Patents
Literature
587 results about "Triacontagon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
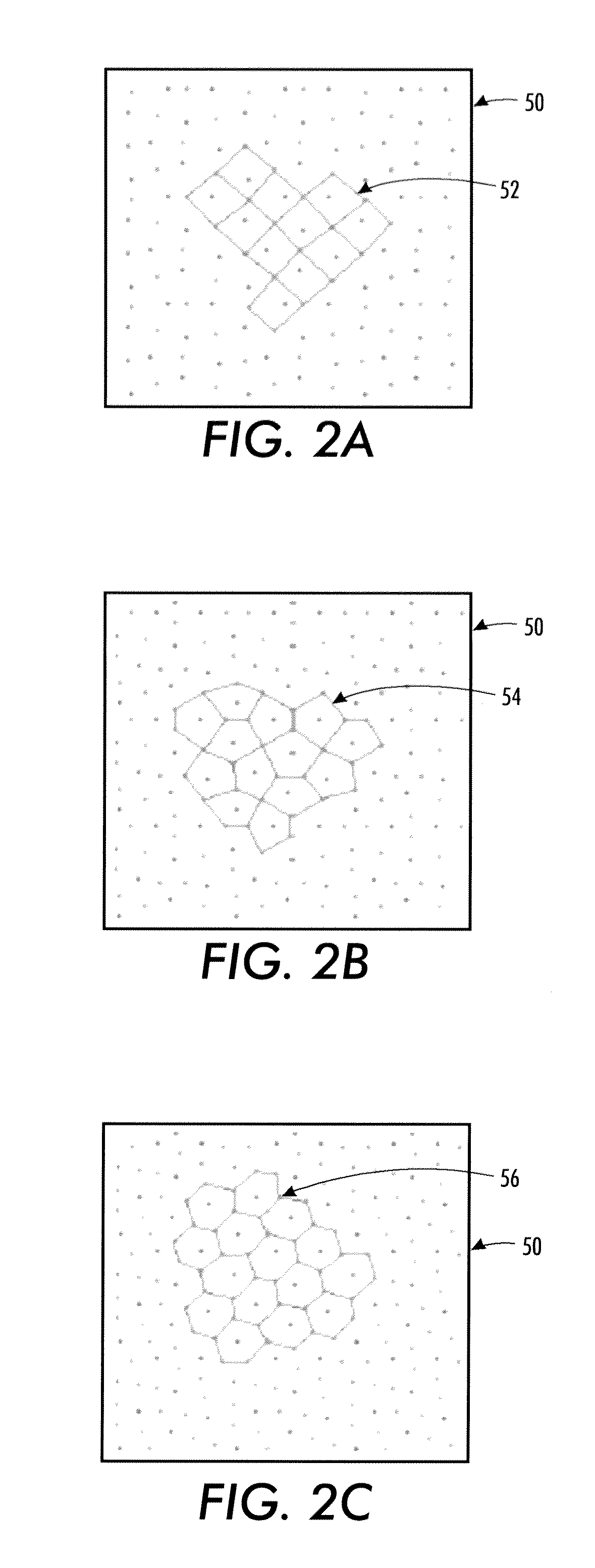
In geometry, a triacontagon or 30-gon is a thirty-sided polygon. The sum of any triacontagon's interior angles is 5040 degrees.
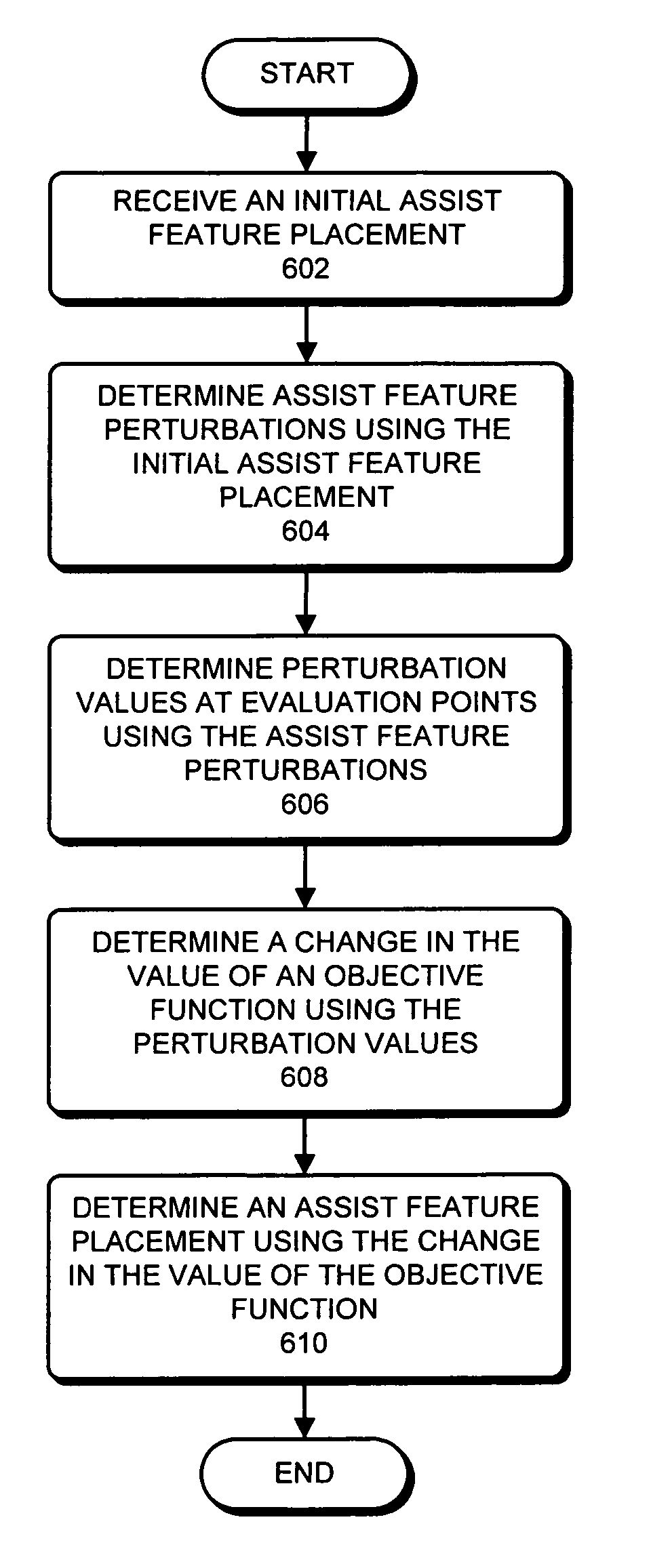
Assist feature placement using a process-sensitivity model
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
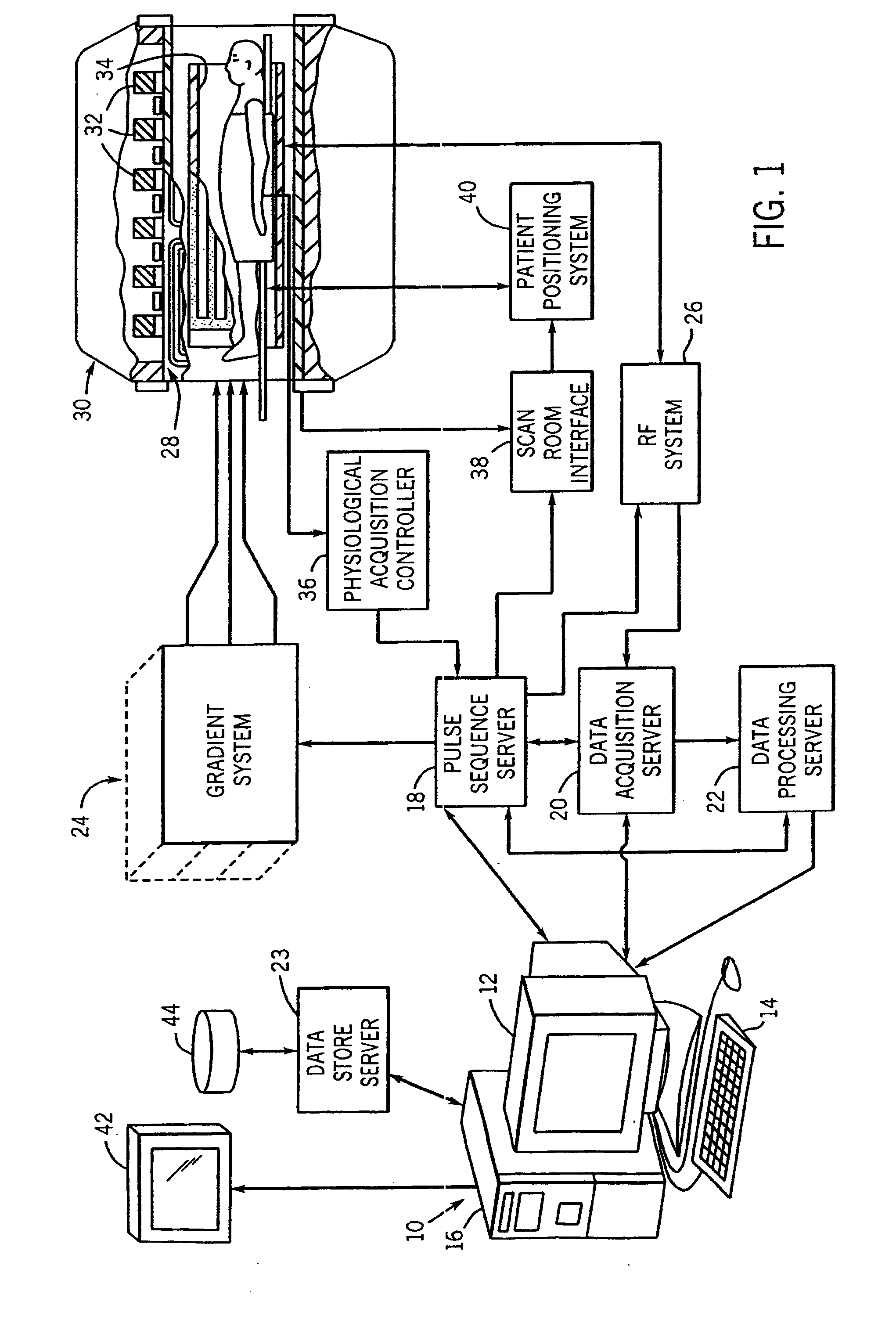
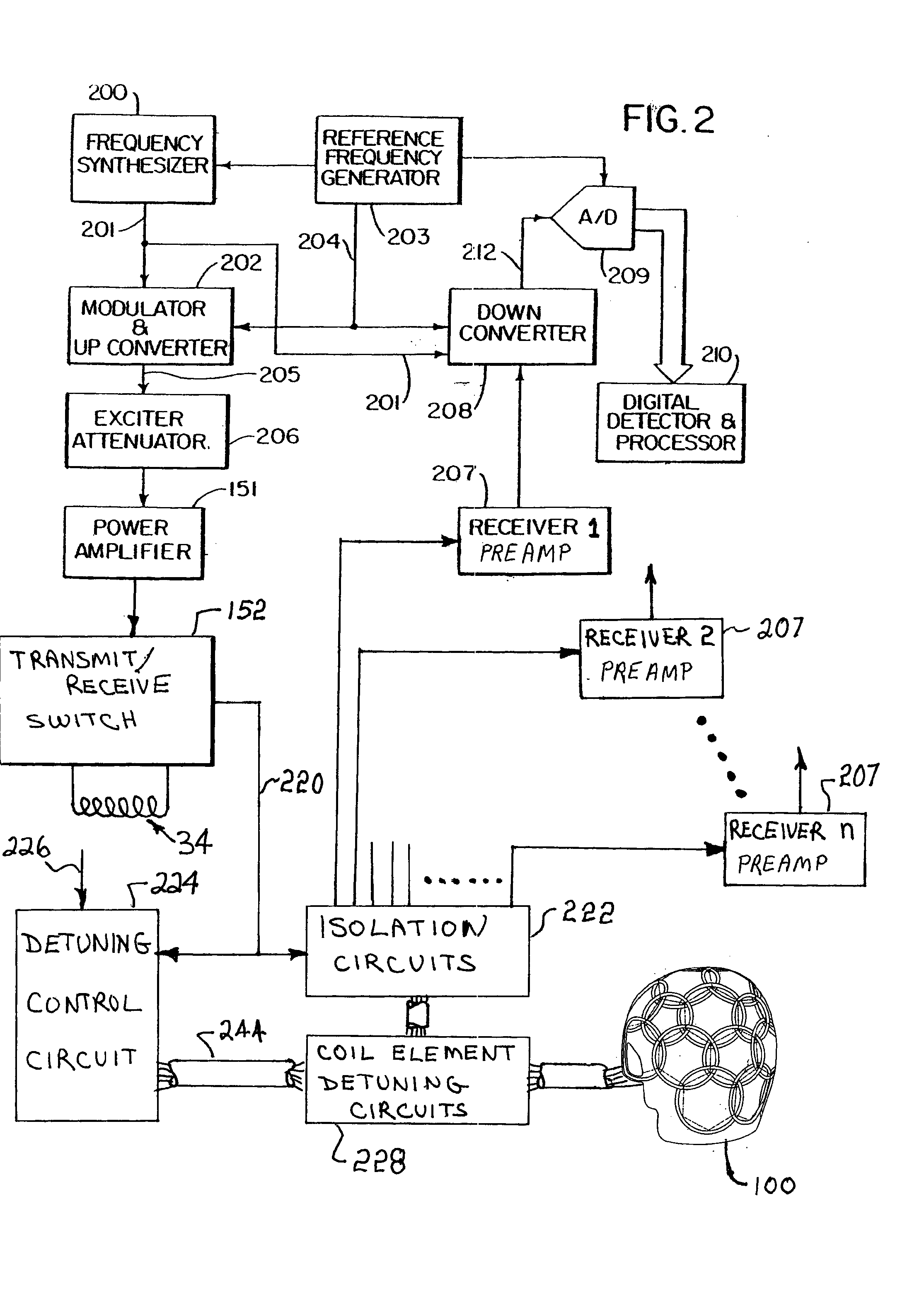
Shaped MRI Coil Array
ActiveUS20080007250A1Minimize mutual inductanceMutual inductance is minimizedElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsRadio frequencyEngineering
An MRI rf coil array is comprised of a large number of separate coil elements that are supported on a substrate that is shaped to the contour of the anatomy being imaged. The coil elements overlap each other to reduce mutual inductance and their location is determined by tiling the surface of the substrate with regular, substantially same sized polygons. The center of each coil element is aligned with the center of a polygon. By using a mixture of different polygons, such as hexagons and pentagons, an arrangement of coil elements may be formed that cover a surface with non-zero Gaussian curvature where each coil is overlapped with its neighbors such that their mutual inductance is nulled.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
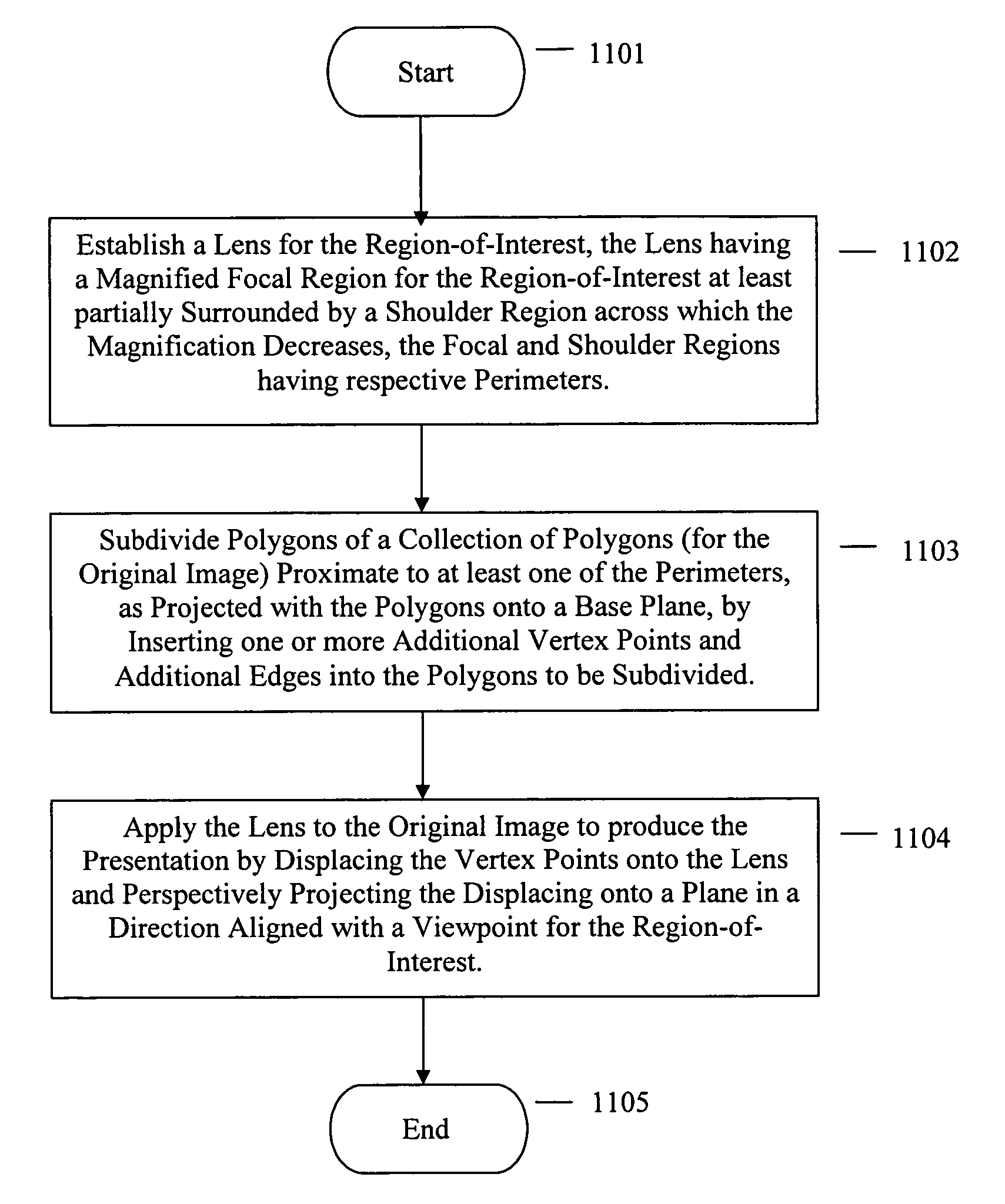
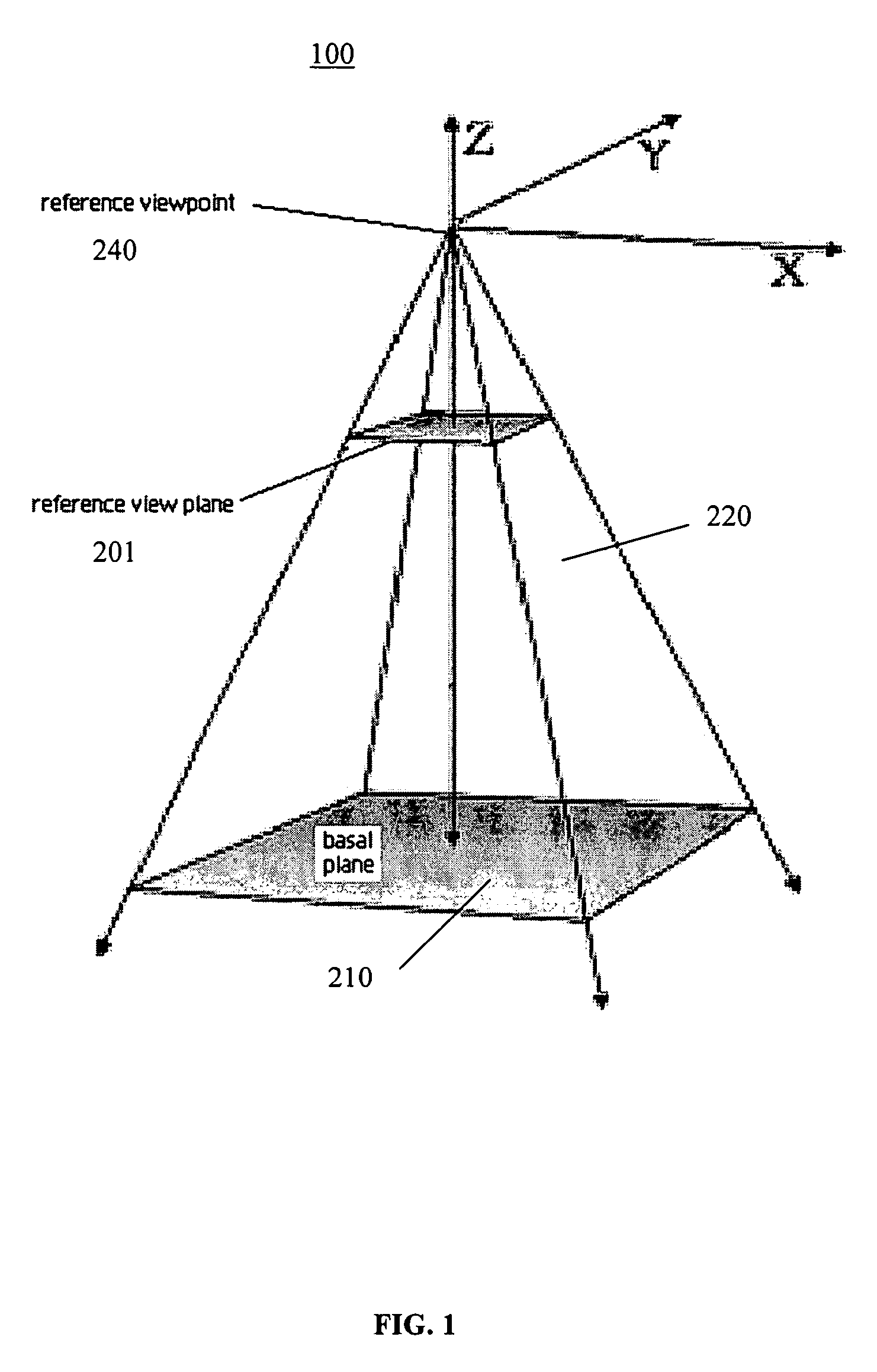
Occlusion reduction and magnification for multidimensional data presentations
ActiveUS7714859B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsTriacontagonMultidimensional data
A method in a computer system for generating a presentation of a region-of-interest in an original image for display on a display screen, the original image being a collection of polygons having polygons defined by three or more shared edges joined at vertex points, the method comprising: establishing a lens for the region-of-interest, the lens having a magnified focal region for the region-of-interest at least partially surrounded by a shoulder region across which the magnification decreases, the focal and shoulder regions having respective perimeters; subdividing polygons in the collection of polygons proximate to at least one of the perimeters, as projected with the polygons onto a base plane, by inserting one or more additional vertex points and additional edges into the polygons to be subdivided; and, applying the lens to the original image to produce the presentation by displacing the vertex points onto the lens and perspectively projecting the displacing onto a view plane in a direction aligned with a viewpoint for the region-of-interest.
