Optical information device, and information recording/reproducing device
A technology for information recording and optical information, which is applied to optical recording/reproducing, optical recording heads, beam guiding devices, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
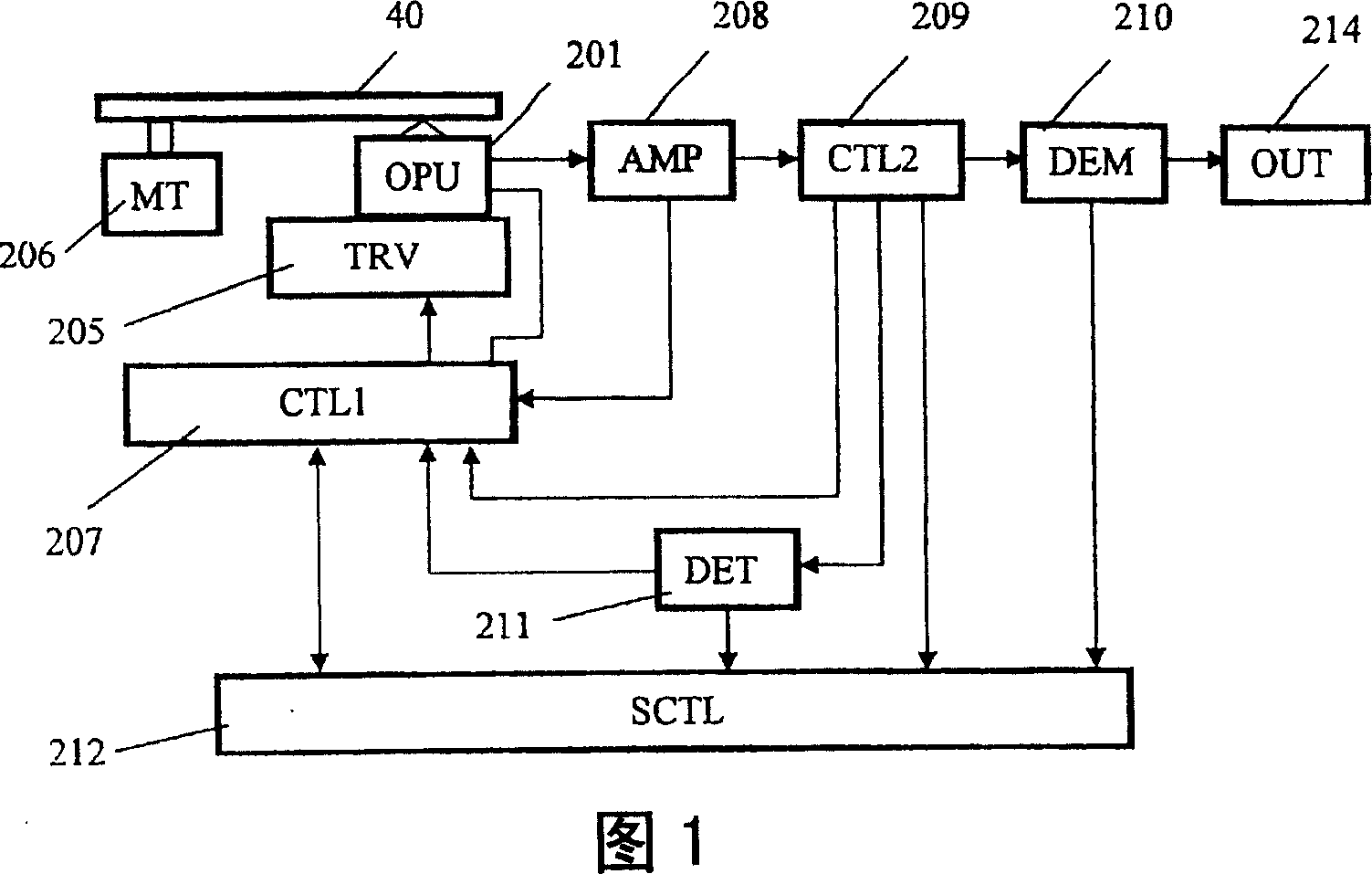
[0054] FIG. 1 shows the configuration of an optical information device according to this embodiment.
