Method for actively controlling lamination slippage in composite material component
A composite material component, active control technology, applied in the direction of household components, household appliances, other household appliances, etc., can solve the problem of uncontrollable lamination slip process, avoid lamination wrinkles and overhead defects, easy to operate, enhance Effects of Design and Manufacturing Limits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0035] Example 1: In this example, a large-thickness composite material component is selected to illustrate the method of actively controlling the lamination slip during the molding process, which is not limited to this example.
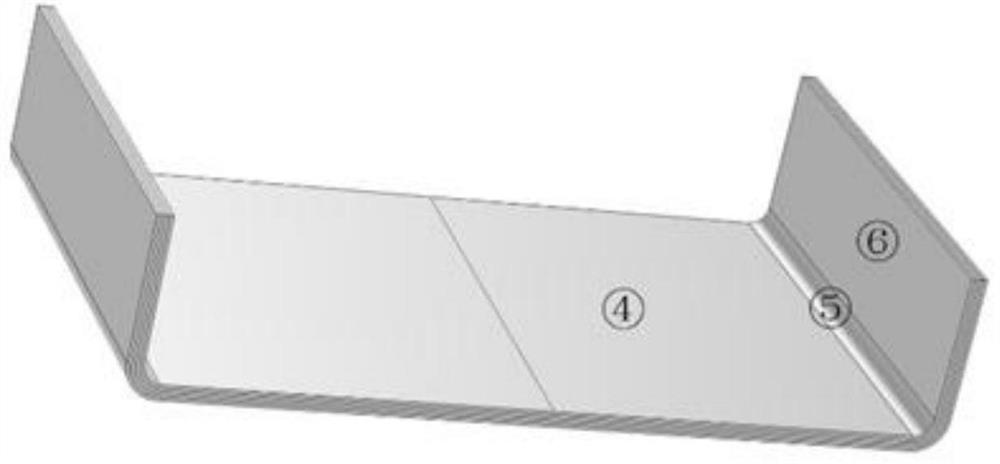
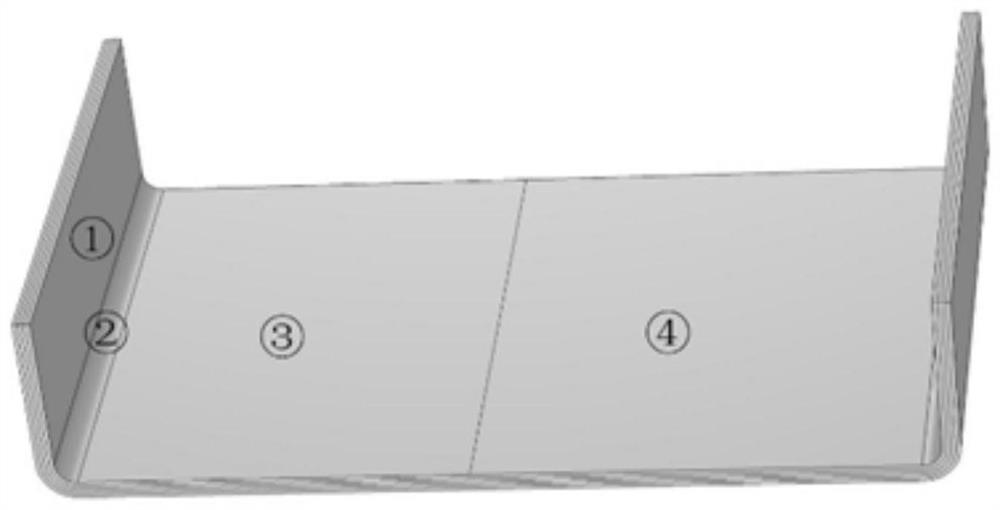
[0036] A constant pressure field of 600KPa is applied to the composite member by finite element, and a number of discrete points are extracted according to the slip rate distribution and profile curvature distribution, and the mapping relationship between profile curvature and slip rate is established by numerical fitting. The first derivative of the curve is obtained to obtain the sensitivity of the slip rate to the profile curvature. Taking the sensitivity of the slip rate to the profile curvature as the first zoning criterion, the regions are initially divided according to the same sensitivity tolerance, and the region boundaries are determined in turn. The U-shaped composite components are preliminarily divided into ①, ②, ⑤, ⑥, ③+④ five areas (su...
example 2
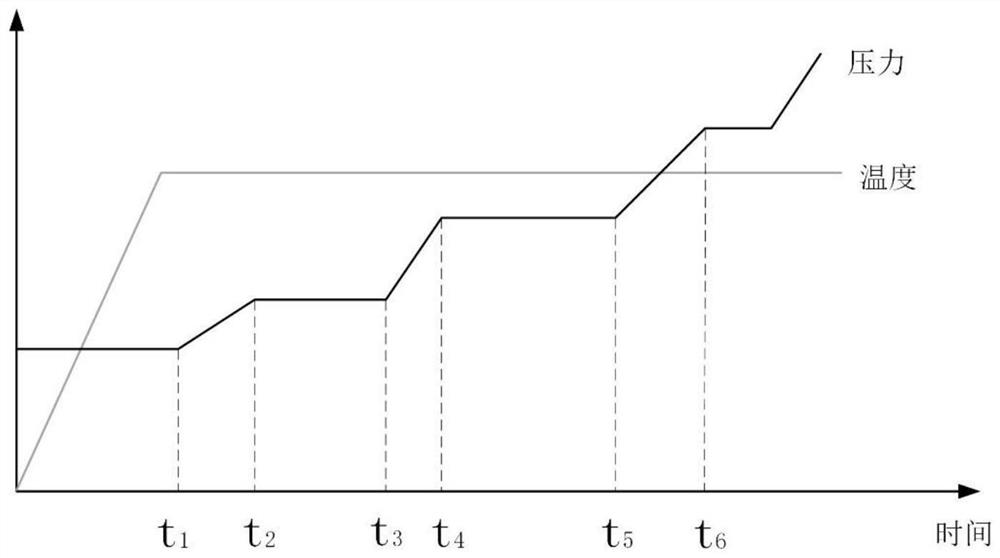
[0042] The difference between this example and example 1 is that the lamination slip process is actively controlled by adjusting the temperature. like Figure 8 As shown in the figure, when the resin in the composite material does not have fluidity at 35 °C, a constant compaction pressure of 600KPa recommended by the material manufacturer is applied to the component, and then the temperature is applied in sequence at multiple times, and the sliding rate is monitored in real time. The temperature actively controls the lamination slip, and the rest is the same as the above example 1.
example 3
[0044] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the shape of the composite material component is a hyperboloid (such as Figure 9 shown), with a thickness of 2 mm, and a fiber optic sensor placed in the center of each area to monitor the lamination slip rate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com