Adjustably fitted protective apparel with rotary tension adjuster
a technology of tension adjuster and adjustable fitting, which is applied in the direction of protective clothing, mechanical equipment, cables, etc., can solve the problems of vests made only from kevlarTM materials that are generally ineffective, wearers could still receive blunt force trauma, and vests made only from kevlarTM materials are generally ineffectiv
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
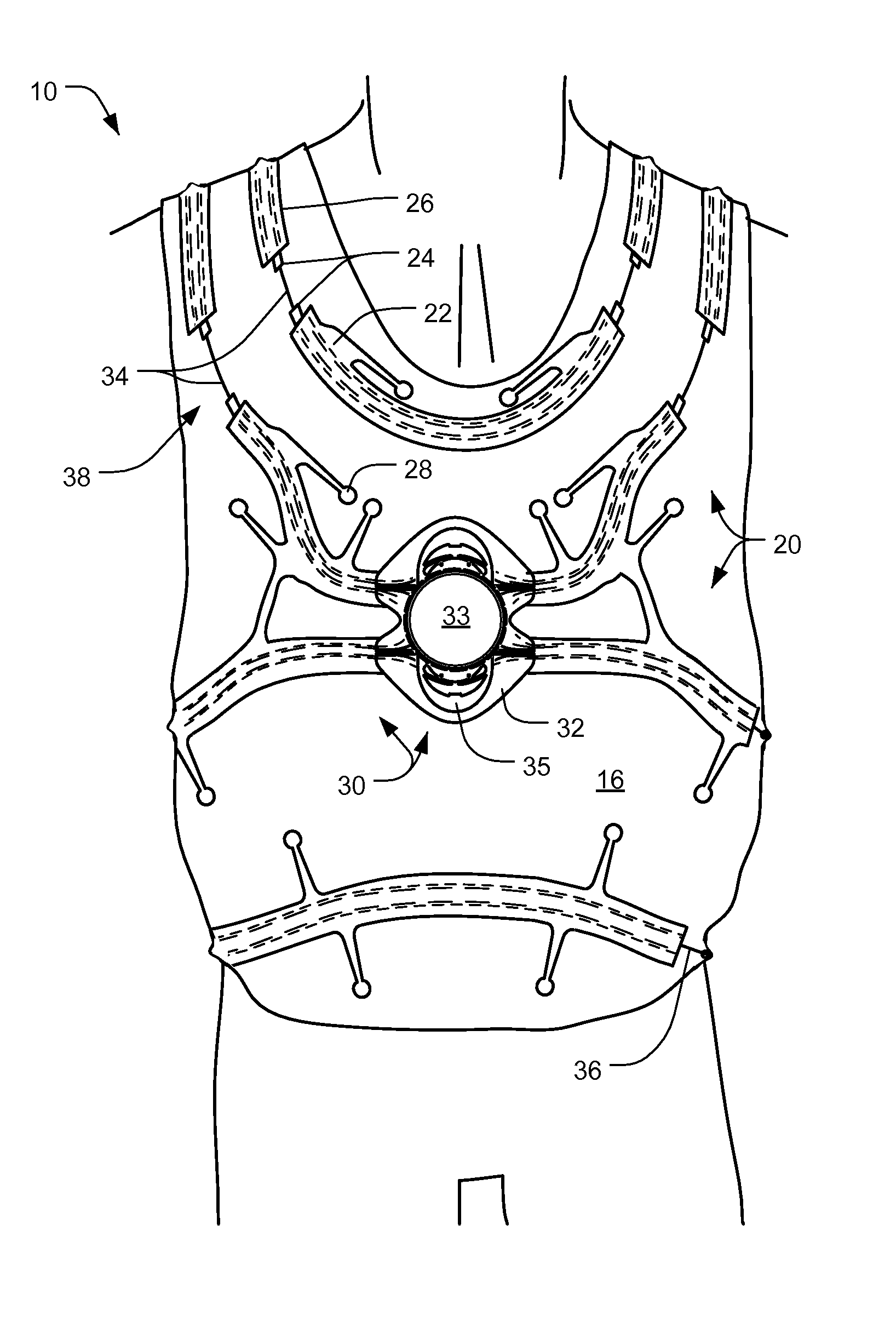
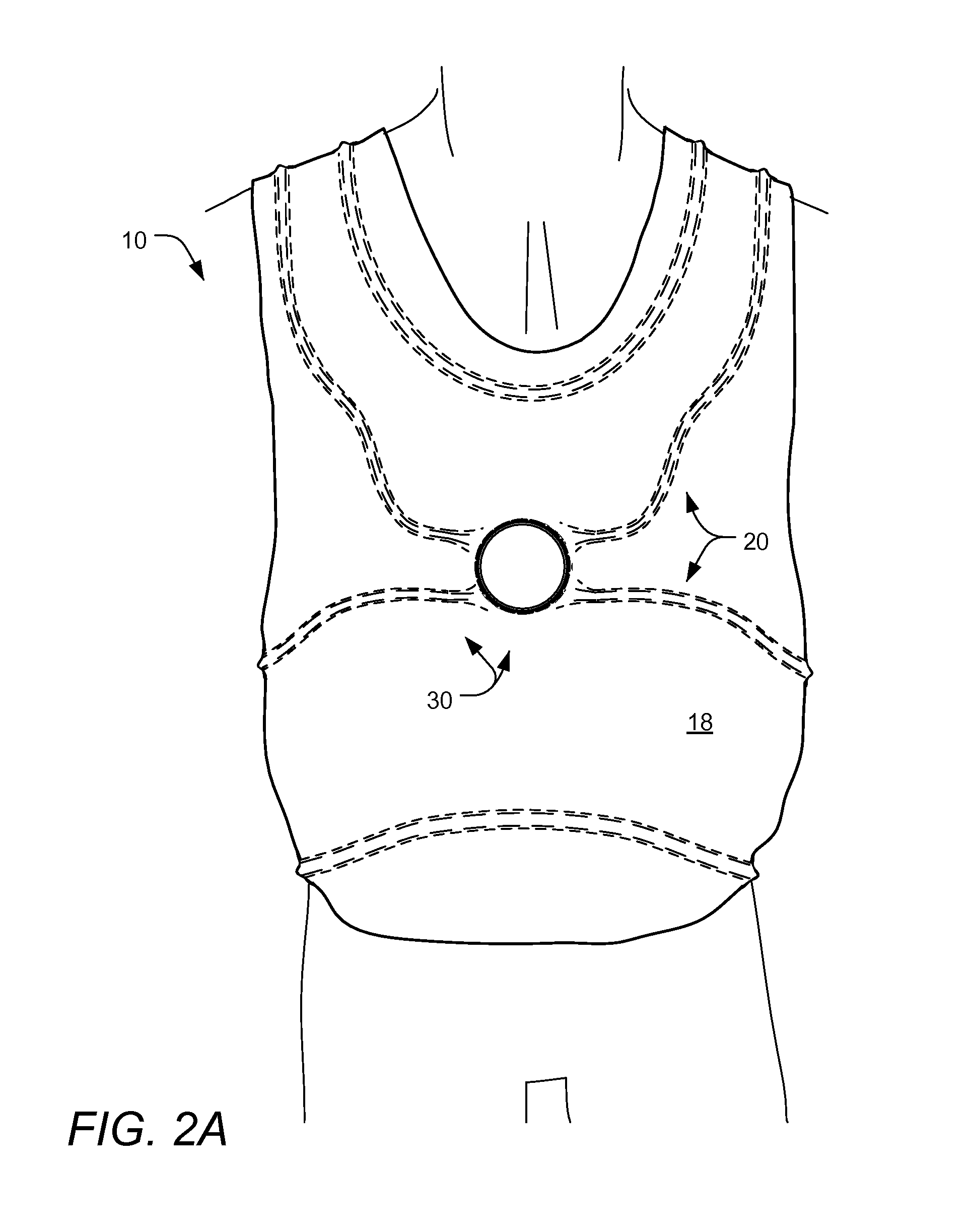
[0062]FIG. 2A is a front view of an article of adjustably fitted protective apparel 10, worn by a user, according to the present invention; FIG. 2B is a front view of the article of protective apparel 10 of FIG. 2A, still worn by a user, but shown with an outer cover 18 removed for clarity; FIG. 2C is a front view of the article of protective apparel 10 of FIG. 2A, shown in an unworn disposition; and FIG. 3A is a side cross-sectional view of a portion of the right side of the article of protective apparel 10 of FIG. 2C, taken along line 3-3. As collectively shown therein, the illustrated article 10, often generally referred to hereinafter as a bullet-proof vest, comprises one or more protective panels 12, an inner cover 14, a middle cover 16, an outer cover 18, a channel distribution system 20 and an adjustable tensioning system 30.
[0063]The adjustable tensioning system 30 comprises a rotary tension adjuster 32 and a plurality of tensioning lines 34, 36, while the channel distributi...
third embodiment
