Relay protection device
A relay protection device and relay technology, which is applied in the direction of circuit devices, emergency protection circuit devices, emergency protection devices with automatic disconnection, etc., can solve the problems of discrimination, inaccurate direction discrimination, instability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
[0126] Referring to Figure 1 and figure 2 The first embodiment will be described.
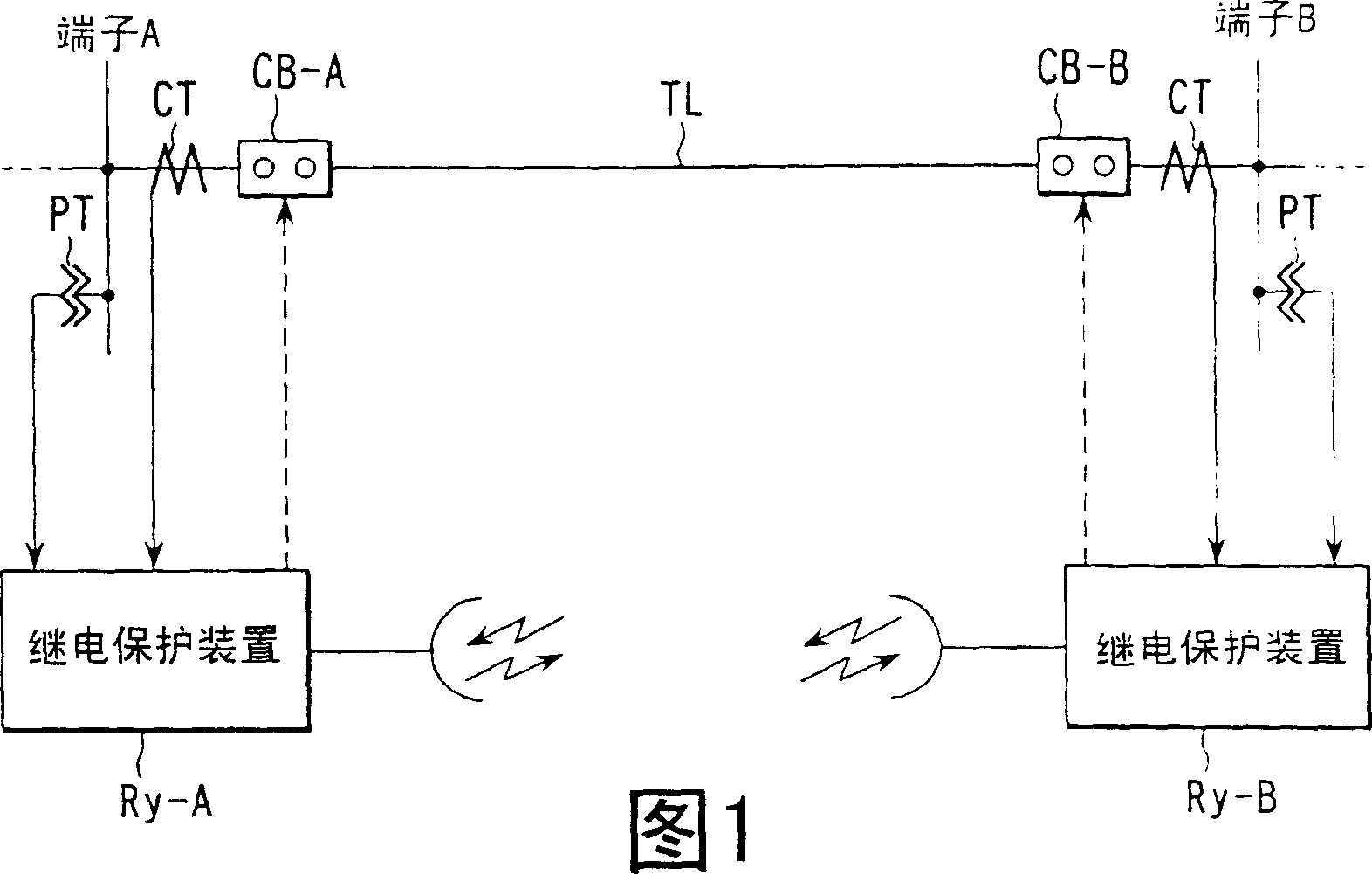
[0127] First, in FIG. 1 , TL is a transmission line to be protected between the A terminal and the B terminal connecting the power system. The relay protection device R that extracts the current (I) and voltage (II) through the current transformer CT and the voltage transformer to perform protection calculations is installed on the A terminal and the B terminal respectively. y -A and R y -B.
[0128] Since the two relay protection devices R y -A, R y -B has the same structure, so the relay protection device R y -A represents their internal structure.
