Method for adapting link weights in ralation to optimized traffic distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
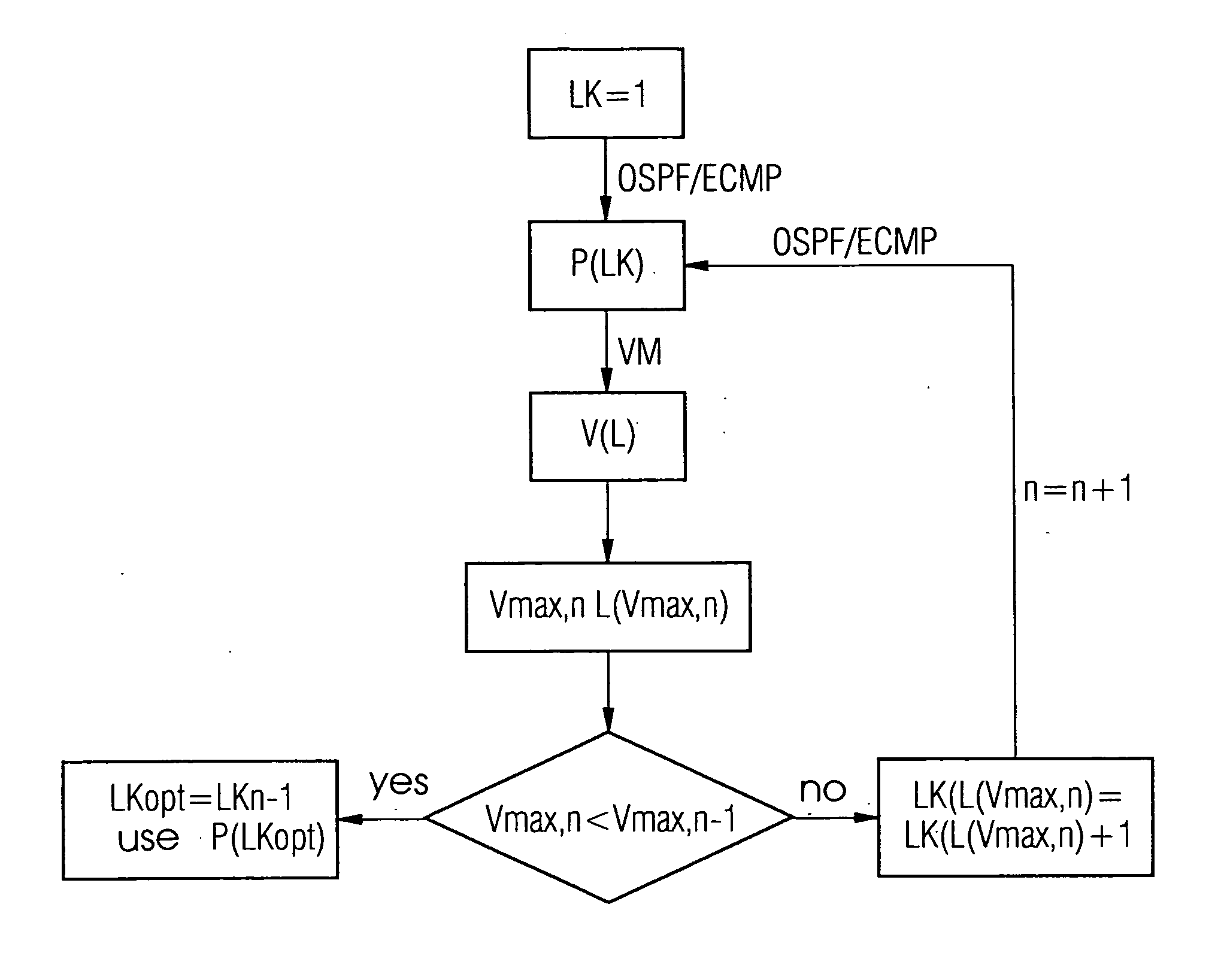
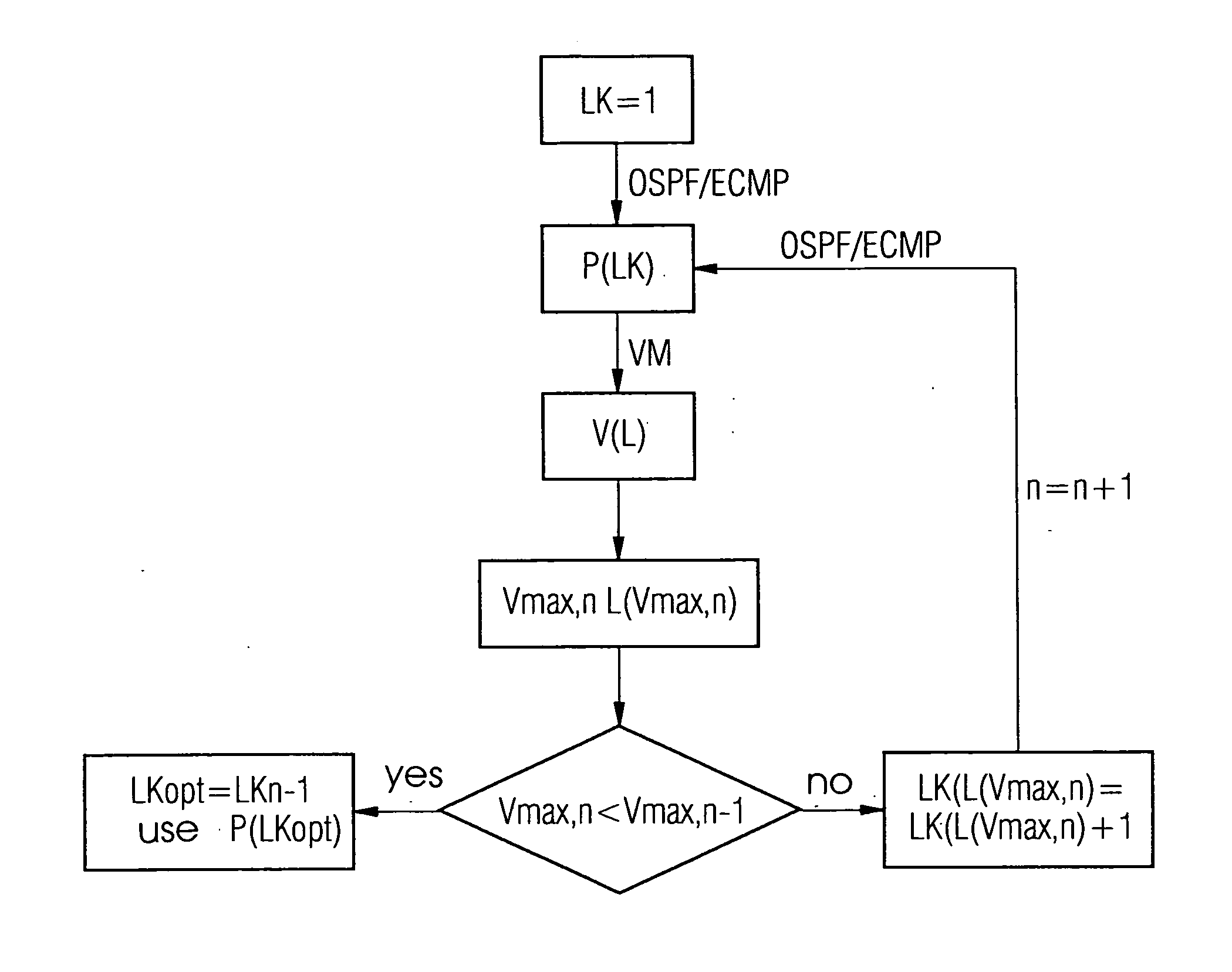
[0015] The exemplary embodiment starts from the assumption that the communication network is an IP network which is formed with nodes and links and that paths are to be determined for routing within the framework of the ECMP concept. To begin with the link costs LK are initialized with the value 1. On the basis of these link costs LK the ECMP paths P(LK) are then calculated. The calculation is undertaken by determining the paths with the lowest accumulated link costs LK for routing between two nodes, as is provided for in the OSPF protocol.
[0016] Least-cost paths to a destination node can for example be determined in the following way. All neighboring nodes of the destination node are initially determined and these neighboring nodes are assigned the link costs as node costs. This defines the routing for this first ring of nodes around the destination node. The procedure below is undertaken ring-by-ring, moving up from a ring to the next higher ring in each case. A ring in this case...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com