Video signal coding method
a video signal and signal coding technology, applied in the field of video signal coding methods, can solve the problems of objectionable poor quality of pictures reproduced discontinuous contents of pictures generated by interpolation at the receiver, and objectionable poor quality of pictures reproduced with such motion vectors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
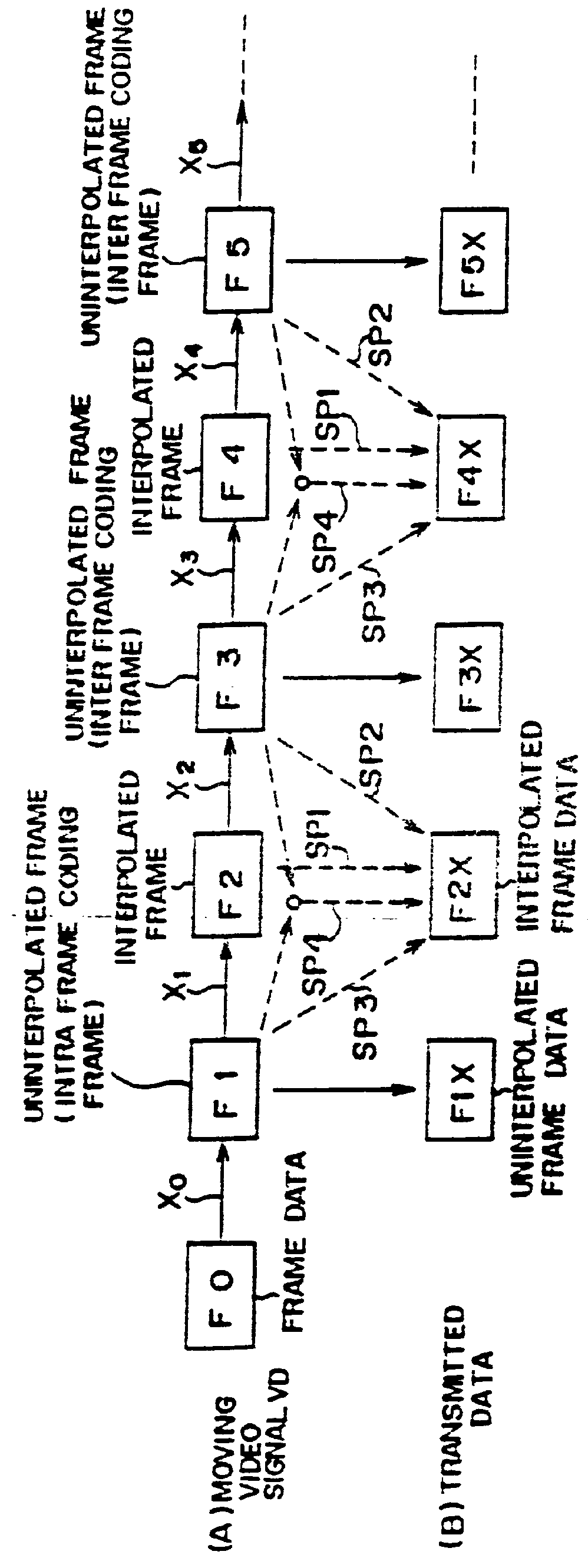
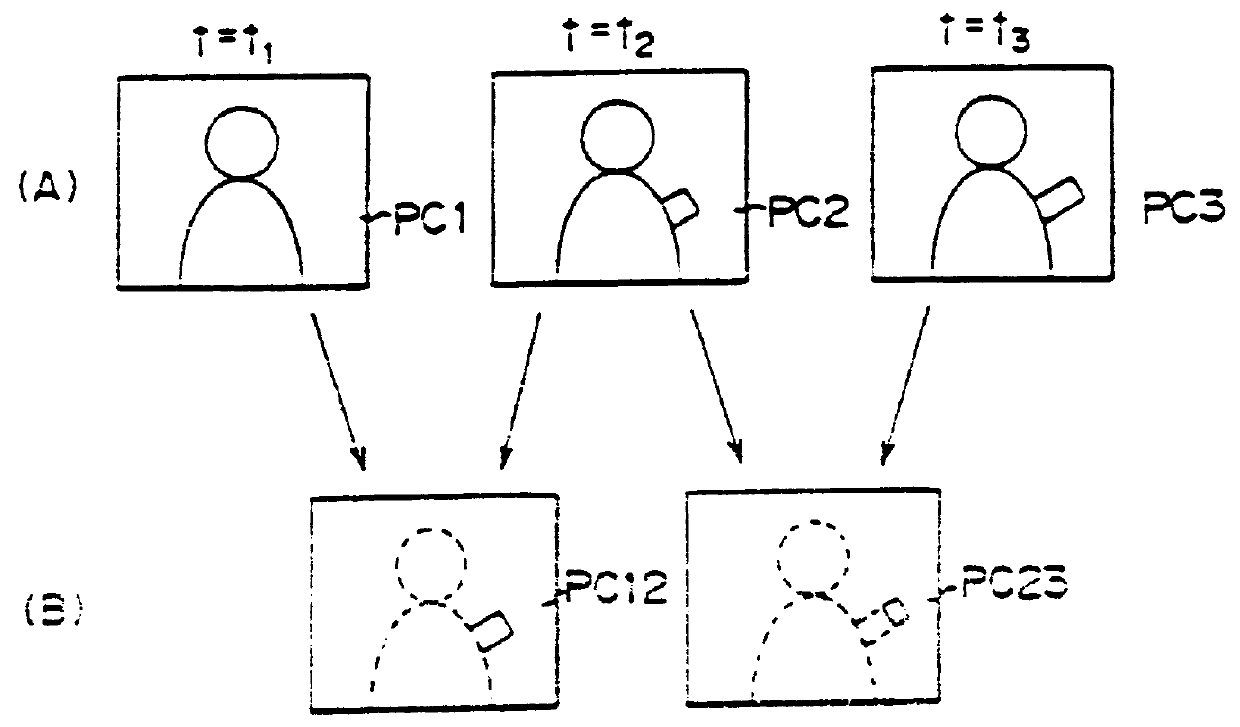
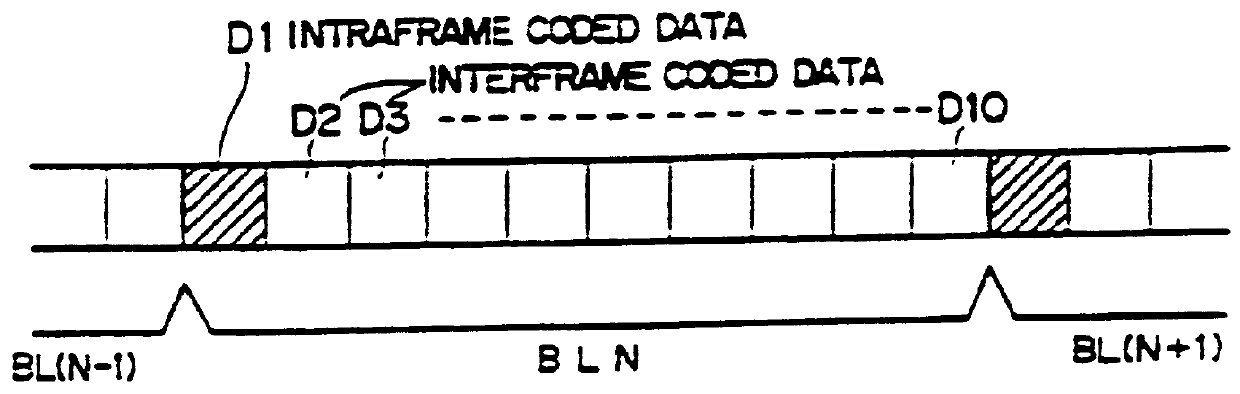
With reference first to FIG. 1, a video signal coding method in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention is illustrated therein as a method of operating a moving picture signal transmission system. In the illustrated method, picture data in the form of successive frames including frames formed by interpolation are produced by a transmitter and transmitted thereby to a receiver.
As shown in line (A) of FIG. 1, a moving video signal VD to be encoded for transmission includes successive frames of data comprising an initial frame F0 and successively arranged frames F1, F2, F3, . . . . Motion vectors x.sub.0, x.sub.1, x.sub.2, x.sub.3, etc., represent motion respectively between the frames F0 and F1, F1 and F2, F2 and F3, F3 and F4, etc. The transmitter applies an interpolation process to the even numbered frames F2, F4, . . . , to thereby generate respective interpolated frame data F2X, F4X, etc. as illustrated in line (B) of FIG. 1 and transmits the interpolated frame dat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com