Owner:ACCESSIFY LLC
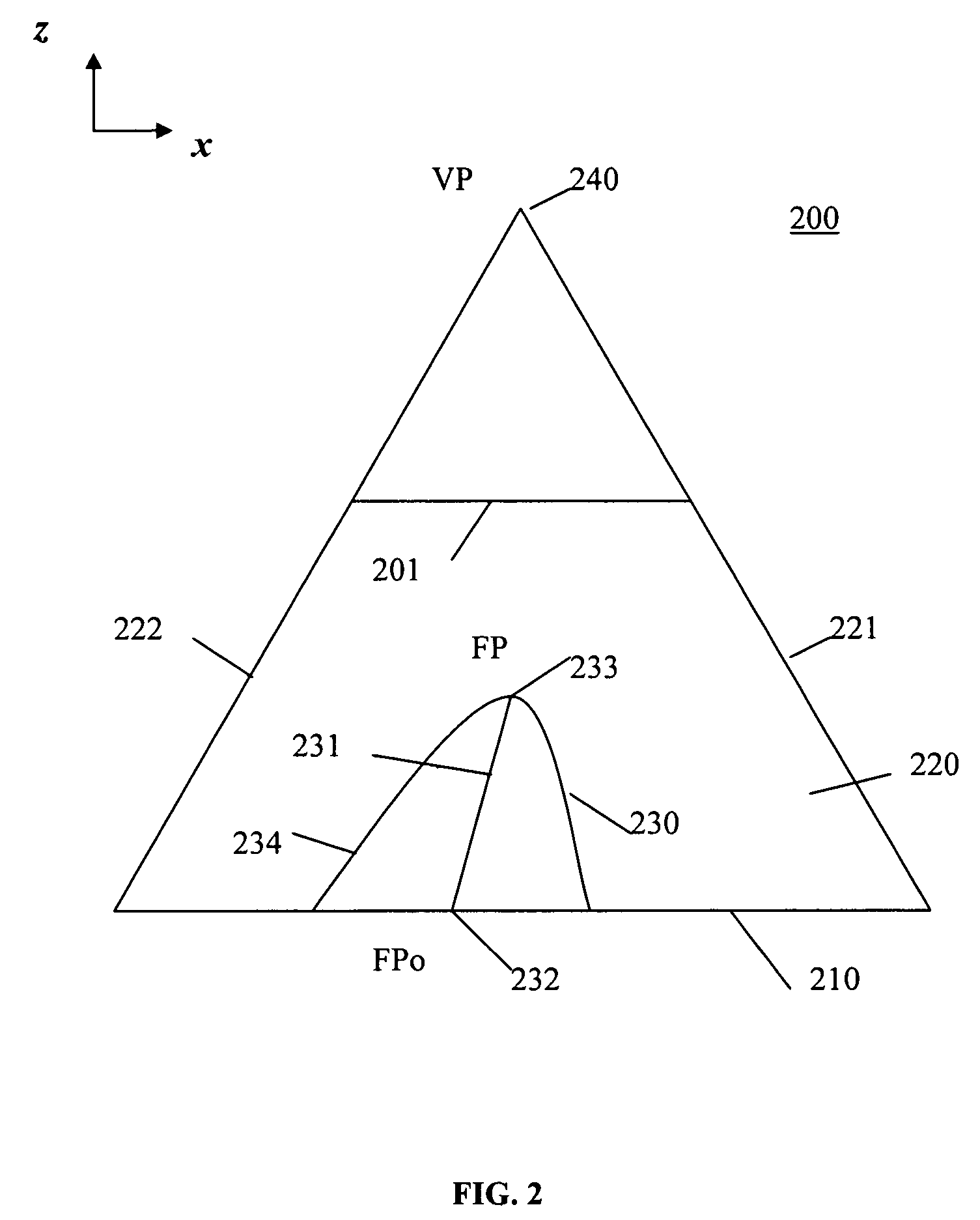
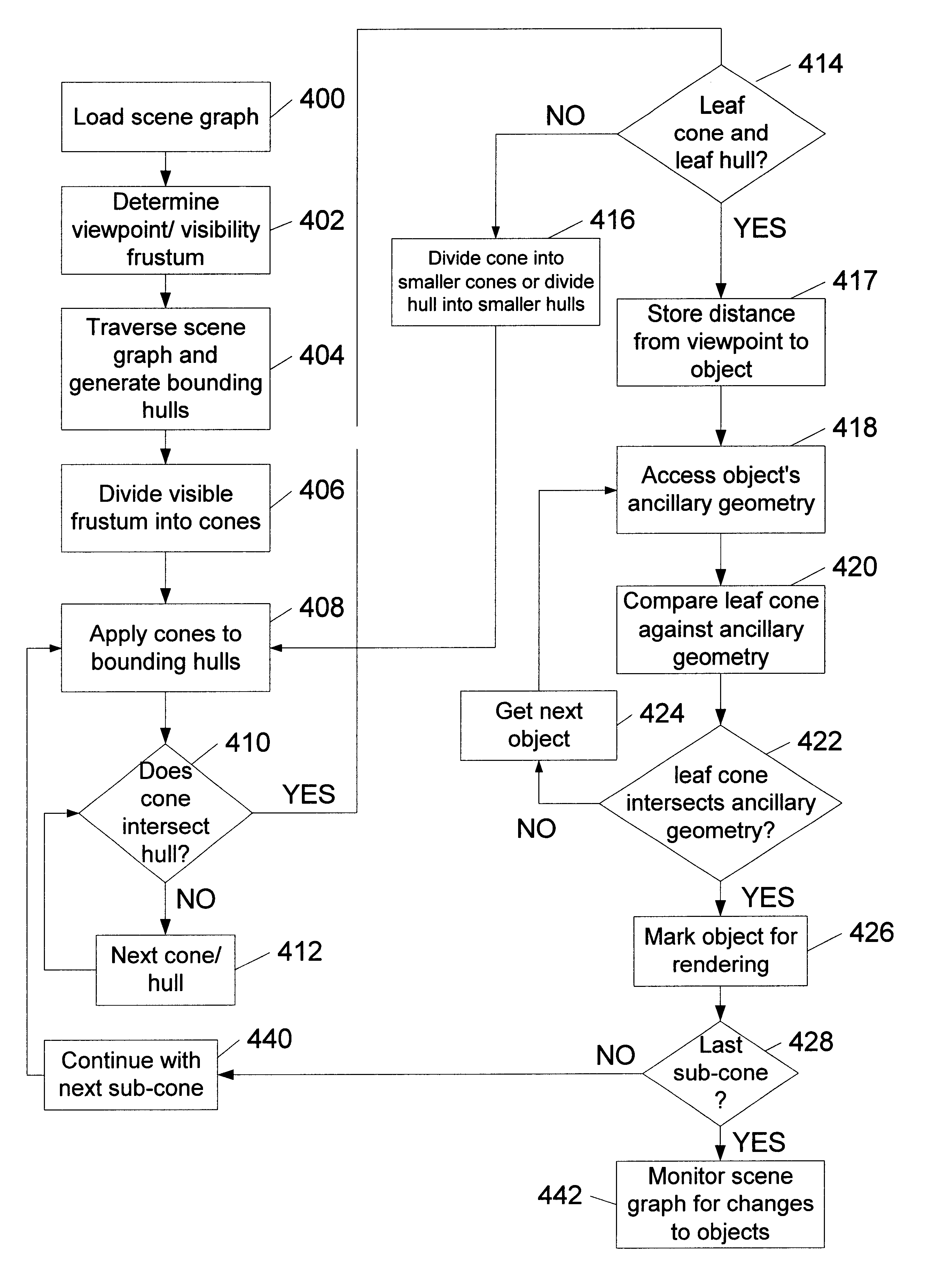
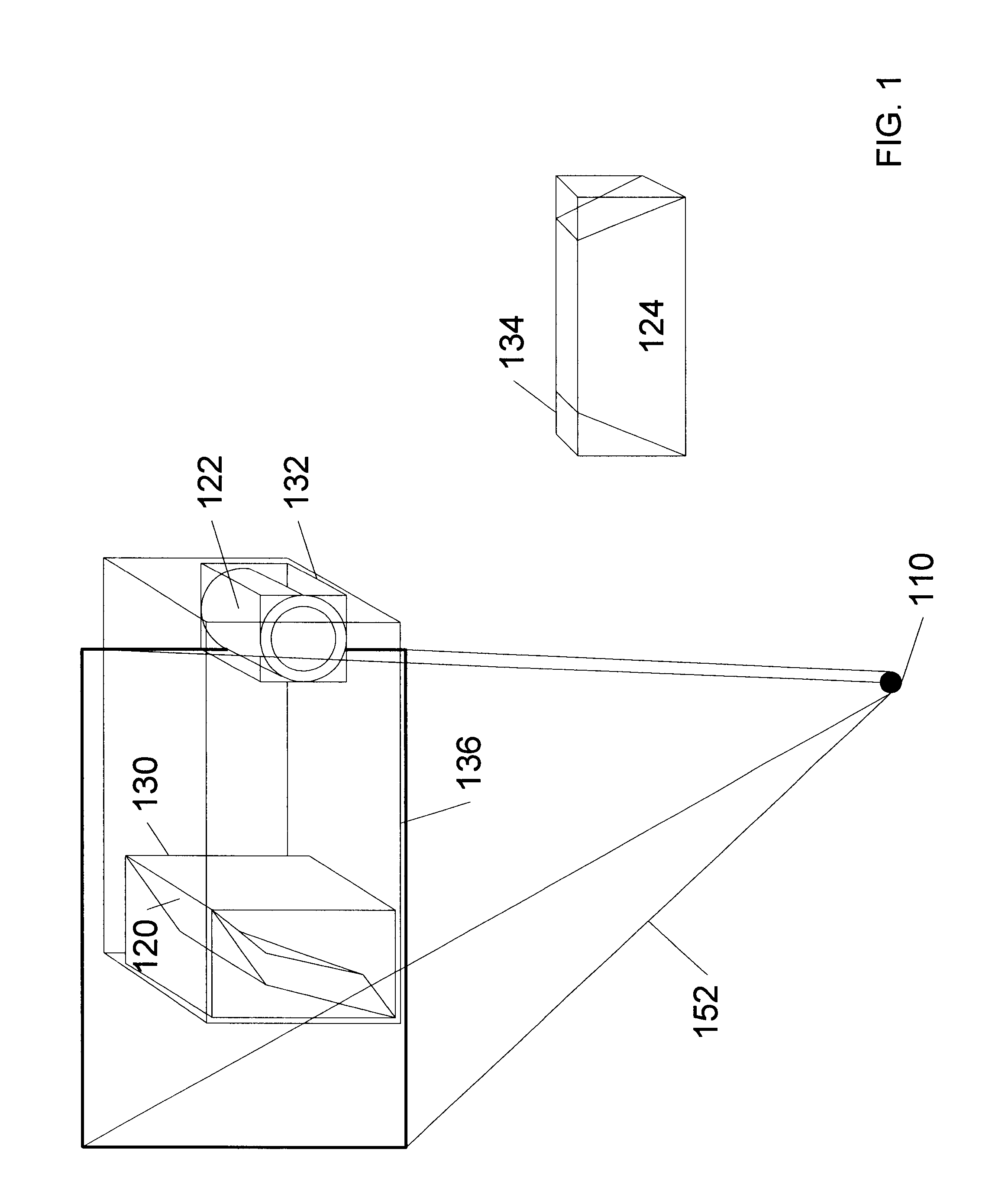
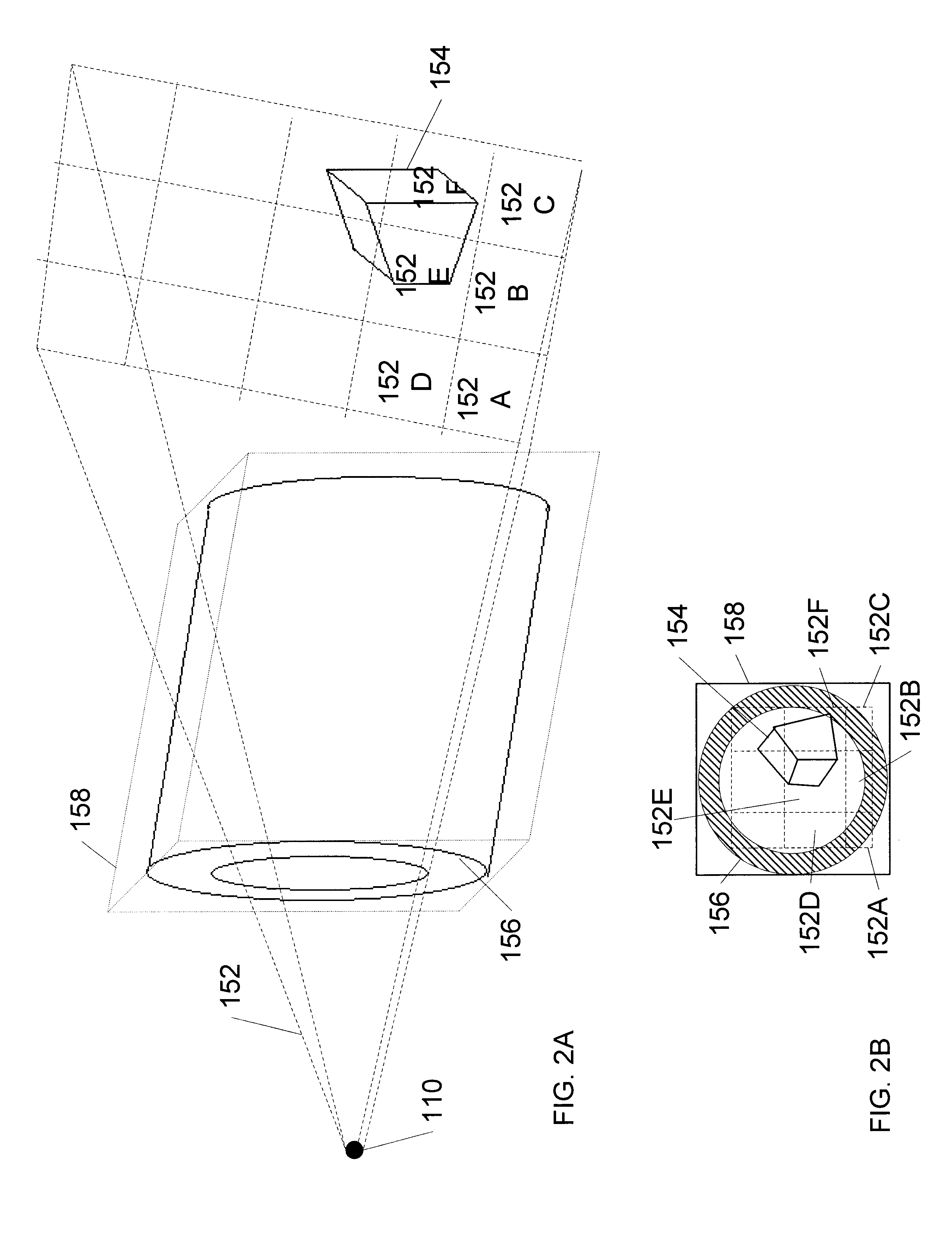
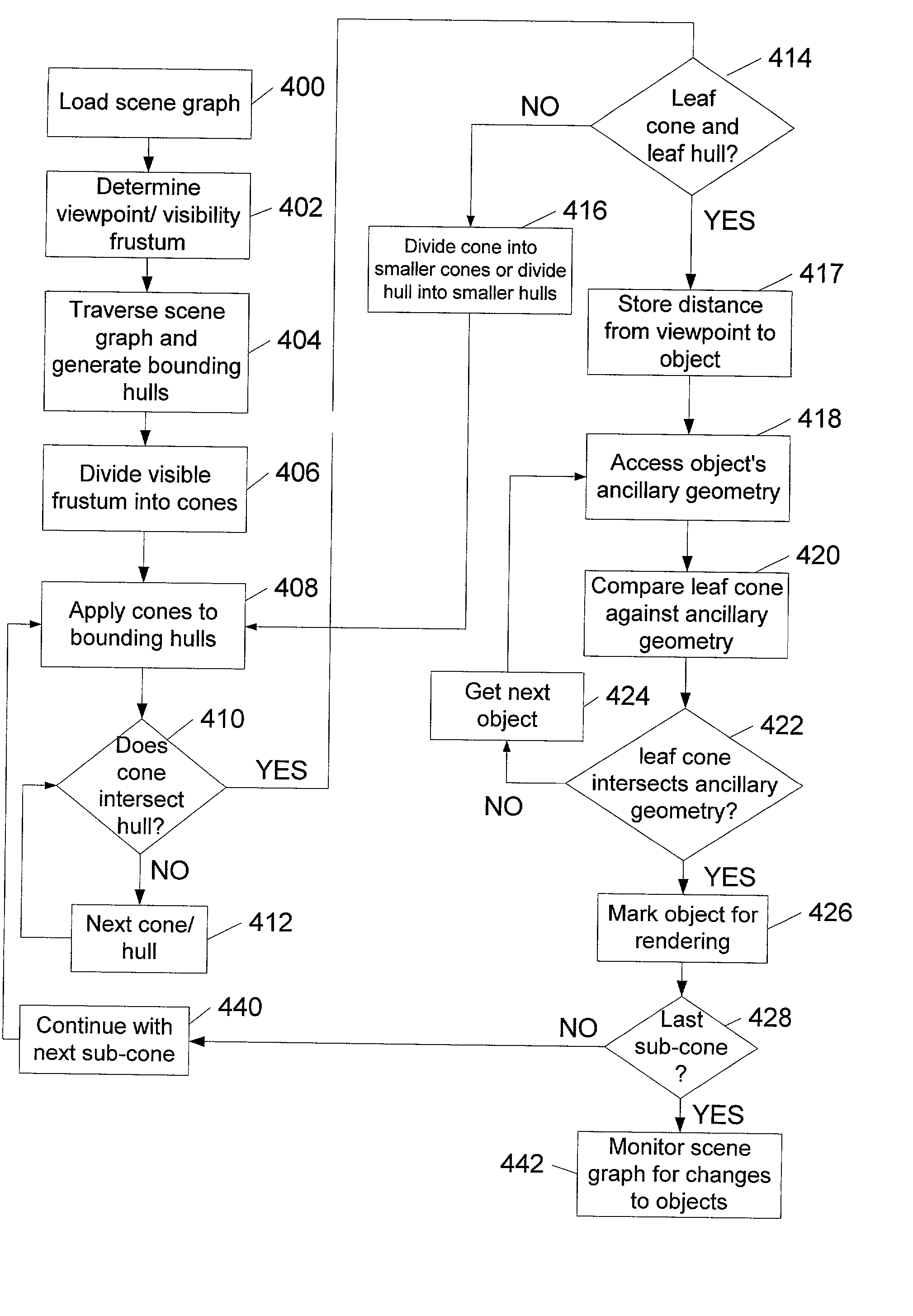
Using ancillary geometry for visibility determination
A system and method for determining graphical object visibility by utilizing ancillary geometry. When comparing visibility cones with bounding hulls of scene graph hierarchy leaf nodes, ancillary geometry may be used in place of the bounding hulls and the leaf node's actual geometry. The ancillary geometry may be created through a manual process, or by an automated decimation process. The ancillary geometry may be a simplistic analytic surface (e.g., a sphere or a cylinder), a NURB surface, a collection of polygons, or a combination of surfaces and polygons.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Interface and method of interfacing between a parametric modelling unit and a polygon based rendering system
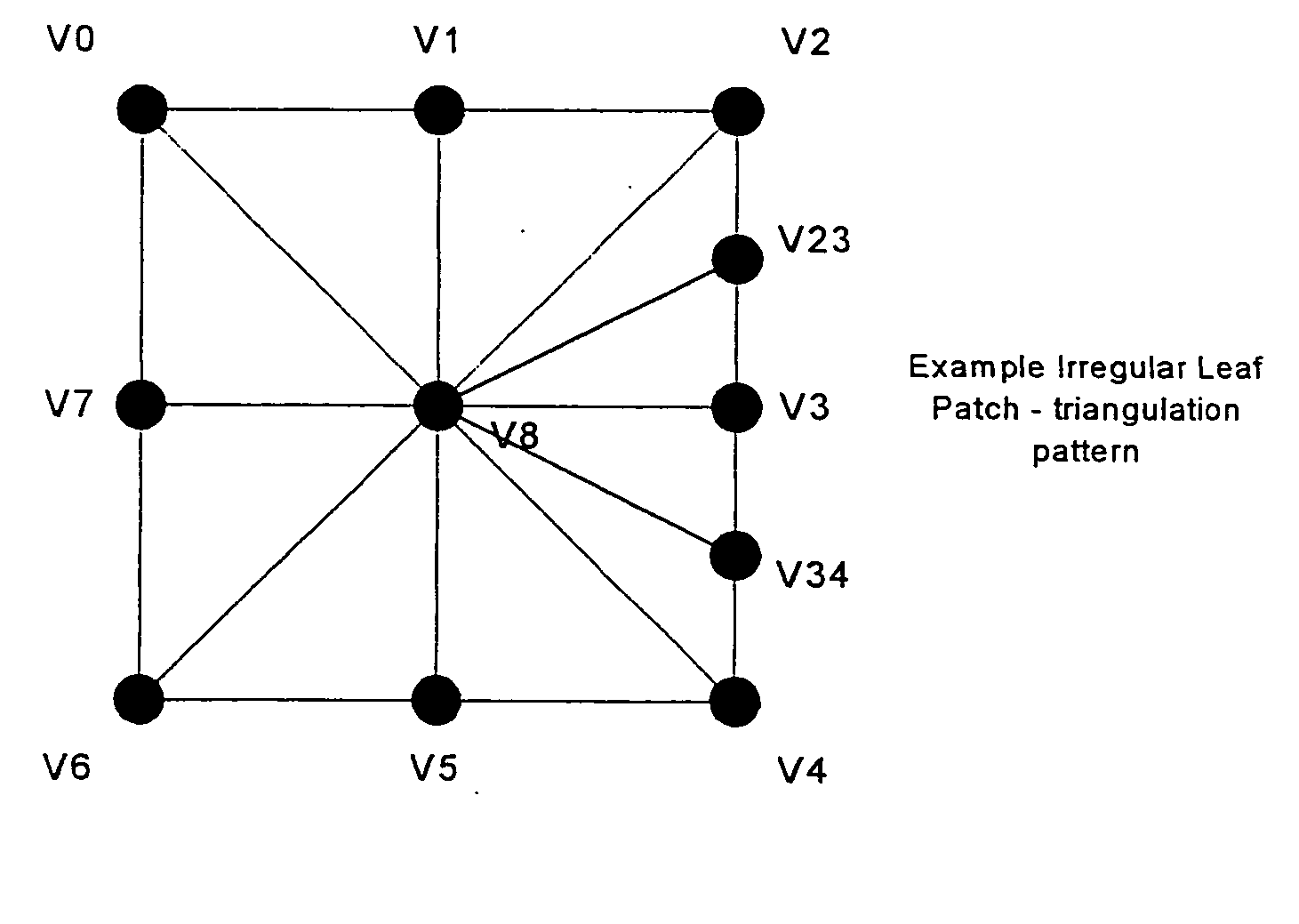
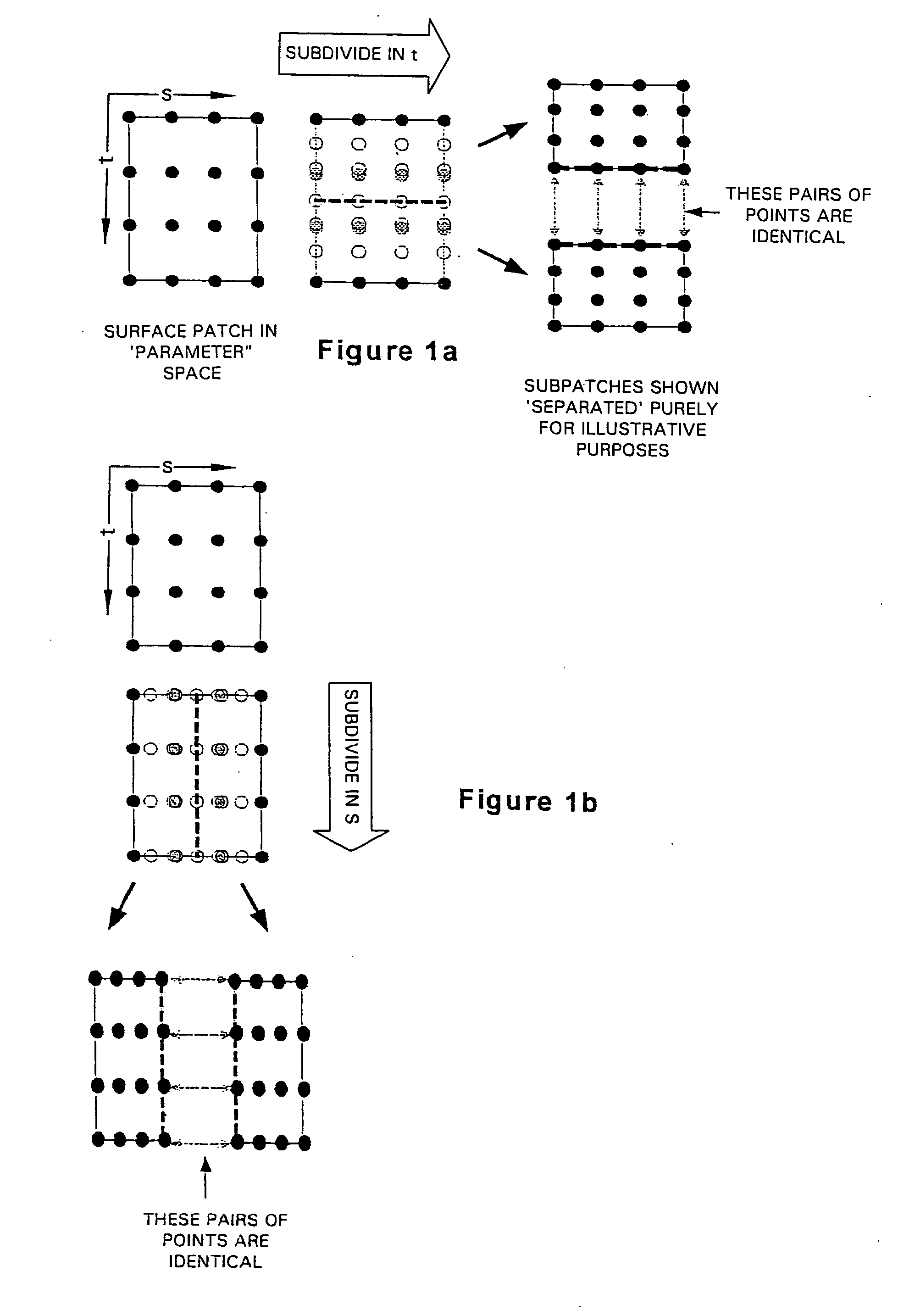
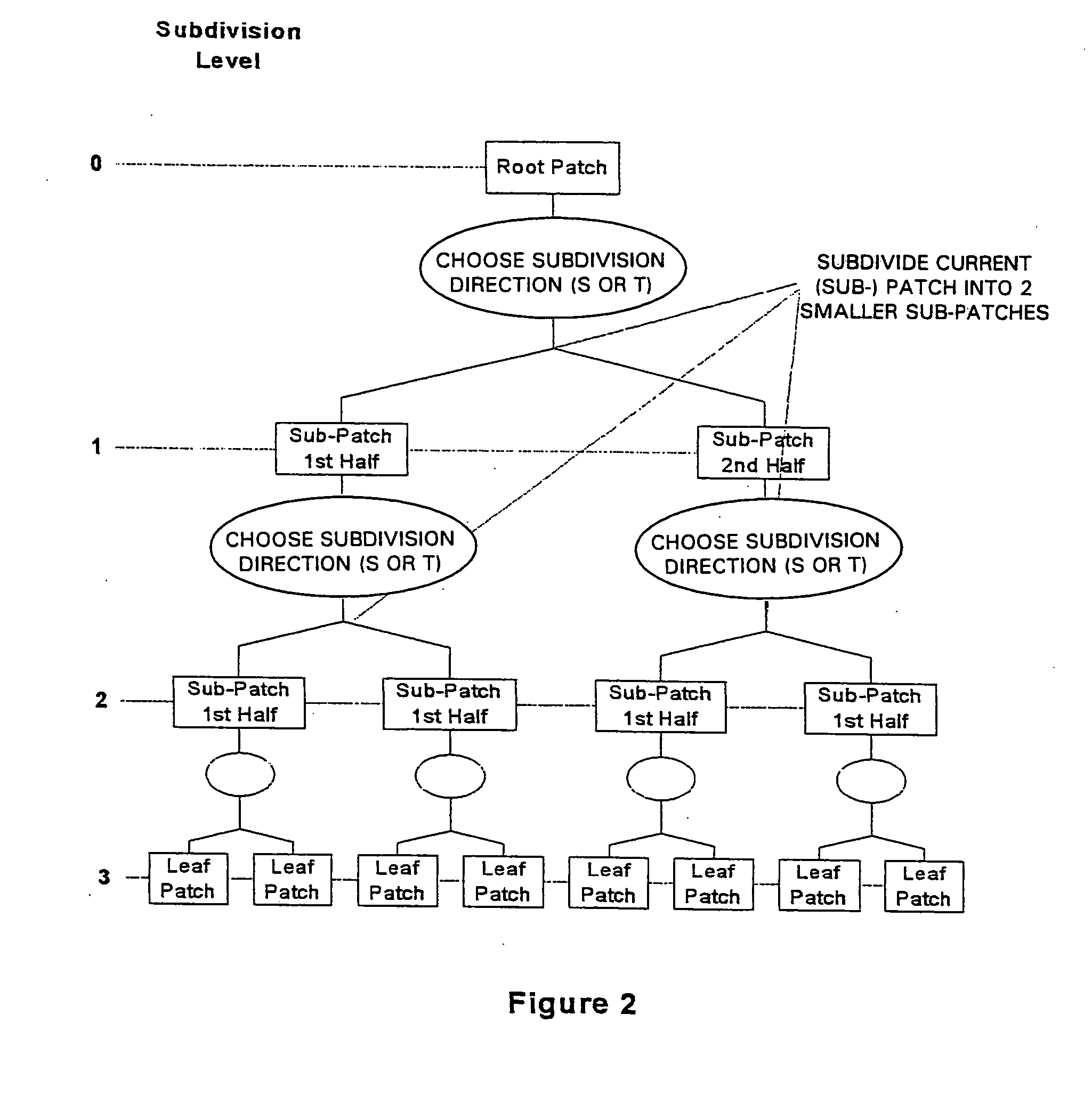
An interface for use in a 3-d graphics system comprising a parametric modelling unit for modelling objects as high order surfaces, and a polygon based rendering system for rendering polygon modelled objects for display. The interface comprises an input for receiving data and a subdivision unit coupled to the input for processing the data. The interface includes a converter coupled to the subdivision unit for determining from leaf patch data a first plurality of values representing vertices of tessellating polygons describing the leaf patch, and for determining from sub-leaf patch data a second plurality of values representing the vertices of tessellating polygons describing the sub-leaf patch. The interface also has a combiner, coupled to the converter, for combining the values to form leaf polygon data defining the polygon vertices at a first subdivision level, and an output coupled to the combiner for outputting the leaf polygon data.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Program, recording medium, game character rendering method, and game apparatus
A program which can dynamically and realistically express an impact which a game character rendered by motion data receives is provided. In bullet ball-related processing (S114), determination is made about whether a bullet ball hits either one of node assigned balls. When the determination is affirmative, a torque at a hit point is calculated as an impact magnitude and the node assigned balls are disposed, through calculation of a rotation angle per frame, to nodes whose coordinate positions are corrected in metaball update processing (S120), density is calculated for each vertex of voxels from a reference position of each metaball towards the minimum direction and the maximum direction of a voxel index of the voxels according to a calculation equation expressing a solid shape in density distribution processing (S122), and vertex coordinates of polygons are calculated based upon density of each metaball at the vertex coordinates of the voxels and a predetermined threshold in marching cube processing (S124).
