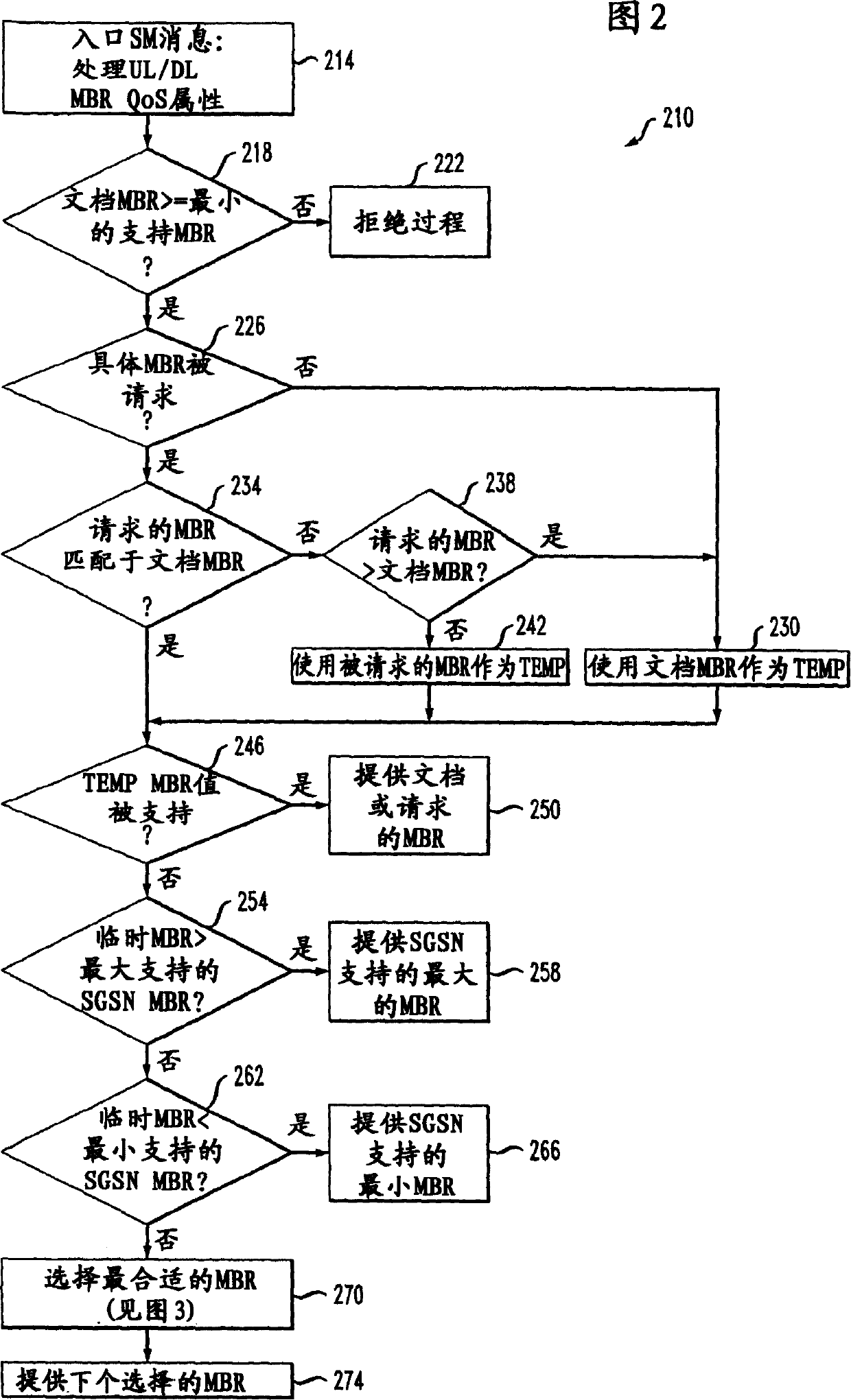
Decision tree logic for determining the optimal value for QOS uplink and downlink maximum bitrate
A technology of maximum bit rate and attribute value, applied in communication between multiple stations, digital transmission system, data exchange network, etc., can solve problems such as long call preparation time, control network, and inefficient utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
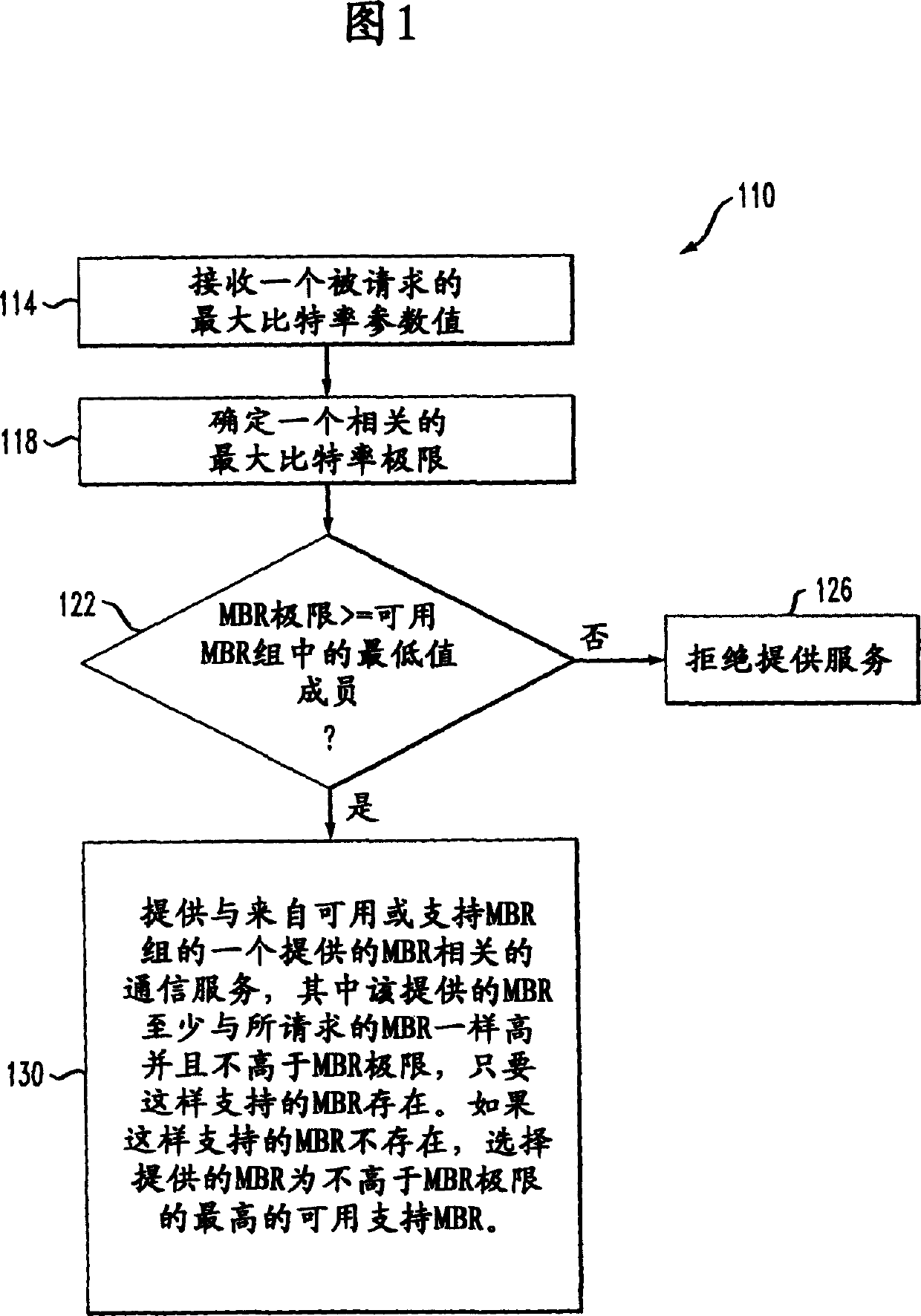
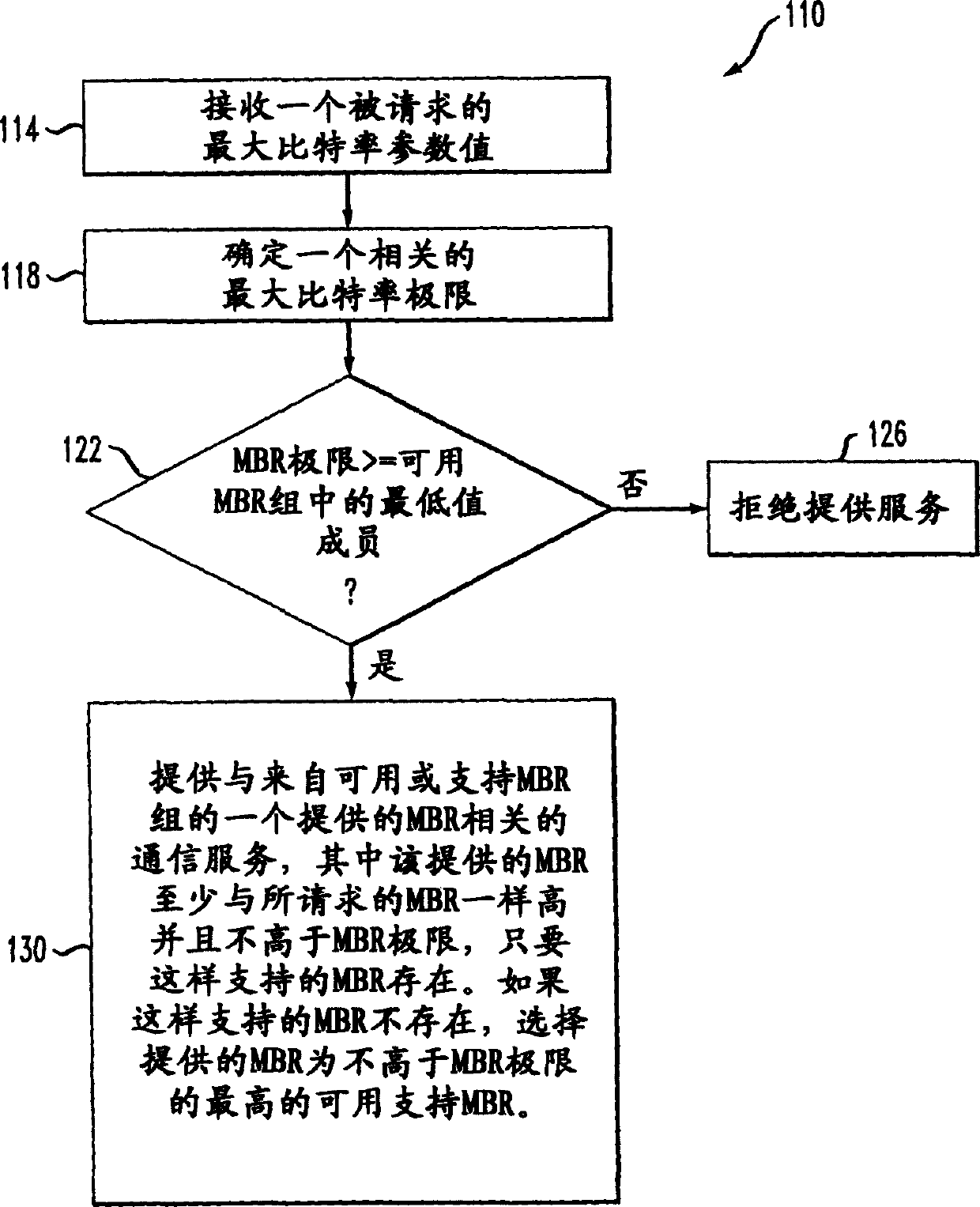
[0031] Referring to FIG. 1, a method 110 for a network element, such as a Serving General Packet Radio Support Node (SGSN), responding to a user equipment maximum bit rate request of a user includes receiving 114 a requested maximum bit rate attribute or parameter value, determining 118 an associated maximum bit rate limit and determining 122 whether said maximum bit rate limit is greater than or equal to a lowest value member of an available maximum bit rate (MBR) set. Providing the requested service requires a network element (such as an SGSN, Node B (base station) or GGSN) to Communications related to MBR requests contribute more network resources (eg, network bandwidth) than the user has contracted for. Accordingly, the network refuses to provide the requested service 126 . If the MBR limit is at least higher than the lowest member value of the set of available MBRs, offer 130 a communication service associated with the offered MBR value. The provided MBR is selected fro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com