A method and apparatus for predicting branch instructions
一种分支指令、指令的技术,应用在程序控制设计、仪器、计算等方向,能够解决减小预测精度等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
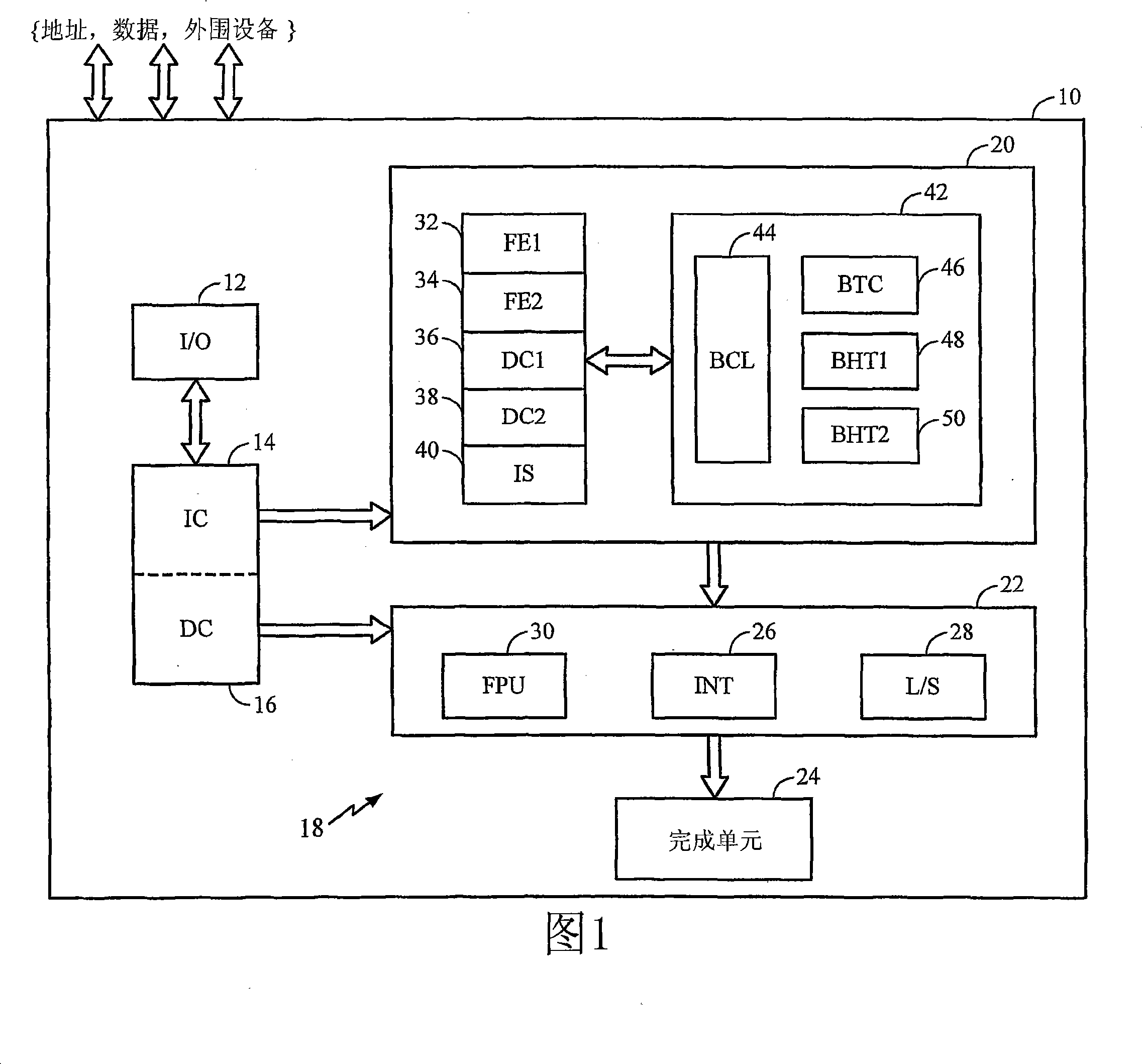
[0017] By way of non-limiting example, FIG. 1 illustrates a microprocessor 10, which may comprise a pipelined RISC microprocessor. In the illustrated embodiment, microprocessor 10 includes input / output (I / O) circuitry 12, instruction cache 14, data cache 16, and instruction pipeline 18, which includes front-end circuitry 20, execution units 22 and complete unit 24.
