Thin film transistor and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of thin film transistor and manufacturing method, applied in transistor, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components and other directions, can solve problems such as light leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
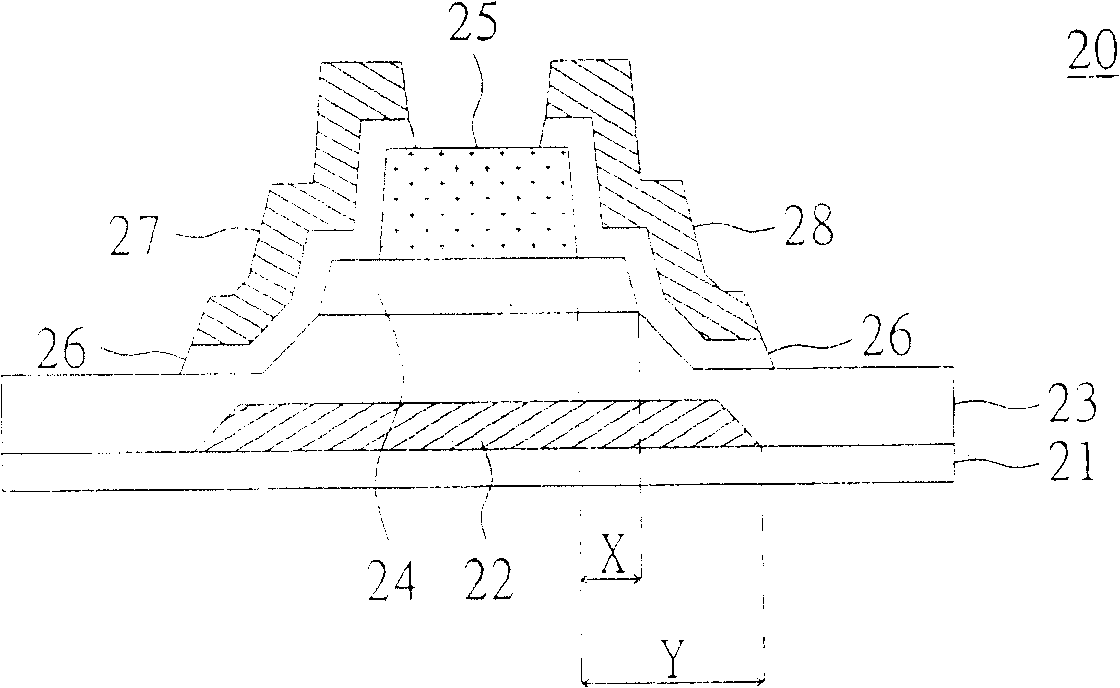
[0060] Please refer to figure 2 , Which shows a cross-sectional view of the structure of a thin film transistor according to the first embodiment of the present invention. in figure 2 The thin film transistor 20 includes a gate 22, an insulating layer 23, a channel layer 24, an etching stop layer 25, an ohmic contact layer 26, a source electrode 27, and a drain electrode 28. The gate 22 is disposed on a substrate 21. The insulating layer 23 is disposed on the substrate 21 and covers the gate 22. The channel layer 24 is disposed on a part of the insulating layer 23 and corresponds to the gate 22, and the width of the channel layer 24 is less than or equal to the width of the gate 22. The etching stop layer 25 is disposed on a part of the channel layer 24 and corresponds to the gate 22, and the width of the etching stop layer 25 is smaller than the width of the channel layer 24. The ohmic contact layer 26 is disposed on a part of the insulating layer 23 and covers the two ends of ...
