Wireless electrical temperature regulator for food and beverages
a temperature regulator and wireless technology, applied in the field of accessories, can solve the problems of inconvenience for consumers, devices are generally not able to keep food or beverages hot for an extended period of time, and food and beverages may not be desirable,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example # 1
Example #1
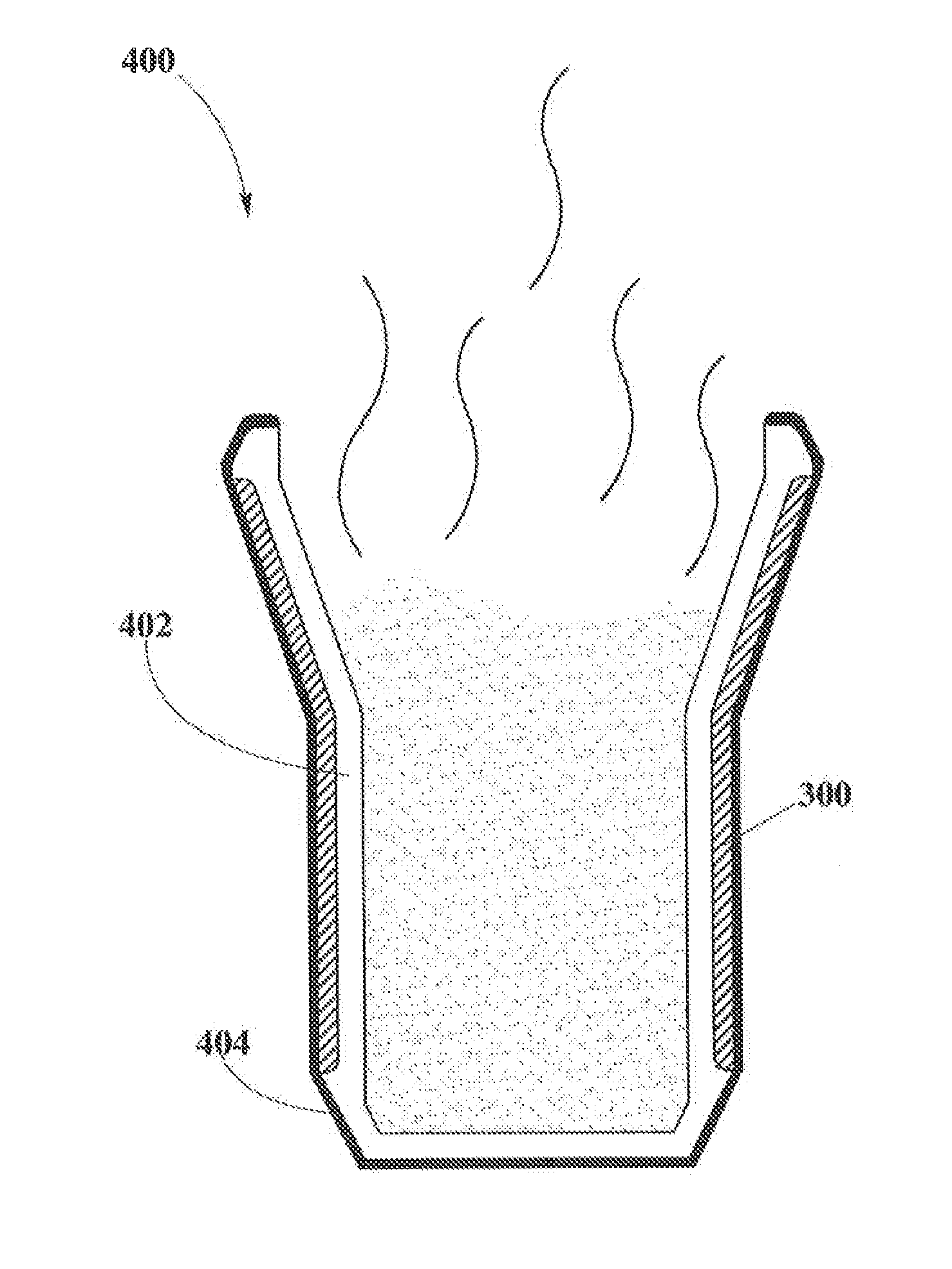
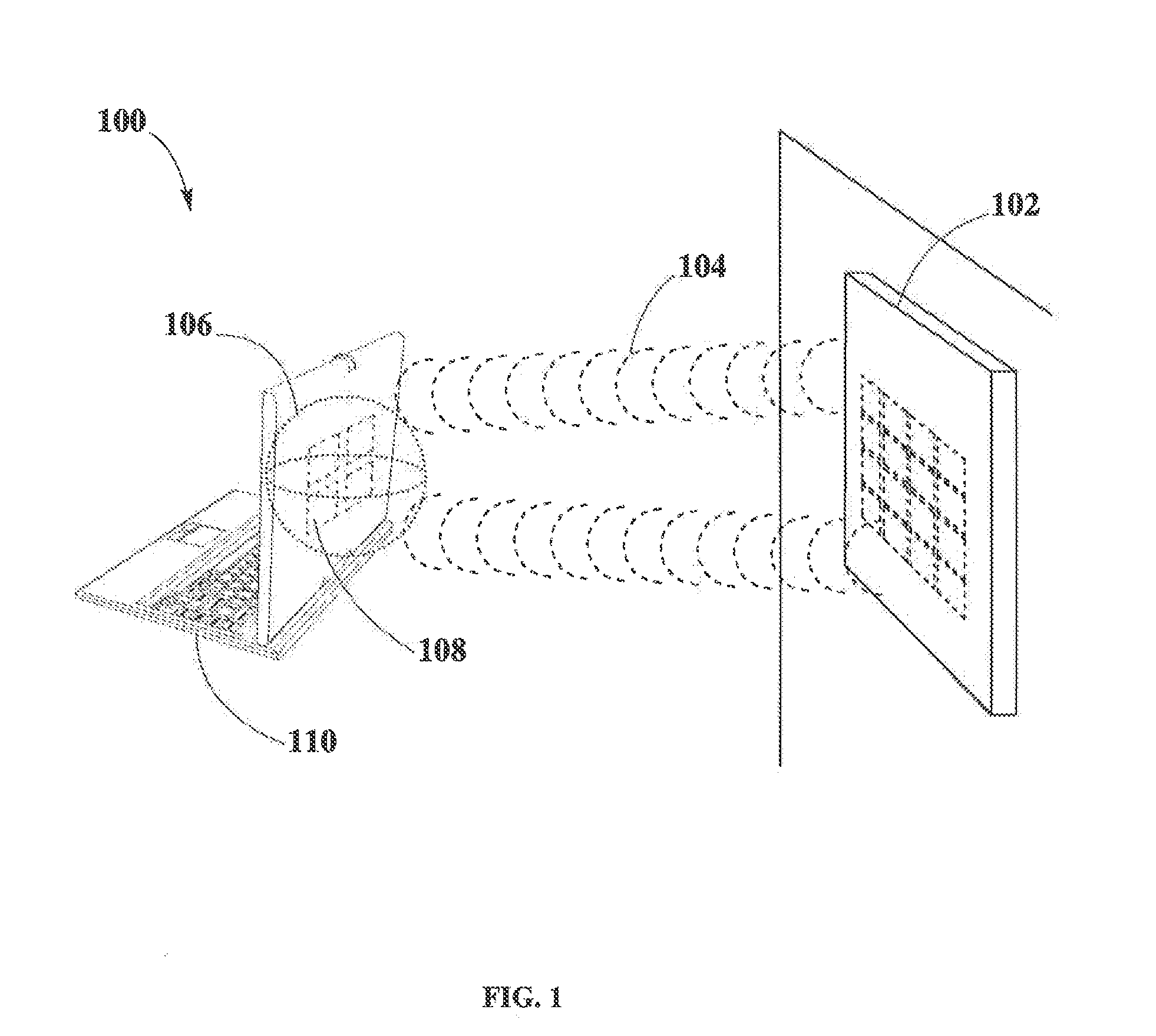
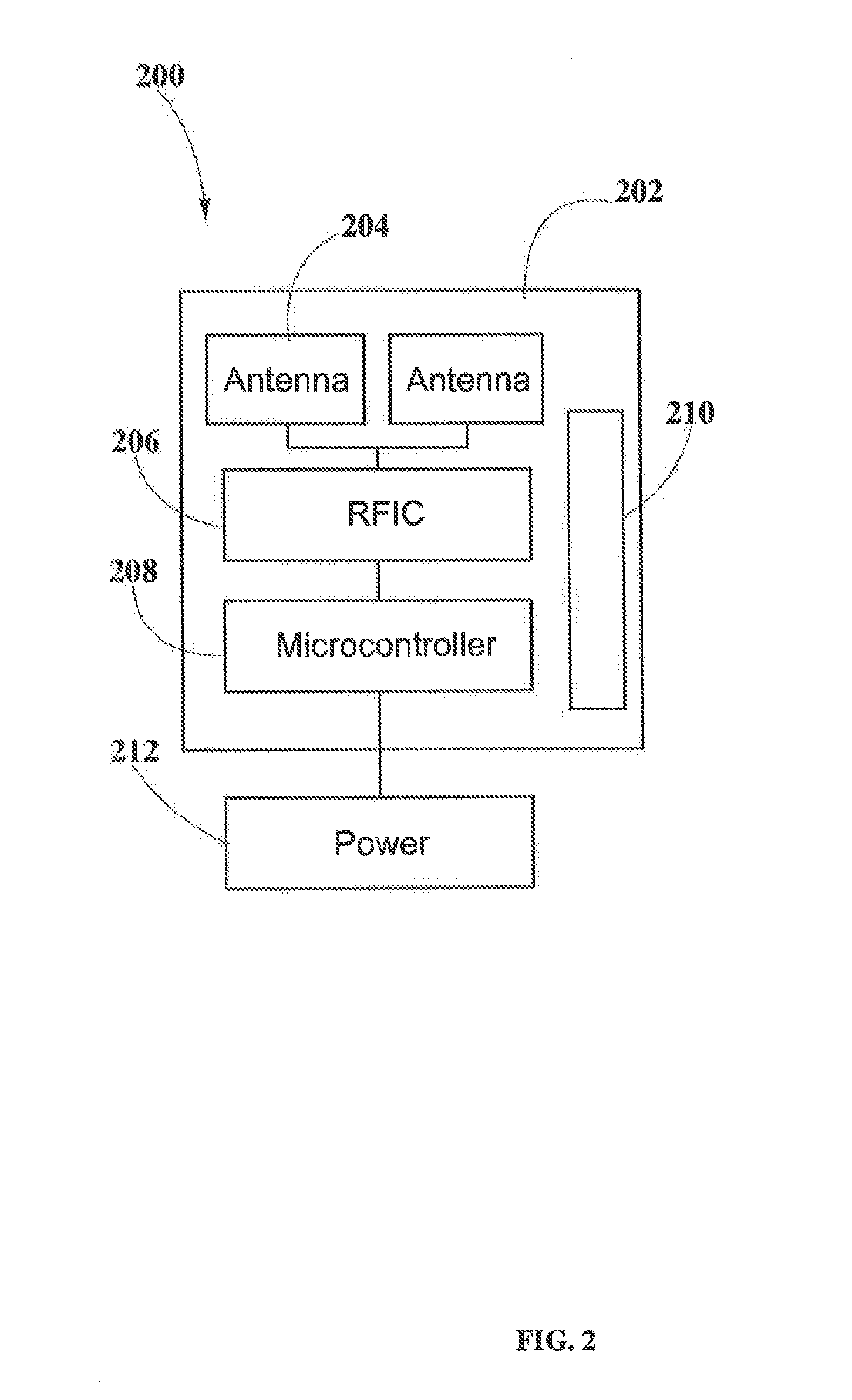
[0029]is a coffee shop in which hot beverages are served using cups 400 described in FIG. 4. The cups 400 may be made of cheap materials, such as cardboard, for discardable purposes or made of more sophisticated materials like plastic