Dynamic pipeline arrangement method
A layout method and pipeline technology, applied in the direction of hoses, pipes, pipe supports, etc., can solve the problems of pipeline winding, twisting, scraping, etc., achieve smooth flow, ensure bending radius, and avoid twisting and bending
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
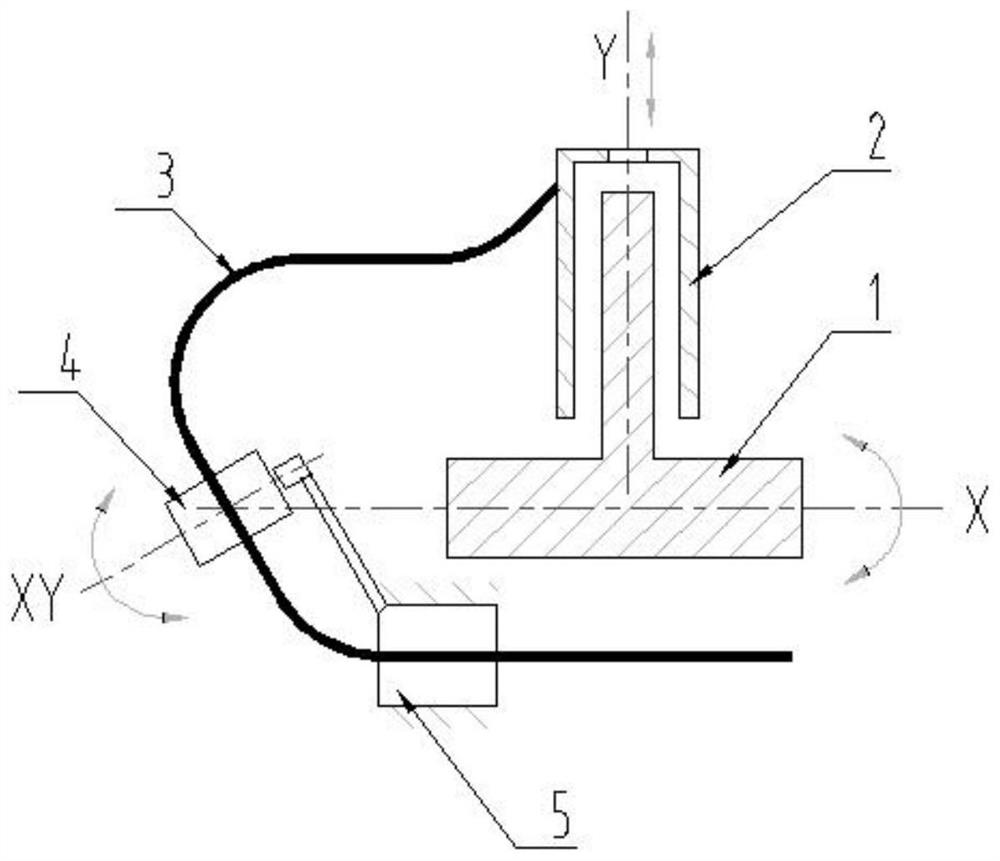
[0026] see figure 1 , a dynamic pipeline arrangement method, the pipeline 3 has a rotational movement around the rotational axis and a telescopic movement along a plane perpendicular to the rotational axis, wherein the telescopic structure 2 for the telescopic movement is arranged on the rotational structure 1 for the rotational movement, and the telescopic structure and the rotational movement The structures are all prior art, and the specific structural composition of the telescopic structure and the rotating structure will not be described in this embodiment. see figure 1 , the rotating structure 1 drives the pipeline 3 to rotate around the X axis (the X axis is the rotation axis), the telescopic structure drives the pipeline 3 to perform telescopic movement along the Y axis, and at least one point of the pipeline 3 is constrained by a pipe clamp, and the pipe clamp It is a fixed setting or a movable setting; the pipe clamp is set independently of the rotating structure 1 ...
Embodiment 2
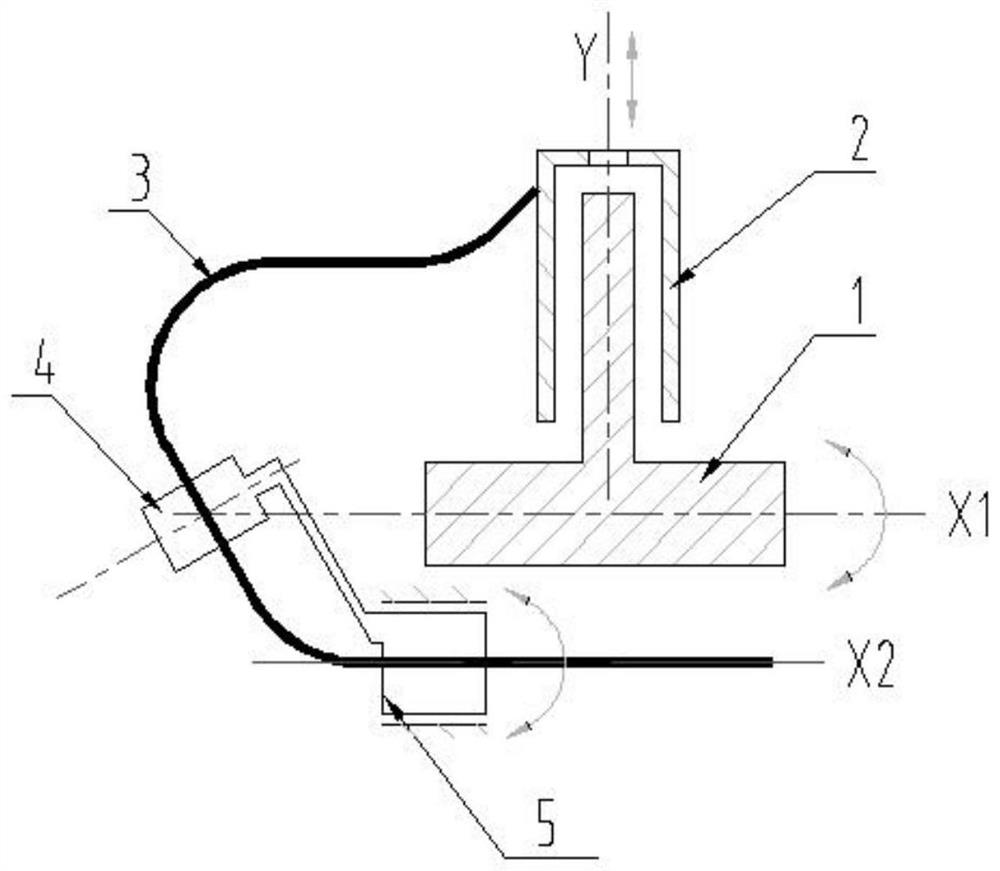
[0035] see figure 2 , the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the first pipe clamp 4 is fixedly arranged on the connector of the second pipe clamp 5, the second pipe clamp 5 is rotated, and the pipeline 3 drives the second pipe clamp 5 turn. Preferably, the axis of rotation of the