Owner:GLORY KOGYO KK
Using ancillary geometry for visibility determination
InactiveUS20020163515A1Cathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphicsVisibility determination
A system and method for determining graphical object visibility by utilizing ancillary geometry. When comparing visibility cones with bounding hulls of scene graph hierarchy leaf nodes, ancillary geometry may be used in place of the bounding hulls and the leaf node's actual geometry. The ancillary geometry may be created through a manual process, or by an automated decimation process. The ancillary geometry may be a simplistic analytic surface (e.g., a sphere or a cylinder), a NURB surface, a collection of polygons, or a combination of surfaces and polygons.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
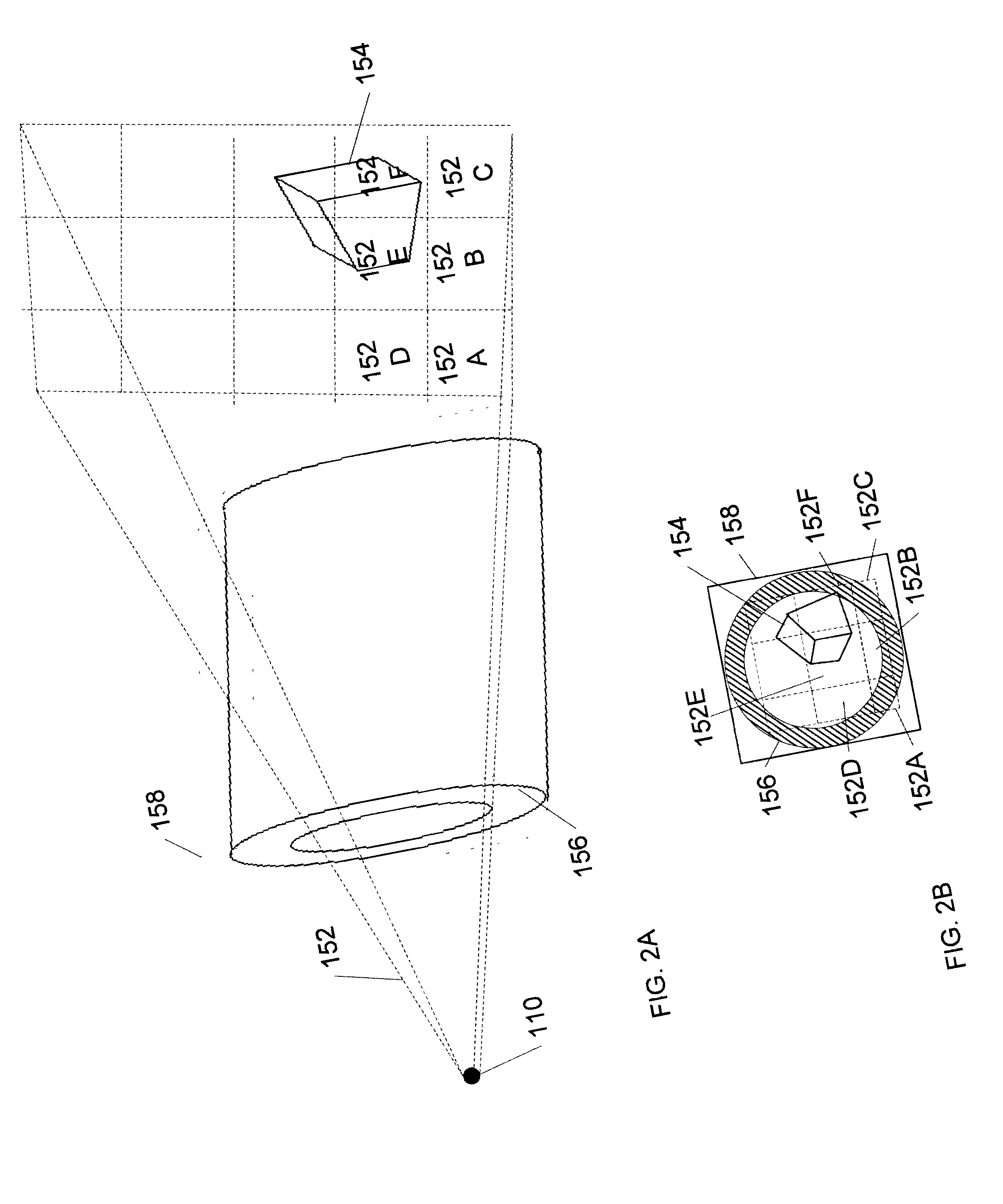
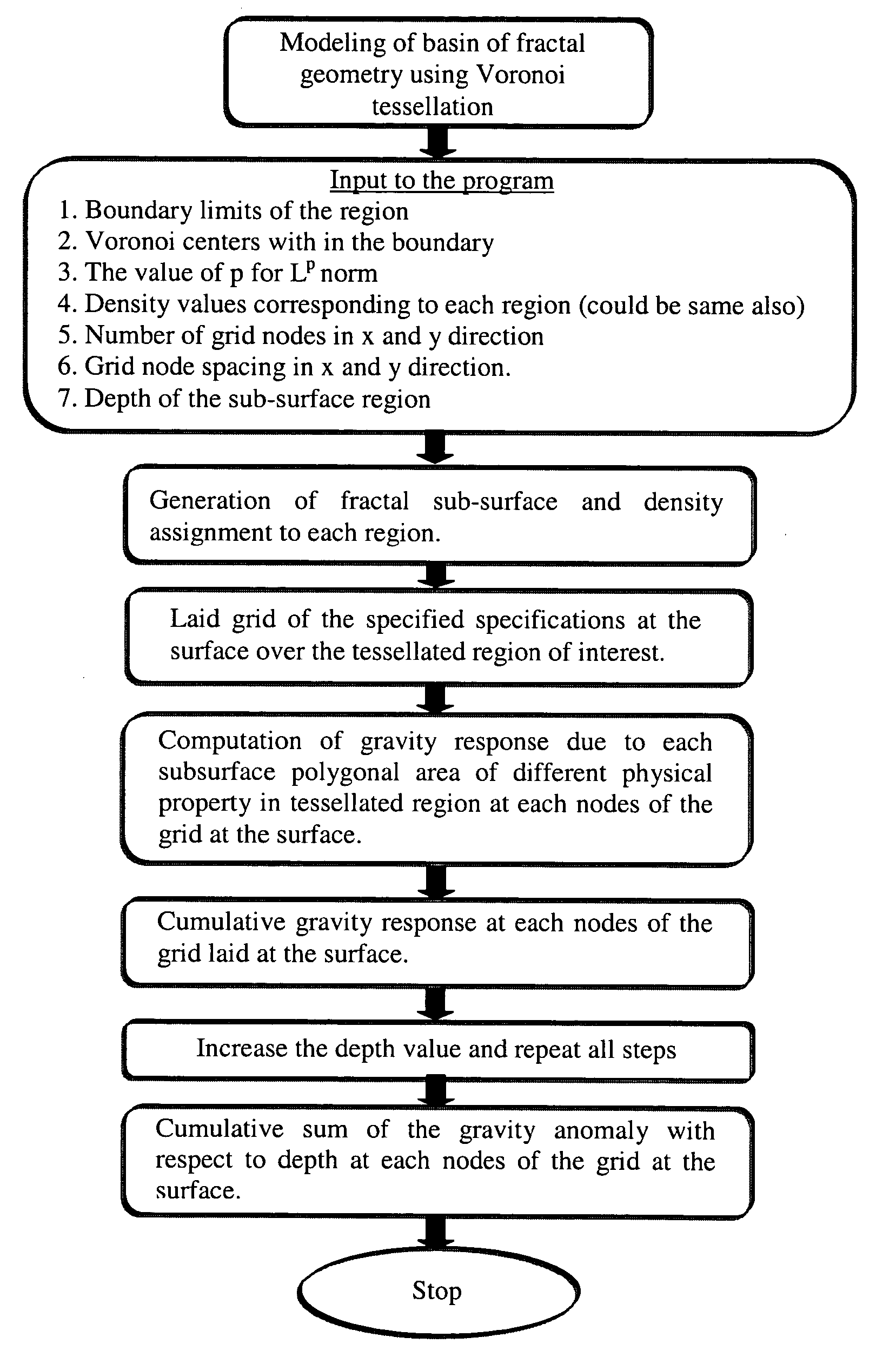
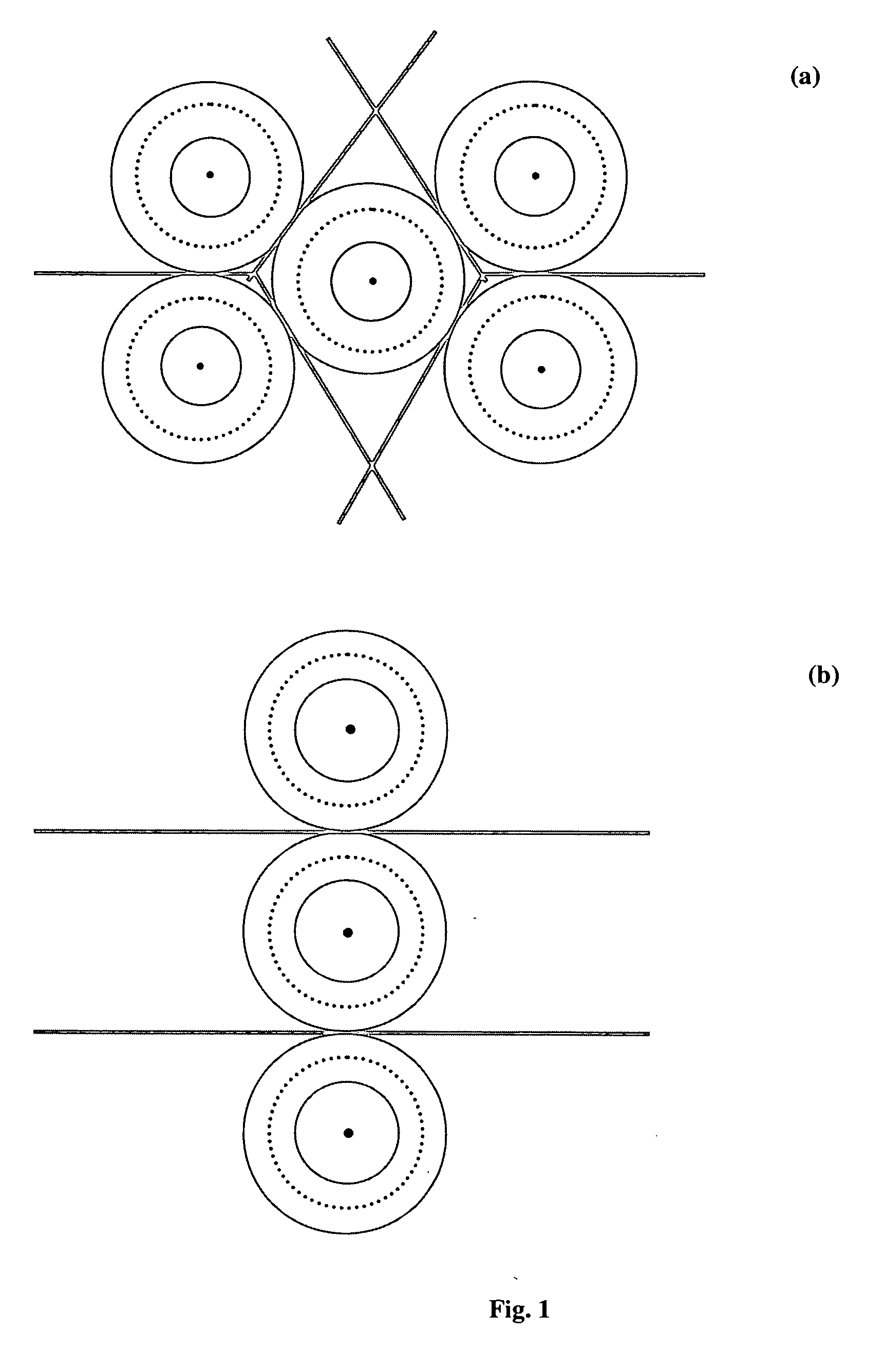
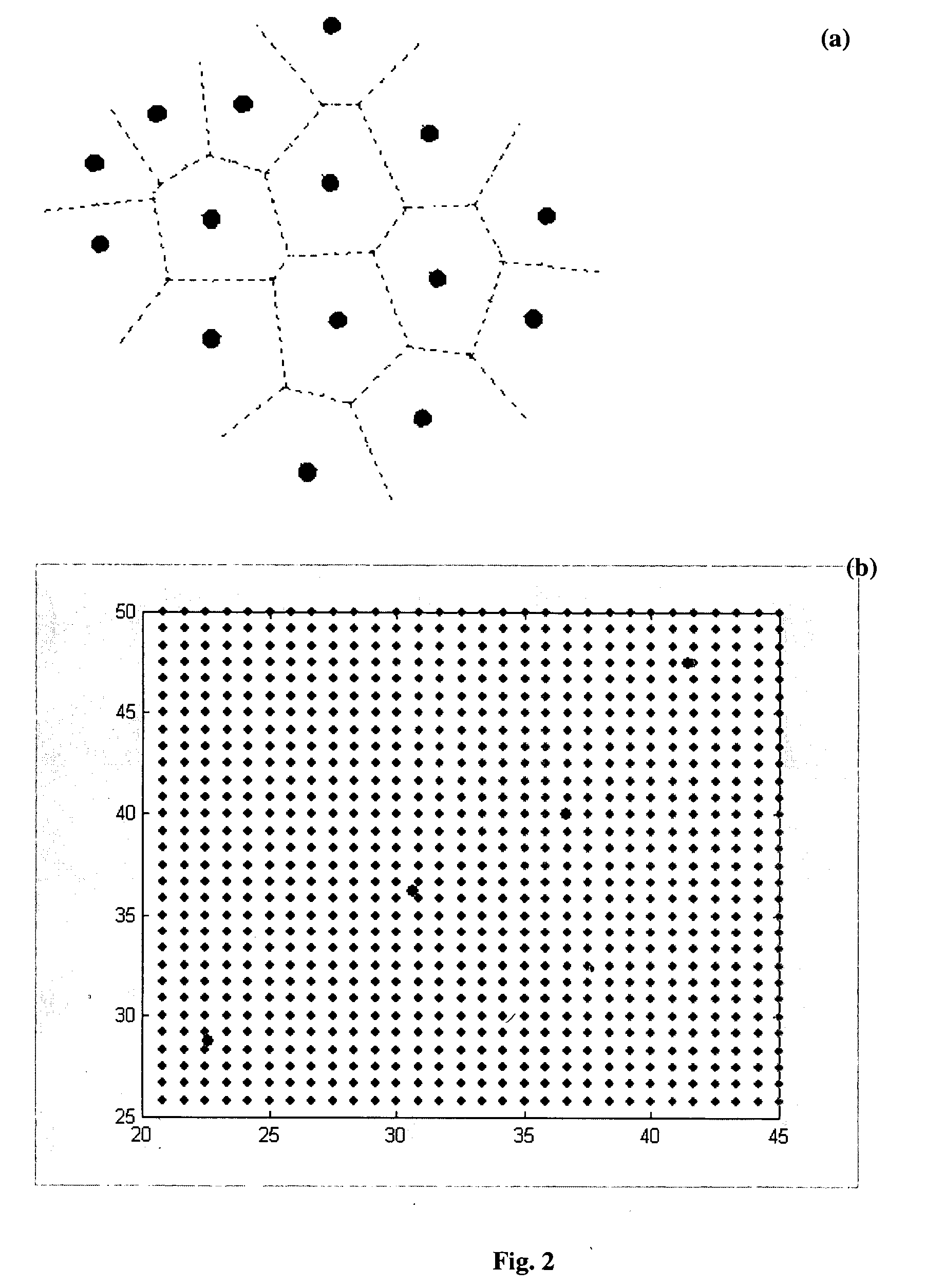
Generation of three dimensional fractal subsurface structure by Voronoi Tessellation and computation of gravity response of such fractal structure
ActiveUS20040201585A1Generate efficientlyImprove variationGravitational wave measurement3D-image renderingTriacontagonPetroleum exploration
The invention is an entirely new application of domain characterization generated by Voronoi tessellation, which is very close to realistic geology and computation of gravity response of such domain, which has three dimensional fractal basin structure, and is favorable for oil exploration. In this work the interfaces or tessellating domains are represented by a set of parameters, which are referred as Voronoi centers. These parameters can be perturbed by any amount without getting into representational problems as faced by the conventional techniques. To accomplish such representation Voronoi tessellation is used, which in two dimensional space consists of enclosing every Voronoi center by a Voronoi polygon such that the common edge of adjacent polygons is perpendicular bisector to the line joining the Voronoi centers on both the sides of that edge. In this invention instead of using conventional Euclidian distances, the notion of Voronoi tessellation is generalized by using Ldistances, where p can hold any real value so that Voronoi domains are not necessarily polygonal. Desired fractal subsurface is generated using this approach that is quite close to the natural settings than the conventional planer or polygonal representation. Next, the gravity response due to this fractal subsurface structure has been computed. The new invention has a significant advantage over the conventional methods especially in geophysical inversion where initial model parameters are updated in each iteration, which can be done more easily and efficiently by Voronoi tessellation merely by changing Voronoi centers.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
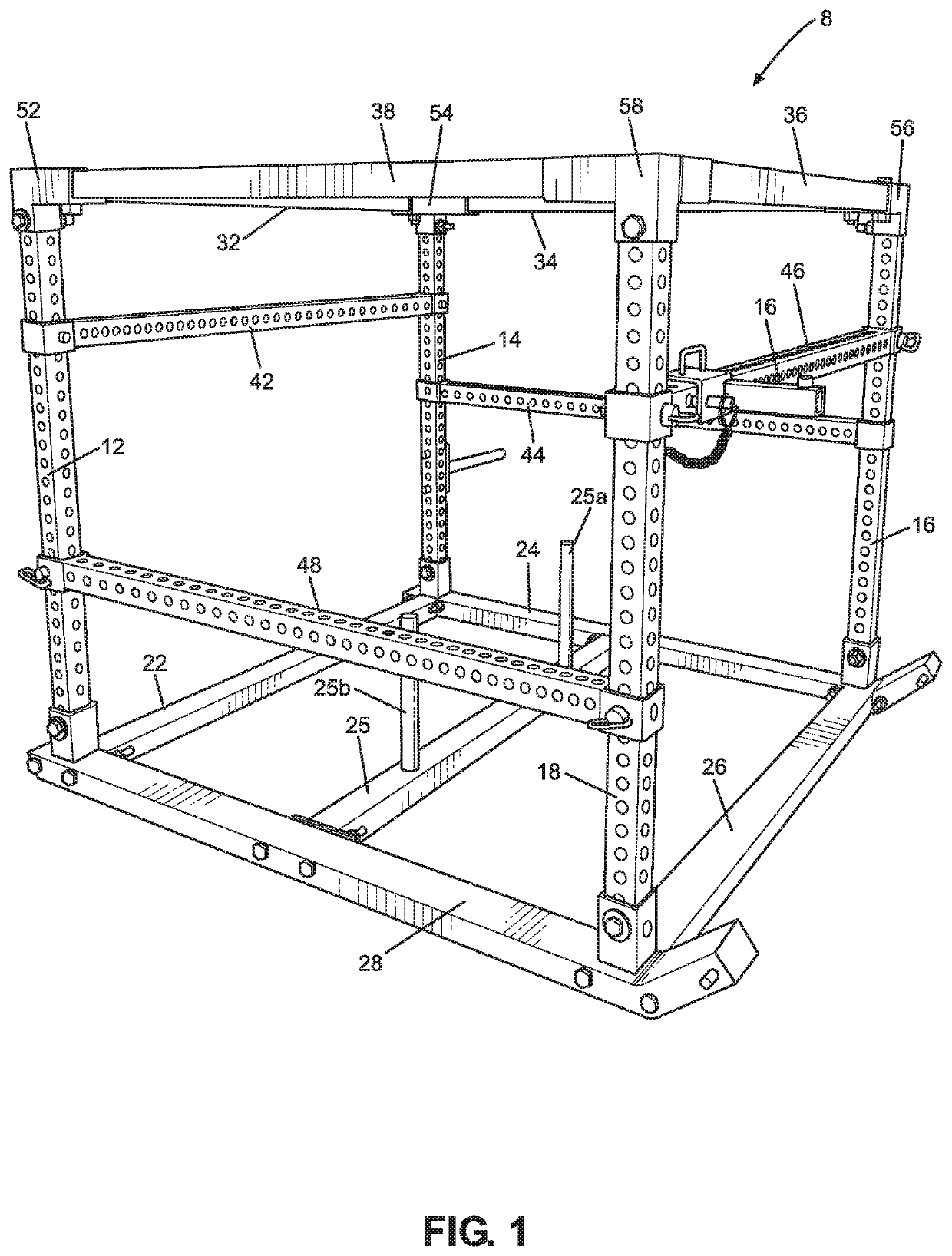
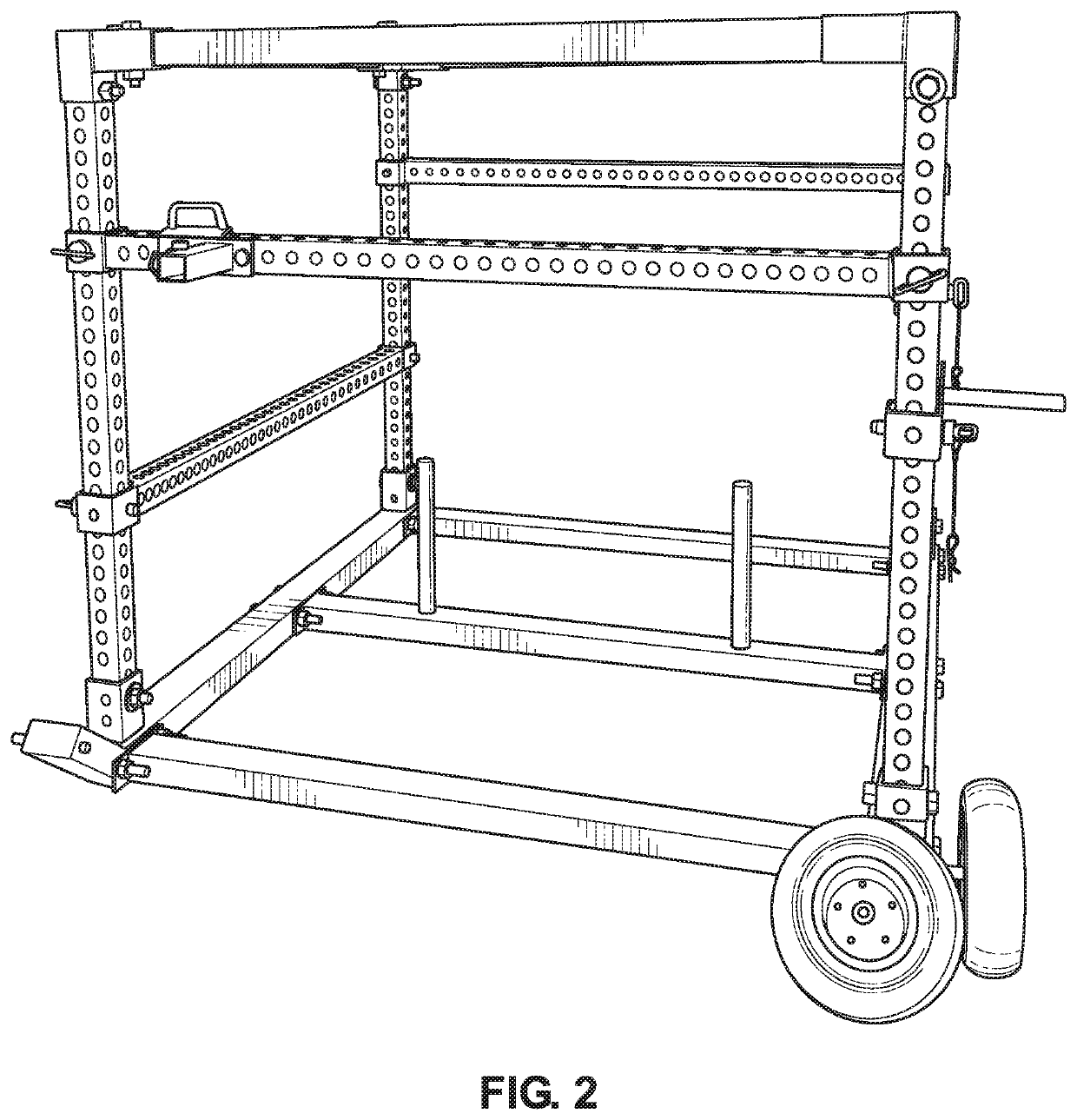
Modular exercise apparatus
Owner:SCHLEGEL ANTHONY
Surface patch techniques for computational geometry
InactiveUS8836701B1Fine surfaceImproved visualGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsComputer Aided DesignMorphing
A method and system for computer aided design (CAD) is disclosed for designing geometric objects, wherein interpolation and / or blending between such objects is performed while deformation data is being input. Thus, a designer obtains immediate feedback to input modifications without separately entering a command(s) for performing such deformations. A novel N-sided surface generation technique is also disclosed herein to efficiently and accurately convert surfaces of high polynomial degree into a collection of lower degree surfaces. E.g., the N-sided surface generation technique disclosed herein subdivides parameter space objects (e.g., polygons) of seven or more sides into a collection of subpolygons, wherein each subpolygon has a reduced number of sides. More particularly, each subpolygon has 3 or 4 sides. The present disclosure is particularly useful for designing the shape of surfaces. Thus, the present disclosure is applicable to various design domains such as the design of, e.g., bottles, vehicles, and watercraft. Additionally, the present disclosure provides for efficient animation via repeatedly modifying surfaces of an animated object such as a representation of a face.