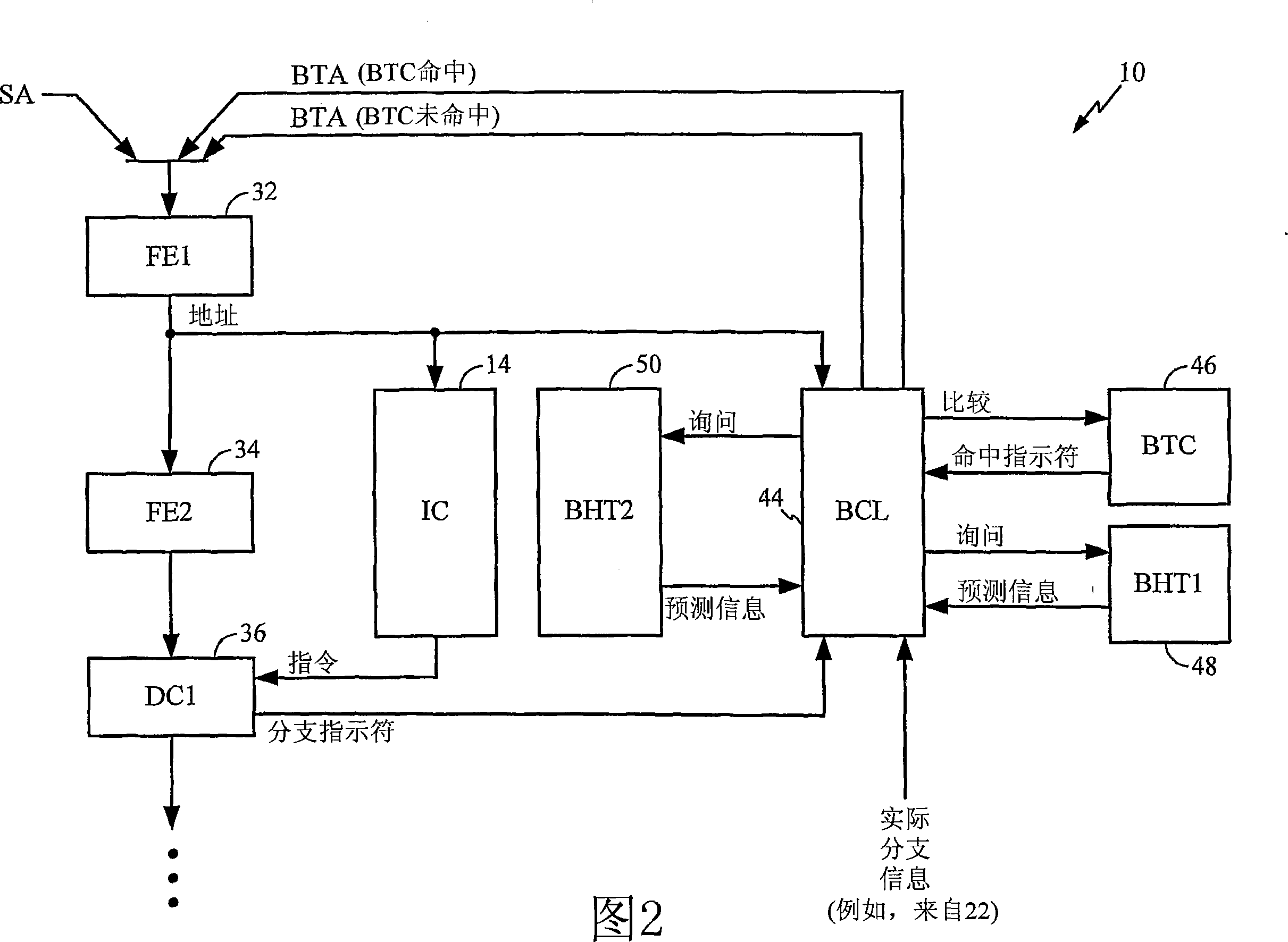
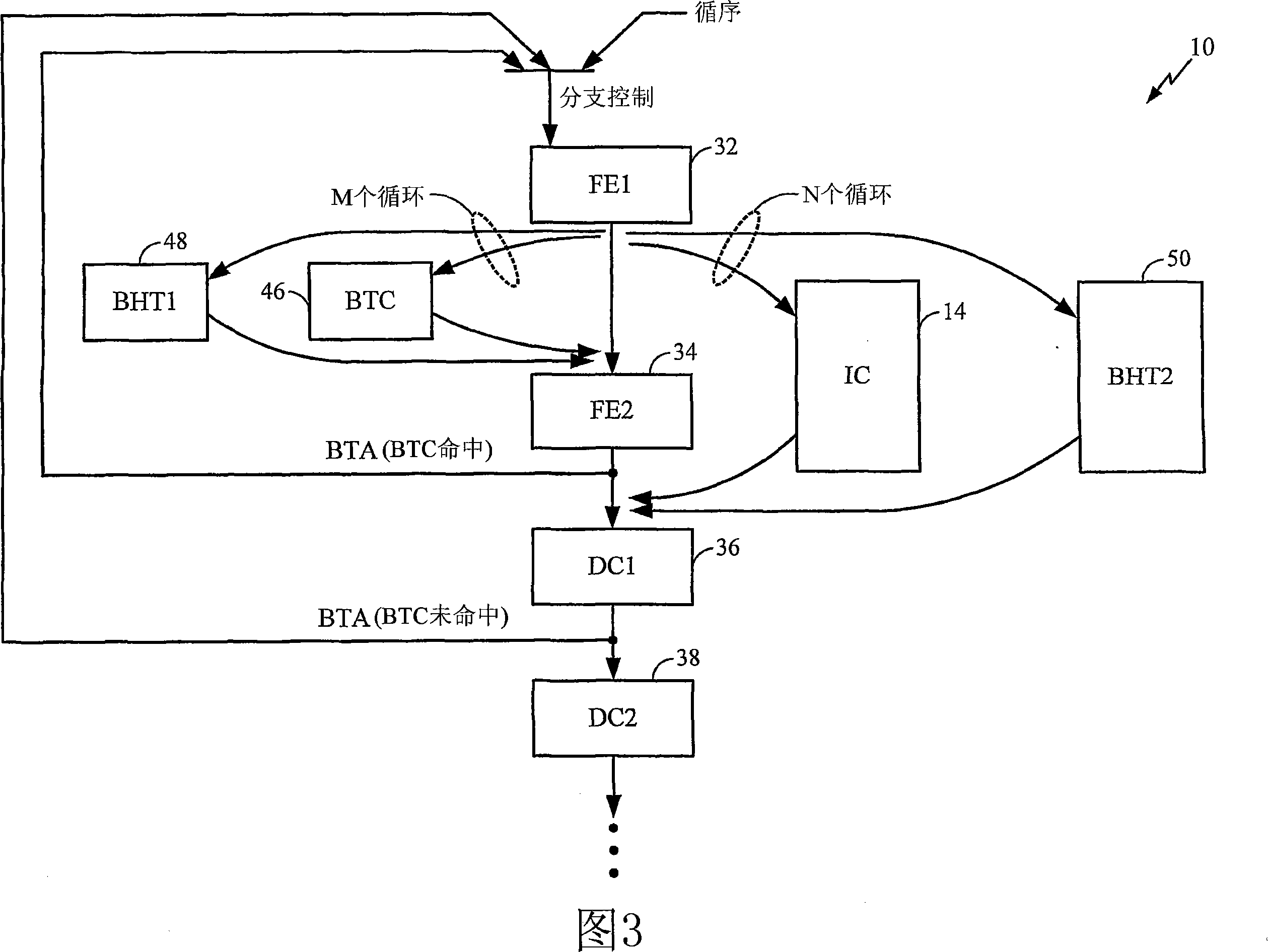
[0018] In operation, front-end circuitry 20 fetches instructions from instruction cache 14, which may be an on-board level 1 (L1) cache. Instructions are fetched according to a defined computer program flow that may include program branches or branches. Microprocessor 10 uses branch prediction to predict whether a conditional branch will or will not be taken so that it does not normally interrupt its instruction fetch operation when a conditional branch instruction is encountered.
[0019] The fetched instructions are decoded and issued to execution units 22, which may be implemented according to a superscalar a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com