or metal for reusable purposes. The coffee shop may have a wireless transmitter 200. Pockets of energy 106 may be formed by transmitter 200 and sent to receivers 300 in cups 400 that are within the scope of the wireless power transmission. Cups 400 may then apply heat to the beverages in order to keep them hot depending on the customers preferences.
example # 2
Example #2
[0030]is a restaurant in which food is served using plates 500 described in FIG. 5. Plates 500 may be made of cheap materials, such as cardboard, for discardable purposes or made of more sophisticated materials like plastic or metal for reusable purposes. The restaurant may have a wireless transmitter 200. Pockets of energy 106 may be formed by transmitter 200 and sent to receivers 300 in plates 500 that are within the scope of the wireless power transmission. Plates 500 may then apply heat in order to keep the food hot depending on the customers preferences.
example # 3
Example #3
[0031]is a Bar in which cold drinks are served using cups 400 described in FIG. 4. Cups 400 may be made of cheap materials, such as cardboard, for discardable purposes or made of more sophisticated materials like plastic, glass or metal for reusable purposes. The bar may have a wireless transmitter 200. Pockets of energy 106 may be formed by transmitter 200 and sent to receivers 300 in cups 400 that are within the scope of the wireless power transmission. Cups 400 may then cool drinks depending on the customers preferences.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com