Device and method for measuring brain activity
A technology of brain activity and brain electrical activity, which is used in diagnostic recording/measurement, application, medical science, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0074] overview
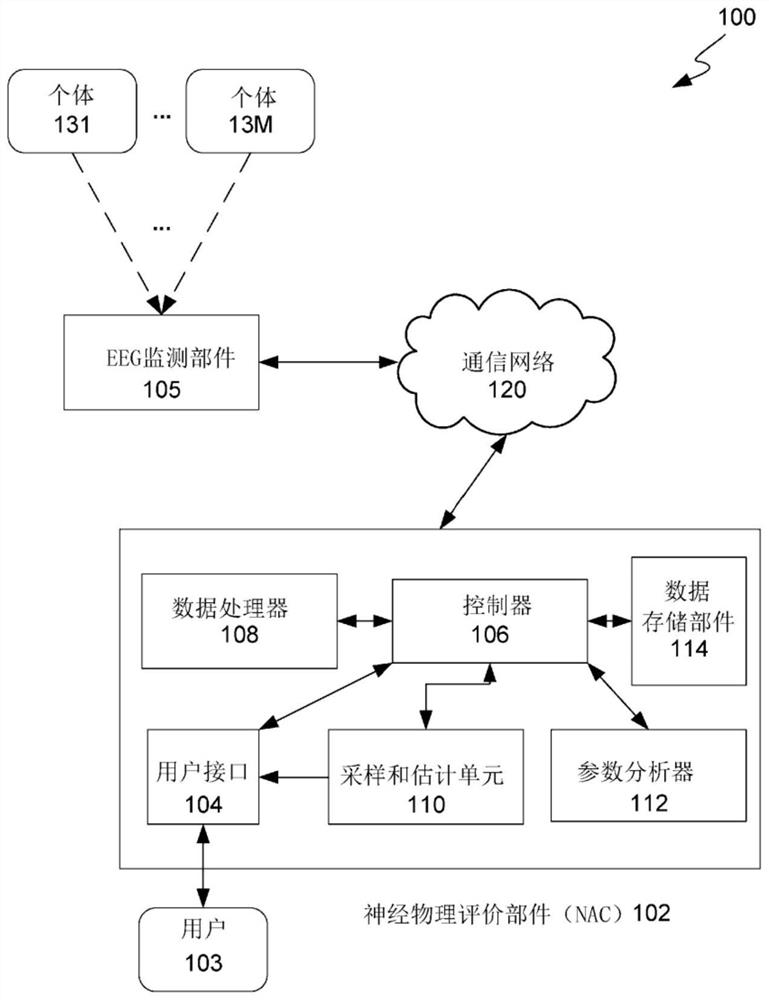
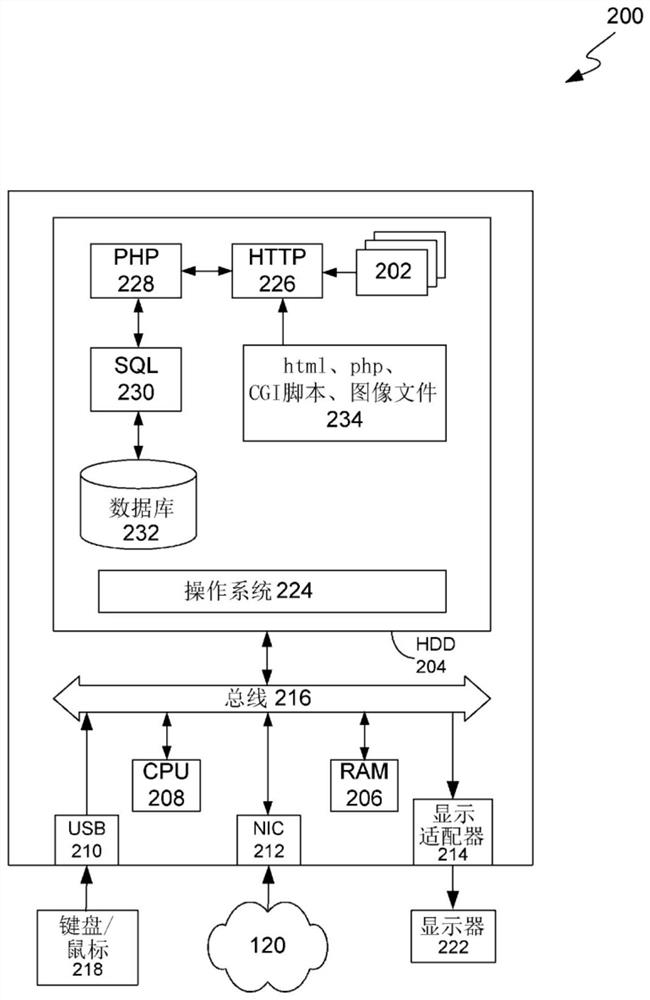
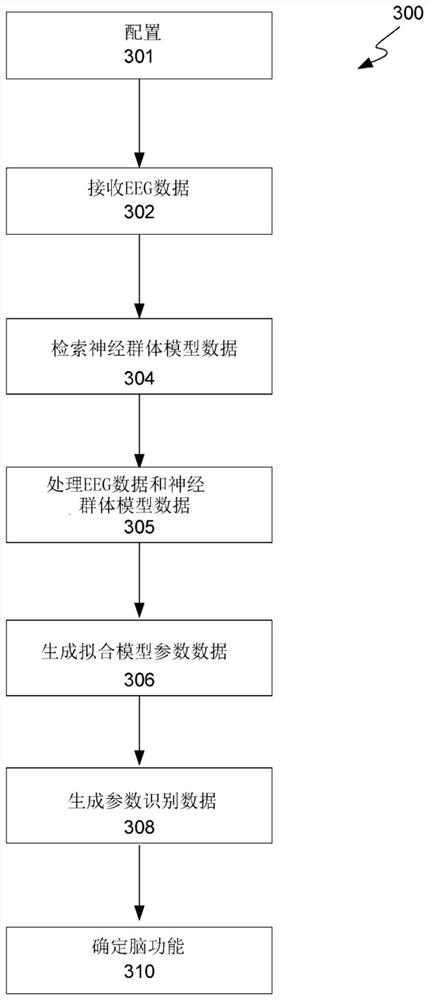
[0075] There is an important clinical need to be able to measure brain activity of a subject, especially in real time during medical interventions such as surgery, and to be able to monitor anesthesia levels during surgery. Features of EEG signals from human individuals are related to their brain activity. For example, alpha rhythm is a defining feature of resting EEG signals in humans and has played a central role in the phenomenological description of brain electromagnetic activity during cognition. The macroscopic approach for assessing brain function via representation of EEG features such as alpha rhythm (referred to herein as "neurophysical assessment") is based on neural population models. Typically, neural population model parameters are determined by iterative tuning methods, where the best parameters are selected from the tuning set as the model produces (or "predicts") EEG signals exhibiting specific features of the observed EEG signals (e.g., spe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com