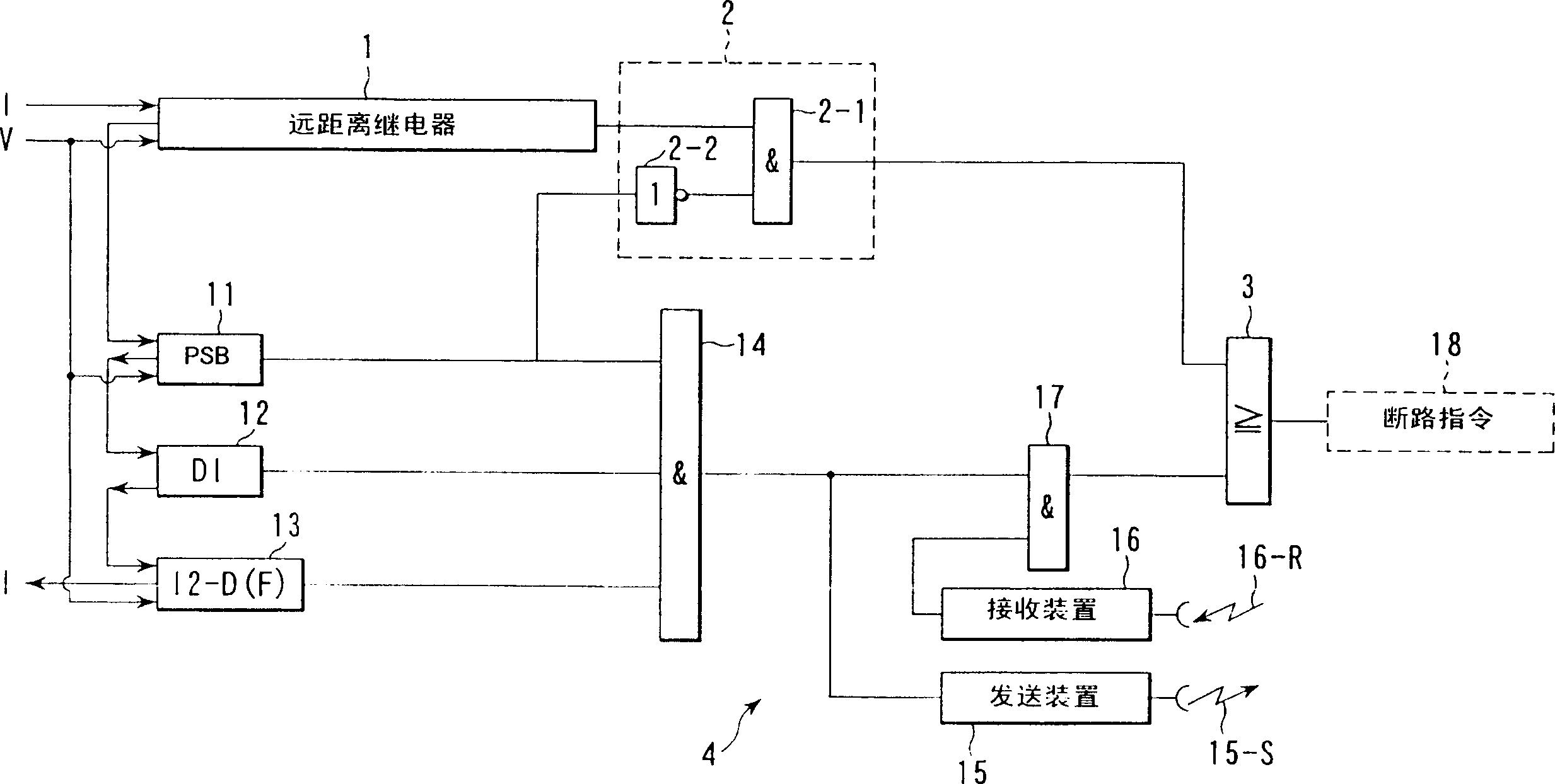
[0129] figure 2 is the relay protection device R in Figure 1 y -A detailed structure diagram.
[0130] 1 is a long-distance relay for main protection. The remote relay 1 performs a distance measurement calculation based on the voltage and current extracted from the terminal A, and operates when the obtained distance measurement impeda...
no. 2 Embodiment
[0148] Next, refer to Figure 4 The second embodiment will be described. In addition, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same parts as the already described relays and logic circuits, and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0149] Figure 4 and figure 2 The difference is that: Figure 4 will be figure 2 The detection relay 12 of the current change part is replaced by a failure detection circuit 20 represented by a dotted line frame. Since the other components are the same as those described above, only the fault detection circuit 20 will be introduced here.