second pipe clamp 5 is arranged parallel to the axis of rotation. It should be noted that setting the axis of rotation of the second pipe clamp parallel to the axis of rotation is only an optimal arrangement, and the rotation of the second pipe clamp The non-parallel setting of the axis and the rotation axis can also satisfy the requirement that the second pipe clamp rotates following the pipeline. see figure 2 , X1 in the figure is the axis of rotation, and X2 is the axis of rotation.
[0036] In this embodiment, the pipeline 3 directly drives the second pipe clamp 5 to rotate, and the first pipe clamp only serves to fix the pipeline.
Embodiment 3
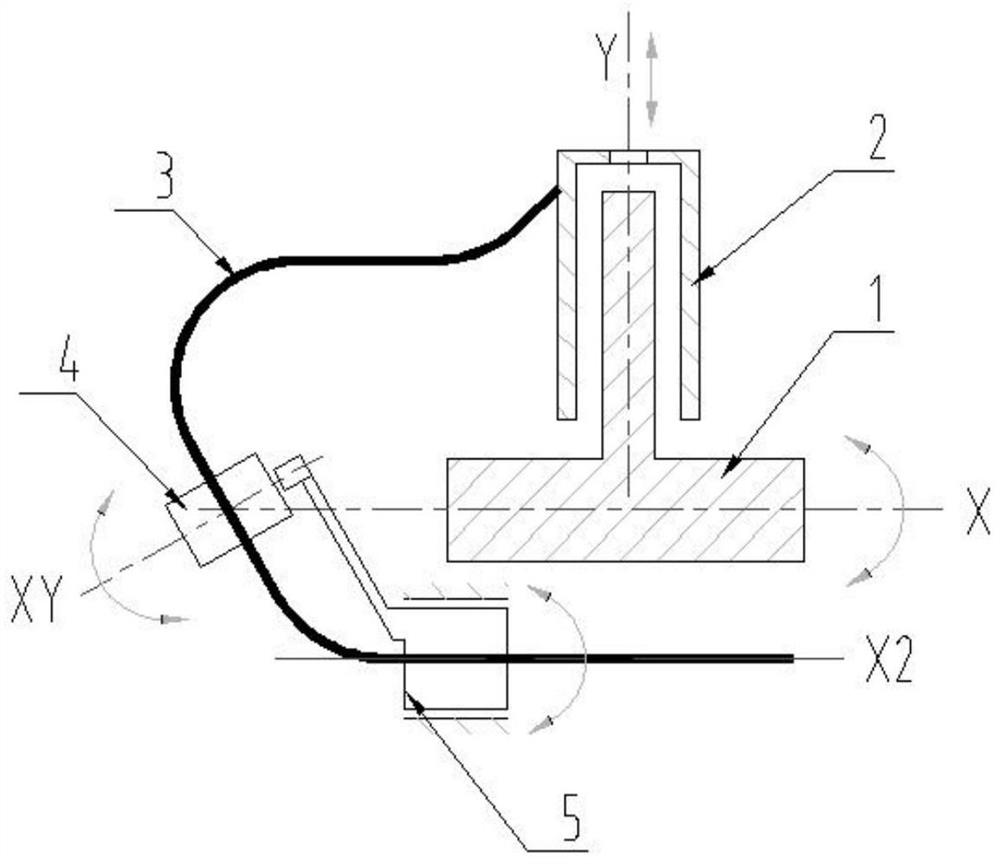
[0038] see image 3 , the difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the first pipe clamp 4 is rotatably arranged on the connector of the second pipe clamp 5, the second pipe clamp 5 is rotatably arranged, and the pipeline 3 drives the first pipe clamp 4 and the second pipe clamp 5 rotate. Preferably, the axis of rotation of the second pipe clamp 5 is arranged parallel to the axis of rotation. It should be noted that setting the axis of rotation of the second pipe clamp parallel to the axis of rotation is only an optimal arrangement, and the rotation of the second pipe clamp The non-parallel setting of the axis and the rotation axis can also satisfy the requirement that the second pipe clamp rotates following the pipeline. see image 3 , the X axis is the rotation axis of the rotating structure, X2 is the rotation axis of the second pipe clamp 5, and XY is the rotation axis of the first pipe clamp.
[0039]In this embodiment, the pipeline is constrained by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com