Real-time rendering method for very large geometry based on continuous simplification
A real-time rendering and geometry technology, applied in the field of visual scene processing, which can solve problems such as reducing data accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the real-time rendering method of super-large geometry based on continuous simplification, including the preprocessing stage and the implementation rendering stage;
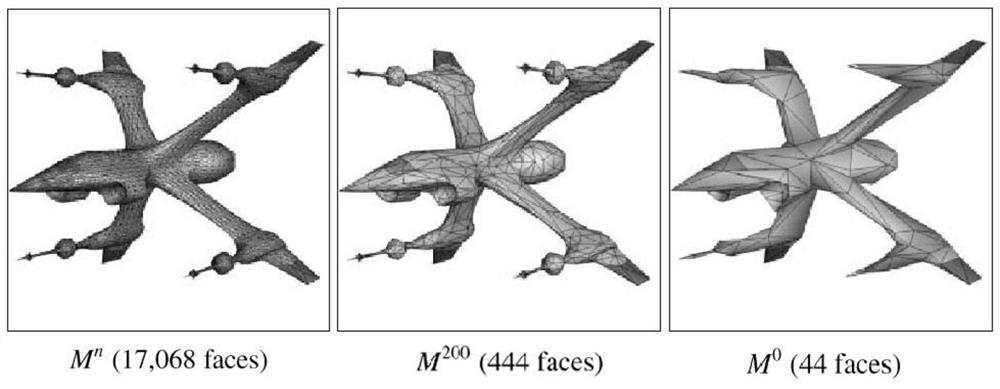
[0025] Specifically, the preprocessing stage creates a continuous simplified model for the geometry and converts it into another representation to form continuous LOD data; the simplified model includes the following steps:
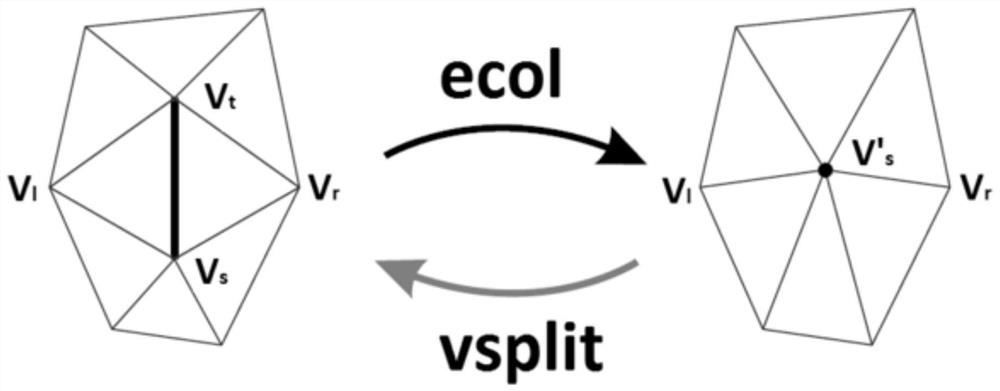
[0026] S11: Find and select the most redundant edge in the model, that is, the edge that has the least impact on information after removal;
[0027] S12: Use the edge selected in S11 to figure 1 The method is removed, and the two vertices connected by this edge are fused;
[0028] S13: Repeat steps S11 and S12 until it cannot be simplified at the end, such as figure 2 ;
[0029] S14: Record the edge fusion operations performed in steps S12 and S13, and form continuous LOD data together with the simplified model obtained in step S13.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com