A method for robots to simulate the passive dynamic state of human limb muscles
A robot and muscle tension technology, applied in the field of robot simulation, can solve problems such as timing lag, affecting learning progress, learning effect and learning system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
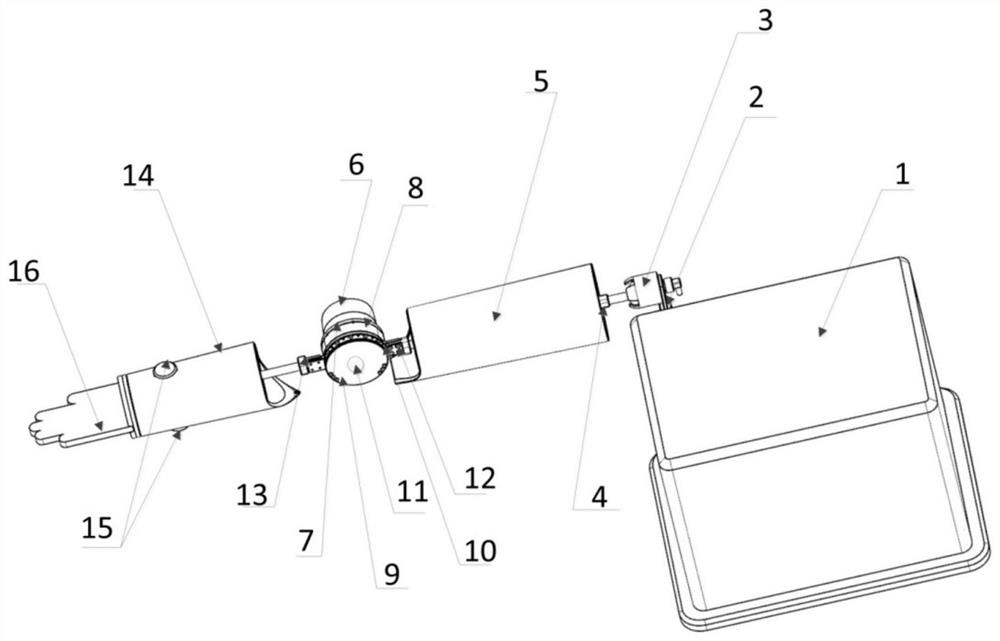
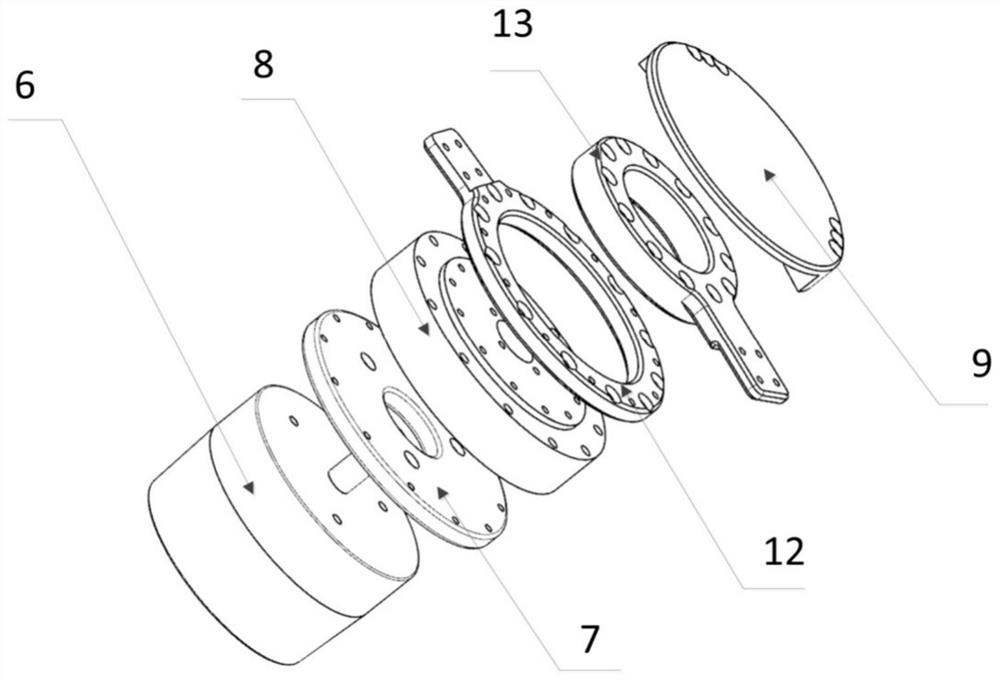
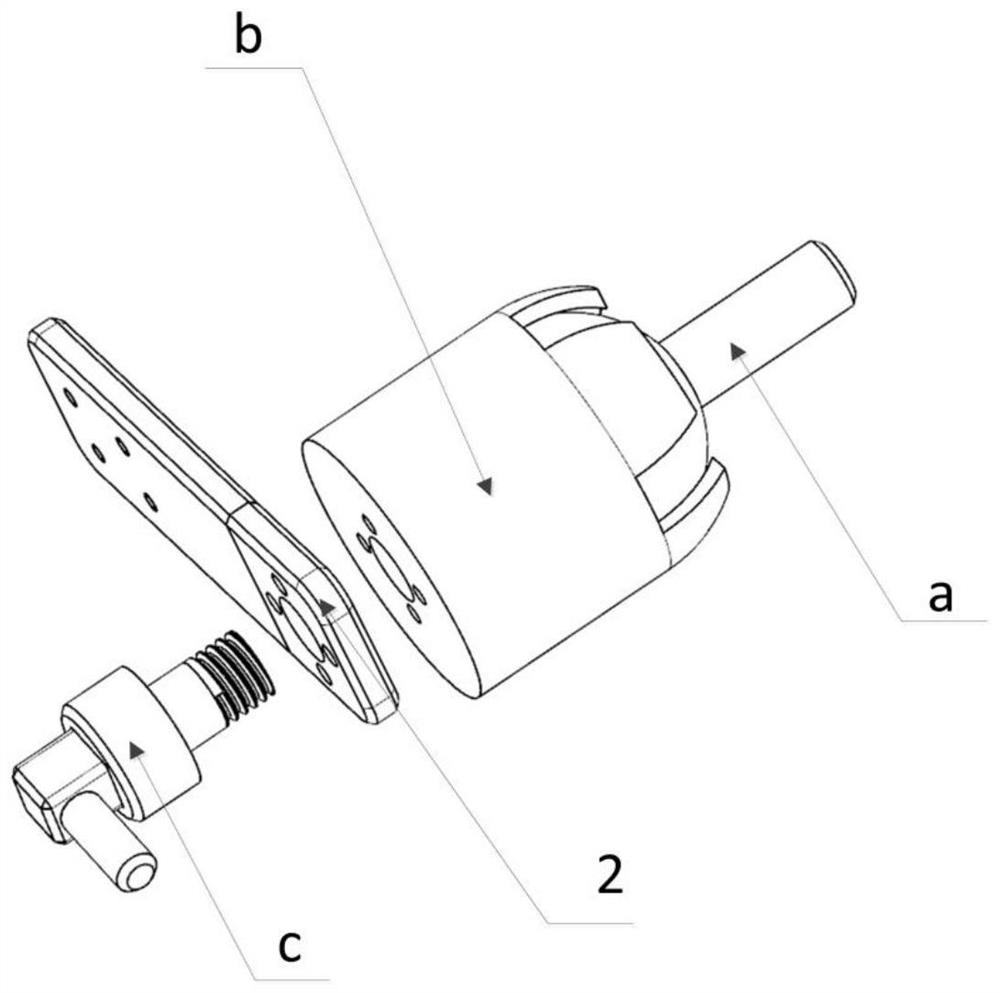
[0057] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 4 , the present embodiment provides a robot for simulating the dynamic state of the muscles of the limbs of the human body, including a base 1, a shoulder joint assembly, a large arm 5, an elbow joint assembly, a forearm 14 and a palm 16; the shoulder joint assembly includes a shoulder joint fixation Part 2 and the shoulder joint movable part 3, one end of the shoulder joint fixed part 2 is fixed on the base, the other end is connected to the shoulder joint movable part 3, the shoulder joint movable part 3 is fixedly connected with the upper arm 5 and can drive the upper arm to rotate in all directions The elbow assembly includes a drive motor 6 and a motor reducer 8, the input end of the motor reducer 8 is connected to the drive motor 6, the boom 5 and the small arm 14 are located on both sides of the output shaft end of the motor reducer, and the motor reducer 8 is fixed on On the big arm 5, the motor reducer 8 drives the small arm 14 to r...
Embodiment 2
[0069] refer to Figure 5 and Figure 6 In the following, the method for simulating the muscle tension of different levels of elbow flexion muscles of the human body by the robot shown in Embodiment 1 is taken as an example to illustrate the method for the robot of the present invention to simulate the dynamic state of the muscles of the limbs of the human body.