Owner:CAD-SENSE LLC
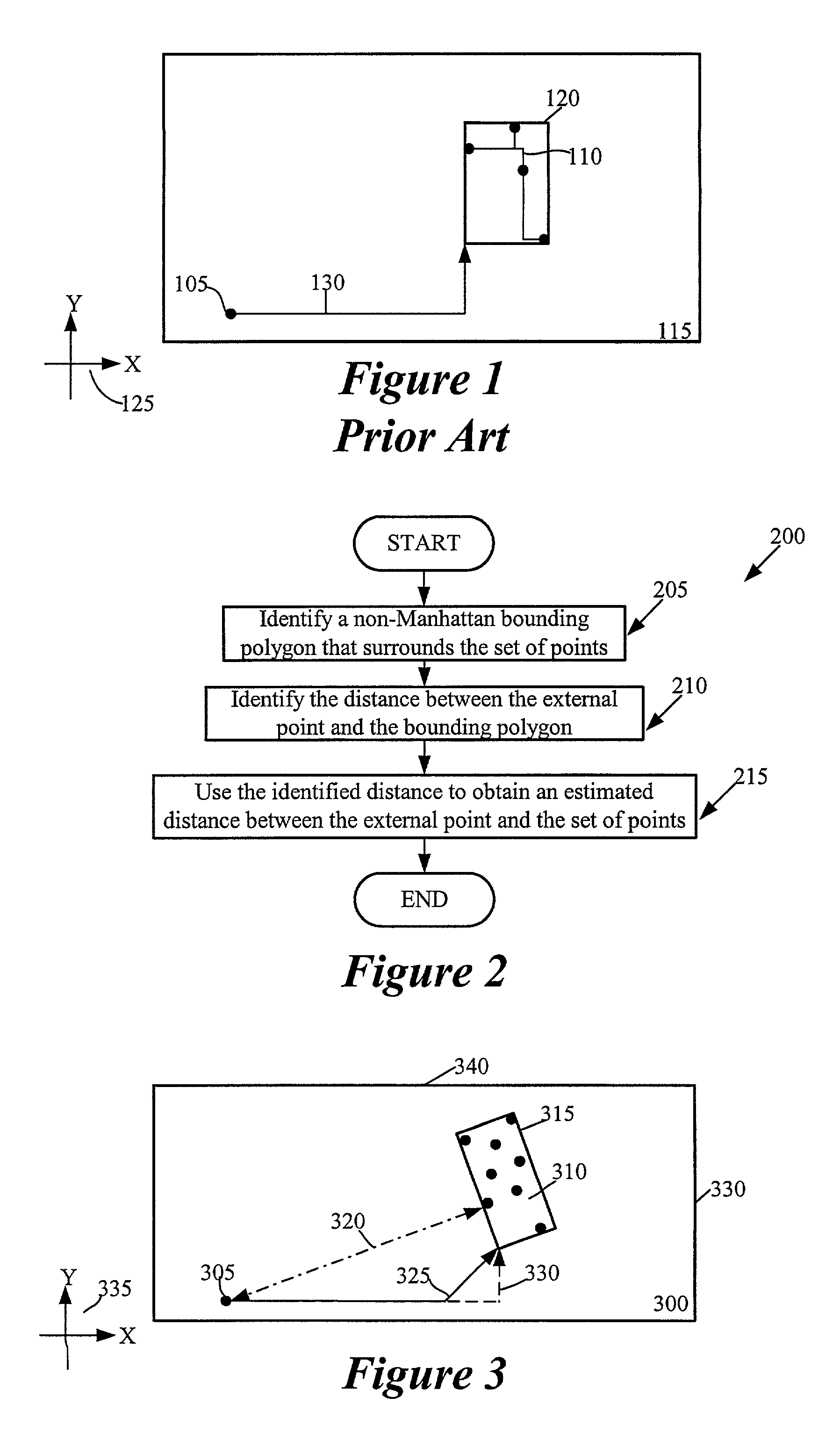
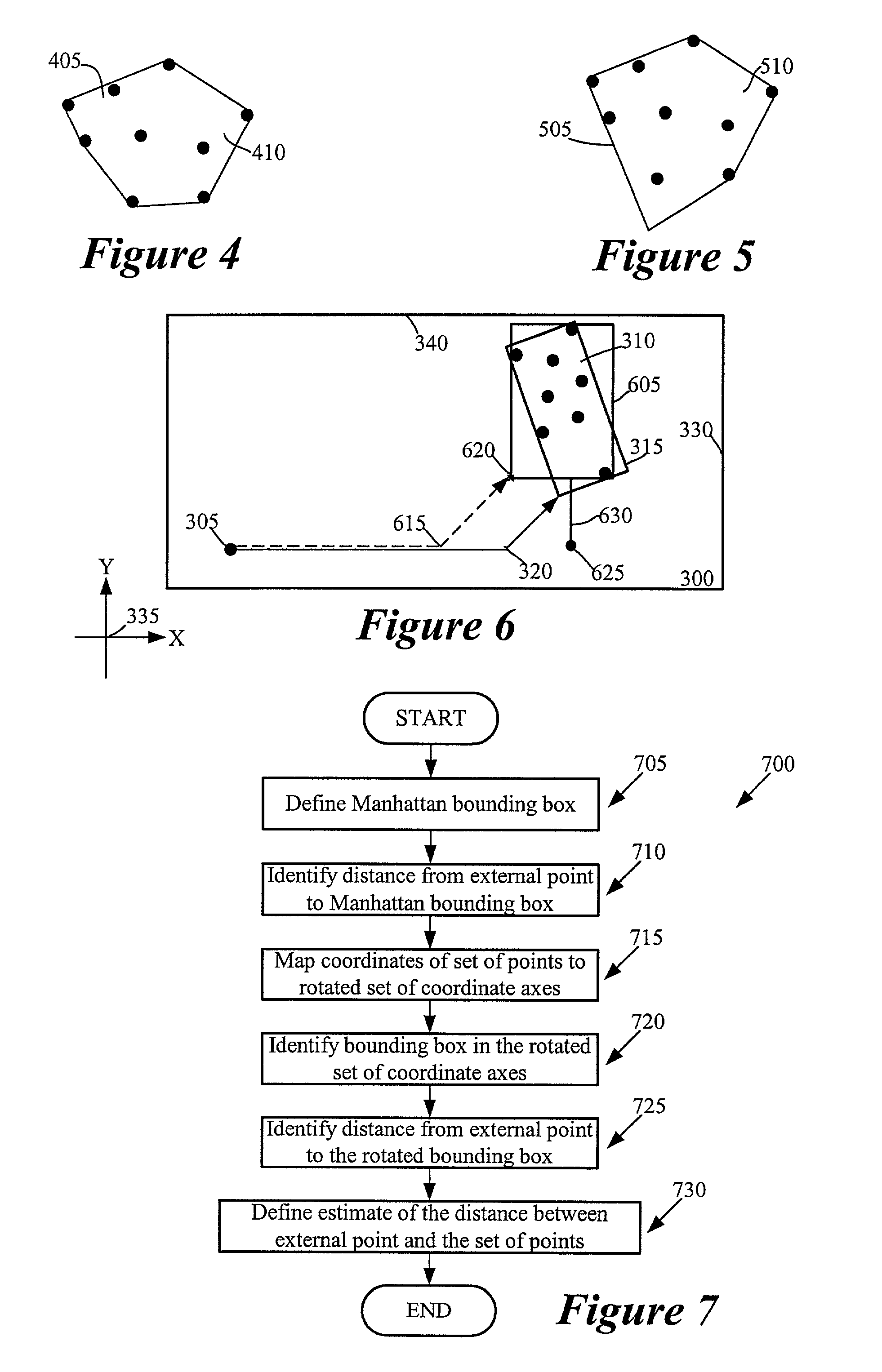
Method and apparatus for computing capacity of a region for non-Manhattan routing
InactiveUS7080342B2Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsParallel computingTriacontagon
For a router that allows routing in at least one non-Manhattan direction, some embodiments of the invention provide a method of computing a capacity for non-Manhattan routing in a region. The method identifies a polygon about the region, where the polygon has at least one side that is not aligned with either Manhattan direction. It then identifies a set of potential obstacles within the polygon. The method then calculates the capacity of the region for non-Manhattan routing, based on the identified set of potential obstacles.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Generation of free-form surface model by reversible rounding operation
InactiveUS6867769B1Drawing from basic elementsSpecial data processing applicationsFree formLinear transform
Owner:RICOH KK +1
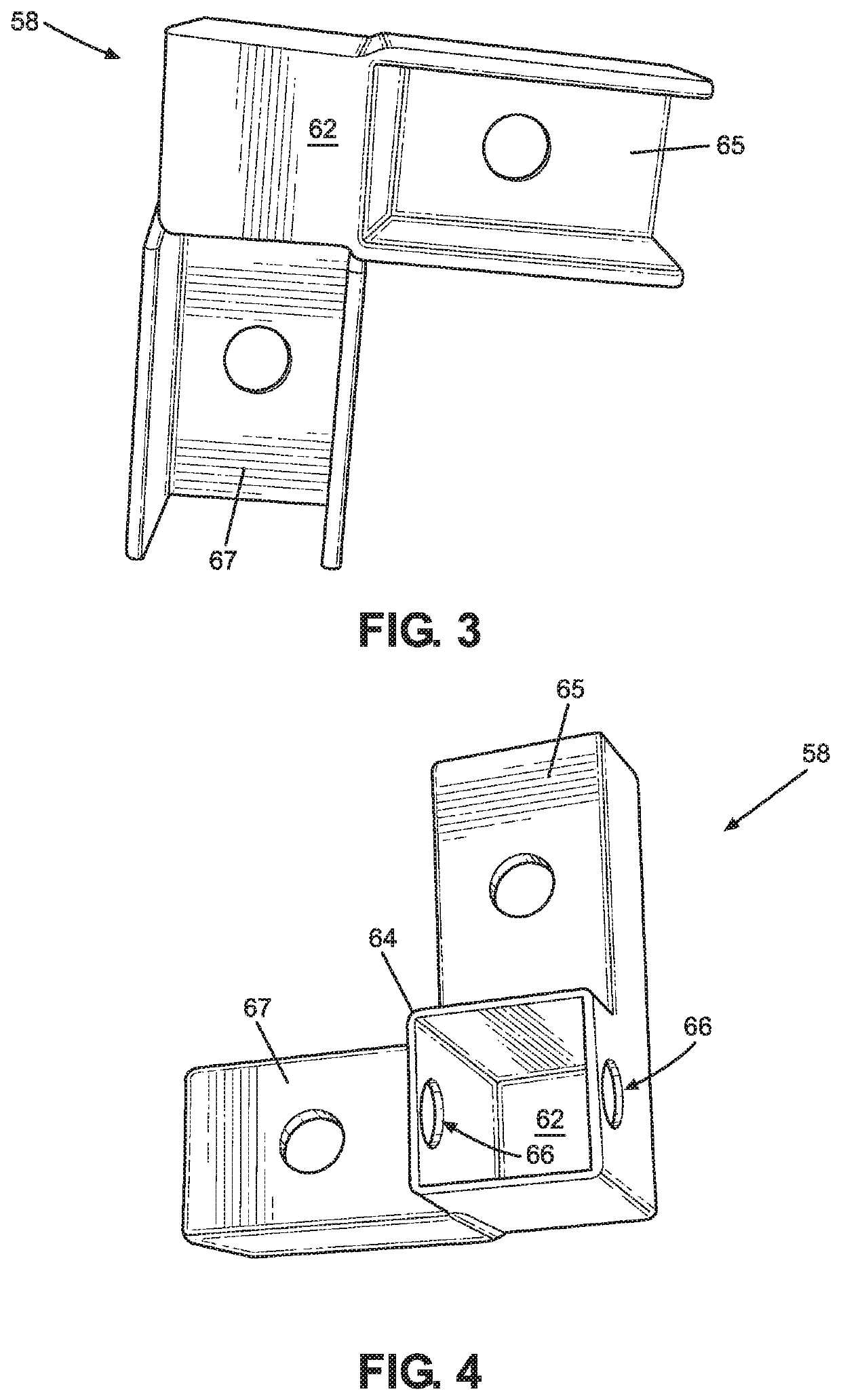
Frame for a sign
A frame for a sign. The frame comprises a plurality of struts and corner brackets. The struts have an exposed front surface including a gripping means. Each corner bracket slidably engages with two of the struts at an angle. The corner brackets also have an exposed front surface including a gripping means. The gripping means of the struts is substantially continuous with the gripping means of the corner brackets so that when the corner brackets and struts are engaged to form a polygon, the polygon includes a substantially continuous gripping means that is engageable with a sign to mount the sign on the frame.
Owner:VERDE FASTFRAME
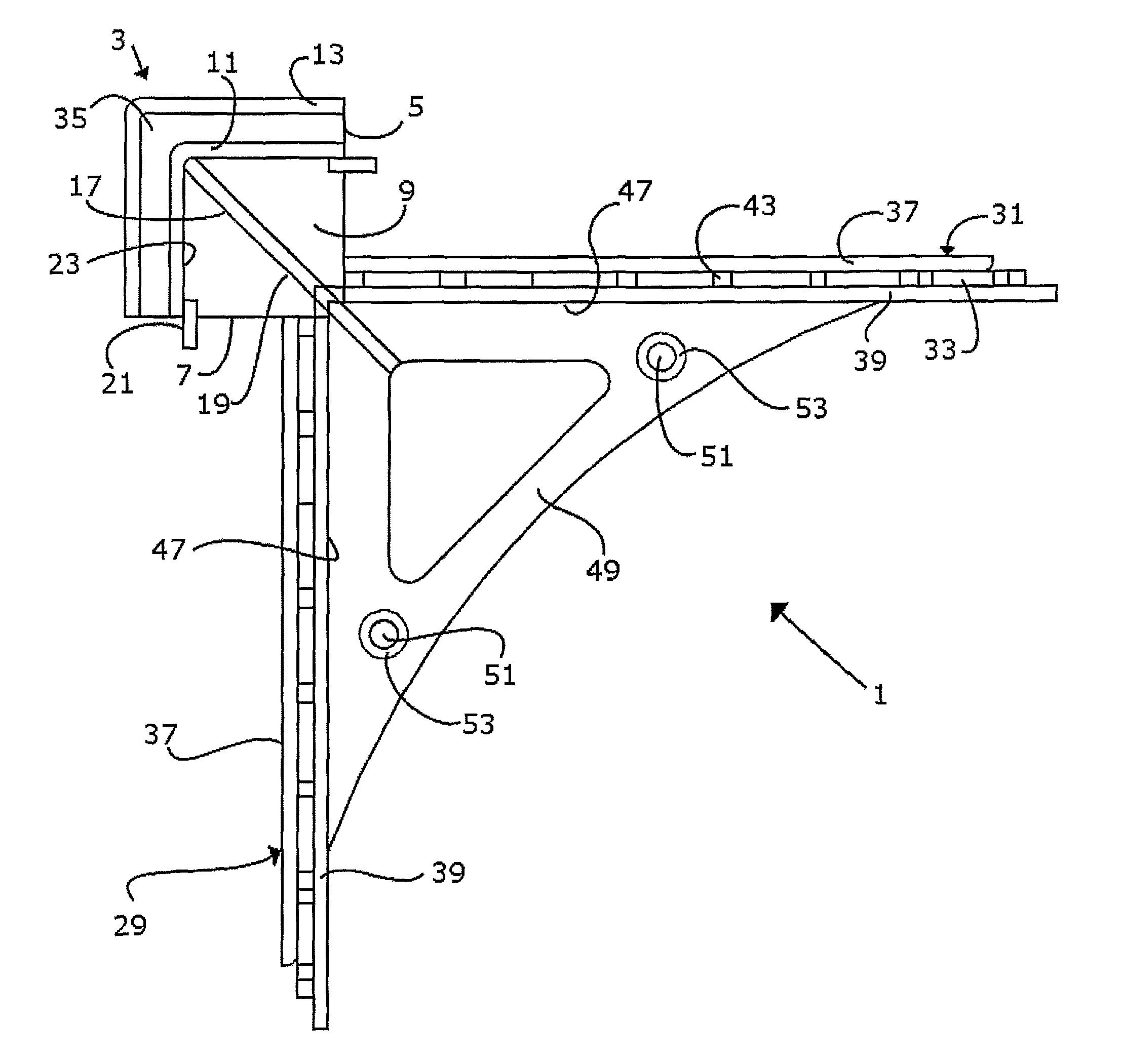
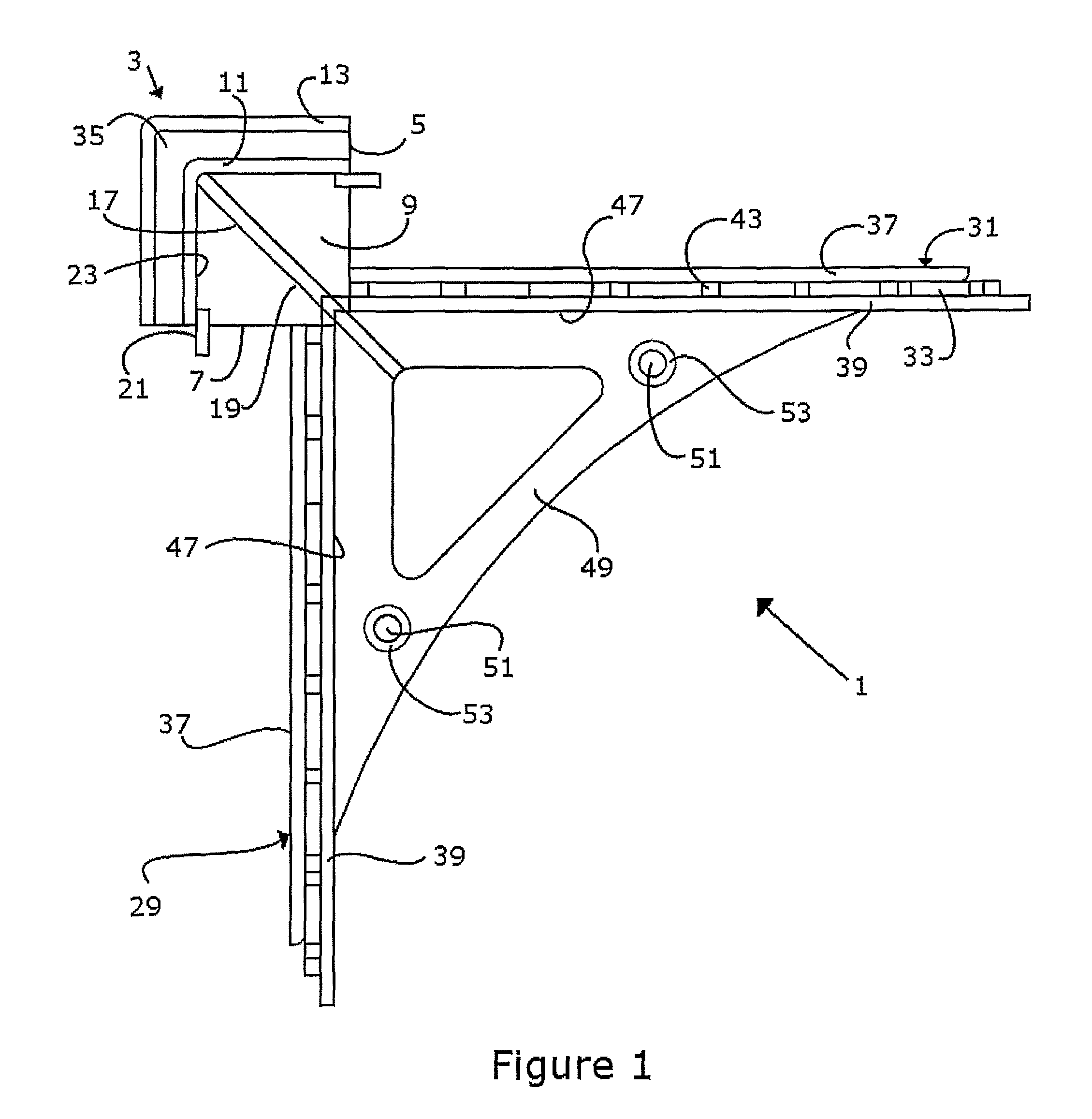
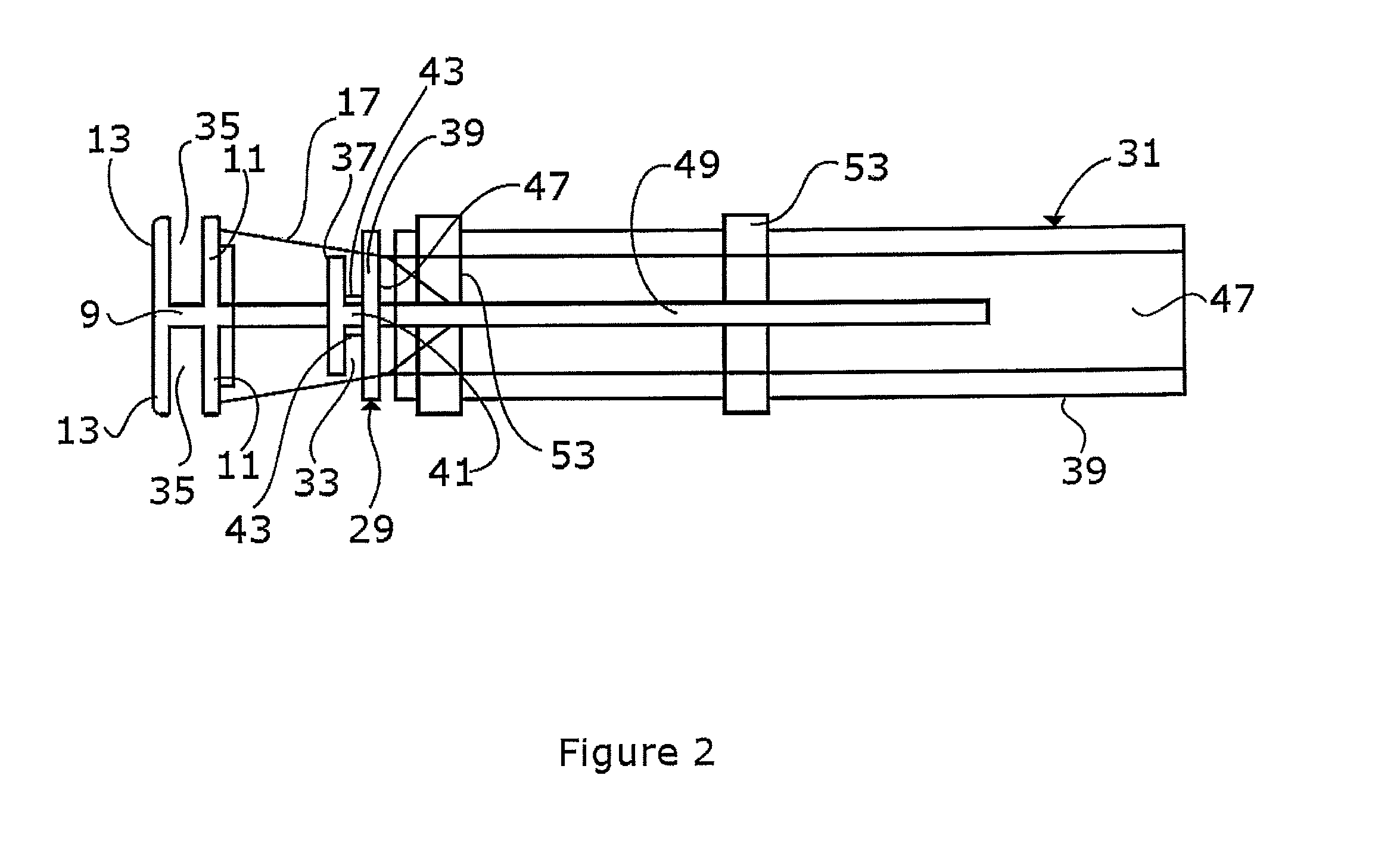
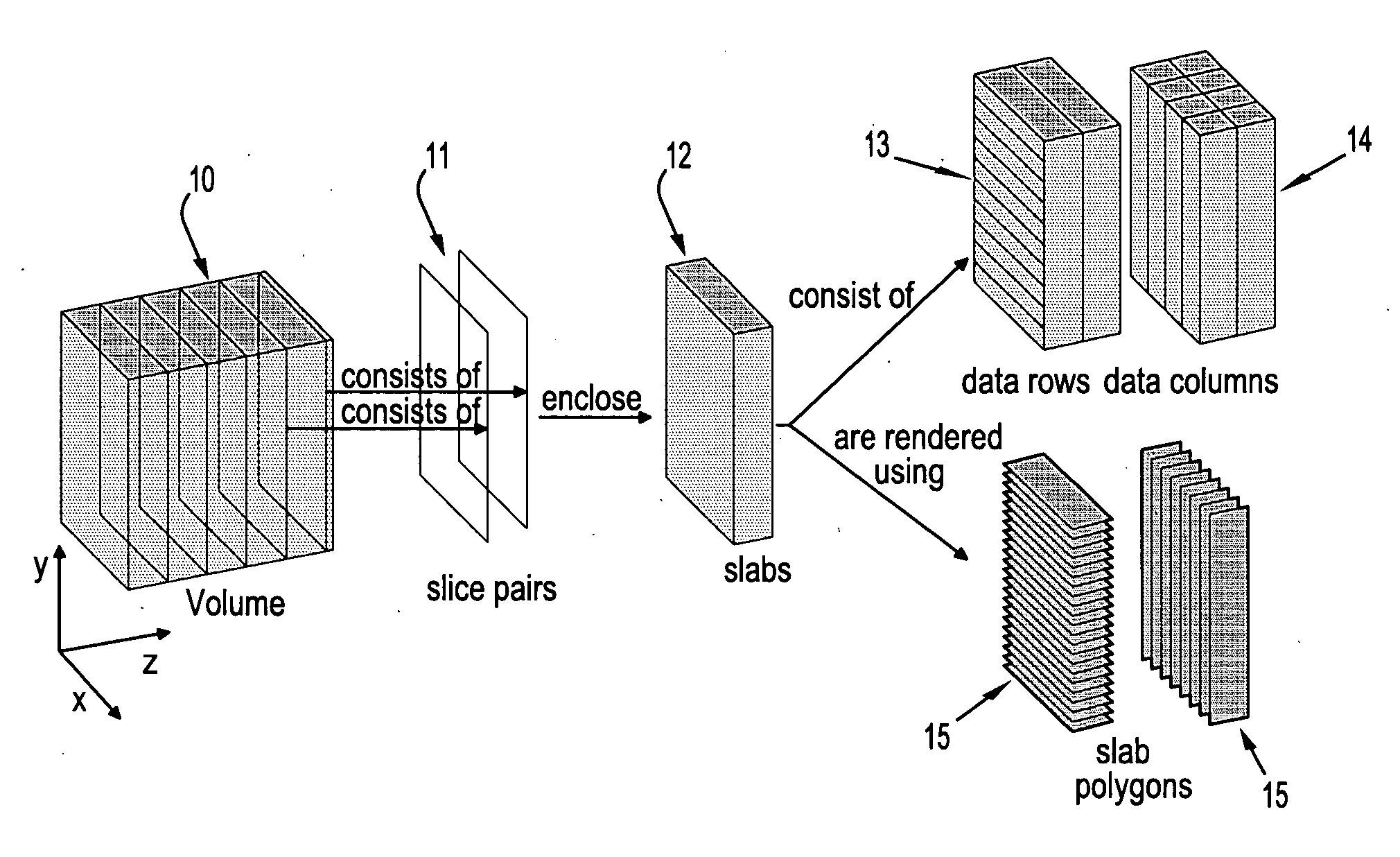
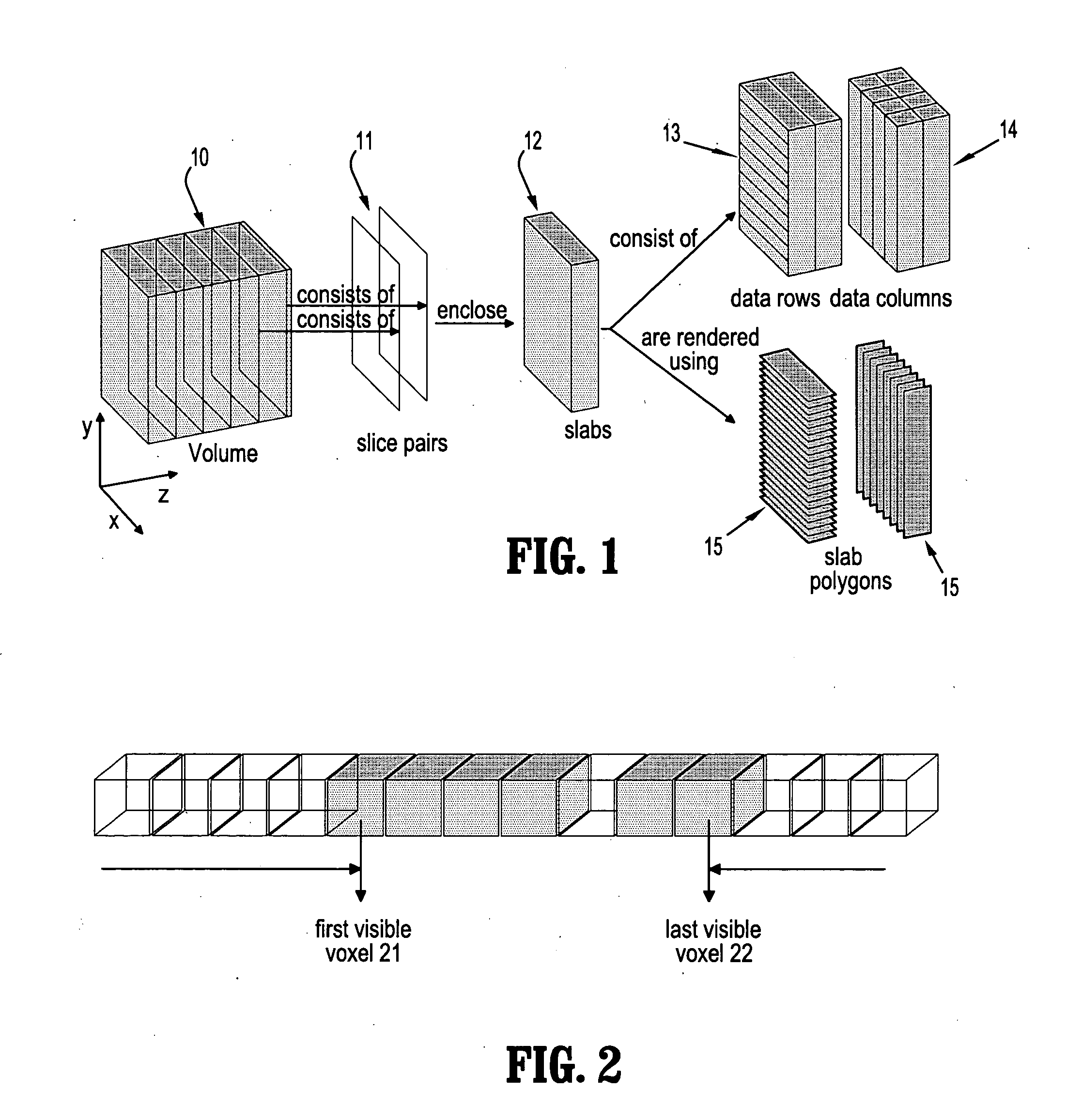
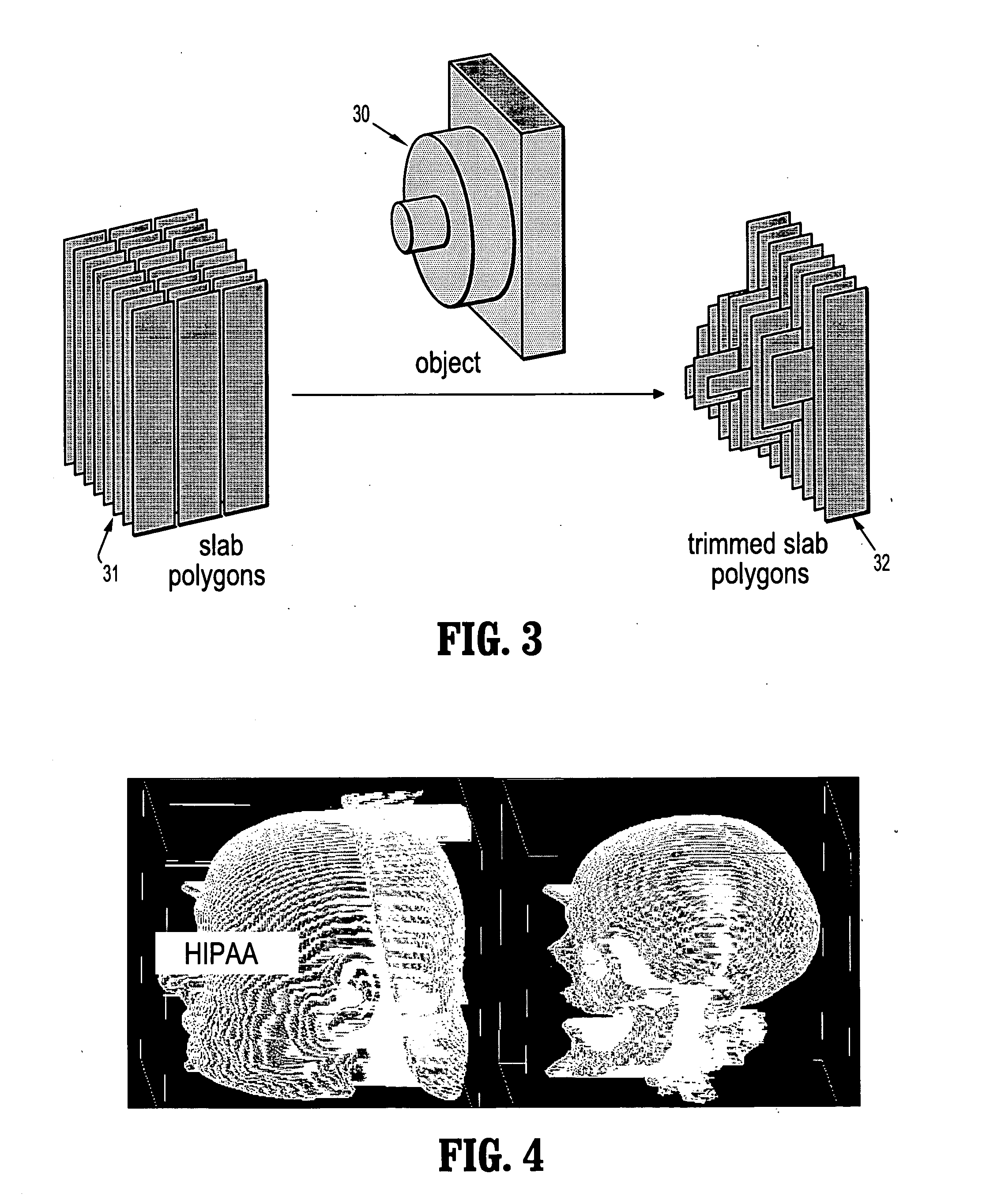
System and method for empty space skipping in sliding texture based volume rendering by trimming slab polygons
A method for volume rendering a digitized image includes providing a pair of adjacent 2-dimensional images of texture data, identifying a plurality of polygons extending in slabs between said adjacent two dimensional textures, and finding the first and last visible voxel for the data rows and data columns of each said polygon. The minimum and maximum bounds of each data row and for each data column are determined, those data rows and data columns that do not contain any visible voxels are marked as invisible, and the polygons are rendered along a direction orthogonal to a dominant viewing direction, wherein rendering of texture data is restricted by the outer bounds of polygons that are trimmed to the minimum and maximum bounds of two neighboring data rows or data columns, and wherein those data rows and data columns marked as invisible are skipped.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
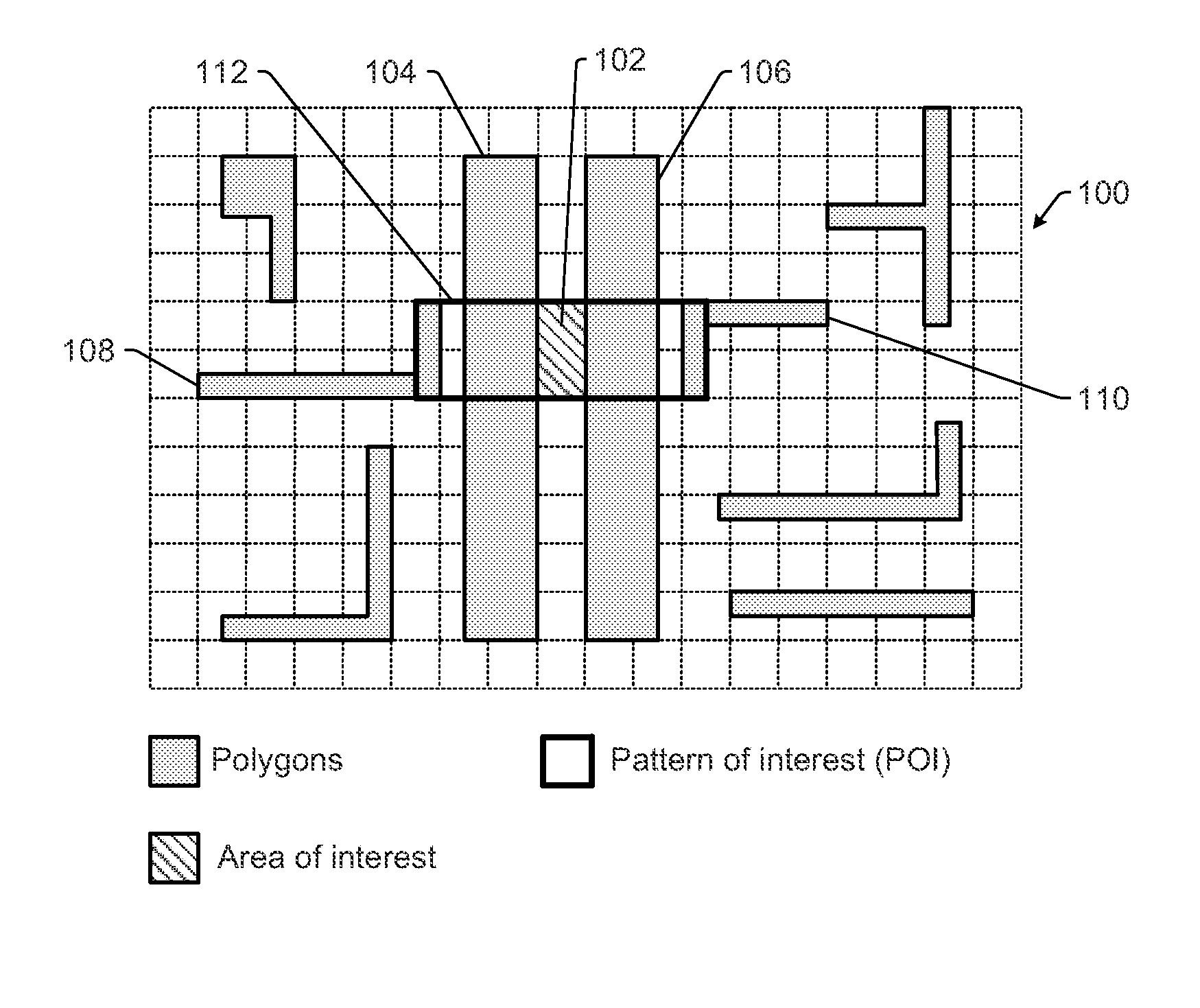
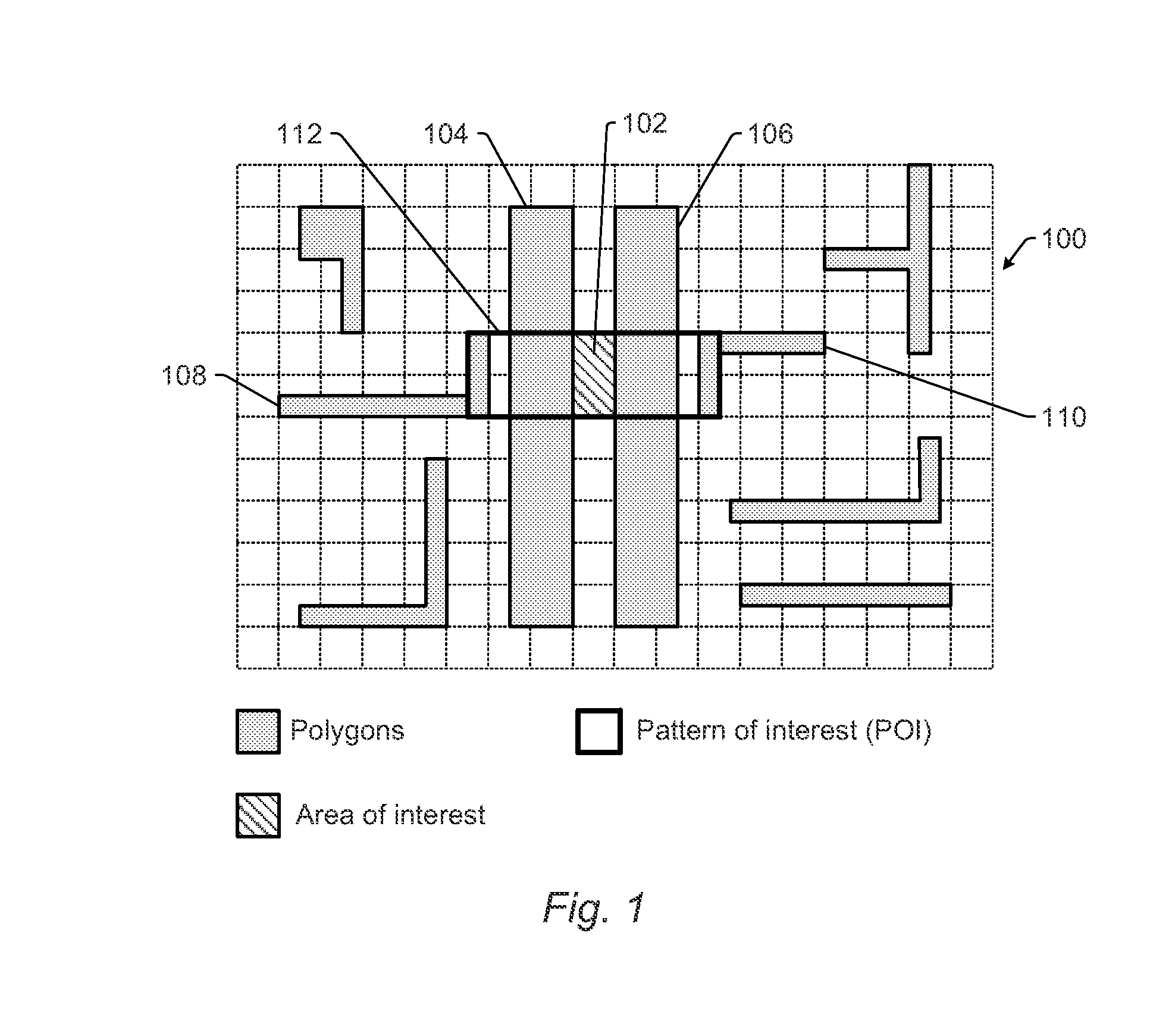
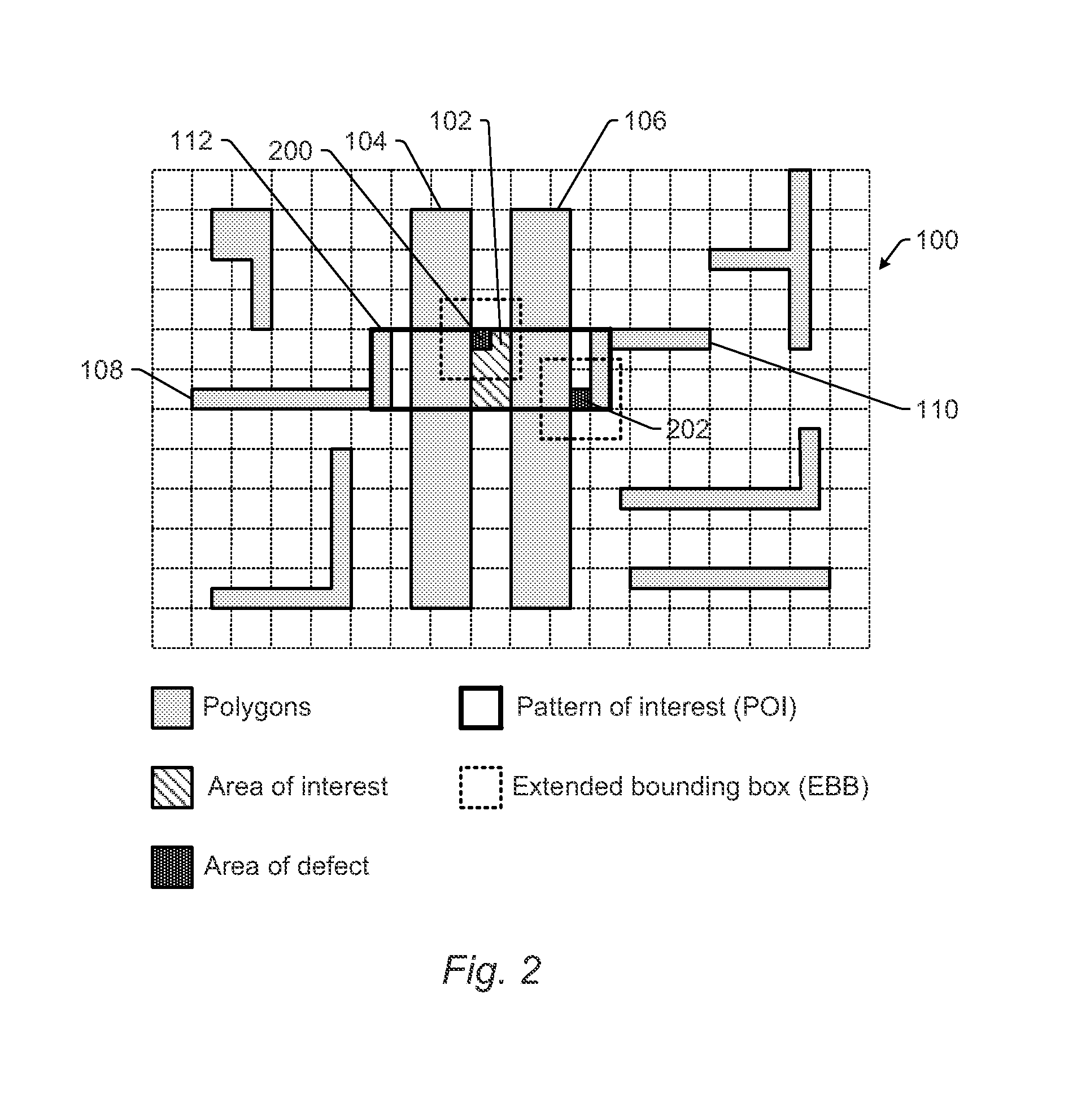
High Accuracy Design Based Classification
Systems and methods for classifying defects on a wafer are provided. One method includes dilating an extended bounding box (EBB) surrounding a defect position on a wafer in two dimensions in proportion to a width and height of a pattern of interest (POI) for a hot spot closest to the defect position. The method also includes determining if polygons in the POI match polygons in the dilated bounding box. If the polygons in the POI do not match the polygons in the dilated bounding box, the defect is classified as a non-hot spot defect. If the polygons in the POI match the polygons in the dilated bounding box, the defect is classified as a hot spot defect if the area of the EBB intersects the area of interest associated with the hot spot and a non-hot spot defect if the EBB area does not intersect the area of interest.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
High effectiveness low pressure drop heat exchanger
ActiveUS20160054071A1Minimized pressure dropMaximize heat transferGas turbine plantsHeat exchanger casingsCounter flowHoneycomb
A heat exchanger in the form of a honeycomb with a plurality of rectangular or otherwise polygon in cross-section passages which share common walls with adjacent passages. Two or more flow paths each comprises a plurality of serially connected passages. Each flow path passes through the heat exchanger in a helical pathway, thus through one passage in a first vertical stack of passages, then through a lower passage in an adjacent second vertical stack of passages, then through a lower passage in the first vertical stack, then through a lower passage in the second vertical stack and in this helical manner to the outlet from the heat exchanger. Thus, the flow path comprises alternate passages in each vertical stack, and another flow path comprises the alternate passages in at least one of the vertical stacks not taken up by the first flow path, whereby the flow paths at least partially overlap each other thereby providing both counter-flow and co-flow.
