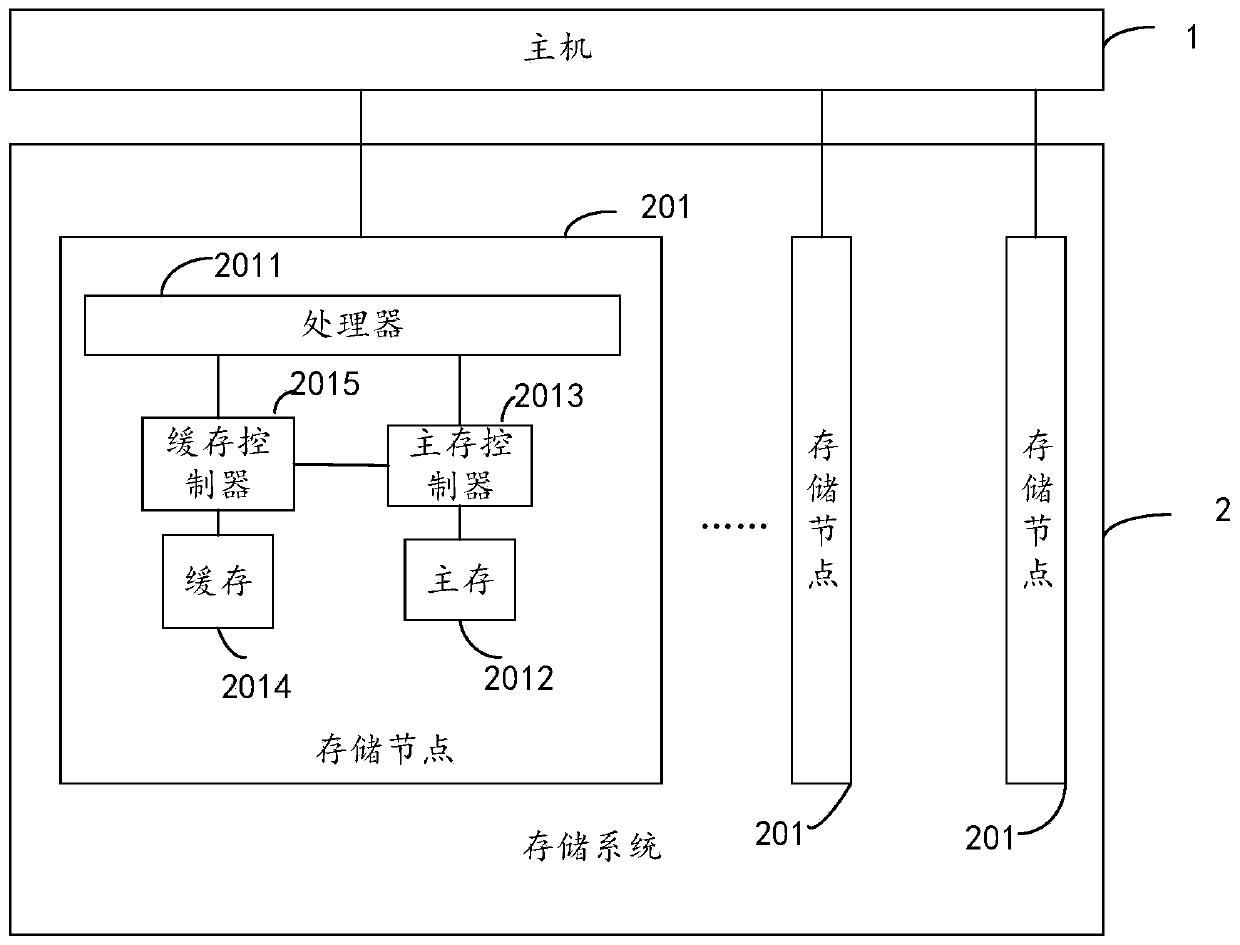
[0053] like Figure 4 As shown, it is a schematic flowchart of a metadata management method provided in the embodiment of the present application. Exemplary, this embodiment can be applied to figure 1 , figure 2 The system architecture shown. Figure 4 The illustrated method may include the steps of:
[0054] S101: The cache controller receives a write request sent by the processor. The write request includes write request data and a logical address range of the write request data. Wherein, the logical address range of the write request data is the logical address range of the storage space used to store the write request data in the main memory.