[0083]FIGS. 5A and 5B are front views of an article of adjustably fitted protective apparel 210 according to the present invention, and FIG. 6 is a front view of the article of adjustably fitted protective apparel 210 of FIG. 5A. In this embodiment, four tension loops 234 extend from a rotary tension adjuster 232 centrally located at the sternum area of the front of the vest. Each loop 234 extends from the rotary tension adjuster 232 and through a respective clip 237. The clips 237 are each removably attached to holed bands 239 attached to the vest 210. Respective left and right yoke bands 239 extend from the front pectoral areas to the back shoulder blade areas of the vest 210. As shown in FIG. 6, a single waist band 239 passes across the lower portion of the back of the vest 210 and has respective opposite ends that extend beneath the arms along the ribs toward the adjuster 232. Each band 239 provides a number of holes 241 for receiving a clip 237 so that positioning each clip 237...
fourth embodiment
[0084]FIG. 7 is a front view of an article of adjustably fitted protective apparel 310 according to the present invention. In this embodiment, a receiving pocket 250 is formed in the article for receiving a tension adjuster. One or more apertures are defined in the pocket for extension there through of control elements of a tension adjuster so that the tension adjuster can be manipulated without removal from the pocket. Furthermore, in this embodiment, yoke portions of the article comprise crossed belts, for example woven nylon belts, that provide strength and that are covered by fabric portions for comfort.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com