Embodiment 2
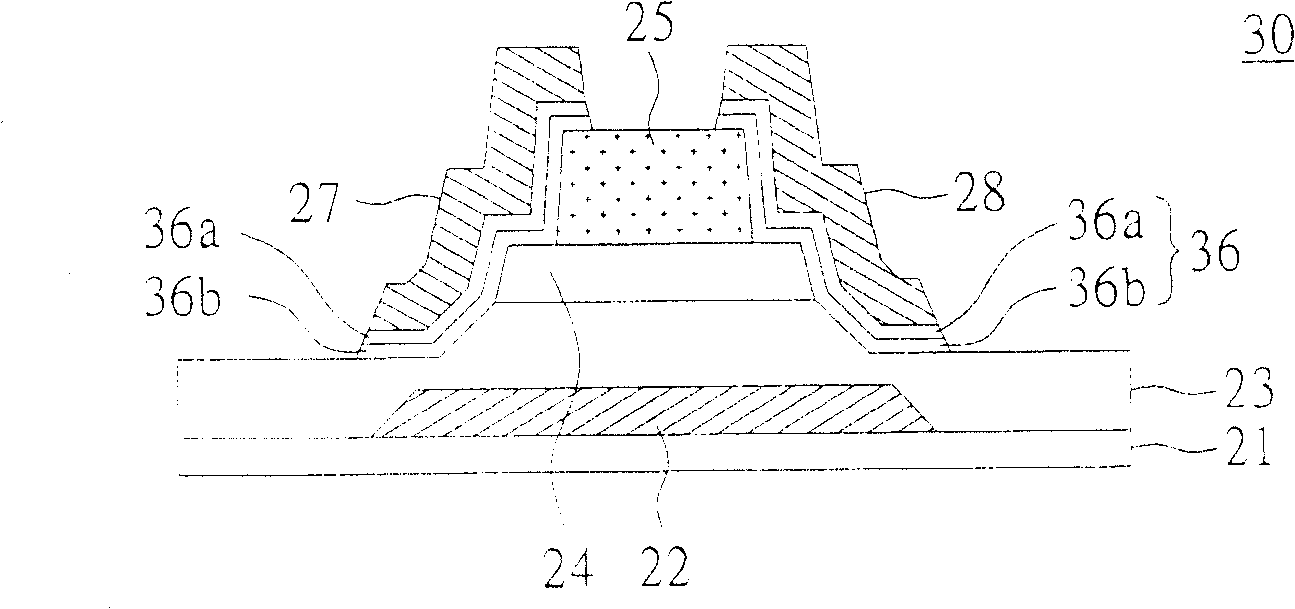
[0065] Please refer to image 3 , Which shows a cross-sectional view of the structure of a thin film transistor according to the second embodiment of the present invention. The difference between the thin film transistor 30 of this embodiment and the thin film transistor 20 of the first embodiment is the ohmic contact layer 36, and the remaining same constituent elements continue to use the reference numerals, and the connection relationship between them will not be repeated.
[0066] in image 3 Wherein, the ohmic contact layer 36 includes a first sub-ohmic contact layer 36a and a second sub-ohmic contact layer 36b. The second sub-ohmic contact layer 36b covers the etching stop layer. Two ends of 25, two ends of the channel layer 24, and part of the insulating layer 23. The first ohmic contact layer 36a covers the second ohmic contact layer 36b, and the source 27 and the drain 28 cover the first ohmic contact layer 36a. Wherein, the doping concentration of the first ohmic contact...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Please also refer to Figure 4~5L , Figure 4 Shown is a flowchart of a method for manufacturing a thin film transistor according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Figure 5A~5L The drawing is a process cross-sectional view of a thin film transistor according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Please also refer to Figure 2~3 ,in Figure 4 Here, first, in step 41, a gate 22 is formed on a substrate 21. Such as Figure 5A As shown, the gate 22 covers a part of the substrate 21, and the gate 22 includes a metal, a metal alloy, or a combination thereof, and may be a single-layer or multi-layer structure. The substrate 21 includes an insulating substrate, a glass substrate, a ceramic substrate, a plastic substrate or a flexible substrate.
[0070] Then, in step 42, an insulating layer 23 is formed on the substrate 21 and covers the gate 22. As shown in FIG. 5B, the insulating layer 23 covers the gate 22 and part of the substrate 21, and the insula...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com