Single salient pole permanent magnetic paster bias magnetic motor scheme
A permanent magnet and chip technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, magnetic circuit static parts, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory manufacturability, and achieve the effect of reducing low-speed torque pulsation, reasonable design, and eliminating magnetic flux leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
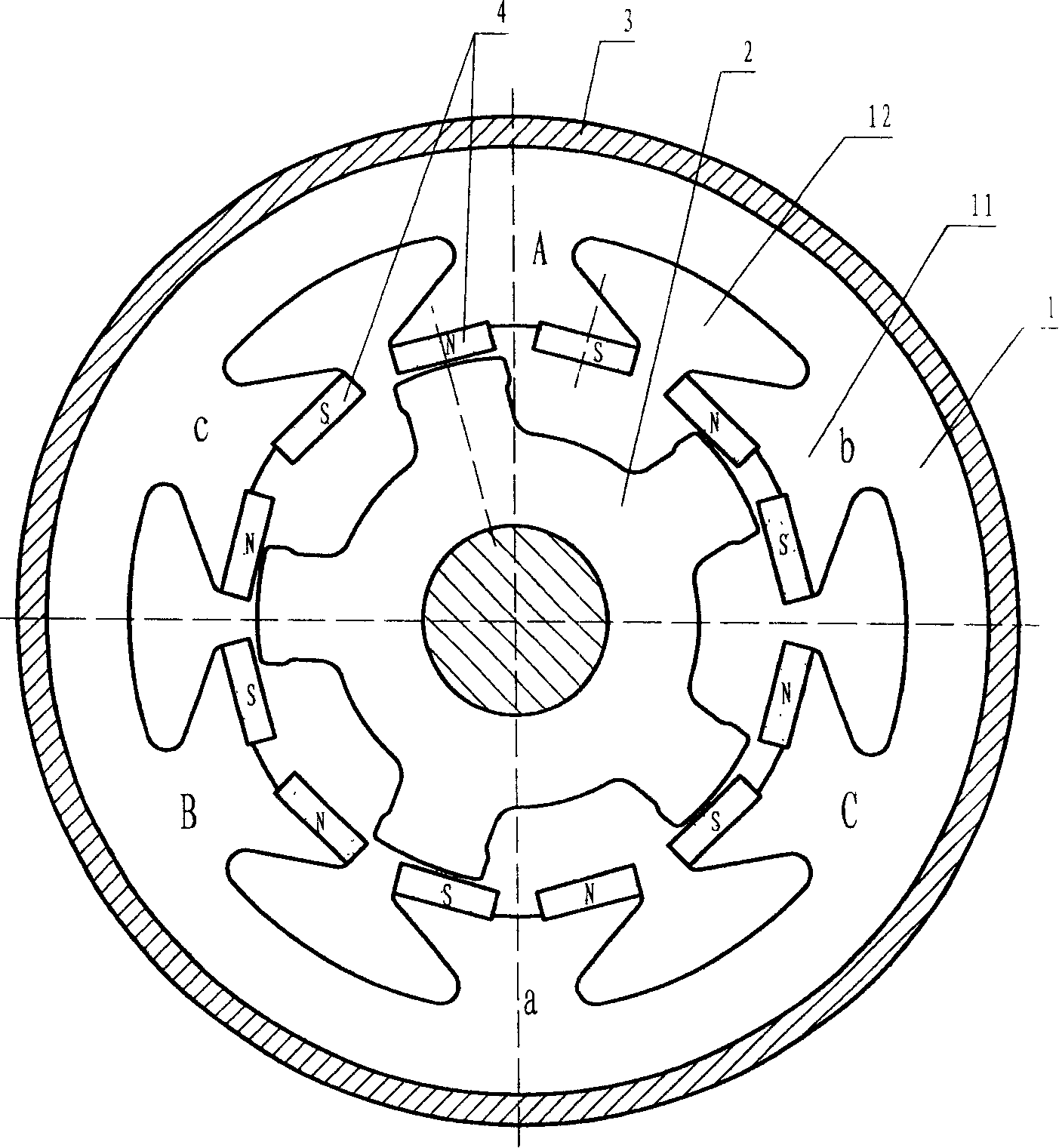
[0029] Example 1: Single-salient pole permanent magnet patch bias three-phase six-pole five-tooth motor
[0030] refer to figure 1 , among the figure (1) is the stator core, (11) is the stator pole, (12) is the line groove, (2) is the rotor, (3) is the shell, (4) is the permanent magnet.
[0031] There are 6 magnetic poles on the stator core as shown, and a pair of permanent magnets are pasted on each magnetic pole. The magnetization polarities of each adjacent permanent magnet are all opposite, and each piece of permanent magnet is evenly arranged on the circumference. In order to ensure that the sticking position of the permanent magnet is accurate, a small boss is designed in the middle of each magnetic pole. The stator winding can be single-span centralized or multi-span distributed.
