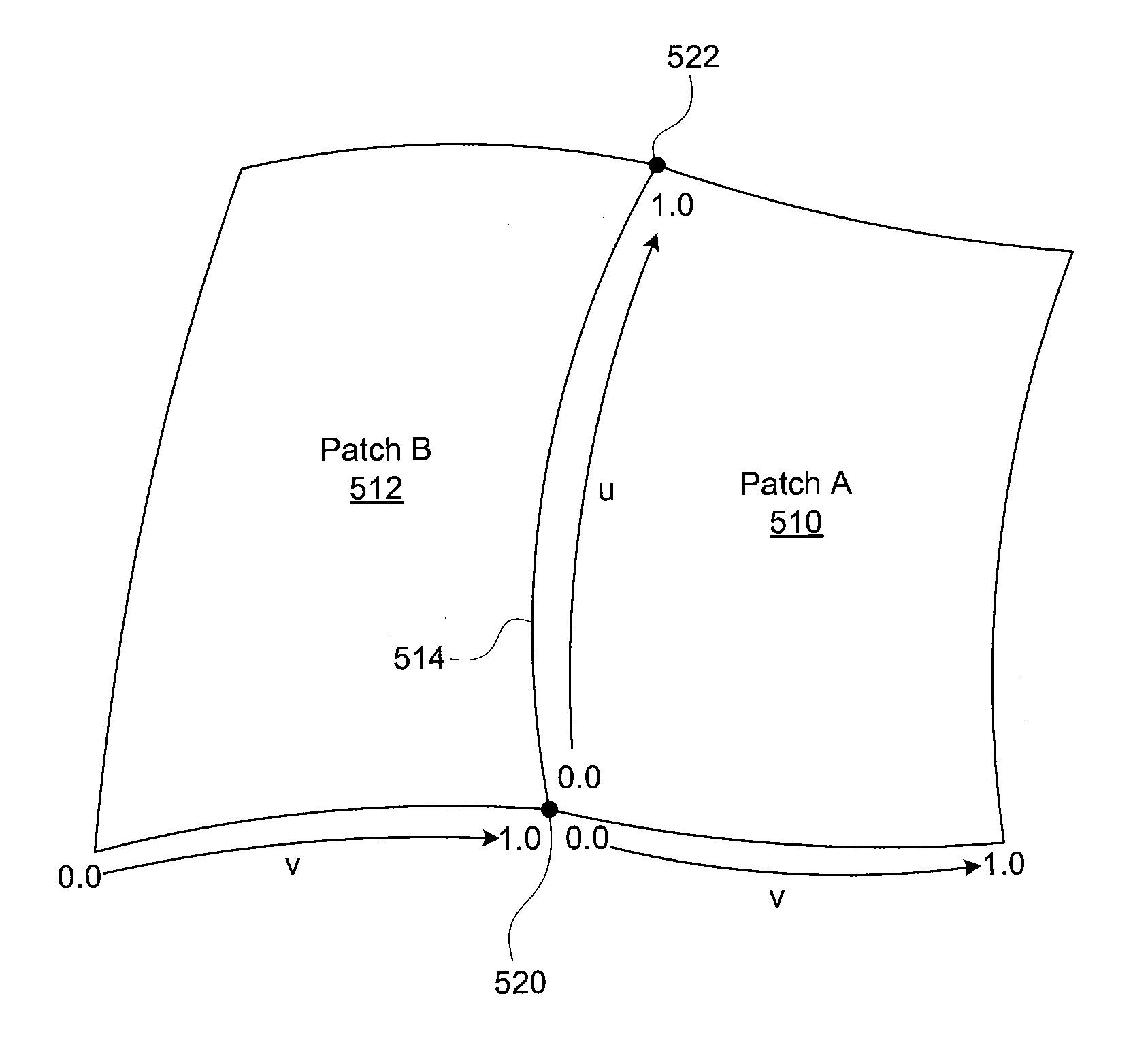
Patents
Literature
80 results about "Subdivision surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
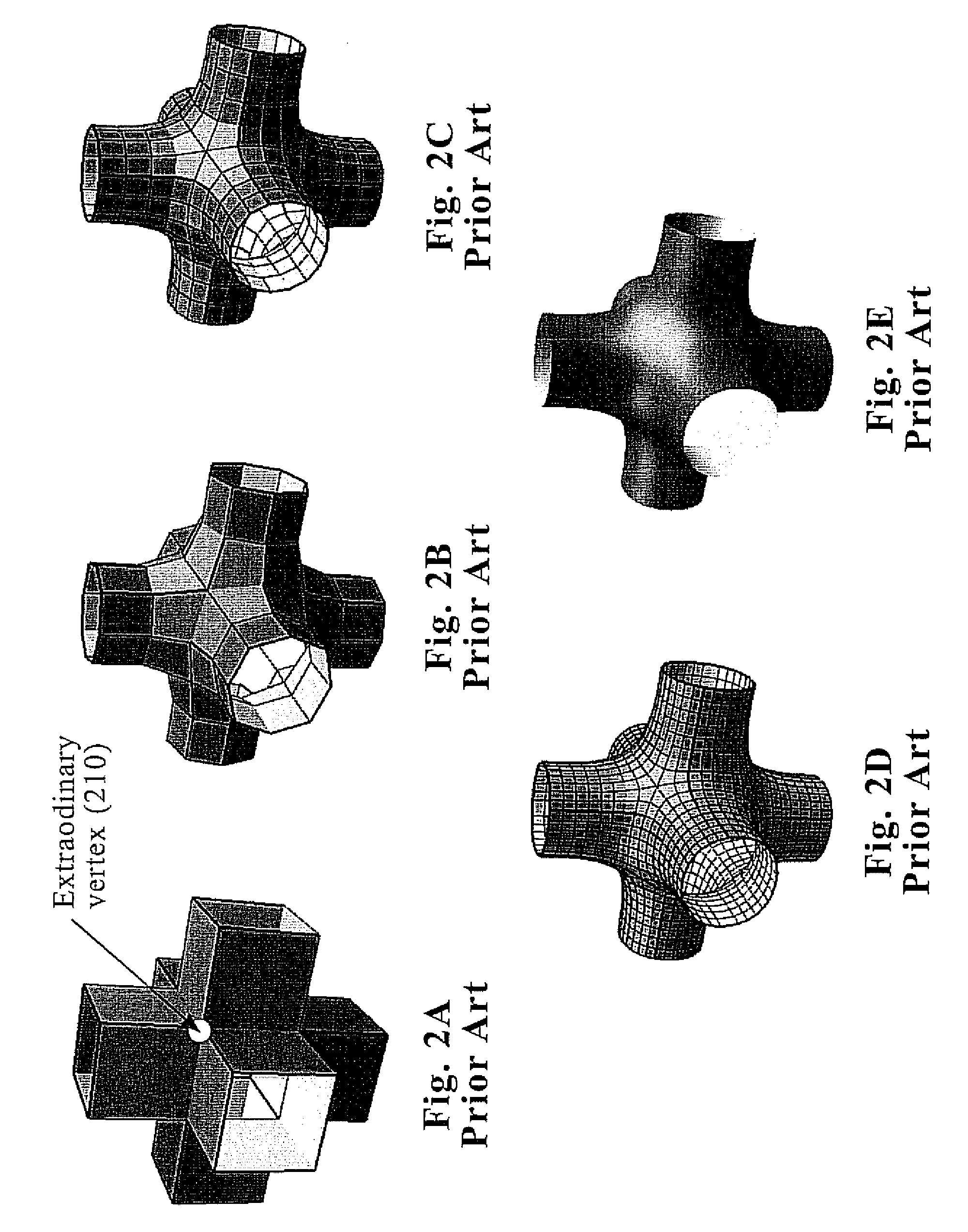
In the field of 3D computer graphics, a subdivision surface is a representation of a smooth surface via the specification of a coarser piecewise linear polygon mesh. The smooth surface can be calculated from the coarse mesh as the limit of recursive subdivision of each polygonal face into smaller faces that better approximate the smooth surface. A number of schemes are used to approximate the smooth limit surface, the Catmull-Clark technique being the most well-known.
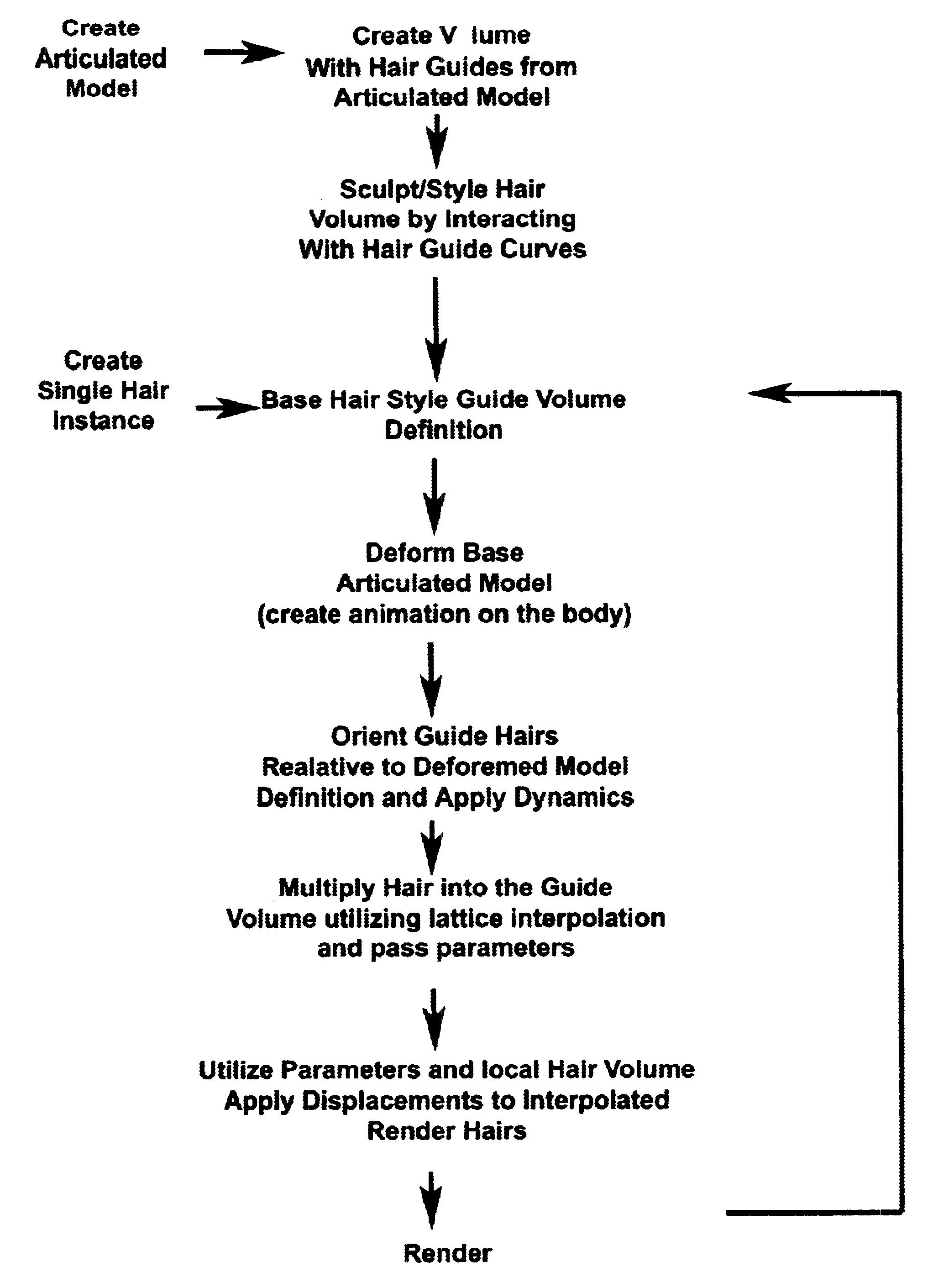
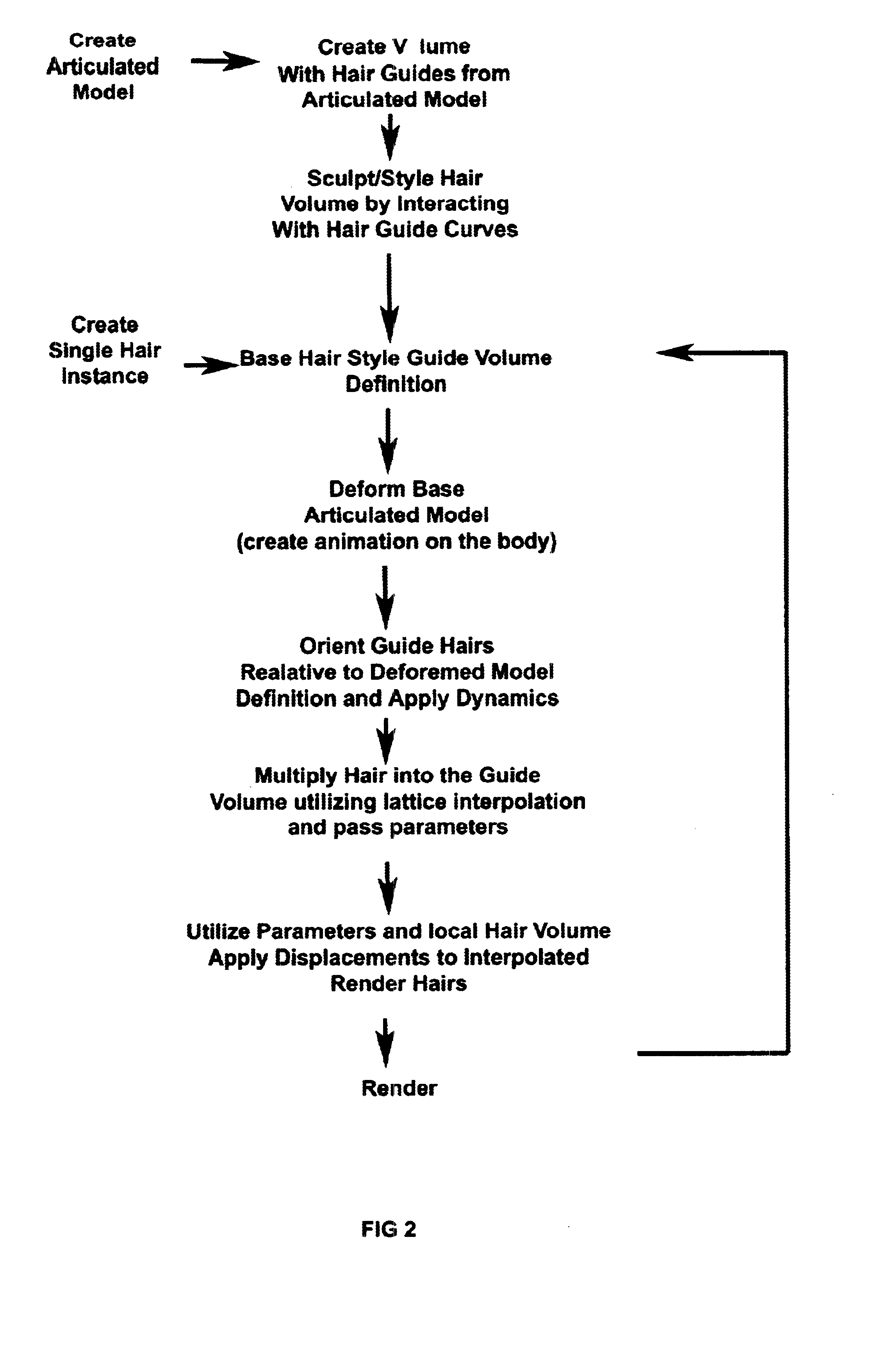
Hair generation and other natural phenomena with surface derived control volumes in computer graphics and animation
Methods for defining smooth and continuous coordinate systems in a volume comprised of a lattice structure of guide columns derived from arbitrarily modeled surface topologies involving polygons, nurbs, linear segments, and subdivision surfaces. Applications of these techniques in computer graphics and computer animation include: (1) the definition of pseudo-coordinate systems for use in creating geometry which must grow from said surface (2) the creation of a highly stable coordinate system involving guide columns in which Cartesian physical simulations may be carried out and rendered as well as deformed and rerendered if desired.
Owner:EPIC GAMES INC
Adaptive computation of subdivision surfaces
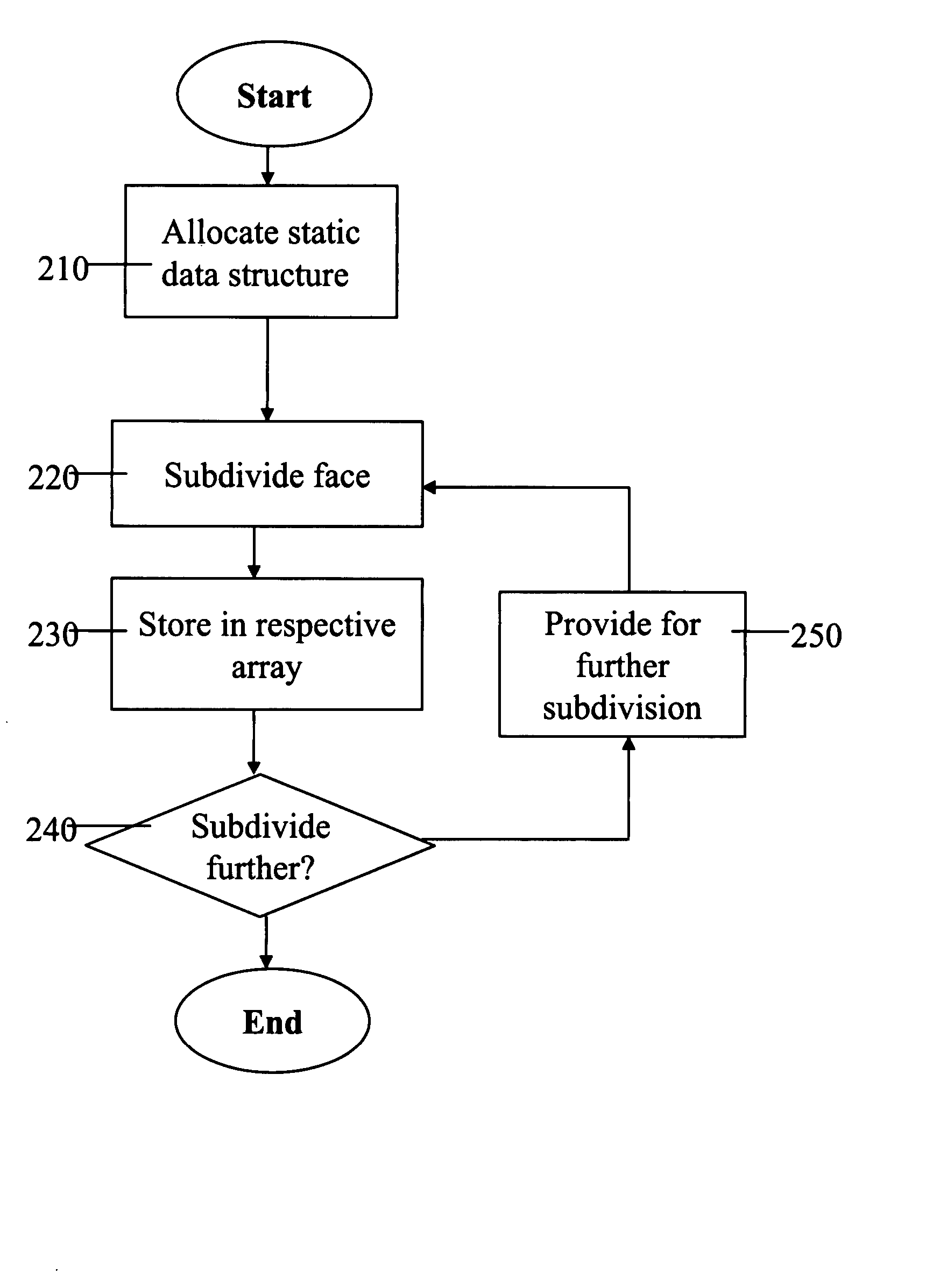
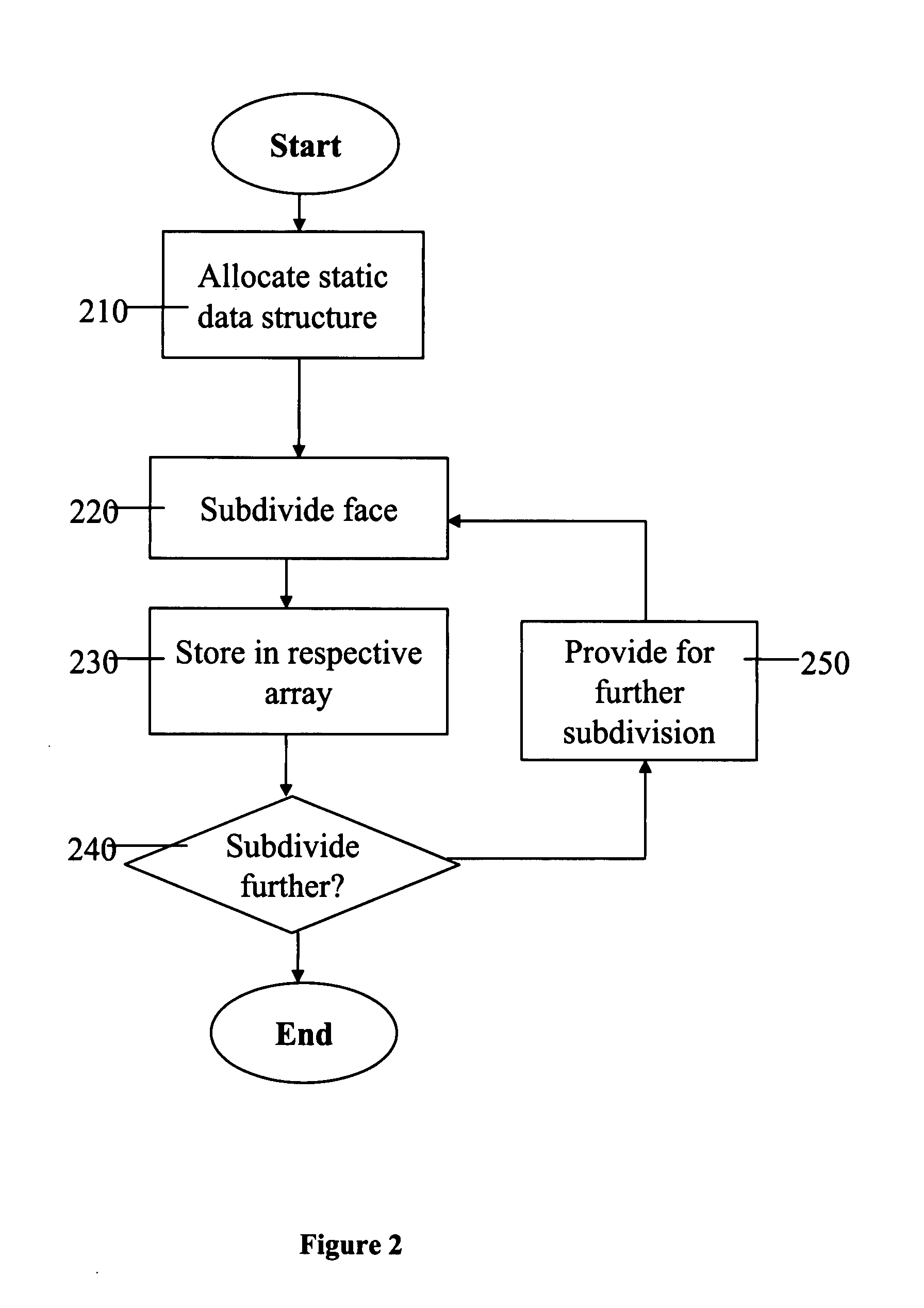
A method for the computation of a subdivision surface from a base mesh of coarse faces which requires no dynamic allocations is performed as follows. First, a static data structure is allocated. The static data structure includes a hierarchy of data arrays, where each of the data arrays is for storing control mesh data for a single coarse face at a respective subdivision level. The size of each of the data arrays is determined by the respective subdivision level. A subdivision algorithm is then applied to each of the base mesh coarse faces in turn. During the subdivision of a single coarse face, the resulting data for each subdivision level is stored in the respective data array. The static data structure may store further data for each subdivision level respectively, such as a tag for each of the sub-faces at the given level. The subdivision may be applied adaptively, by applying level-of-detail control information at intermediate subdivision levels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for tessellation of subdivision surfaces
A method and system for performing adaptive tessellation of a subdivision surface. The method includes the step of accessing a model of a surface for subdivision processing. The model is converted to an intermediate form to facilitate subdivision processing. The intermediate form of the model is then tessellated.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
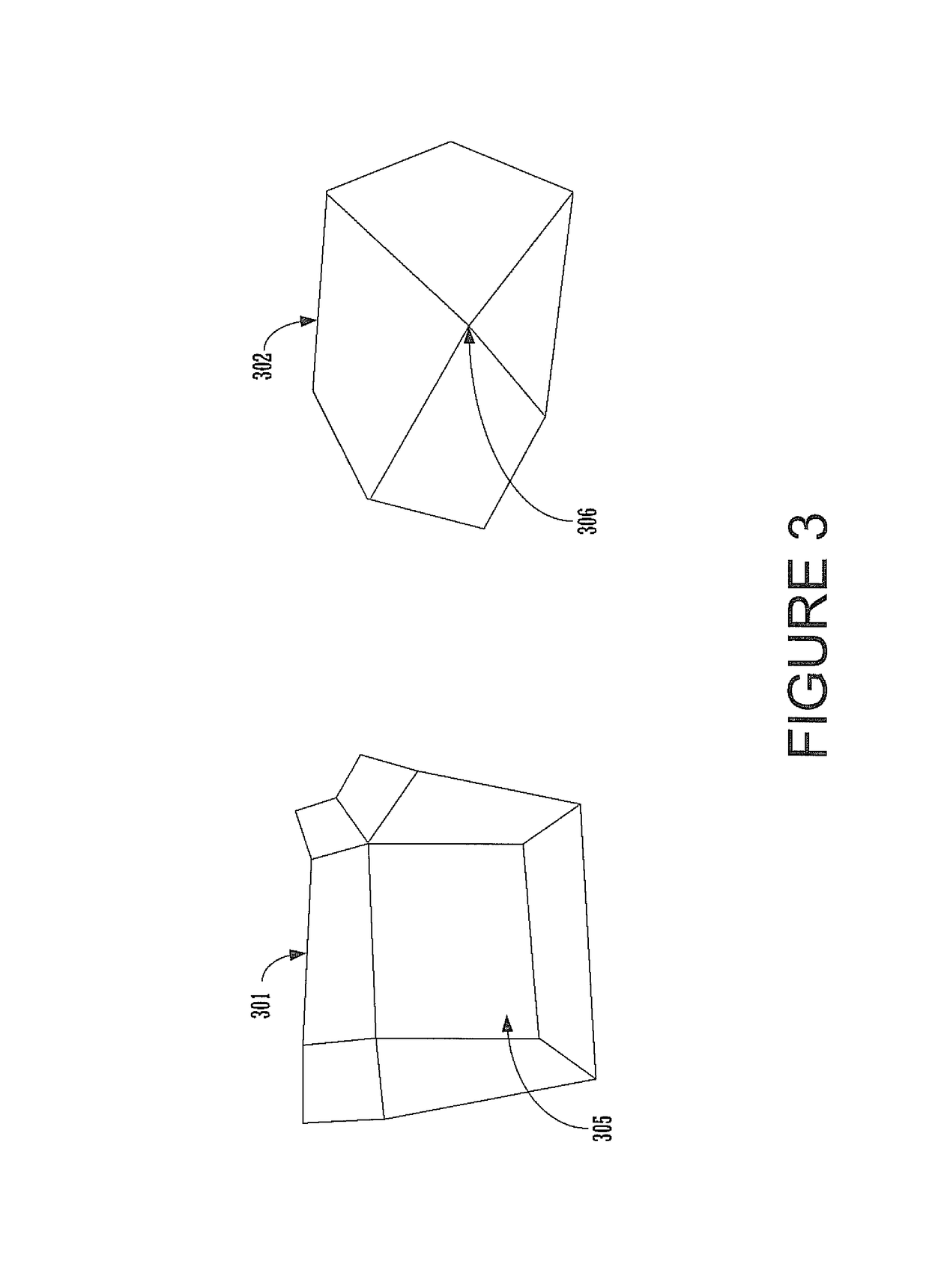
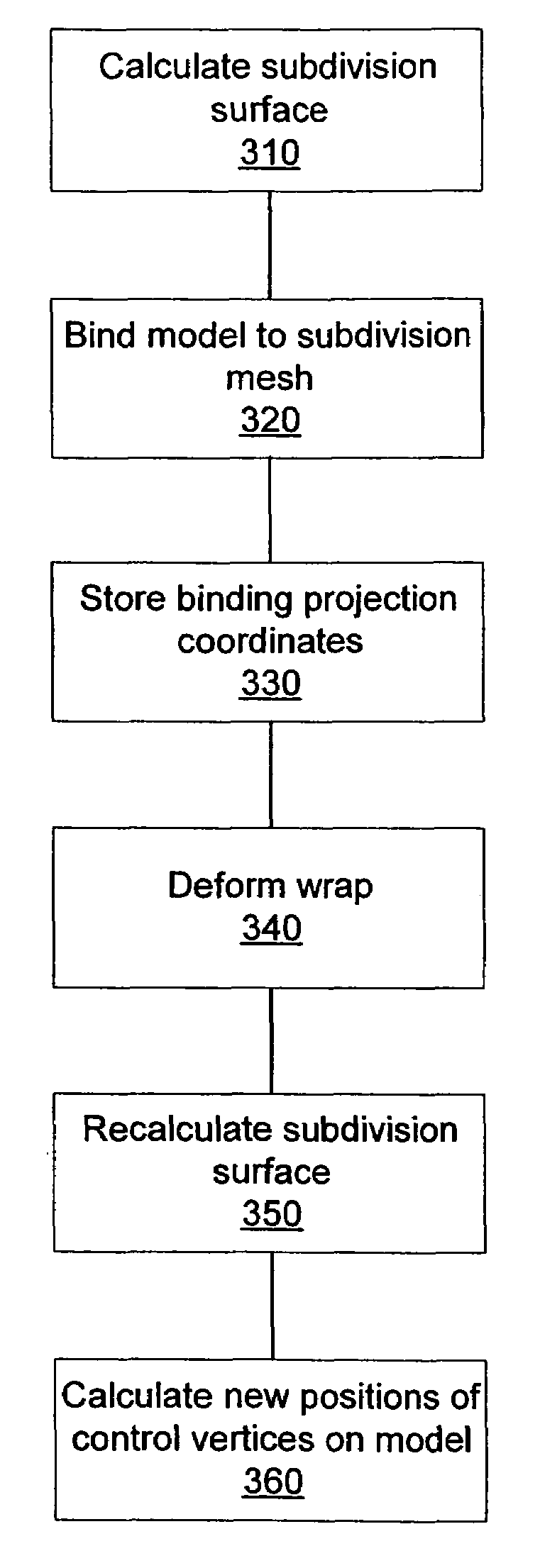
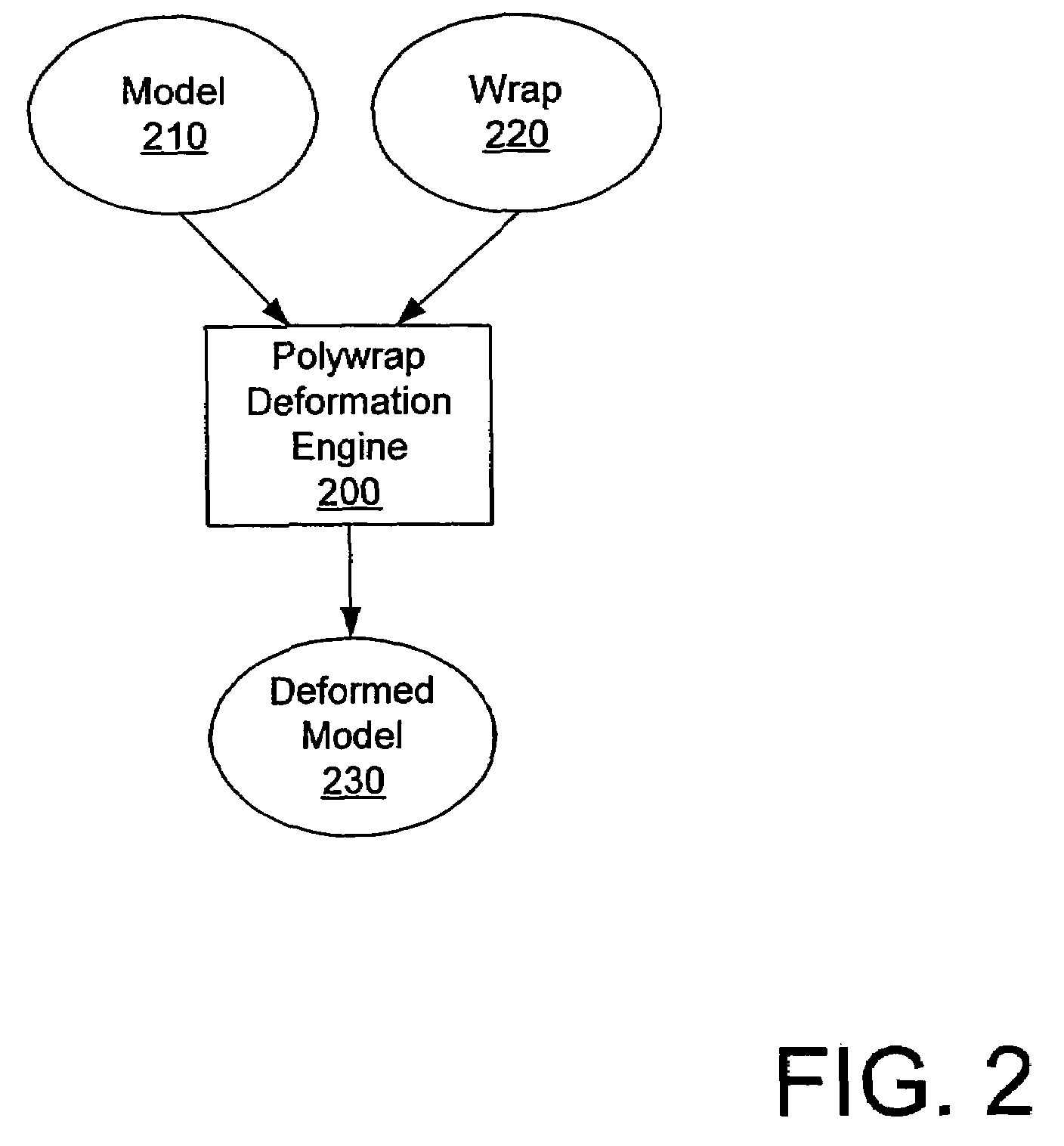
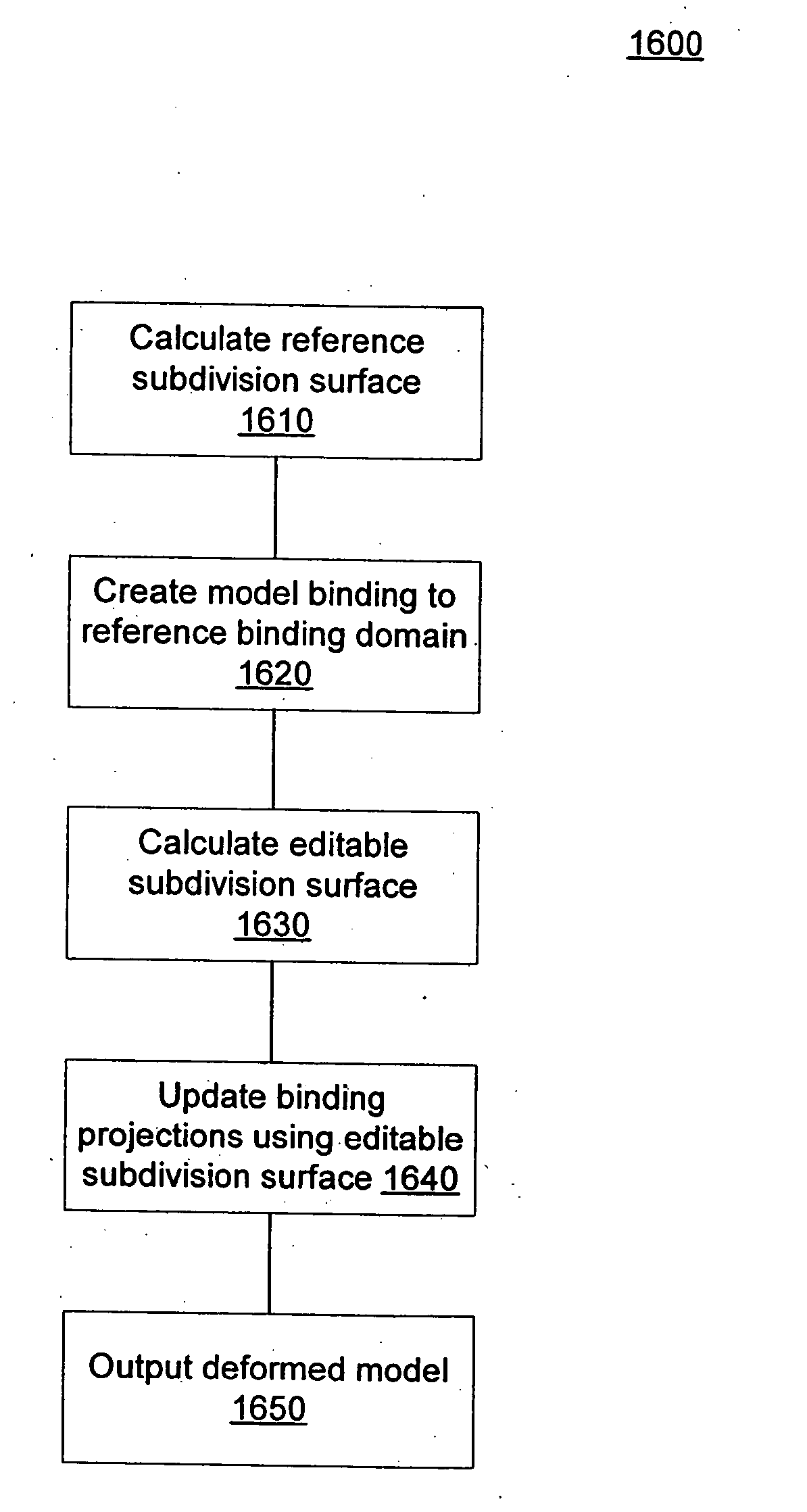
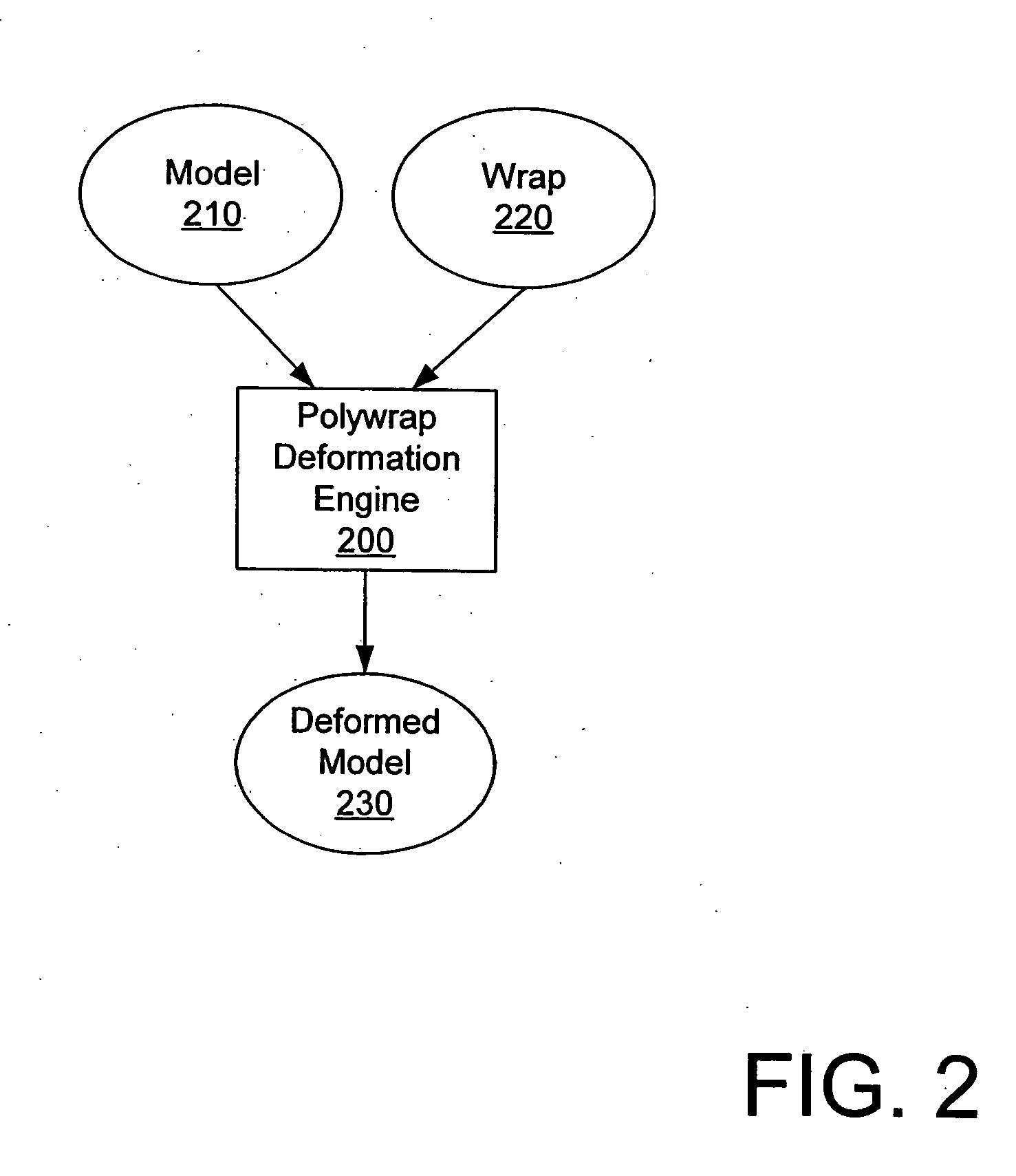
Wrap deformation using subdivision surfaces
ActiveUS7236170B2Minimizing introductionCooking vesselsCathode-ray tube indicatorsEngineeringSubdivision surface
Deformations are applied to a model using a subdivision surface. Given a wrap and model, a subdivision surface is calculated from the wrap. The model is then bound to the subdivision surface. When the wrap is deformed, the subdivision surface is recalculated. The model is then deformed based on changes in the subdivision surface. Binding parameters may be assigned to control vertices in the wrap to control the application of the deformation to the surface.
