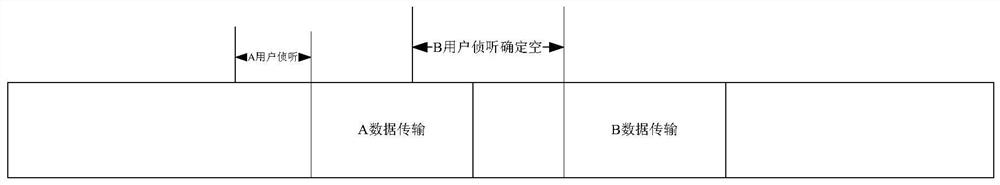
A method for channel time division multiplexing in autonomous network system
A time division multiplexing, autonomous network technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of high CSMA aggregation risk, waste of TDMA time slots, etc., to avoid aggregation effect, avoid disorderly competition, and ensure the effect of scheduling time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in combination with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that these descriptions are exemplary only, and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. Also, in the following description, descriptions of well-known structures and techniques are omitted to avoid unnecessarily obscuring the concept of the present invention.
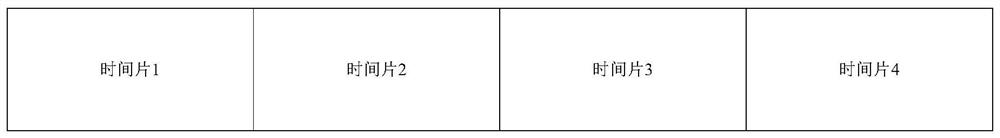
[0051] see image 3 A typical time division multiplexing principle is: divide the channel into several time slices according to time, and use them for multiple signals in turn. Each time slice is occupied by a multiplexed signal alone, and multiple digital signals can be transmitted and arrived as required within a specified time, thus realizing the transmission of multiple digital signals on one physical channel.
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com