[0032] figure 1 The rotor retains the salient pole structure of the traditional reluctance motor. The number of rotor teeth Z is equal to the logarithm of the stator permanent magnets 6, ...
Embodiment 2
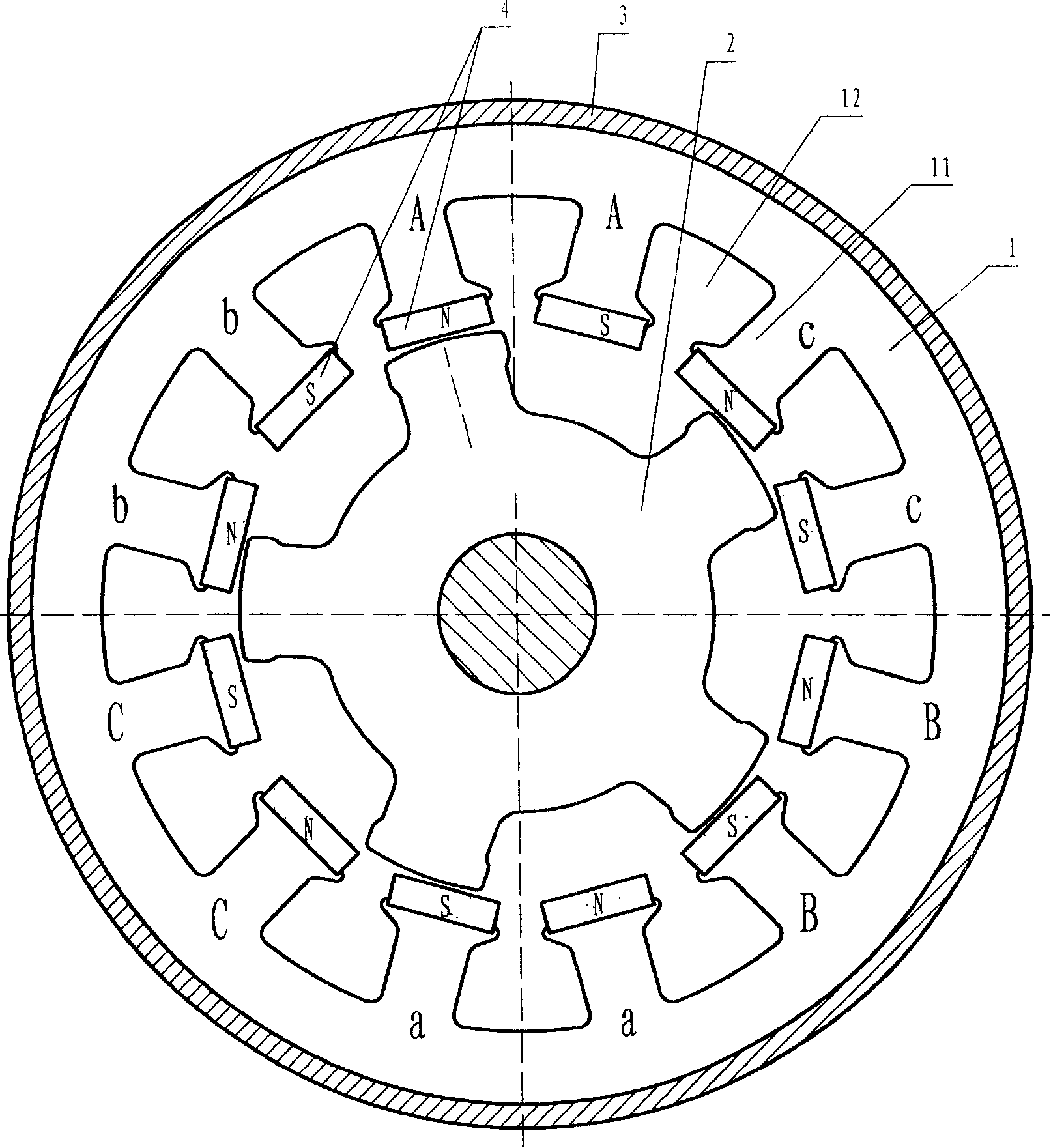
[0034] Embodiment 2: Single-salient pole permanent magnet patch bias three-phase twelve-pole five-tooth motor
[0035] refer to figure 2 , which is a schematic diagram of a three-phase, twelve-pole, five-tooth motor with a single-salient-pole permanent-magnet patch-bias bias.
[0036] figure 2 The stator core of the motor has 12 magnetic poles in total, and only one permanent magnet is pasted on each magnetic pole, and the magnetization polarity of adjacent permanent magnets is opposite; the rotor has 5 teeth. with the example figure 1 compared to, figure 2 only in figure 1 Basically, keep the position of the permanent magnet unchanged, divide each magnetic pole into two, and open a wire slot in the middle. figure 2 The pole distribution in the figure 1 It is basically the same. After doubling the capacity of the wire slot, the wiring is more flexible, which is conducive to the use of centralized windings with smaller spans, and is more conducive to the design of dis...