Owner:DREAMWORKS ANIMATION LLC
Hermite gregory patch for watertight tessellation
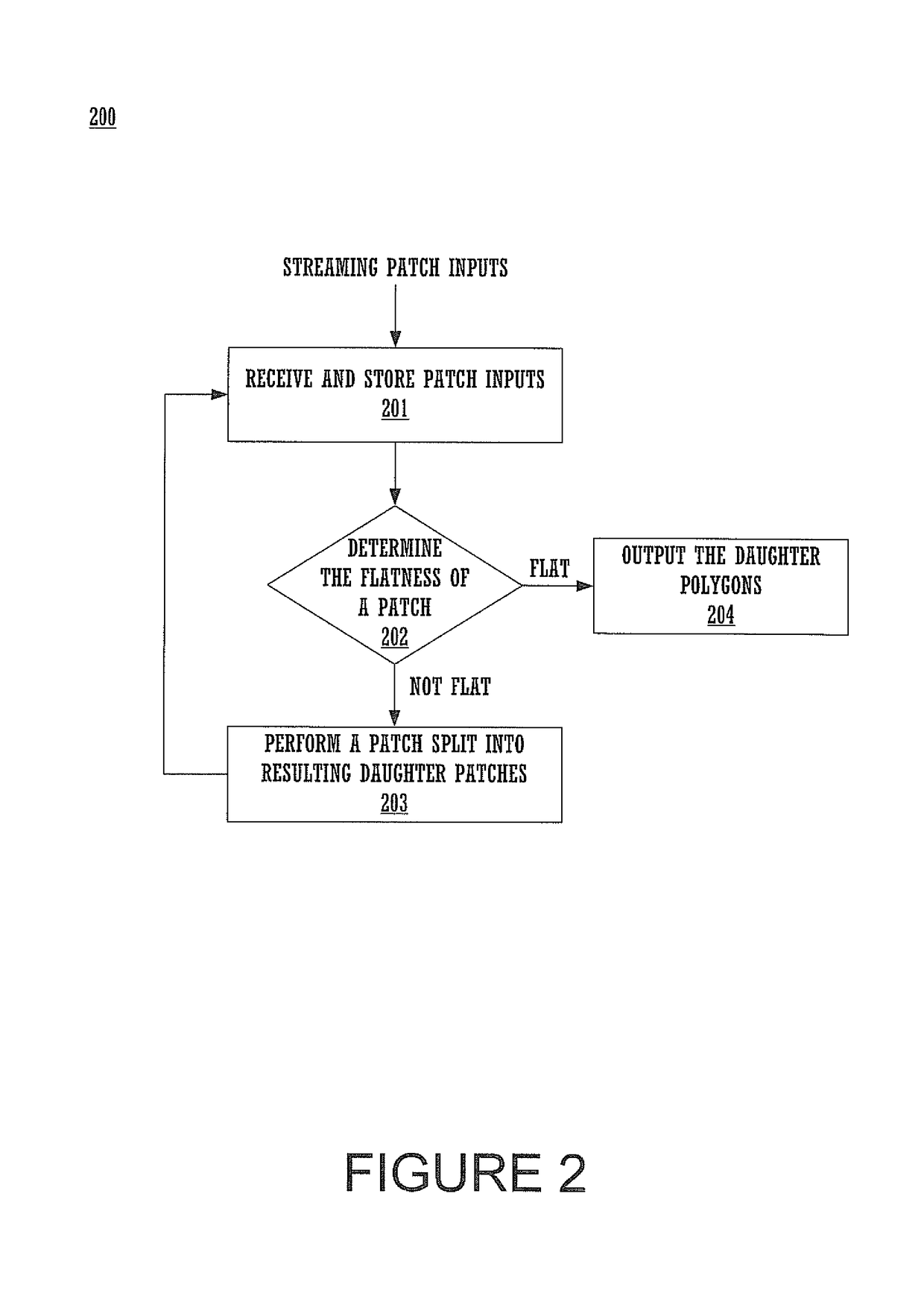
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth technique for watertight tessellation in a displaced subdivision surface. A subdivision surface is represented as a novel parametric quad patch that is continuous with respect to position (C0) and partial derivatives (C1) along boundaries as well as interior regions. The novel parametric quad patch is referred to herein as a Hermite Gregory patch and comprises a Hermite patch augmented to include a pair of twist vector parameters per vertex. Each pair of twist vectors is combined into one twist vector during evaluation, according to weights based on proximity to parametric boundaries. Evaluation yields an approximation mesh comprising a position for each vertex and a corresponding normal vector for the vertex. Displacement is performed based on the approximation mesh and a displacement map to generate a displaced approximation mesh that is reflective of the displaced subdivision surface.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
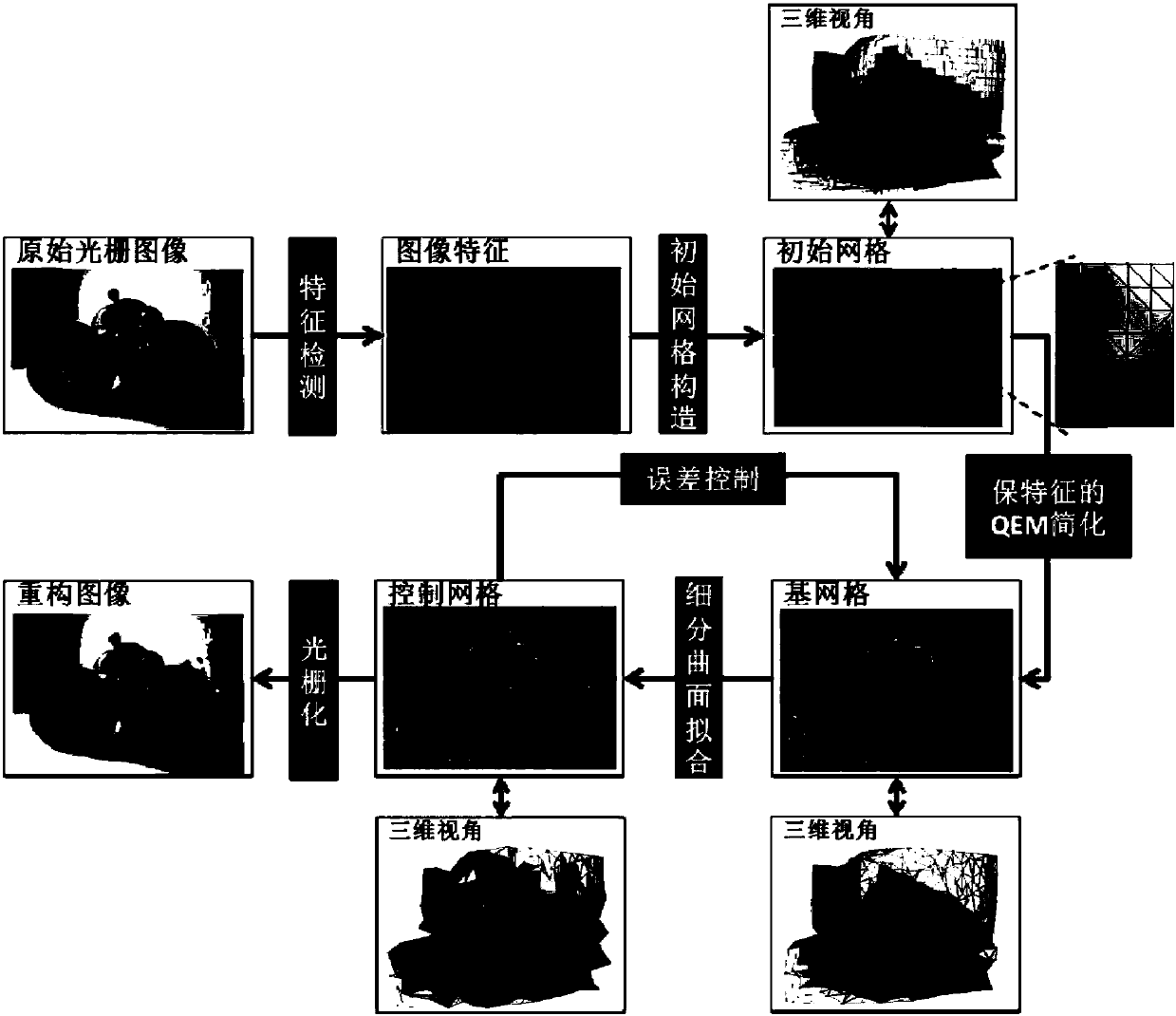
Error-controllable subdivision surface image vectorization method
ActiveCN107256557AEasy to captureQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionGrating
The invention discloses an error-controllable subdivision surface image vectorization method, and the method comprises the following steps: 1), detecting the edge features of an image, and obtaining an initial image feature line segment with the one-pixel width; 2), constructing an initial grid based on the image features, and marking the image features in the grid; 3), simplifying the initial grid, and constructing a base grid maintaining the image features; 4), carrying out the error-controllable Loop subdivision surface fitting, and obtaining a control grid; 5), carrying out the rasterization vector expression. The method can obtain a better vector image through a raster image. If the error of an initial reconstruction result cannot meet the demands of a user, the method can measure the error of a vectorized reconstruction image and an original image. The adaptive subdividing of the base grid is used for achieving a specific error in a certain range, thereby achieving the error controllability. The method employs the subdivision surface technology for image vectorization, and aims at the conversion of the raster image to the vector expression meeting the error requirements, and has the practical value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
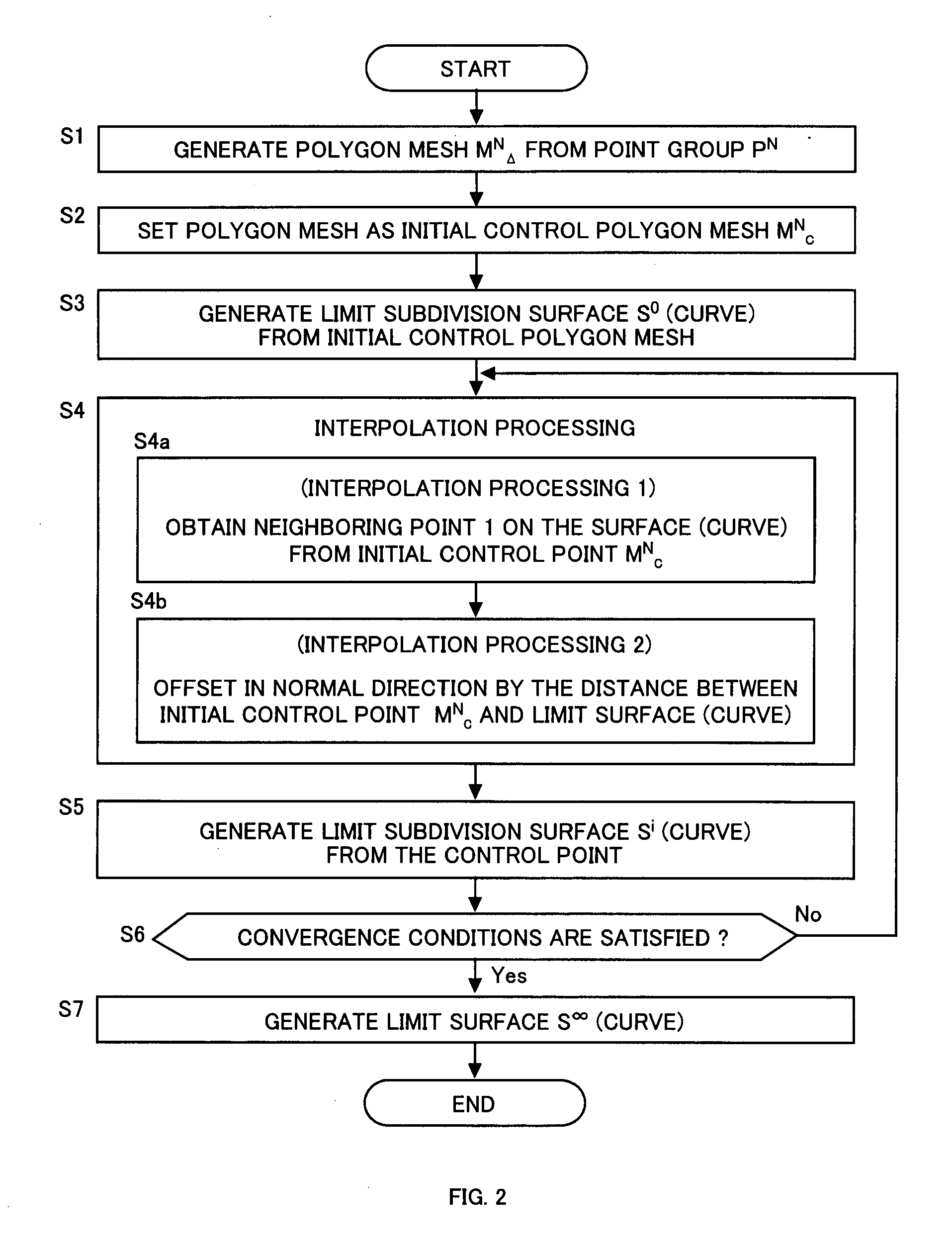
Interpolation processing method, interpolation processing device, shape evaluation method, and shape evaluation device
InactiveUS20090303235A1Additional processing stepsHigh precisionDrawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionShortest distanceTime segment
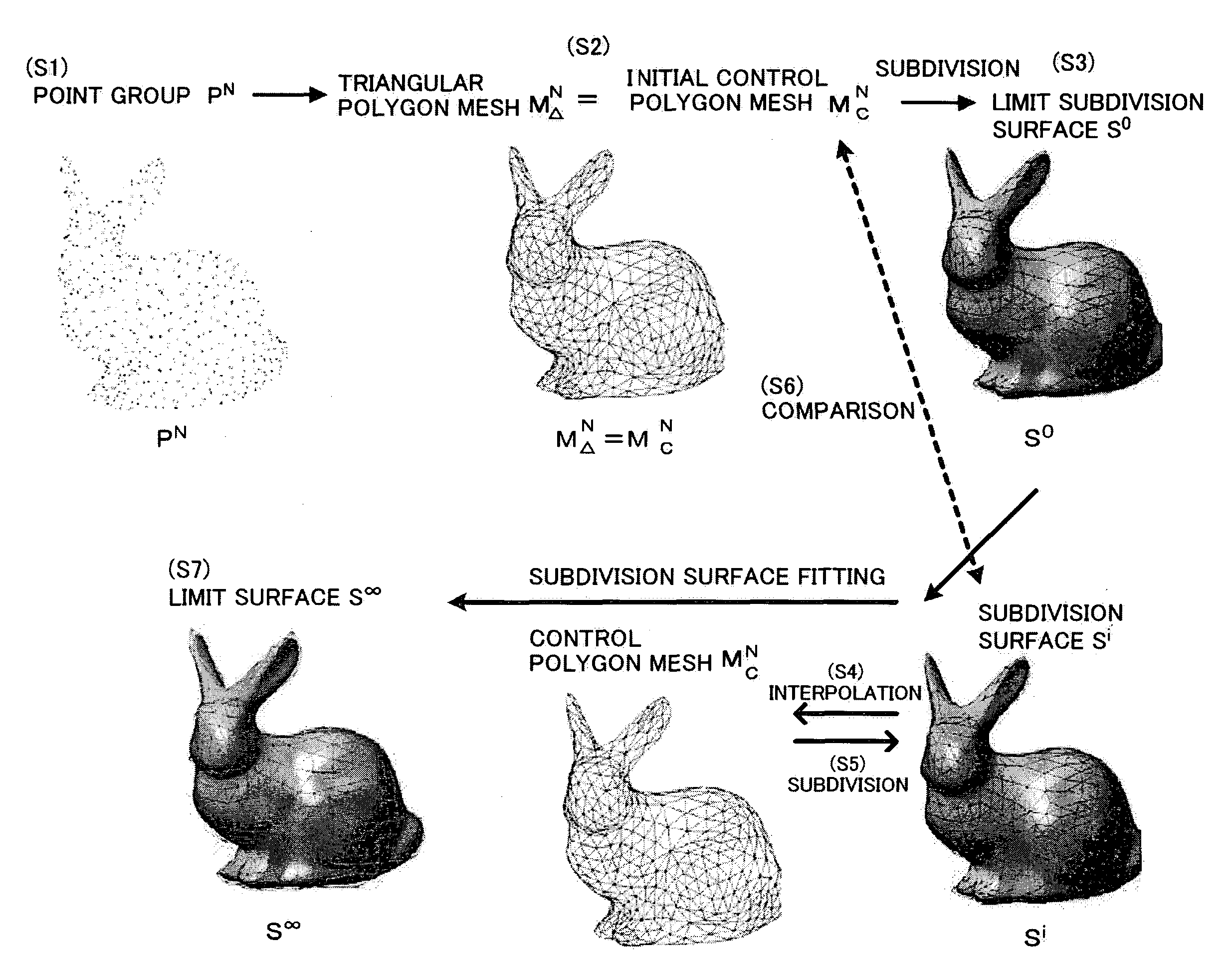
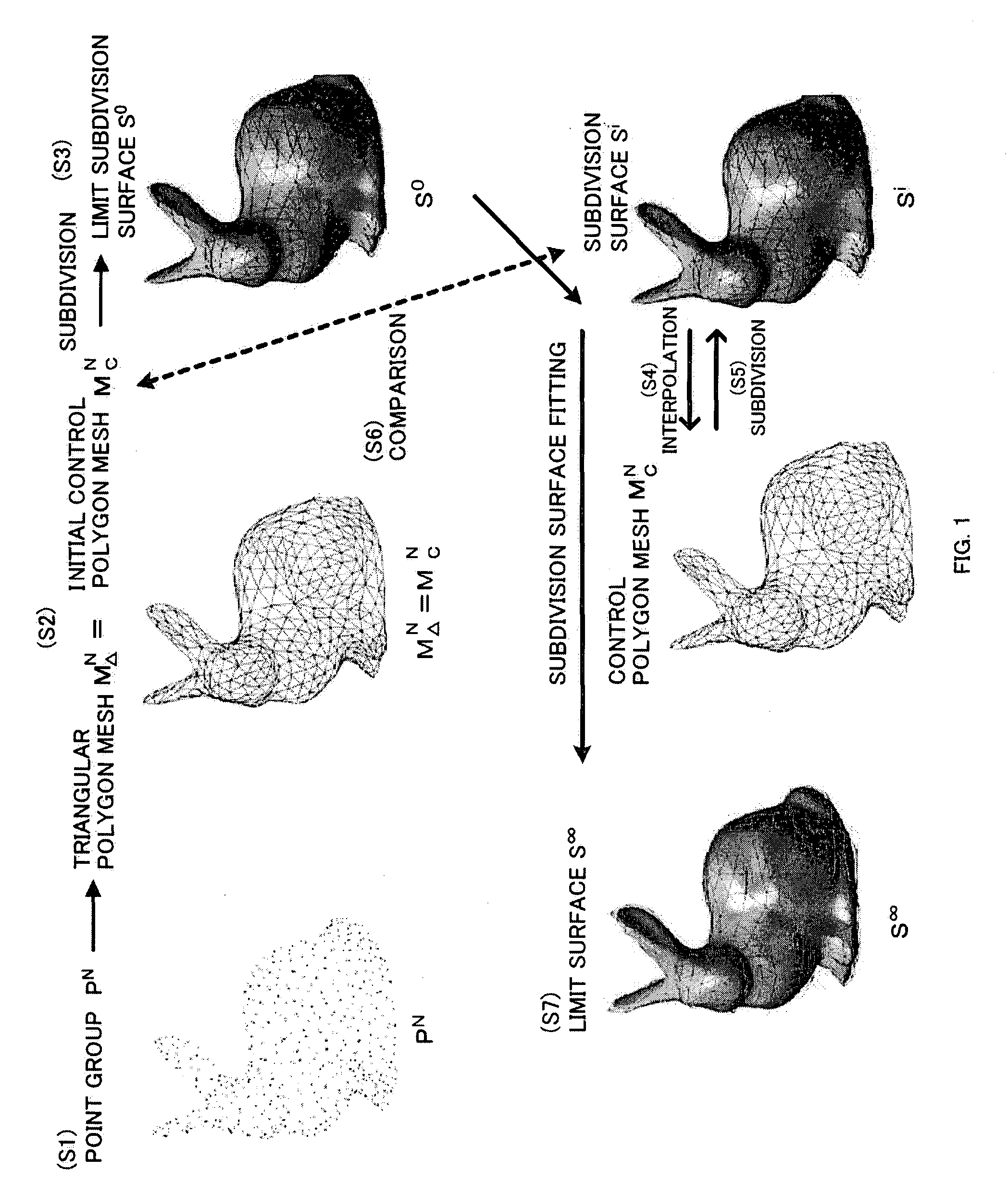
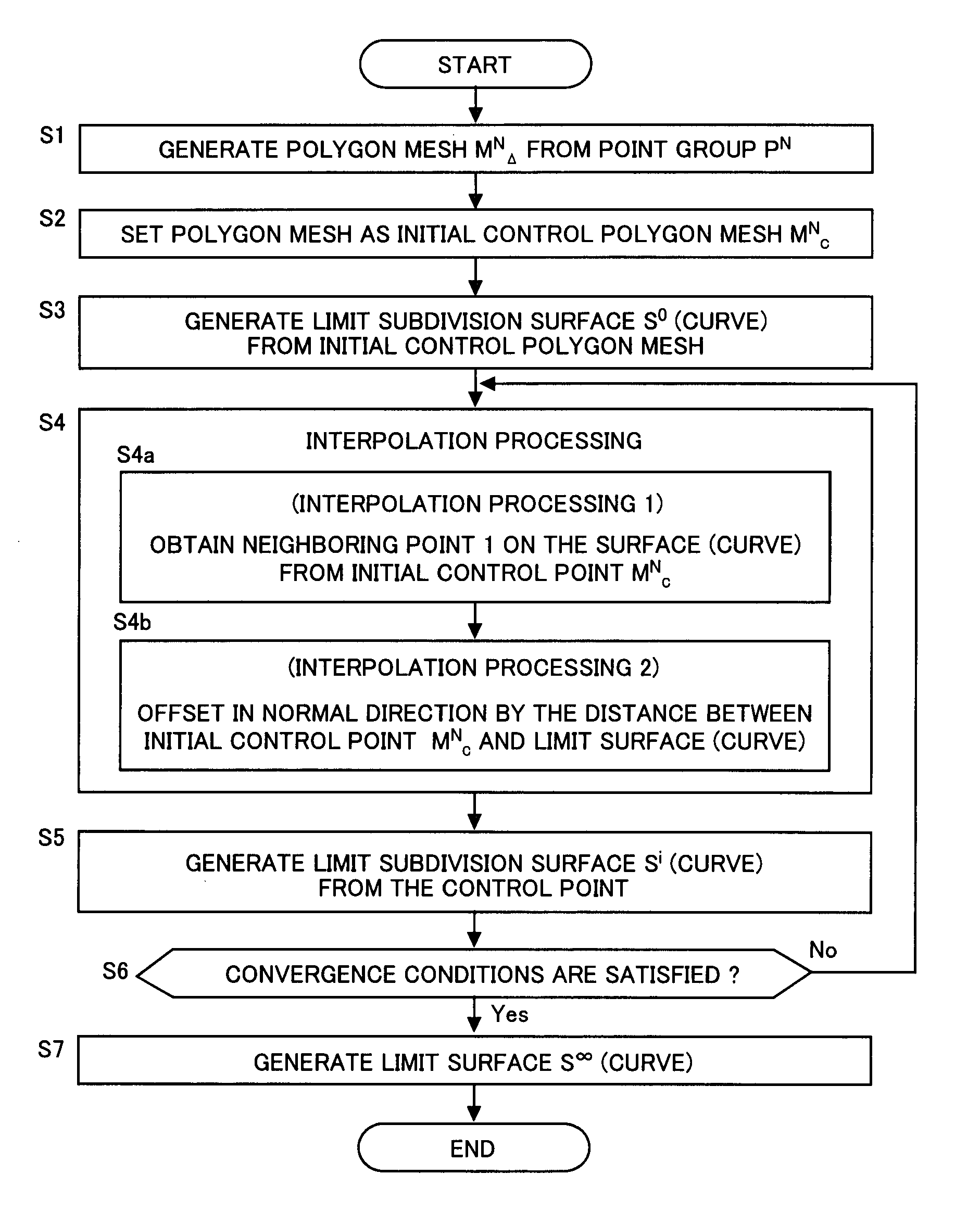
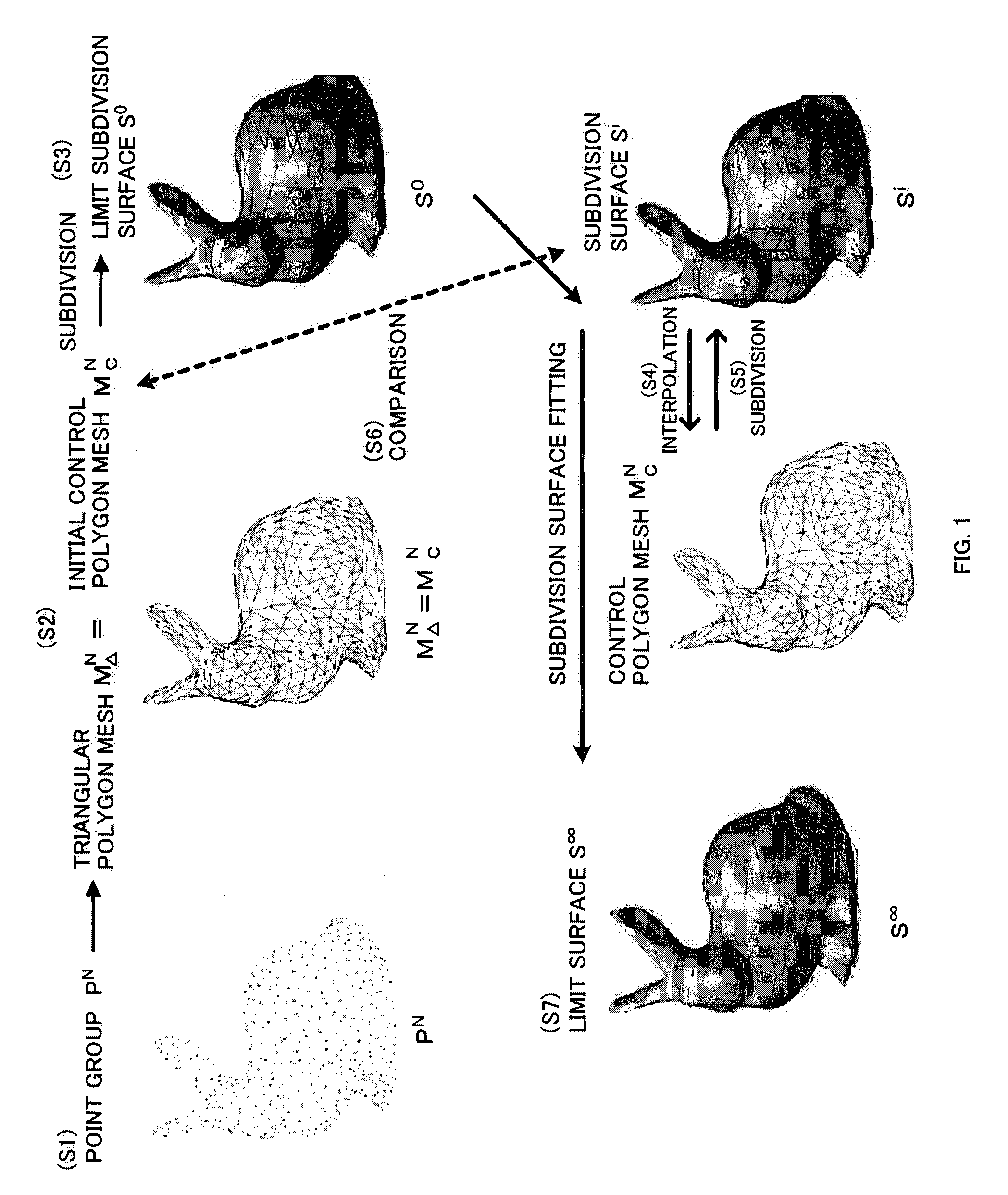
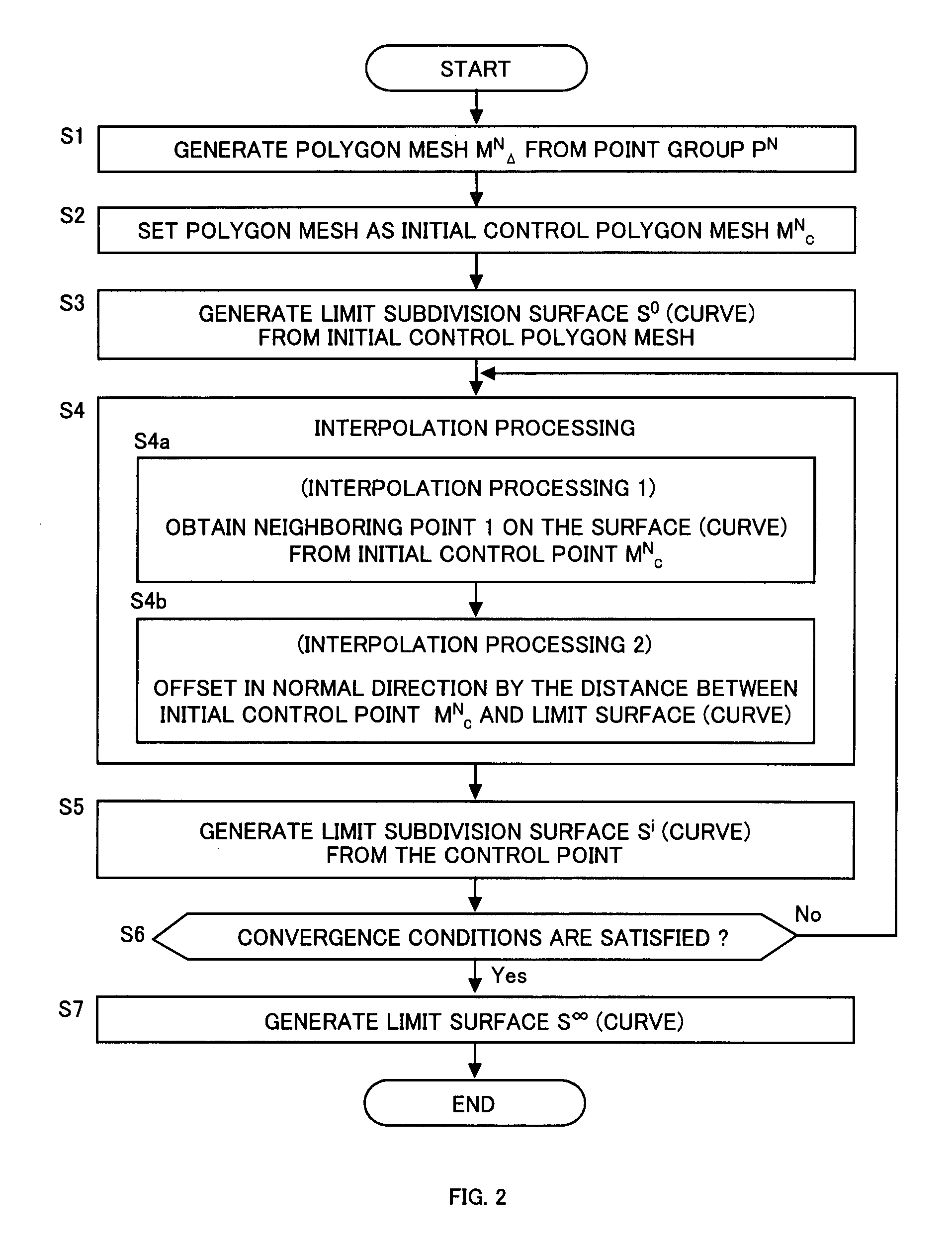
An initial polygon obtained from a point group is used as a control polygon, and a control point of the control polygon is offset in a normal direction by the shortest distance from a limit surface generated by the control polygon, so that the position of new control point is determined to allow a subdivision surface to interpolate the initial polygon, thereby generating the subdivision surface which interpolates the point group. A first process to determine the point on the subdivision surface at the shortest distance from each control point, and a second process to move and offset the control point in the normal direction from the surface by the distance between the point on the surface and the initial control point, are iterated until the distance between the initial point group and the point on the surface satisfies the threshold or becomes smaller than the threshold, thereby generating the subdivision surface interpolating the initial polygon. Consequently, the subdivision surface interpolating the point group is generated within a short operation time period, without solving a linear system.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA NAT UNIV
