Block level space time transmit diversity in wireless communications
a technology of block level space time and transmit diversity, applied in the direction of pulse technique, electromagnetic wave modulation, polarisation/directional diversity, etc., can solve the problem of high overhead associated with their implementation, the well-known disadvantageous phenomenon of fading, and the expense of throughpu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
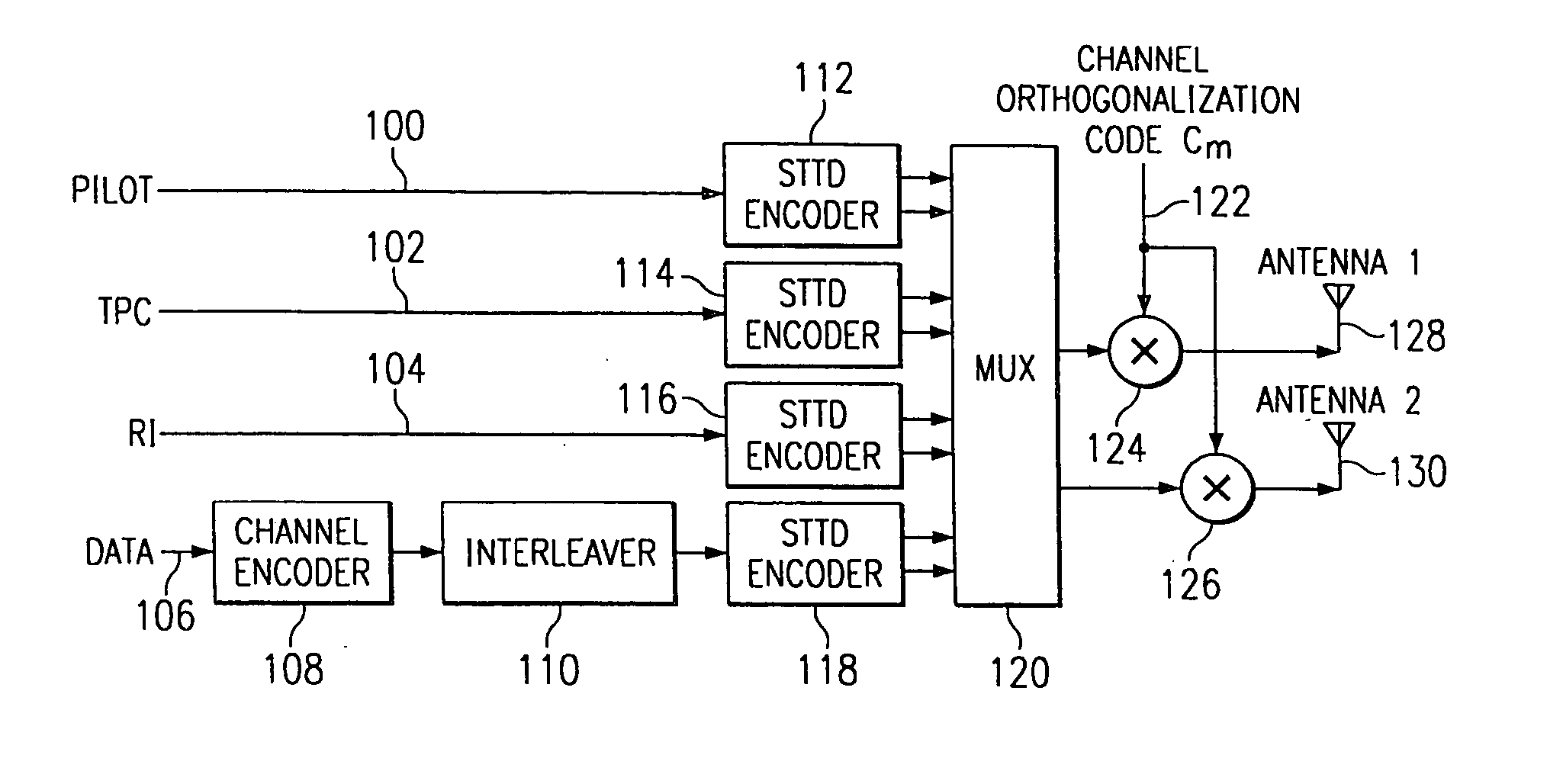
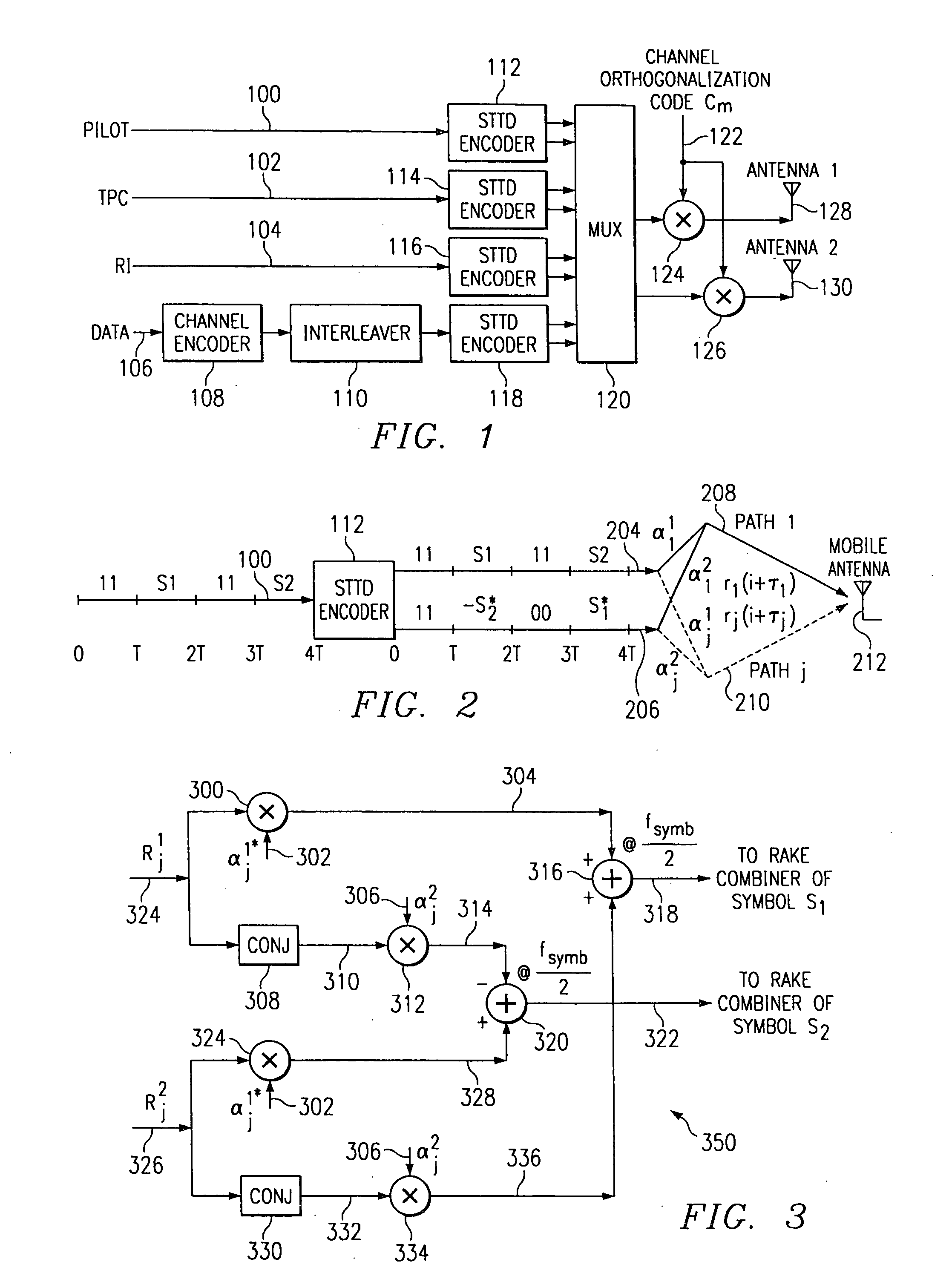
[0016]FIG. 1 diagrammatically illustrates pertinent portions of exemplary embodiments of a transmitting station according to the invention. For example, the transmitting station of FIG. 1 could be a Bluetooth master or slave device. In FIG. 1, input digital information bits are applied to a block formatter 11 which establishes from the input bits an original block of bits having two parts x1 and x2, shown generally at 12. Parts x1 and x2 each include a plurality of bits. The two-part block of bits 12 is input to a nonlinear modulator such as an FSK (or GFSK) modulator 13 which uses conventional techniques to modulate a carrier signal with the block of bits to produce at 14 a modulated block of information including a first part a and a second part b which respectively correspond to the parts x1 and X2 at 12.
[0017] The two-part modulated block at 14 is input to an STTD encoder 15 which outputs at 9 a re-ordered two part block including a first part −b* which represents the negative ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com