Golf club shaft
a golf club and shaft technology, applied in the direction of golf clubs, golf courses, sport apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of low torsional rigidity of carbon shafts, low strength, and inability to hit balls in the direction of balls, and achieve the effect of good feeling when the player swings and a proper degree of flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
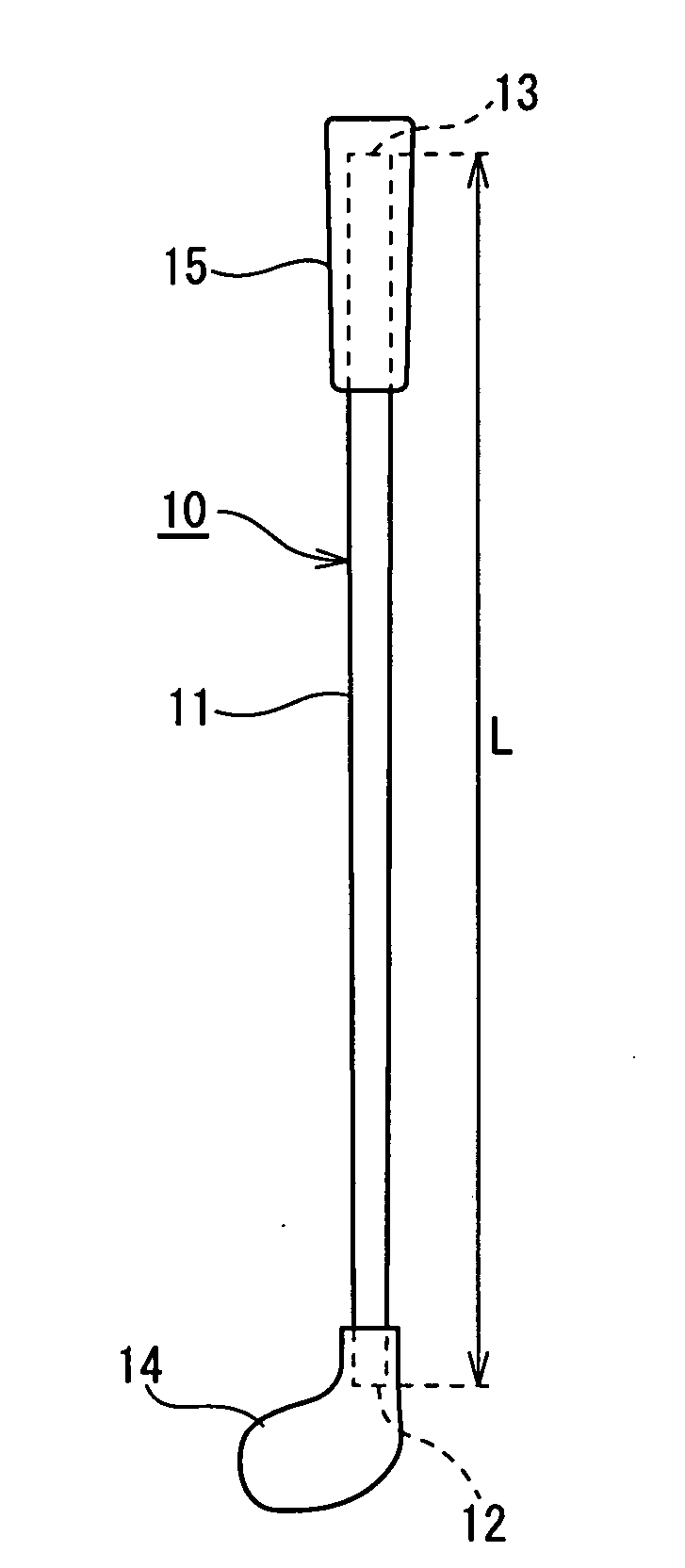
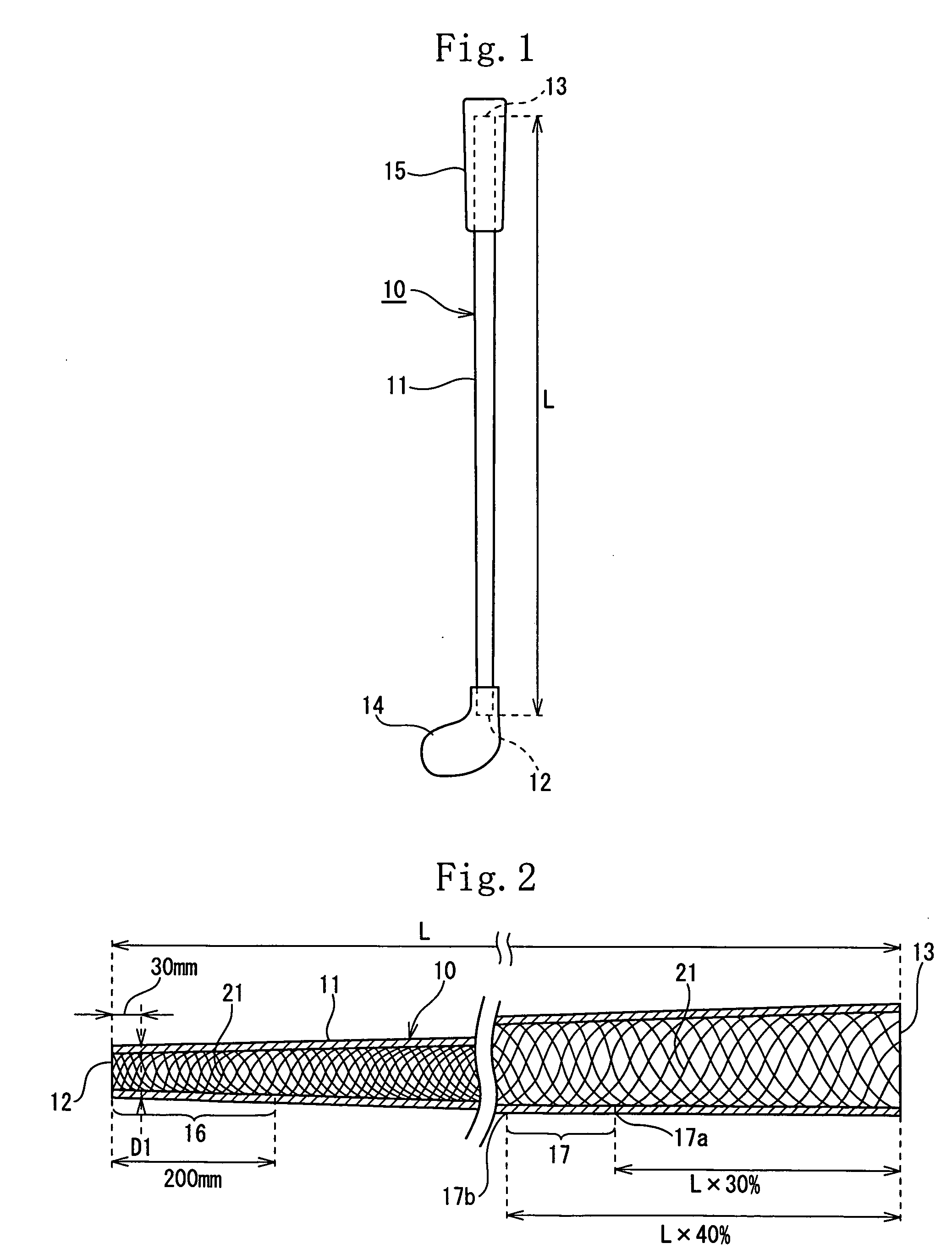
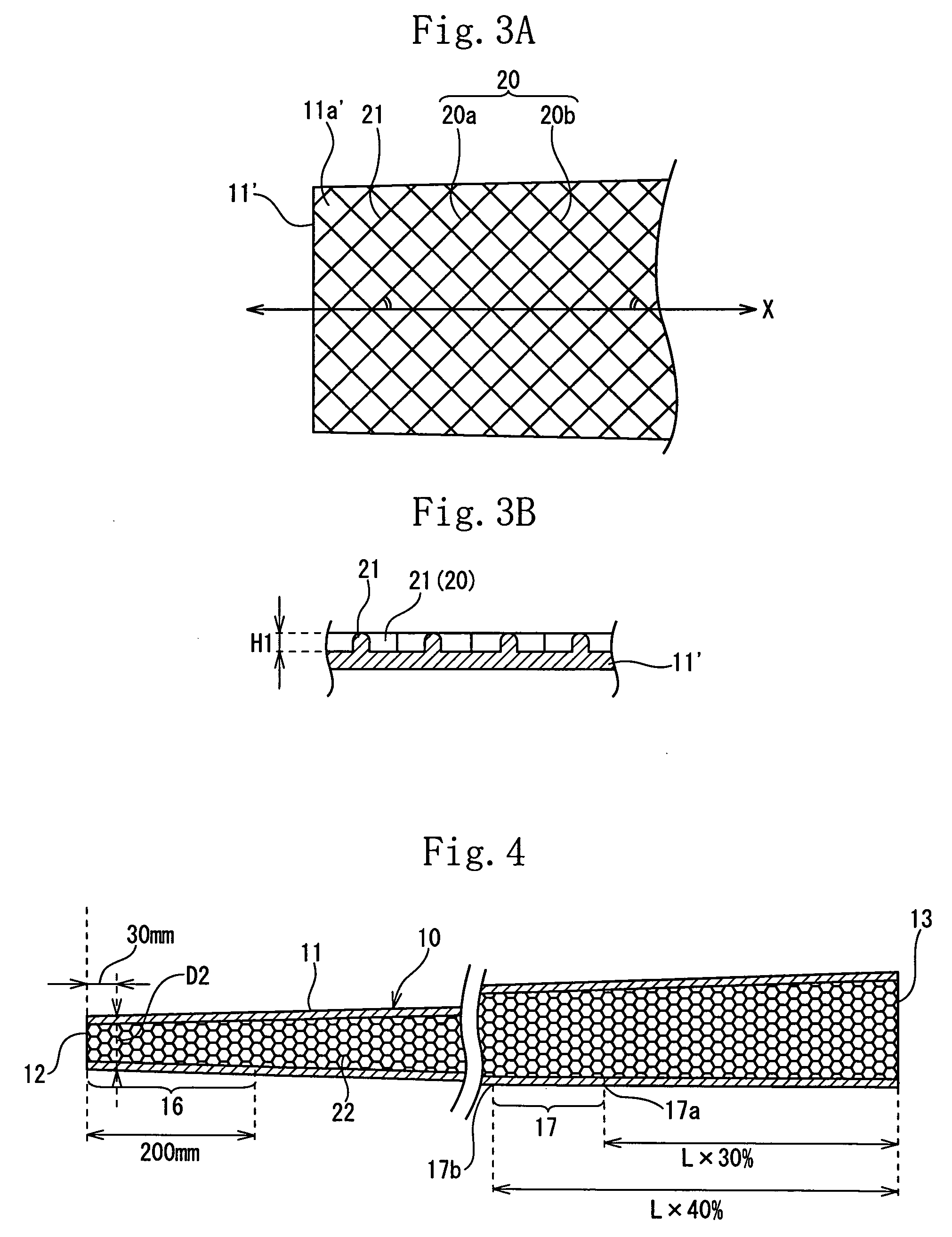
[0101] The shaft of the example 1 had the same construction as that of the shaft of the first embodiment. More specifically, the weight of the shaft was set to 65 g. The outer diameter of the shaft at the position spaced at 30 mm from the head-side front end 12 was set to 9.5 mm. The internal rib 21 was composed of the spiral rib 20a and the spiral rib 20b intersected with the spiral rib 20a. The internal rib 21 was formed over the full length of the shaft 10. The internal rib 21 was