Underwater robot optimization decision-making method for non-wide area target search task
An underwater robot and target search technology, applied in the field of optimal decision-making of underwater robots, can solve problems such as increasing the complexity of problems, no search value, lack of quantitative analysis and optimization strategy guidance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0064] Hereinafter, specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
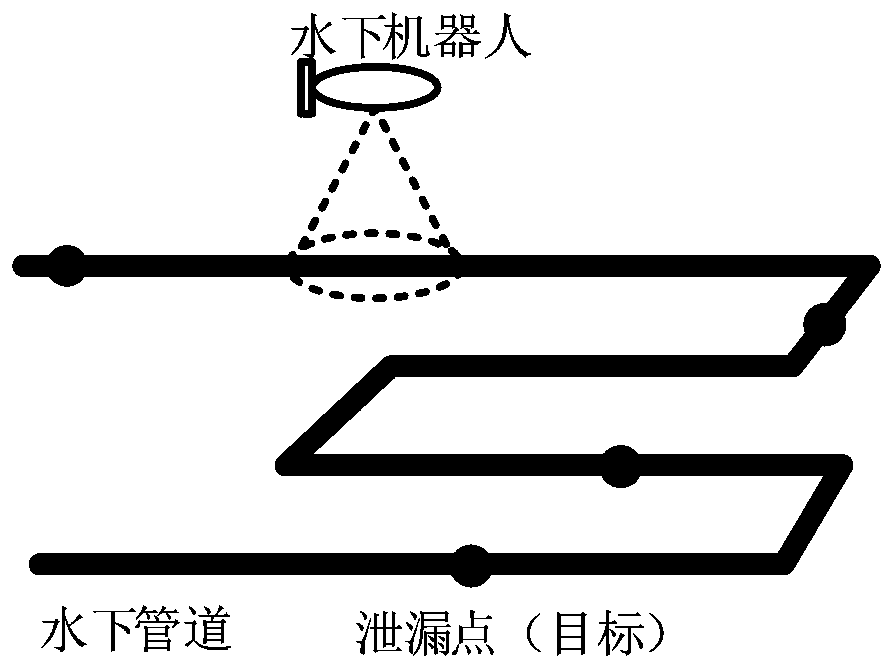
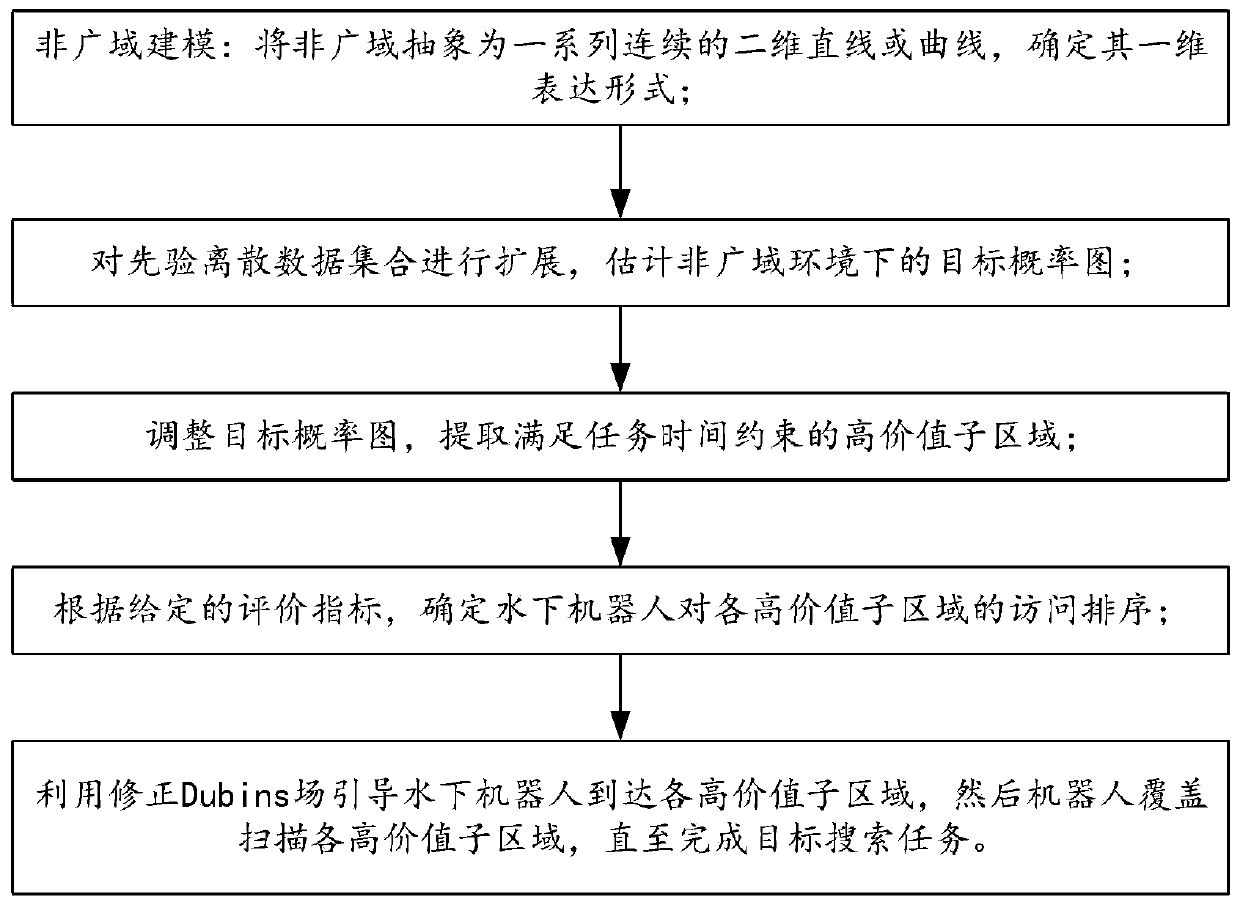
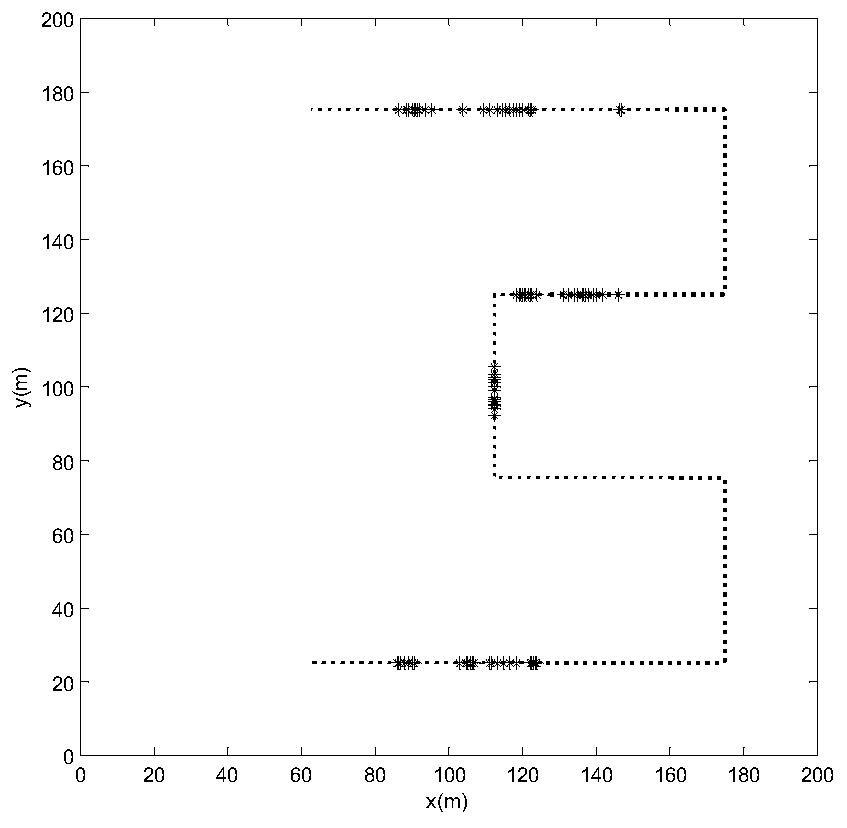
[0065] The present invention takes underwater oil pipeline inspection as an example, such as figure 1 As shown, when the underwater robot is navigating above the oil pipeline, the camera on the robot scans the pipeline downwards to search for leakage targets. Since the field of view of the camera is often wider than the width of the pipeline, the oil pipeline can be approximately regarded as a series of continuous two-dimensional line or curve. In order to distinguish it from traditional broad areas, special narrow and long areas such as oil pipelines, coastlines, and island reef lines are called non-wide areas.
[0066] In many cases, the non-wide-area environment can be described as a collection of straight lines or curves. At this time, the information of the two-dimensional search map can be further simplified into a one-dimensional ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com