Accessing radio content from a non-radio source
a radio content and non-radio source technology, applied in the field of accessing radio content and radio segments from a non-radio source, can solve the problems of not always having access to the radio broadcast stream or media broadcast stream provided by the content provider, user may not be able to finish listening to the segment, and miss parts of broadcast content, etc., to achieve accurate perspective of user's listening history, easy to find segments, and update play counts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
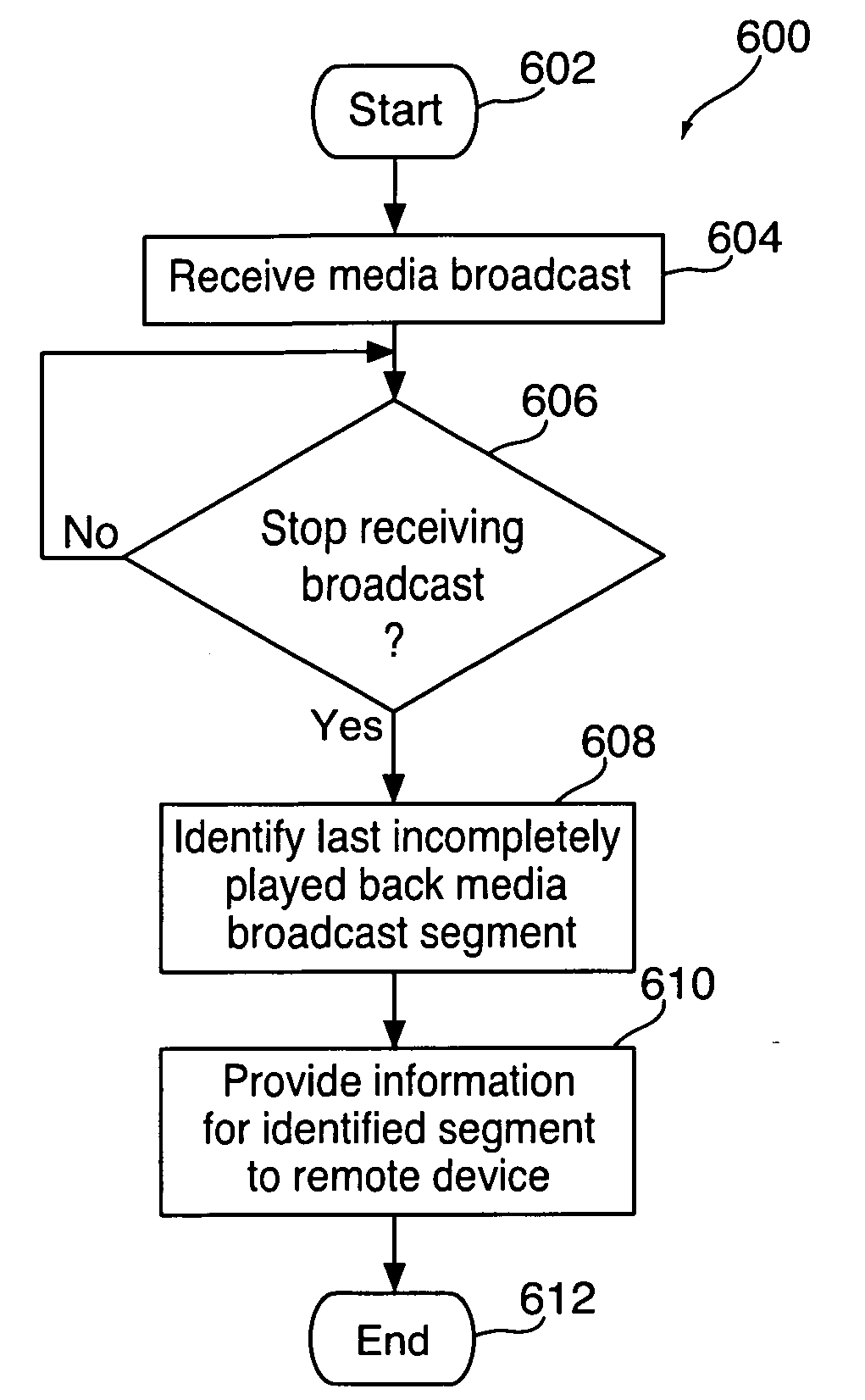
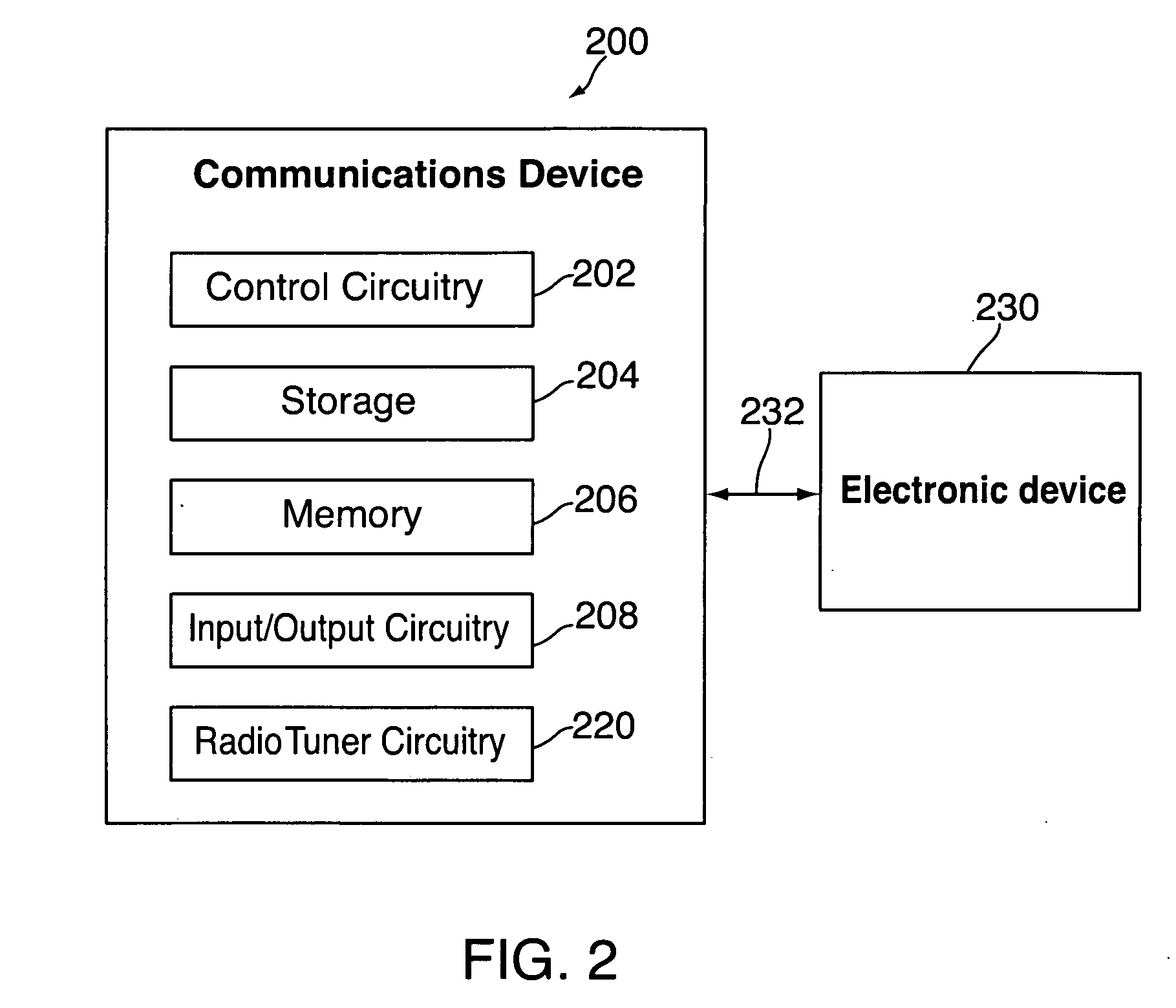
[0018]Using a communications device, a user can tune to and receive a broadcast stream of media items for playback. A media or content source can provide the broadcast stream over any type of communications network. For example, a user can direct a device having radio tuning circuitry to tune to a radio broadcast provided by a radio station. The communications device can include a stand-alone device, such as a portable radio, or communications circuitry (e.g., dedicated circuitry) for selecting and receiving specific broadcasts (e.g., radio circuitry in a car). In some embodiments, the communications device can communicate with a remote server or cloud, a distinct electronic device, or other component of the communications device to provide an indication of the currently received broadcast. For example, the communications device can provide the information at regular intervals (e.g., every 20 seconds, or every minute). As another example, the communications device can provide inform...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com