Blockchain-based v2g transaction privacy protection method, device and system
A blockchain and block technology, applied in the field of blockchain and privacy protection, can solve problems such as energy waste, achieve the effect of protecting privacy, preventing dishonesty, and saving transaction costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a blockchain-based V2G transaction privacy protection method;
[0044] Blockchain-based V2G transaction privacy protection methods, including:
[0045] The blockchain node receives the transaction parameters anonymously sent by the buyer's client, and records the transaction parameters and the first zero-knowledge proof generated by the buyer's client on the blockchain; the blockchain node verifies the correctness of the first zero-knowledge proof , and record the verified transaction parameters on the blockchain;
[0046] The blockchain node receives the guarantee fee anonymously sent by the buyer's client, and records the guarantee fee and the second zero-knowledge proof generated by the buyer's client on the blockchain in the form of a smart contract; the blockchain node verifies the second zero-knowledge proof. The correctness of the knowledge proof, and the guarantee fee for the verification is recorded on the blockchain;
...
Embodiment 11
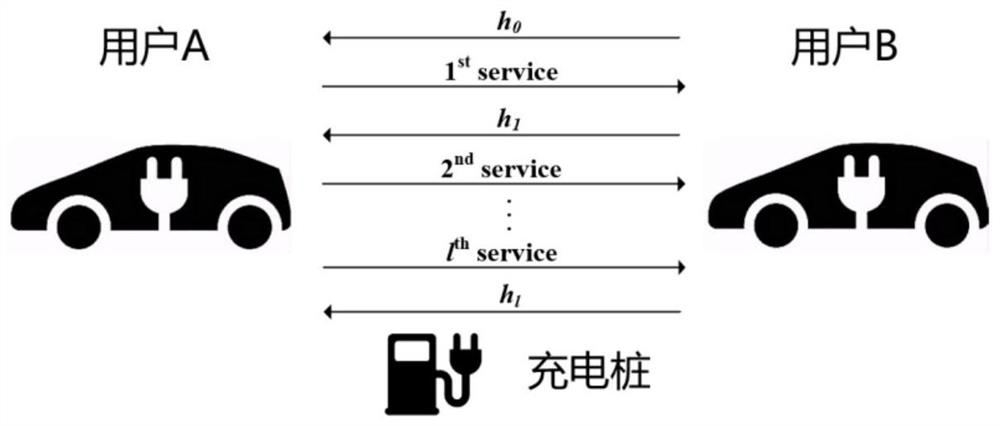
[0134] Consider the specific actions of the seller in the transaction. User A is an electric vehicle user, and the zero-knowledge balance in his account is cmt A =SHA256(v A ,sn A ,r A ), he wants to sell the electricity in the electric car to user B, including the following steps:
[0135] 1.1.1 User A and User B negotiate the transaction parameters cmt offline c , N, pk A , pk B , and then wait for User B to deploy the smart contract in the blockchain;
[0136] 1.1.2 After the smart contract is deployed on the blockchain, user A checks whether the transaction parameters in the contract are the same as the parameters negotiated by the two parties before, and checks whether there is the correct amount of guarantee fee in the contract.
[0137] If the parameters are the same and the number of guarantee fees is correct, proceed to the next step of the transaction;
[0138] If the parameters are different or the number of guarantee fees is incorrect, it is considered that...
Embodiment 12
[0144] Consider the specific actions of the buyer in the transaction. User B is an EV user, and the zero-knowledge balance in his account is cmt B =SHA256(v B ,sn B ,r B ), he wants to purchase user A's electricity, including the following steps:
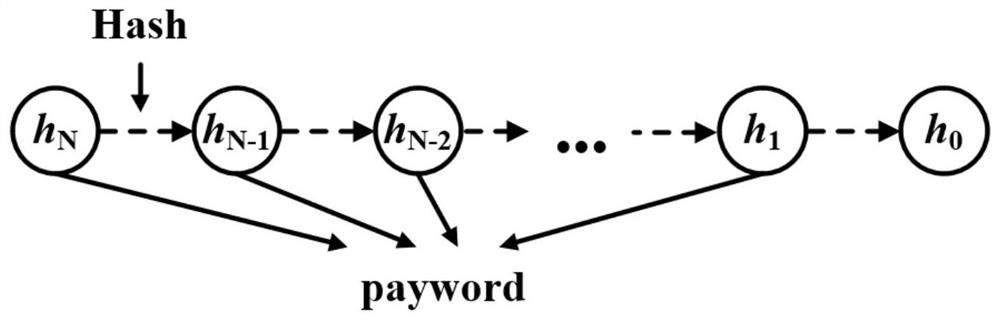
[0145] 1.2.1 User B generates guarantee fee certificate cmt c =SHA256(amt,r c ), negotiate the transaction parameters cmt with user A offline c , N, pk A , pk B , then user B generates a hash chain of length N, the hash root is h 0 .
[0146] 1.2.2 User B generates parameters and constructs a zero-knowledge amount cmt v =SHA256(amt,sn v ,r v ), and construct a zero-knowledge balance cmt after use B ’=SHA256(v B ’, sn B ',r B ’). User B generates a zero-knowledge proof π based on these parameters convert , and set the sn B , cmt B , cmt v , cmt B ’ and pi convert , sent to the blockchain, after waiting for miners to verify, cmt v Be a valid zero-knowledge amount.
[0147] 1.2.3 User B deploys a smart contract...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com