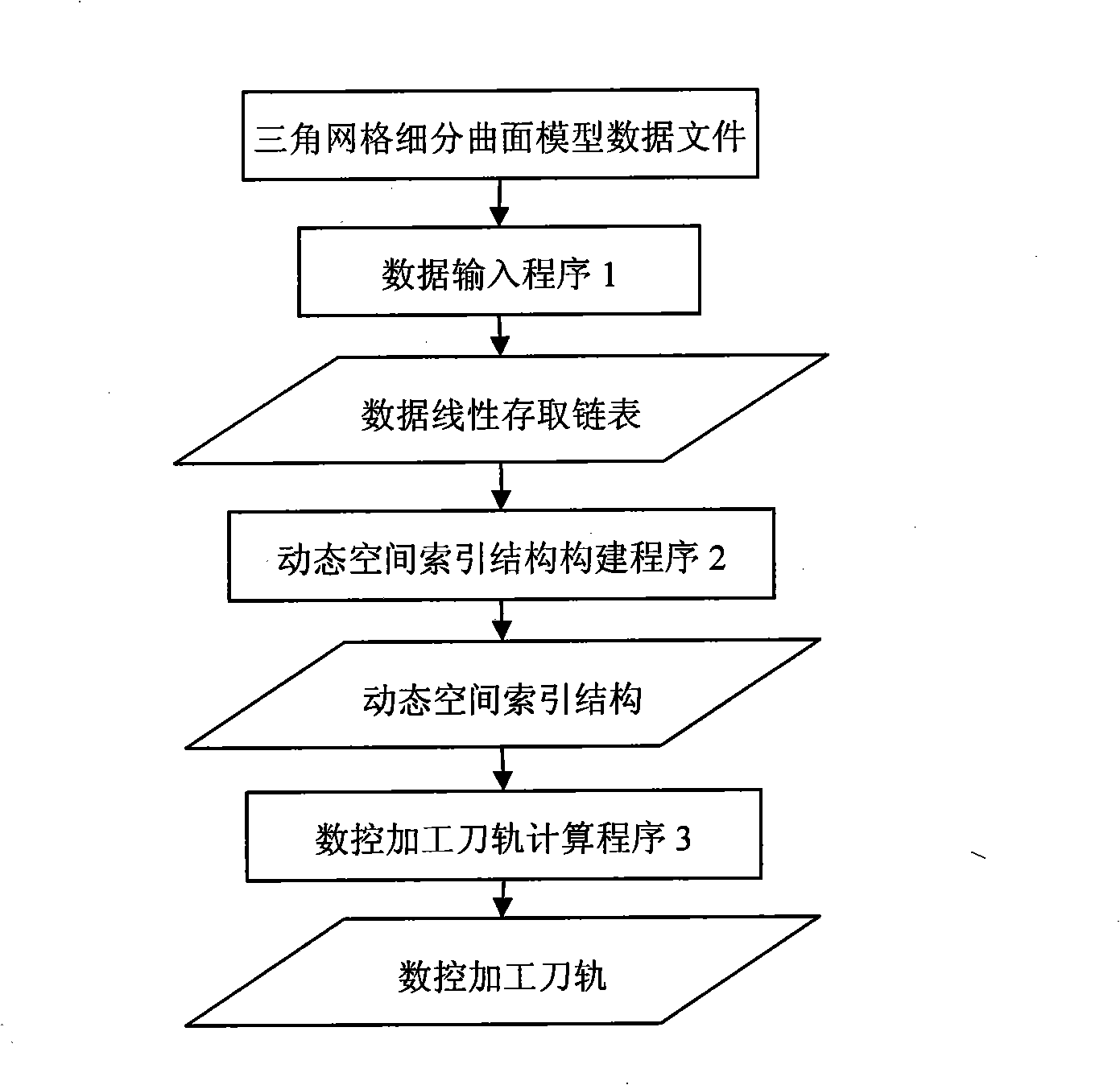
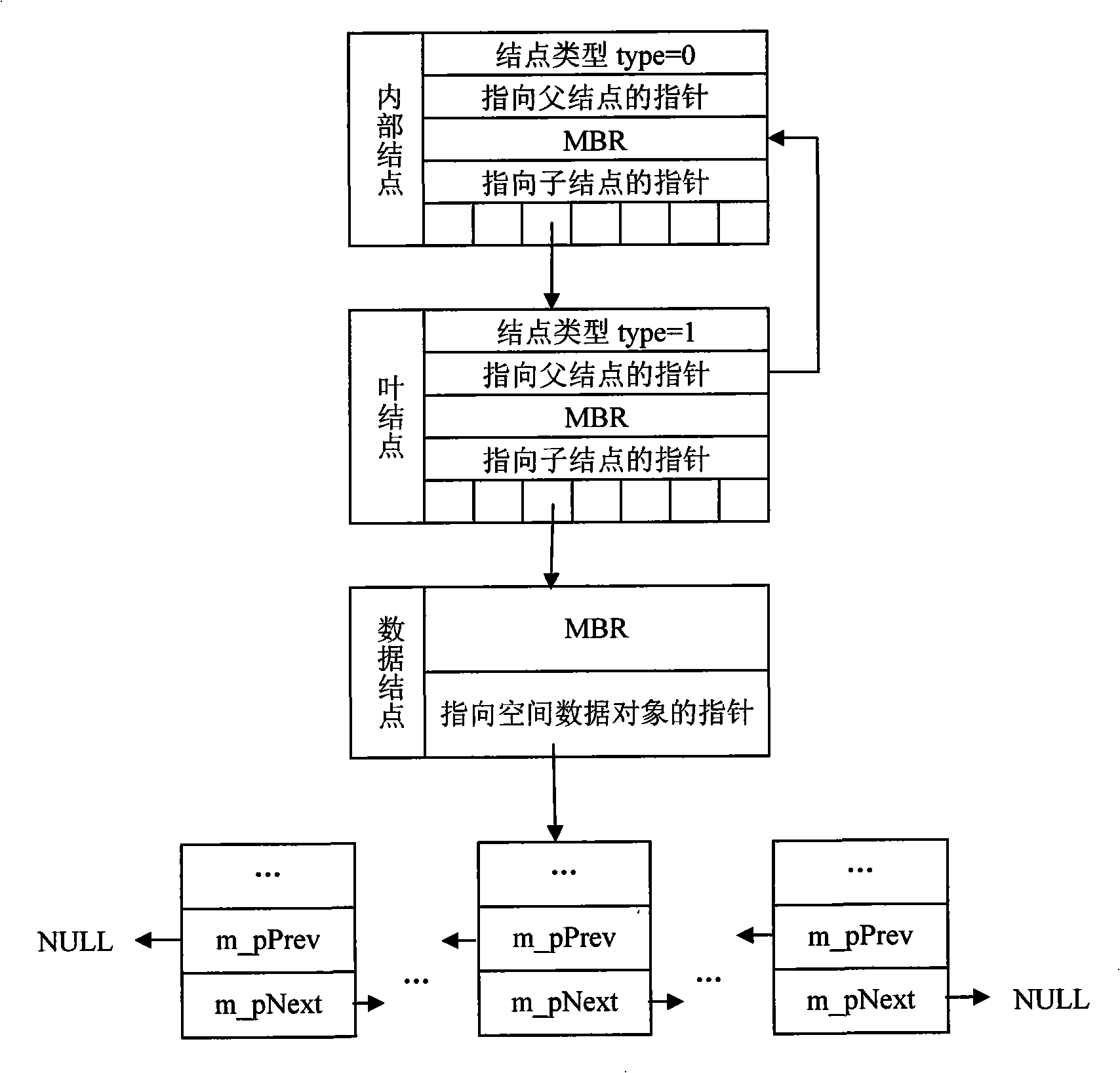
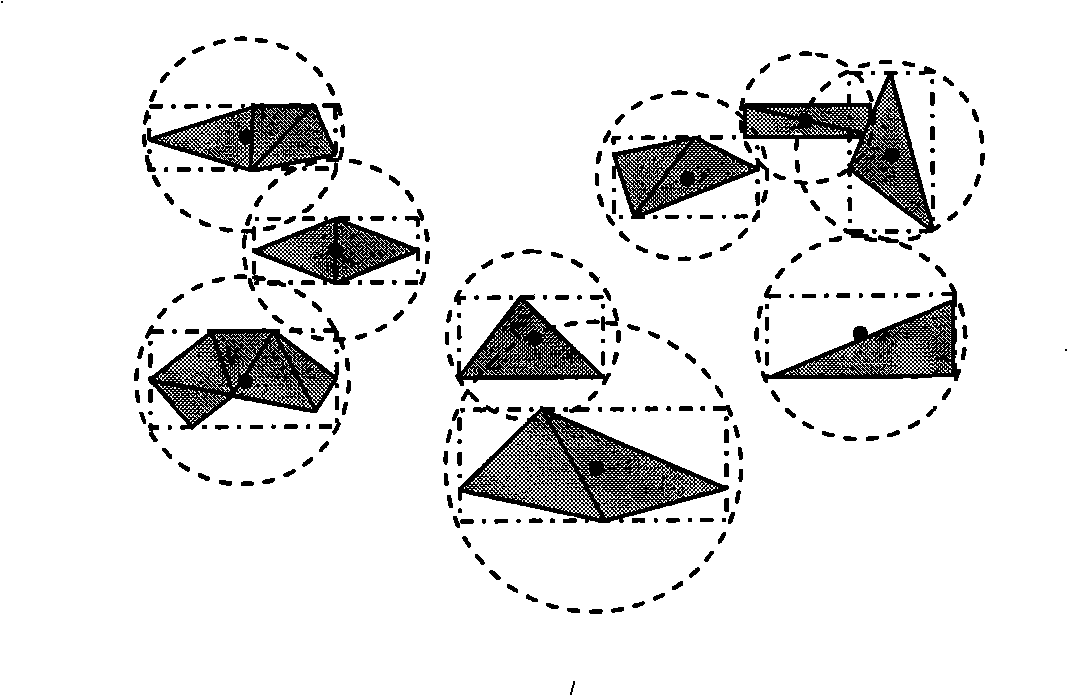
Triangular gridding subdivision curved surface NC tool track fast generation method
InactiveCN101403909AImprove production efficiencyQuick turnProgramme controlComputer controlMesh modelPoint set
The invention provides a generation method of a NC tool path in a triangular mesh subdivision surface. The generation method is characterized in that a spatial clustered index structure of a triangular mesh subdivision surface model is established firstly, then a tool contact set is obtained by realizing fast and precise intersection between the mesh model and the section of the tool path based on the structure, tool position points are determined according to the differential geometrical properties of the curved surface positions corresponding to the tool contacts as well as the type and parameters of a milling tool, and finally the tool path is generated by the minimal spanning tree algorithm to sort the point set of the tool positions. Examples prove that the generation method can effectively improve the generation efficiency and precision of the tool path of a complex curved surface model.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for collecting three-dimensional geometric drawing member on pattern processor
ActiveCN101271585AMeet the needs of real-time interactionAvoid switching3D-image renderingGraphicsGeometric primitive
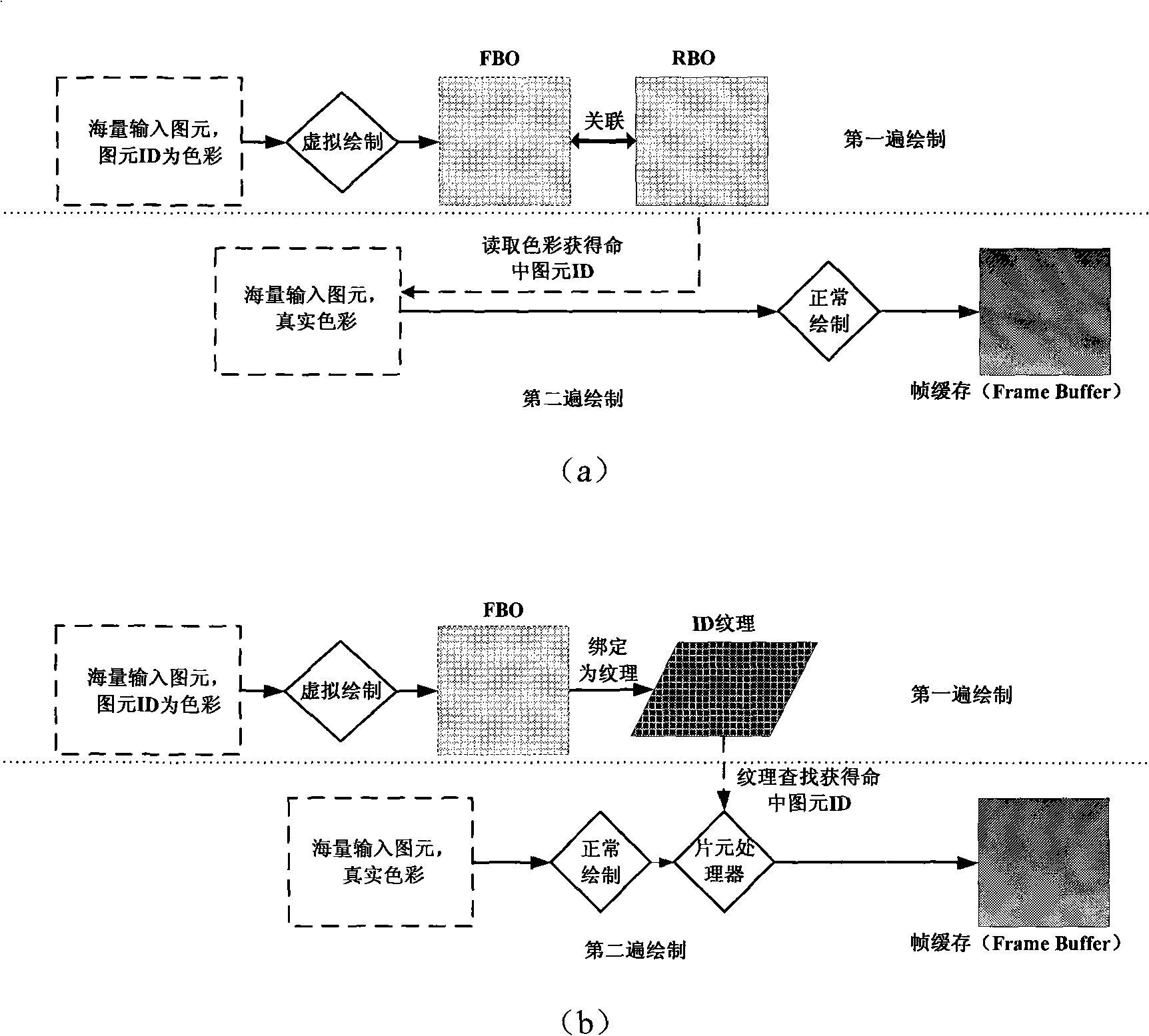
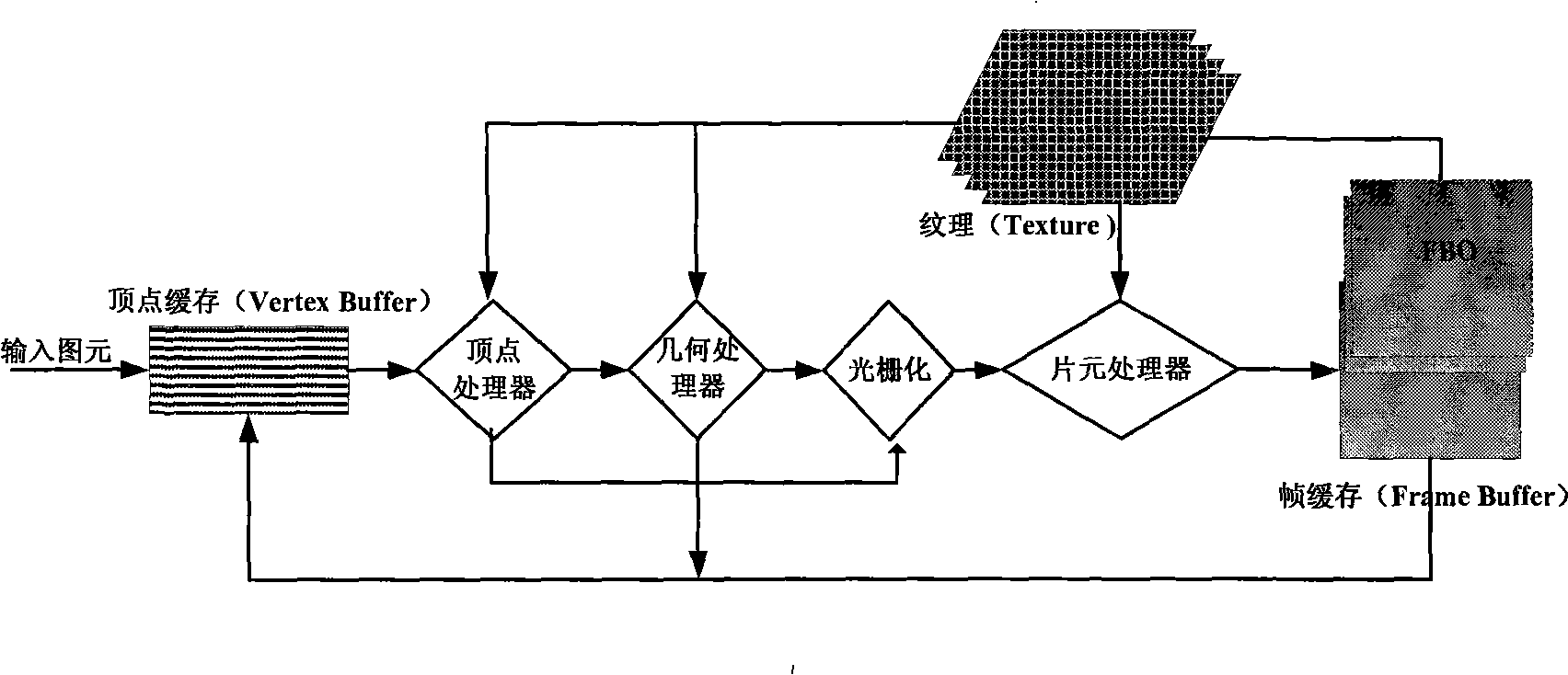
The invention discloses a method picking up a three-dimensional geometric graphic primitive on a graphic processing unit GPU, belonging to the technical field of picking up a mass of graphic primitives. The method draws a three-dimensional graph with an ID code of the geometric graphic primitive to an off-screen buffer FBO on the graphic processing unit GPU; the FBO is associated with a RBO to read the ID of the graphic primitive; or the FBO is bound to a texture, by which a texture research is carried on; thereby the geometric graphic primitive selected by a current mouse hotspot or a geometric graphic primitive set in a choice box selected by the mouse can be obtained fast. The invention is the method based on the graphic processing unit GPU which picks up fast and accurately a complicated geometric model comprising a large number of geometric graphic primitives and also can be applied to a constructor of a characteristic of a subdivision surface to help a user to construct the fine characteristics interactively and fast on the curved surface. The method of picking up the three-dimensional geometric graphic primitive on the graphic processing unit GPU provided by the invention is capable of improving the speed and the precision of a pick-up movement, thereby enhancing the efficiency relating to an interactive operation of the geometric model.
Owner:北京通建泰利特智能系统工程技术有限公司
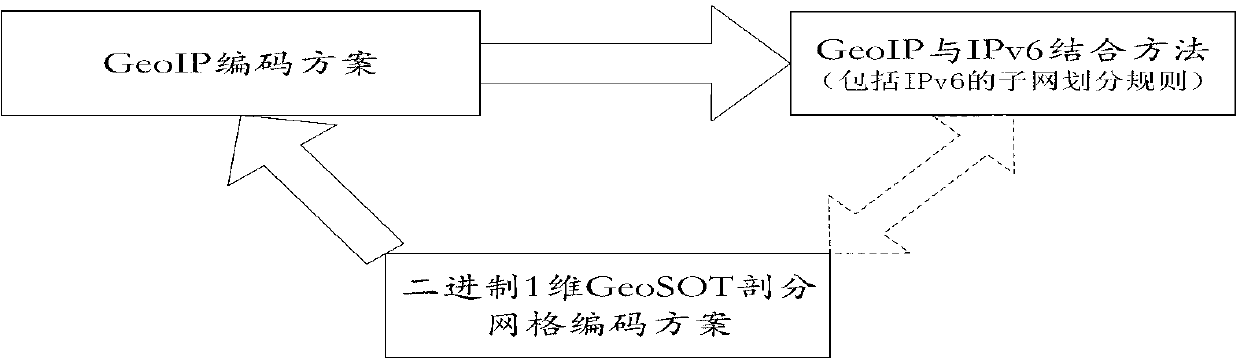
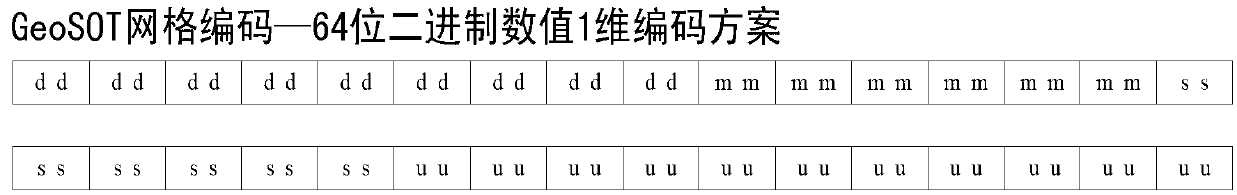
Network address design method and data resource scheduling method based on geographic SOT (GeoSOT) subdivision codes