Owner:MOHAWK INNOVATIVE TECH
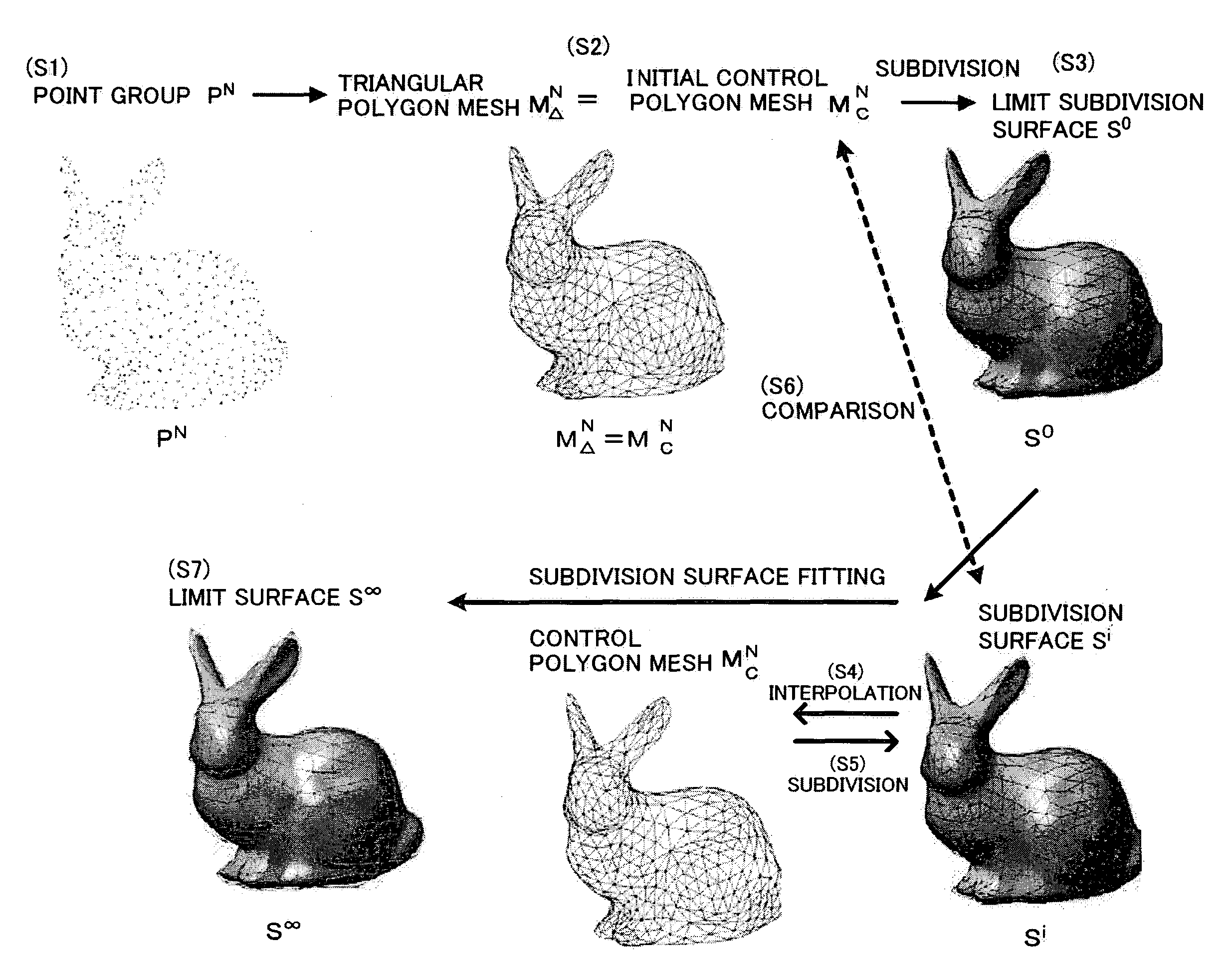
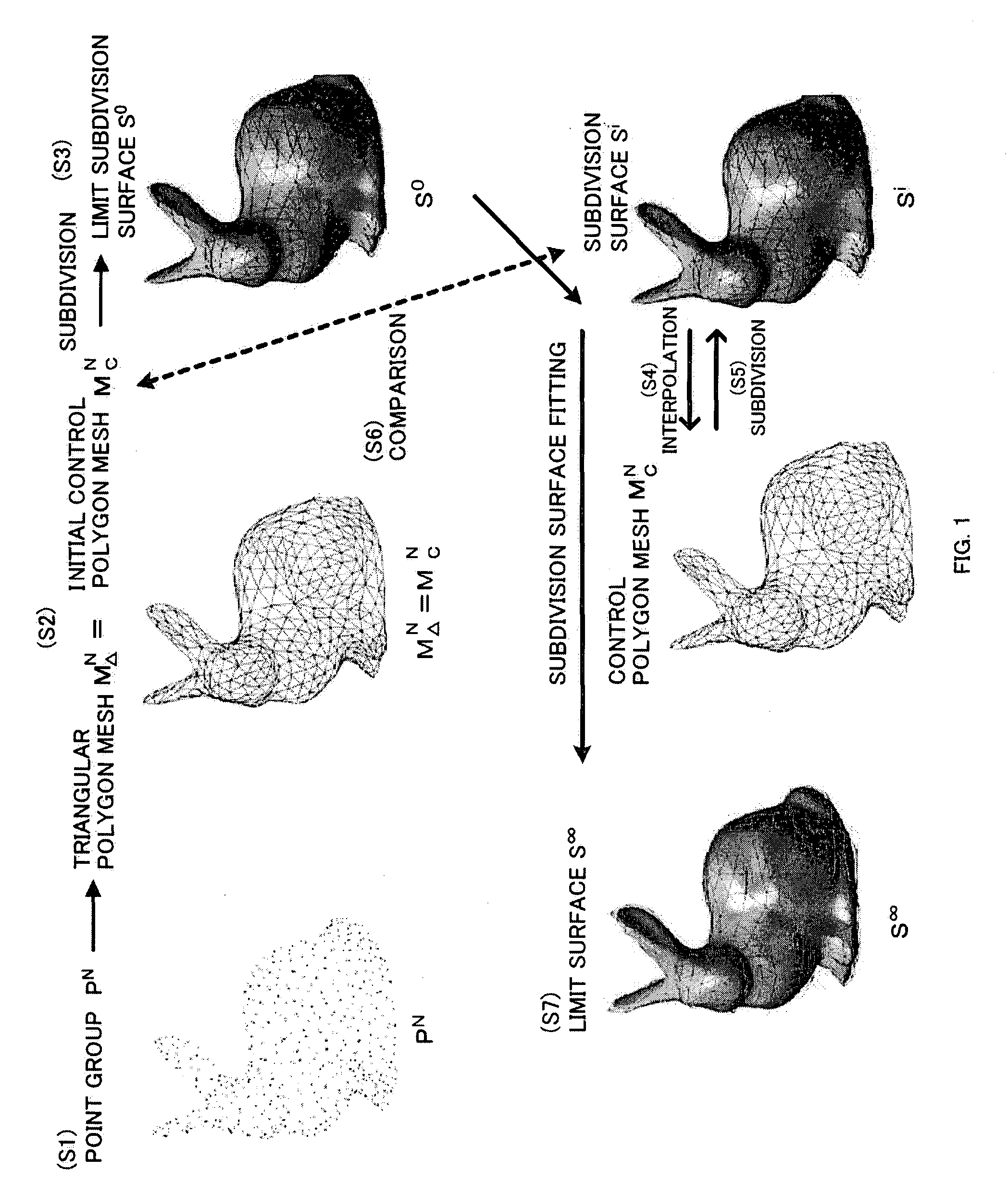
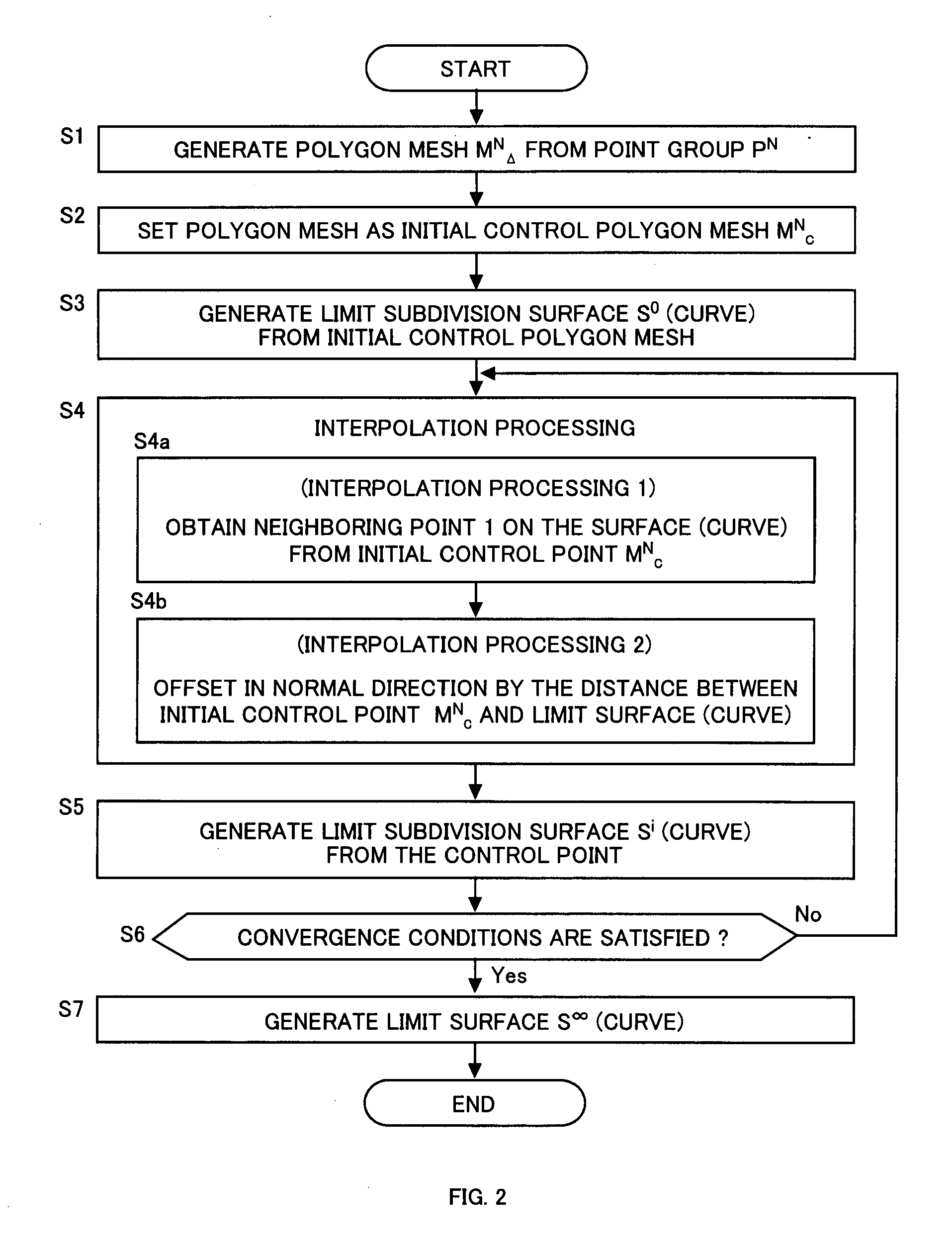
Interpolation processing method, interpolation processing device, shape evaluation method, and shape evaluation device
InactiveUS20090303235A1Additional processing stepsHigh precisionDrawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionShortest distanceTime segment
An initial polygon obtained from a point group is used as a control polygon, and a control point of the control polygon is offset in a normal direction by the shortest distance from a limit surface generated by the control polygon, so that the position of new control point is determined to allow a subdivision surface to interpolate the initial polygon, thereby generating the subdivision surface which interpolates the point group. A first process to determine the point on the subdivision surface at the shortest distance from each control point, and a second process to move and offset the control point in the normal direction from the surface by the distance between the point on the surface and the initial control point, are iterated until the distance between the initial point group and the point on the surface satisfies the threshold or becomes smaller than the threshold, thereby generating the subdivision surface interpolating the initial polygon. Consequently, the subdivision surface interpolating the point group is generated within a short operation time period, without solving a linear system.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA NAT UNIV
Method and apparatus for constructing a convex polygon that encloses a set of points in a region
Some embodiments of the invention provide a method for constructing a convex polygon that encloses a set of points in a region. This method identifies a first polygon that encloses the set of points. It then identifies a second polygon that encloses the set of points. The method then specifies the convex polygon as the intersection of the first and second polygons.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
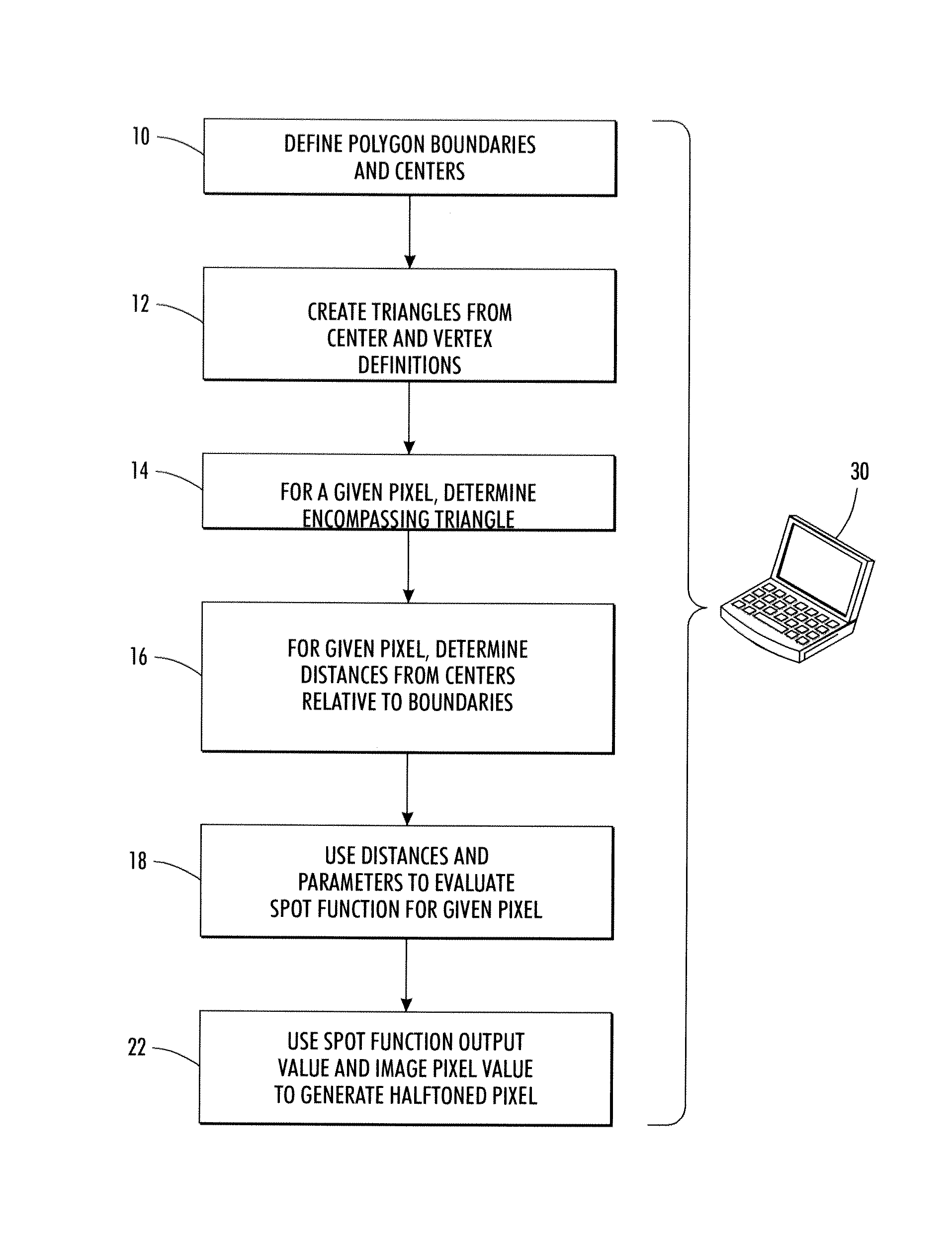
Polygonal-boundary-based halftone method
InactiveUS20120274984A1Image enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImage contentComputer graphics (images)
As set forth herein, computer-implemented methods and systems facilitate halftoning using boundaries and centers of a polygonal tiling with a parameterized spot function that operates within the tiles. Defining the halftone structure includes defining the polygonal tiling with a specification of the polygon boundaries and center, and setting and applying parameters of the spot function, which utilizes center-to-boundary distances. The tiling can be defined explicitly, by defining a tile structure, or providing centers, one per polygon, and vertices for the polygons. The vertices and centers are used to generate the polygon boundaries. The polygonal tiling can be regular (e.g., repetitive) or irregular, and can also be varied in a manner adapted to the image content or to data that is being embedded.
Owner:XEROX CORP
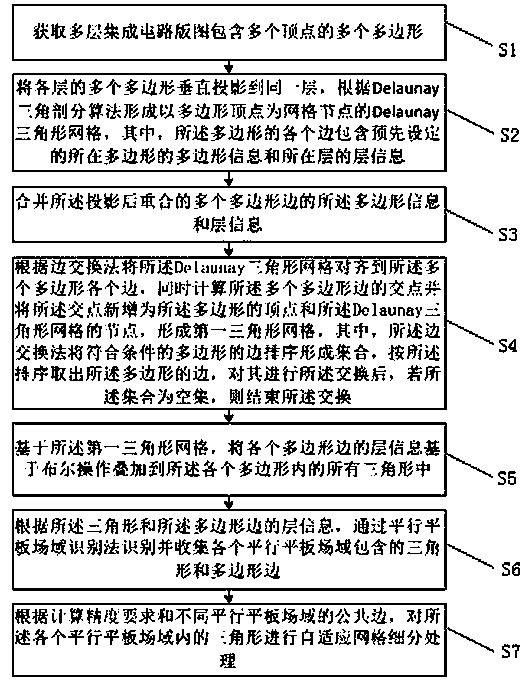
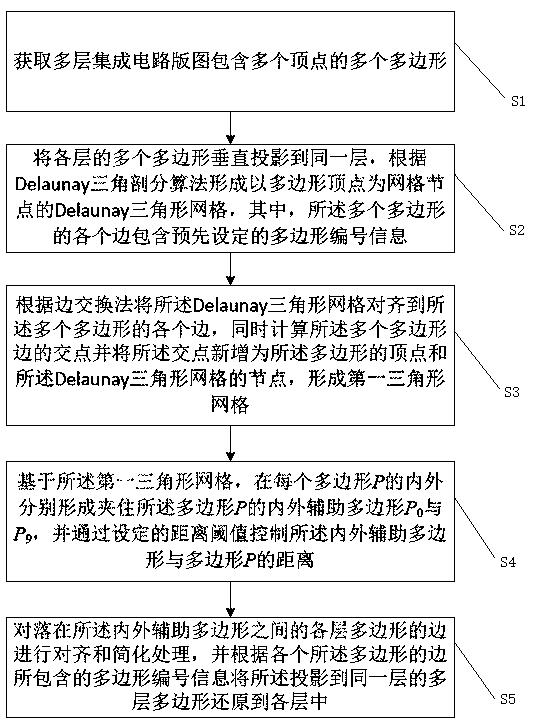
Integrated circuit layout field domain identification and grid subdivision processing method and device
ActiveCN110689569AGuaranteed accuracyIntegrity guaranteedImage analysisGeometric image transformationComputer graphics (images)Triacontagon
The embodiment of the invention discloses an integrated circuit layout field domain identification and grid subdivision processing method and device. The method comprises the following steps: vertically projecting a plurality of polygons of each layer of integrated circuit layout to the same layer to form a Delaunay triangular grid; combining the polygon information and the layer information of the edges of the polygons which are superposed after projection; aligning the grids to the edges of each polygon, calculating the intersection points of the edges of each polygon, adding the intersection points into polygon vertexes and grid nodes to form a first triangular grid, forming a set by the edges of the polygons by an edge exchange method, taking out the edges of the polygons, exchanging the edges of the polygons, and if the set is a null set, ending the exchange; superposing the layer information of the edges of the polygons into all triangles in the polygons; identifying and collecting triangles and polygonal edges contained in each parallel flat plate field domain according to the layer information of the triangles and polygonal edges; and carrying out grid subdivision processing on triangles in each parallel flat plate field domain. According to the invention, the accuracy and high efficiency of the field domain identification and grid subdivision processing method can be ensured.
