Self-intersection mode identification and processing method for multi-ring polygon
A processing method and pattern recognition technology, applied in the field of cartography, can solve problems such as limited self-intersection types, topological errors in processing results, and space occupation conflicts, so as to ensure topology consistency, avoid space occupation conflicts, and simplify results. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
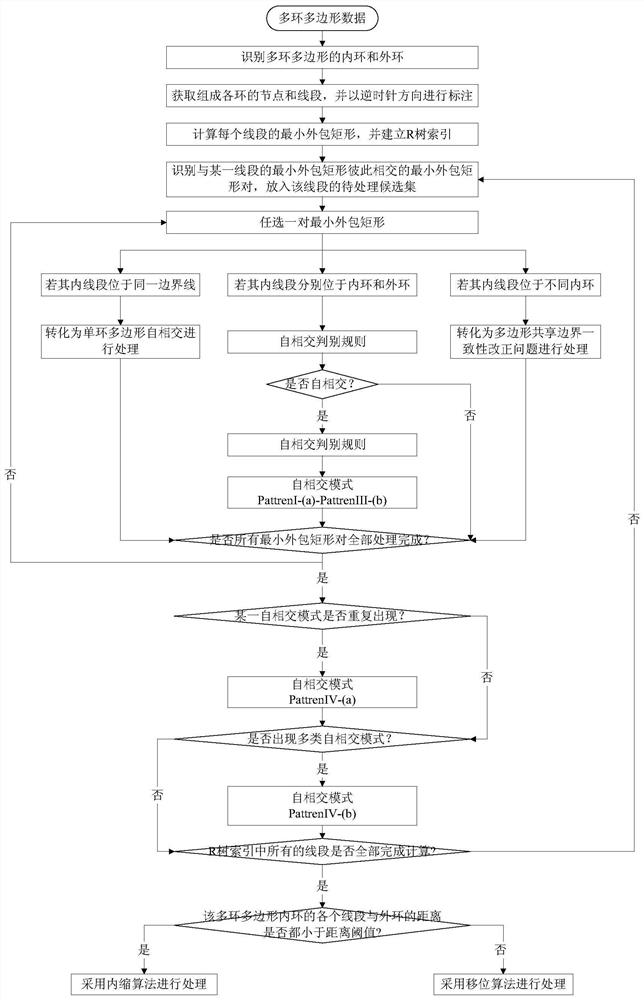
[0048] like Figure 1 to Figure 5 As shown, in the present embodiment, a kind of multi-ring polygon self-intersecting pattern recognition and processing method are provided, comprising the following steps,
[0049] S1. Obtain the nodes and line segments that form the multi-ring polygon in the multi-ring polygon, mark it counterclockwise, and obtain the outer ring and inner ring of the multi-ring polygon;
[0050] S2. Calculate the minimum enclosing rectangle of each line segment, and establish an R-tree index, identify all minimum enclosing rectangles intersecting each other with the minimum enclosing rectangle of a certain line segment, form a plurality of minimum enclosing rectangle pairs, and put them into the pending candidates of the line segment concentrated;
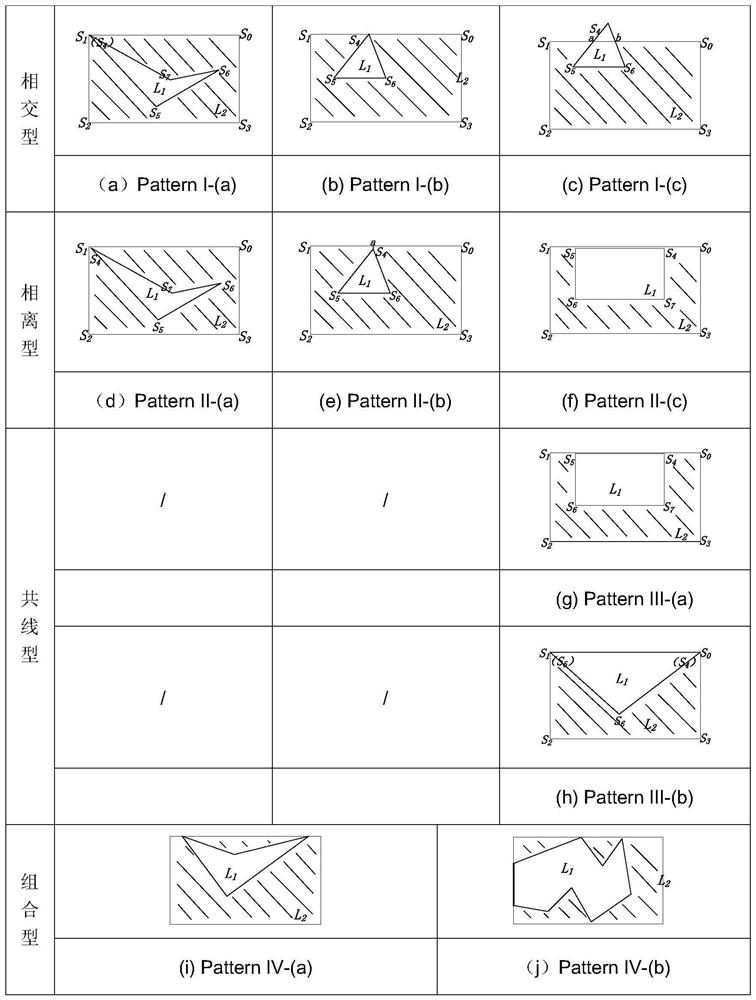
[0051] S3. Select a minimum enclosing rectangle pair in the candidate set of the line segment to be processed, and judge the mutual positions of the inner line segments. If the inner line segments are located on ...
Embodiment 2
[0096] like Image 6 and Figure 7 , in this embodiment, relying on the WJ-III map workstation developed by the Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping Sciences, embedding the multi-ring polygon self-intersecting pattern recognition and simplification method proposed by the present invention, using actual data to verify the rationality and feasibility of the method of the present invention .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com