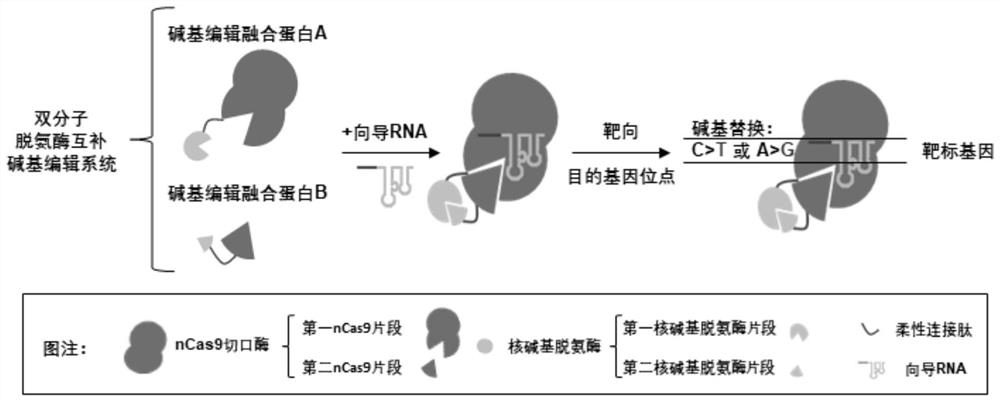
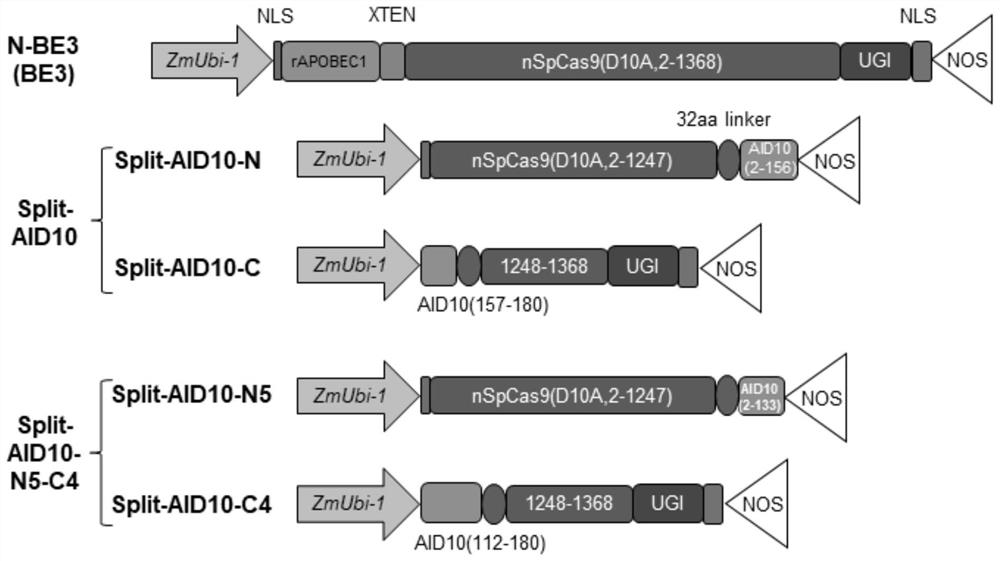
Base editing system based on bimolecular deaminase complementation and application thereof
A technology of base editing and deaminase, applied in the directions of hydrolase, peptide, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of increasing safety hazards, uncertainty of clinical application, etc., and achieve the effect of high-efficiency target activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
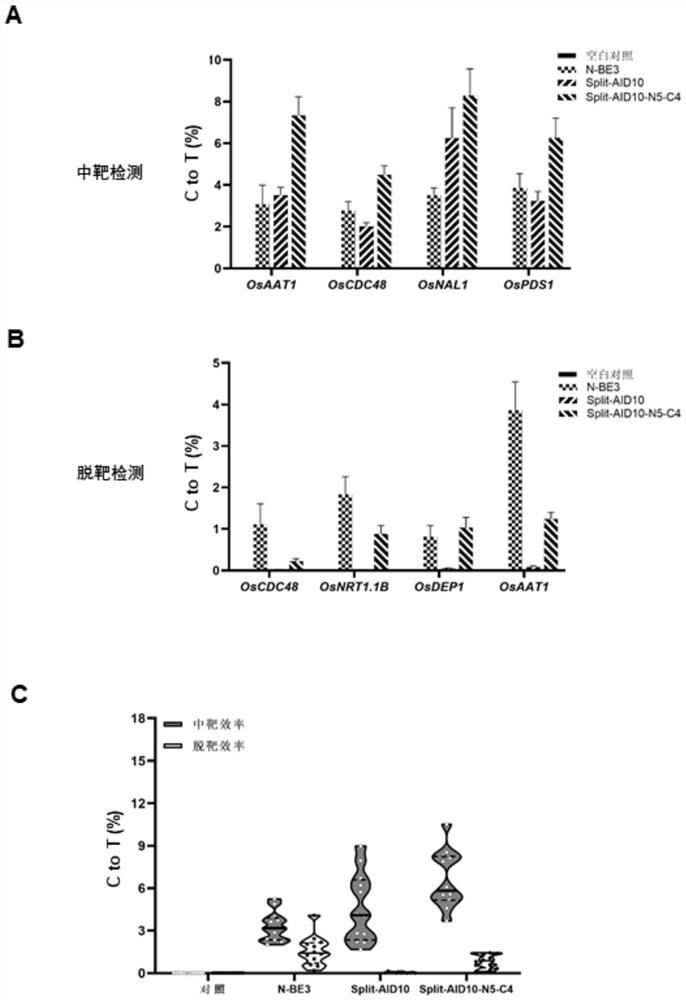
[0071] Example 1 Evaluation of the on-target and off-target efficiencies of a bimolecular deaminase complementation-based cytosine base editing system in the monocot model plant rice.
[0072] 1. Experimental materials: The wild-type rice variety used in this example is japonica Zhonghua 11 (Oryza sativa L.ssp.japonica ZH11).
[0073] 2. Construction of base editing related rice protoplast transient expression vector
[0074] The expression vector pHBT-rAPOBEC1-nCas9-UGI of the base editor "N-BE3" (or called "BE3") was independently constructed by our laboratory. The promoter used is the maize ZmUbi-1 promoter and the terminator used is NOS terminator.
[0075]Cytosine base editor "Split-AID10" based on bimolecular deaminase complementation is composed of "Split-AID10-N" expression vector and "Split-AID10-C" expression vector; by Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (SangonBiotech.Co., Ltd.) commercialized the synthesis of a polynucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptid...
Embodiment 2
[0116] Example 2 Efficient base editing was also achieved in transgenic Arabidopsis plants using the bimolecular deaminase complementation-based cytosine base editing system Split-AID10.
[0117] 1. Experimental materials