The invention discloses a network address design method and a data resource scheduling method based on geographic SOT (GeoSOT) subdivision codes, and belongs to the field of geographic space information organizations, geographic information systems and computer networks. The network address design method comprises the steps of obtaining a binary system one-dimensional GeoSOT code containing the smallest GeoSOT subdivision surface patch of a geographic range of user host machine management data resources, obtaining a 64-bit host machine code, enabling a hierarchy where the subdivision surface patch is located to be converted to be a 5-bit binary system code, obtaining a subdivision hierarchy code, combining the subdivision hierarchy code and the host machine code to be a geographic internet protocol (GeoIP) code which serves as rear 69 bits in an internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) address, obtaining a GeoIP address, conducting subnet division on the GeoIP address, and setting a subnet mask. The data resource scheduling method comprises the steps of designing a GeoIP address of a user host machine, confirming a GeoIP address of a receiving host machine by a sending host machine according to the geographic space range which the obtained data relate to, packaging the data and the GeoIP address of the receiving host machine to be a GeoIP data packet, and transmitting the GeoIP data packet to the receiving host machine. The network address design method and the data resource scheduling method based on GeoSOT subdivision codes are applicable to space-time organizations of network space data resources.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Accurate boolean operations for subdivision surfaces and relaxed fitting
An apparatus, method, and computer readable storage medium for accurately performing Boolean operations on subdivision surfaces. The present invention produces a base mesh which subdivides into a surface which represents the Boolean operation of two subdivision surfaces. The method includes (a) chopping pieces of two Catmull-Clark bases meshes which correspond to pieces of a Boolean surface computed from limit surfaces of the two base meshes; (b) creating new edges on the chopped pieces to create quadrilaterals and triangles; and (c) merging the chopped pieces with the new edges into a Boolean base mesh which approximates the Boolean surface.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Wrap deformation using subdivision surfaces
ActiveUS20050168463A1Overcome limitationsMinimizing introductionCooking vesselsCathode-ray tube indicatorsEngineeringSubdivision surface
Deformations are applied to a model using a subdivision surface. Given a wrap and model, a subdivision surface is calculated from the wrap. The model is then bound to the subdivision surface. When the wrap is deformed, the subdivision surface is recalculated. The model is then deformed based on changes in the subdivision surface. Binding parameters may be assigned to control vertices in the wrap to control the application of the deformation to the surface.
Owner:DREAMWORKS ANIMATION LLC
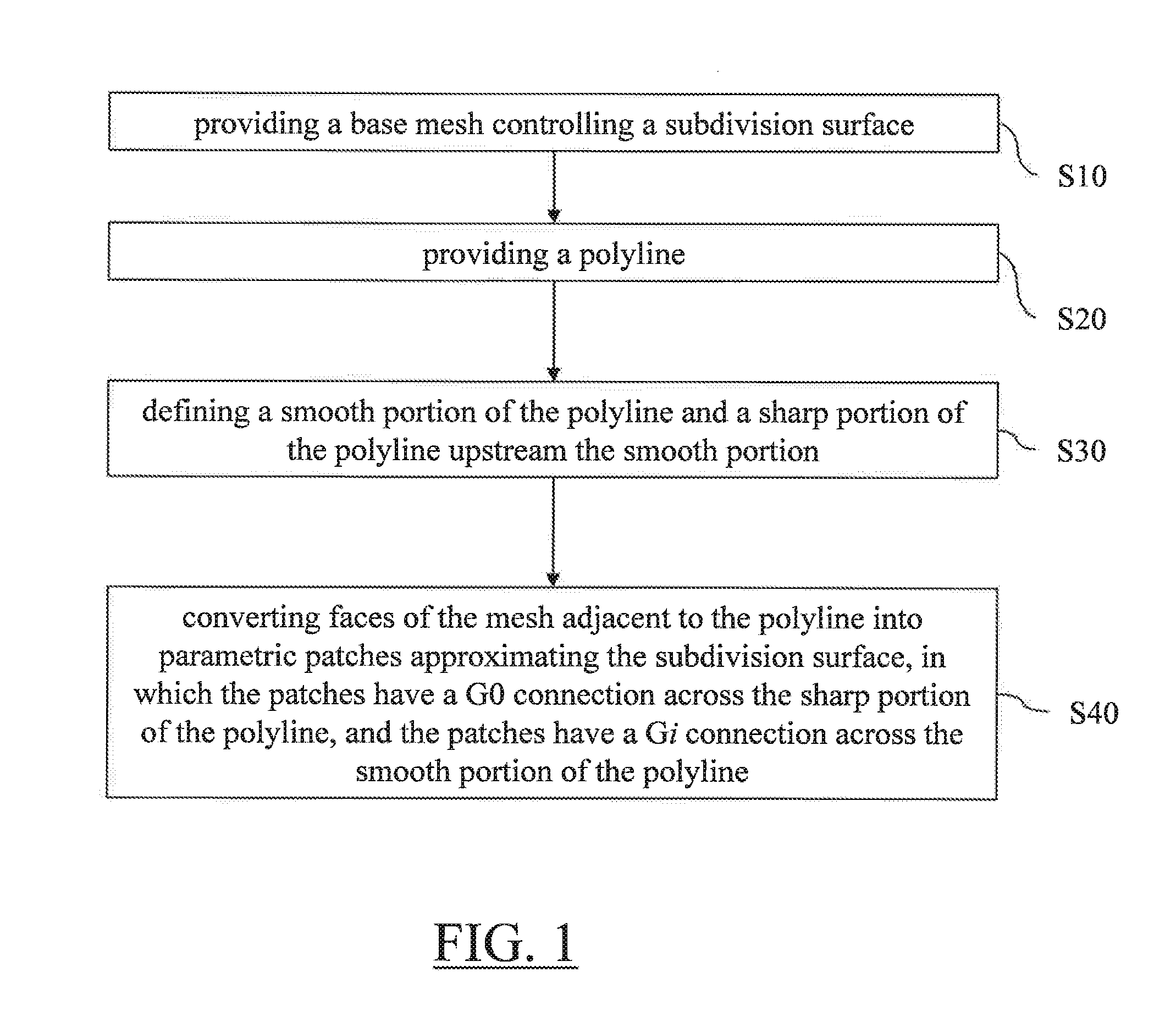
Designing A 3D Modeled Object
ActiveUS20130293541A1Geometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsPolygonal lineComputer science
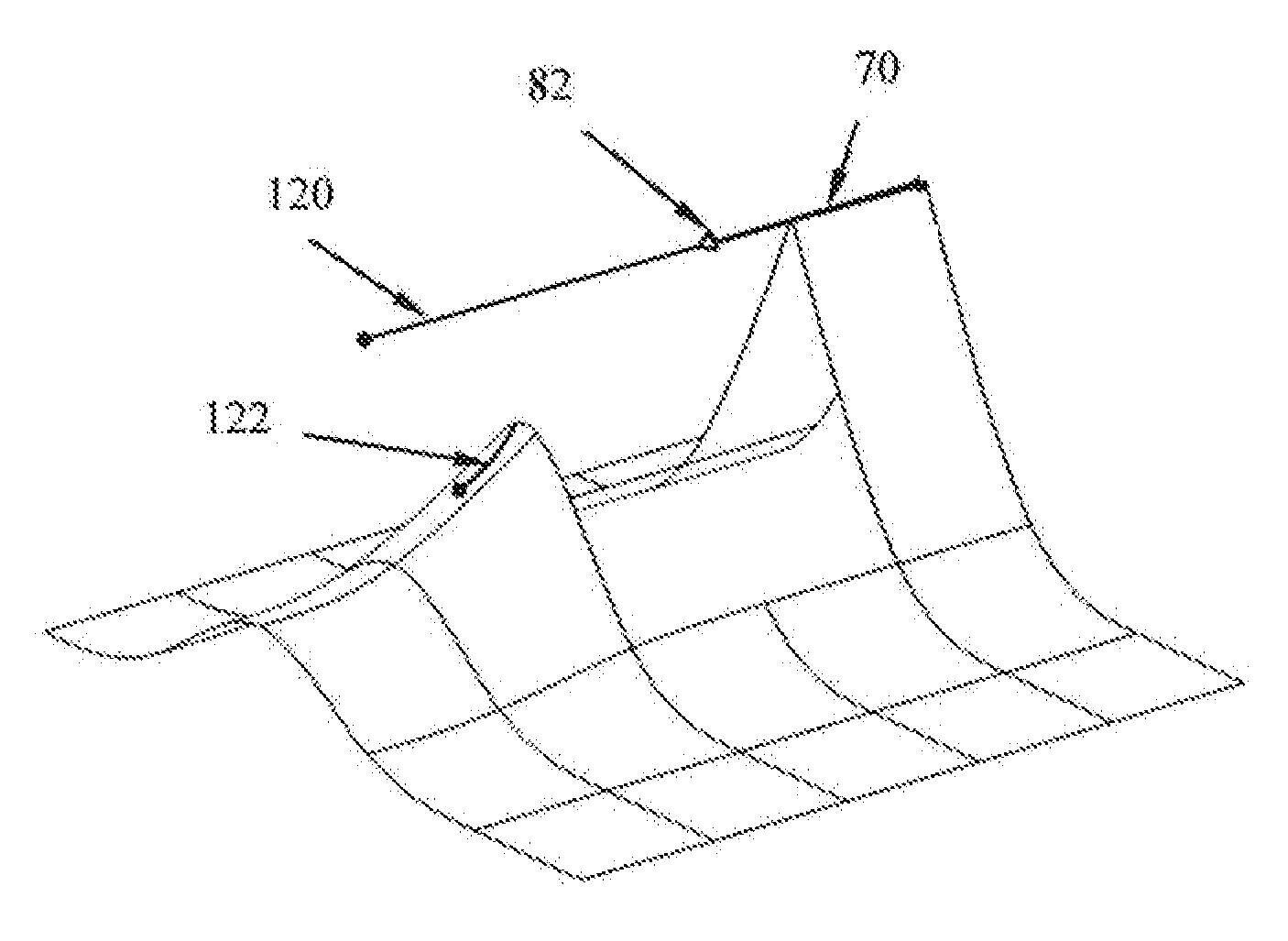
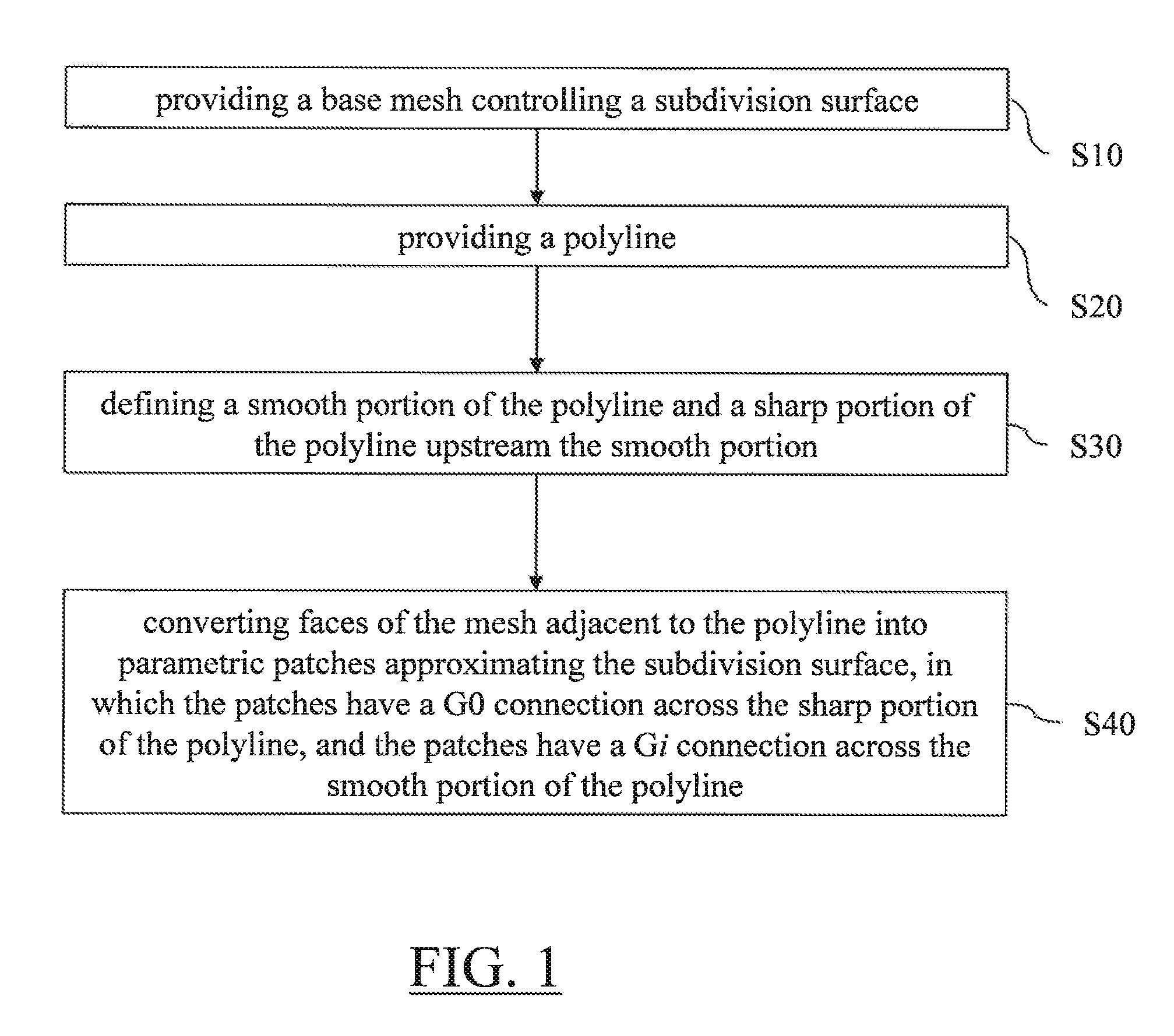
It is provided a computer-implemented method for designing a 3D modeled object. The method comprises providing a base mesh controlling a subdivision surface. The subdivision surface models the 3D modeled object. The method also comprises providing a polyline consisting of connected edges of the base mesh and defining a smooth portion of the polyline comprising an extremity of the polyline and a sharp portion of the polyline upstream the smooth portion. The method also comprises converting faces of the mesh adjacent to the polyline into parametric patches approximating the subdivision surface. The patches have a G0 connection across the sharp portion of the polyline, and the patches have a Gi connection across the smooth portion of the polyline, where i is an integer higher or equal to 1.Such a method improves the design of a 3D modeled object modeled by a subdivision surface.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES
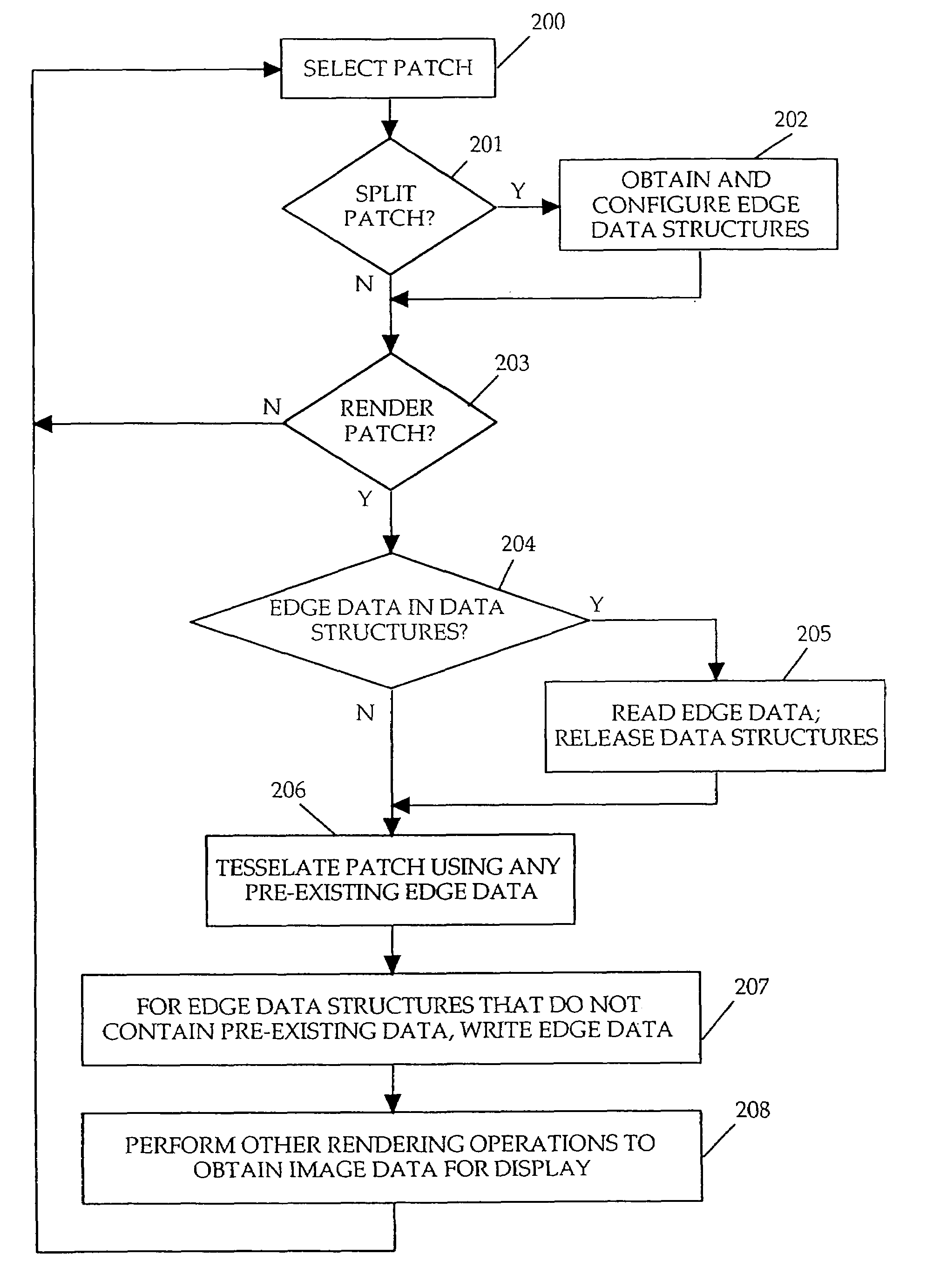
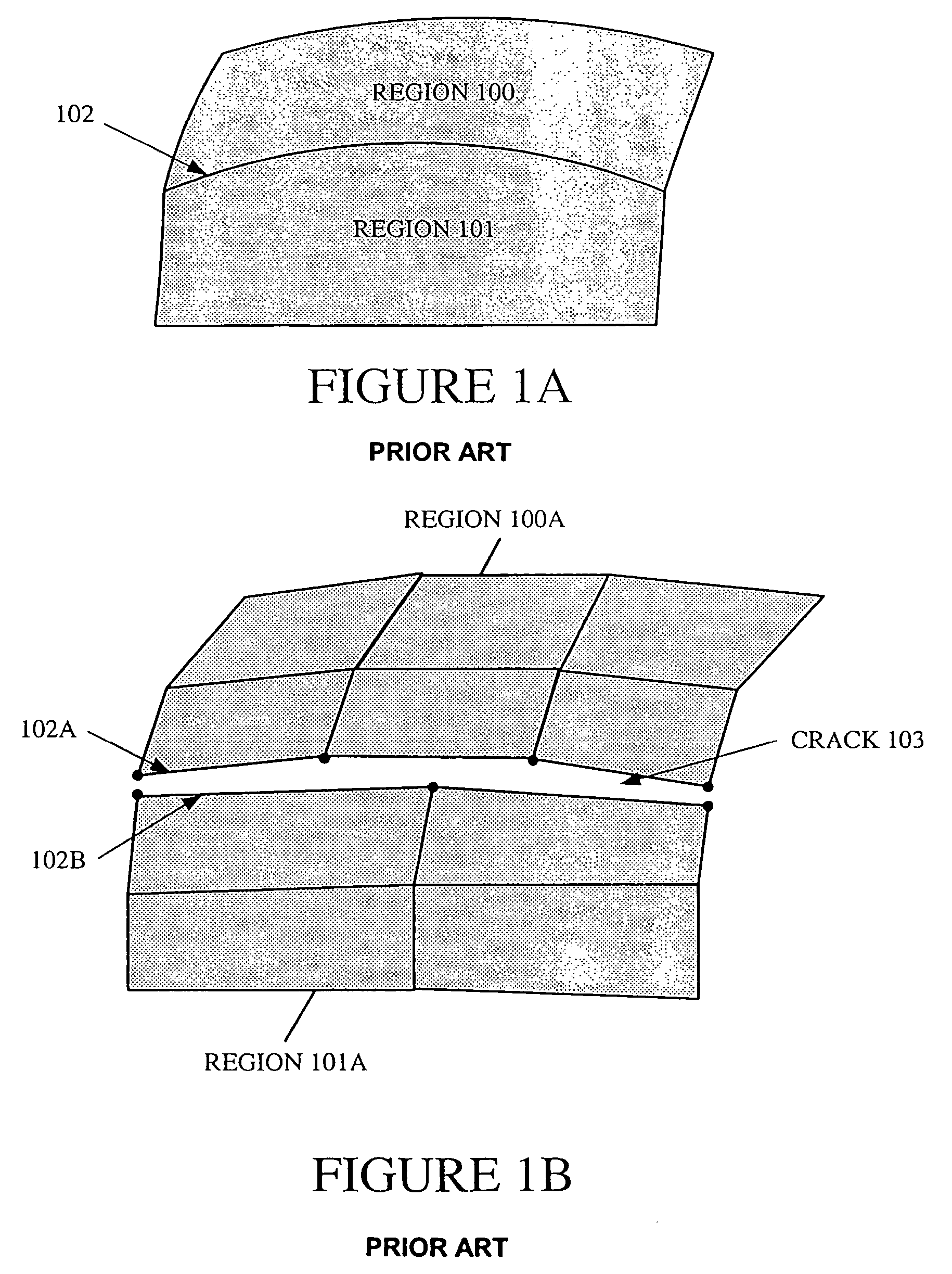
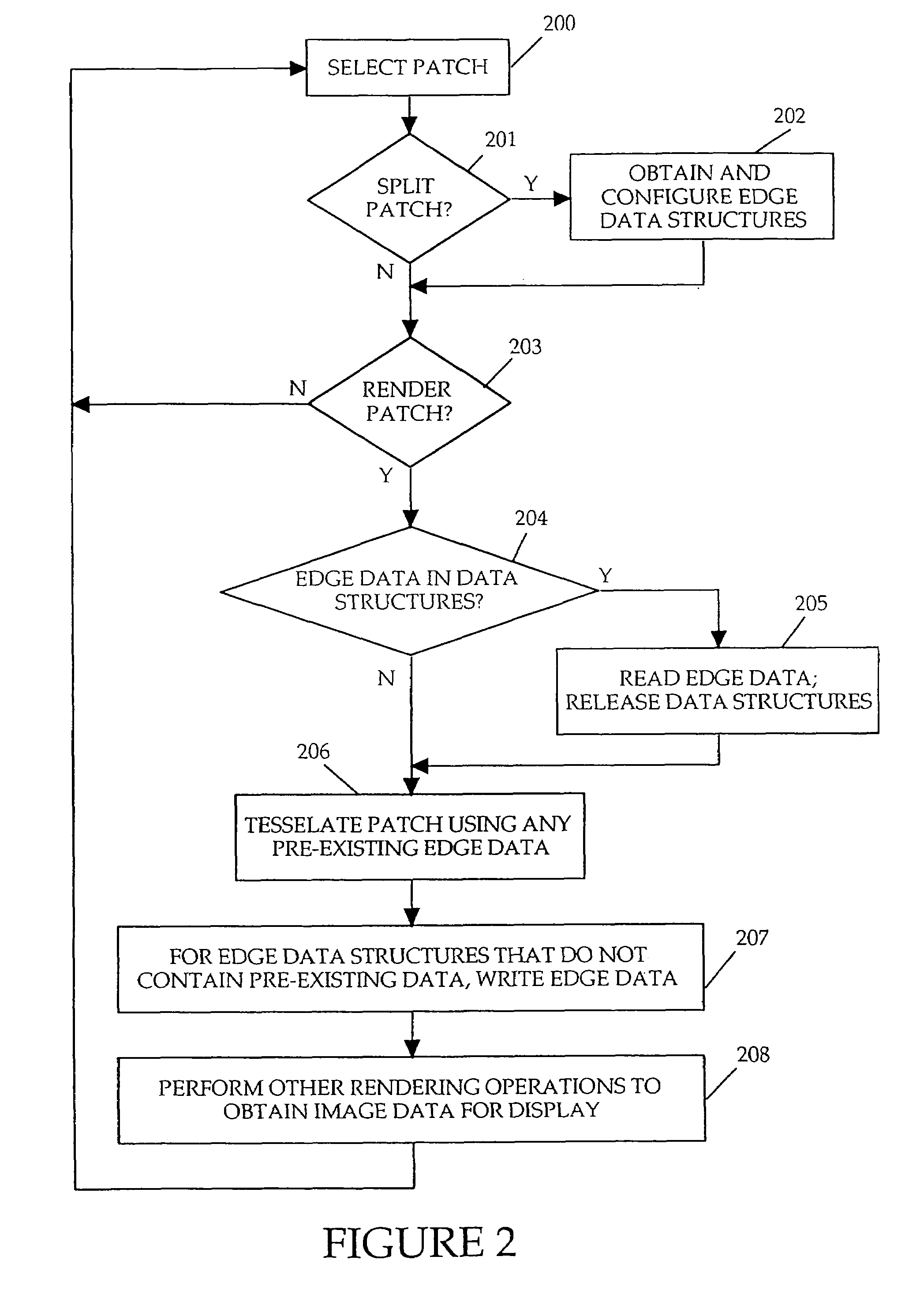
Method and apparatus for surface approximation without cracks
InactiveUS7277096B2Shorten the timeReduce memory requirements3D-image rendering3D modellingComputer scienceT-vertices
A method and apparatus for surface approximation without cracks. In one or more embodiments, a surface to be rendered is split into multiple adjacent regions (e.g., subdivision surfaces or patches). A data structure is associated with each boundary edge between two regions for storage of adjacency information in the form of a sequence of tessellation vertices. Adjacency information for a given edge is written into the data structure when an adjacent region is first tessellated. When the remaining adjacent region is tessellated, the adjacency information is read from the data structure and used to achieve tessellation without cracks. In one embodiment, visible cracks due to T-vertices are prevented by forming an overlap of adjacent regions at the location of each T-vertex. This technique allows regions to be tessellated and rendered without any advance knowledge of how the adjacent regions will be split. The regions may be tessellated and rendered separately and in any order, reducing time and memory requirements for rendering.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
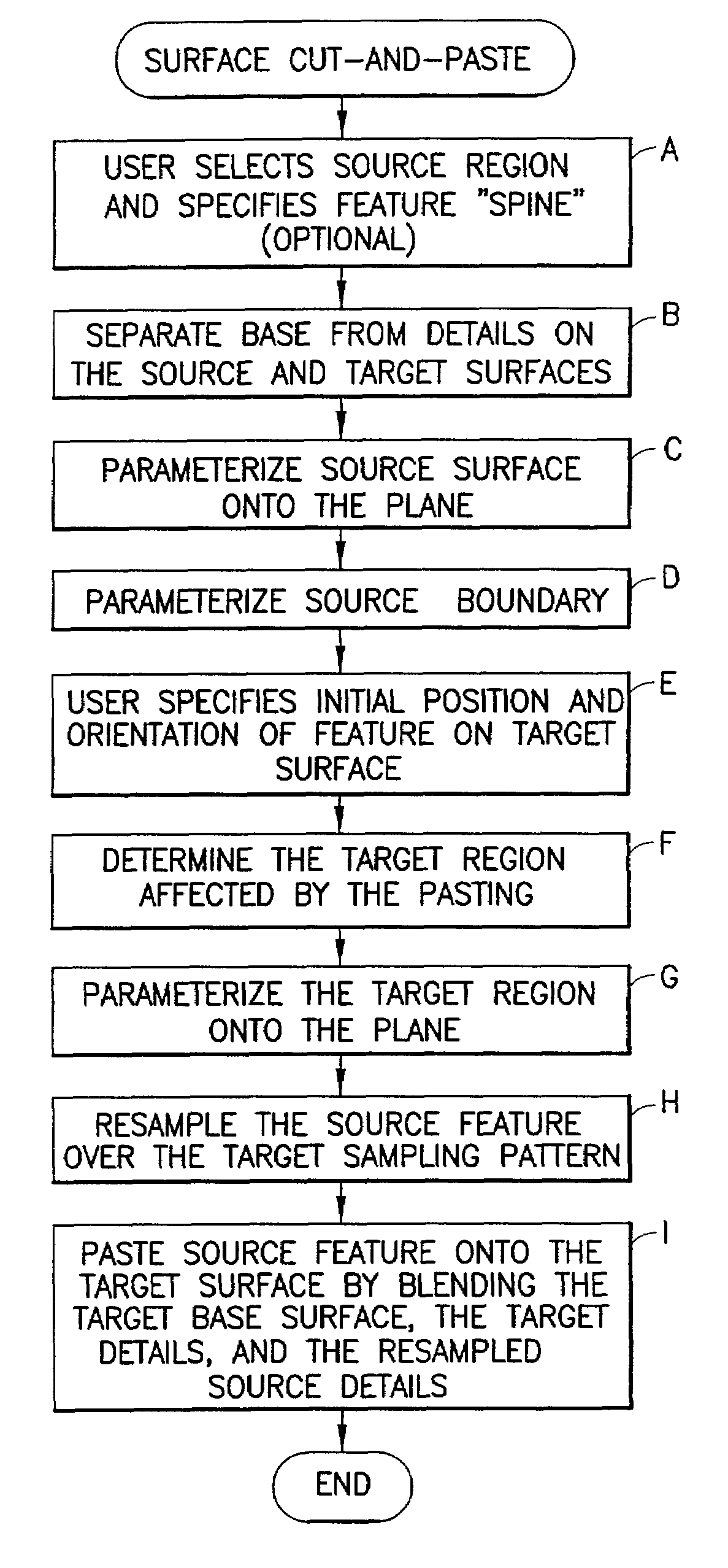
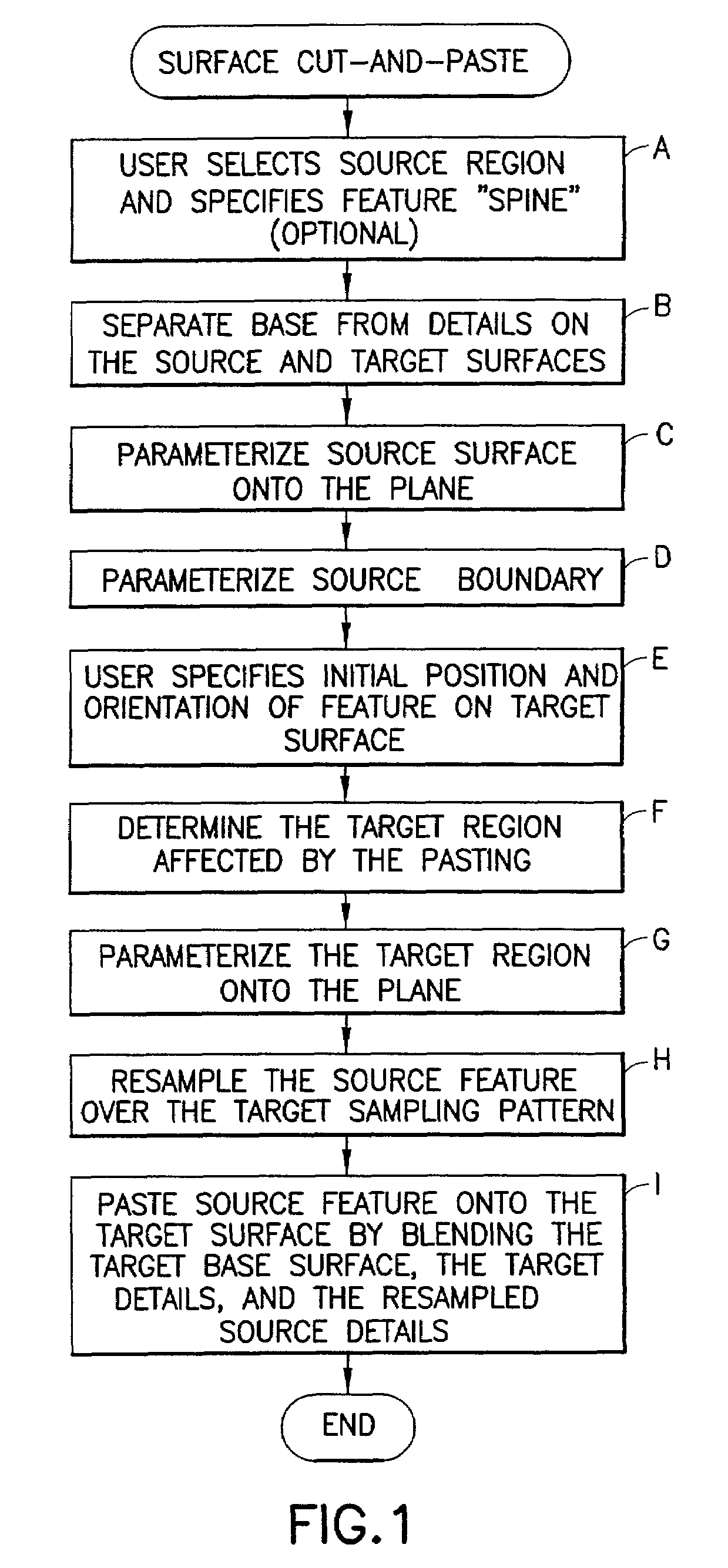
Methods and apparatus for cut-and-paste editing of multiresolution surfaces
In this invention there are described a set of algorithms based on multiresolution subdivision surfaces that perform at interactive rates and enable intuitive surface cut-and-paste operations. The method includes separating a source region of interest of a source surface into a source base surface and a source detail surface; separating a target region of interest of a target surface into a target base surface and a target detail surface; and pasting the source detail surface onto the target base surface in accordance with a mapping. The step of pasting includes parameterizing and mapping the parameterized regions of interest of the source and target surfaces into an intermediate plane, and aligning the parameterizations using a linear transformation that compensates for first order distortions.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Machining method for improving form and position precision of large gearbox body device
InactiveCN105750601AImprove finishing efficiencyReduce adjustment and deformation errorsMilling equipment detailsOther workshop equipmentEngineeringMachine tool
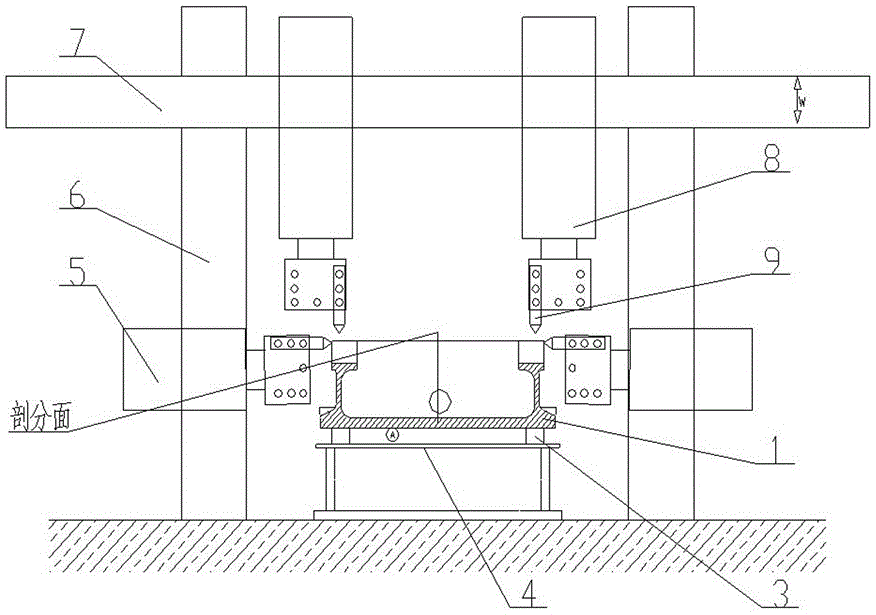
The invention relates to a machining method for improving the form and position precision of a large gearbox body device. The processing method comprises the following steps: marking out, performing rough machining on the subdivision surface and a semi-axle hole of each separated gearbox body, performing artificial failure, marking out secondarily, carrying out semifinishing on the subdivision surface and the semi-axle hole of each separated gearbox body, performing natural failure, performing finishing on the subdivision surface of each separated gearbox body, assembling a gearbox body device, performing finishing on the axle holes of the gearbox body device, and checking finally. According to the machining method, since semifinishing and finishing of each separated gearbox body and the gearbox device are performed by the same machine tool on the same locating basis, the machining precision is greatly improved.