Embodiment 3
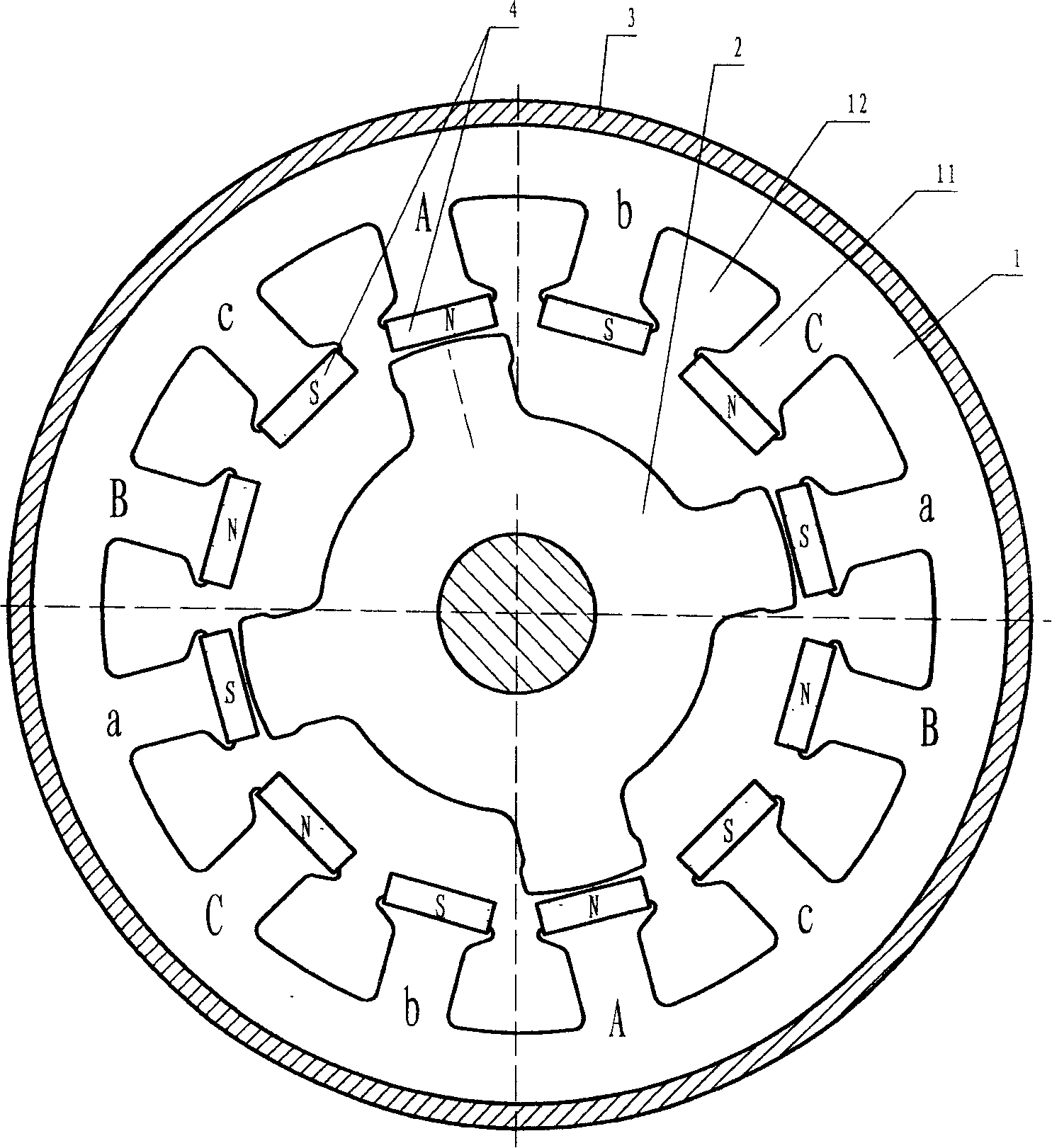
[0038] Embodiment 3: Single-salient pole permanent magnet patch bias three-phase twelve-pole four-tooth motor
[0039] refer to image 3 , the three-phase motor stator shown in the figure has 12 magnetic poles, and a permanent magnet is attached to each magnetic pole; the rotor has 4 teeth. From the point of view of mechanical structure, this example is similar to figure 2 The stator is the same, only the phase sequence arrangement of the magnetic poles is different. figure 2 The arrangement of the 4 magnetic poles of each phase is: every two adjacent magnetic poles form a group, and the two groups are arranged opposite to each other; image 3 The 4 magnetic poles of each phase are: each magnetic pole occupies a corner and is evenly distributed. image 3 This arrangement of magnetic poles makes the calculation method of the number of teeth of the rotor different, and the difference between the number of rotor teeth and the number of magnetic pole pairs is equal to the num...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com