Method for reclaiming metal stibium from waste fluorination catalyst antimony pentachloride
A fluorination catalyst, antimony pentachloride technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems such as no technical inspiration for recovering simple metal antimony, achieve the effect of simple and easy treatment process, and reduce the impact on the environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
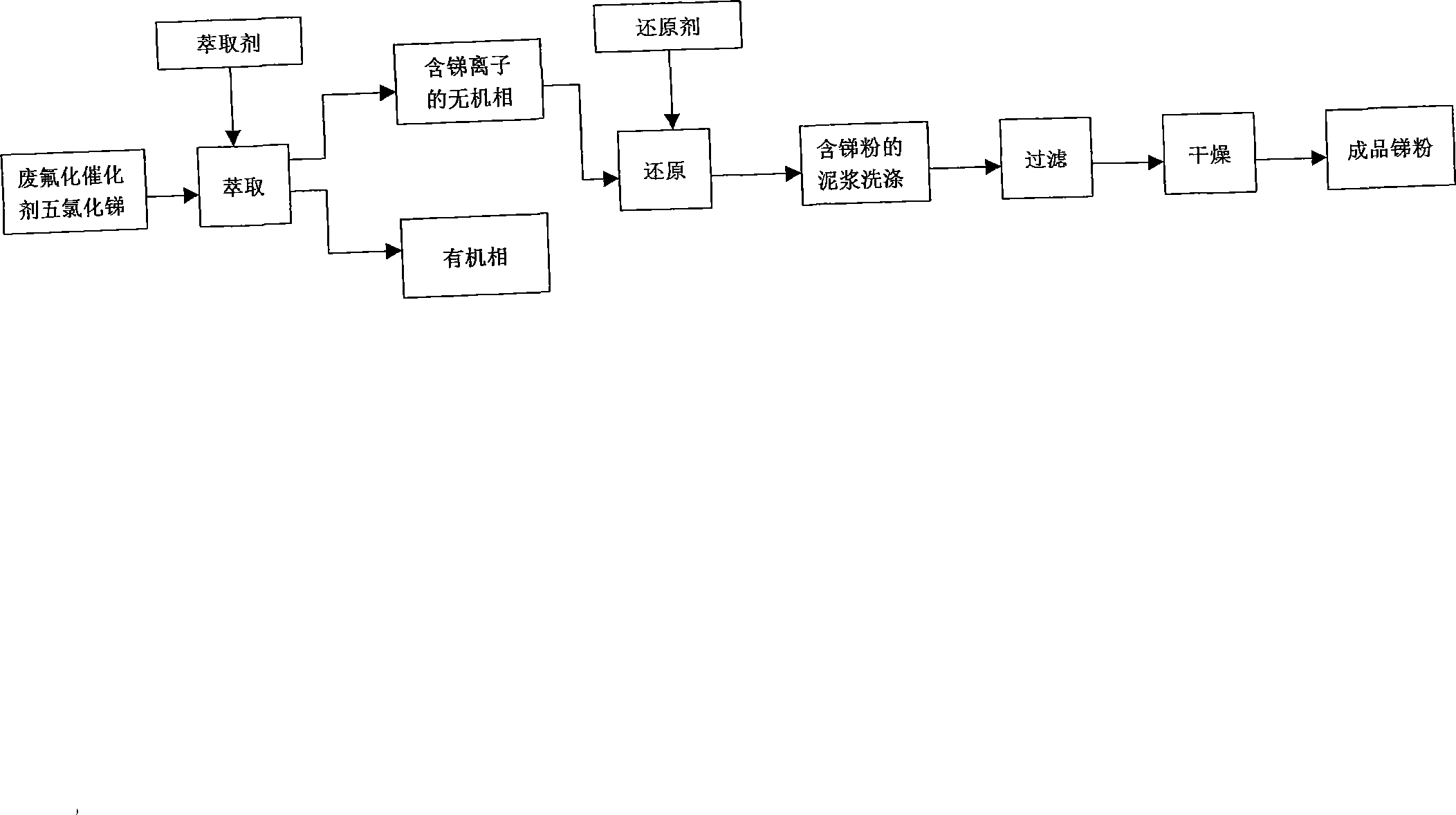
[0018] According to the technological process shown in the accompanying drawing, metal elemental antimony was recovered from 402.4 g of spent fluorination catalyst antimony pentachloride.
[0019] A), extraction, get 402.4g spent fluorination catalyst antimony pentachloride, wherein SbCl 5-m f m (m is 0~5), SbCl 3-n f n (n is 0 to 3) and hydrogen fluoride and a variety of organic substances with different boiling points are extracted with 24% hydrochloric acid at a ratio of 1:1 by volume. Carbon organic phase, the upper layer is an inorganic phase containing antimony ions, the separated organic phase is then extracted according to the above ratio, after layering, the organic phase is incinerated, and the inorganic phase is mixed with the previous inorganic phase to obtain antimony ion-containing Inorganic phase extract;
[0020] B), reduction, adding aluminum to the inorganic phase extract containing antimony ions in a weight ratio of 1:5 (aluminum: inorganic phase extract...
Embodiment 2
[0022] According to the process flow of the accompanying drawing, metal elemental antimony is recovered from the spent fluorination catalyst antimony pentachloride from the same spent catalyst as in Example 1.
[0023] A), extraction, take 400.3g spent fluorination catalyst antimony pentachloride, extract with 6% hydrochloric acid according to the ratio of volume ratio 3:1, after stirring and mixing evenly, static layering, the lower layer is dichloromethane, polychlorofluoro Carbon organic phase, the upper layer is an inorganic phase containing antimony ions, the separated organic phase is then extracted according to the above ratio, after layering, the organic phase is incinerated, and the inorganic phase is mixed with the previous inorganic phase to obtain antimony ion-containing Inorganic phase extract;
[0024] B), reduction, adding aluminum to the inorganic phase extract containing antimony ions in a weight ratio of 1: 13 (aluminum: inorganic phase extract), during which...
Embodiment 3
[0026] According to the process flow of the accompanying drawing, metal elemental antimony is recovered from the spent fluorination catalyst antimony pentachloride from the same spent catalyst as in Example 1.
[0027] A), extraction, take 403.6g of spent fluorination catalyst antimony pentachloride, extract with 6% hydrochloric acid according to the ratio of volume ratio 5.8:1, after stirring and mixing evenly, static layering, the lower layer is dichloromethane, polychlorofluoro Carbon organic phase, the upper layer is an inorganic phase containing antimony ions, the separated organic phase is then extracted according to the above ratio, after layering, the organic phase is incinerated, and the inorganic phase is mixed with the previous inorganic phase to obtain antimony ion-containing Inorganic phase extract;
[0028] B), reduction, adding aluminum to the inorganic phase extract containing antimony ions in a weight ratio of 1: 15.7 (aluminum: inorganic phase extract), durin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com