Owner:CITIC HEAVY INDUSTRIES CO LTD
System, method, and program product for extracting a multiresolution quadrilateral-based subdivision surface representation from an arbitrary two-manifold polygon mesh
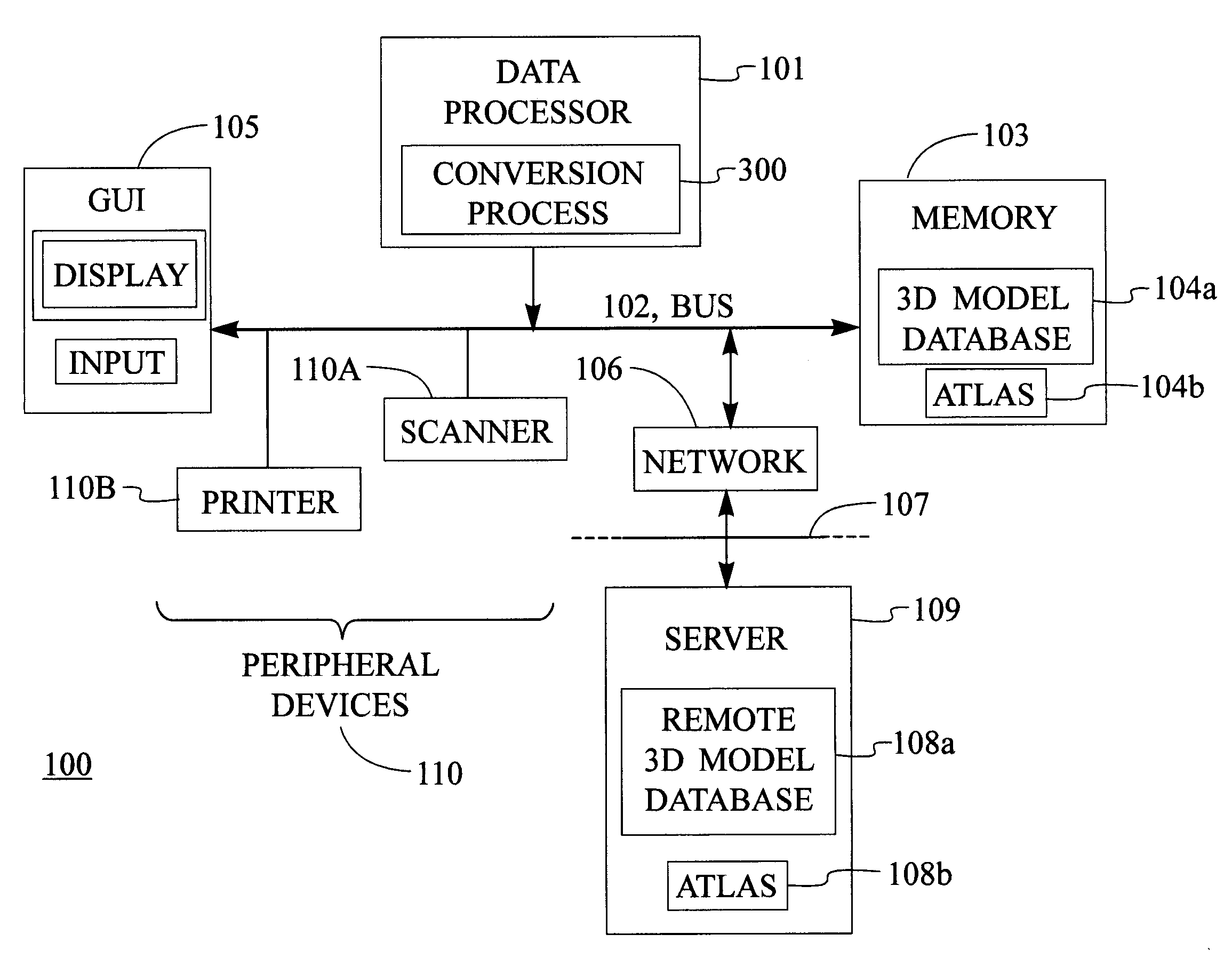
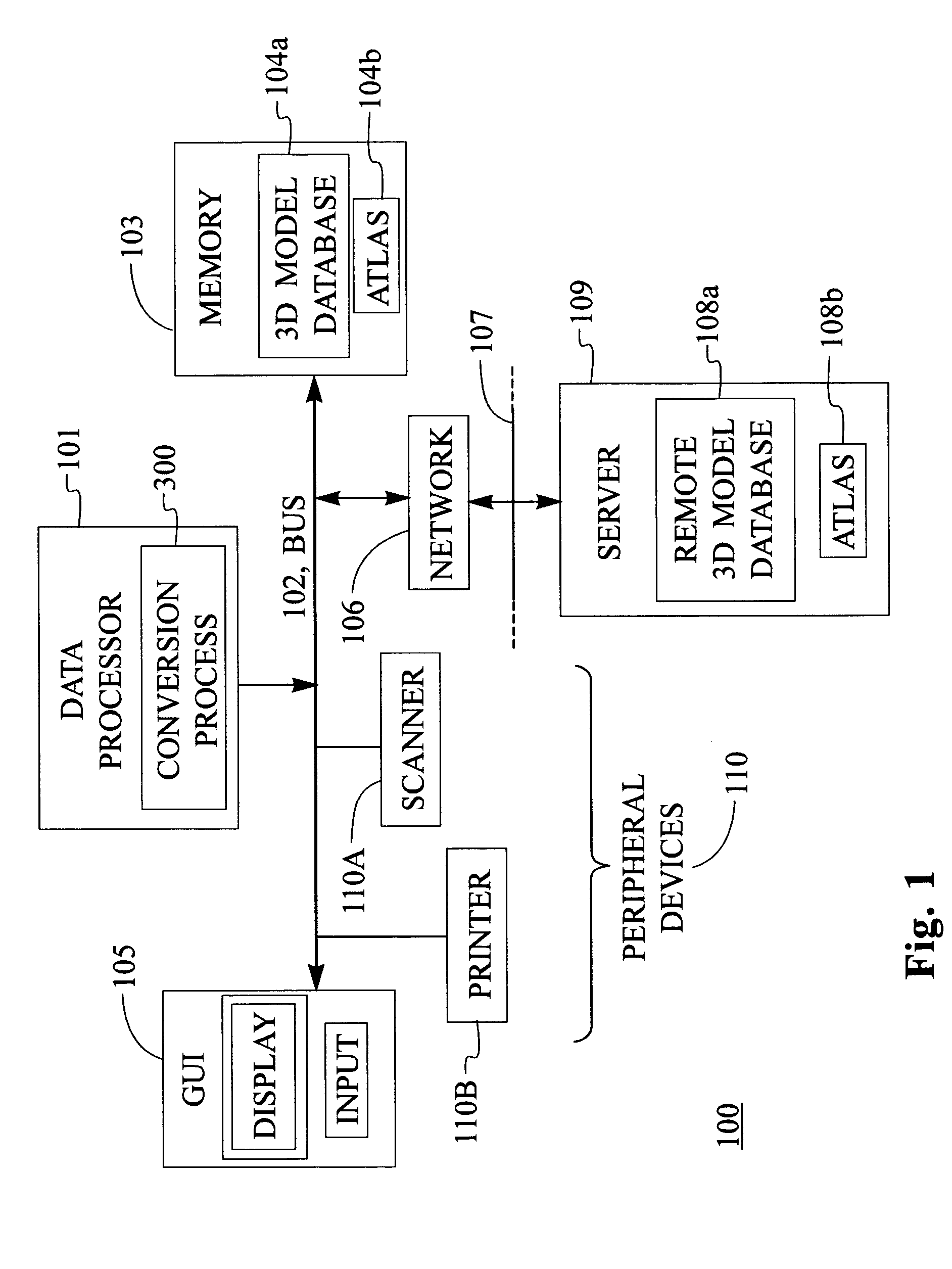
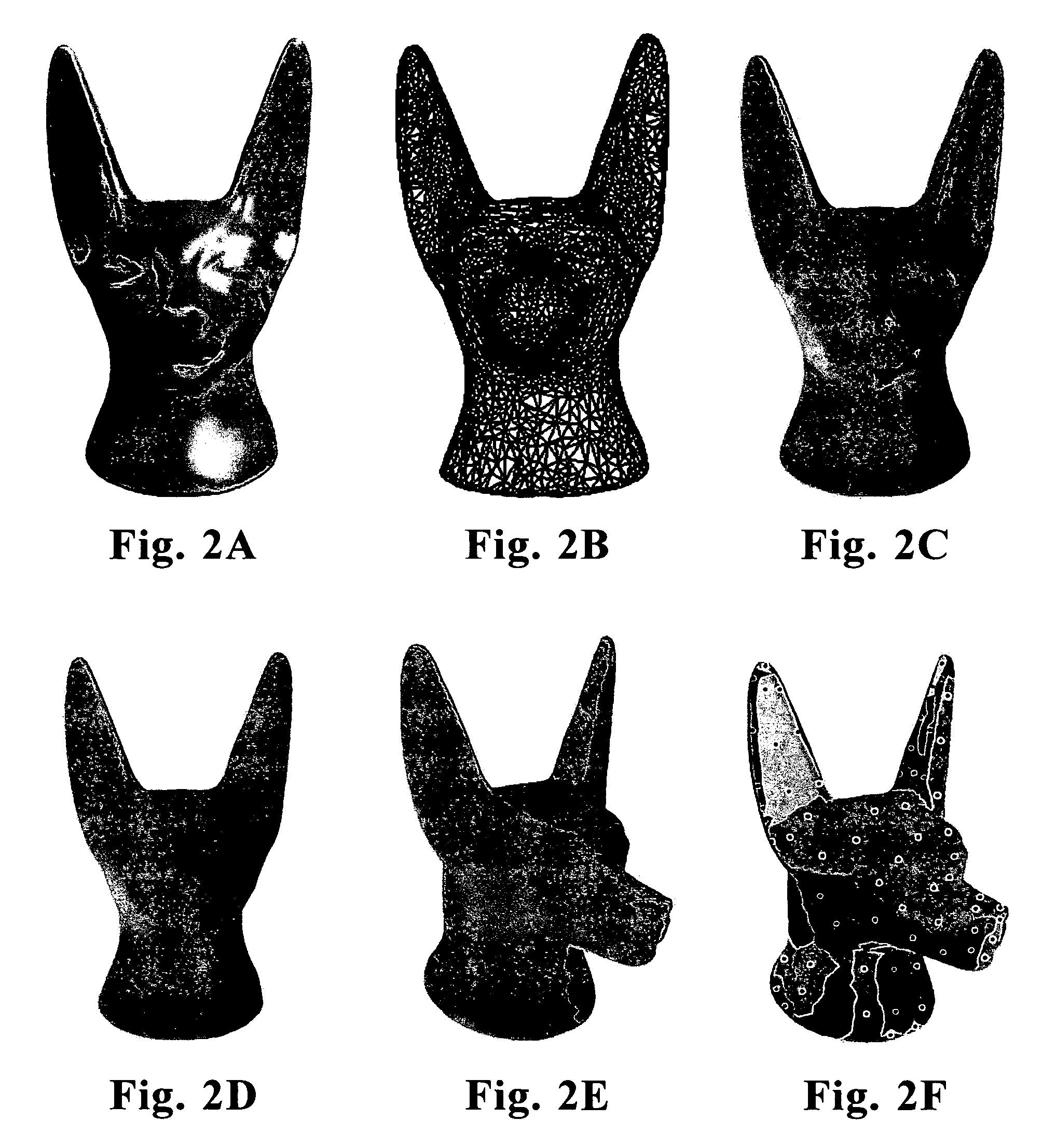
Disclosed is an improved computer system, method, and program product that has one or more input devices for receiving one or more input meshes representing a three dimensional model. The three dimensional model is capable of being represented as a 2-manifold triangular mesh. A conversion process automatically converts the input mesh to a multiresolution quadrilateral-based subdivision surface (MQSS) representation.
Owner:IBM CORP
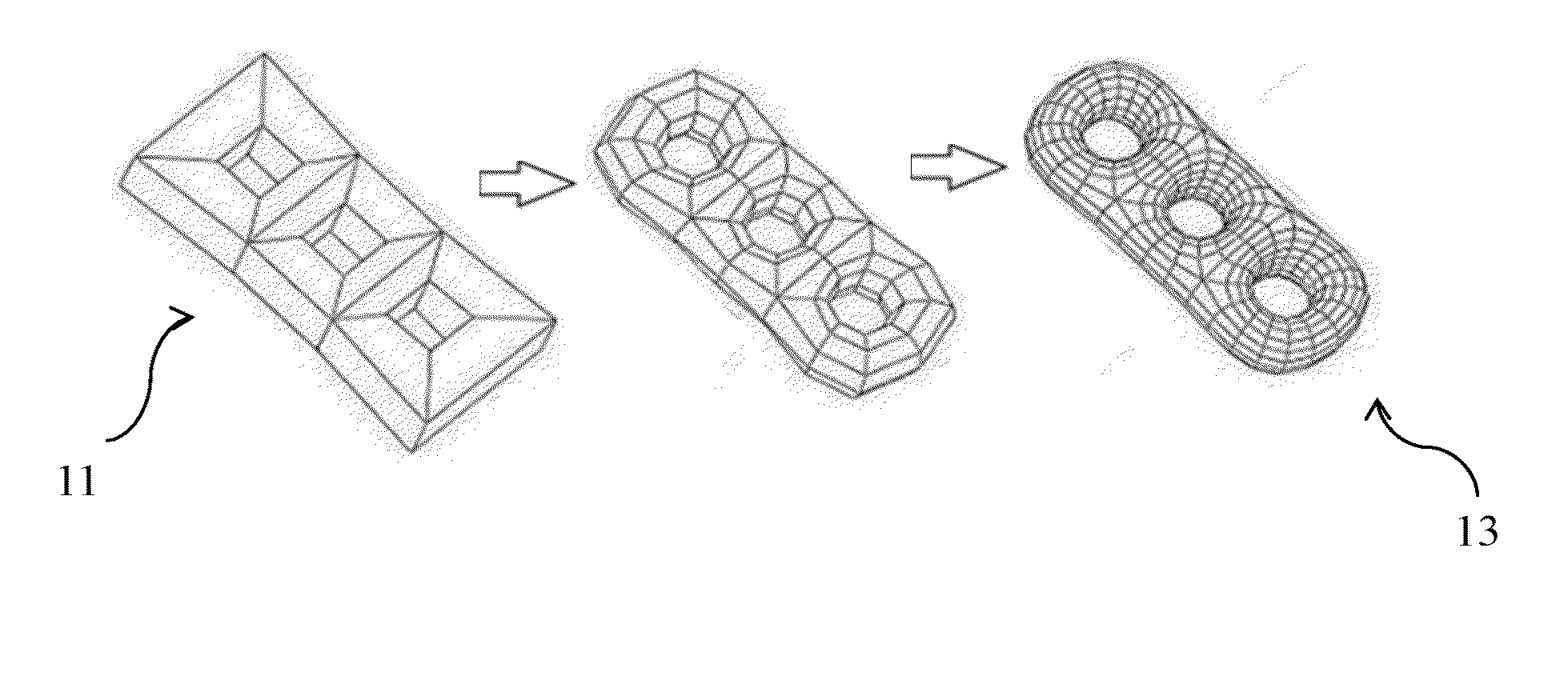
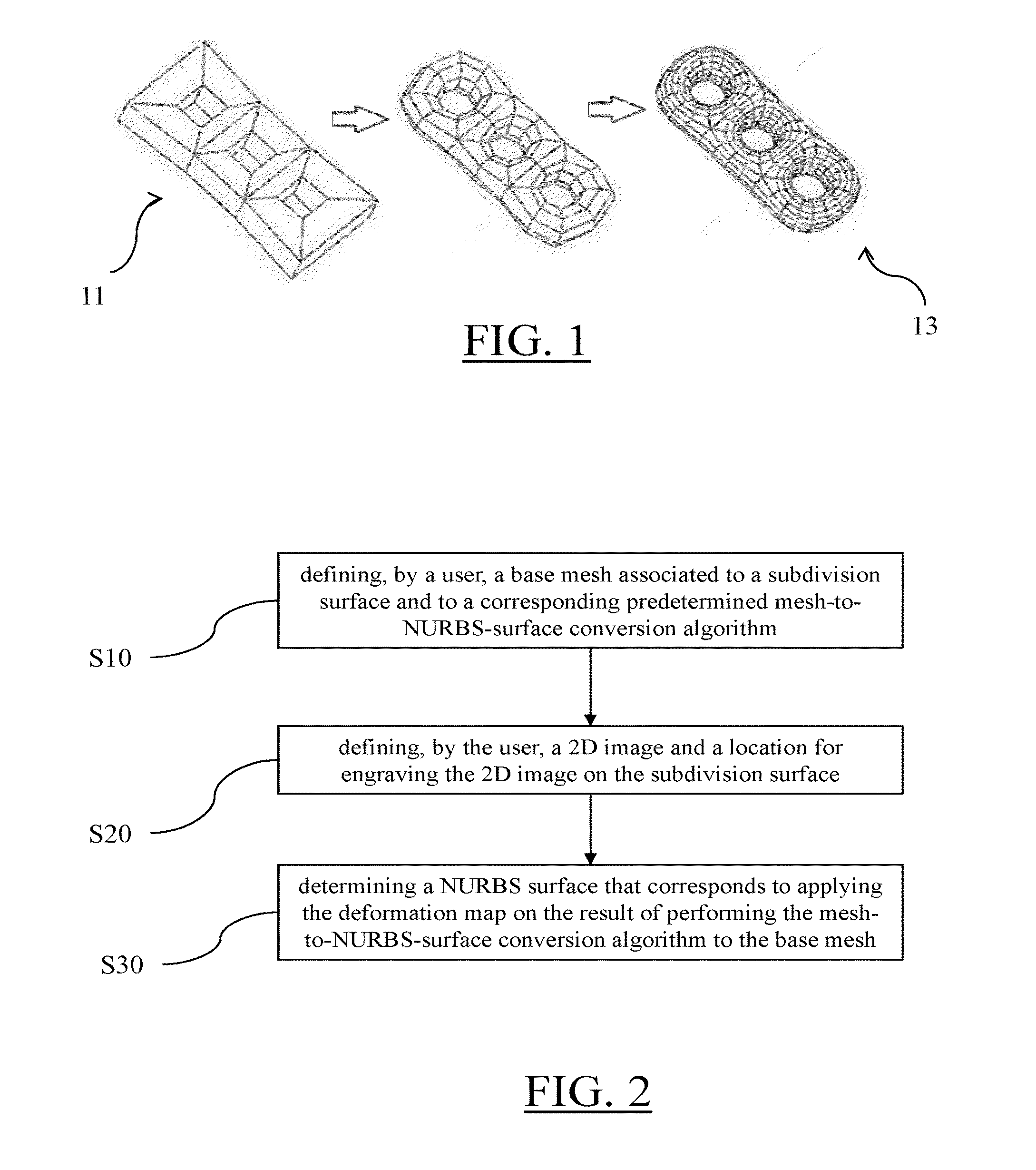
Engraving a 2d image on a subdivision surface
ActiveUS20160224693A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsTransformation algorithmMesh grid
It is the method comprising the steps of defining, by a user, a base mesh associated to a subdivision surface and to a corresponding predetermined mesh-to-NURBS-surface conversion algorithm, the subdivision surface representing the 3D modeled object; defining, by the user, a 2D image and a location for engraving the 2D image on the subdivision surface; and determining a NURBS surface that corresponds to applying a deformation map on the result of performing the mesh-to-NURBS-surface conversion algorithm to the base mesh, the deformation map including displacement vectors provided for positions of the result of performing the mesh-to-NURBS-surface conversion algorithm to the base mesh, the positions corresponding to the location for engraving the 2D image, the displacement vectors being computed based on corresponding pixel values of the 2D image. Such a method improves the design of a 3D modeled object.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES
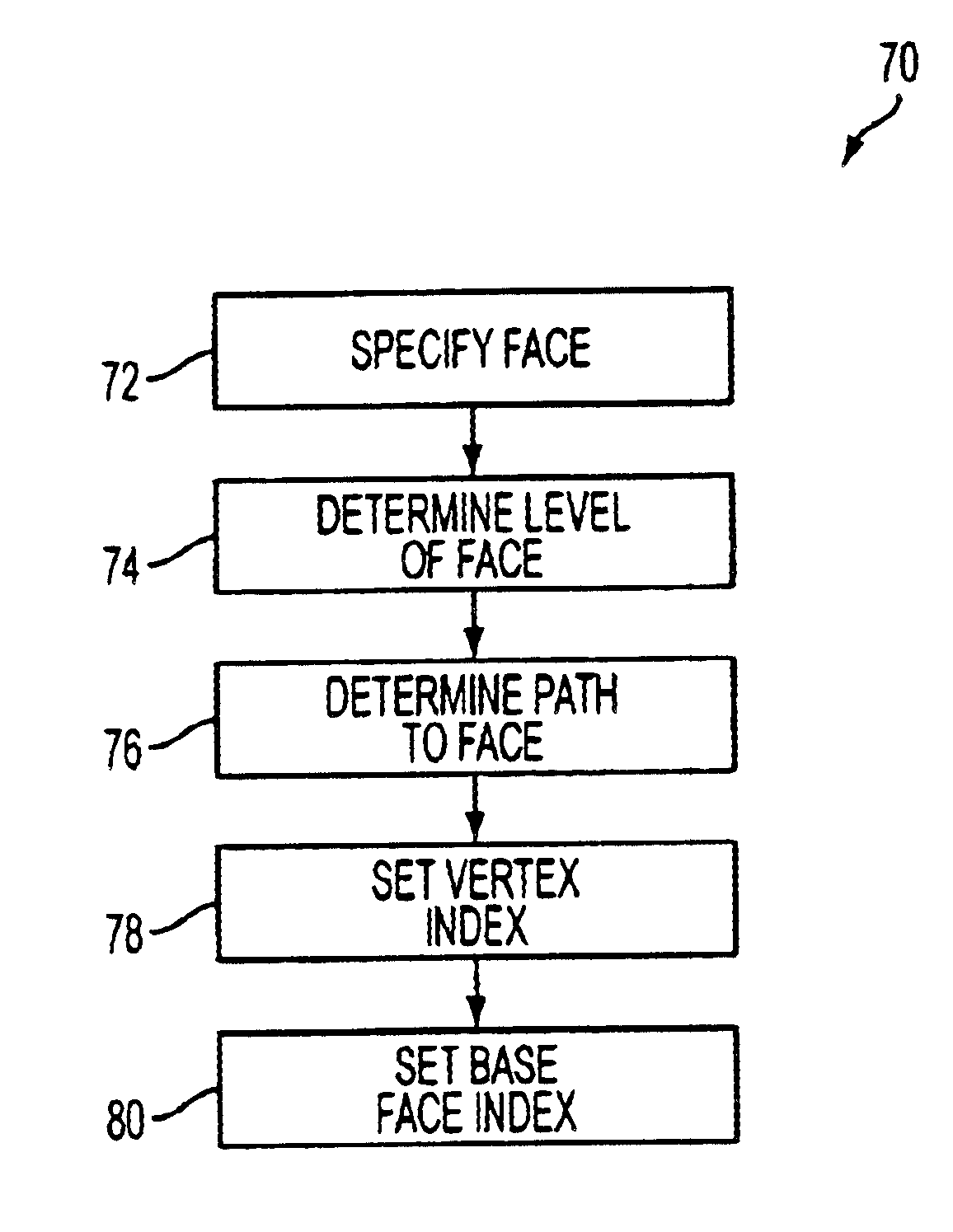
System for naming faces and vertices in an adaptive hierarchical subdivision surface
InactiveUS6850638B1Improve system efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognition3D modellingArtificial intelligenceFixed length
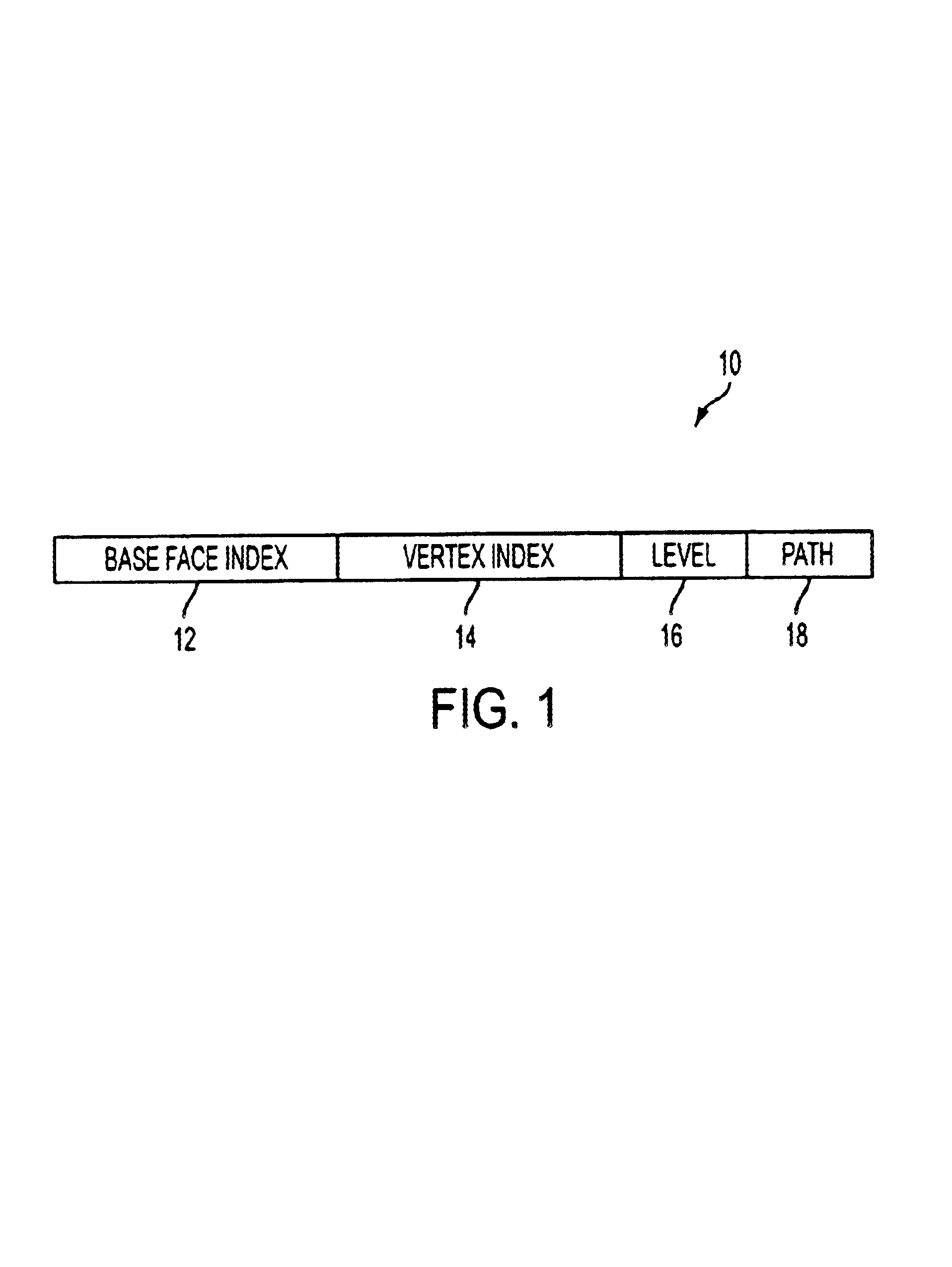
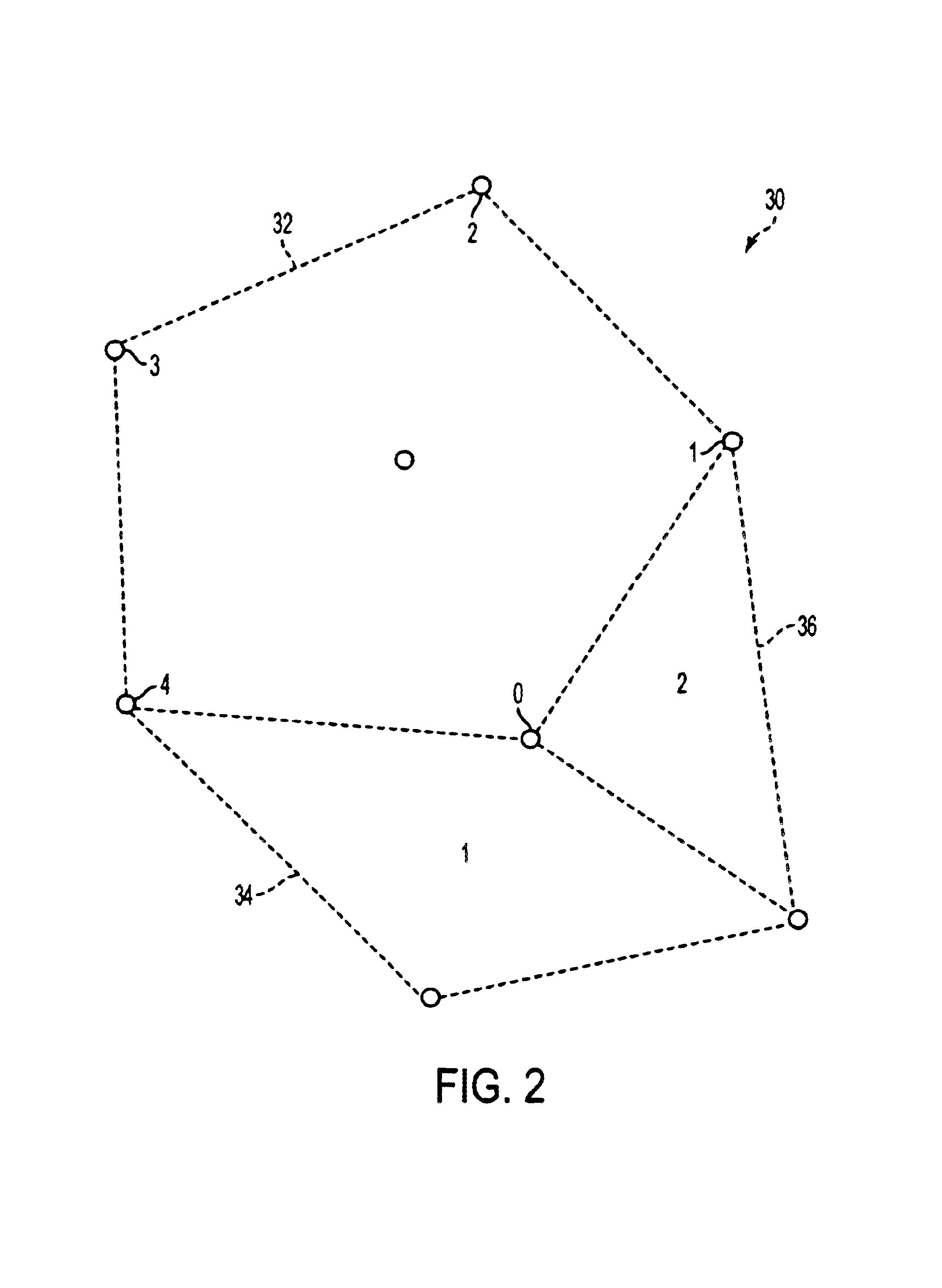
The present invention assigns a unique name or identifier to a face of a subdivision surface that can be stored and manipulated as a fixed length integer. The face name representation includes a base face index field identifying the base mesh face from which the face being named is derived, a vertex index field identifying the base mesh vertex from which the face is derived, a level field identifying the level of the subdivision face and a path field that identifies the path to the face. The vertices and edges of each face can also be assigned unique names.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
System, method, and program product for re-parameterizing three dimensional models represented as catmull-clark subdivision surfaces
InactiveUS20090102833A1Computation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsComputational physicsMechanical engineering
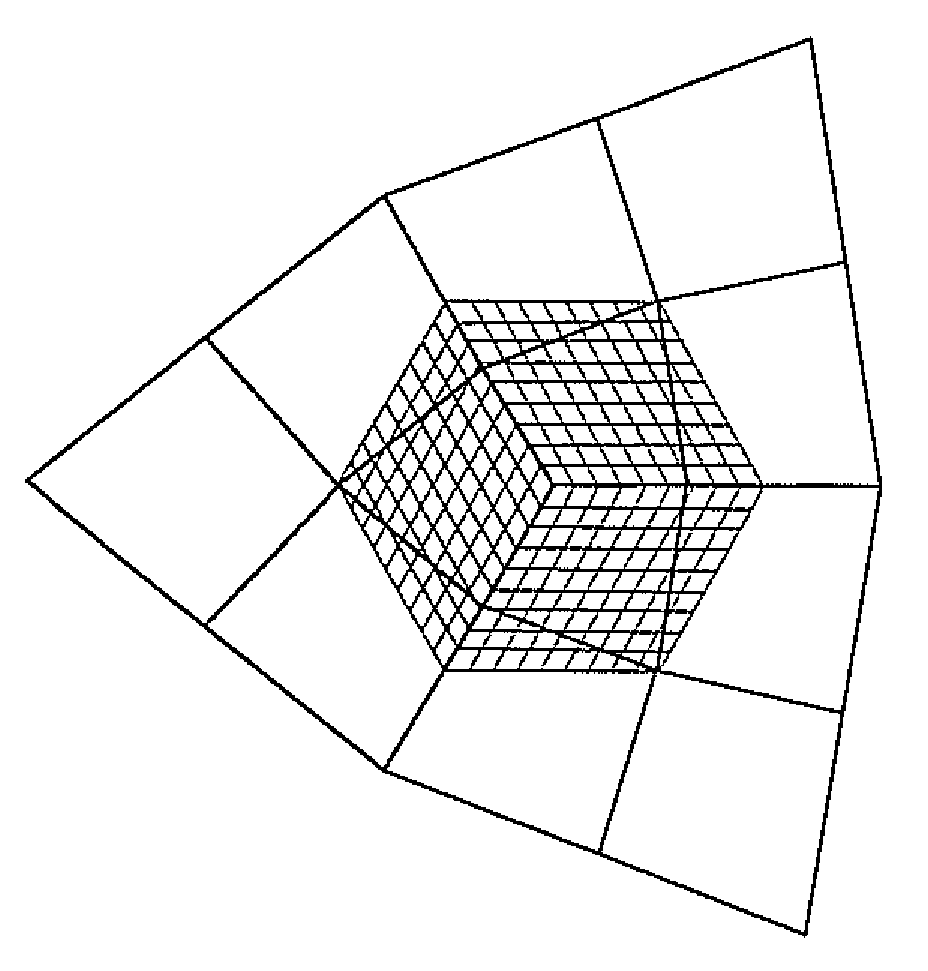
A system, method, and program product for re-parameterizing one or more three-dimensional Catmull-Clark models is disclosed. Each of the models has one or more surfaces and one or more extraordinary vertices. One or more adjacent iso-parameter lines of the model have a spacing between them that increases as the iso-parameter lines approach the extraordinary vertex. A re-parameterization process that re-parameterizes the model so that one or more of the extraordinary vertices have adjacent iso-parameter lines with spacing that does not increase as the lines approach the extraordinary vertex.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Interpolation processing method, interpolation processing device, shape evaluation method, and shape evaluation device
InactiveUS8228329B2Enormous amount of operation processingEasy to operateDrawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionShortest distanceShort distance
An initial polygon obtained from a point group is used as a control polygon, and a control point of the control polygon is offset in a normal direction by the shortest distance from a limit surface generated by the control polygon, so that the position of new control point is determined to allow a subdivision surface to interpolate the initial polygon, thereby generating the subdivision surface which interpolates the point group. A first process to determine the point on the subdivision surface at the shortest distance from each control point, and a second process to move and offset the control point in the normal direction from the surface by the distance between the point on the surface and the initial control point, are iterated until the distance between the initial point group and the point on the surface satisfies the threshold or becomes smaller than the threshold, thereby generating the subdivision surface interpolating the initial polygon. Consequently, the subdivision surface interpolating the point group is generated within a short operation time period, without solving a linear system.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA NAT UNIV