Owner:北京智芯仿真科技有限公司
Metallic hollow columnar member
ActiveUS20140021709A1Improve absorbing performanceImprove robustnessSteering linkagesUnderstructuresEngineeringTriacontagon
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
System and Methods for Parallelizing Polygon Overlay Computation in Multiprocessing Environment
InactiveUS20120320087A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails involving image processing hardwareComputational scienceOverlay
In a system for parallelizing polygon overlay operations, a potential for intersection between polygons is determined by the bounding box of each polygon on a base layer in relation to the bounding box of each polygon on an overlay layer. The potential for intersection exists when a vertex of a bounding box around an overlay layer feature is within a bounding box around a base layer feature and vice versa. Calculations to determine the presence of vertices within bounding blocks are performed in parallel on multiple processors. Polygon overlay operations are performed only between features that have a potential to intersect.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
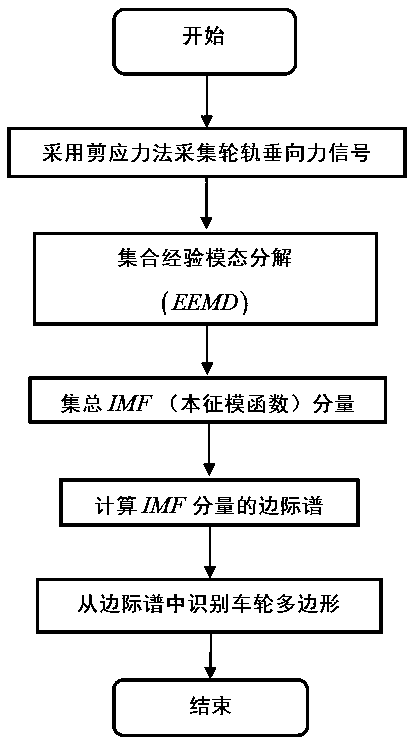
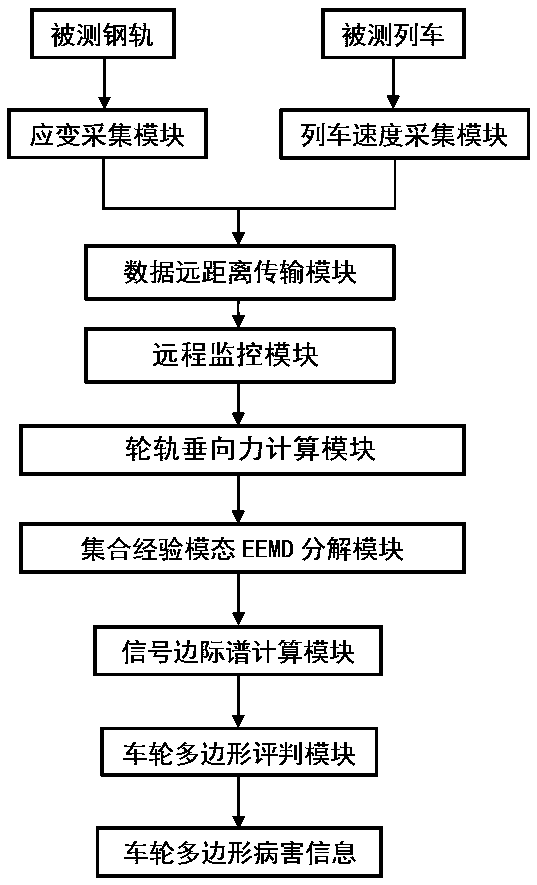
Wheel polygon identification method based on wheel-rail vertical force and device thereof
InactiveCN107650945AAvoid safety accidentsEasy to handleMeasurement devicesWheel-rims surveying/measuringDiseaseShear stress
The invention discloses a wheel polygon identification method based on the wheel-rail vertical force and a device thereof. The identification method comprises the following steps: collecting the wheel-rail vertical force signal by the shear stress method; and analyzing the collected wheel-rail vertical force signal Carry out the EEMD decomposition of the ensemble empirical mode to obtain the aggregated intrinsic mode function IMF component; calculate the marginal spectrum of the intrinsic mode function IMF containing the wheel polygonal disease characteristic information; according to the obtained marginal spectrum of the intrinsic mode function IMF, obtain The damage characteristic frequency f is used to identify whether the wheel has polygons and the type of polygons according to the preset judgment criteria. Its advantages are: it can carry out real-time monitoring and damage evaluation on the vehicles passing through the monitoring section, and it has the characteristics of fast and accurate; The marginal spectrum of the wheel-rail vertical force damage characteristic frequency after polygonal damage of the wheel is obtained.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
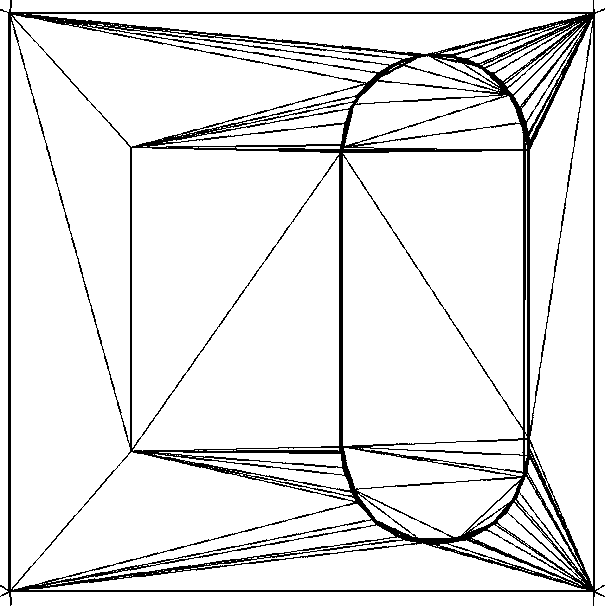
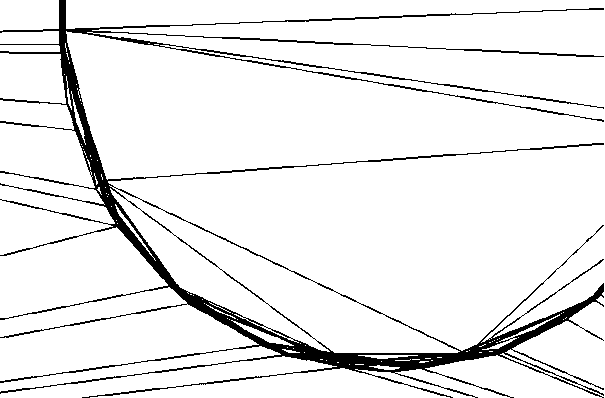
Multi-layer integrated circuit layout polygon alignment and simplification processing method and device
The embodiment of the invention discloses a multi-layer integrated circuit layout polygon alignment and simplification processing method and device. The method comprises the following steps of projecting a plurality of polygons of a multilayer integrated circuit layout to a same layer, and forming a Delaunay triangular mesh according to a Delaunay triangulation algorithm; aligning the Delaunay triangular mesh to each edge of each polygon, calculating the intersection points of the edges of each polygon, and adding the intersection points into the polygon vertexes and the Delaunay triangular mesh nodes to form a first triangular mesh; on the basis, forming the inner and outer auxiliary polygons for clamping the polygons inside and outside each polygon, and controlling the distances betweenthe inner and outer auxiliary polygons and the polygons through the distance thresholds; and aligning and simplifying the edges of each layer of polygons falling between the inner and outer auxiliarypolygons. According to the present invention, the fragmentation problem after the multilayer polygons form the parallel flat plate field domain can be reduced, the unnecessary dense grids are reduced,the analysis and solving time and the required memory of the multilayer integrated circuit are shortened, the gaps among the polygons can be reserved, and the integrated circuit layout shape is basically not changed.
Owner:北京智芯仿真科技有限公司
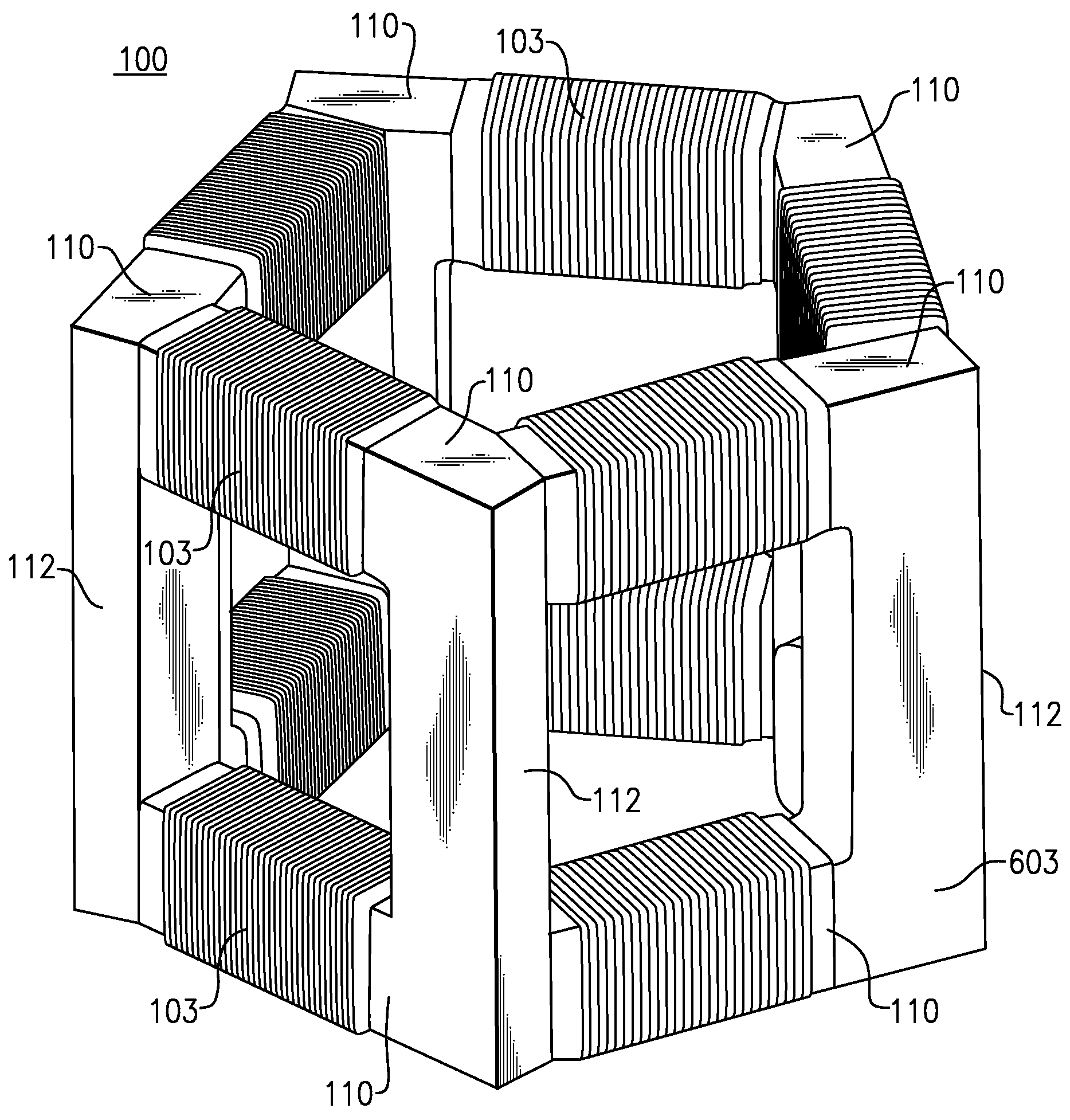
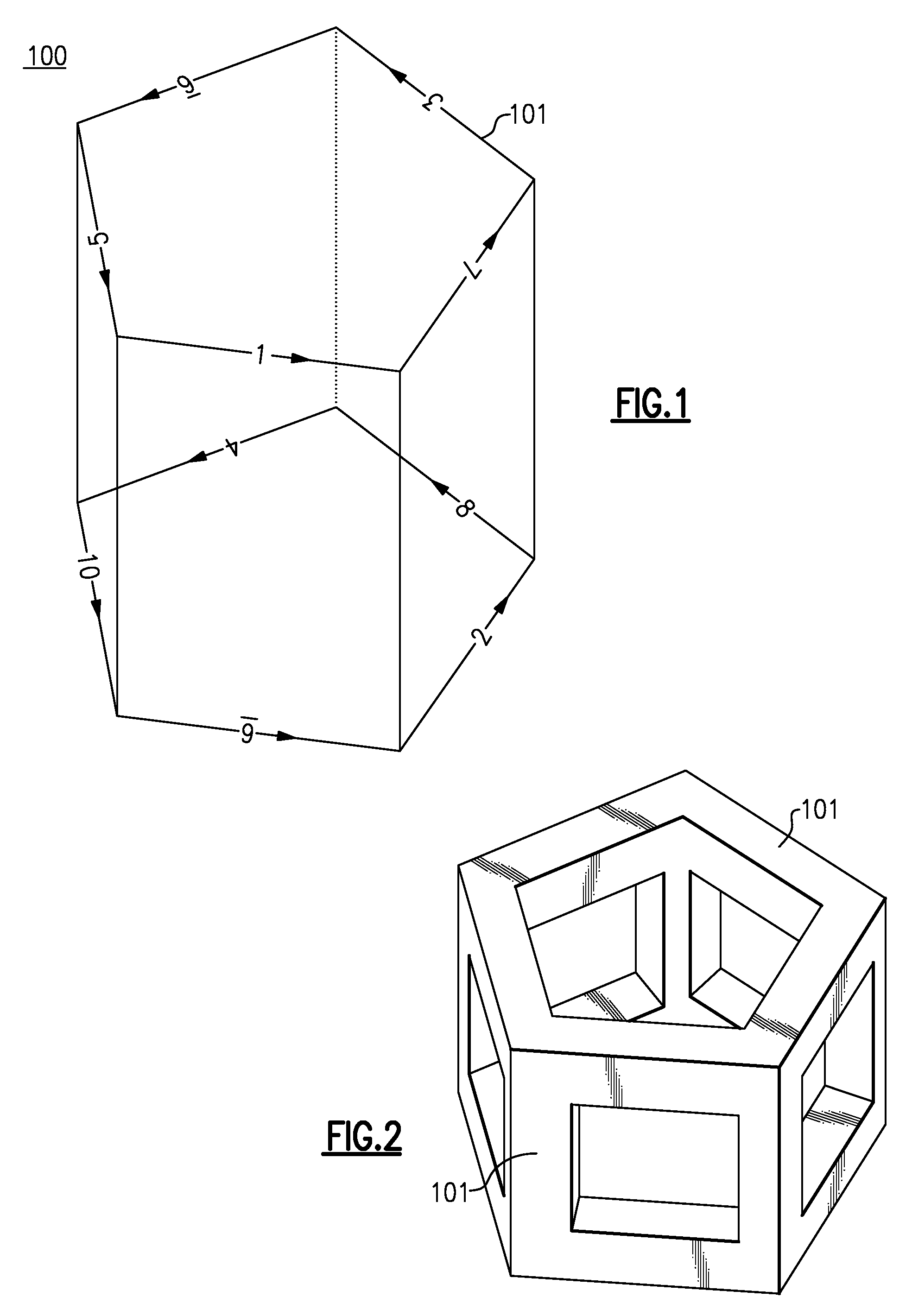
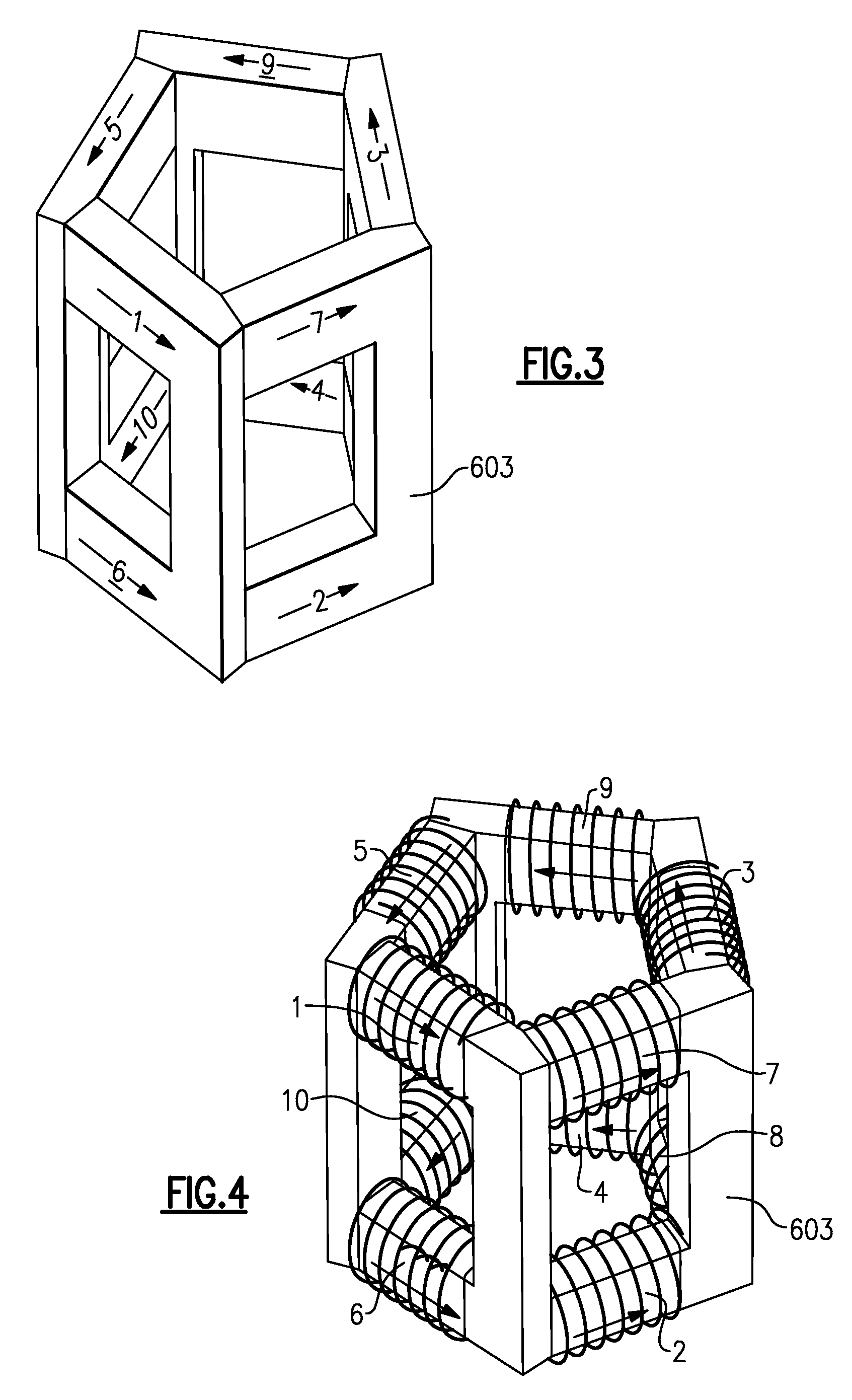
3D poly-phase transformer
InactiveUS20090257560A1Transformers/inductances magnetic coresInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureTriacontagonEngineering
A three dimensional (3D) poly-phase transformer includes a plurality of transformer ribs mechanically and magnetically coupled such that each transformer rib forms a leg of a polygon. A plurality of the polygons forms a 3D polyhedron structure. At least two base planes of the 3D poly-phase transformer including a polygon have a plurality of base ribs. At least four side ribs of the 3D poly-phase transformer are disposed between the base planes. The 3D poly-phase transformer includes a plurality of primary and secondary transformer windings. Another 3D poly-phase transformer includes at least two base planes having a closed curve. Each closed curve includes a plurality of curved base ribs, and at least four side ribs of the 3D poly-phase transformer disposed between the base planes. Methods of manufacturing three dimensional (3D) poly-phase transformers are also described.
Owner:CODY TRANSFORMER
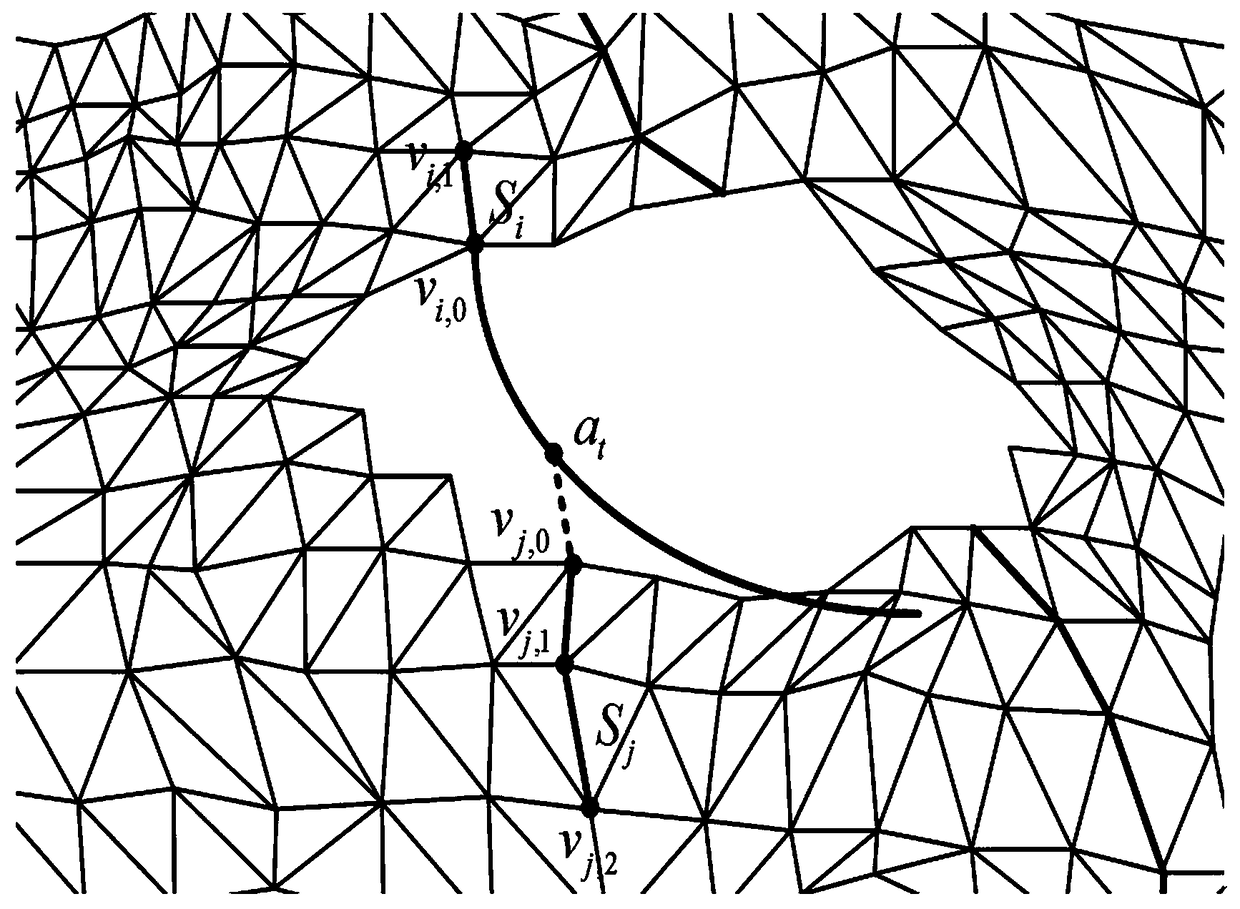
A method for repairing defects and holes in three-dimensional mesh model based on characteristic lines
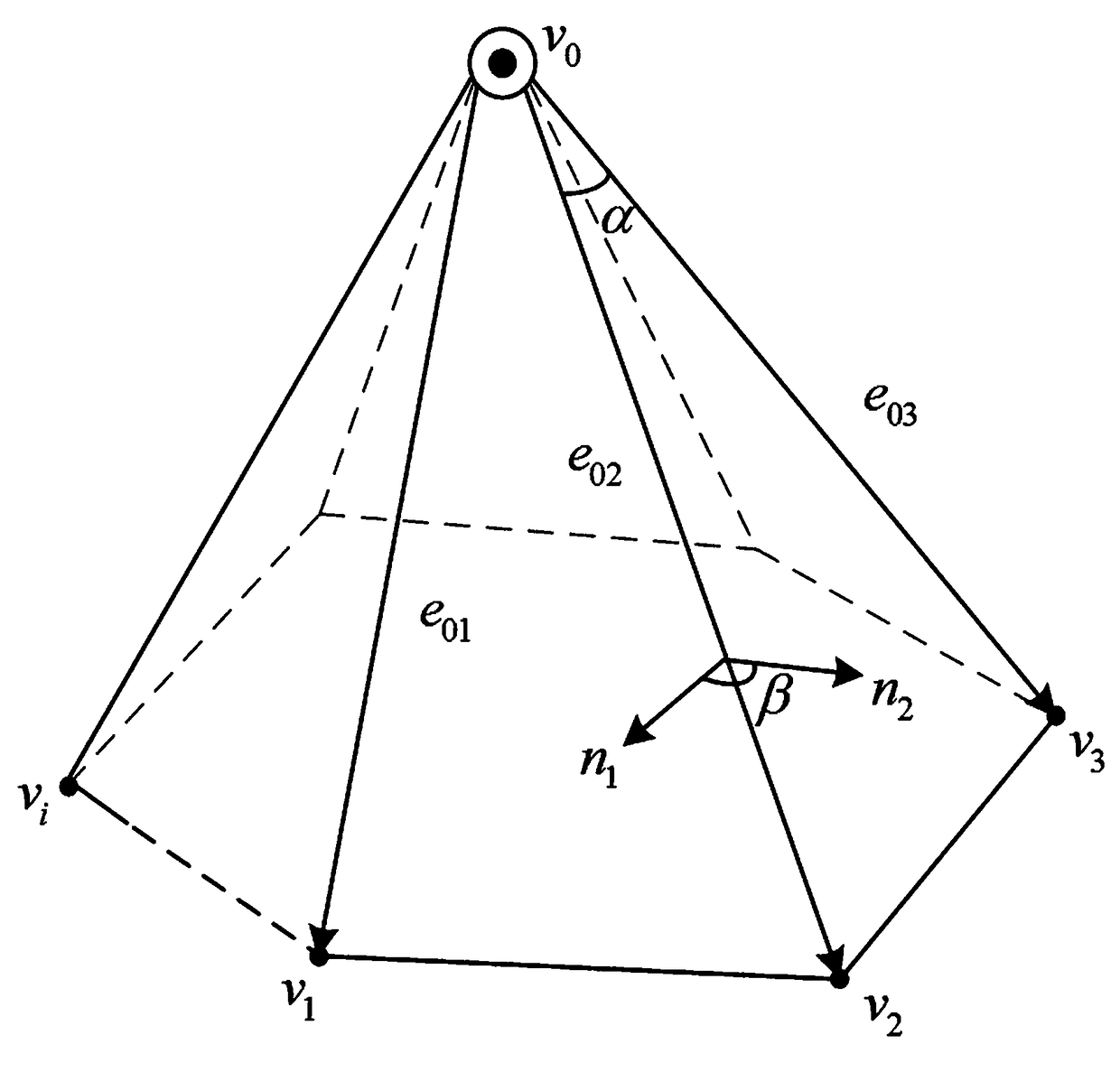
PendingCN109410334AQuality improvementImprove visual effects3D modellingPrincipal directionMesh grid
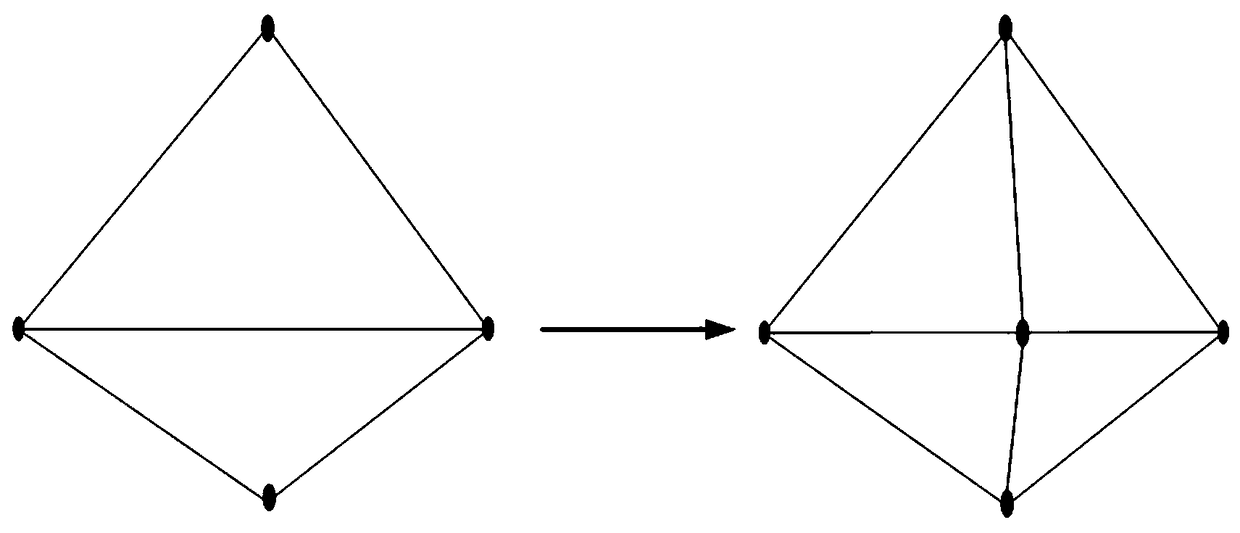
