Optical zoom focusing method, projection device and storage medium
An optical zoom and projection technology, applied in the field of projectors, can solve the problems of blurred picture and poor user experience, and achieve the effect of ensuring the picture, reducing the number of operations, precise adjustment and stable adjustment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
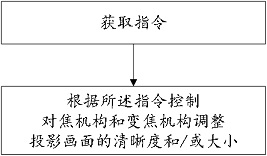
[0043] A motorized focusing method for optical zooming, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0044] Get instructions;
[0045]Control the focus mechanism and the zoom mechanism according to the instructions to adjust the definition and / or size of the projected picture.
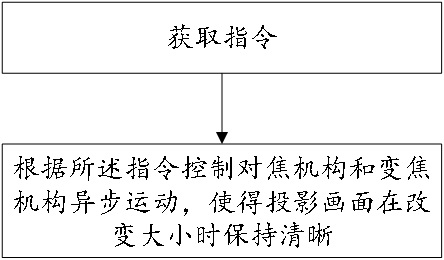
[0046] Specifically, such as figure 1 As shown, the focus mechanism and the zoom mechanism are controlled to move asynchronously according to the instructions, so that the projected picture remains clear or relatively clear when changing its size.
[0047] After receiving the command, control the focus mechanism to rotate in the first direction, and then control the zoom mechanism to rotate in the first direction or the second direction opposite to the first direction. The rotation direction is set according to the specific design. The first direction can be clockwise , can also be counterclockwise; correspondingly, the second direction is counterclockwise or clockwise.
[0048] Among...
Embodiment 2
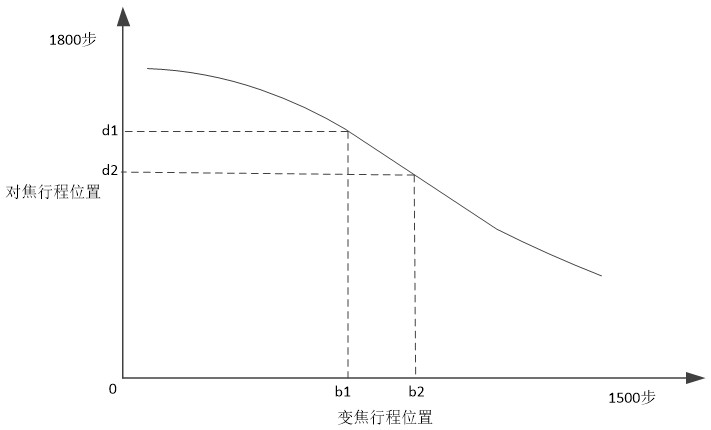
[0059] The difference between this embodiment and the embodiment is that the focus mechanism and the zoom mechanism are controlled to move asynchronously at a non-fixed projection distance according to the second relational expression, and the second relational expression is to move, and the second relational expression is z=f ' (x,y) , y Indicates the number of zoom travel steps of the zoom mechanism, x represents the projection distance, z Indicates the number of focusing travel steps of the focusing mechanism, f ' () Indicates the functional relationship among the projection distance, the zoom travel steps of the zoom mechanism, and the focus travel steps of the focus mechanism.
[0060] The acquisition of the second relational expression comprises the following steps:
[0061] Under multiple projection distances, change the zoom travel steps of the zoom mechanism, and record the focus travel steps of the focus mechanism corresponding to the clear point at the same t...
Embodiment 3
[0068] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that this embodiment optimizes the asynchronous motion, and the details are as follows:
[0069] Under the fixed projection distance, if the projection picture is clear before adjustment, controlling the focus mechanism and the zoom mechanism to perform asynchronous movement includes controlling the movement of the focus mechanism after controlling the movement of the zoom mechanism according to the first relational expression. That is, at a fixed distance, when the projected image is clear and the zoom and focus are triggered, the zoom motor moves first, and then the focus motor moves again; the minimum movement unit of movement is as described in the following embodiments, and is not limited here; at the same time, the size of the screen changes during the above process After or when it changes, the sharpness also changes, and the sharpness changes from clear to fuzzy (the change of the zoom focal length a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com