Soybean symbiotic nitrogen-fixing lipopolysaccharide gene or its protein and application
A soybean and nitrogen fixation technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems such as the impact of symbiotic nitrogen fixation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Example 1. Isolation and structural analysis of the GmLBP6 gene in soybean
[0055] (1) Isolation of genes
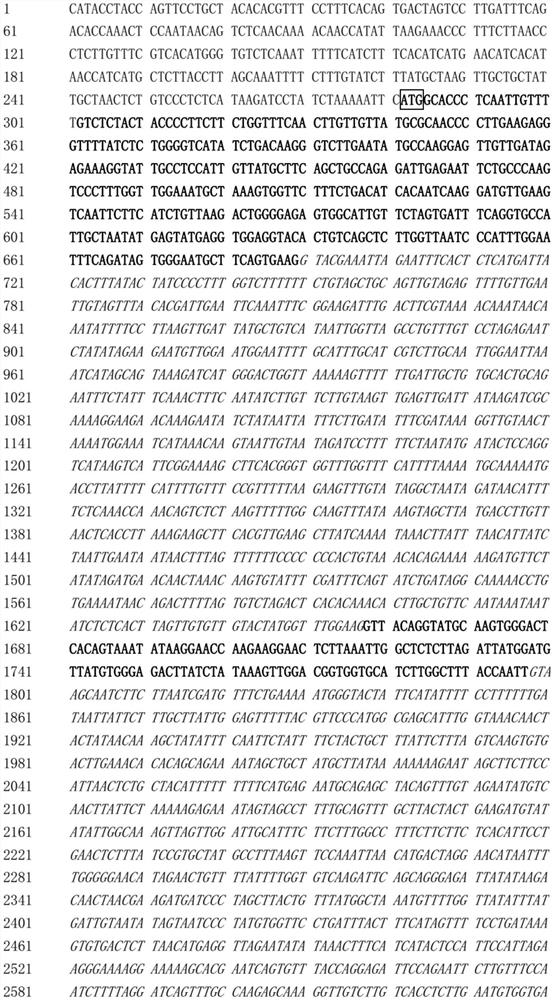
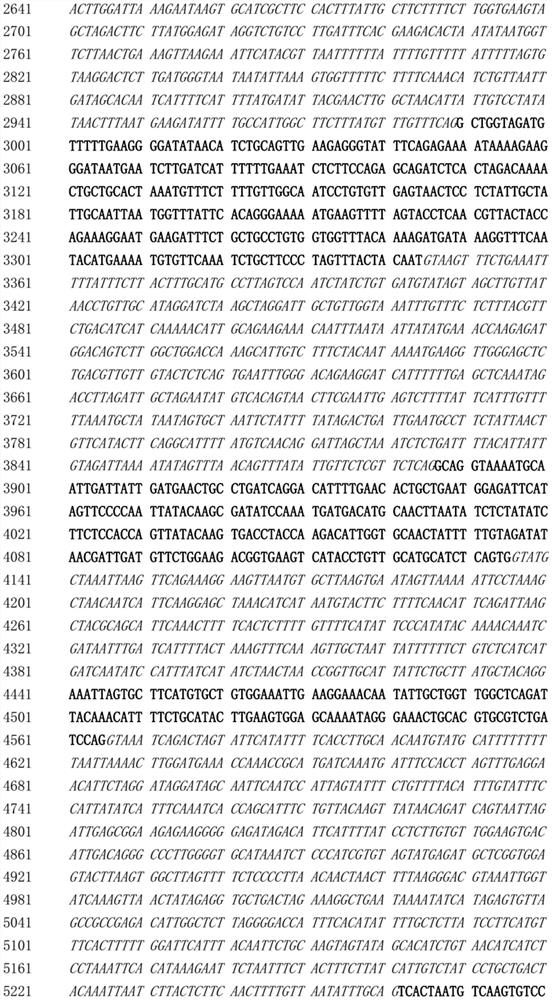
[0056] The mRNA was isolated from young leaves of soybean variety—Williams82, and the first strand of cDNA was synthesized using the mRNA as a template and Oligo(T)17 as a primer. Then, using the first strand of the cDNA as a template, primers (5'-ATGGCACCCTCAATTGTTTTG-3') and primers (5'-TTATGAAACATAAGCTAACT-3') were used for PCR amplification, and a 1482bp cDNA fragment of the GmLPP6 gene was obtained , cloned into pGEM T Easy vector (TaKaRa Company) and named pGEM T Easy-GmLBP6.
[0057] The GmLBP6 CDS sequence contained in pGEM T Easy-GmLBP6 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, with a total of 1482 bp, which encodes a protein of 493 amino acids (SEQ ID NO: 1).
[0058] (2) Gene structure analysis
[0059] The young leaves of Williams82 were used as materials to extract DNA from them, and then the genomic DNA was used as a template to amplify the fragment of the GmLBP...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2. Soybean GmLBP6 gene does not affect plant growth
[0061] Using Williams82 as the background, we established a Tilling population containing about 5000 strains. Using this platform, we screened 1,200 strains and found a total of 15 mutant strains with nucleotide changes. After identification, 6 of the strains had missense mutations in the amino acids of the LBP6 protein. In the lbp6-5 mutant, LBP6 The 38th leucine of the protein is changed to proline. This position is a very conserved amino acid in the BPI domain, so we first selected lbp6-5 for subsequent experiments. By detecting the growth morphology of the plants before and after inoculation with rhizobia, it was found that the leaves of the Gmlbp6-5 mutant were slightly yellower than those of the Williams82 wild type, and there was no difference in other phenotypes such as plant height ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3. Soybean GmLBP6 gene regulates the number of root nodules
[0063] (1) Soybean GmLP6 gene regulates the number of root nodules
[0064] Regardless of inoculation with rhizobia, the number of nodules in the Gmlbp6-5 mutant was more than that of the Williams82 wild type, and in the absence of inoculation with rhizobia, the number of nodules in the Gmlbp6-5 mutant was 13 times that of the Williams82 wild type, In the case of inoculation with rhizobia, the number of nodules of the Gmlbp6-5 mutant was more than twice that of the Williams82 wild type ( image 3 ).
[0065] (2) Soybean GmLBP6 gene regulation does not participate in the control of root nitrogenase activity
[0066] Although inoculated with rhizobia, the Gmlbp6-5 mutant formed more nodules than the wild type (the former was more than 2 times that of the latter). However, the nitrogenase activity of the mutant to form nodules was not significantly different from that of the wild type ( Figure 4 ). ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com