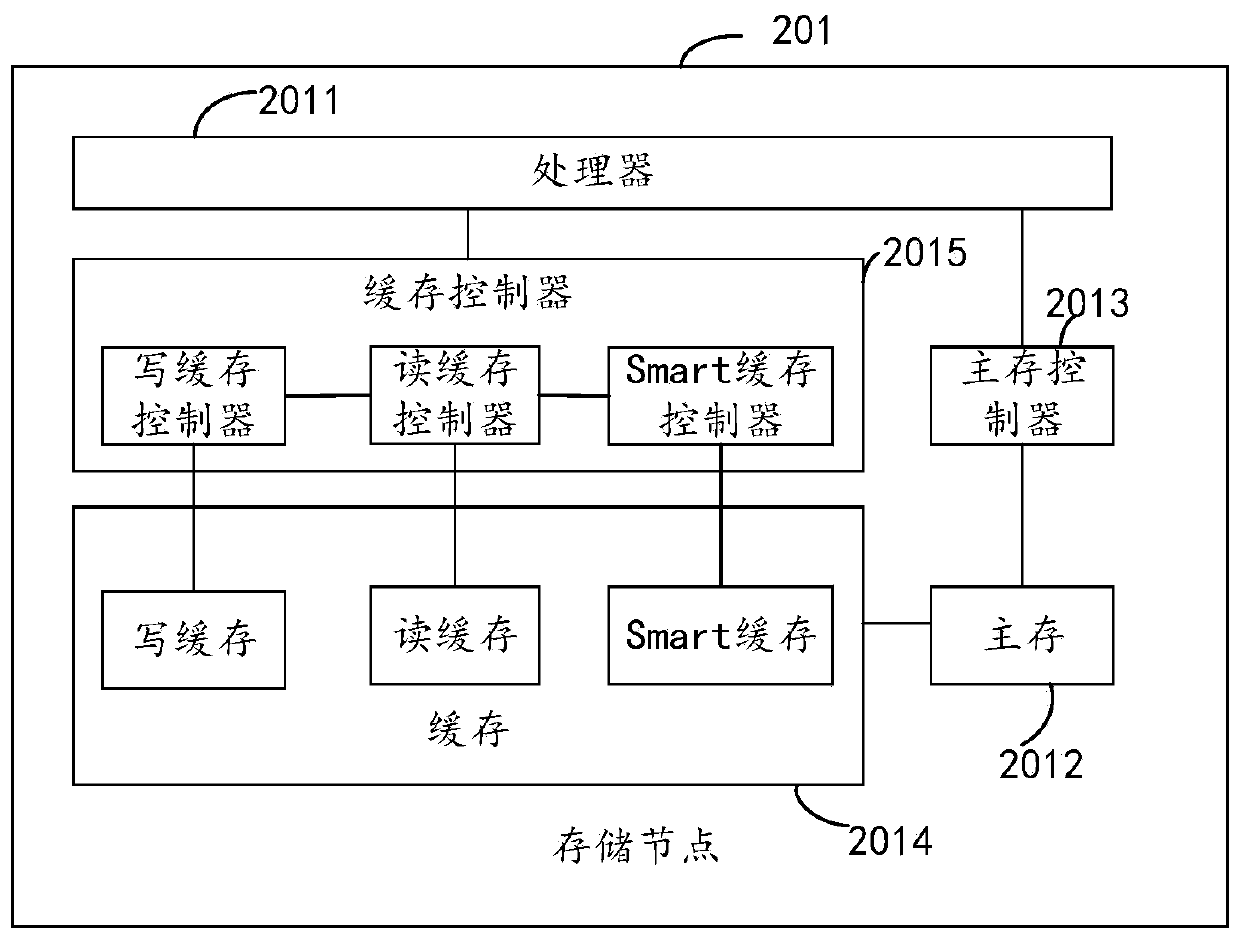
[0055] When the cache controller is a write cache controller, in a write request scenario, after receiving the write request sent by the host, the processor sends the write request to the write cache controller.
[0056] When the cache controller is a read cache controller, and in the read request scenario, neither the read c...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Assume that the target metadata storage unit stores metadata of M times of writing cache data, wherein each writing of metadata includes a logical address range. M is an integer greater than or equal to 1, then, when the first logical address range includes one or more logical address ranges in the M logical address ranges, after S105 and before S106, the method further includes: deleting the one or Metadata where multiple logical address ranges reside.