The invention discloses a method for repairing defects and holes of a three-dimensional mesh model based on characteristic lines, which comprises the following steps: 1) detecting characteristic lines: describing the corresponding principal direction curvature fitting extreme value on the mathematical definition of the characteristic lines on the surface of the three-dimensional mesh model which can represent the prominent geometrical characteristics; 2) matching of characteristic lines: selecting an optimal matching pair through a matching probability measurement standard for the characteristic lines detected in the step 1); 3) triangulation and thinning adjustment: after matching and bridging the characteristic lines, the original hole is partially changed into a plurality of polygonal sub-holes, and the basic surface is constructed; then Delaunay triangulation and edge scoring function are calculated for each polygon sub-hole, and an influence factor is assigned to each edge of thepolygon sub-hole to realize the anisotropic refinement of the mesh and the repair of the damaged area of the hole. The damaged area of the repaired holes can keep the same density with the surroundingtriangular mesh, and can be naturally connected with each other.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Rapid bridging method of polygonal area containing plurality of holes
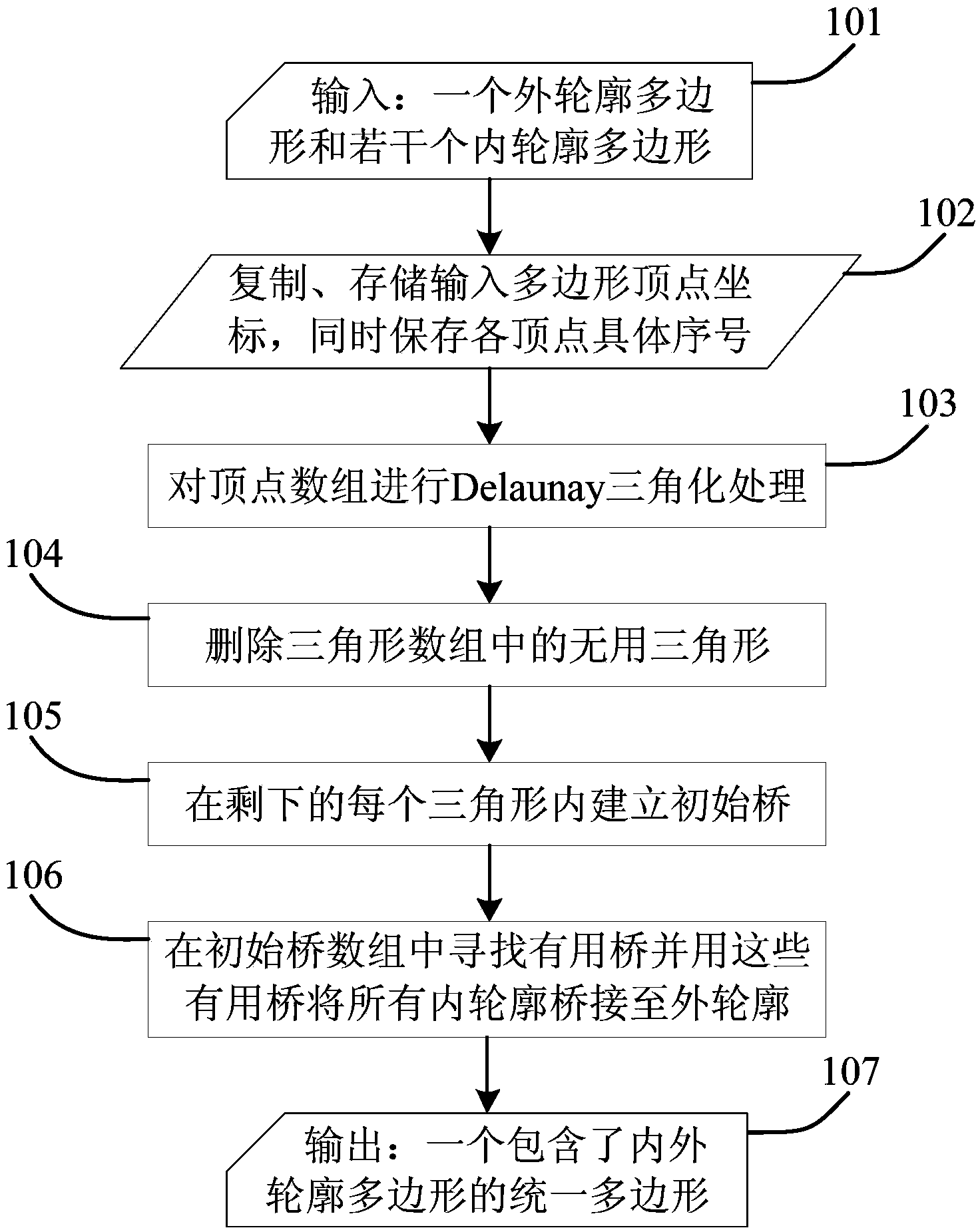
InactiveCN103817938AImprove production efficiencyDrawing from basic elementsArray data structurePath generation
The invention discloses a rapid bridging method of a polygonal area containing plurality of holes. The method comprises the following steps: inputting an outer-contour polygon and several inner-contour polygons; copying and storing coordinate of vertexes of each polygon and simultaneously recording serial number of each vertex on corresponding polygon and serial number of the polygon in the polygon array so as to obtain a planar point cloud; carrying out Delaunay triangularization on the point cloud to obtain a plane triangle array; deleting useless triangles in the plane triangle array; establishing an initial bridge inside each triangle remaining to connect two corresponding polygons so as to obtain an initial bridge array; finding out several useful bridges in the array and using the bridges to bridge all inner-contour polygons to the outer-contour polygon; and finally outputting an unified polygon containing the inner-contour polygons and the outer-contour polygon. According to the invention, a plurality of inner-contour polygons on a plane domain can be bridged to an outer-contour polygon within approximate linear time. Rough-machining path generation efficiency is raised.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
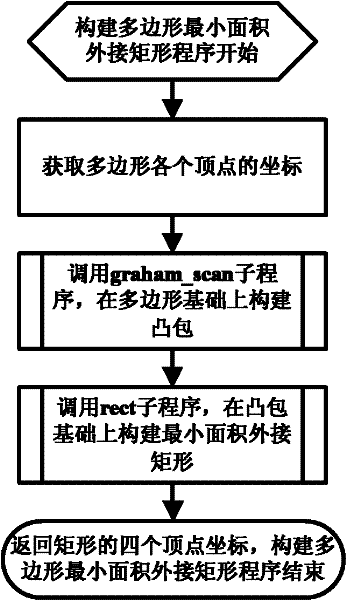
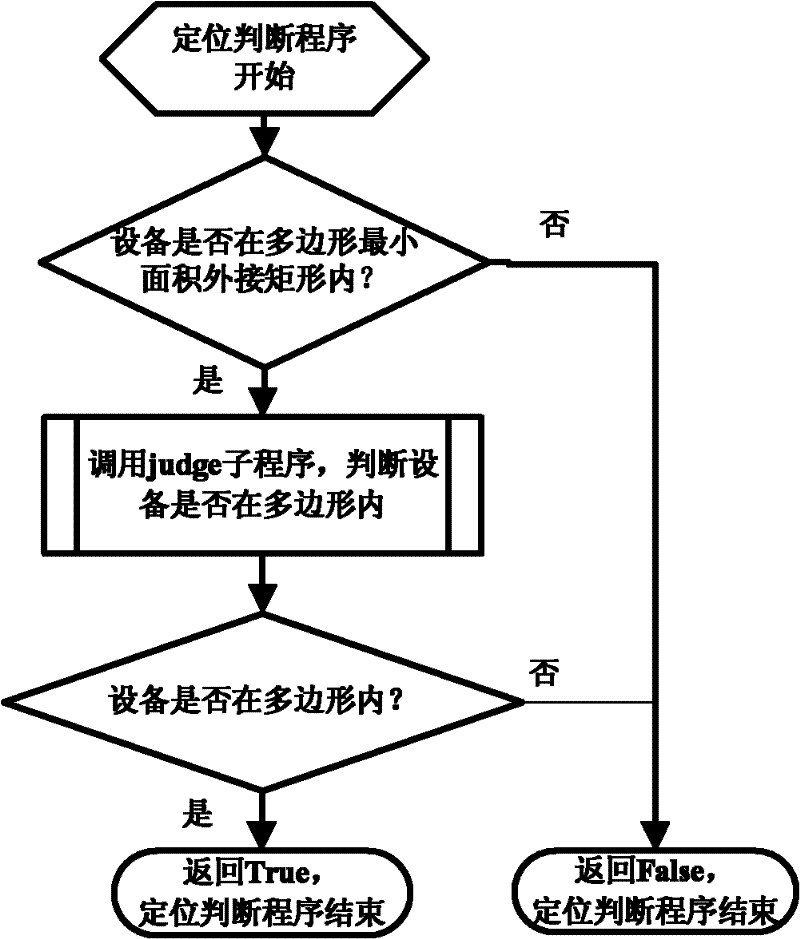
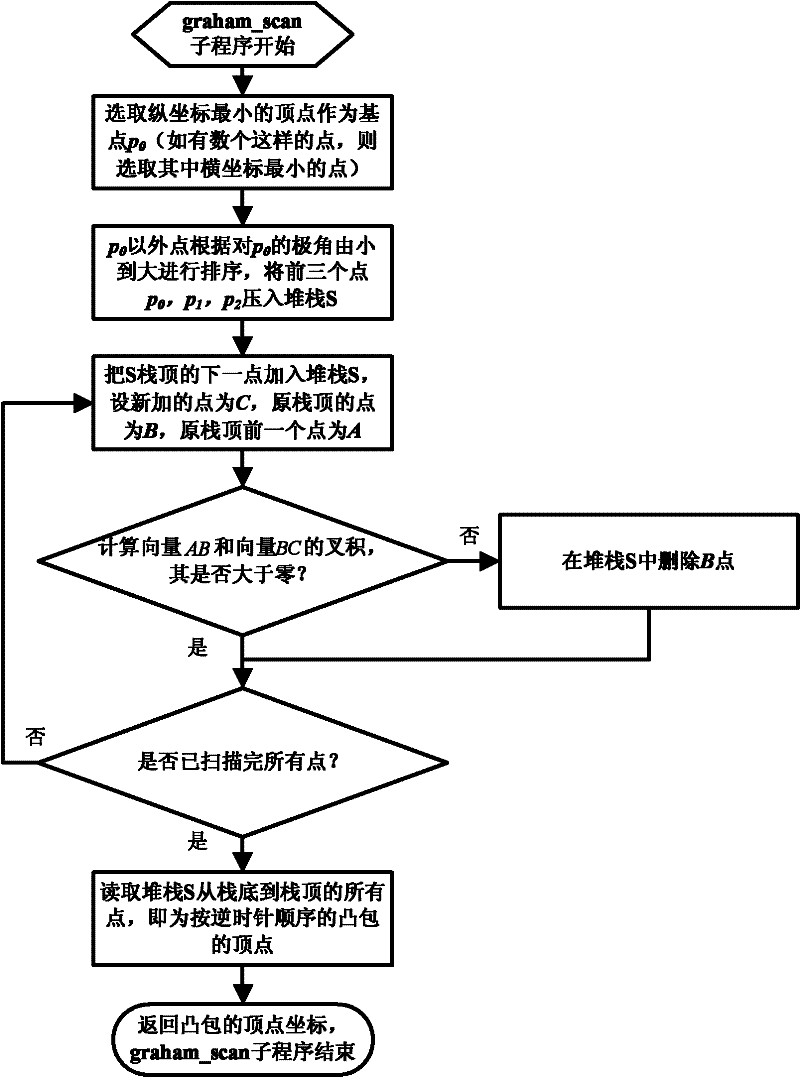
Positioning control method for closed region of vehicle-mounted GPS (Global Positioning System)
InactiveCN102213767AReduce occupancySimple calculationSatellite radio beaconingIn vehicleTriacontagon
The invention relates to a positioning control method for the closed region of a vehicle-mounted GPS (Global Positioning System), wherein the closed region is a polygon. The positioning control method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) the convex hulls of the polygon are established; (2) the circumscribed rectangle with the minimum area of the polygon is established; (3) the positioning judgment courses are as follows: 3.1) judging whether the current point is in the circumscribed rectangle with the minimum area or not; if the point is outside the circumscribed rectangle with the minimum area, judging that the current point is not in the closed region; if the point is in the circumscribed rectangle with the minimum area, carrying out the next step; and 3.2) judging whether the point is in the simple polygon or not. The positioning control method provided by the invention has the advantages that the computation is simplified; the speed is high; and the occupation of the closed region of the vehicle-mounted GPS on CPU (Central Processing Unit) resources is greatly reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
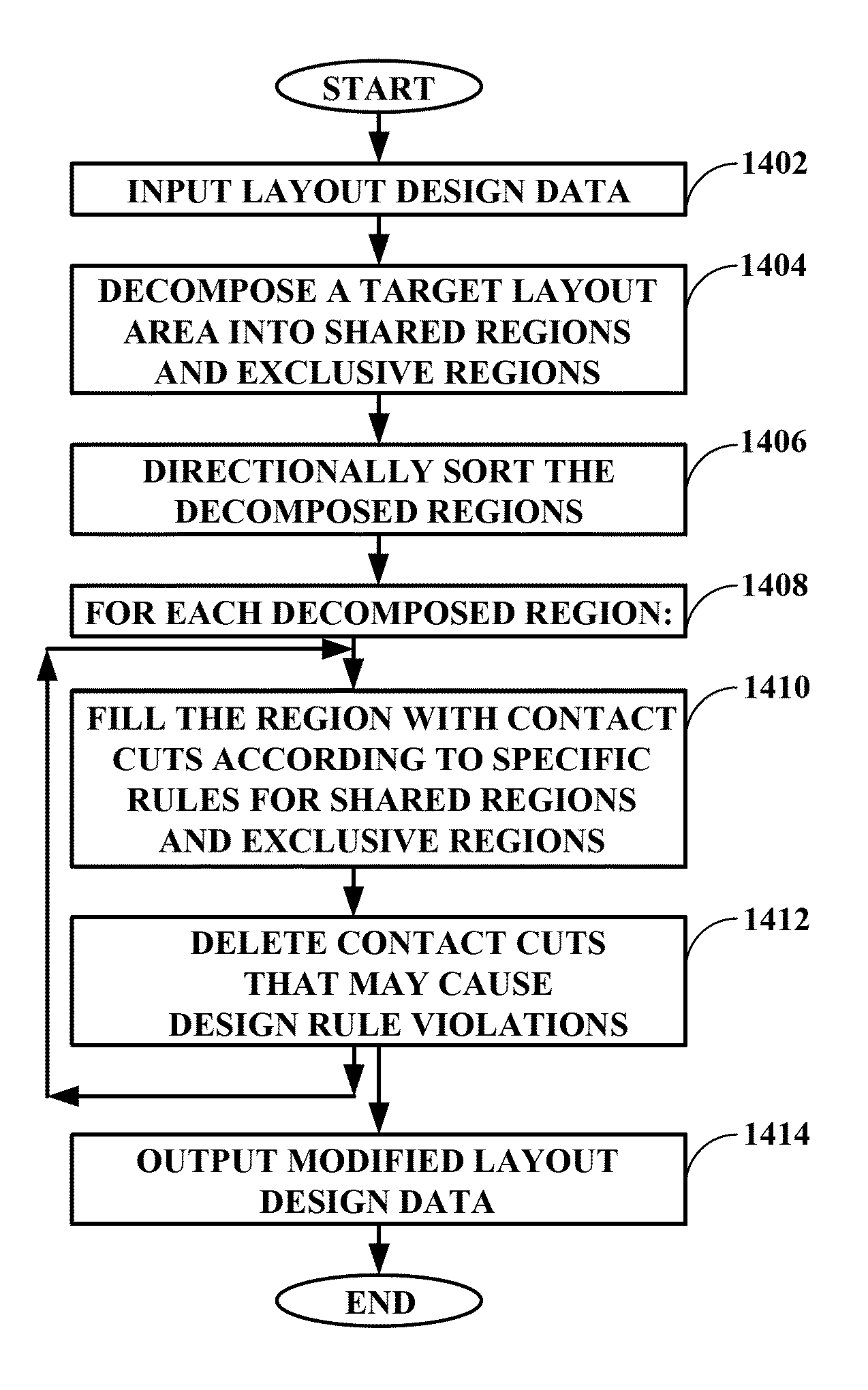
System and method for automatic placement of contact cuts and similar structures in integrated circuit layouts
InactiveUS8490038B1Maximizing numberComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsInter layerMostly True
A system, method, and computer program product for automatically placing contact cuts in integrated circuit layouts, particularly in guard rings, inter-layer via connections, and various space-filling structures typically defined by polygons or paths. Areas to be filled with contact cuts are partitioned horizontally and vertically, and decomposed into shared and exclusive type regions that are sorted directionally. Contact cuts are placed in each region according to its type and according to relevant design rules on contact cut spacing and enclosure constraints. Contact cuts that may cause design rule violations are deleted. Narrow jogs or cuts, merged shared regions, and non-orthogonal edges or segments in the decomposed regions are handled by alternate embodiments. The result is automated contact cut placement, even for merged / chopped layout features, that is generally more symmetric, collinear, and adds an optimal number of contact cuts in most cases than with existing tools.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
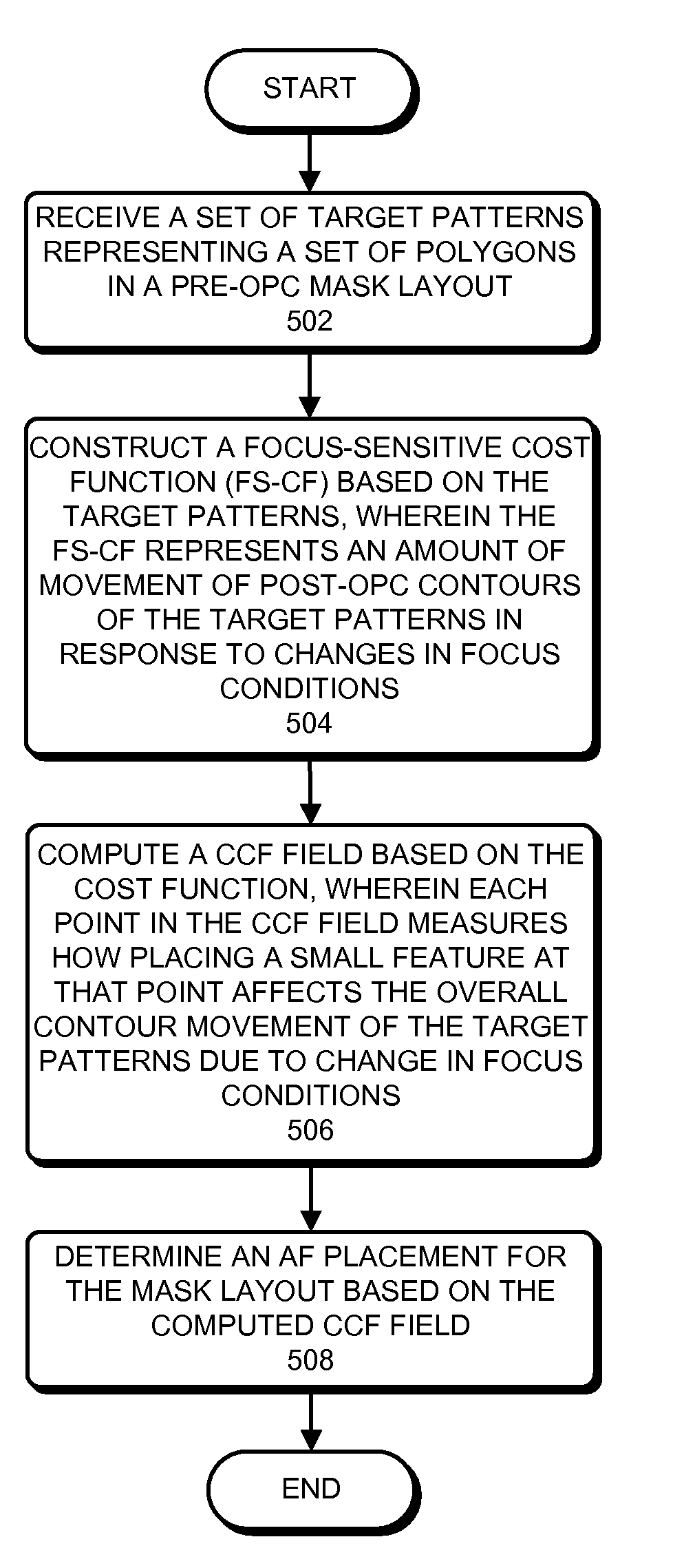
Assist feature placement based on a focus-sensitive cost-covariance field
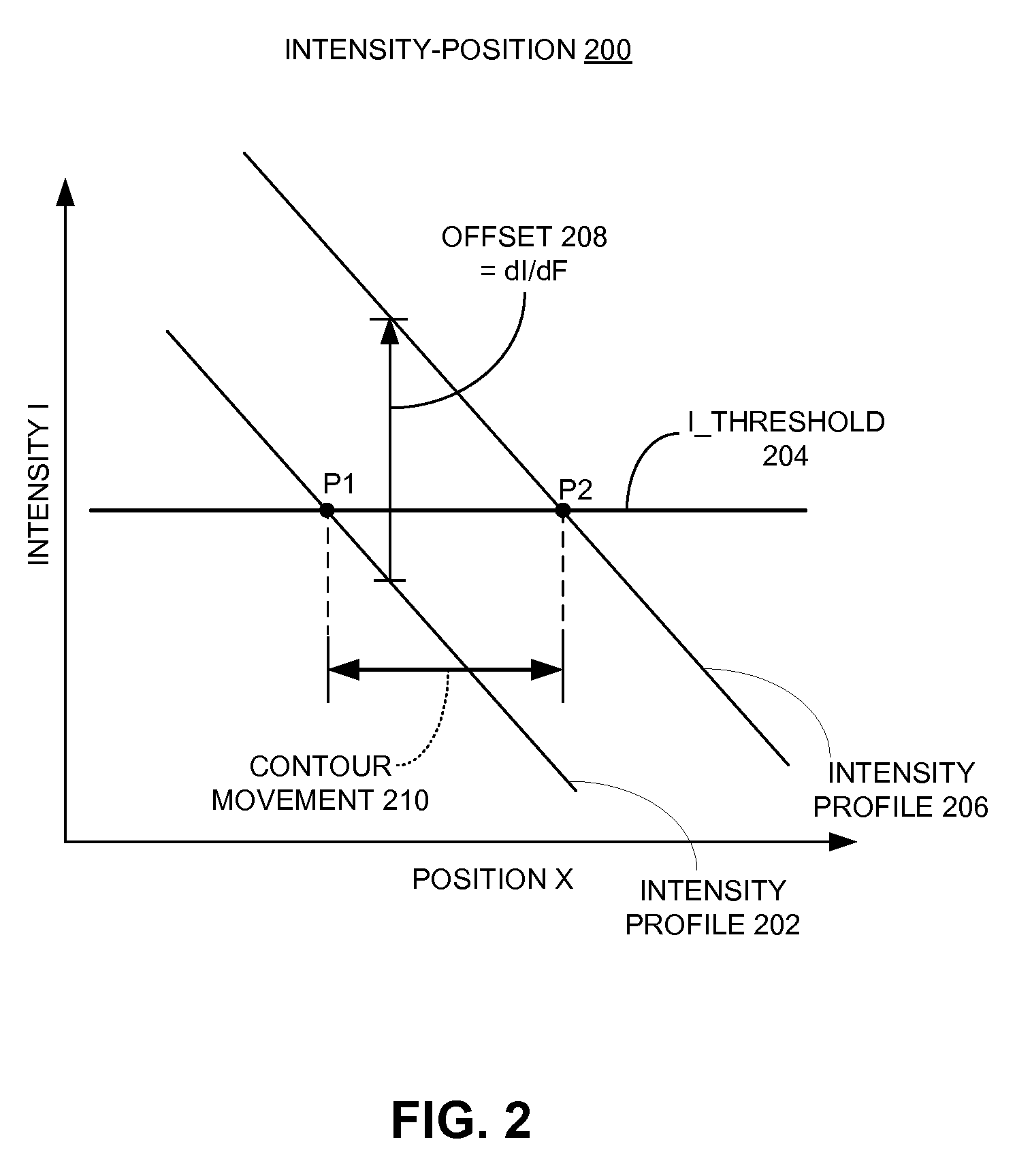
ActiveUS7954071B2Photomechanical apparatusCharacter and pattern recognitionLithographic artistCovariance
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that determines an assist feature placement within a post-optical proximity correction (post-OPC) mask layout. During operation, the system receives a set of target patterns which represent a set of polygons in a pre-OPC mask layout. The system then constructs a focus-sensitive cost function based on the target patterns, wherein the focus-sensitive cost function represents an amount of movement of post-OPC contours of the target patterns in response to changes in focus condition of the lithography system. Note that the contours of the target patterns substantially coincide with the edges of set of the polygons. Next, the system computes a cost-covariance field (CCF field) based on the focus-sensitive cost function, wherein the CCF field is a two-dimensional (2D) map representing changes to the focus-sensitive cost function due to an addition of a pattern at a given location within the post-OPC mask layout. Finally, the system generates assist features for the post-OPC mask layout based on the CCF field.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com