[0118] The wild-type Arabidopsis used in this example is the Col-0 ecotype (Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0).
[0119] 2. Arabidopsis genetic transformation
[0120] For the construction of the Arabidopsis genetic transformation vector used in this example, refer to the published article [15] In accordance with the method described in Example 1, respective genetic transformation vectors were constructed for two different targets (see Table 1 for guide RNA target sequence information). The aforementioned vectors were respectively transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 by electroporation, and Arabidopsis plants were transformed by pollen tube introduction method. Specifically, the GV3101 bacterial solution containing the target vector was in...
Embodiment 3
[0125] Example 3 The cytosine base editing systems Split-AID10 and Split-BE3 based on bimolecular deaminase complementation also exhibited good on-target editing and very low genome-wide random off-targets in unicellular eukaryotic yeast.
[0126] 1. Experimental materials
[0127] Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 was used in this example.
[0128] 2. Construction of base editing related yeast expression vector
[0129] Reference published articles for base editing related expression vector construction [16] , to obtain expression vectors pGAL1-rAPOBEC1-nCas9-UGI(N-BE3), pGAL1-Split-AID10 and pGAL1-Split-BE3. Wherein, the amino acid sequences of Split-AID10-N and Split-AID10-N contained in the pGAL1-Split-AID10 expression vector are as described above, and the amino acid sequence of Split-BE3-N contained in the pGAL1-Split-BE3 expression vector is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 8, the amino acid sequence of Split-BE3-C is shown in SEQ ID NO: 9. The yeast U6 promoter was directly ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap