Pressure Sensitive Bypass Defrost System
a bypass defrost and pressure-sensitive technology, which is applied in the field of defrost arrangement of air exchange ventilators, can solve the problems of increasing pressure drop and building up, and achieve the effects of limiting the depressurization effect, increasing pressure drop, and maintaining the heating capacity of the heat exchanger
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
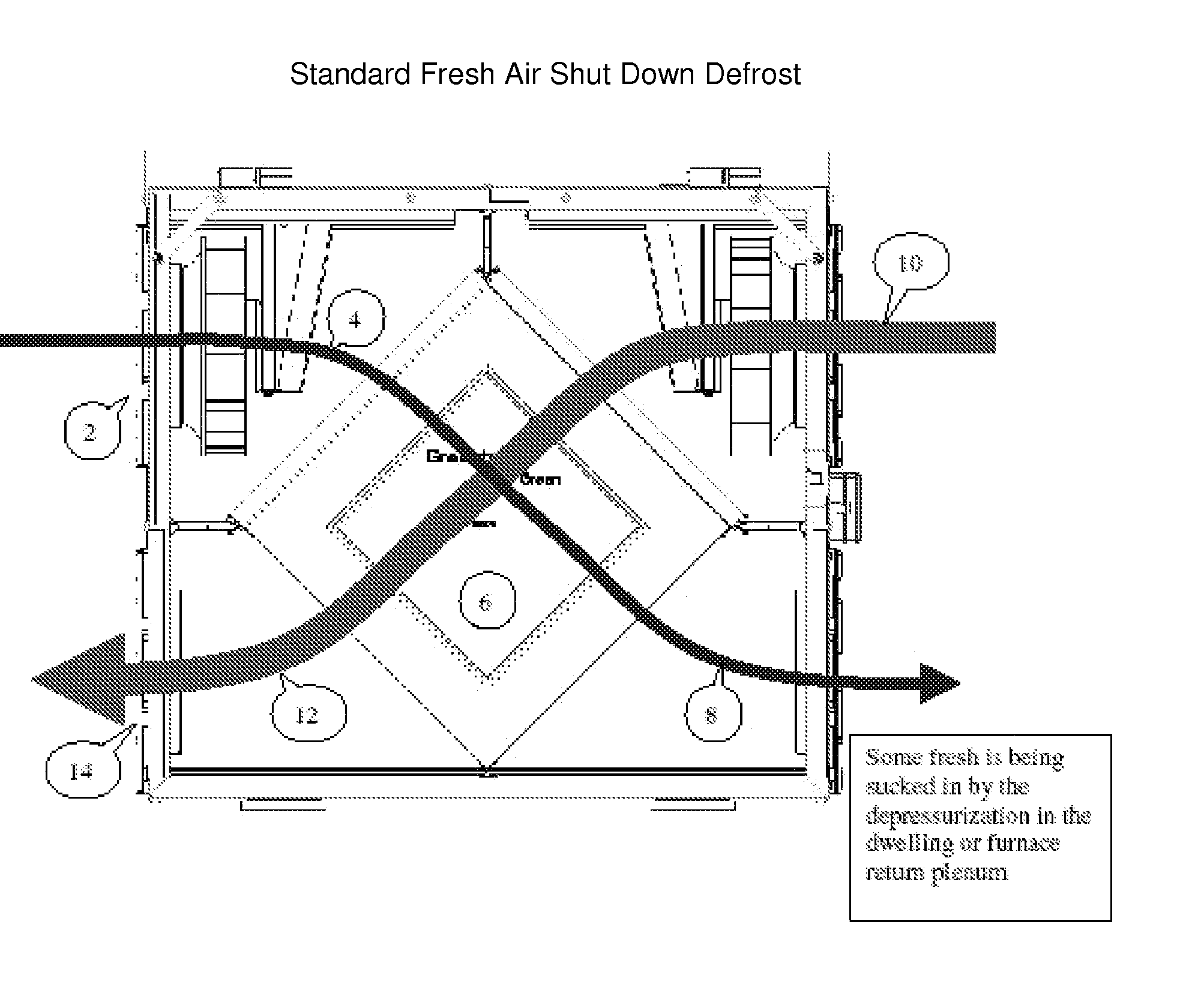
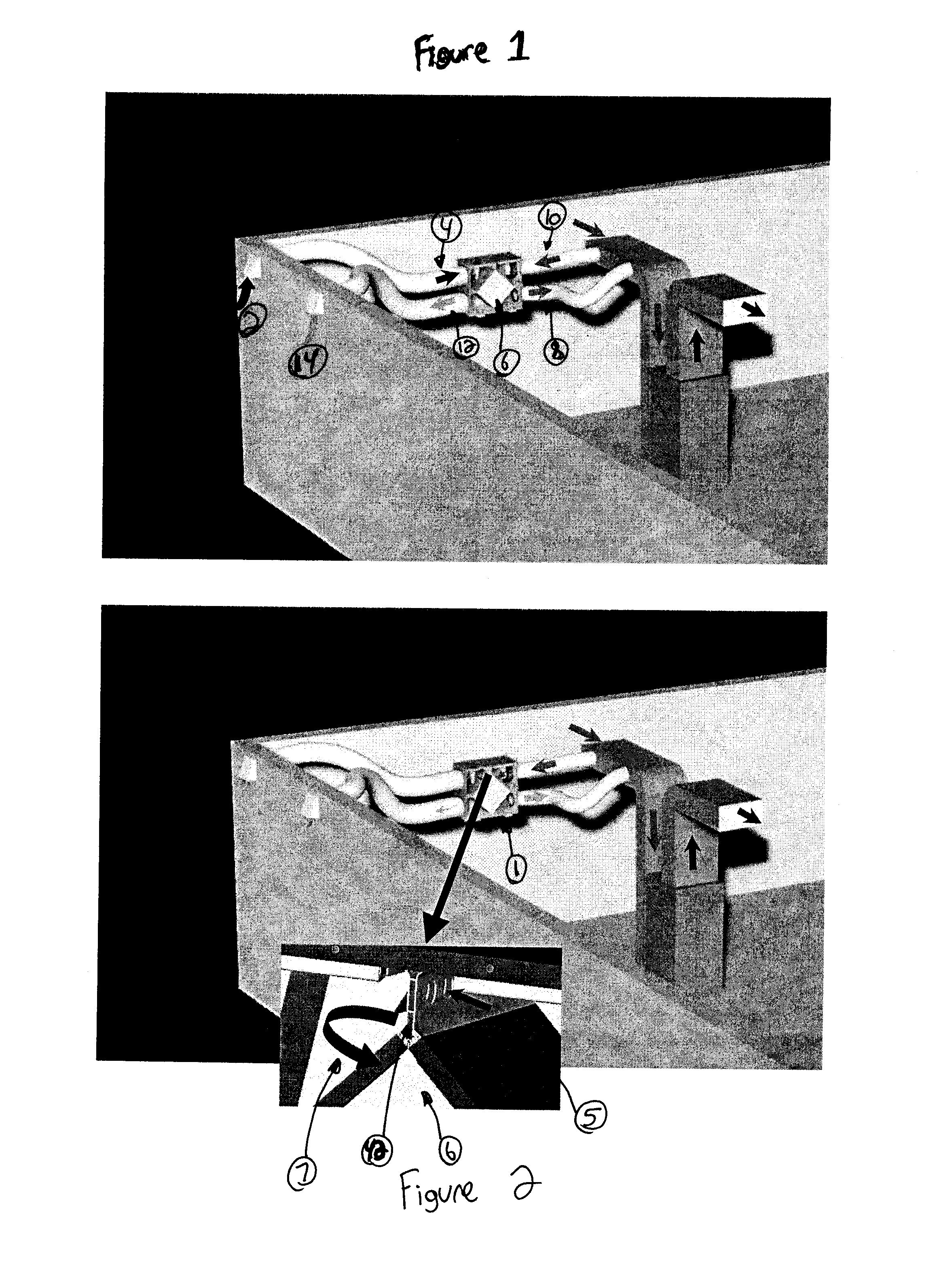
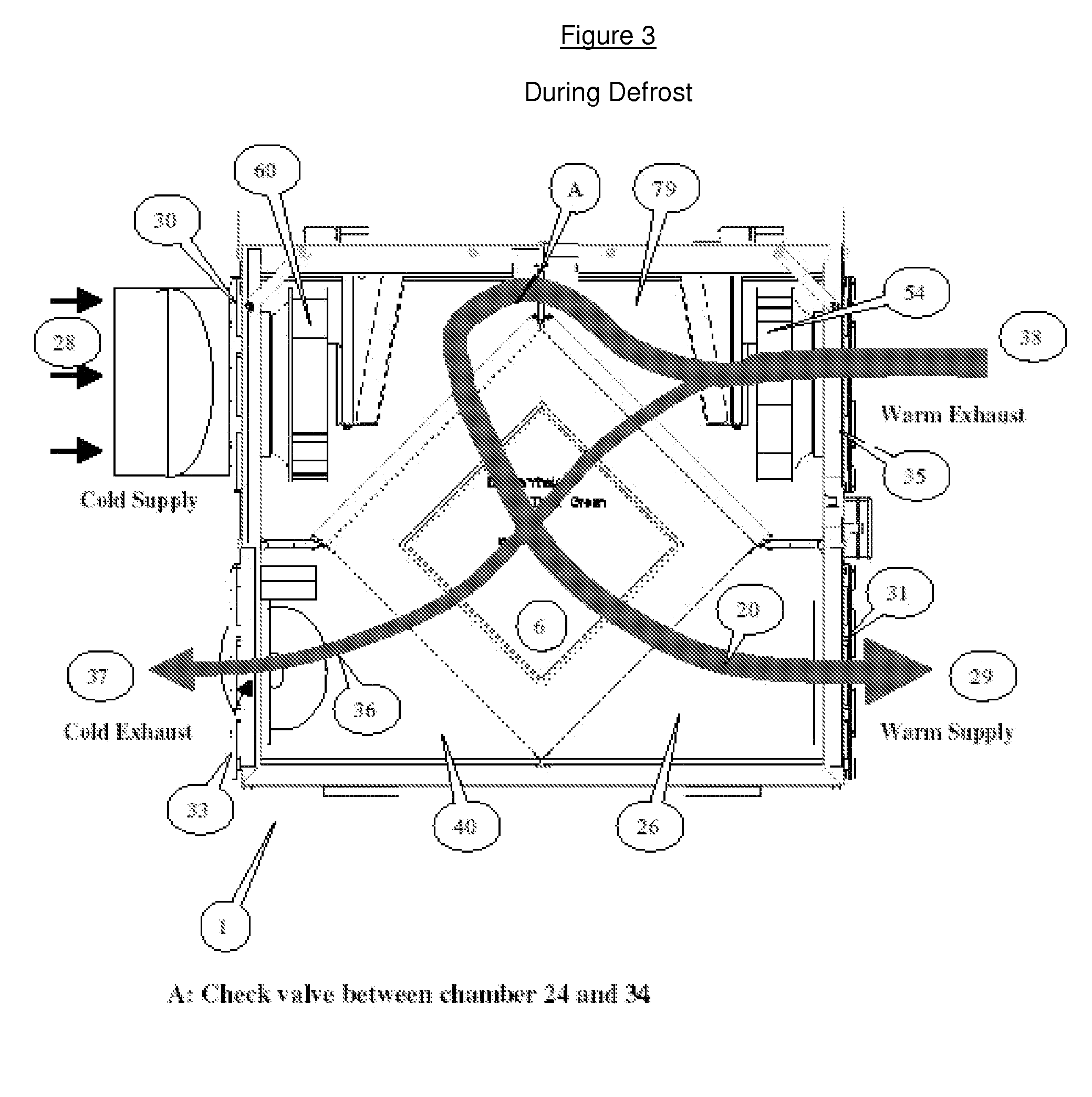
[0028] The present invention provides a defrost arrangement for air exchange ventilators which includes a heat exchanger to extract heat from the stale air and transfer it to the incoming fresh air, and which introduces warm air in both channels of the heat exchanger to accelerate defrost, continue some ventilation of stale warm air, and recirculate a portion of the stale air flow at mild temperatures as opposed to the lower temperatures of incoming fresh air. In conventional systems, during the defrost mode the fresh air motor shuts off, and warm stale air is used to defrost the heat exchanger. This air is then totally expelled outdoors which can contributes to the depressurization within the dwelling or building. With reference to FIGS. 1 and 4, incoming fresh air is admitted into the air exchange system at (2) to flow through an inlet passageway (4), which is then passed through the heat exchanger (6), to flow (8) into an enclosure. Exhaust air to be discharged from the enclosure...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com