Designing a 3D modeled object
It is provided a computer-implemented method for designing a 3D modeled object. The method comprises providing a base mesh controlling a subdivision surface. The subdivision surface models the 3D modeled object. The method also comprises providing a polyline consisting of connected edges of the base mesh and defining a smooth portion of the polyline comprising an extremity of the polyline and a sharp portion of the polyline upstream the smooth portion. The method also comprises converting faces of the mesh adjacent to the polyline into parametric patches approximating the subdivision surface. The patches have a G0 connection across the sharp portion of the polyline, and the patches have a Gi connection across the smooth portion of the polyline, where i is an integer higher or equal to 1.Such a method improves the design of a 3D modeled object modeled by a subdivision surface.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES
Electrical property evaluation method and device for radome
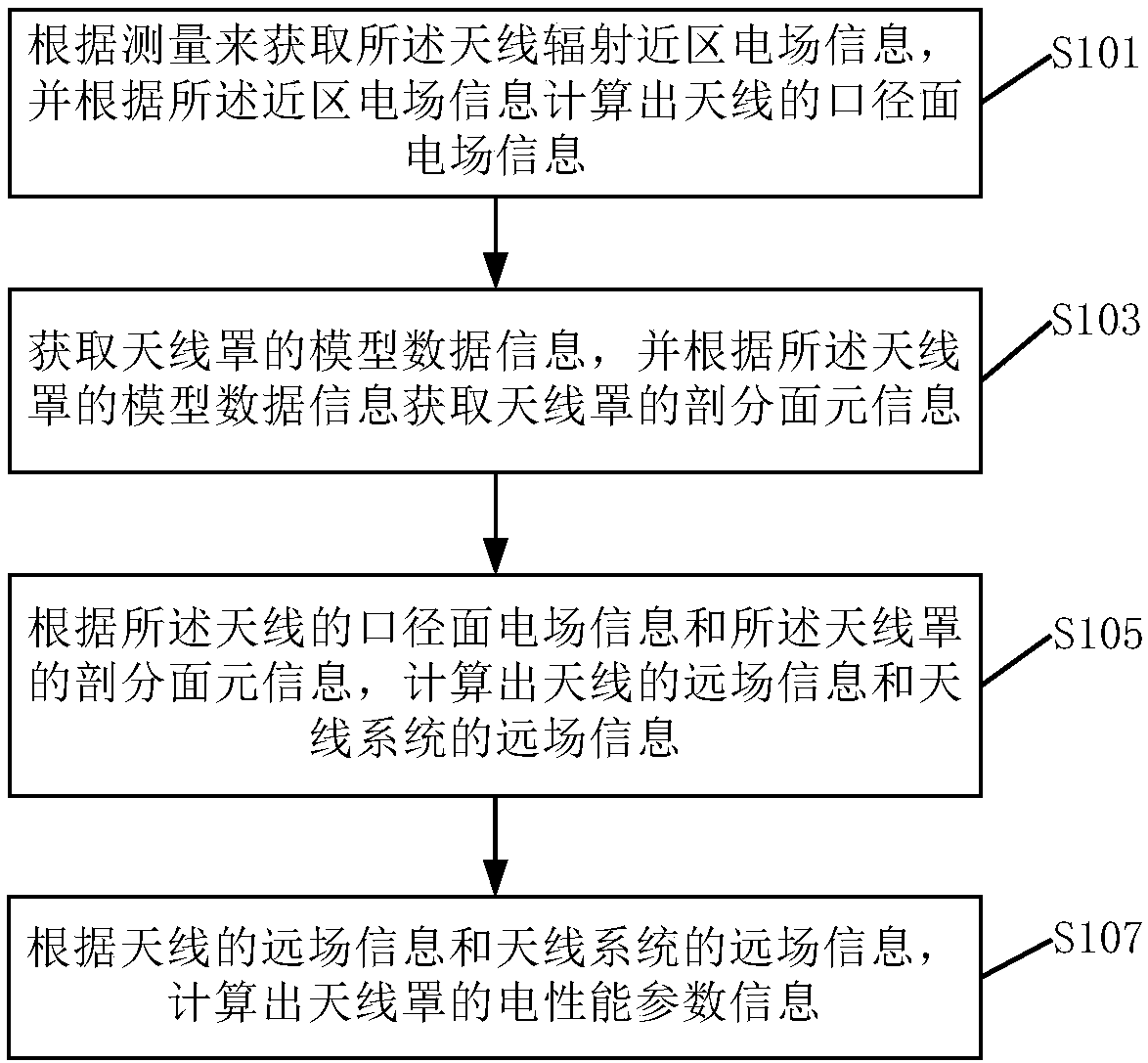
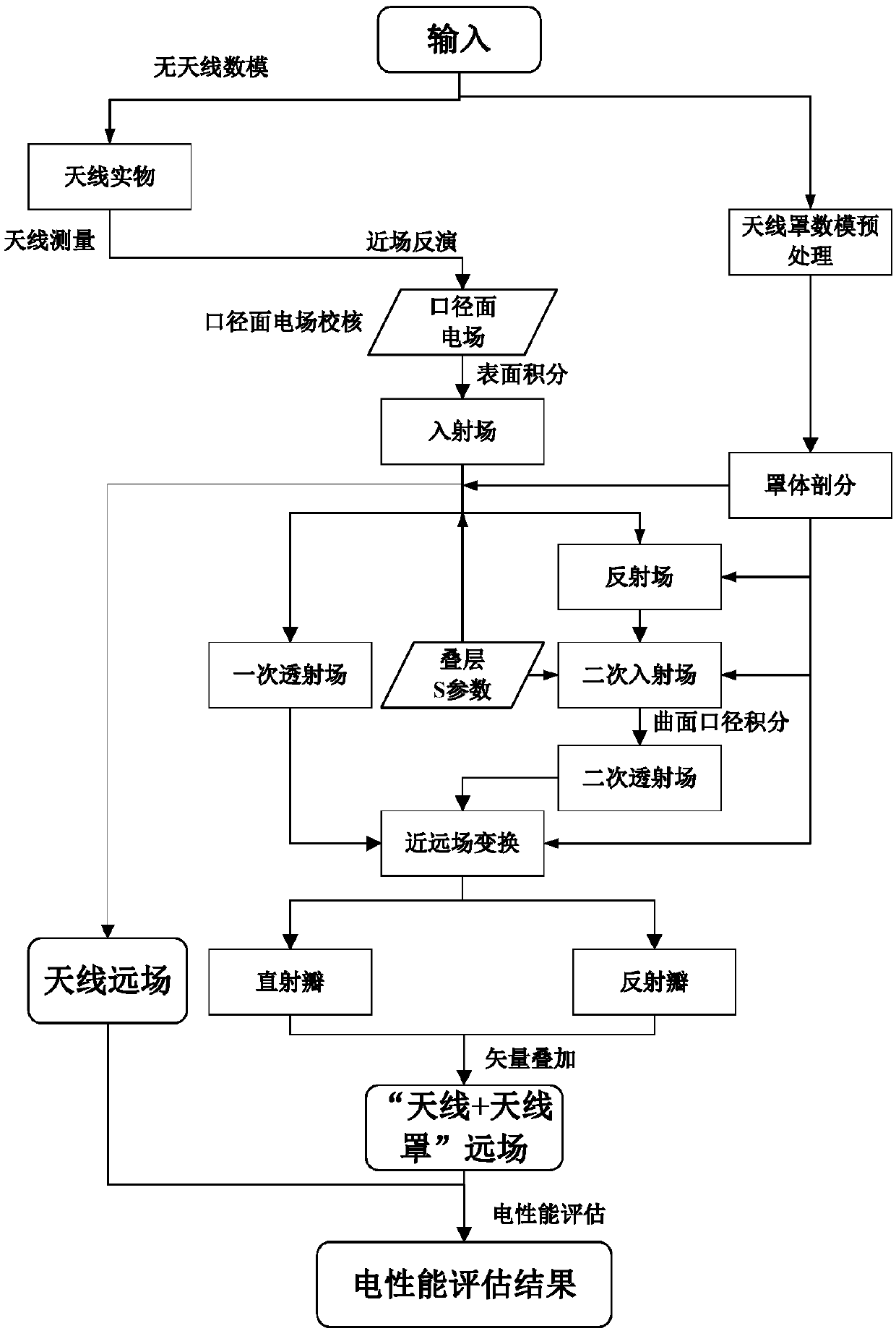
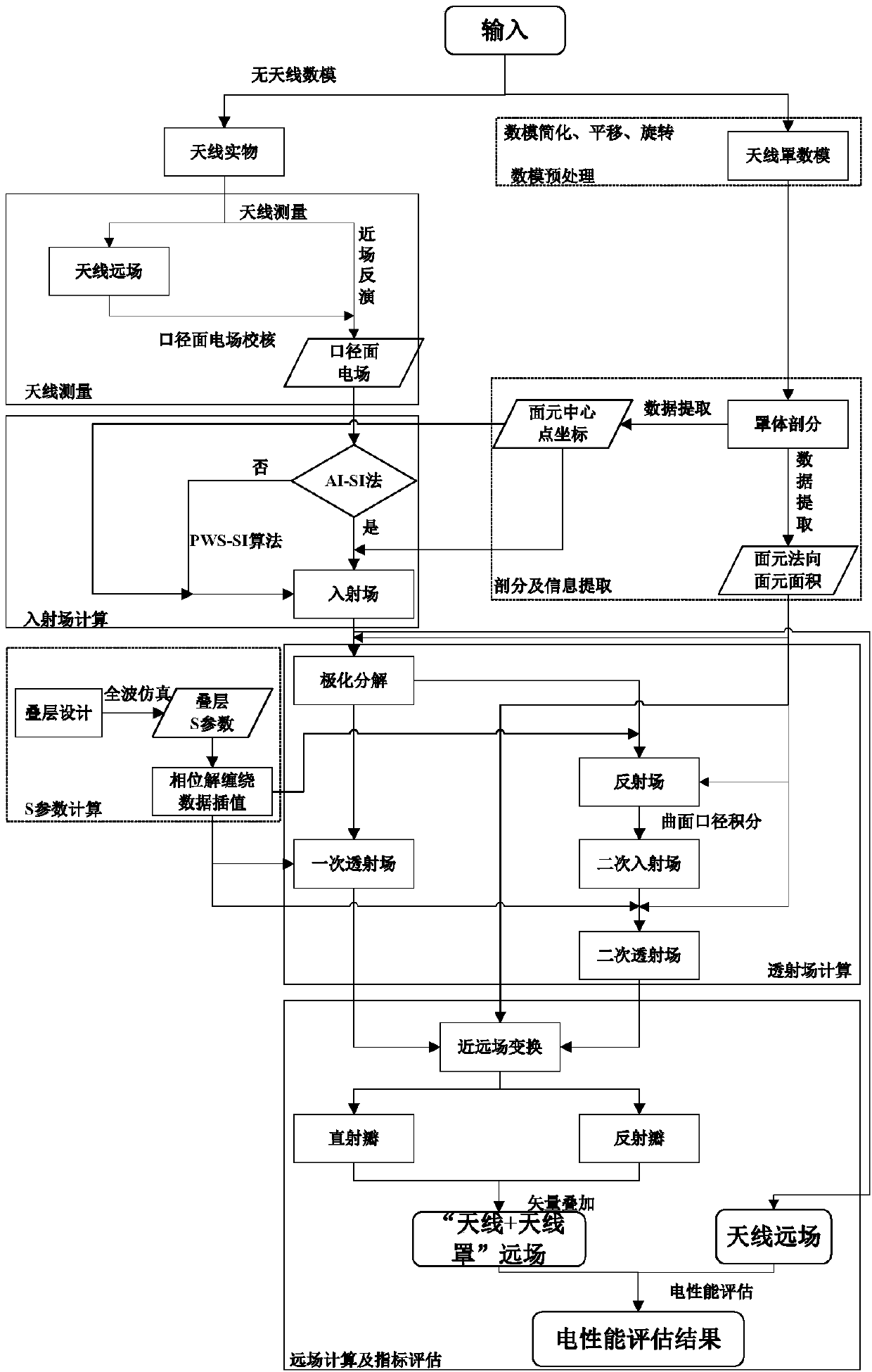
ActiveCN108268674AEasy to operateGuaranteed calculation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsData informationOperability
The invention discloses an electrical property evaluation method and device for a radome. The electrical property evaluation method for the radome comprises the following steps that: according to measurement, obtaining antenna radiation near region electric field information, and calculating the caliber surface electric field information of the antenna according to the near region electric field information; obtaining the model data information of the radome, and obtaining the subdivision surface meta-information of the radome according to the model data information of the radome; according tothe caliber surface electric field information of the antenna and the subdivision surface meta-information of the radome, calculating the far field information of the antenna and the far field information of an antenna system; and according to the far field information of the antenna and the far field information of an antenna system, calculating the electrical property parameter information of the radome. The radiation near region electric field information of the antenna is practically measured to obtain the caliber surface electric field information of the antenna so as to obtain the performance parameter information of the radome, calculation accuracy is guaranteed under a situation that antenna digital-to-analogue input is not depended, and the maneuverability of the electrical property evaluation of the antenna system of ''antenna+radome'' can be greatly improved.
Owner:KUANG CHI INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for realizing target electromagnetic scattering characteristic modeling and analysis based on GPU parallel SBR
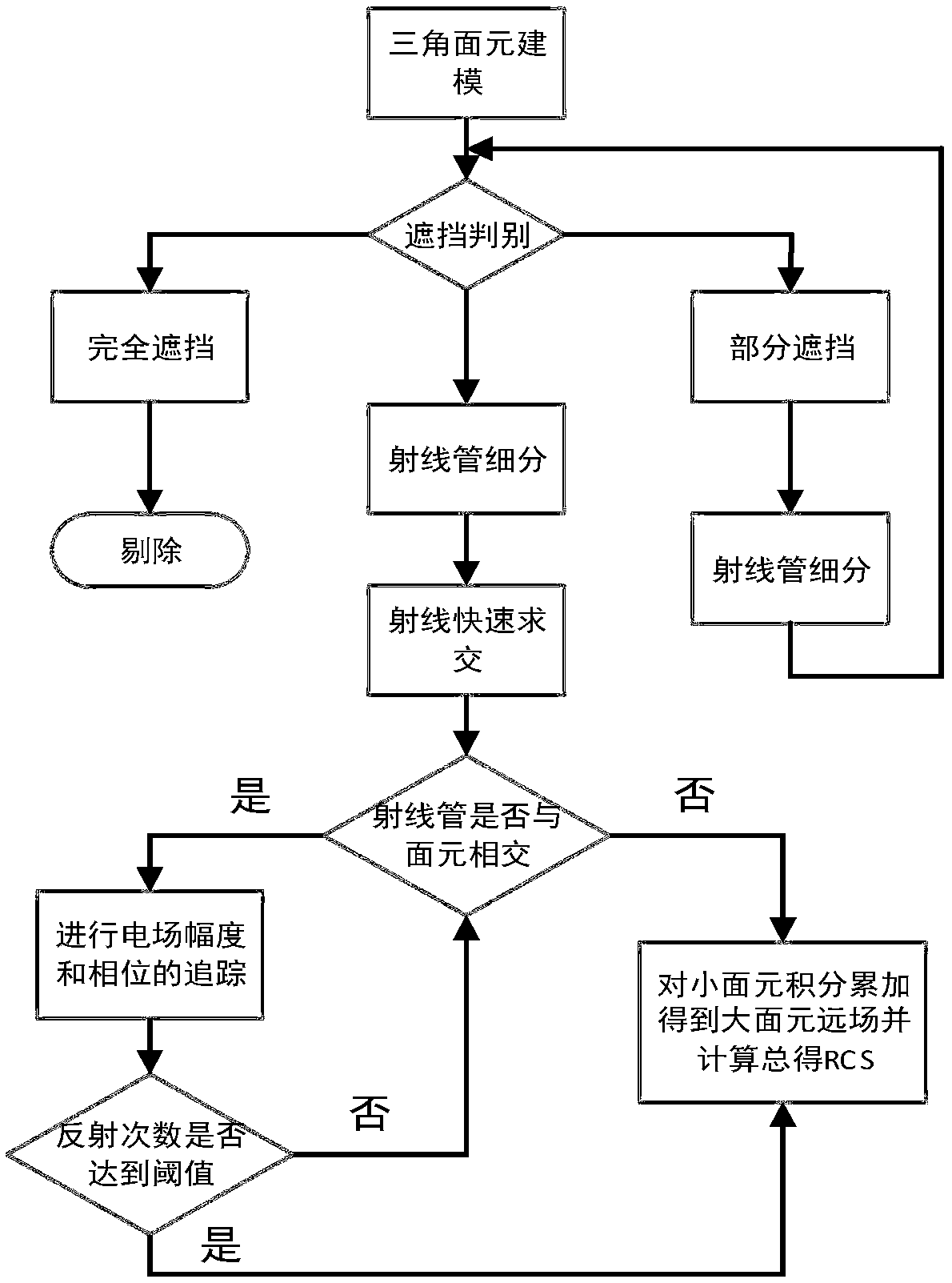
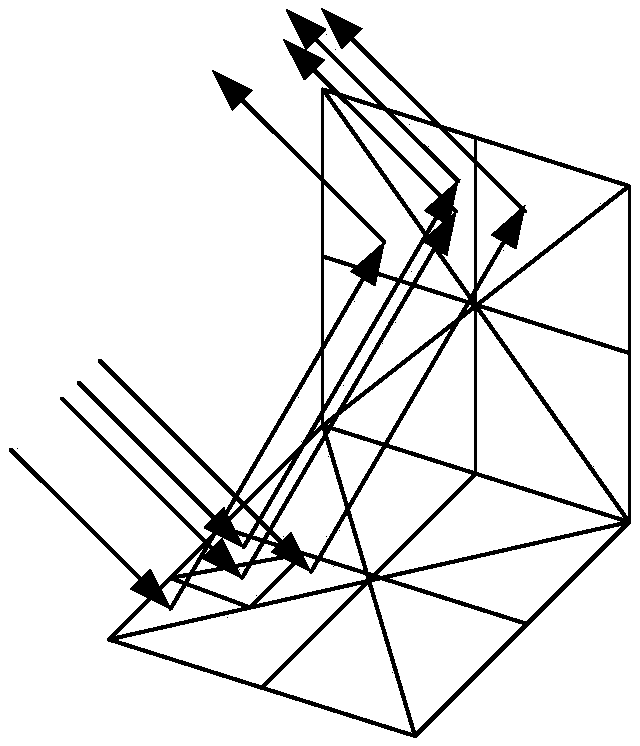
PendingCN110580742AReduce in quantityReduce memory requirementsDetails involving 3D image dataProcessor architectures/configurationGeometric modelingPhysical shape
The invention discloses a method for realizing target electromagnetic scattering characteristic modeling and analysis based on GPU parallel SBR. For a target of a submillimeter wave band, geometric modeling is firstly carried out to simulate the physical shape of the target, and triangular surface elements are used to divide grids. The method comprises steps of fitting the shape of the target by using a small number of triangular surface elements for the target part; subdividing the initial subdivision surface elements to meet the requirement of the SBR method on the aperture of the ray tube;meanwhile, in the process of judging occlusion, using self-adaptive subdivision for subdividing all partially occluded surface elements into an occlusion type and a non-occlusion type, then carrying out ray tracing and field intensity tracing on the subdivided ray tubes in parallel through a GPU to obtain RCS of the ray tubes, and obtaining the total RCS of the target by accumulating the RCS of all the ray tubes. For each ray tube, the frequency of intersection needing to be tested is greatly reduced, and the calculation time of the SBR method is shortened. For a flattened target, a small number of triangular surface elements can fit the surface shape of the target, and the method does not lose the calculation precision of the SBR method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Generating subdivision surfaces on a graphics hardware with floating-point fragment shaders
One or more fragment programs are executed on a graphics processor to generate the vertices of a subdivision curve or subdivision surface (using an arbitrary subdivision scheme) into a floating point texture. A plurality of faces are simultaneously processed during each subdivision iteration by using a super buffer that contains the vertices, their neighbors, and information about each face. Following the subdivision iterations, the texture is mapped as a vertex array (or a readback is performed), and the subdivided faces are rendered as complex curves or surfaces.