[0150] 21 is an undervoltage relay (abbreviated as UV in the figure), and it works when the voltage is less than a stable value because of a failure at the nearest end. Only one is shown here, and in practical application, it is desirable to set the phase voltage UV for detecting a ground fault and the line voltage UV for detecting a short circuit fault.
[0151] 22 is a zero-phase overcurrent relay ...
no. 3 Embodiment
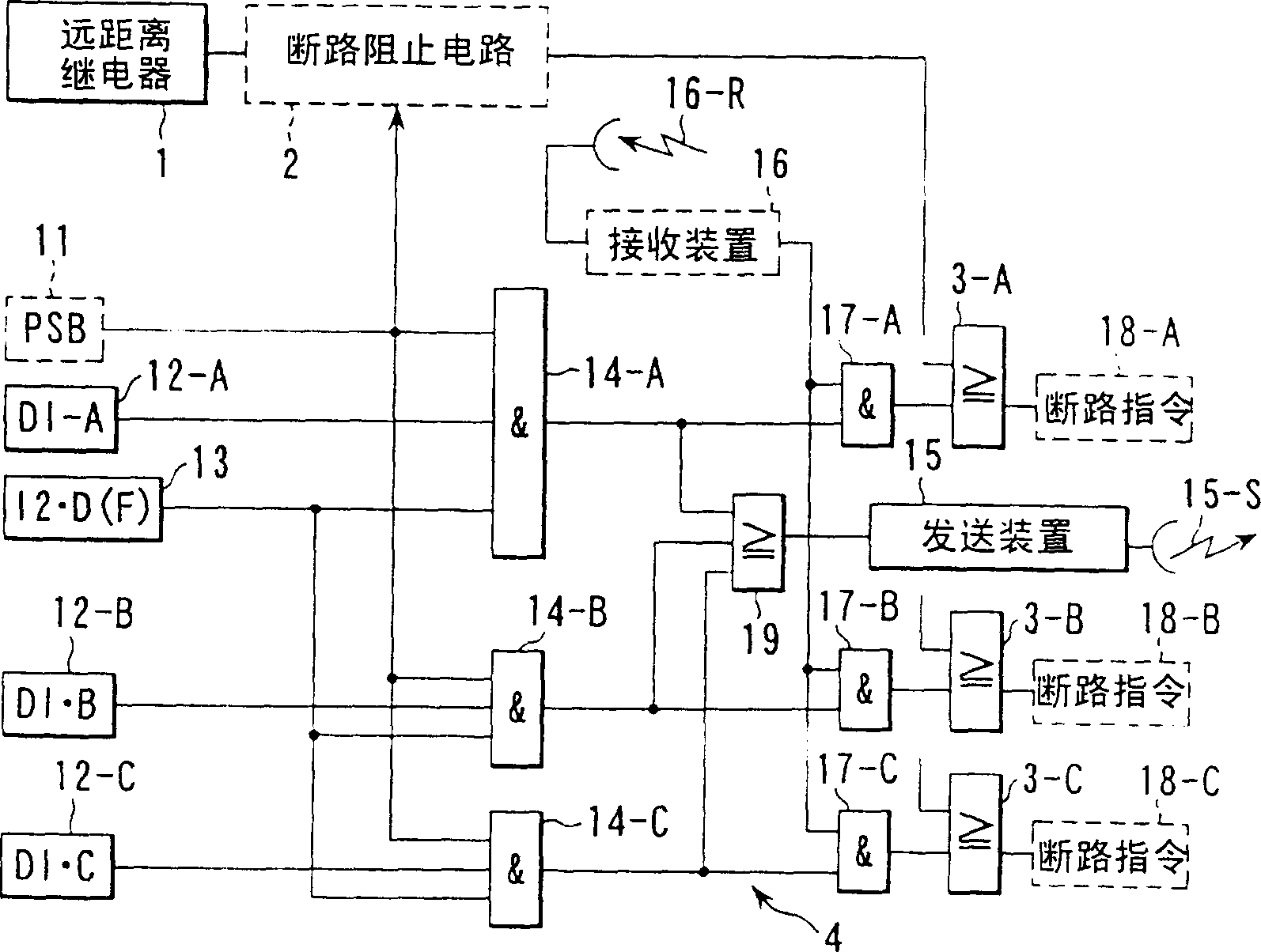
[0156] Refer below Figure 5 The third embodiment will be described. In addition, for the relays already described, the same parts of the logic circuit are attached with the same symbols and their explanations are omitted.
[0157] This embodiment is to figure 2 circuit for fault detection relays with Figure 4 The fault detection relay is combined. If it is this embodiment, because among the four relays of the zero-phase overcurrent relay 22, the reverse phase overcurrent relay 23, the circuit change part detection relay 12 and the undervoltage relay 24, no matter which one works, the system failure can be detected , so the fault detection accuracy can be improved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com