[0091] Based on this, in S106, the target metadata is the latest metadata written in the metadata written to the cache for N times, wherein the metadata written in the cache for N times is deleted from the metadata written in the cache for M times The remaining metadata after the metadata corresponding to one or more logical address ranges.
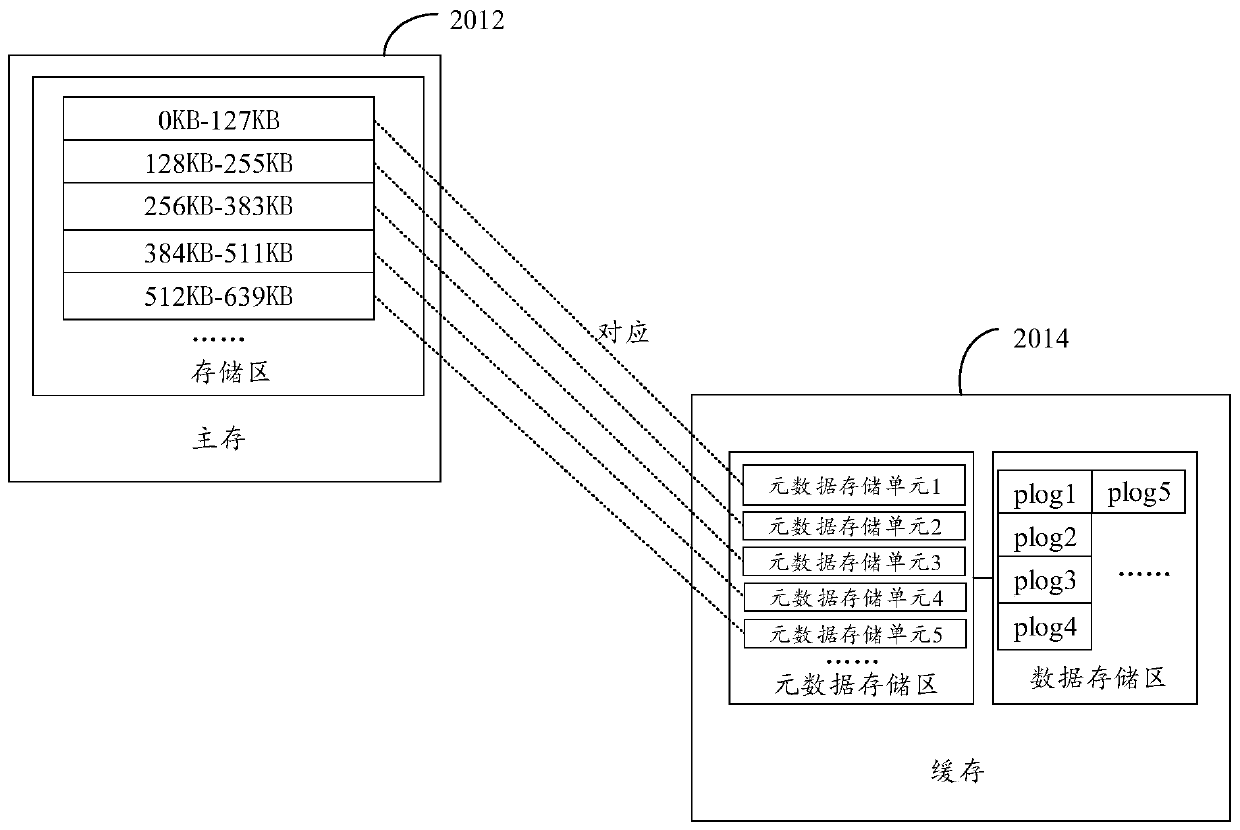
[0092] Exemplarily, it is assumed that the first logical address range is 8KB-30KB, based on the example in Table 2. There are two logical address ranges in the target metadata ...
Embodiment 3
[0102] like Image 6 As shown in , it is a schematic flowchart of another method for managing metadata provided by the embodiment of the present application. This embodiment may be executed after the above-mentioned Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 is executed. Exemplary, this embodiment can be applied to figure 1 The system architecture shown. Image 6 The illustrated method may include the steps of:
[0103] S301: The cache controller acquires the quantity M of all metadata in the target metadata storage unit.
[0104] Optionally, when the logical address range in the read request received by the cache controller intersects with any logical address range stored in the target metadata storage unit, the cache controller obtains all metadata in the target metadata storage unit The number M, wherein the preset logical address range corresponding to the target metadata storage unit includes the logical address range in the read request.
[0105] Exemplarily, it is assumed that t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com