Method and apparatus for indicating congestion in a source routed network
a source routed network and congestion detection technology, applied in the field of networkwork, can solve the problems of high level of line noise, lack of available bandwidth, and inability to support the available network bandwidth at that time, and achieve the effect of achieving the full bandwidth potential of the path
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
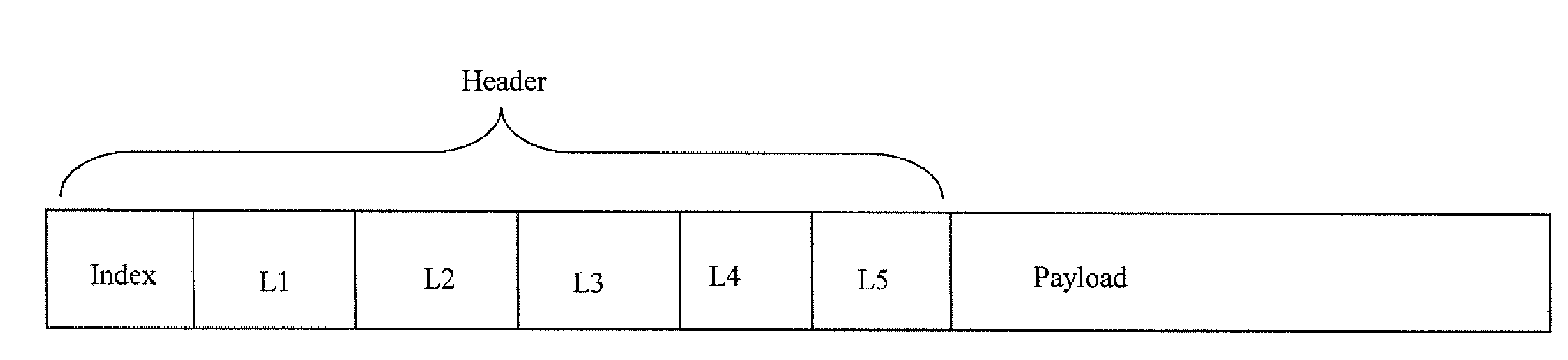
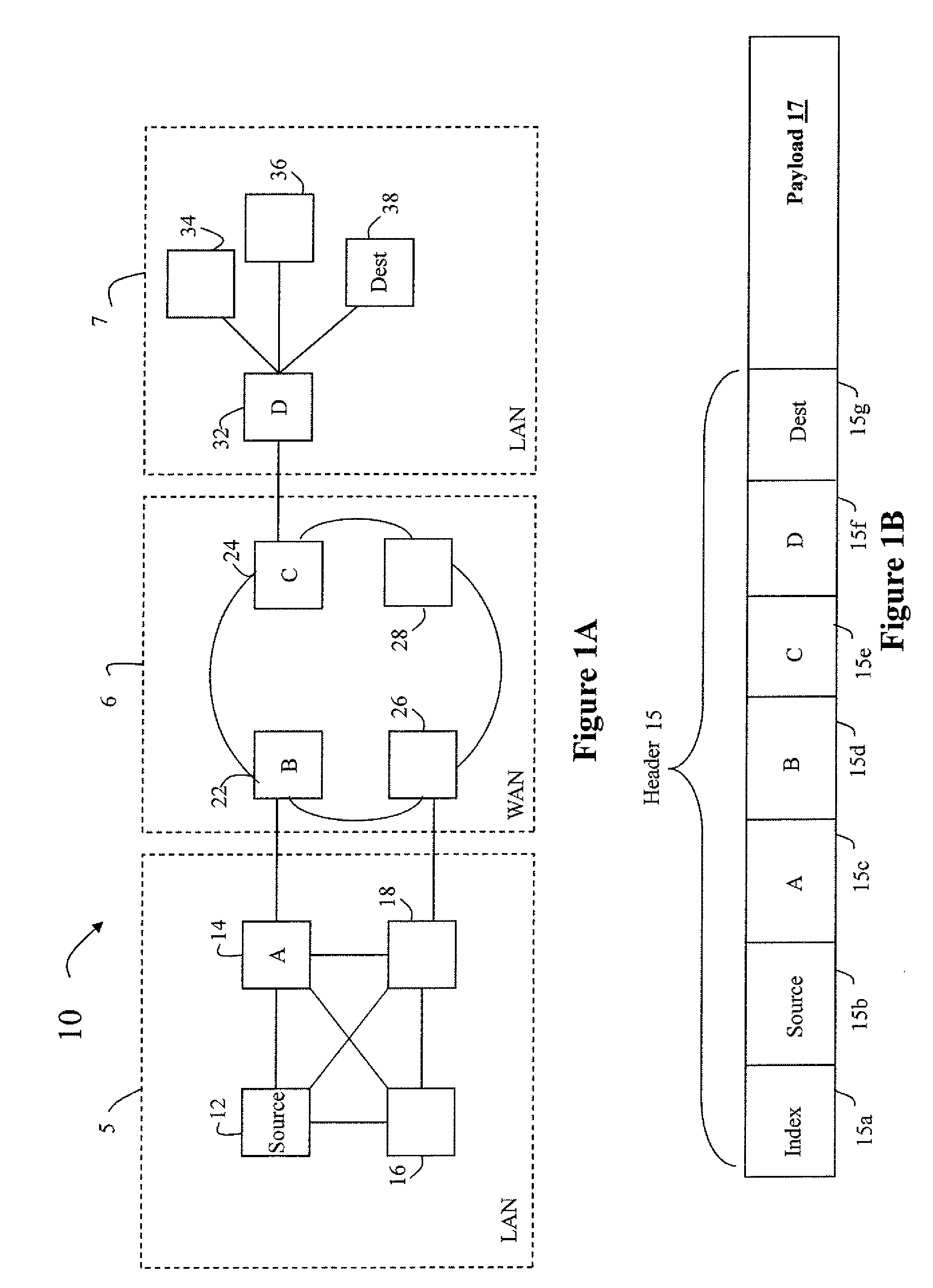
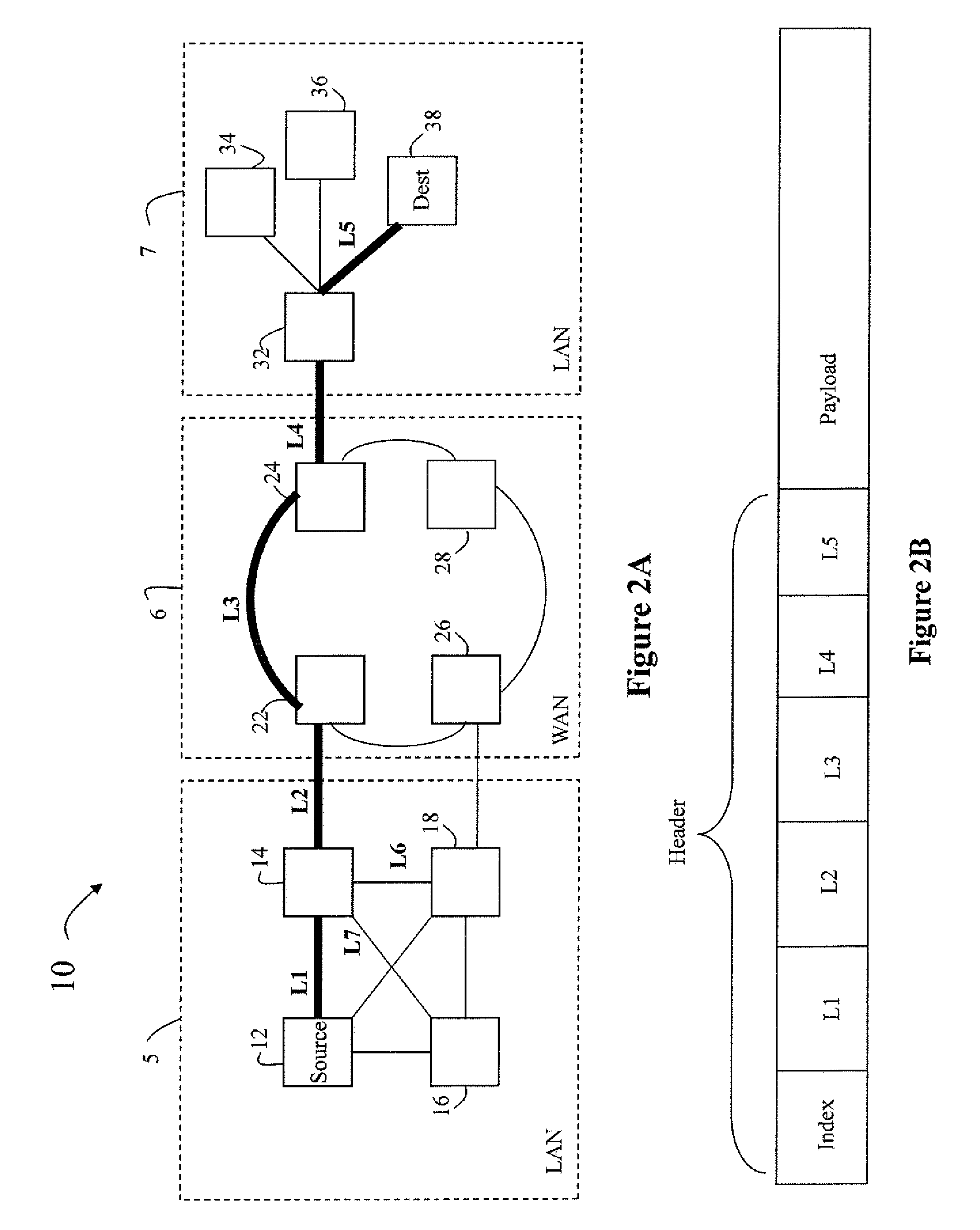
[0024]As it is known in the art, in a source routed network, each source node essentially directs the flow of traffic from the source through any intermediate nodes in the network to the destination. The source pre-computes the preferred route, based upon any known routing protocol, compiles a list of the intermediate ‘hops’ that direct the packet over the preferred route, and appends the list of hops to the packet header. As the packet header is parsed at each intermediate node, the next ‘hop’ is retrieved from the list and the packet is forwarded to the next hop by the intermediate node. Source routing thus removes the need for routing calculations to be performed at intermediate nodes, allowing faster packet forwarding techniques to be used to improve communication bandwidth.
[0025]Referring now to FIG. 1A, an exemplary network 10 in which source routing may be used is shown. A source device 12 that seeks to communicate with a destination device 38 executes a transport layer routi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com