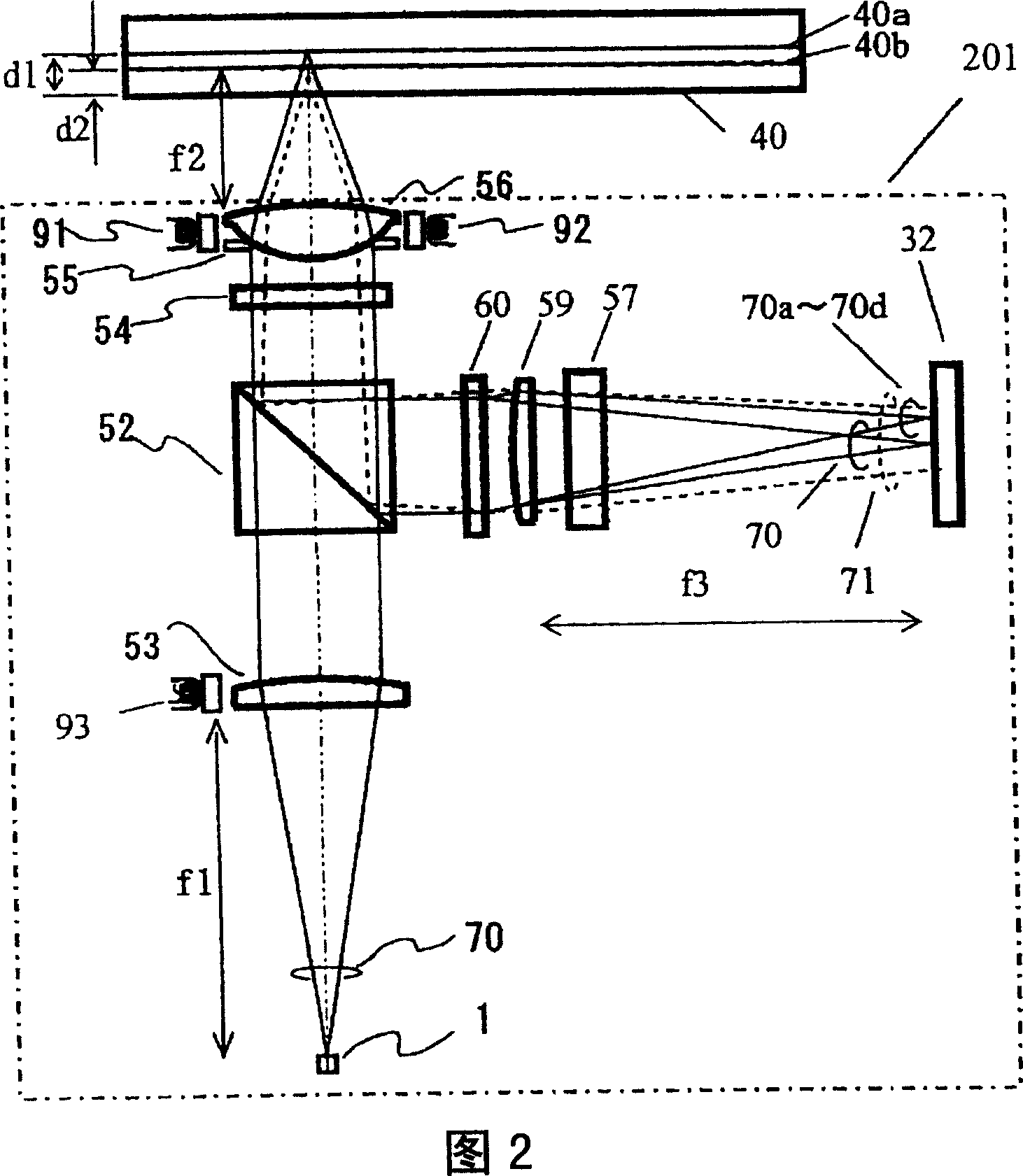
[0055] The optical pickup device 201 (or also called "optical pickup") irradiates the optical recording medium 40 with laser light having a wavelength λ of 405 nm, and reproduces the signal recorded on the optical recording medium 40 . The transport controller 205 moves the optical pickup device 201 along the radial direction of the optical recording medium 40 in order to record or reproduce information at an arbitrary position on the optical recording medium 40 . The motor 206 of the optical recording medium 40 is driven to rotate the optical recording medium 40 . The controller 207 controls the optical pickup device 201 , the transfer controller 205 and the motor 206 .
[0056] The amplifier 208 amplifies the signal read by the optical sensor head device 201 . The controller 209 receives the output signal from the amplifier 208 . Based on the signal, the controller 209 g...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0068] FIG. 8 is a diagram schematically showing the photodetector 33 used in this embodiment and the relationship between the light beam 70, the light beam 71, and the light beams 70a to 70d received by the photodetector 33, respectively.
[0069] The optical pickup of this embodiment differs from the optical pickup of the first embodiment in that a photodetector 33 is used instead of the photodetector 32 . The difference between the photodetector 32 and the photodetector 33 is that, with respect to the center of the light beam 71 reflected from the information recording surface 40b that is not in focus, the photodetectors are arranged at positions approximately symmetrical to the axis of the photodetectors 33e to 33h. 33i~33l. When K is a real number, the TE signal when using such a photodetector 33 can be given by (I33e-I33j)-(I33f-I33i)-K·(I33h-I33k)-(I33g-I33l).