projected at a height H1 of 0.3 mm from the inner peripheral surface of the shaft 10. The rigidity value (EI value) of the shaft 10 at the position spaced at 90 mm from the head-side front end 12 was set to 1.4 kg·mm2. The rigidity value of the grip-side reinforcing region 17 was set to 4.2 kg·mm2.
example 2
[0102] The shaft of the example 2 had the same construction as that of the shaft of the second embodiment. More specifically, the weight of the shaft was set to 55 g. The outer diameter of the shaft at the position spaced at 30 mm from the head-side front end 12 was set to 10.1 mm. The internal rib 22 was honeycomb. The internal rib 22 was formed over the full length of the shaft 10. The internal rib 22 was projected at a height H1 of 0.3 mm from the surface of the shaft 10. The rigidity value (EI value) of the shaft 10 at the position spaced at 90 mm from the head-side front end 12 was set to 1.5 kg·mm2. The rigidity value of the grip-side reinforcing region 17 was set to 4.5 kg·mm2.
example 3
[0103] The shaft of the example 3 had the same construction as that of the shaft of the third embodiment. More specifically, the weight of the shaft was set to 65 g. The outer diameter of the shaft at the position spaced at 30 mm from the head-side front end 12 was set to 9.5 mm. The internal rib 23 was composed of the spiral rib 23A which is formed at head side of the shaft 10 and the spiral rib 23B which is formed at grip side thereof. The internal ribs 23 were formed in the region ranging from the head-side front end 12 to the position spaced at 180 mm from the head-side front end 12 and in the region ranging from the grip-side rear end 13 to the position spaced at 200 mm from the grip-side rear end 13. The internal rib 23 was projected at a height H1 of 0.5 mm from the inner peripheral surface of the shaft 10. The rigidity value (EI value) of the shaft 10 at the position spaced at 90 mm from the head-side front end 12 was set to 1.4 kg·mm2. The rigidity value of the grip-side re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com