Insertion tool for ocular implant and method for using same
A technology for inserting tools and implants, applied in ophthalmic surgery, ophthalmic treatment, etc., which can solve problems such as wrong positioning, inability of inserting tools to position shunts correctly, and weakened visibility of hands
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
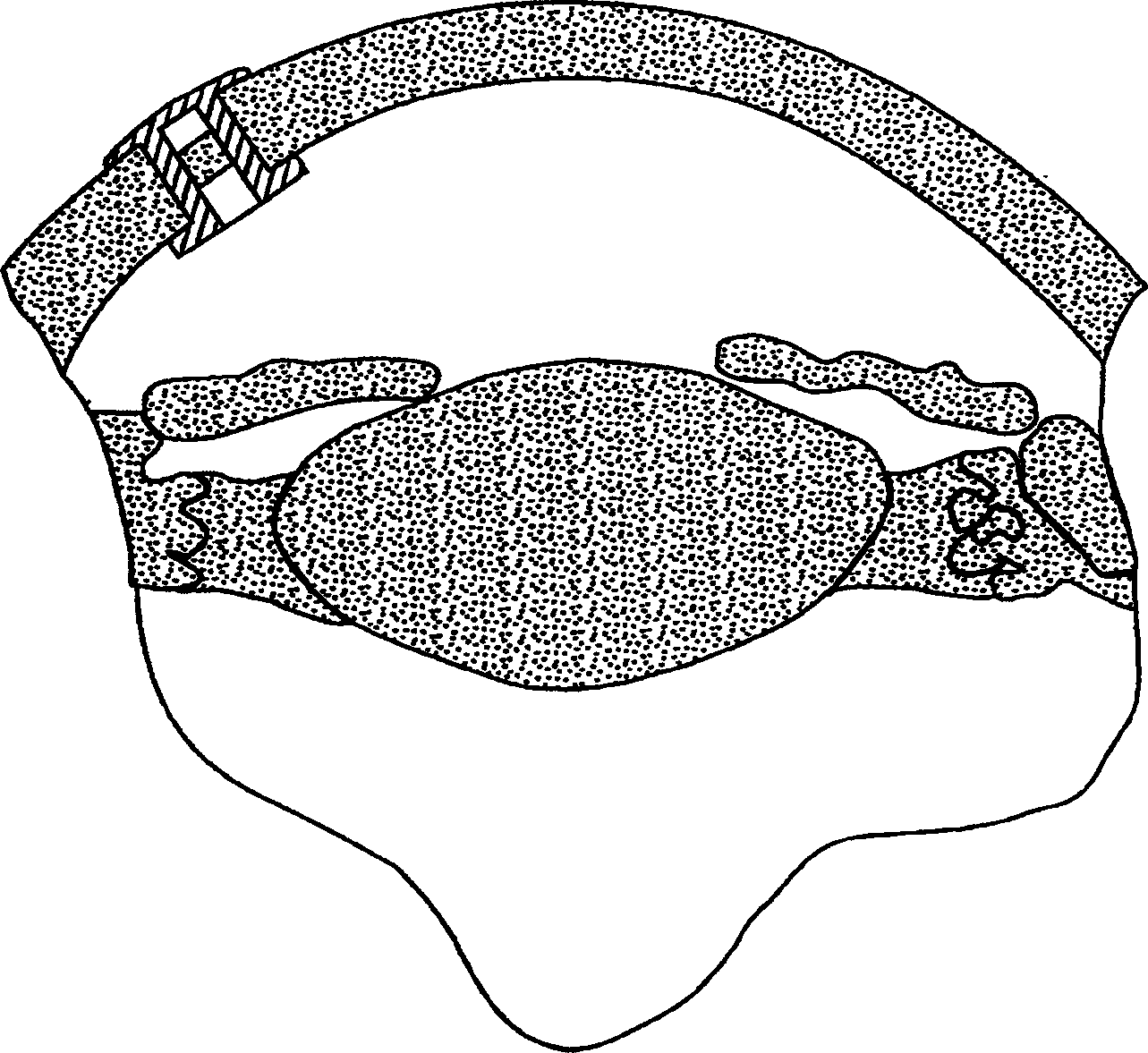
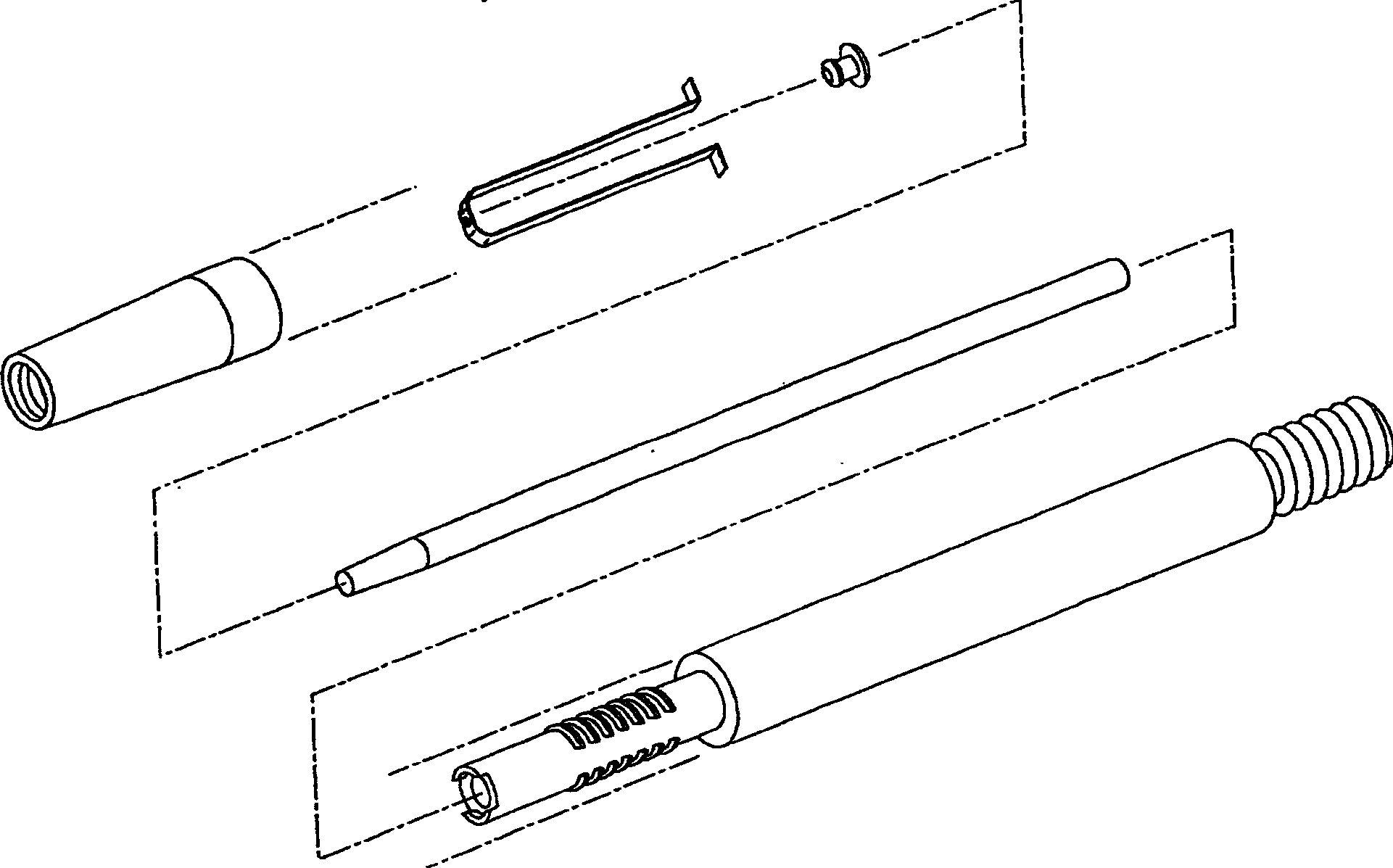
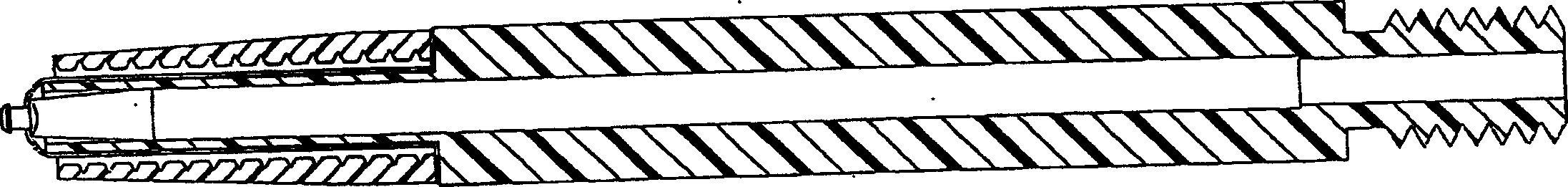
[0040] A shunt that penetrates the cornea (hereinafter referred to as a shunt) is used to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) in the eye by draining aqueous humor from the inner chamber of the eyeball through the cornea to the terafilum. To do this, a shunt must be implanted in the cornea of the eye through a small incision and run through the inner and outer surfaces of the cornea. However, shunts are very small and difficult to manipulate and handle during such insertions. To address this problem, embodiments of the present invention described below enable the surgeon to hold the shunt in place by gently manipulating the shunt at the distal end of the installation tool using a thin elastic material until manually released. The elastic material can include many polymeric materials such as polybutadiene, polyisobutylene and polyisoprene or natural rubber. Preferably, only a small portion of the shunt is secured during installation in each additional embodiment, so that the ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com