[0070] The method for the application robot to simulate different grades of elbow flexion muscle tension of the human body includes:
[0071] Level 0: The operator places the robot in a position where the shoulder joints naturally droop, the elbow joints droop naturally, and the palms face forward, and start the control system; then the operator rests one hand on the back of the lower end of the robot's upper arm, and holds the robot with the other hand. Gently lift the upper limb at the front end of the forearm of the robot, so that the robot is in the position of shoulder joint flexion angle of 45°, abduction angl...
Embodiment 3
[0079] refer to Figure 5 and Figure 7 Next, the method for simulating the extensor muscle tension of different levels of the human body by the robot shown in Embodiment 1 is taken as an example to illustrate the method for the robot of the present invention to simulate the dynamic state of the muscles of the limbs of the human body.
[0080] The method for the application robot to simulate different levels of elbow extension muscle tension of the human body includes:
[0081] Level 0: The operator places the robot in a position where the shoulder joints naturally droop, the elbow joints naturally droop, and the palms face forward, and the control system is activated. Then, the operator rests one hand on the back of the lower end of the robot's upper arm, and holds it with the other hand. Gently lift the upper limb at the front end of the forearm of the robot, so that the robot is in the position of shoulder joint flexion angle of 45°, abduction angle of 30°, internal rotation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com