[0070]At this time, the stray light of the light beam 71 incident on the information recording surface 40b o...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0072] FIG. 9 is a diagram schematically showing the photodetector 34 used in this embodiment and the relationship between the light beam 70 received by the photodetector 34 and the light beams 70a to 70n, respectively.
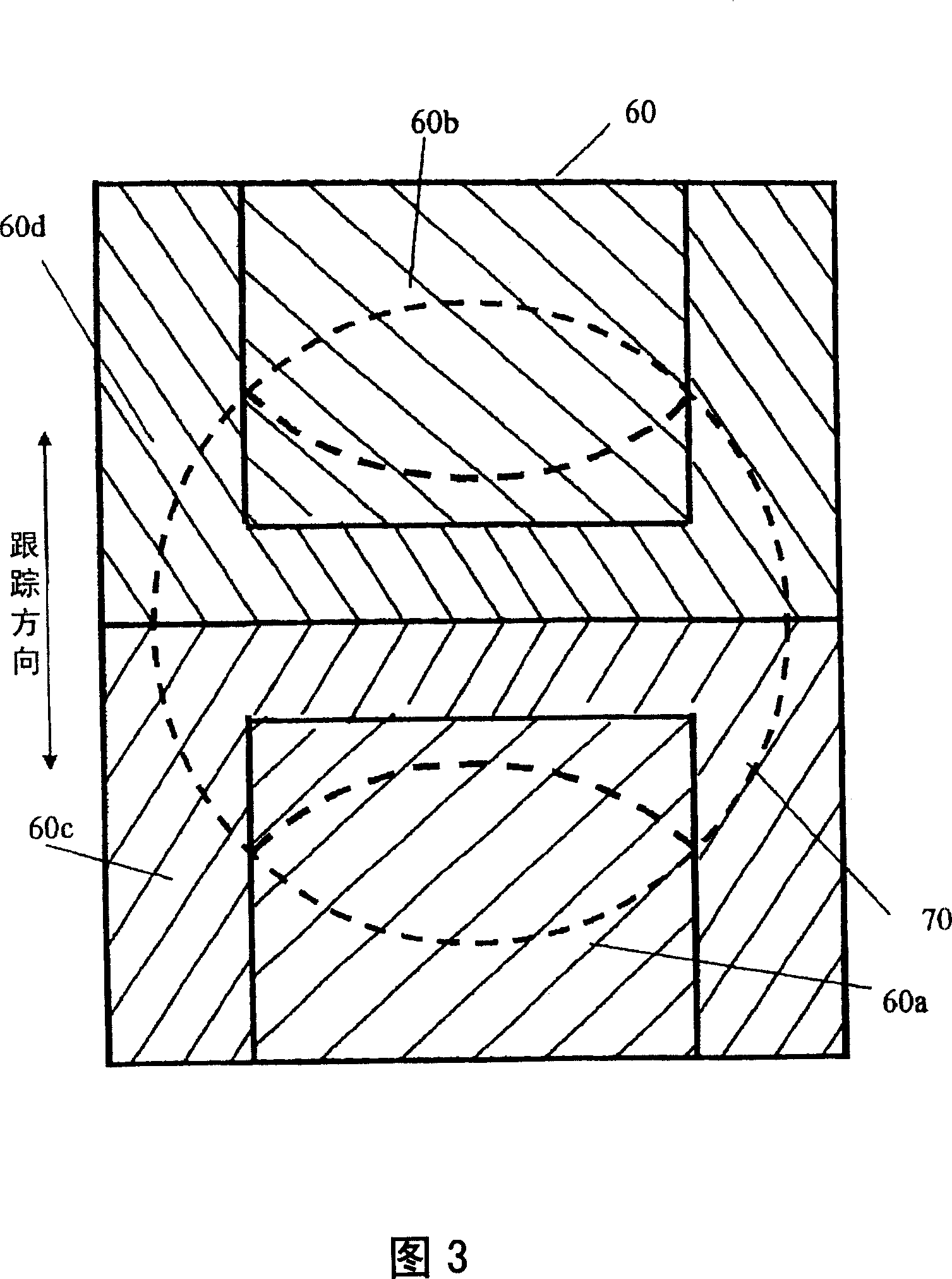
[0073] The difference between the optical pickup of this embodiment and the optical pickup of the first embodiment is that instead of the diffraction grating 60, an unillustrated diffraction grating 61 is used; device 34. In the first embodiment, the groove cross-sectional shape of the diffraction grating 60 may be any of a simple groove shape or a stepped or zigzag grating shape. However, the diffraction grating 61 of this embodiment has a simple groove shape that generates ± diffracted light. In addition, like the diffraction grating 60 of FIG. 3 , it has four types of regions 61a to 61d.
[0074] Next, the beam split by the diffraction grating 61 will be described. The +1st-order diffracted light reflected by the information recording surface 40b and di...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com