Owner:SILICON GRAPHICS +1
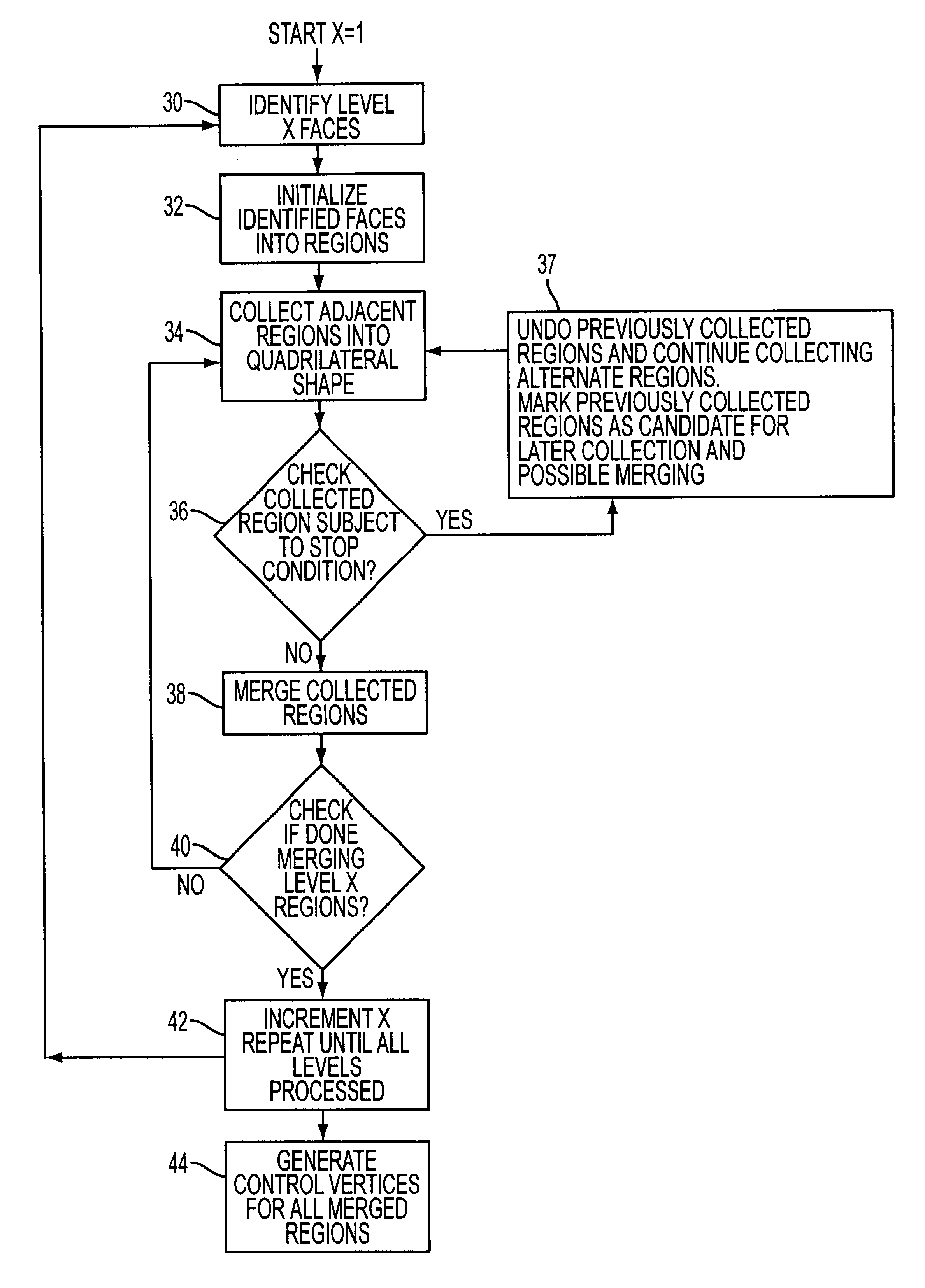
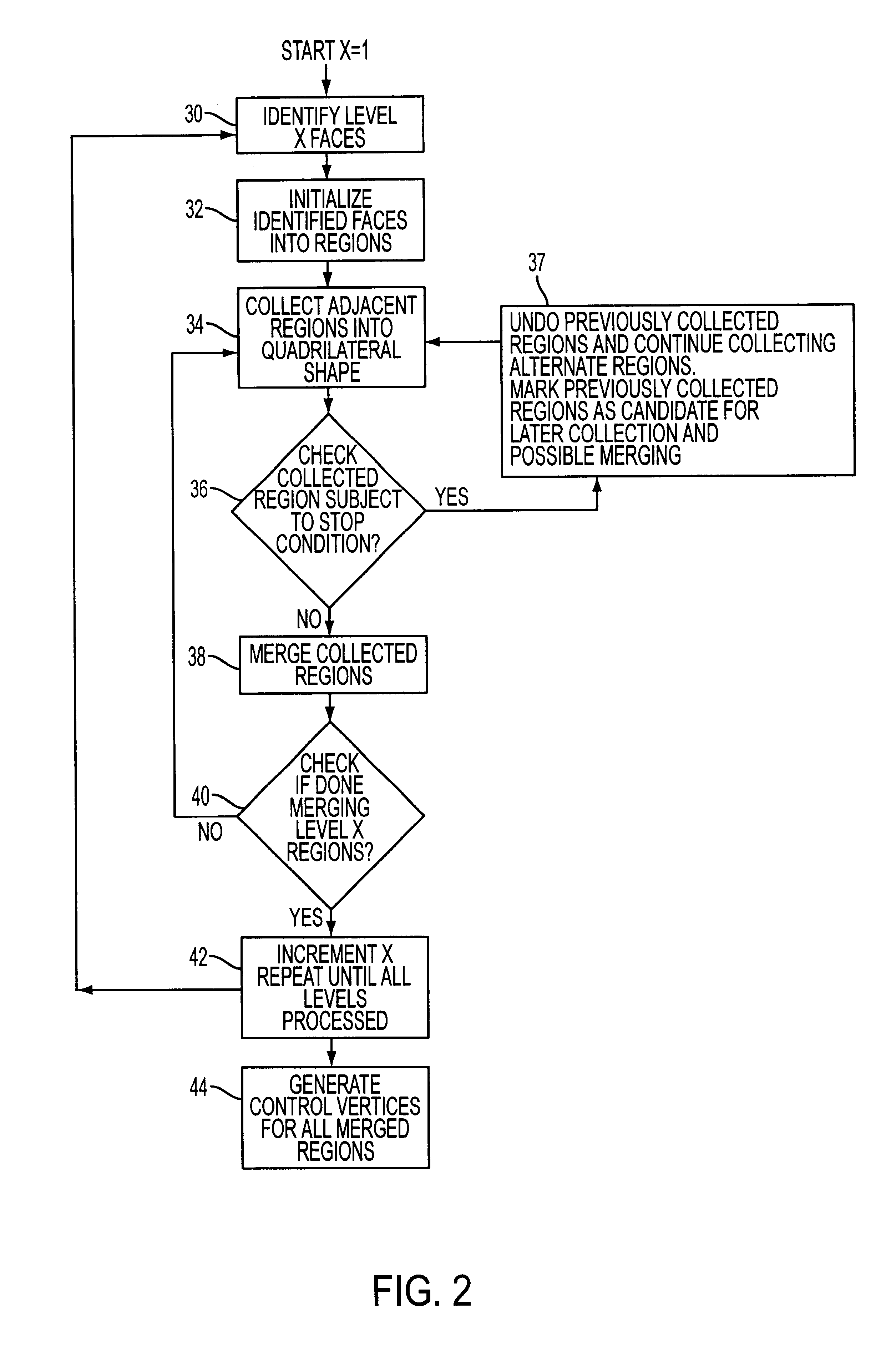
Conversion of a hierarchical subdivision surface to nurbs
A method of converting a subdivision surface to a NURBS representation. Adjacent faces of a subdivision surface are merged into a quadrilateral region, and vertices of the rectangular regions are used to generate a NURBS surface. The merging of faces reduces the number of vertices needed. Faces should not be merged if they do not comprise a quadrilateral region; if they cross an extraordinary point; if they cross a crease; or a face has already been merged. Imaginary vertices can be generated if not enough vertices are present for a face in the subdivision surface to create a corresponding NURBS patch for that face.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Unified subdivision scheme for polygonal modeling
InactiveUS7227545B2More controlledCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingPresent methodComputer science
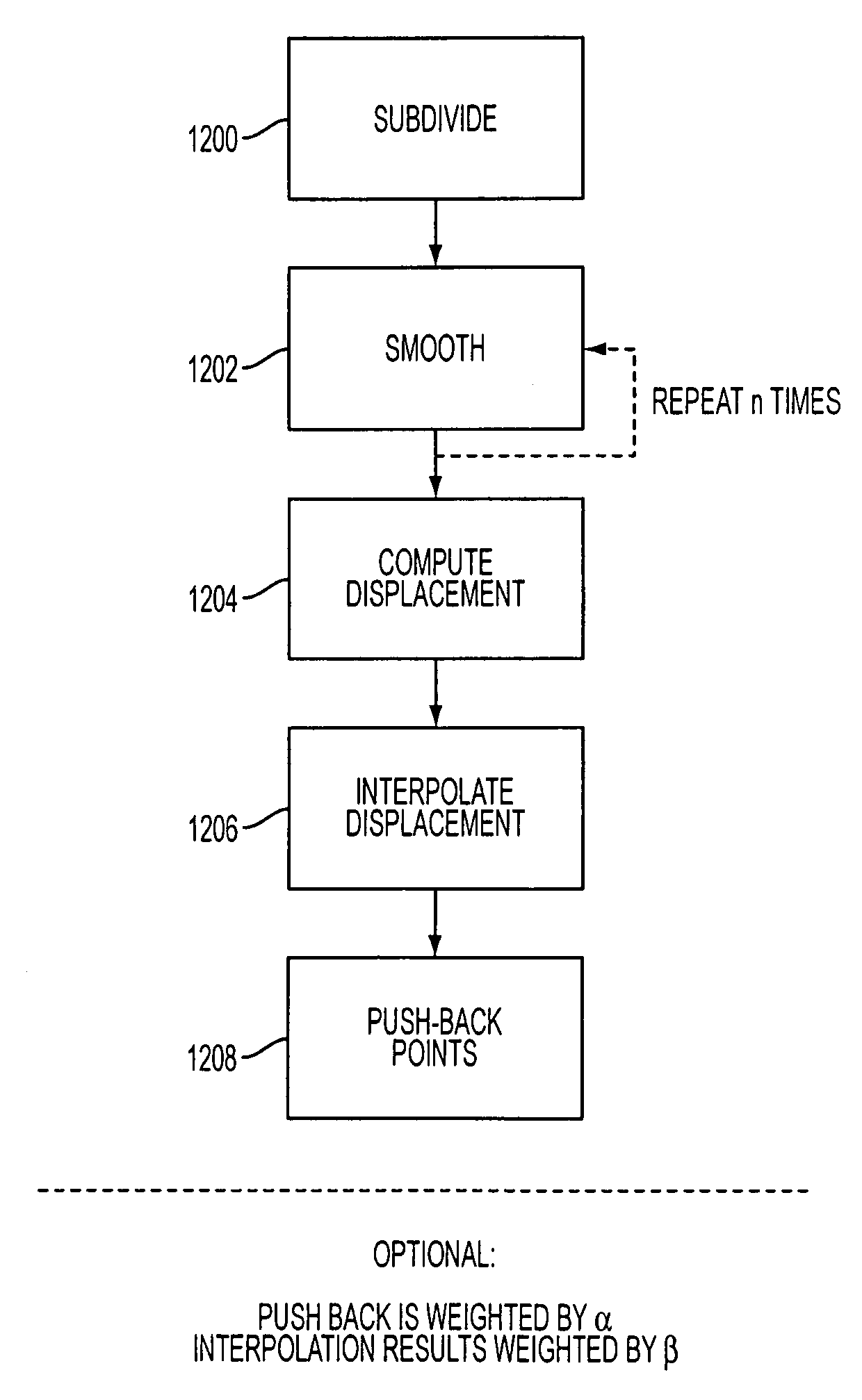
A method, computer readable storage, and apparatus for improving subdivision schemes for subdivision surfaces. The present method can correct distortion from the base mesh caused by prior art subdivision and smoothing schemes. In one embodiment, the method includes: (a) subdividing a curve having original vertices producing additional vertices; (b) smoothing the curve into smoothed vertices comprising smoothed original vertices and smoothed additional vertices; and (c) adjusting positions of the smoothed vertices.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
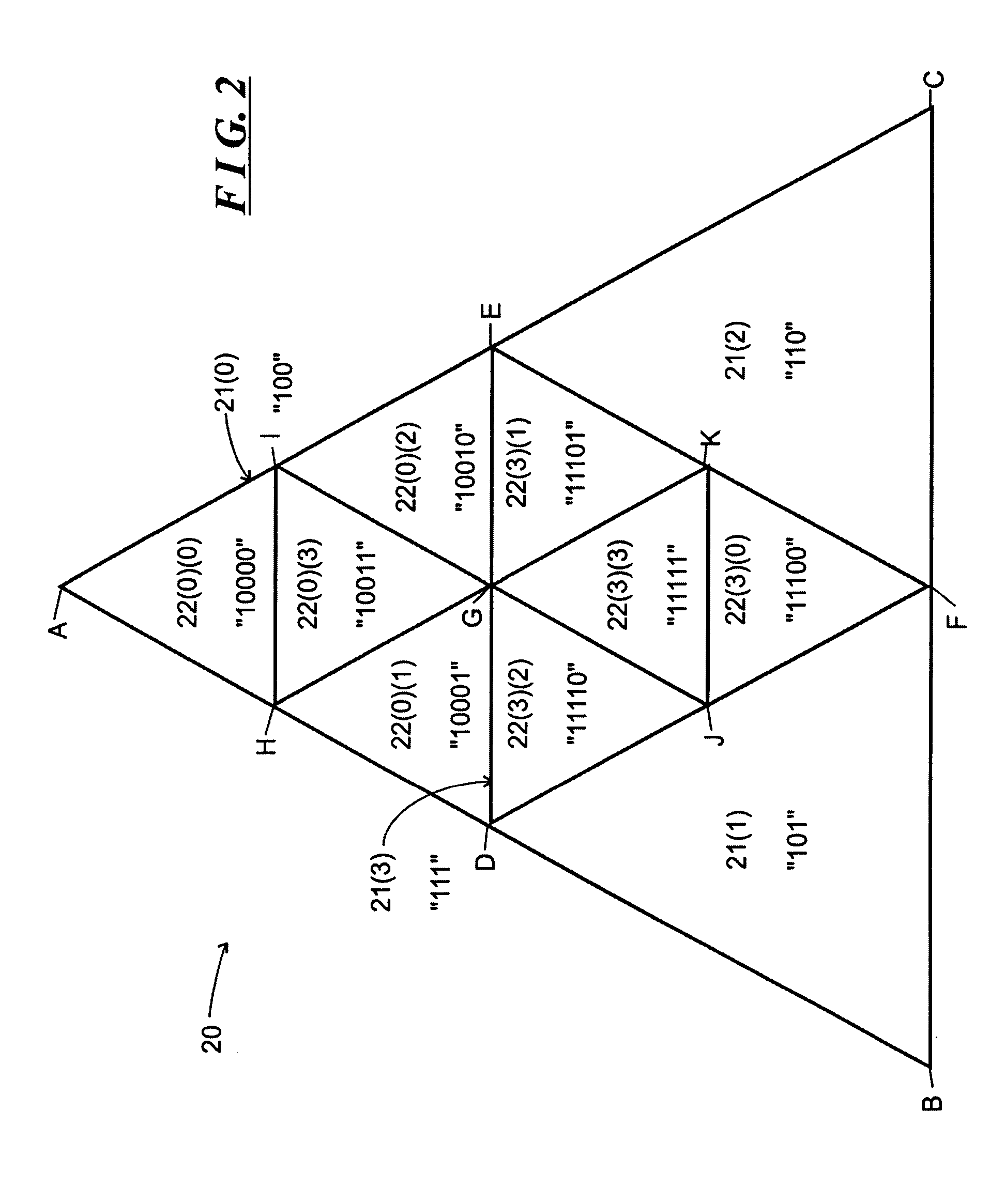
Computer graphic system and method for efficiently encoding subdivision triangular surfaces of a triangular surface element and for recovering their coordinates
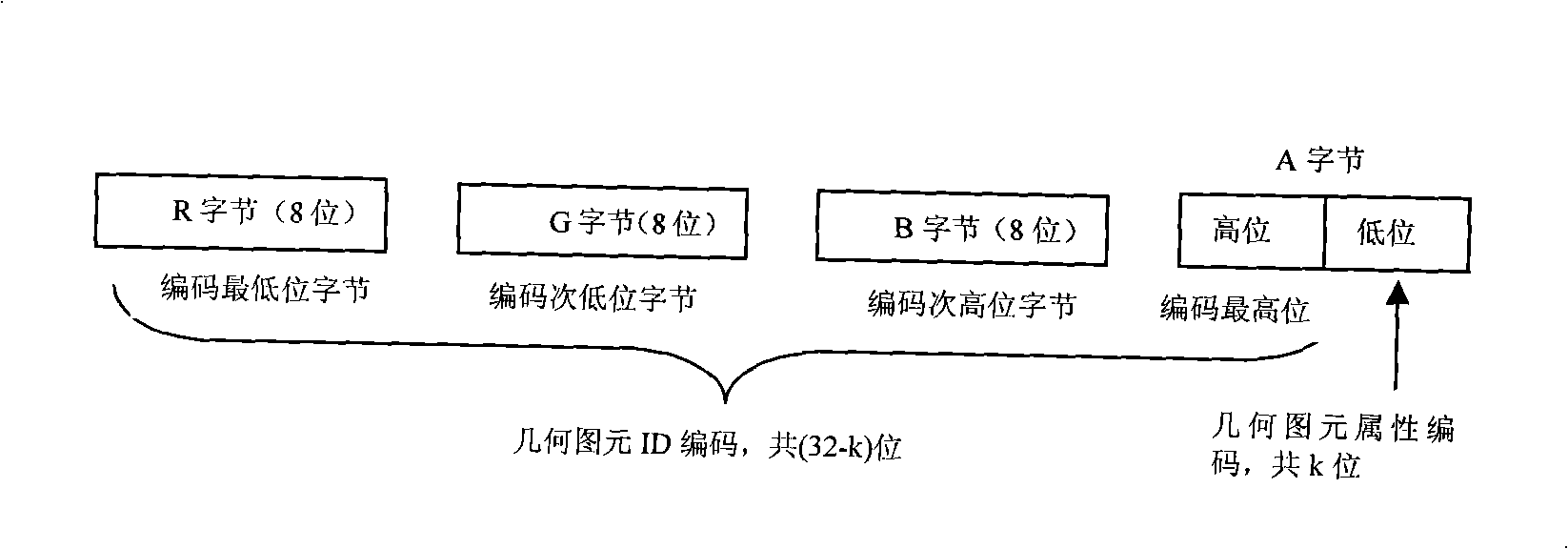
ActiveUS7167174B2Efficient codingReduce storageImage codingImage data processing detailsGraphicsGraphic system
A system is described for generating a plurality of identifiers, each associated with one of a like plurality of subdivision surfaces of a surface element, and for generating, using an identifier for a subdivision surface, coordinates for the subdivision surface. Each identifier includes one or more position codes. Each position code indicates the position of a subdivision surface at a respective level relative to the next higher level, so that successive position codes in the identifier indicate the positions of subdivision surfaces through successive subdivision levels. To generate coordinates for a subdivision surface from the identifier associated with the subdivision surface, the system sequences through successive position codes in the identifier to determine locations of the subdivision surfaces through the successive levels.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
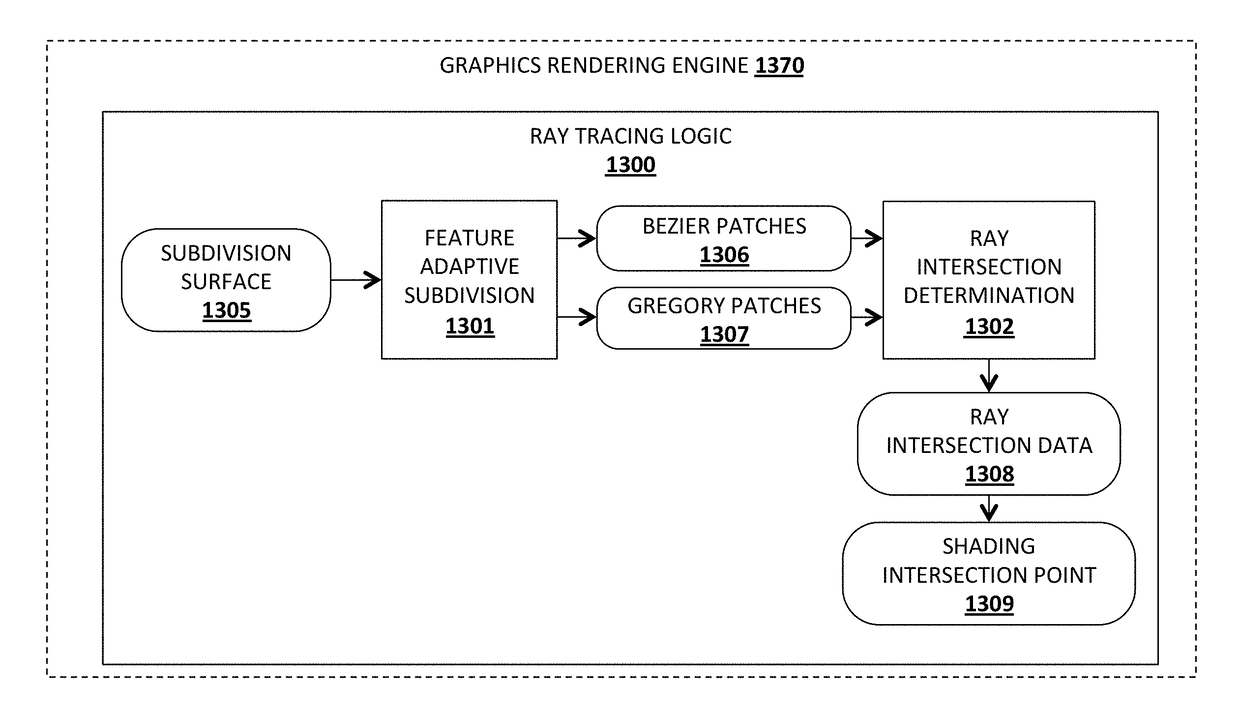
Method and apparatus for direct and interactive ray tracing of a subdivision surface
ActiveUS9805498B2Instruction analysisProcessor architectures/configurationPattern recognitionDisposal Technique
An apparatus and method are described for ray tracing. In particular, one embodiment of an apparatus for ray tracing comprises: feature adaptive subdivision logic to analyze faces on a subdivision surface and to responsively identify the faces as being of a first type or a second type, the feature adaptive subdivision logic to employ a first set of processing techniques to faces of the first type to generate a first patch type and to employ a second set of processing techniques to faces of the second type to generate a second patch type; and ray intersection determination logic to determine an intersection point between a ray and each of the patches of the first patch type and the second patch type.
Owner:INTEL CORP
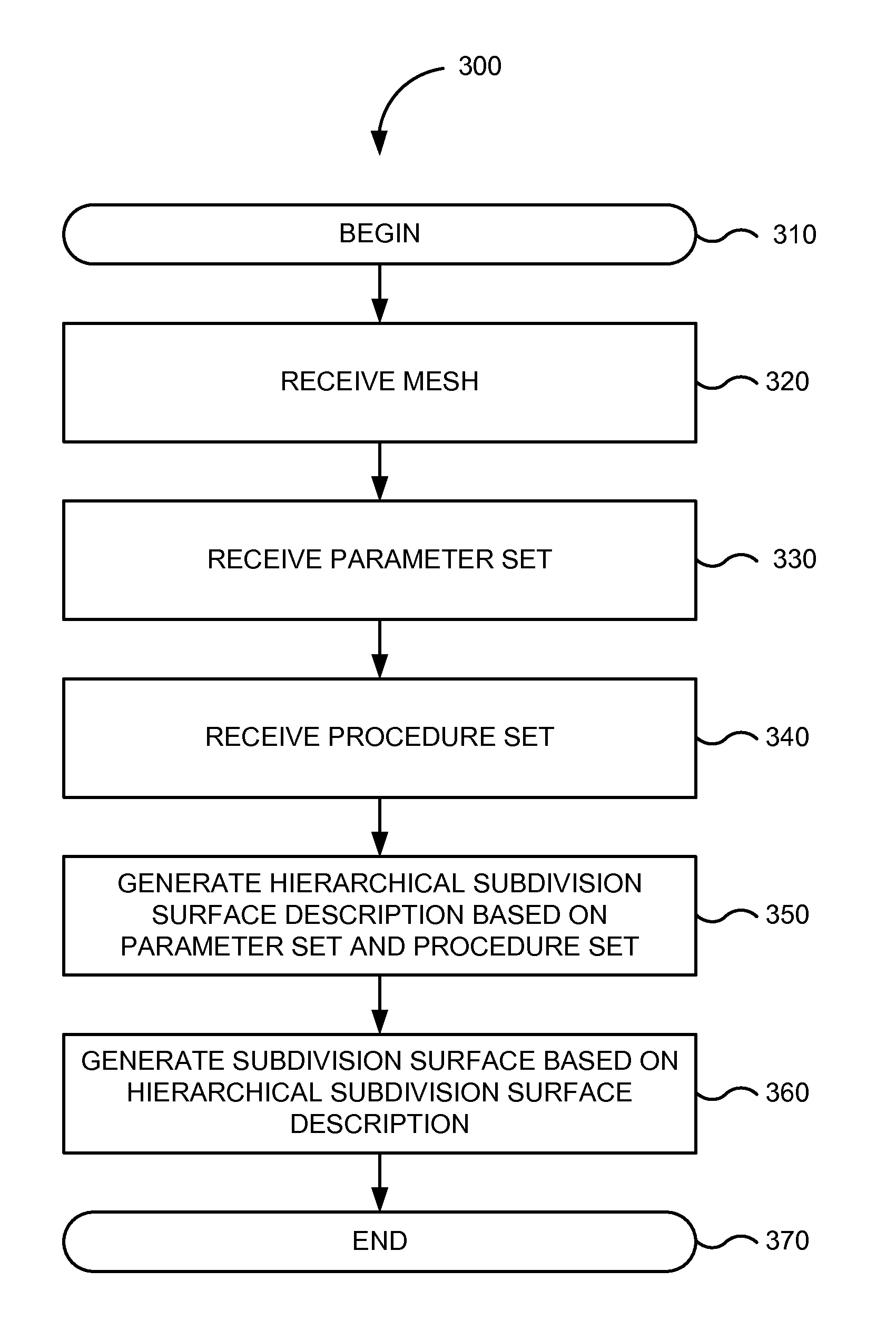
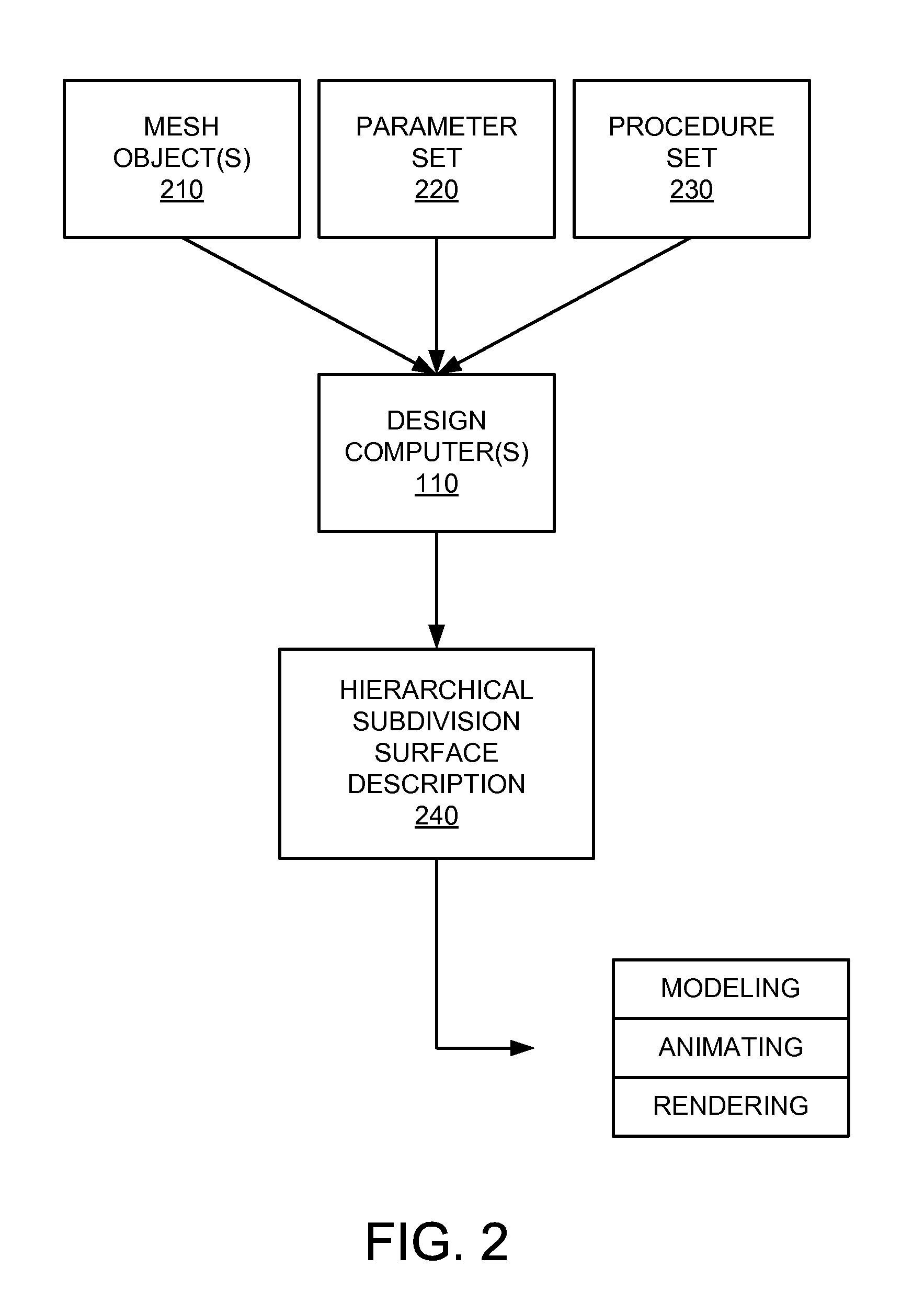
Procedural methods for editing hierarchical subdivision surface geometry
Methods and techniques are provided for procedurally editing hierarchical subdivision surfaces. A procedure set and a parameter set may be received. The procedure set may include one or more produces for generating detail coefficients. The parameter set may include one or more parameters, such as granularity and sharpness, while further specifying deltas or other jitter in parameter values or locations. A hierarchical subdivision surface description can be generated based on a mesh, the procedure set, and the parameter set.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com